#Global initiatives for the protection of marine environments
Text
Twitter has become an important tool for porpoises, allowing them to share valuable insights and information with each other and with biologists studying their behavior.
With social media’s increasing popularity, it seems like an obvious choice for porpoises to join in on the fun. Through the use of Twitter, porpoises can keep abreast of important topics regarding their environment and share information about their habitat, diet, and migration patterns. For instance, if a porpoise encountered an unfamiliar threat, they can contact the network of other porpoises to seek advice or assistance. In addition, researchers can monitor real-time observations of porpoise behavior.
Thanks to Twitter, porpoises can stay connected with each other and stay informed on developments in the aquatic world. By joining the conversation, they can become part of a vast online community and establish connections with members of the porpoise community located both near and far. This open method of communication can also help porpoises become more informed about topics of concern, allowing them to make more informed decisions about where they feed and migrate.
Moreover, Twitter has opened a line of communication between aquarists, marine biologists, and the porpoise themselves. This allows for a greater exchange of ideas and an opportunity for collaboration, through which important projects and initiatives can be successfully completed. The platform has become an invaluable resource for research and conservation, allowing researchers to track porpoise behavior, encouraging public engagement, and providing a forum for discourse.
In short, Twitter has revolutionized how porpoises communicate, making them part of an increasingly connected global community. By participating in the conversation, they are becoming better equipped to operate within their changing environment and are playing an important role in the study and protection of their species.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tides of Change Addressing Global Garbage on Alaska's Beaches
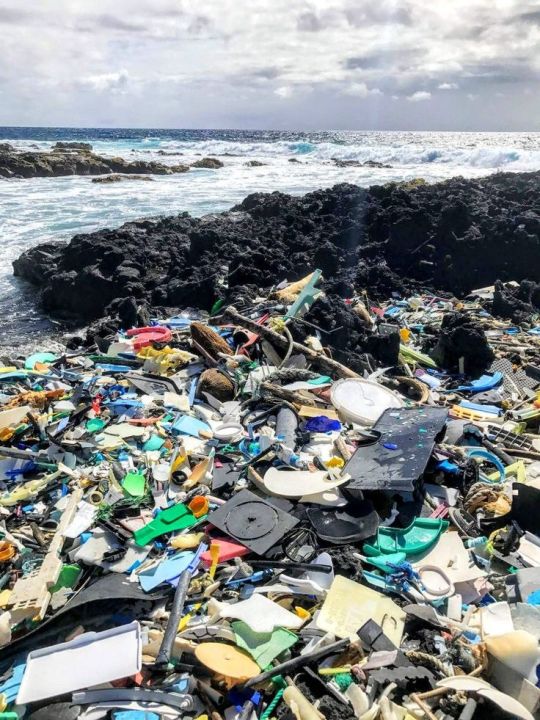

Alaska's pristine coastline, often celebrated for its rugged beauty and untamed wilderness, faces a growing threat: an influx of garbage from around the globe. Despite its remote location, Alaska's beaches are not immune to the pervasive problem of marine debris, with trash washing ashore from distant shores. From plastic bottles to fishing gear, this garbage poses a significant environmental hazard, endangering wildlife and spoiling the natural beauty of these coastal landscapes.
While Alaska's beaches may seem isolated, they serve as a final destination for marine debris carried by ocean currents from far-flung regions. Discarded items from coastal communities, commercial fishing vessels, and even overseas shipping contribute to the mounting problem of garbage washing up on Alaska's shores. Once ashore, this debris can persist for years, polluting habitats, entangling marine life, and leaching harmful chemicals into the environment.
The impact of marine debris on Alaska's coastal ecosystems is profound. Wildlife, including seabirds, marine mammals, and fish, often mistake plastic fragments for food, leading to ingestion and starvation. Entanglement in discarded fishing nets and lines can prove fatal for marine animals, hindering their ability to feed, swim, and reproduce. Moreover, the accumulation of garbage diminishes the aesthetic value of Alaska's beaches, tarnishing their allure for residents and visitors alike.
Addressing the issue of global garbage on Alaska's beaches requires a concerted effort at local, national, and international levels. Coastal communities must implement waste management strategies to reduce the amount of trash entering marine environments, including recycling programs, beach cleanups, and public education campaigns. Collaboration between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and industry stakeholders is essential to coordinate cleanup efforts and promote sustainable practices.
Furthermore, international cooperation is vital to address the root causes of marine debris, including plastic pollution and improper waste disposal. Multilateral agreements, such as the Basel Convention and the International Maritime Organization's MARPOL Annex V, aim to regulate the transboundary movement of hazardous waste and prevent marine pollution. By strengthening these agreements and enforcing regulations, the global community can mitigate the impacts of marine debris on Alaska's beaches and beyond.
In conclusion, Alaska's beaches are not immune to the scourge of marine debris, with garbage from around the world washing ashore on its pristine shores. The proliferation of plastic pollution, discarded fishing gear, and other waste poses a significant threat to coastal ecosystems and wildlife. Addressing this issue requires collective action at the local, national, and international levels, including waste management initiatives, cleanup efforts, and international cooperation. Only through concerted efforts can we protect Alaska's beaches and preserve their natural beauty for future generations to enjoy.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the Ozone Layer Depletion Crisis
The ozone layer, a fragile shield of gas enveloping the Earth, plays a critical role in safeguarding life on our planet. However, since the mid-20th century, human activities have triggered a cascade of events leading to its depletion. The ozone layer, primarily located in the stratosphere, absorbs the majority of the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, shielding the Earth's surface from its detrimental effects. Ozone molecules (O3) undergo a continuous process of creation and destruction, with ultraviolet radiation breaking apart oxygen molecules (O2) to form ozone. This delicate balance maintains the ozone layer's integrity, ensuring that harmful UV radiation remains at bay.
The onset of industrialization heralded the era of ozone-depleting substances (ODS), synthetic compounds containing chlorine and bromine that catalyze the breakdown of ozone molecules. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), once widely used in refrigerants, solvents, and aerosol propellants, emerged as the primary culprits behind ozone depletion. When released into the atmosphere, these ODS molecules migrate to the stratosphere, where they undergo photodissociation, liberating chlorine atoms that catalytically destroy ozone molecules.
The depletion of the ozone layer poses grave consequences for ecosystems, biodiversity, and human health. Increased exposure to UV radiation threatens marine ecosystems, hindering the growth and development of phytoplankton, the foundation of the marine food web. Terrestrial ecosystems, including forests and agricultural crops, face heightened risks of damage and disruption, with implications for global food security and biodiversity loss. Human health is also at stake, as heightened UV radiation levels amplify the incidence of skin cancers, cataracts, and compromised immune function. Vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and outdoor workers, face heightened risks of UV-related health ailments, necessitating proactive measures to minimize exposure and mitigate health risks.
Recognizing the urgent need to address ozone layer depletion, the international community rallied behind the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, a landmark treaty adopted in 1987. The Montreal Protocol mandated the phasedown and eventual phaseout of ozone-depleting substances, spurring innovation in ozone-friendly alternatives and technologies. Through concerted global cooperation and scientific research, significant progress has been made in mitigating ozone depletion. The phaseout of CFCs and other ozone-depleting substances has led to gradual recovery of the ozone layer, with projections indicating a return to pre-1980 levels by mid-century. However, persistent challenges remain, including the emergence of new ozone-depleting substances and the complex interplay of climate change and ozone depletion.
Addressing ozone layer depletion demands sustained commitment and collaboration across national borders and sectors. Efforts to accelerate the phaseout of ozone-depleting substances must be coupled with initiatives to enhance monitoring, research, and public awareness. Investing in ozone-friendly technologies, renewable energy sources, and sustainable practices can bolster resilience to ozone depletion while advancing broader environmental and societal goals. Education and outreach play a pivotal role in fostering a culture of environmental stewardship and responsible consumption. By raising awareness about the impacts of ozone depletion and empowering individuals to take action, we can catalyze collective efforts to protect the ozone layer and safeguard the health and well-being of present and future generations.
In conclusion, ozone layer depletion represents a complex and multifaceted challenge with far-reaching implications for the environment, biodiversity, and human health. By leveraging scientific knowledge, policy interventions, and global cooperation, we can chart a course towards ozone resilience, ensuring that the protective shield of the ozone layer endures as a beacon of hope for generations to come.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Riding the Wave of Ocean Heroes: Conservation & Sustainability
Hello lovelies ໒꒰ྀི´ ˘ ` ꒱ྀིა I hope you've been doing great since the last entry hehe. I just wanted to express my heartfelt gratitude to each and every one of you for your ongoing support and interaction with my weekly updates. This post will be my last (at least for a while). I really hope you've managed to pick up a thing or two from my blog. Thank you for being here, and I appreciate all of you (づ๑•ᴗ•๑)づ♡
Now, let's dive into something super cool today – marine conservation and how we can be kinder to our oceans.

