#Global Ocean Warming
Text

#August 1999#Spongebob Squarepants#screenshot#Spongebob#climate change#newspaper#Global Ocean Warming#cartoon#cartoons
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
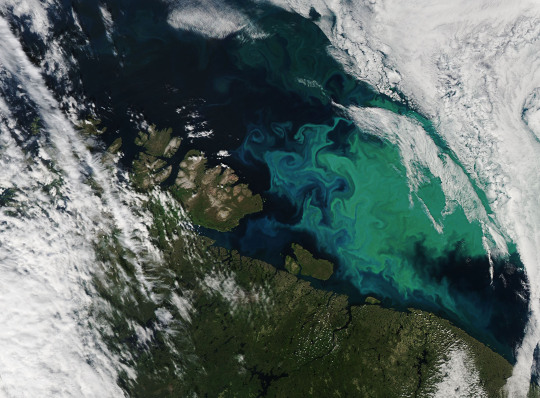
Sharpening Our View of Climate Change with the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Satellite
As our planet warms, Earth’s ocean and atmosphere are changing.
Climate change has a lot of impact on the ocean, from sea level rise to marine heat waves to a loss of biodiversity. Meanwhile, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide continue to warm our atmosphere.
NASA’s upcoming satellite, PACE, is soon to be on the case!
Set to launch on Feb. 6, 2024, the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission will help us better understand the complex systems driving the global changes that come with a warming climate.
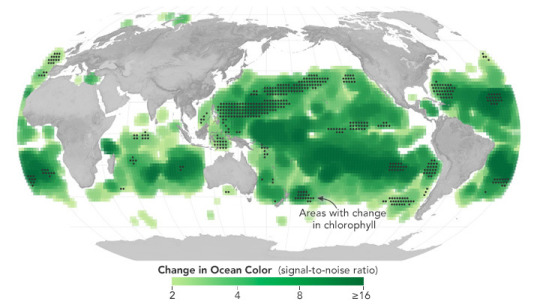
Earth’s ocean is becoming greener due to climate change. PACE will see the ocean in more hues than ever before.
While a single phytoplankton typically can’t be seen with the naked eye, communities of trillions of phytoplankton, called blooms, can be seen from space. Blooms often take on a greenish tinge due to the pigments that phytoplankton (similar to plants on land) use to make energy through photosynthesis.
In a 2023 study, scientists found that portions of the ocean had turned greener because there were more chlorophyll-carrying phytoplankton. PACE has a hyperspectral sensor, the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), that will be able to discern subtle shifts in hue. This will allow scientists to monitor changes in phytoplankton communities and ocean health overall due to climate change.
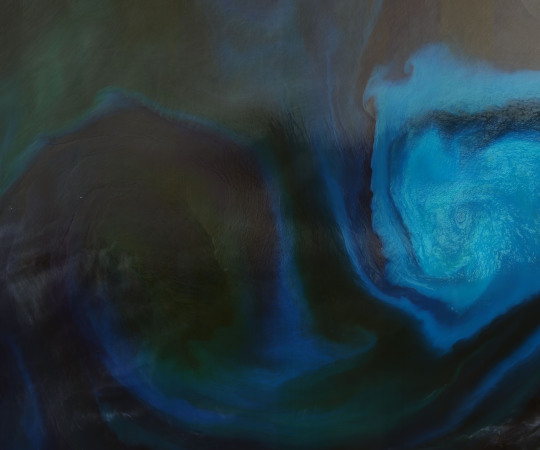

Phytoplankton play a key role in helping the ocean absorb carbon from the atmosphere. PACE will identify different phytoplankton species from space.
With PACE, scientists will be able to tell what phytoplankton communities are present – from space! Before, this could only be done by analyzing a sample of seawater.
Telling “who’s who” in a phytoplankton bloom is key because different phytoplankton play vastly different roles in aquatic ecosystems. They can fuel the food chain and draw down carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to photosynthesize. Some phytoplankton populations capture carbon as they die and sink to the deep ocean; others release the gas back into the atmosphere as they decay near the surface.
