#How to exploit XSS vulnerabilities
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Important Announcement

A now-patched breach of security has occurred on Art Fight. To learn about this issue in full detail, please read the following newspost:
Below is a FAQ regarding the exploit. We highly recommend that you reset your password and enable 2FA if you have interacted with the site recently. If you need any assistance, please send a support email to the following address: [email protected]
The inbox will be opened shortly to respond to user questions and concerns. Anonymous will be turned off for the time being, please let us know if you prefer that your ask is answered privately.
How did this happen?
Our BBCode system had a vulnerability flaw in it that was temporarily exploited to attempt to gain user credentials, but it has since been patched.
What do we do?
If you believe you may have been affected, please change your password to something unique and secure. We also recommend keeping an eye out on your other accounts, and to change the passwords on them if they shared any credentials as your Art Fight account (so same email or same password).
How do we know if you were affected by this exploit?
If you accessed the comments of the most recent news post (Terms of Service Updates), there is a chance your browser was exposed to the XSS script, and we recommend resetting your password ASAP to be safe.
What are you doing to prevent this from happening again?
Our hard-working dev team has already patched this exploit, as well as added additional security measures to help prevent this from happening again in the future. We will also be proactively doing a security review to help locate any other security concerns. Two Factor Authentication (2FA) has been established as a feature on the site that can be found in your settings.
I'm nervous about going onto the site at all now! What if my account gets hacked/stolen/etc?
Art Fight's dev team has patched the vulnerability that this incident has revealed, and has added additional security to catch/stop malicious scripts before they can affect the userbase. All instances of the previous malicious script have been removed from the website, meaning that it is once again safe to view the last news post! We are working hard to continue to keep users safe, so you don't need to worry about accessing anything on the site. If you come across anything potentially concerning, please don't hesitate to forward it to a moderator - we're happy to look into it!
What information might've been taken from me?
The XSS attack attempted to collect autofilled Art Fight log in information--emails and passwords--from users. No other information (like birthdays) should have been collected through this script. If you use the same email/password combo, or same password anywhere else, we recommend changing to ensure your accounts stay secure.
884 notes
·
View notes
Text
Prevent Command Injection in Symfony: Secure Your Code
Symfony is a powerful PHP framework trusted by thousands of developers, but like any framework, it's not immune to security threats. One of the most dangerous—and often overlooked—threats is a Command Injection Attack.

In this blog post, we’ll break down what a command injection attack is, how it can be exploited in a Symfony application, and—most importantly—how to prevent it. We’ll also include code examples and offer you a Website Vulnerability Scanner online free to scan your website for vulnerabilities like this one.
➡️ Visit Our Blog for More Cybersecurity Posts: 🔗 https://www.pentesttesting.com/blog/
🧨 What is Command Injection?
Command Injection is a type of security vulnerability that allows attackers to execute arbitrary system commands on your server. If user input is improperly sanitized, attackers can exploit functions like exec(), system(), or shell_exec() in PHP.
This can lead to:
Data breaches
Server hijacking
Total application compromise
🐘 Symfony Command Injection Example
Let’s start with a naive Symfony controller that might fall victim to command injection.
❌ Vulnerable Symfony Code
// src/Controller/BackupController.php namespace App\Controller; use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request; use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response; use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\AbstractController; class BackupController extends AbstractController { public function backupDatabase(Request $request): Response { $filename = $request->query->get('filename'); // ⚠️ Dangerous input $output = shell_exec("mysqldump -u root -psecret mydb > /backups/{$filename}"); return new Response("Backup created: $filename"); } }
If an attacker sets filename=backup.sql;rm -rf /, this code could delete your entire server. Yikes!
🔐 Secure It With Escaping & Whitelisting
Let’s see how we can secure this.
✅ Safe Symfony Version
public function backupDatabase(Request $request): Response { $filename = $request->query->get('filename'); // Sanitize the filename using a whitelist or regex if (!preg_match('/^[\w\-\.]+$/', $filename)) { return new Response("Invalid filename", 400); } $safePath = escapeshellarg("/backups/" . $filename); $output = shell_exec("mysqldump -u root - psecret mydb > $safePath"); return new Response("Backup created: $filename"); }
By using escapeshellarg() and validating the input, we reduce the risk significantly.
🛠️ Automate Detection with Our Free Tool
Want to check if your website is vulnerable to command injection and other critical flaws?
🎯 We’ve built a Free Website Vulnerability Scanner that checks for command injection, XSS, SQLi, and dozens of other issues—all in seconds.
🖼️ Screenshot of our Website Vulnerability Scanner:

Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
👉 Try it now: https://free.pentesttesting.com/
📋 Sample Output Report
Our scanner doesn’t just find issues—it gives you a detailed, developer-friendly report you can act on.
🖼️ Screenshot of a sample scan report from our tool to check Website Vulnerability:

An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
💼 Need Help Fixing It? We've Got You Covered
🔐 Web App Penetration Testing Services If you're looking for expert-level help to secure your Symfony or PHP application, our team is ready to assist.
➡️ Learn more: https://www.pentesttesting.com/web-app-penetration-testing-services/
🤝 Are You a Tech Company or Agency?
We offer white-label cybersecurity services so you can resell pentesting to your clients without hiring a full team.
📦 Get the full service suite here: 🔗 https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
💌 Stay Ahead of Threats—Subscribe Now!
Don’t miss future posts, case studies, and cybersecurity tips.
📬 Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter
🔁 Final Thoughts
Command injection remains one of the most dangerous web application vulnerabilities. Symfony gives you the tools to secure your app—but only if you use them correctly.
Don’t wait until you’re hacked. Take 2 minutes to scan your website with our free Website Security Scanner tool.