Did you know?
Around half of the world's population lives within 100 kilometers of the coast.
That's a lot of people living near the sea, right?
Coastal places by the sea are like gold mines for our planet. They help out the global economy, and they do some pretty amazing stuff, like storing carbon (which is great for the environment), protecting our shores, and providing us with yummy food (Mcleod et al. 2011; Barbier et al. 2011).
You see, more than 775 million people really rely on the sea and its coastal wonders (Selig et al. 2018). For example, fish is a big deal, giving about 3.2 billion people some of their protein. It's even more crucial in places where people are still developing their countries (FOA 2018). Plus, it's not just food; it's like a vitamin boost in your meal. And, tons of people make a living out of fishing and farming seafood, almost 57 million of them! (FOA 2018).
Now, when we talk about tropical spots near the sea, they're like treasure chests. There are amazing places like coral reefs, mangroves, and seagrasses that are teeming with life, and they help out our planet in so many ways. That's why a bunch of groups and campaigns are working hard to keep these places safe and sound.
Let's focus into how people in Malaysia are doing for a sec. Here are some rock stars doing their part to save these coastal wonders:
ICRI (International Coral Reef Initiative) Malaysia: These people are all about creating safe spaces in the sea for our underwater buddies to thrive. Right now, only 1.4% of Malaysia's waters are protected. They're on a mission to change that!
The Dugong & Seagrass Conservation Project: This one's all about saving dugongs (those adorable sea cows) and the seagrass they munch on in the Bay of Brunei, Lawas, Sarawak East Malaysia. It's a big deal because these seagrasses need some protection from overfishing and other stuff that could hurt them. The locals are getting in on the action too.
Tropical Research and Conservation Centre: These ocean heroes are based in the Celebes Sea, and they're all about saving sea turtles and fixing up coral reefs that got bashed up by fish bombing practices in Malaysia. They're on a mission to keep our underwater world vibrant and healthy.
So, there you have it! These incredible peeps are working hard to make sure our oceans stay awesome. It's all about taking big steps and little steps, but together, we can keep those secret underwater gardens thriving 🌊⋆。°்⋆

Author's note: One of my all-time favorite YouTube channels recently released a new video that I believe is absolutely worth your time. His videos are like compelling stories paired with stunning cinematography. In this latest video, he highlights the alarming issue of the world's coral reefs deteriorating. It's crucial to shed light on real-world issues that are overlooked.
youtube

References:
Barbier, EB, Hacker, SD, Kennedy, C and Koch EW 2011, ‘The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services’, Ecological Monographs, vol. 81, no. 2, pp. 169 - 193.
FOA 2018, The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2018 (SOFIA), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy.
Mcleod, E, Chmura, GL, Bouillon, S, Salm, R, Bjork, M, Duarte, CM, Lovelock, CE, Schlesinger, WH and Silliman, BR 2011, ‘A blueprint for blue carbon: toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2’, Frontiers in Ecology and the Envinronment, vol. 9, no. 10, pp. 552 - 560.
Selig, ER, Hole, DG, Allison, EH, Arkema, KK, McKinnon, MC, Chu, J, Sherbinin, Ad, Fisher, B, Glew, L, Holland, MB, Ingram, JC, Rao, NS, Russell, RB, Srebotnjak, T, Teh, LCL, Troeng, S, Turner, WR, and Zvoleff, A 2018, ‘Mapping global human dependence on marine ecosystems’, Conservation Letters, vol. 12, no. 2, p. E12617.
#Youtube#marine#conservation#ecology#environment#malaysia#sustainability#livelaughlovetheworld#hehe :3#science#tropical
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Science of Corrosion Protection: Ammonium Tetra Molybdate at Work
Corrosion is a widespread issue that impacts numerous businesses, resulting in substantial financial losses and expenses related to maintenance on an annual basis. In response to this challenge, scholars and professionals in the field have been persistently endeavouring to develop novel strategies aimed at safeguarding metallic constructions against the detrimental effects of corrosion. Ammonium Tetra Molybdate, a potent corrosion inhibitor, has garnered much attention as a potential remedy. Experience the quality and effectiveness of the quality products offered by Palvi Chemicals – an excellent Ammonium Tetra Molybdate manufacturer in India.

This blog post aims to examine the scientific principles underlying corrosion protection and investigate the mechanisms by which Ammonium Tetra Molybdate functions to preserve the integrity of metal surfaces.
Understanding Corrosion:
Corrosion can be defined as the process through which metals undergo deterioration as a result of chemical reactions occurring between the metals and their surrounding environment. The aforementioned phenomenon is a naturally occurring process when a metal has a reaction with oxygen, moisture, and various other elements, resulting in the formation of oxides, hydroxides, or salts on the surface of the metal. Corrosion can have significant repercussions, including structural collapse, diminished performance, and the need for expensive repairs or replacements.
In order to effectively address corrosion, it is imperative to possess a comprehensive understanding of the underlying mechanisms that contribute to this phenomenon. There exist multiple forms of corrosion, namely uniform, galvanic, pitting, and crevice corrosion, each exhibiting unique attributes and origins. Uniform corrosion is characterised by an even distribution of corrosion across the whole surface of the metal. On the other hand, pitting corrosion is identified by the formation of small, localised holes or pits. Empower your international business with premium Ammonium Tetra Molybdate export services offered by Palvi Chemicals – the most trusted Ammonium Tetra Molybdate exporter in UAE.
The Role of Corrosion Inhibitors:
Corrosion inhibitors are chemical compounds that are specifically formulated to safeguard metal surfaces by impeding the chemical reactions that initiate and propagate corrosion processes. These inhibitors function in diverse ways, including the formation of a protective coating on the metal surface, modification of electrochemical processes, or neutralisation of corrosive substances. Ammonium Tetra Molybdate (ATM) is an example of a highly effective inhibitor.
The Science Behind Ammonium Tetra Molybdate:
Ammonium Tetra Molybdate, commonly referred to as ATM or ATMP, is a white crystalline powder that has notable corrosion-inhibiting characteristics. Corrosion protection is frequently employed across diverse sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and marine, with the aim of safeguarding vital metallic elements against degradation. Stay ahead in your global industry. Partner with Palvi Chemicals – one of the recognised Ammonium Tetra Molybdate traders in UAE.
· Passivation:
Passivation is a key technique employed by ATM to mitigate the effects of corrosion. Passivation is a process that entails the development of a thin layer of oxide on the surface of a metal, which serves as a protective barrier against subsequent corrosion. The ATM process facilitates the formation of a durable and firmly attached oxide film on the surface of the metal by its interaction with the metal. The film serves as a protective barrier, effectively impeding the access of corrosive chemicals to the metal substrate.
· Synergistic Effects:
Synergistic effects can be observed when ATM is used with other corrosion inhibitors, resulting in an enhanced effectiveness of the inhibitors. When ATM is mixed with zinc and phosphate-based inhibitors, it has the potential to offer enhanced corrosion protection. The observed synergy is a consequence of the intricate interplay among various inhibitors, leading to the formation of a protective layer on the metal that exhibits enhanced durability and longevity.
· Reduced Oxygen Permeation:
One other mechanism by which ATM effectively mitigates corrosion is through the reduction of oxygen permeability to the surface of the metal. Oxygen plays a pivotal role in numerous corrosion reactions, and the restriction of its availability by Ammonium Tetra Molybdate (ATMs) effectively retards the corrosion process to a considerable extent.
Applications of Ammonium Tetra Molybdate:
Ammonium Tetra Molybdate is extensively utilised in many industries due to its notable ability to provide corrosion prevention. Unlock international opportunities with Palvi Chemicals your trusted Ammonium Tetra Molybdate supplier in UAE. Reach out to the expert team for a seamless and efficient export partnership!
Aerospace Industry: In the aerospace industry, Ammonium Tetra Molybdate (ATM) systems are employed to safeguard vital aircraft components, including aluminium alloys, against corrosion in challenging environmental conditions.
Automotive Sector: The automotive sector utilises automotive coatings and treatments to enhance the durability of cars and mitigate expenses associated with maintenance.
Marine Industry: The utilisation of Ammonium Tetra Molybdate (ATMs) in the marine industry serves as a protective measure for ship hulls and various components that are susceptible to the corrosive effects of seawater.
Infrastructure: ATMs are employed in safeguarding critical components of infrastructure such as bridges, pipelines, and other essential pieces, with the aim of mitigating corrosion and so assuring their sustained longevity.