Studying these teeny tiny critters from space will help scientists learn how and where phytoplankton are affected by climate change, and how changes in these communities may affect other creatures and ocean ecosystems.
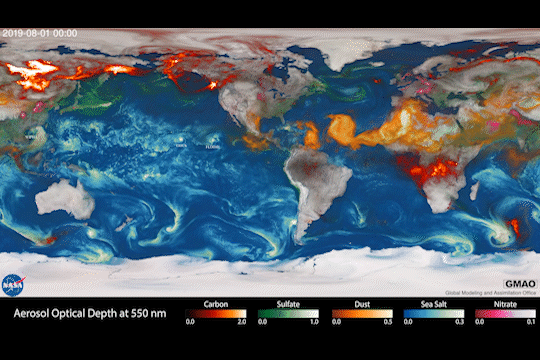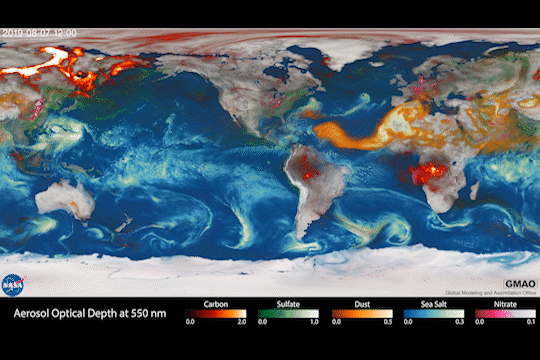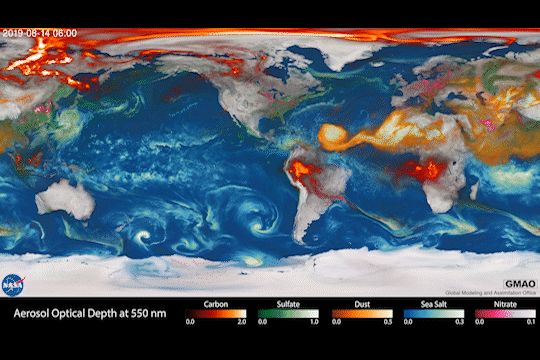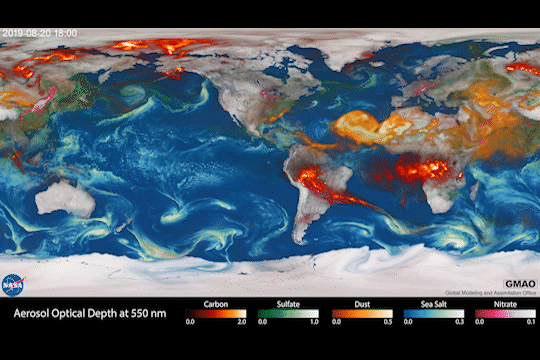
Climate models are one of our most powerful tools to understand how Earth is changing. PACE data will improve the data these models rely on.
The PACE mission will offer important insights on airborne particles of sea salt, smoke, human-made pollutants, and dust – collectively called aerosols – by observing how they interact with light.
With two instruments called polarimeters, SPEXone and HARP2, PACE will allow scientists to measure the size, composition, and abundance of these microscopic particles in our atmosphere. This information is crucial to figuring out how climate and air quality are changing.
PACE data will help scientists answer key climate questions, like how aerosols affect cloud formation or how ice clouds and liquid clouds differ.
It will also enable scientists to examine one of the trickiest components of climate change to model: how clouds and aerosols interact. Once PACE is operational, scientists can replace the estimates currently used to fill data gaps in climate models with measurements from the new satellite.

With a view of the whole planet every two days, PACE will track both microscopic organisms in the ocean and microscopic particles in the atmosphere. PACE’s unique view will help us learn more about the ways climate change is impacting our planet’s ocean and atmosphere.
Stay up to date on the NASA PACE blog, and make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of sPACE!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


clownfish swimming through bleached anemones | jonoallenphotography on ig
if you have a moment and are mentally able, please read the text accompanying the original instagram post, located at the source link above, and this short article by The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. if not, please just share it around.
it's true this video is strikingly beautiful, but the truth behind it is, in my opinion, necessary for everyone to know.