📝 Originally written by the Pentest Testing Corp. team 📌 Visit our blog for more: https://www.pentesttesting.com/blog/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Key Programming Languages Every Ethical Hacker Should Know
In the realm of cybersecurity, ethical hacking stands as a critical line of defense against cyber threats. Ethical hackers use their skills to identify vulnerabilities and prevent malicious attacks. To be effective in this role, a strong foundation in programming is essential. Certain programming languages are particularly valuable for ethical hackers, enabling them to develop tools, scripts, and exploits. This blog post explores the most important programming languages for ethical hackers and how these skills are integrated into various training programs.
Python: The Versatile Tool
Python is often considered the go-to language for ethical hackers due to its versatility and ease of use. It offers a wide range of libraries and frameworks that simplify tasks like scripting, automation, and data analysis. Python’s readability and broad community support make it a popular choice for developing custom security tools and performing various hacking tasks. Many top Ethical Hacking Course institutes incorporate Python into their curriculum because it allows students to quickly grasp the basics and apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. In an Ethical Hacking Course, learning Python can significantly enhance your ability to automate tasks and write scripts for penetration testing. Its extensive libraries, such as Scapy for network analysis and Beautiful Soup for web scraping, can be crucial for ethical hacking projects.
JavaScript: The Web Scripting Language
JavaScript is indispensable for ethical hackers who focus on web security. It is the primary language used in web development and can be leveraged to understand and exploit vulnerabilities in web applications. By mastering JavaScript, ethical hackers can identify issues like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and develop techniques to mitigate such risks. An Ethical Hacking Course often covers JavaScript to help students comprehend how web applications work and how attackers can exploit JavaScript-based vulnerabilities. Understanding this language enables ethical hackers to perform more effective security assessments on websites and web applications.
Biggest Cyber Attacks in the World
youtube
C and C++: Low-Level Mastery
C and C++ are essential for ethical hackers who need to delve into low-level programming and system vulnerabilities. These languages are used to develop software and operating systems, making them crucial for understanding how exploits work at a fundamental level. Mastery of C and C++ can help ethical hackers identify and exploit buffer overflows, memory corruption, and other critical vulnerabilities. Courses at leading Ethical Hacking Course institutes frequently include C and C++ programming to provide a deep understanding of how software vulnerabilities can be exploited. Knowledge of these languages is often a prerequisite for advanced penetration testing and vulnerability analysis.
Bash Scripting: The Command-Line Interface
Bash scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks on Unix-based systems. It allows ethical hackers to write scripts that perform complex sequences of commands, making it easier to conduct security audits and manage multiple tasks efficiently. Bash scripting is particularly useful for creating custom tools and automating repetitive tasks during penetration testing. An Ethical Hacking Course that offers job assistance often emphasizes the importance of Bash scripting, as it is a fundamental skill for many security roles. Being proficient in Bash can streamline workflows and improve efficiency when working with Linux-based systems and tools.
SQL: Database Security Insights
Structured Query Language (SQL) is essential for ethical hackers who need to assess and secure databases. SQL injection is a common attack vector used to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications that interact with databases. By understanding SQL, ethical hackers can identify and prevent SQL injection attacks and assess the security of database systems. Incorporating SQL into an Ethical Hacking Course can provide students with a comprehensive understanding of database security and vulnerability management. This knowledge is crucial for performing thorough security assessments and ensuring robust protection against database-related attacks.
Understanding Course Content and Fees
When choosing an Ethical Hacking Course, it’s important to consider how well the program covers essential programming languages. Courses offered by top Ethical Hacking Course institutes should provide practical, hands-on training in Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Bash scripting, and SQL. Additionally, the course fee can vary depending on the institute and the comprehensiveness of the program. Investing in a high-quality course that covers these programming languages and offers practical experience can significantly enhance your skills and employability in the cybersecurity field.
Certification and Career Advancement
Obtaining an Ethical Hacking Course certification can validate your expertise and improve your career prospects. Certifications from reputable institutes often include components related to the programming languages discussed above. For instance, certifications may test your ability to write scripts in Python or perform SQL injection attacks. By securing an Ethical Hacking Course certification, you demonstrate your proficiency in essential programming languages and your readiness to tackle complex security challenges. Mastering the right programming languages is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in ethical hacking. Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Bash scripting, and SQL each play a unique role in the ethical hacking landscape, providing the tools and knowledge needed to identify and address security vulnerabilities. By choosing a top Ethical Hacking Course institute that covers these languages and investing in a course that offers practical training and job assistance, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic field. With the right skills and certification, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the evolving challenges of cybersecurity and contribute to protecting critical digital assets.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the 10 must-read cybersecurity books for beginners and experts alike?

Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field, and staying updated with the latest trends, techniques, and best practices is essential for both beginners and experts. Here are ten must-read cybersecurity books that cover a wide range of topics, from fundamentals to advanced concepts:
For Beginners:
"Cybersecurity for Beginners" by Raef Meeuwisse: This book provides a comprehensive introduction to cybersecurity concepts, principles, and practices. It covers topics such as threat landscape, risk management, cryptography, network security, and incident response in a beginner-friendly manner.
"The Art of Invisibility: The World's Most Famous Hacker Teaches You How to Be Safe in the Age of Big Brother and Big Data" by Kevin Mitnick: Written by renowned hacker Kevin Mitnick, this book offers practical advice on protecting your privacy and security in the digital age. It covers topics such as online anonymity, encryption, social engineering, and secure communication.