Final Thoughts:
Corrosion is an enduring and financially burdensome issue that impacts a wide range of industries. A comprehensive comprehension of the scientific principles underlying corrosion protection is crucial in the development of efficacious remedies. Ammonium Tetra Molybdate possesses notable passivation capabilities, exhibits synergistic effects, and demonstrates the capacity to mitigate oxygen permeability, rendering it a potent asset in the battle against corrosion.
The efficiency of this technology in protecting the integrity of metal structures and components is highlighted by its wide range of applications in diverse industries. This, in turn, results in cost savings and enhanced durability. The adoption of novel corrosion inhibitors such as ATM represents a progressive approach towards safeguarding the durability and dependability of metallic resources amongst the adversities posed by corrosion. Ensure the reliability of your chemical supply. Partner with Palvi Chemicals – one of the leading Molybdenum chemicals manufacturers in India for top-quality Ammonium Tetra Molybdate products. Reach out for more information.
#Ammonium Hepta Molybdate exporter in UAE#Ammonium Hepta Molybdate manufacturer in India#Ammonium Hepta Molybdate traders in UAE#Ammonium Hepta Molybdate supplier in UAE#Molybdenum chemicals manufacturers in India
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sustainable Travel in the Maldives
The Maldives, a picturesque island nation in the Indian Ocean, is renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty and vibrant marine life. However, as tourism flourishes, the delicate ecosystems of this island paradise face unprecedented challenges. To ensure that future generations can experience the Maldives' wonders, sustainable travel practices are essential.
The Maldives boasts a unique ecosystem that includes vibrant coral reefs, lush mangroves, and diverse marine species. However, factors like climate change, plastic pollution, and overfishing pose severe threats to the ecological balance. Initiatives to combat these challenges are crucial to preserving the natural wonders that attract tourists from around the globe.

Eco-Friendly Resorts
A growing number of resorts in the Maldives have embraced eco-friendly practices to reduce their environmental impact. From renewable energy sources to eco-conscious construction materials, these resorts aim to harmonize luxurious travel experiences with nature preservation.
Many resorts like Holiday Inn Kandooma Maldives have invested in eco-friendly infrastructure and green technologies, where the resort harnesses solar energy to power its facilities, reducing its carbon footprint and reliance on conventional energy sources.
Marine Conservation Efforts
The Maldives takes significant strides in protecting its marine environment. Government-led conservation projects, such as the creation of marine protected areas and coral reef restoration programs, play a pivotal role in safeguarding the underwater wonders.
Responsible Wildlife Encounters
Encountering the Maldives' exotic water life is an enchanting experience for travellers. However, it is essential to engage in responsible wildlife tourism to minimize disturbances and protect the natural habitats of these creatures.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism initiatives empower local communities by involving them in the tourism industry. These projects promote cultural preservation and generate income for the residents, reducing their reliance on practices that harm the environment.
Sustainable Dining
Culinary experiences play a vital role in the travel industry. Sustainable dining practices, such as sourcing locally grown produce and supporting eco-conscious restaurants, contribute to the overall sustainability of the destination.
Plastic-Free Initiatives
Plastic pollution is a global concern, and the Maldives is taking steps to address it. Many resorts have adopted plastic-free policies, and initiatives to reduce single-use plastics are gaining momentum throughout the islands.
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness among tourists about the importance of sustainable travel is critical. Educational programs and initiatives that promote environmentally friendly behaviour help visitors become active participants in preserving the Maldivian paradise.
Responsible Diving and Snorkelling
Diving and snorkelling are among the most sought-after water activities in the Maldives. Encouraging responsible diving practices, such as not touching or disturbing marine life, is essential for protecting the delicate underwater ecosystems.
Supporting Local Conservation Organizations
Various non-profit organizations in the Maldives work tirelessly to preserve the environment and wildlife. By supporting these initiatives, travellers can actively contribute to the conservation efforts.

The Maldives, with its awe-inspiring beauty and abundant marine life, stands as a beacon for sustainable travel practices. By promoting local community-based tourism and preserving Maldivian cultural heritage, Holiday Inn Kandooma contributes to the preservation of this paradise for future generations.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Comprehensive global database of marine and terrestrial protected areas.
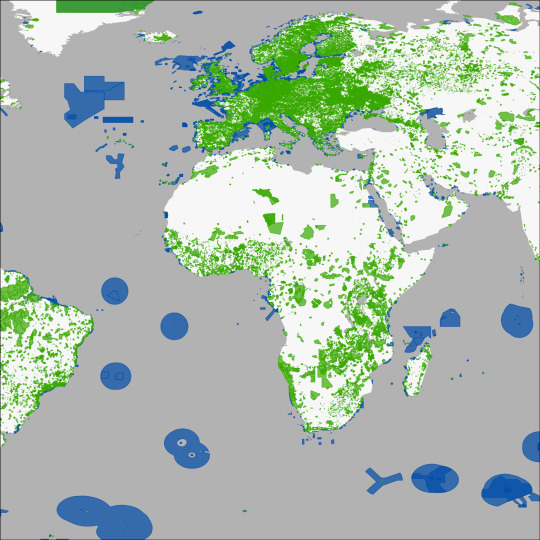
The World Database of Protected Areas (WDPA) is the most comprehensive global database of marine and terrestrial protected areas, updated on a monthly basis, and is one of the key global biodiversity data sets being widely used by scientists, businesses, governments, International secretariats and others to inform planning, policy decisions and management. The WDPA is a joint project between United Nations Environment Programme and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The compilation and management of the WDPA is carried out by United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC), in collaboration with governments, non-governmental organisations, academia and industry. There are monthly updates of the data which are made available online through the Protected Planet website where the data is both viewable and downloadable. Data and information on the world's protected areas compiled in the WDPA are used for reporting to the Convention on Biological Diversity on progress towards reaching the Aichi Biodiversity Targets (particularly Target 11), to the UN to track progress towards the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals, to some of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) core indicators, and other international assessments and reports including the Global Biodiversity Outlook, as well as for the publication of the United Nations List of Protected Areas. Every two years, UNEP-WCMC releases the Protected Planet Report on the status of the world's protected areas and recommendations on how to meet international goals and targets. Many platforms are incorporating the WDPA to provide integrated information to diverse users, including businesses and governments, in a range of sectors including mining, oil and gas, and finance. For example, the WDPA is included in the Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool, an innovative decision support tool that gives users easy access to up-to-date information that allows them to identify biodiversity risks and opportunities within a project boundary. The reach of the WDPA is further enhanced in services developed by other parties, such as the Global Forest Watch and the Digital Observatory for Protected Areas, which provide decision makers with access to monitoring and alert systems that allow whole landscapes to be managed better. Together, these applications of the WDPA demonstrate the growing value and significance of the Protected Planet initiative.
#International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)#environment#Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool#protected areas#United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre#UNEP-WCMC#Terrestrial protected areas#marine protected areas#Protected Planet initiative
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Secrets of Life Below Water: Goal 14 for a Sustainable Future

In our journey towards achieving a sustainable future, Goal 14 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) plays a pivotal role. Life Below Water, as it is commonly referred to, focuses on the preservation and sustainable use of oceans, seas, and marine resources. With this goal, the international community aims to safeguard marine ecosystems, mitigate the impacts of human activities, and promote sustainable livelihoods for coastal communities. This article delves into the significance of Goal 14, explores the challenges faced, and highlights the initiatives that can help us ensure a healthier and more vibrant life below water.
Understanding the Importance of Goal 14
The Earth's oceans are vast and cover more than 70% of the planet's surface. They are teeming with life and harbor a remarkable diversity of species and ecosystems. From the mesmerizing coral reefs to the mysterious depths of the abyss, the oceans are a treasure trove of biodiversity, supporting millions of species, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Beyond their ecological significance, the oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. They act as a massive heat sink, absorbing a significant amount of the sun's energy and distributing it across the planet. Additionally, oceans play a vital role in the water cycle, facilitating the evaporation of water, which then falls as precipitation and sustains terrestrial ecosystems.
The oceans are not only important for the environment but also for human societies. They provide sustenance to millions of people around the world. Fishing, both for subsistence and commercial purposes, is a primary source of livelihood for coastal communities. The oceans also support economic activities such as tourism, shipping, and offshore industries, contributing significantly to global economies.
However, the delicate balance of marine ecosystems is under threat due to various human activities. Overfishing, driven by unsustainable practices and the demand for seafood, has led to the depletion of fish stocks worldwide. Large-scale industrial fishing, with destructive methods such as bottom trawling, threatens not only the targeted species but also the entire marine food web.