#stim#clownfish#coral reefs#climate change#sfw#orange#black#white#blue#animals#global warming#marine life#sea creatures#fish#underwater#cnidarians#sea anemones#oceans#coral bleaching#climate change awareness#global warming awareness#ishy gifs#postish
339 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Julia Conley
Common Dreams
April 25, 2023
Scientists are so alarmed by a new study on ocean warming that some declined to speak about it on the record, the BBC reported Tuesday.
"One spoke of being 'extremely worried and completely stressed,'" the outlet reported regarding a scientist who was approached about research published in the journal Earth System Science Data on April 17, as the study warned that the ocean is heating up more rapidly than experts previously realized—posing a greater risk for sea-level rise, extreme weather, and the loss of marine ecosystems.
Scientists from institutions including Mercator Ocean International in France, Scripps Institution of Oceanography in the United States, and Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research collaborated to discover that as the planet has accumulated as much heat in the past 15 years as it did in the previous 45 years, the majority of the excess heat has been absorbed by the oceans.
In March, researchers examining the ocean off the east coast of North America found that the water's surface was 13.8°C, or 14.8°F, hotter than the average temperature between 1981 and 2011.
The study notes that a rapid drop in shipping-related pollution could be behind some of the most recent warming, since fuel regulations introduced in 2020 by the International Maritime Organization reduced the heat-reflecting aerosol particles in the atmosphere and caused the ocean to absorb more energy.
But that doesn't account for the average global ocean surface temperature rising by 0.9°C from preindustrial levels, with 0.6°C taking place in the last four decades.
The study represents "one of those 'sit up and read very carefully' moments," said former BBC science editor David Shukman.
Lead study author Karina Von Schuckmann of Mercator Ocean International told the BBC that "it's not yet well established, why such a rapid change, and such a huge change is happening."
"We have doubled the heat in the climate system the last 15 years, I don't want to say this is climate change, or natural variability or a mixture of both, we don't know yet," she said. "But we do see this change."
Scientists have consistently warned that the continued burning of fossil fuels by humans is heating the planet, including the oceans. Hotter oceans could lead to further glacial melting—in turn weakening ocean currents that carry warm water across the globe and support the global food chain—as well as intensified hurricanes and tropical storms, ocean acidification, and rising sea levels due to thermal expansion.
A study published earlier this year also found that rising ocean temperatures combined with high levels of salinity lead to the "stratification" of the oceans, and in turn, a loss of oxygen in the water.
"Deoxygenation itself is a nightmare for not only marine life and ecosystems but also for humans and our terrestrial ecosystems," researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Center for Atmospheric Research, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said in January. "Reducing oceanic diversity and displacing important species can wreak havoc on fishing-dependent communities and their economies, and this can have a ripple effect on the way most people are able to interact with their environment."
The unusual warming trend over recent years has been detected as a strong El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is expected to form in the coming months—a naturally occurring phenomenon that warms oceans and will reverse the cooling impact of La Niña, which has been in effect for the past three years.
"If a new El Niño comes on top of it, we will probably have additional global warming of 0.2-0.25°C," Dr. Josef Ludescher of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Research told the BBC.
The world's oceans are a crucial tool in moderating the climate, as they absorb heat trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases.
Too much warming has led to concerns among scientists that "as more heat goes into the ocean, the waters may be less able to store excess energy," the BBC reported.
The anxiety of climate experts regarding the new findings, said the global climate action movement Extinction Rebellion, drives home the point that "scientists are just people with lives and families who've learnt to understand the implications of data better."
Read more.