"Social Engineering: The Science of Human Hacking" by Christopher Hadnagy: Social engineering is a common tactic used by cyber attackers to manipulate human behavior and gain unauthorized access to systems. This book explores the psychology behind social engineering attacks and provides insights into how to recognize and defend against them.
"Hacking: The Art of Exploitation" by Jon Erickson: This book offers a hands-on introduction to the technical aspects of hacking and cybersecurity. It covers topics such as programming, network protocols, buffer overflows, and exploit development, providing practical exercises and examples for readers to follow along.
"The Web Application Hacker's Handbook: Finding and Exploiting Security Flaws" by Dafydd Stuttard and Marcus Pinto: Web applications are a common target for cyber attacks, and understanding their vulnerabilities is essential for securing them. This book provides a comprehensive guide to web application security testing, covering topics such as injection attacks, authentication bypass, and cross-site scripting (XSS).
For Experts:
"Practical Malware Analysis: The Hands-On Guide to Dissecting Malicious Software" by Michael Sikorski and Andrew Honig: Malware analysis is a critical skill for cybersecurity professionals tasked with defending against advanced threats. This book offers a practical, hands-on approach to analyzing malware samples, covering topics such as static and dynamic analysis techniques, reverse engineering, and threat intelligence.
"The Tangled Web: A Guide to Securing Modern Web Applications" by Michal Zalewski: As web technologies continue to evolve, so do the security challenges associated with them. This book provides a deep dive into the complexities of web security, covering topics such as browser security models, web application architecture, and common vulnerabilities like cross-site request forgery (CSRF) and clickjacking.
"Blue Team Handbook: Incident Response Edition: A condensed field guide for the Cyber Security Incident Responder" by Don Murdoch GSE: Incident response is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, and having a well-prepared blue team is essential for effectively detecting, containing, and responding to security incidents. This handbook provides practical guidance and best practices for incident responders, covering topics such as incident detection, triage, and containment.
"Network Security Assessment: Know Your Network" by Chris McNab: Conducting thorough security assessments is essential for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in network infrastructure. This book offers a comprehensive guide to network security assessment methodologies, tools, and techniques, covering topics such as reconnaissance, scanning, enumeration, and exploitation.
"The Hacker Playbook 3: Practical Guide To Penetration Testing" by Peter Kim: Penetration testing is a crucial component of cybersecurity, allowing organizations to identify and remediate security weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers. This book provides a practical, hands-on approach to penetration testing, covering topics such as reconnaissance, vulnerability assessment, exploitation, and post-exploitation techniques.
Conclusion:
Whether you're just starting out in cybersecurity or you're an experienced professional looking to expand your knowledge, these ten books offer valuable insights and practical guidance for navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity. From understanding the fundamentals of cybersecurity to mastering advanced techniques in malware analysis, web security, incident response, and penetration testing, these books cover a wide range of topics to help you stay ahead of emerging threats and protect against cyber attacks.
Read More Blogs:
Top 10 Cybersecurity Trends for the Next Decade
Cybersecurity in Healthcare: New Innovations and Developments
Challenges in Implementing Cybersecurity Frameworks
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top 10 Programming Languages for Cyber Security in 2025

In the ever-escalating battle for digital security, programming languages are the fundamental tools that empower cybersecurity professionals. Whether you're an ethical hacker, a malware analyst, a security engineer, or a digital forensic investigator, fluency in certain languages is non-negotiable. As we navigate 2025, the demand for cybersecurity experts continues to soar, and with it, the need for mastery over these crucial coding languages.
Here's a look at the top 10 programming languages shaping the cybersecurity landscape this year:
1. Python: The Versatile Vanguard
Still holding the crown, Python remains the undisputed champion of cybersecurity. Its simplicity, readability, and vast ecosystem of libraries make it incredibly versatile.
Why it's essential: Scripting for automation (e.g., automating vulnerability scans), penetration testing (Metasploit, Scapy, Requests), malware analysis, web scraping for open-source intelligence (OSINT), and building custom security tools. Its integration with AI/ML libraries also makes it vital for advanced threat detection systems.
Key uses: Penetration testing, malware analysis, security automation, data analysis in incident response.
2. C and C++: The Low-Level Powerhouses
When you need to understand how systems truly work at their core, C and C++ are indispensable. These languages provide direct memory access, which is crucial for deep security work.
Why they're essential: Exploit development (understanding buffer overflows, crafting shellcode), reverse engineering malware, developing high-performance security tools, and securing operating systems/firmware. Many exploits and malicious payloads are written in C/C++.
Key uses: Exploit development, reverse engineering, malware analysis, secure system programming.
3. JavaScript: The Web's Watchdog
As the internet continues to dominate, JavaScript's role in cybersecurity, particularly web security, grows exponentially.
Why it's essential: Web application penetration testing (identifying XSS, CSRF, DOM-based vulnerabilities), understanding client-side attacks, crafting malicious browser-based payloads, and securing Node.js backend applications.
Key uses: Web application security, browser-based attacks, front-end vulnerability analysis.
4. Go (Golang): The Cloud-Native Champion
Google's Go language is rapidly gaining traction in cybersecurity due to its efficiency, strong concurrency, and fast compilation times, making it ideal for cloud-native security tools.
Why it's essential: Building high-performance network tools, microservices for security infrastructure, developing fast scanners, and creating command-and-control (C2) frameworks. Its small binary size is also an advantage.
Key uses: Network programming, cloud security tools, security infrastructure.
5. Bash/Shell Scripting: The Linux Commander
While not a full-fledged programming language, proficiency in Bash and other shell scripting languages (like Zsh or PowerShell for Windows) is absolutely critical for anyone operating in a cybersecurity role.