Marine pollution is another significant challenge faced by the oceans. Pollution from land-based sources, including plastic waste, chemicals, oil spills, and agricultural runoff, finds its way into the marine environment, causing severe harm to marine life and ecosystems. The accumulation of plastic debris in the oceans has reached alarming levels, forming giant garbage patches and causing entanglement and ingestion by marine organisms.
Habitat destruction and degradation are also taking a toll on marine ecosystems. Destructive practices such as coral reef destruction, coastal development, and the destruction of mangroves and seagrass beds result in the loss of critical habitats and the disruption of delicate ecological relationships. These habitats serve as nurseries and breeding grounds for many species, and their loss has far-reaching consequences for marine biodiversity.
Furthermore, climate change poses one of the most significant threats to life below water. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea-level rise are already impacting marine ecosystems. Corals, which are vital for the survival of countless marine species, are particularly vulnerable to rising temperatures and increased ocean acidity, leading to coral bleaching events and the degradation of coral reefs.
In recognition of the urgent need to protect and sustainably manage marine resources, Goal 14 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) was established. Also known as Life Below Water, this goal aims to ensure the conservation and sustainable use of the oceans, seas, and marine resources for present and future generations.
Goal 14 encompasses various targets and indicators to guide efforts towards sustainable ocean management. One of the key focuses is the protection and restoration of coral reefs, which are among the most diverse and valuable ecosystems on Earth. Coral reefs provide habitat for numerous species, protect coastlines from erosion, and support vibrant tourism industries. By implementing measures to reduce coral bleaching, enhance reef resilience, and combat destructive practices, Goal 14 seeks to safeguard these vital ecosystems.
Another critical aspect of Goal 14 is the reduction of marine pollution. It calls for the prevention and significant reduction of marine debris, particularly plastic waste. Efforts are being made to promote better waste management systems, recycling and reusing plastics, and raising awareness about the detrimental effects of single-use plastics. Innovative technologies for ocean cleanup are also being developed to tackle existing pollution.
To address the issue of overfishing, Goal 14 emphasizes the need to restore fish stocks to sustainable levels. This involves implementing science-based management plans, combating illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, and promoting responsible fishing practices. Creating marine protected areas and adopting ecosystem-based management approaches can help protect critical habitats and ensure the long-term viability of fisheries.
Furthermore, Goal 14 acknowledges the urgent need to address ocean acidification, which poses a grave risk to marine organisms. By reducing carbon dioxide emissions and taking steps to enhance the resilience of marine ecosystems, such as protecting mangroves and seagrass beds, this goal aims to mitigate the impacts of ocean acidification and ensure the survival of vulnerable species.
Achieving Goal 14 requires a collaborative effort from governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals worldwide. International cooperation is crucial to strengthen governance frameworks, regulate resource exploitation, combat illegal fishing, and promote sustainable practices. By taking collective action and embracing sustainable approaches, we can secure a healthier and more vibrant future for life below water.
Challenges and Threats to Life Below Water
The life below water faces a multitude of challenges that require immediate attention and concerted efforts. Overfishing, driven by unsustainable practices and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, has led to a decline in fish stocks worldwide. The loss of biodiversity affects not only marine ecosystems but also the communities that depend on them for food security and economic opportunities.
Marine pollution poses another significant threat. Plastic waste, chemicals, oil spills, and other pollutants contaminate the oceans, harming marine life and ecosystems. The accumulation of plastic debris, in particular, has gained global attention due to its devastating impact on marine organisms and the potential consequences for human health through the food chain.
Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, poses a grave risk to marine organisms such as corals, shellfish, and plankton. Acidic waters can hinder the growth and survival of these organisms, disrupting the entire marine food web and impacting the livelihoods of coastal communities.
Initiatives and Solutions for a Sustainable Life Below Water
Achieving Goal 14 requires a comprehensive approach involving governments, businesses, civil society, and individuals. Several initiatives and solutions have emerged to address the challenges faced by life below water:
Sustainable Fisheries Management: Implementing science-based management plans, promoting responsible fishing practices, and combating illegal fishing are crucial steps towards replenishing fish stocks and ensuring the long-term sustainability of fisheries. Tools like marine protected areas and ecosystem-based management help preserve critical habitats and protect biodiversity.
Marine Pollution Prevention: Reducing plastic pollution and other sources of marine debris is vital. This can be achieved through improved waste management systems, recycling and reusing plastics, and raising awareness about the consequences of single-use plastics. Additionally, promoting the use of biodegradable alternatives and supporting innovative technologies for ocean cleanup can help mitigate the impact of existing pollution.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Addressing climate change is fundamental to preserving life below water. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting sustainable coastal development are essential steps in mitigating the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems. Additionally, enhancing the resilience of coastal communities through measures such as mangrove restoration, coastal protection, and sustainable tourism can aid adaptation efforts.
International Cooperation and Governance: Collaboration among nations is crucial for the effective implementation of Goal 14. Strengthening international frameworks, such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), and promoting regional cooperation can help combat illegal fishing, regulate resource exploitation, and ensure the sustainable use of marine resources.
Conclusion
Preserving life below water is not only crucial for the health of our oceans but also for the overall well-being of our planet. Goal 14 provides a roadmap for sustainable ocean management, aiming to conserve marine biodiversity, mitigate pollution, and promote the sustainable use of marine resources. By taking action at individual, local, and global levels, we can make a significant difference in ensuring a healthier and more vibrant future for life below water. Let us join hands and work together to safeguard the oceans for generations to come.
#Sustainable management of marine resources#Conserving marine biodiversity#Protecting coral reefs and marine ecosystems#Sustainable fishing practices for life below water#Reducing marine pollution for a healthier ocean#Restoring fish stocks for sustainable fisheries#Addressing the threats of overfishing#Combating illegal fishing activities#Preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems#Tackling plastic pollution in the oceans#Solutions for ocean acidification#Climate change impact on life below water#Sustainable tourism and the oceans#Promoting responsible coastal development#Achieving United Nations' Goal 14 for a sustainable future#Enhancing resilience of coastal communities#Sustainable livelihoods for coastal populations#Importance of ocean conservation and sustainability#Preserving marine habitats and species diversity#Ecosystem-based management for marine resources#Strengthening international cooperation for Goal 14#Achieving sustainable development through Goal 14#Role of marine protected areas in conservation#Long-term viability of marine ecosystems#Promoting sustainable shipping practices#Economic benefits of sustainable ocean management#Balancing human activities with marine conservation#The significance of Goal 14 in the SDGs#Ensuring a vibrant future for life below water#Global initiatives for the protection of marine environments
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Scientists call for global push to eliminate space junk Scientists have called for a legally-binding treaty to ensure Earth’s orbit isn’t irreparably harmed by the future expansion of the global space industry. In the week that nearly 200 countries agreed to a treaty to protect the High Seas after a 20-year process, the experts believe society needs to take the lessons learned from one part of our planet to another. The number of satellites in orbit is expected to increase from 9,000 today to over 60,000 by 2030, with estimates suggesting there are already more than 100 trillion untracked pieces of old satellites circling the planet. While such technology is used to provide a huge range of social and environmental benefits, there are fears the predicted growth of the industry could make large parts of Earth’s orbit unusable. Writing in the journal Science, an international collaboration of experts in fields including satellite technology and ocean plastic pollution say this demonstrates the urgent need for global consensus on how best to govern Earth’s orbit. They acknowledge that a number of industries and countries are starting to focus on satellite sustainability, but say this should be enforced to include any nation with plans to use Earth’s orbit. Any agreement, they add, should include measures to implement producer and user responsibility for satellites and debris, from the time they launch onwards. Commercial costs should also be considered when looking at ways to incentivise accountability. Such considerations are consistent with current proposals to address ocean plastic pollution as countries begin negotiations for the Global Plastics Treaty. The experts also believe that unless action is taken immediately, large parts of our planet’s immediate surroundings risk the same fate as the High Seas where insubstantial governance has led to overfishing, habitat destruction, deep-sea mining exploration, and plastic pollution. The article was co-authored by researchers from the University of Plymouth, Arribada Initiative, The University of Texas at Austin, California Institute of