#climate change#global warming#ocean warming#ocean acidification#deep ocean currents#degradation of ecosystems#ocean deoxygenation
967 notes
·
View notes
Text
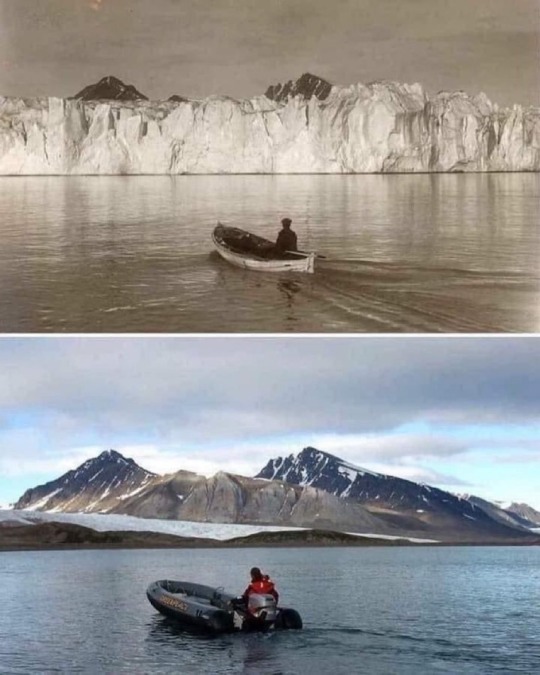

This is the same exact spot in the Arctic Ocean photographed 105 years ago vs what it looks like today. But sure, climate change is a hoax
961 notes
·
View notes
Text
Abnormally warm patches of water in the Pacific Ocean, often referred to as 'blobs', have been having a disastrous effect on marine ecosystems since 2010. Now we may know what's causing them to keep appearing.
A new study from an international team of researchers, and involving some detailed computer simulations, has linked the blobs to a reduction in aerosol emissions in China – so a policy designed to improve environmental conditions may have also come with negative consequences attached.
The reason is that these tiny airborne particles released by factories and power plants do a very good job at reflecting sunlight back into space, and keeping our atmosphere cooler.
Without that cover, the Pacific is more exposed to heat from the Sun, which combines with increasing heat from human-made global warming.
Continue Reading.
94 notes
·
View notes
Text



breaking the law and outing myself on the internet because i'm showcasing my senior dance thesis on april 28 at 6:30 and 8:30 pm Eastern Standard Time and i want You to see it
we don't have a livestream link yet but we will. in the meantime look at these cool posters and this cool blurb. ok now save the date SEE YOU SOON
#my stuff#my art#these posters went through 14 separate drafts. it was a harrowing and difficult experience#i am Fully Going through it which means 1) physical health is suffering 2) social life also but 3) the thing is going to be so fucking good#sarus is gonna be the best thing ive ever made when we finish it. i Know it#so i want you to see it because it's one of those ambitious stories where everything's bigger than life#and the world is old and young and scary and kind and people live fearlessly and with cowardice#BUT EVERYTHING WILL BE OK. IF YOU JUST KEEP WALKING. this is going to be one of those stories#so many dance blurbs and descriptions are like stupid technical like oh we explored the effect of weighing down our hands and feet#on our Center of Gravity and how it altered the rotational momentum of turns and jumps#or else they're stupid esoteric like oh the wind blew..... and the children wept and all over the world the oceans rose... (global warming)#so i was determined to make this blurb (which is going in the schoolwide email blast) accessible and provocative#and inviting#in a provocative way#im very Locked in rn. im Hyperfocused as fuck. i am not eating as well asi should be but IM TRYING#AND THATS WHAT MATTERS#im inviting all of u bc this is a piece that is going to try and say something and i want everyone ive ever loved to hear it#oghey bye
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
Honestly it really riles me up that people are mean to ocean animals because they are less understood than land animals (yes even dolphins as publically liked as they are) I think everyone should put a little more effort into understanding the ocean and the animals in it and the processes they help. You dont have to like the ocean you just need to understand it and understand that its 3/4ths of our planet's surface and that it's indispensable for life because the second that people stop caring about whats in it and what it does the door opens up for people to not care about what happens to it and how big companies destroy it and continue their needless pollution due to lack of care from the general public
#thunderclap#'who cares if this animal is killed its evil/i dont care about it' your brain is the size of a pea you should work on fixing that#did you know the ocean isnt just the Big Water where the Weird Animals live?#its also the earths main thermoregulator and actually regulates the entire atmosphere including the oxygen we breathe#if this cycle is upset (it is threatened by ocean mining operations; overfishing; and global warming) the whole earth will go kaput#it wont be a 'well the Big Water has no more Weird Animals in it' it will be the planet kaput#and caring about that long term starts by people caring about the animals in it#this has been my ted talk thank u for coming
207 notes
·
View notes
Text
The 1987 Montreal Protocol, which phased out the production and use of chemicals that were depleting the ozone layer, has long been considered one of the most successful environmental treaties in history. New research finds that the global pact achieved another unforeseen benefit: delaying the melting of Arctic sea ice.