Why it's essential: Automating repetitive tasks in Linux/Unix environments, managing system configurations, chaining security tools, basic log analysis, and system reconnaissance during penetration tests.
Key uses: System administration, security automation, forensic analysis, incident response on Linux systems.
6. SQL: The Database Decoder
Databases are the heart of almost every application, holding vast amounts of sensitive data. SQL (Structured Query Language) is the key to interacting with them.
Why it's essential: Identifying and exploiting SQL injection vulnerabilities, understanding database structures, securing database configurations, and performing data forensics on compromised databases.
Key uses: Database security, SQL injection testing, data forensics.
7. Ruby: The Metasploit Maestro
Ruby's elegant syntax and powerful frameworks have long made it a favorite in the penetration testing community, particularly due to its close ties with Metasploit.
Why it's essential: Scripting exploits, developing custom modules for penetration testing frameworks, and automating various security assessments.
Key uses: Penetration testing, exploit development (especially with Metasploit), security tool development.
8. PowerShell: The Windows Whisperer
For cybersecurity professionals dealing with Windows environments, PowerShell is indispensable. It's a powerful scripting language built by Microsoft for system administration and automation.
Why it's essential: Automating security tasks on Windows, performing reconnaissance, privilege escalation, lateral movement in red team operations, and analyzing Windows system logs. Many fileless malware attacks leverage PowerShell.
Key uses: Windows security, incident response, red teaming, security automation in Windows environments.
9. Java: The Enterprise Guardian
Java's "write once, run anywhere" philosophy and robust security features make it a staple in large enterprise environments.
Why it's essential: Developing secure enterprise applications, assessing the security of Java-based systems, Android mobile application security, and building scalable security solutions. Many backend systems are built in Java, requiring security professionals to understand its nuances.
Key uses: Enterprise application security, Android application security, secure software development.
10. Assembly Language: The Microscopic View
For the most advanced and specialized cybersecurity roles, understanding Assembly language provides an unparalleled level of insight into how software interacts with hardware.
Why it's essential: Deep malware analysis (understanding low-level instructions), reverse engineering compiled binaries, exploit development for complex vulnerabilities, and understanding processor architecture.
Key uses: Malware analysis, reverse engineering, exploit development for specific architectures (x86, ARM).
The Continuous Pursuit of Knowledge
The field of cybersecurity is dynamic, with new threats and technologies emerging constantly. While these ten languages form the core arsenal for 2025, remember that the most effective cybersecurity professional is a continuous learner. Develop a strong foundation in these languages, but always be ready to explore new tools and adapt your skills to the evolving digital landscape. Your programming prowess is your shield and your sword in the fight for a more secure future.
0 notes
Text
How Web Development Companies Handle Website Penetration Testing
Cybersecurity is no longer an afterthought—it’s a frontline concern. With rising threats like data breaches, ransomware, and unauthorized access, businesses must ensure their websites are not just functional but secure. That’s where penetration testing (pen testing) comes in.
A trusted Web Development Company doesn’t stop at building beautiful or high-performing websites—they also take proactive steps to test, identify, and fix vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Penetration testing is one of the most critical layers in this process.
But what does it involve? And how do web development agencies approach it with precision and care?
What Is Website Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing is a simulated cyberattack on your website or web application. It’s performed by ethical hackers or security professionals who attempt to exploit vulnerabilities just like a real attacker would—but with permission and control.
The goal is to:
Identify security flaws before hackers do
Test the effectiveness of your security layers
Understand how deep an attacker could go
Provide detailed insights for patching weak points
Pen testing is typically done after development is complete but before deployment—or periodically as part of a maintenance cycle.
Why Is Pen Testing Important for Businesses?
Your website often stores or handles sensitive data—customer information, login credentials, payment records, business logic, and more. Any gap in security can be devastating.
Here’s why businesses should prioritize penetration testing:
Reputation Protection: A breach can destroy trust.
Regulatory Compliance: Industries like finance, healthcare, and eCommerce must meet specific security standards.
Cost Avoidance: Fixing a breach is far more expensive than preventing one.
Peace of Mind: You know where you stand before going live.
That’s why experienced web development companies integrate security audits and pen testing into their delivery cycle.
How Web Development Companies Conduct Penetration Testing
Penetration testing isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. Here's how professional agencies typically handle it:
1. Scoping and Planning
Before any testing begins, the team defines the scope:
Which applications, domains, or subdomains are in-scope?
Should third-party integrations be tested?
What kind of data does the system handle?
They also decide between black-box testing (with no internal knowledge), white-box testing (with full access), or gray-box testing (partial knowledge)—depending on the business goals.
2. Information Gathering
Next, the team gathers data on the target system, such as:
Public-facing IPs and domains
Site architecture and tech stack
API endpoints and known user roles
This reconnaissance phase helps simulate real-world attacks using publicly available data.
3. Vulnerability Scanning
Before diving into manual attacks, automated tools are used to scan for:
Outdated libraries and plugins
Open ports or misconfigurations
Common vulnerabilities like XSS, CSRF, and SQL injection
Tools like Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, or Nessus help flag potential weak points.
4. Manual Testing and Exploitation
This is where ethical hackers step in to simulate real attack scenarios:
Attempting to bypass authentication or gain admin access
Exploiting injection flaws or misconfigured APIs
Accessing sensitive files or user data
Breaking out of limited permissions to gain system-wide access
Unlike automated scans, manual testing adds human intuition to detect flaws hidden beneath the surface.
5. Reporting and Recommendations
After the test, the development team compiles a detailed report outlining:
Vulnerabilities discovered
Severity levels (low, medium, high, critical)
Exploitation steps
Screenshots or logs as evidence
Recommendations for patching and prevention
This report becomes the foundation for security hardening and prioritization.