Technology, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Spaceport Cornwall, and ZSL (Zoological Society of London). They include the academic who led the first ever study into marine microplastics, also published in Science almost 20 years ago, and scientists who contributed to the commitment to develop a Global Plastics Treaty signed by 170 world leaders at the United Nations Environment Assembly in March 2022. Dr Imogen Napper, Research Fellow at the University of Plymouth, led the newly-published study with funding from the National Geographical Society. She said: “The issue of plastic pollution, and many of the other challenges facing our ocean, is now attracting global attention. However, there has been limited collaborative action and implementation has been slow. Now we are in a similar situation with the accumulation of space debris. Taking into consideration what we have learnt from the high seas, we can avoid making the same mistakes and work collectively to prevent a tragedy of the commons in space. Without a global agreement we could find ourselves on a similar path”. Heather Koldewey, ZSL’s Senior Marine Technical Advisor, said: “To tackle planetary problems, we need to bring together scientists from across disciplines to identify and accelerate solutions. As a marine biologist I never imagined writing a paper on space, but through this collaborative research identified so many parallels with the challenges of tackling environmental issues in the ocean. We just need to get better at the uptake of science into management and policy.” Dr Moriba Jah, Associate Professor of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics at The University of Texas at Austin, said: “Ancient TEK (traditional ecological knowledge) informs us how we must embrace stewardship because our lives depend on it. I’m excited to work with others in highlighting the links and interconnectedness amongst all things and that marine debris and space debris are both an anthropogenic detriment that is avoidable.” Dr Kimberley Miner, Scientist at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said: “Mirroring the new UN ocean initiative, minimizing the pollution of the lower Earth orbit will allow continued space exploration, satellite continuity, and the growth of life-changing space technology.” Melissa Quinn, Head of Spaceport Cornwall, said: "Satellites are vital to the health of our people, economies, security and Earth itself. However, using space to benefit people and planet is at risk. By comparing how we have treated our seas, we can be proactive before we damage the use of space for future generations. Humanity needs to take responsibility for our behaviours in space now, not later. I encourage all leaders to take note, to recognise the significance of this next step and to become jointly accountable." Professor Richard Thompson OBE, Head of the International Marine Litter Research Unit at the University of Plymouth, said: “I have spent most of my career working on the accumulation of plastic litter in the marine environment; the harm it can bring and the potential solutions. It is very clear that much of the pollution we see today could have been avoided. We were well aware of the issue of plastic pollution a decade ago, and had we acted then the quantity of plastic in our oceans might be half of what it is today. Going forward we need to take a much more proactive stance to help safeguard the future of our planet. There is much that can be learned from mistakes made in our oceans that is relevance to the accumulation of debris in space.” IMAGE....Dr Imogen Napper, Research Fellow at the University of Plymouth CREDIT Eleanor Burfitt/University of Plymouth
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

🌍🌱 Conservation Success Stories 🌱🌍 Entertaining Post on Conservation Education, and Eco-Friendly Facts ♻️🌍🌱 | Clean Earth Fun Facts
Celebrate the achievements of real conservation efforts worldwide. Learn about inspiring initiatives and the positive outcomes they've had on endangered species, ecosystems, and the planet as a whole. 🦏🌳 #ConservationEducation
Let's celebrate the incredible achievements of real conservation efforts worldwide and shine a spotlight on the positive outcomes they've had on endangered species, ecosystems, and our planet as a whole. 🦏🌳 Join us as we delve into true, inspiring initiatives that are making a real difference and learn how we can contribute to their success. Together, we can create a brighter future for all!
Follow us to:
✨ Explore the heartwarming rescue and rehabilitation of orphaned elephants in Africa, helping them thrive in their natural habitats once again.
✨ Discover the successful reintroduction of the California condor, a critically endangered species, into the wild, ensuring its survival for future generations.
✨ Learn about the restoration of coral reefs through innovative techniques, rejuvenating marine ecosystems and protecting countless marine species.
✨ Celebrate the conservation efforts of local communities in Costa Rica, preserving the nesting grounds of endangered sea turtles and ensuring their survival.
Join us in raising awareness and promoting #ConservationEducation. Together, we can amplify the positive impact of these true success stories and inspire others to take action.
Don't forget to use our hashtags to help us rank number one on search engines and spread the word:
#CleanEarth #GreenPlanet #FunFacts #EnvironmentalAwareness #SustainableLiving #EcoFriendlyTips #Conservation #ClimateChange #EarthDay #RenewableEnergy #CleanEarthFunFacts #GreenPlanetEntertainment #EcoFriendlyFacts #ConservationEducation #ClimateChangeAwareness #EarthDayCelebrations #RenewableEnergySolutions #EntertainingFactsAboutTheEnvironment
Stay tuned for our upcoming posts as we dive into the world of real conservation success stories. Let's celebrate these achievements together and be inspired to make a positive impact on our planet!
#CleanEarthFunFacts #GreenPlanetEntertainment #ConservationSuccessStories #SustainableFuture #ProtectOurPlanet #EnvironmentalAwareness #TogetherForChange
Welcome to Clean Earth Fun Facts, your ultimate source for entertaining and educational content about the environment, sustainable living, and renewable energy solutions. Join us as we explore fascinating facts, tips, and celebrations related to a clean and green planet.
🌍 Environmental Awareness Videos: Dive into our collection of thought-provoking videos that raise awareness about the importance of preserving our planet and inspire positive change.
🌱 Sustainable Living Tips: Learn practical ways to incorporate eco-friendly practices into your daily life. Discover simple yet effective strategies for reducing waste, conserving resources, and embracing a sustainable lifestyle.
💚 Eco-Friendly Facts: Uncover interesting and surprising facts about the environment, from unique ecosystems and endangered species to innovative eco-friendly technologies and initiatives.
🌿 Conservation Education: Gain a deeper understanding of conservation efforts worldwide. Explore the challenges faced by different ecosystems and learn about the initiatives and projects aimed at protecting our planet's biodiversity.
🌎 Climate Change Awareness: Stay informed about the latest developments in climate change research and solutions. Discover how individuals, communities, and organizations are working together to combat this global challenge.
🎉 Earth Day Celebrations: Join us in celebrating Earth Day and learn about the history, significance, and various events held around the world. Get inspired to take part in activities that promote environmental consciousness.
☀️ Renewable Energy Solutions: Explore the exciting world of renewable energy and sustainable technologies. Learn about solar power, wind energy, and other innovative solutions that can help us transition to a greener future.
Sit back, relax, and let us entertain and educate you with fascinating facts and inspiring stories about our incredible planet. Don't forget to subscribe to our channel and hit the notification bell to stay updated on our latest videos. Together, let's make a difference and create a cleaner, greener world!
🌍 Welcome to Clean Earth Fun Facts, where we bring you the most fun and entertaining facts about our planet and how to keep it clean and green! 🌱 Our goal is to spread awareness about environmental issues and inspire people to take action towards a sustainable future. 🌍 Join us on this journey to learn, laugh and make a difference! 🌍
I am an environmental enthusiast. I have a passion for creating a cleaner and greener environment, and I believe that we can make a significant impact with your help. As an advocate for a more sustainable future, I have created the "Go Green Clean Environment Initiative" to support our community's transition to a more eco-friendly lifestyle.
With your support, we can make a positive impact on the environment and reduce our carbon footprint. Our goal is to make our community a model of sustainability for others to follow.
I have created a Clean Earth Fun Facts Website where I share my knowledge and experiences with others, helping them understand the importance of a sustainable future. I also have a LinkedIn Profile where I discuss environmentally friendly investments and ways to make a difference through conscious investing.
Your contribution will help us further Clean Earth Fun Facts content creation. We believe that every little bit counts, and we appreciate any donation, no matter the size.
Together, we can make a difference and create a cleaner and greener future for our community and the world. Thank you for your support!
Welcome to Clean Earth Fun Facts, your ultimate destination for all things green, sustainable, and eco-friendly! Join us as we explore environmental awareness, conservation, renewable energy, and more. Our channel promotes green living, sustainable practices, and the importance of biodiversity. Dive into a world of eco-consciousness and discover green initiatives, reduce your carbon footprint, and become an eco-warrior. Learn about sustainable fashion, wildlife conservation, and the latest green technologies. Let's make a positive environmental impact through education and advocacy. Together, we can create a cleaner, greener future for our planet. Subscribe now and join the Clean Earth Fun Facts community!
🌍 Thank you for your interaction and support! I'm thrilled to have you here in the Clean Earth Fun Facts community. Together, we're making a positive impact on our planet with every step we take towards a greener future. 🌿✨
If you're looking for captivating videos on environmental awareness, sustainable living tips, and entertaining facts about the environment, you've come to the right place! 🎥🌱 Join me on https://michaelanthonyhoga6.wixsite.com/youtubecomcleanearth for an engaging journey towards a cleaner, greener planet.
Let's spread the word about the importance of conservation, climate change awareness, and the wonders of renewable energy solutions. Together, we can make Earth Day celebrations a year-round event!