In a study published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from the University of Exeter and Columbia University found that the implementation of the Montreal Protocol is delaying the first ice-free Arctic summer by up to 15 years. That’s because the chemicals banned under the agreement are also potent greenhouse gases.
“Our results show that the climate benefits from the Montreal Protocol are not in some faraway future: the protocol is delaying the melting of Arctic sea ice at this very moment,” Lorenzo Polvani, one of the study’s authors, said in a press release.
The study authors ran a series of climate models based on two different scenarios: one that included levels of ozone-depleting substances that would be expected if the Montreal Protocol never existed, and another accounting for the global treaty. The researchers concluded that the protocol is postponing the first ice-free Arctic summer by a decade or more, and entirely due to the phasedown of ozone-depleting chemicals.
The Montreal Protocol was created to address a hole in the stratospheric ozone layer over the Antarctic. The ozone layer protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation that causes skin cancer and cataracts in humans. The treaty phased out almost 100 chemicals — including aerosols used in hair spray and other products, refrigerants, and solvents — that were found to be responsible for destroying stratospheric ozone.
Those banned chemicals, collectively called ozone-depleting substances, or ODS, are also potent greenhouse gases, with up to tens of thousands times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide. The report authors estimate that 1 metric ton of avoided ODS emissions leads to 7,000 square meters (more than 75,000 square feet) of avoided Arctic sea loss. By way of comparison, 1 metric ton of carbon dioxide emissions results in about 3 square meters (about 32 square feet) of sea ice loss.
Given the potency of ODSs as a greenhouse gas, the authors are not surprised at this outsize impact on Arctic sea ice levels. “Nonetheless, such a large mitigating impact of the Montreal Protocol on Arctic sea ice loss is remarkable if one keeps in mind that the protocol was aimed at preventing ozone depletion in the Antarctic stratosphere, and little was known of its effect on Arctic sea ice when the protocol was signed,” the authors noted.
According to their projections, the Montreal Protocol has already prevented more than half a million square kilometers (about 193,000 square miles) of sea ice loss. By 2030, that amount will rise to more than 1 million square kilometers, and to 2 million square kilometers of prevented Arctic sea ice loss by 2040.
-via Grist, 5/24/23
#arctic#arctic circle#arctic ocean#arctic ice#sea ice#climate change#global warming#sea level rise#montreal protocol#cfc#hfc#greenhouse gasses#carbon dioxide#if we hurry#we can absolutely buy ourselves the time to save ourselves#as someone constantly looking at good news developments in the environment and green tech I truly believe that#good news#hope
418 notes
·
View notes
Text
An “unheard of” marine heatwave off the coasts of the UK and Ireland poses a serious threat to species, scientists have warned.
Sea temperatures, particularly off the north-east coast of England and the west of Ireland, are several degrees above normal, smashing records for late spring and early summer. The North Sea and north Atlantic are experiencing higher temperatures, data shows.
Daniela Schmidt, a professor of earth sciences at the University of Bristol, said: “The extreme and unprecedented temperatures show the power of the combination of human-induced warming and natural climate variability like El Niño."
“While marine heatwaves are found in warmer seas like the Mediterranean, such anomalous temperatures in this part of the north Atlantic are unheard of. They have been linked to less dust from the Sahara but also the North Atlantic climate variability, which will need further understanding to unravel."