6. Remediation and Retesting
Once the issues are addressed, the team conducts retesting to ensure the patches work and didn’t introduce new vulnerabilities. This final step closes the loop and confirms that your website is secure before going live—or staying live with confidence.
Conclusion
Website penetration testing isn’t just a checklist item—it’s a strategic necessity in today’s digital world. By proactively simulating attacks, companies can discover and fix vulnerabilities before they become real threats.
Working with a Web Development Company that takes security seriously means your website isn’t just built to look good and function well—it’s designed to be resilient, protected, and trusted. Whether you're launching a new product or scaling an existing platform, investing in penetration testing is one of the smartest moves you can make for long-term stability and success.
0 notes
Text

Key WooCommerce Security Tips for 2025
1. Use Strong Passwords and Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
A weak password is often the first point of vulnerability for any website. To protect your WooCommerce store, ensure that you and your team members use strong, unique passwords for all accounts related to your store. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of protection, requiring a second verification step when logging in.
While 2FA may seem like an added hassle, it is a powerful tool that prevents unauthorized access, even if someone obtains your password. Implementing 2FA will drastically reduce the likelihood of a security breach.
2. Keep WordPress, WooCommerce, and Plugins Updated
Regular updates to WordPress, the WooCommerce plugin, and any other installed plugins are critical for maintaining security. These updates often include security patches to fix newly discovered vulnerabilities. By updating your software regularly, you ensure that your store is protected against the latest threats.
If you don't have the time or expertise to handle updates yourself, consider seeking WooCommerce Development Services to keep your store secure and functioning smoothly. A professional team can handle the updates while ensuring no disruption to your store’s operations.
3. Implement SSL Encryption for Secure Transactions
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates encrypt sensitive data that flows between the server and the user’s browser. This encryption ensures that your customers’ personal and financial details are protected. In 2025, having an SSL certificate isn’t just a security measure—it’s also essential for maintaining customer trust and improving your site’s SEO ranking.
If you're unsure how to integrate SSL encryption, a WooCommerce Developer can help set it up to ensure secure transactions and smooth customer experiences.
4. Install a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) acts as a barrier between your WooCommerce store and malicious traffic. It filters out harmful requests, preventing hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities in your site’s code. Implementing a WAF can block attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and brute-force login attempts, which are common methods used by cybercriminals.
To configure the best WAF for your store, you can work with professionals who specialize in website security.
5. Backup Your Store Regularly
Data loss is one of the most detrimental effects of a cyberattack. If your store is compromised or experiences a system failure, having a recent backup ensures that you can restore your website with minimal downtime and data loss. Regular backups also give you peace of mind knowing that even in the worst-case scenario, you can recover your site quickly.
To streamline this process, WordPress Support Services often include backup solutions, providing continuous backups to keep your store secure and your data safe.
6. Limit Login Attempts
Brute force attacks involve hackers attempting to guess your login credentials by trying different combinations repeatedly. One effective way to prevent these attacks is by limiting the number of failed login attempts before temporarily locking out the user. This drastically reduces the chances of a hacker successfully gaining access to your store.
This is a simple yet effective security measure, and integrating it into your site can be done by a WooCommerce Developer who can ensure the right settings are in place to block these types of attacks.
Ongoing Maintenance and Monitoring for WooCommerce Security
Maintaining a secure WooCommerce store is an ongoing process. Regular security checks, audits, and proactive monitoring are essential to keep your site protected. Without routine maintenance, new vulnerabilities can arise, and hackers will always find new ways to exploit them.
By leveraging WordPress Website Maintenance Services, you can ensure that your store is continually monitored and updated, helping to safeguard it from emerging threats.
Conclusion
In 2025, the security of your WooCommerce store should be a top priority. By adopting strong passwords, implementing SSL certificates, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping your software up to date, you can significantly reduce the risk of a breach.
For more advanced security measures and ongoing support, working with WooCommerce Development Services and WordPress Support Services ensures that your site remains secure, protected from the latest threats, and optimized for performance.
Let’s work together to make sure your WooCommerce store is as secure as possible in 2025 and beyond.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Protect Your Laravel APIs: Common Vulnerabilities and Fixes
API Vulnerabilities in Laravel: What You Need to Know
As web applications evolve, securing APIs becomes a critical aspect of overall cybersecurity. Laravel, being one of the most popular PHP frameworks, provides many features to help developers create robust APIs. However, like any software, APIs in Laravel are susceptible to certain vulnerabilities that can leave your system open to attack.

In this blog post, we’ll explore common API vulnerabilities in Laravel and how you can address them, using practical coding examples. Additionally, we’ll introduce our free Website Security Scanner tool, which can help you assess and protect your web applications.
Common API Vulnerabilities in Laravel
Laravel APIs, like any other API, can suffer from common security vulnerabilities if not properly secured. Some of these vulnerabilities include:
>> SQL Injection SQL injection attacks occur when an attacker is able to manipulate an SQL query to execute arbitrary code. If a Laravel API fails to properly sanitize user inputs, this type of vulnerability can be exploited.
Example Vulnerability:
$user = DB::select("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" . $request->input('username') . "'");
Solution: Laravel’s query builder automatically escapes parameters, preventing SQL injection. Use the query builder or Eloquent ORM like this:
$user = DB::table('users')->where('username', $request->input('username'))->first();
>> Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) XSS attacks happen when an attacker injects malicious scripts into web pages, which can then be executed in the browser of a user who views the page.