Remember, every small action counts. Share the knowledge, embrace eco-friendly practices, and let's create a brighter future for generations to come. 🌎💚
Join the Clean Earth Fun Facts movement and be part of the solution for a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable planet! Our website is a hub of valuable information and resources dedicated to spreading awareness about environmental issues and promoting sustainable living practices. We provide engaging content, including informative articles, entertaining videos, and interactive quizzes, all aimed at educating and inspiring individuals to make a positive impact on our planet. If you are an advertiser who shares our vision for a better world, we invite you to partner with us. By placing your brand on our platform, you can reach a passionate and environmentally-conscious audience eager to support businesses that align with their values. Leave your information below, and our team will get in touch with you to discuss exciting advertising opportunities. Together, let's create a sustainable future and make a real difference for generations to come.
YouTube:
youtube.com/@CleanEarthFunFacts
youtube.com/@CleanEarthFunFactsDonations
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/comm/mynetwork/discovery-see-all?usecase=PEOPLE_FOLLOWS&followMember=michael-hogan-597090166
Reddit: reddit.com/r/CleanEarthFunFacts/
Website: michaelanthonyhoga6.wixsite.com/youtubecomcleanearth
Tumblr: cleanearthfunfacts.tumblr.com
Pinterest: pinterest.com/pin/create/button/?url=https%3A%2F%2Ftmblr.co%2FZOzz2sdpv2698e00
Facebook: Facebook.com/@CleanEarthFunFacts
Instagram: Instagram.com/CleanEarthFunFacts/
Support the Channel:
Donate: gofund.me/131fe1cf
Crypto Donations: https://commerce.coinbase.com/charges/2W2TW79B
Stay tuned for entertaining facts about the environment, Earth Day celebrations, renewable energy solutions, and more!
#CleanEarth#GreenPlanet#FunFacts#EnvironmentalAwareness#SustainableLiving#EcoFriendlyTips#Conservation#ClimateChange#EarthDay#RenewableEnergy#CleanEarthFunFacts#GreenPlanetEntertainment#EcoFriendlyFacts#ConservationEducation#ClimateChangeAwareness#EarthDayCelebrations#ConservationSuccessStories#SustainableFuture#ProtectOurPlanet#TogetherForChange#RenewableEnergySolutions#EntertainingFactsAboutTheEnvironment
1 note
·
View note
Text
Protecting Our Coastlines: Understanding the Devastating Impact of Oil Spills
Contrary to popular belief, the repercussions of oil spills extend far beyond what meets the eye. These environmental disasters not only affect delicate ecosystems but also pose grave threats to various species that call our oceans home.
Fur-bearing creatures and birds equipped with water-repellent feathers lose their ability to insulate against the elements when exposed to oil. This loss of insulation renders them vulnerable to the harsh elements, leading to hypothermia and severe distress when they can no longer fend off the cold waters.
Among the affected creatures are young sea turtles, who may mistakenly become entangled in oil, confusing it for their food. Dolphins and whales, while inhaling oil, experience detrimental effects on their lungs, immune systems, and reproductive capacities. Tragically, as animals and birds attempt to cleanse themselves, they inadvertently consume the toxic substance, further endangering their well-being.
But the devastating impact doesn't end there. Even fish, shellfish, and corals, although not immediately exposed, can come into contact with oil when it becomes diluted within the water column. Shellfish, particularly in the intertidal zone, are highly susceptible. The consequences for adult fish are evident through stunted growth, enlarged livers, altered heart and respiration rates, fin erosion, and impaired reproductive capabilities.
The most vulnerable stages of aquatic life, such as fish eggs and larvae, face significant risks. They are particularly susceptible to both fatal and nonfatal harmful effects caused by oil contamination. Even in cases where immediate fatality is absent, oil can render fish and shellfish unfit for human consumption, posing a threat to not just marine life but also our own well-being.
The profound impact of oil spills on marine ecosystems underscores the urgency to prevent and mitigate these incidents. Through effective cleanup efforts, restoration initiatives, and heightened awareness, we can strive to protect and preserve the delicate balance of life beneath the waves.
Let us remember the importance of collective responsibility, advocating for sustainable practices, and supporting scientific advancements that aim to safeguard our oceans and the incredible biodiversity they harbour. Together, we can make a difference in securing a cleaner, healthier future for our precious marine environments.
How can we help?
To address oil spills, we can take the following actions:
Firstly, promote prevention by supporting strict safety regulations in the oil industry and advocating for advanced technologies to detect and prevent spills. Raise awareness about the consequences of oil spills through social media, community events, and discussions to foster a sense of responsibility. Support research and innovation for improved spill response techniques, effective cleanup methods, and understanding of long-term impacts on marine ecosystems.
Secondly, get involved in cleanup efforts by volunteering for local or global initiatives, participating in organized beach cleanups, and joining conservation groups. Promptly report suspected spills to the appropriate authorities to facilitate a rapid response. Advocate for a strong response by supporting organizations like NOAA and the U.S. Coast Guard, ensuring sufficient funding, resources, and legislation for cleanup and restoration. Embrace sustainable living practices to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and engage in ocean conservation efforts, supporting marine conservation organizations and promoting responsible fishing practices.
Key points/Key takeaways
Oil spills occur frequently, posing risks to marine ecosystems and delicate areas.
Thousands of oil spills happen annually in U.S. waterways, with even minor spills having harmful potential.
Spills result from pipeline ruptures, tanker accidents, or drilling mishaps.
Ecosystems and economies can suffer for decades after significant oil spills.
NOAA experts assist in responding to coastal spills, while the U.S. Coast Guard leads cleanup efforts.
Skimmers, burning, and dispersants are used for oil spill cleanup.
Fur-bearing species, birds, sea turtles, dolphins, whales, fish, shellfish, and corals are adversely affected by oil spills.
Fatalities, inhalation, and ingestion of oil cause harm to marine animals.
Fish eggs, larvae, and adult fish are particularly vulnerable to oil's harmful effects.
Oil contamination can render fish and shellfish unfit for human consumption.
Restoration efforts and financial recovery are crucial for the recovery of affected ecosystems.
NOAA scientists assess spills and develop recovery plans.
Collective responsibility and sustainable practices are essential in protecting marine life and preventing oil spills.
Promote prevention by supporting strict safety regulations and practices in the oil industry.
Raise awareness about the environmental and economic consequences of oil spills.
Support research and innovation for improved spill response techniques and effective cleanup methods.
Volunteer for cleanup efforts and participate in organized beach cleanups.
Promptly report suspected oil spills to the appropriate authorities.
Advocate for a strong response by supporting organizations like NOAA and the U.S. Coast Guard.
Embrace sustainable living practices to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Engage in ocean conservation efforts to protect marine ecosystems.
Encourage responsible fishing practices to maintain the health of marine life.
Foster collective responsibility and promote sustainable practices in oil-related activities.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, oil spills pose significant threats to marine ecosystems and the delicate balance of our planet's oceans. The frequency of spills, even minor ones, emphasizes the urgent need for proactive measures to prevent, respond to, and mitigate their devastating effects. By promoting prevention, raising awareness, supporting research, volunteering for cleanup efforts, and advocating for a strong response, we can actively contribute to minimizing the impact of oil spills on marine life and coastal habitats.
Embracing sustainable living practices and engaging in ocean conservation efforts further strengthen our collective efforts to protect and preserve our oceans. The responsibility falls on all of us to support strict safety regulations, promote innovative technologies, and foster a sense of environmental stewardship. Together, we can create a future where oil spills are minimized, marine ecosystems thrive, and the well-being of our planet is safeguarded.
Let us strive for a world where the beauty and diversity of our oceans are preserved, and where future generations can experience the wonder of marine life in its pristine form. Through collective action and a shared commitment to protecting our oceans, we can make a lasting difference and ensure a healthier, more sustainable future for our planet and all its inhabitants.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Combatting Ocean Pollution. Urgent Actions for Marine Conservation

Ocean pollution is a critical issue with far-reaching consequences for marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and human health globally. The pervasive presence of plastic waste, chemical pollutants, oil spills, and nutrient runoff from various human activities poses a severe threat to the delicate balance of marine environments. Urgent and concerted action is imperative to address this pressing crisis and mitigate its devastating impacts.
Stricter regulations must be enforced to control waste disposal practices and prevent further contamination of ocean waters. Additionally, promoting and adopting sustainable practices, such as reducing single-use plastics, implementing effective waste management systems, and promoting eco-friendly alternatives, are essential steps in combating ocean pollution.
Raising public awareness about the importance of ocean conservation is paramount in fostering a sense of responsibility and encouraging proactive measures to protect marine ecosystems. Education initiatives, community engagement programs, and advocacy efforts play a crucial role in mobilizing individuals, communities, and governments to take action against ocean pollution.