“Heat, like on land, stresses marine organisms. In other parts of the world, we have seen several mass mortalities of marine plants and animals caused by ocean heatwave which have caused hundreds of millions of pounds of losses, in fisheries income, carbon storage, cultural values and habitat loss. As long as we are not dramatically cutting emissions, these heatwaves will continue to destroy our ecosystems. But as this is happening below the surface of the ocean, it will go unnoticed.”
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Since 1971, the ocean is estimated to have absorbed heat equivalent to the energy of more than 25bn Hiroshima-scale atomic bombs. No, I can’t get my head around that either. But payback – in the form of ice melt, sea level rise, more intense cyclones, increased flooding risk and damage to marine life – was always coming. A recent study found a deep ocean current, known as the Southern Ocean overturning circulation, has already slowed by about a third since the 1990s – far more rapidly than forecast in climate models. It means there is less cold, deep ocean water pushing north. The ramifications for regional and global temperatures and weather patterns will take time to unfold, but are expected to be substantial and cascading.”
139 notes
·
View notes
Text
But Republicans told me the climate crisis was a hoax.
#climate crisis#global warming#climate change#an inconvenient truth#hot enough for you?#it ain't getting any cooler from here on out#environment#environmentalism#the atlantic ocean is a hot tub now
115 notes
·
View notes
Text

sun jelly
#🎐art#art#procreate#jellyfish#moon jelly#flooding#ocean#abandoned#ruins#worldbuilding#orange#yellow#blue#climate change#climate crisis#global warming#<-this art is about climate change and also just a challenge for environment design
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Climate experts fear Donald Trump will follow a blueprint created by his allies to gut the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), disbanding its work on climate science and tailoring its operations to business interests.
Joe Biden’s presidency has increased the profile of the science-based federal agency but its future has been put in doubt if Trump wins a second term and at a time when climate impacts continue to worsen.
The plan to “break up NOAA” is laid out in the Project 2025 document written by more than 350 rightwingers and helmed by the Heritage Foundation. Called the Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise, it is meant to guide the first 180 days of presidency for an incoming Republican president.
The document bears the fingerprints of Trump allies, including Johnny McEntee, who was one of Trump’s closest aides and is a senior adviser to Project 2025. “The National Oceanographic [sic] and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) should be dismantled and many of its functions eliminated, sent to other agencies, privatized, or placed under the control of states and territories,” the proposal says.
That’s a sign that the far right has “no interest in climate truth”, said Chris Gloninger, who last year left his job as a meteorologist in Iowa after receiving death threats over his spotlighting of global warming.
The guidebook chapter detailing the strategy, which was recently spotlighted by E&E News, describes NOAA as a “colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future US prosperity”. It was written by Thomas Gilman, a former Chrysler executive who during Trump’s presidency was chief financial officer for NOAA’S parent body, the Commerce Department.
Gilman writes that one of NOAA’S six main offices, the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research, should be “disbanded” because it issues “theoretical” science and is “the source of much of Noaa’s climate alarmism”. Though he admits it serves “important public safety and business functions as well as academic functions”, Gilman says data from the National Hurricane Center must be “presented neutrally, without adjustments intended to support any one side in the climate debate”.
But NOAA’S research and data are “largely neutral right now”, said Andrew Rosenberg, a former NOAA official who is now a fellow at the University of New Hampshire. “It in fact basically reports the science as the scientific evidence accumulates and has been quite cautious about reporting climate effects,” he said. “It’s not pushing some agenda.”
The rhetoric harkens back to the Trump administration’s scrubbing of climate crisis-related webpages from government websites and stifling climate scientists, said Gloninger, who now works at an environmental consulting firm, the Woods Hole Group.
“It’s one of those things where it seems like if you stop talking about climate change, I think that they truly believe it will just go away,” he said. “They say this term ‘climate alarmism’ … and well, the existential crisis of our lifetime is alarming.”
NOAA also houses the National Weather Service (NWS), which provides weather and climate forecasts and warnings. Gilman calls for the service to “fully commercialize its forecasting operations”.