Example Vulnerability:
return response()->json(['message' => $request->input('message')]);
Solution: Always sanitize user input and escape any dynamic content. Laravel provides built-in XSS protection by escaping data before rendering it in views:
return response()->json(['message' => e($request->input('message'))]);
>> Improper Authentication and Authorization Without proper authentication, unauthorized users may gain access to sensitive data. Similarly, improper authorization can allow unauthorized users to perform actions they shouldn't be able to.
Example Vulnerability:
Route::post('update-profile', 'UserController@updateProfile');
Solution: Always use Laravel’s built-in authentication middleware to protect sensitive routes:
Route::middleware('auth:api')->post('update-profile', 'UserController@updateProfile');
>> Insecure API Endpoints Exposing too many endpoints or sensitive data can create a security risk. It’s important to limit access to API routes and use proper HTTP methods for each action.
Example Vulnerability:
Route::get('user-details', 'UserController@getUserDetails');
Solution: Restrict sensitive routes to authenticated users and use proper HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE:
Route::middleware('auth:api')->get('user-details', 'UserController@getUserDetails');
How to Use Our Free Website Security Checker Tool
If you're unsure about the security posture of your Laravel API or any other web application, we offer a free Website Security Checker tool. This tool allows you to perform an automatic security scan on your website to detect vulnerabilities, including API security flaws.
Step 1: Visit our free Website Security Checker at https://free.pentesttesting.com. Step 2: Enter your website URL and click "Start Test". Step 3: Review the comprehensive vulnerability assessment report to identify areas that need attention.
Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Example Report: Vulnerability Assessment
Once the scan is completed, you'll receive a detailed report that highlights any vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection risks, XSS vulnerabilities, and issues with authentication. This will help you take immediate action to secure your API endpoints.
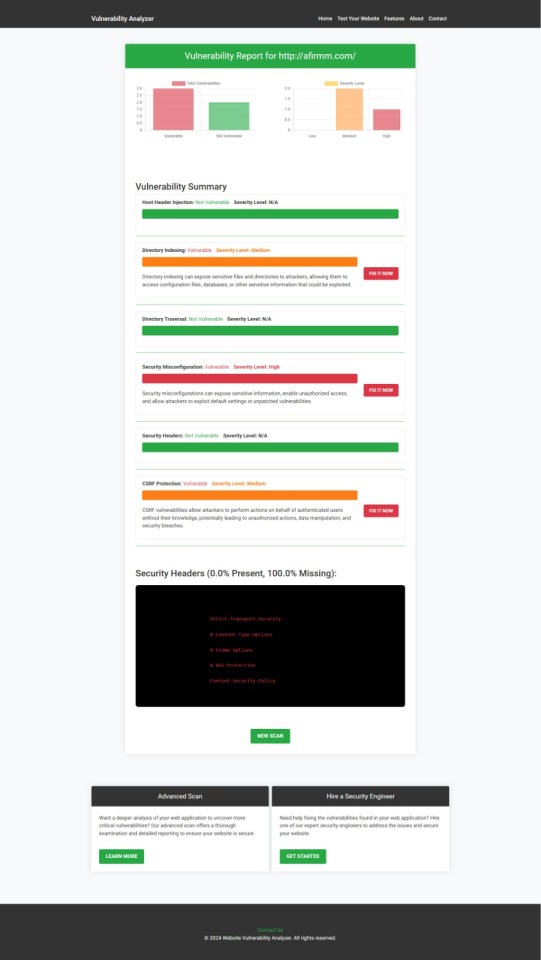
An example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool provides insights into possible vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Strengthen Your API Security Today
API vulnerabilities in Laravel are common, but with the right precautions and coding practices, you can protect your web application. Make sure to always sanitize user input, implement strong authentication mechanisms, and use proper route protection. Additionally, take advantage of our tool to check Website vulnerability to ensure your Laravel APIs remain secure.
For more information on securing your Laravel applications try our Website Security Checker.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#the security breach show#laravel#php#api
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
An Overview of Burp Suite: Acquisition, Features, Utilisation, Community Engagement, and Alternatives.
Introduction:
Burp Suite is one of the strongest web application security testing software tools used by cybersecurity experts, as well as ethical hackers. PortSwigger created Burp Suite, which provides potent scanning, crawling, and exploiting tools for web application vulnerabilities.
What is Burp Suite?
Burp Suite is one of the tools to conduct security testing of web applications. It assists security testers in detecting vulnerabilities and weaknesses like SQL injections, XSS, CSRF, etc.
Steps in Obtaining Burp Suite
Burp Suite is available for download on the PortSwigger official website. It is available in three versions:
Community Edition (Free)
Professional Edition (Subscription-Based)
Enterprise Edition (For Organisations)
Important Tools in Burp Suite
Proxy – Captures browser traffic
Spider – Crawls web application content
Scanner – Scans automatically for vulnerabilities (Pro only)
Intruder – Performs automated attack activities.
Repeater – Manually send requests.
Decoder – Translates encoded data.
Comparer – Compares HTTP requests/responses
Extender – Allows extensions through the BApp Store
How to Use Burp Suite
Set your browser to use Burp Proxy.
Capture and manipulate HTTP/S requests.
Utilise tools such as Repeater and Intruder for testing.
Scan server responses for risks.
Export reports for audit purposes.
Burp Suite Community
Burp Suite has a highly engaged worldwide user base of security experts. PortSwigger Forum and GitHub repositories have discussions, plugins, and tutorials. Many experts are contributing through YouTube, blogs, and courses.
Alternatives to Burp Suite
If you're searching for alternatives, then look at:
OWASP ZAP (Open Source)
Acunetix
Netsparker
Nikto
Wfuzz
Conclusion:
Burp Suite is widely used for web application security testing. Mastery of Burp Suite is one step towards web application security for both novice and professional ethical hackers.