Furthermore, international collaboration and cooperation are essential for addressing ocean pollution comprehensively. By working together across borders, sharing knowledge and resources, and implementing coordinated strategies, the global community can make significant strides towards restoring the health and integrity of our oceans.
Protecting the oceans is not only crucial for preserving marine biodiversity and ecosystems but also for safeguarding human health and well-being. The oceans provide vital resources, regulate the Earth’s climate, and support livelihoods for millions of people worldwide. Therefore, it is imperative that we take immediate and decisive action to reduce pollution, mitigate its impacts, and ensure the long-term health and sustainability of our oceans for future generations.
Read more:
0 notes
Text
Blog #3: Laudato Si
Upon reading Laudato Si', I agree with the Pope that the Earth, our common home, is seriously in disrepair. Looking around, I see many signs that our planet is in trouble. For example, climate change is causing extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and wildfires to become more frequent and intense. These disasters not only destroy homes and habitats but also take lives and displace communities.
Pollution is another big issue. Our oceans are filling with plastic waste, harming marine life and ecosystems. I've read reports about animals like turtles and fish being found with stomachs full of plastic. Air pollution is also a significant problem, especially in big cities, leading to health issues like asthma and other respiratory diseases.
Deforestation is another clear sign of the Earth's disrepair. Large areas of forests, crucial for absorbing carbon dioxide and providing oxygen, are being cut down for agriculture and urban development. This loss of forests contributes to climate change and threatens the biodiversity we depend on.
I also see evidence of the loss of biodiversity. Many species are going extinct at an alarming rate, which disrupts ecosystems and the balance of nature. The extinction of even a single species can have a domino effect, impacting many others in the food chain.
In summary, the signs are all around us. From climate change and pollution to deforestation and loss of biodiversity, it's clear that our planet is suffering. We must take urgent action to protect our common home for future generations.
I agree with Pope Francis that human activity is the leading cause of global warming. Over the last few years, scientists have provided strong evidence that our actions, like burning fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes, release many greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and warm the Earth, leading to climate change.
In our personal lives, we can make simple changes to help reduce our impact. For instance, we can use energy-efficient appliances, reduce our car use by walking, biking, or using public transport, and try to use renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. We can also reduce waste by recycling, composting, and avoiding single-use plastics.
In our communities, we can work together to make more extensive changes. Community gardens can promote local food production, reducing the need for long-distance transportation. We can also support local initiatives that aim to plant more trees and protect green spaces, which help absorb carbon dioxide.
On a more significant social level, we can advocate for policies that protect the environment. This includes supporting laws and regulations that limit carbon emissions, investing in renewable energy, and promoting sustainable agriculture. We can also encourage businesses to adopt greener practices and support companies committed to sustainability.
By taking these actions in our personal, communal, and social lives, we can help address the causes of climate change and protect our planet for future generations. It's about making conscious daily choices and working together for a healthier Earth.
0 notes
Text
Beneath the Surface: Diving into Coral Reef Conservation as a Volunteer
Exploring the vibrant underwater world has long been a passion for many scuba divers. However, in recent years, this passion has evolved into a powerful tool for conservation efforts, particularly in restoring coral reefs. Across the globe, volunteer divers are taking to the depths to marvel at the beauty of coral ecosystems and actively participate in their preservation and restoration. In this article, we delve into the significance of volunteering as a scuba diver to help restore coral reefs, examining the challenges facing these vital ecosystems and divers' role in their protection.
The Coral Conundrum
Coral reefs are often hailed as the rainforests of the sea, harboring immense biodiversity and providing essential ecosystem services. Yet, they face many threats, ranging from climate change and ocean acidification to overfishing and pollution. These stressors have resulted in widespread coral bleaching events, where corals expel the algae in their tissues, leaving them vulnerable and often leading to death. As a result, coral reefs are disappearing at an alarming rate, with some estimates suggesting that up to 90% of the world's reefs could be lost by 2050 if action is not taken.
The Role of Volunteer Divers
Amidst this environmental crisis, volunteer divers have emerged as crucial allies in the fight to save coral reefs. Through organizations such as the Coral Restoration Foundation and Reef Check, divers are trained in coral restoration techniques and actively participate in reef restoration projects worldwide. These projects typically involve activities such as coral gardening, where fragments of healthy corals are grown and then transplanted onto degraded reefs, or monitoring and data collection to assess reef health and track changes over time.
Hands-On Conservation
One of the most compelling aspects of volunteering as a scuba diver for coral reef restoration is the opportunity for hands-on involvement in conservation efforts. Unlike traditional forms of environmental activism, which may feel distant or abstract, coral reef restoration allows divers to witness their work's impact directly beneath the waves. Planting coral fragments, monitoring growth, and seeing once-degraded reefs come back to life can be enriching experiences that foster a deeper connection to the marine environment and a greater sense of stewardship.
Community Engagement
Beyond the tangible benefits to coral reefs, volunteer diving initiatives foster community engagement and education. By involving local communities in restoration projects, these initiatives empower individuals to take action and raise awareness about the importance of coral reefs and the need for their protection. Furthermore, volunteers can exchange knowledge and expertise by working alongside scientists, conservationists, and fellow divers worldwide, contributing to a global network of conservation-minded individuals dedicated to preserving our oceans.
Challenges and Opportunities
While volunteer diving for coral reef restoration offers immense potential for positive impact, it has challenges. Limited funding, logistical constraints, and the scale of the coral reef crisis present formidable obstacles to conservation efforts. Additionally, ensuring restoration projects are conducted responsibly and using scientific best practices is essential to long-term success.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Advances in coral farming techniques, such as microfragmentation and larval propagation, hold promise for scaling up restoration efforts and increasing their efficacy. Moreover, partnerships between governments, NGOs, businesses, and local communities are essential for implementing holistic approaches to coral reef conservation that address both immediate threats and underlying drivers of reef degradation.
Looking Ahead
As we confront the urgent realities of climate change and biodiversity loss, the role of volunteer divers in coral reef conservation will only become more critical. By harnessing the passion and expertise of the diving community, we can work towards a future where vibrant coral reefs continue to thrive for generations to come. Whether you're an experienced diver or new to the sport, there are countless ways to get involved, from participating in restoration projects to supporting organizations financially or spreading awareness in your community. Together, we can make a difference, one dive at a time.
0 notes
Text

Article: Coral bleaching: Fourth global mass stress episode underway - US scientists #NOAA #US #BBC #UK https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-68814016
ArticleSummary: "The world is currently experiencing the fourth global mass coral bleaching event due to record ocean heat, causing coral to turn white and die. The bleaching is triggered by stress from high water temperatures, threatening the ecosystems that rely on coral for sustenance and revenue. Climate change and warming oceans are exacerbating the issue, with the Great Barrier Reef and other coral reefs worldwide being severely affected. Scientists warn that unless significant action is taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and limit ocean warming, coral reefs as we know them may permanently change. Coral restoration efforts are limited in scope, and only global efforts to combat climate change can ensure the survival of coral reefs."
By #www.smukher2.eu #www.smukher2.com #www.smukher2.co.uk #www.smukher2.org #www.smukher2.net #smukher2 to #Everyone:
The world is currently facing a global coral bleaching event, which is the fourth recorded event and the second in the last decade. This is a result of human overpopulation induced abuse of nature that lead to climate change (global warming).
NOAA (National Ocean Services US) scientists have been monitoring extensive bleaching-level heat stress across the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Ocean basins using satellite data. Coral bleaching has been documented in various regions worldwide, including the tropics, Florida, the Caribbean, Brazil, Australia's Great Barrier Reef, and more. The frequency and severity of coral bleaching events are increasing due to warming oceans. NOAA is actively involved in coral reef research, management, and restoration efforts to increase coral resilience. The International Coral Reef Initiative is collaborating with NOAA and other partners to implement resilience-based management actions globally. NOAA's Coral Reef Conservation Program focuses on understanding and conserving coral reef ecosystems amidst climate change challenges.
Coral bleaching occurs when corals expel the algae living in their tissues, causing them to turn white. This process is triggered by environmental stress, such as high water temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry. The algae, known as zooxanthellae, provide corals with energy through photosynthesis and contribute to their vibrant colors. When corals expel the algae, they lose their main source of food and become more vulnerable to disease and death. Global warming is a major factor contributing to coral bleaching. Rising sea temperatures, driven by climate change and increased greenhouse gas emissions, can cause corals to become stressed and expel their algae. The frequency and severity of coral bleaching events have been increasing worldwide as ocean temperatures continue to rise. The relationship between coral bleaching and global warming highlights the urgent need to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions to protect coral reefs and the marine ecosystems that depend on them. Efforts to mitigate global warming and implement conservation measures are essential to safeguard the health and resilience of coral reefs for future generations.