He goes on to say that Americans are already reliant on private weather forecasters, specifically naming AccuWeather and citing a PR release issued by the company to claim that “studies have found that the forecasts and warnings provided by the private companies are more reliable” than the public sector’s. (The mention is noteworthy as Trump once tapped the former CEO of AccuWeather to lead NOAA, though his nomination was soon withdrawn.)
The claims come amid years of attempts from US conservatives to help private companies enter the forecasting arena – proposals that are “nonsense”, said Rosenberg.
Right now, all people can access high-quality forecasts for free through the NWS. But if forecasts were conducted only by private companies that have a profit motive, crucial programming might no longer be available to those in whom business executives don’t see value, said Rosenberg.
“What about air-quality forecasts in underserved communities? What about forecasts available to farmers that aren’t wealthy farmers? Storm-surge forecasts in communities that aren’t wealthy?” he said. “The frontlines of most of climate change are Black and brown communities that have less resources. Are they going to be getting the same service?”
Private companies like Google, thanks to technological advancements in artificial intelligence, may now indeed be producing more accurate forecasts, said Andrew Blum, author of the 2019 book The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the Forecast. Those private forecasts, however, are all built on NOAA’S data and resources.
Fully privatizing forecasting could also threaten the accuracy of forecasts, said Gloninger, who pointed to AccuWeather’s well-known 30- and 60-day forecasts as one example. Analysts have found that these forecasts are only right about half the time, since peer-reviewed research has found that there is an eight- to 10-day limit on the accuracy of forecasts.
“You can say it’s going to be 75 degrees out on May 15, but we’re not at that ability right now in meteorology,” said Gloninger. Privatizing forecasting could incentivize readings even further into the future to increase views and profits, he said.
Commercializing weather forecasts – an “amazing example of intergovernmental, American-led, postwar, technological achievement” – would also betray the very spirit of the endeavor, said Blum.
In the post-second world war era, John F. Kennedy called for a global weather-forecasting system that relied on unprecedented levels of scientific exchange. A privatized system could potentially stymie the exchange of weather data among countries, yielding less accurate results.
The founding of weather forecasting itself showcases the danger of giving profit-driven companies control, said Rosenberg. When British V. Adm Robert FitzRoy first introduced Britain to the concept of forecasts during Victorian times, he was often bitterly attacked by business interests. The reason: workers were unwilling to risk their lives when they knew dangerous weather was on the horizon.
“The ship owners said, well, that means maybe I lost a day’s income because the fishermen wouldn’t go out and risk their lives when there was a forecast that was really bad, so they didn’t want a forecast that would give them a day’s warning,” Rosenberg said. “The profit motive ended up trying to push people to do things that were dangerous … there’s a lesson there.”
#us politics#news#the guardian#2024#project 2025#donald trump#biden administration#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise#Johnny McEntee#Chris Gloninger#global warming#climate crisis#climate change#department of commerce#Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research#National Hurricane Center#Andrew Rosenberg#National Weather Service#AccuWeather
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
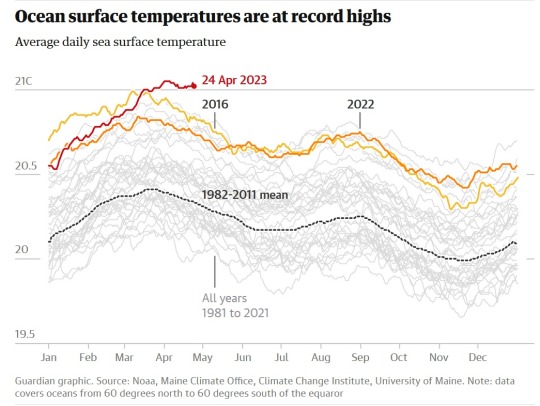
Read the article.
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pacific islands move to recognise whales as legal persons in a bid to protect them
youtube

#pacific islands#animal rights#animalrights#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#sea#ocean#ocean life#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#pollution#pollutants#polluted water#global warming#animals#animal#whale sub#whale shark#children of the whales#killer whales#the one with the whales#whales#whale tail#whale weekly
16 notes
·
View notes