Coral bleaching can have significant impacts on marine life, biodiversity, and human health. When corals bleach and potentially die off, it affects the entire coral reef ecosystem. Here are some ways in which coral bleaching can impact various aspects:
Marine Life: Coral reefs provide essential habitat for a diverse range of marine species. When corals bleach and die, it disrupts the entire ecosystem. Many fish and other marine organisms rely on coral reefs for food, shelter, and breeding grounds. The loss of coral reefs due to bleaching can lead to a decline in fish populations and a reduction in biodiversity.
Biodiversity: Coral reefs are known as the "rainforests of the sea" due to their high biodiversity. When coral reefs bleach and degrade, it can result in a loss of species diversity and ecological balance. This can have cascading effects on the entire marine ecosystem, impacting other species that depend on coral reefs for survival.
Human Health: Coral reefs play a crucial role in supporting coastal communities and economies. They provide food resources, protect coastlines from erosion, support tourism and recreational activities, and offer potential sources of new medicines. The decline of coral reefs due to bleaching can negatively impact these benefits, affecting the livelihoods and well-being of communities that rely on coral reef ecosystems.
The ability of corals to recover after bleaching depends on various factors such as the severity of the bleaching event, the duration of stress, and the overall health of the coral colony. In cases where the bleaching event is mild and short-lived, corals have a higher chance of recovery. If the stress causing the bleaching is alleviated, such as a decrease in water temperature or improvement in water quality, corals can sometimes regain their algae and return to their normal, healthy state. However, if the bleaching event is severe and prolonged, corals may struggle to recover and can face increased vulnerability to disease and mortality. Additionally, repeated bleaching events can weaken corals over time, making them less resilient to future stressors. Conservation efforts, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate global warming, implementing sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution, and creating marine protected areas, are crucial in supporting coral recovery and resilience. These measures can help create healthier marine ecosystems that support the recovery of corals and overall biodiversity.
Overall, the effects of coral bleaching extend beyond the corals themselves and can have far-reaching consequences for marine life, biodiversity, and human health. It underscores the importance of conservation efforts to protect and restore coral reef ecosystems to ensure their long-term health and sustainability.
P.S. The coral reef destruction caused by human overpopulation-induced climate change brings to mind a thought I recently encountered while listening to a science fiction story, "The Sentinel" by Arthur C. Clarke. In this narrative, the protagonist contemplates how the ocean life evolved to land life with amphibians, and how humans tend to destroy what they do not comprehend when they destroy the crystal monolith. Therefore, the absence of understanding often leads to destruction, suggesting that with understanding comes the potential to avert destruction. Despite the abundance of scientific evidence highlighting how human overpopulation-induced climate change is harming our planet Earth and all its inhabitants, why do we persist on this destructive course despite this understanding? As water is the source of all life, even life on land when amphibians evolved (this is scientific fact, not just sci-fi), so in that sense water is our origin our mother still we keep going on with its destruction, and the destruction of mother nature at large, why?Its a puzzle and by the time we begin to unravel it, it may just be too late.
References:
Scientists: Coral Bleaching Happens Around the World - April 16, 2024 | Podcast | Science and Tech https://player.fm/series/science-technology-voa-learning-english/scientists-coral-bleaching-happens-around-the-world-april-16-2024
A global analysis of coral bleaching over the past two decades Nature Communications volume 10, Article number: 1264 (2019) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-09238-2
Coral Bleaching NOAA Ocean Podcast Dec 2023 Explainer Podcast | NOAA US https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/podcast/dec23/nop71-coral-bleaching.html
How does climate change affect coral reefs? NOAA US https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/coralreef-climate.html
"The Sentinel" by Arthur C. Clarke | Internet Archive | Audio https://archive.org/details/SciFiAudioInMp3Format-Part1/ArthurCClarke-theSentinel.mp3
"The Sentinel" by Arthur C. Clarke | Internet Archive | Book https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780760701782/mode/2up
0 notes
Text

Plants @ the Heart of the Latest call for Darwin Initiative Bids
The Darwin Initiative has re-opened for new projects to apply for funding on United Nations International Day of Biological Diversity.

Orchid in a rainforest
The UK government is today (22 May) celebrating United Nations International Day of Biological Diversity by making funding available to protect wildlife across the globe.
The theme for this year is ‘our biodiversity, our food, our health’. It comes as the Darwin Initiative re-opens for new projects to apply for funding in the latest round.
Since 1992, the fund has been putting an emphasis on nature and health, and providing security of food supply to rural communities in some of the most remote parts of the globe - supporting the Sustainable Development Goals on protecting and enhancing nature.
The Illegal Wildlife Trade Challenge Fund, which now accepts bids from projects aimed at combating the illegal trade in plants in addition to animal-focused projects, is also looking to back new schemes. This fund has received the support of £6 million of UK Aid over the next five years to make sure that more vital projects can go ahead.
Recent reports on international nature have put the issue of species loss high on the nation’s agenda. The UN’s Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services report showed nearly a million species are in danger of extinction and the Darwin Initiative is part of the UK government’s response to this emerging issue.
The latest round of funding comes during the government’s Year of Green Action, a year-long drive to help people to connect with, protect and enhance nature.
Environment Minister Thérèse Coffey said:
UN International Day for Biological Diversity celebrates the wonderful diversity of nature and wildlife around our planet.
Nature delivers many environmental benefits including clean air and water, sustainable food supplies, and recovery and resilience to natural disasters.
The Darwin Initiative delivers support for international nature conservation projects and many economic activities depend on nature, including agriculture, forestry, fisheries and tourism.
At the start of May, 32 new projects shared £8.2million in the 25th round of funding from the Darwin Initiative.
There has been continuous progress made by ongoing schemes backed by the Darwin Initiative, with two highlights in Guinea and the Philippines.
Tropical Important Plant Areas in Guinea
Following three years of research, European and Guinean scientists, NGOs and staff of the Guinean Ministry of Environment, Waters and Forests, have evidenced 22 Tropical Important Plant Areas in Guinea. These are the first Tropical Important Plant Areas (TIPAs) that have been identified in Africa.
This designation of the 22 TIPAs, which cover 3.5% of Guinea’s surface area and include more than 60% of 273 threatened species identified in the country, mean those plants will now stand a far greater chance of protection.
Darwin Initiative support of nearly £300,000 over three years has helped to make sure this work takes place.
Dr Martin Cheek, Senior Research Leader at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, said:
This official status is vital in Guinea. Habitat loss has been devastating with calculations that 96% of the country’s original forest has already been cleared, and that which remains is under severe pressure. It looks like as many as 35 species have gone extinct in Guinea, from trees to minute herbs, daisies, peas and clematis, all due to human pressures. Twenty-five of these are globally unique to Guinea. So these are likely global extinctions.
Fisheries protection in the Philippines
The Darwin Initiative has supported two projects with a total of nearly £800,000 both aimed at better protecting important coastal habitats in the Philippines and making sure that local communities have access to sustainable fisheries.
Marine protected areas (MPAs) are a key tool for sustaining marine biodiversity and fish stocks. Twenty-five per cent of the world’s MPAs are in the Philippines, 95% of which are community based.
However, the average size of the critical no-take “replenishment” zones within these MPAs is only 12 hectares, which is inadequate to fulfil conservation objectives, and only 12% were rated as sustained at the last assessment, owing to an overdependence on philanthropic funding.
Small and unsustainable MPAs are driven by a lack of adequate business models underpinning these conservation measures. As a result, marginalised fishing communities faced with the need to feed their families today cannot afford to set aside large enough areas in the hope that they will generate increased fish catches in the future. Additionally, MPAs have traditionally focused on coral reefs and have failed to incorporate other critical habitats.
ZSL’s (Zoological Society of London) Net-Works initiative has been pioneering the iMPA - which describes the “ideal MPA”, but also interpreted as innovative, inclusive, improved. These are bigger in size, better managed and enforced and sustainably financed using the Net-Works business model.
Dr Nick Hill, Senior Technical Specialist at ZSL, said:
Darwin Initiative funding for the first two iMPAs has gained the support of local government. These two MPAs are nearly 50 times the average size of MPAs in the Philippines, with no-take replenishment zones 16 times bigger.
This is a key milestone for ZSL’s project and proves that in the Philippines larger community-based MPAs make a meaningful contribution towards the Philippines’ nationally-mandated target of protecting 15% of municipal waters.
Projects supported by the Darwin Initiative are illustrative of a ‘win-win’ approach, encouraging sustainable livelihoods whilst conserving some of the world’s iconic and endangered species and landscapes, which benefits us all.
0 notes