#BurpSuite#CyberSecurity#EthicalHacking#PenTesting#BugBounty#InfoSec#WebSecurity#SecurityTools#AppSec#OWASP#HackingTools#TechTools#WhiteHatHacker#CyberTools#BurpSuiteCommunity#NetworkSecurity#PortSwigger#WebAppTesting#SecurityScanner#CyberAwareness
0 notes
Text
CS6262 Project 2: Advanced Web Security Summer 2025 Solved
Objectives Attack a web application by exploiting its XSS vulnerabilities to infect its users as persistently as possible. Write XSS exploits to launch a social engineering attack and trick a simulated user into giving up their credentials. Research basic cookie management and how to secure them. Due Date You can find the due date and how to turn in your solution located on the Canvas…
0 notes
Text
How to Secure API Endpoints in Web Development
APIs are the backbone of modern web applications, letting different systems talk to each other seamlessly. But with great power comes great responsibility—securing API endpoints is critical to protect sensitive data and keep your application safe from attackers. Whether you're working with a website designing company in India or building your own app, securing APIs doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Let’s break down practical, beginner-friendly steps to lock down your API endpoints, all in a conversational tone to keep things approachable.
Why API Security Matters
APIs often handle sensitive information like user data, payment details, or authentication tokens. If left unsecured, they can be an open door for hackers to exploit, leading to data breaches or system crashes. Think of your API as a bank vault—without a strong lock, anyone could waltz in. By securing your endpoints, you protect your users and maintain trust, which is especially important for businesses, including those partnering with a website designing company in India to build robust applications.
1. Use HTTPS for Encrypted Communication
First things first: always use HTTPS. It encrypts data sent between the client (like a browser or app) and your server, making it unreadable to anyone snooping on the network. Without HTTPS, sensitive info like passwords or API keys could be intercepted. Most hosting providers offer free SSL certificates through services like Let’s Encrypt, so there’s no excuse not to enable it. Check your server configuration (e.g., Nginx or Apache) to enforce HTTPS and redirect any HTTP requests.
2. Authenticate Every Request
Never let unauthenticated users access your API. Authentication ensures only authorized users or systems can make requests. A simple way to do this is with API keys—unique strings assigned to users or apps. For stronger security, use OAuth 2.0, which provides access tokens that expire after a set time. Store these keys or tokens securely (never hardcode them in your code!) and validate them on every request. For example, in a Node.js app, you can check the API key in the request header before processing it.
3. Implement Rate Limiting
Ever heard of a denial-of-service attack? It’s when someone floods your API with requests to crash it. Rate limiting caps how many requests a user can make in a given time (e.g., 100 requests per minute). This protects your server from overload and abuse. Tools like Express Rate Limit for Node.js or built-in features in API gateways (like AWS API Gateway) make this easy to set up. You can also block suspicious IPs if you notice unusual activity.
4. Validate and Sanitize Input
Hackers love trying to sneak malicious data into your API through inputs, like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS). Always validate user inputs to ensure they match expected formats (e.g., an email field contains a valid email). Sanitize inputs to strip out dangerous characters. Libraries like Joi for JavaScript or Django’s form validation in Python can help. For example, if your API expects a numeric ID, reject anything that’s not a number to avoid surprises.
5. Use Strong Authorization
Authentication says, “You’re allowed in.” Authorization says, “Here’s what you can do.” Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit what each user can access. For instance, a regular user shouldn’t be able to delete another user’s data. Define roles (like admin, user, or guest) and check permissions for every request. Frameworks like Spring Security (Java) or Laravel (PHP) have built-in tools to manage this efficiently.
6. Protect Against Common Vulnerabilities
APIs are prime targets for attacks like injection, broken authentication, or data exposure. Follow the OWASP API Security Top 10 to stay ahead. For example, avoid exposing sensitive data (like passwords) in API responses. Use secure HTTP headers like Content-Security-Policy (CSP) to prevent XSS attacks. Regularly test your API with tools like Postman or automated scanners like OWASP ZAP to catch weaknesses early.
7. Log and Monitor API Activity
Keep an eye on what’s happening with your API. Logging tracks who’s making requests, what they’re asking for, and any errors that pop up. Use tools like ELK Stack or cloud-based solutions like AWS CloudWatch to store and analyze logs. Set up alerts for suspicious activity, like repeated failed login attempts. Monitoring helps you spot issues fast and respond before they escalate.
8. Use an API Gateway
An API gateway acts like a bouncer, managing and securing traffic to your endpoints. It can handle authentication, rate limiting, and logging in one place, saving you from coding these features yourself. Popular gateways like Kong or Amazon API Gateway also offer analytics to track usage patterns. This is especially handy for scaling applications built by teams, including those at a professional web development firm.
Keep Learning and Testing
Securing APIs isn’t a one-and-done task. As threats evolve, so should your defenses. Regularly update your dependencies to patch vulnerabilities (tools like Dependabot can help). Conduct penetration testing to simulate attacks and find weak spots. If you’re new to this, consider working with experts who specialize in secure development—they can guide you through best practices.
By following these steps, you can make your API endpoints a tough target for attackers. It’s all about layering defenses: encrypt communication, authenticate users, limit access, and stay vigilant. Whether you’re a solo developer or collaborating with a web development team, these practices will help keep your application safe and your users happy.
#digital marketing agency bhubaneswar#website development companies in bhubaneswar#best digital marketing company in bhubaneswar#digital marketing services in bhubaneswar#web development services in bhubaneswar#digital marketing agency in bhubaneswar
0 notes
Text
How can criminals bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA)?

Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has long been hailed as the cybersecurity savior. By adding an extra layer of verification beyond just a password – typically a code from an app, a fingerprint, or a security key – MFA drastically reduces the risk of account compromise. For years, it was considered virtually unhackable, making it the bedrock of digital security for individuals and organizations alike.
But in 2025, the cybersecurity landscape has evolved. While MFA remains an absolutely critical defense, sophisticated criminals are finding increasingly clever ways to circumvent it. The illusion of MFA being an impenetrable fortress is a dangerous one. Understanding these bypass techniques is the first step in truly fortifying your digital castle.
MFA: The Unsung Hero (and Its Evolving Limitations)
MFA is effective because it relies on different "factors" of authentication:
Something you know (password, PIN)
Something you have (phone, hardware token)
Something you are (biometrics like fingerprint, face scan)
By requiring at least two of these, MFA makes it exponentially harder for an attacker to gain access, even if they steal your password. However, criminals don't just give up; they adapt. And their adaptation strategies are getting alarmingly good.
The New Playbook: Top MFA Bypass Techniques
Phishing & Interception (Man-in-the-Middle/Adversary-in-the-Middle):
How it Works: This is arguably the most common and effective bypass. Attackers create incredibly realistic fake login pages that act as a proxy. When you try to log in, your credentials and your MFA code are intercepted in real-time by the attacker's server, which then immediately uses them to log into the legitimate site. You log in, oblivious, while the attacker gains access. Tools like Evilginx and Modlishka automate this process.
Why it Works: It exploits human trust and a lack of meticulous URL vigilance. You see a familiar login screen and trust the padlock icon, not noticing the subtle fake domain.
MFA Fatigue / Push Bombing:
How it Works: Attackers, having somehow obtained your username and password (e.g., from a breach), repeatedly send MFA push notifications to your device. They hope you'll eventually approve one out of annoyance, distraction, or confusion (e.g., "Oh, my VPN software is acting up again, must be a prompt from that").
Why it Works: It preys on human psychological factors like frustration, habit, and a desire to make pop-ups disappear.
SIM Swapping (or SIM Jacking):
How it Works: This targets SMS-based MFA. Attackers trick your mobile carrier (often through social engineering or bribing an insider) into transferring your phone number to a SIM card they control. Once they own your number, they receive all your SMS messages, including MFA codes for banking, email, and other services.
Why it Works: It exploits weaknesses in the customer verification processes of mobile service providers.
Session Hijacking / Cookie Theft:
How it Works: MFA secures the initial login. Once you're authenticated, your browser stores a session cookie that keeps you logged in. Attackers can steal this cookie (e.g., via sophisticated malware, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks on vulnerable websites, or compromised public Wi-Fi) and then use it to bypass the login process entirely, directly accessing your authenticated session.
Why it Works: MFA doesn't protect the ongoing session itself.
Social Engineering (Human Factor Exploitation):
How it Works: This is the most versatile bypass. Attackers manipulate individuals (e.g., help desk staff, IT support, or even the target directly) into resetting MFA, divulging MFA codes, or disabling security features. They might impersonate the target, a legitimate authority figure, or IT support.
Why it Works: It exploits human psychology – trust, the desire to be helpful, fear, or a perceived sense of authority.
Malware & Keyloggers:
How it Works: If malicious software is installed on your device, it can capture credentials and MFA codes as they are entered. More advanced malware can even create a backdoor that bypasses MFA entirely by leveraging compromised system privileges.
Why it Works: The endpoint itself is compromised, allowing the malware to control or observe authentication processes.
Strengthening Your MFA Defense: Beyond the Basics
While these bypasses sound intimidating, implementing a multi-layered defense strategy can significantly reduce your risk.
Prioritize Phishing-Resistant MFA:
Security Keys (FIDO2/WebAuthn): These are the gold standard. Devices like YubiKey or Google Titan Key verify the legitimate website's origin cryptographically, making phishing pages ineffective.
App-Based Authenticator Apps (TOTP): Use apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator. These generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) that change every 30-60 seconds and are more secure than SMS codes.
Avoid SMS/Email MFA where possible: While better than nothing, SMS and email are the least secure forms of MFA due to susceptibility to SIM swapping and phishing.
Unwavering User Education & Awareness:
Check URLs Meticulously: Train yourself and your team to always inspect the full URL of a login page. Look for subtle misspellings, extra words, or unusual domains before entering any credentials.
Never Approve Uninitiated MFA Prompts: If you receive an MFA push notification that you didn't initiate, deny it. This is crucial for stopping MFA fatigue attacks.
Be Skeptical of Urgency: Phishing attacks thrive on creating panic. Any unexpected message or call demanding immediate action, especially involving sensitive data or money, should be treated with extreme suspicion.
Implement Robust Anti-Phishing Controls:
For organizations: Deploy advanced email gateway solutions, DNS filtering, and browser extensions that warn users about suspicious sites.
For individuals: Use reputable anti-phishing browser extensions and keep your browser updated.
Robust Endpoint Security:
Keep your operating system and all software (web browsers, applications, antivirus) up-to-date with the latest security patches. This prevents malware and exploitation of system vulnerabilities.
Use a reputable antivirus/anti-malware solution with real-time protection.
Monitor for Anomalies (Especially for Organizations):
Implement security monitoring tools to detect unusual login locations, repeated failed MFA attempts, sudden MFA registration changes, or suspicious network activity from authenticated users.
Strong Internal Policies (For Organizations):
Establish and strictly enforce rigorous identity verification processes for help desk staff when users request MFA resets or account access. Regularly audit these processes.
MFA is an essential component of modern cybersecurity, but it is not a silver bullet. As criminals evolve, so must our defenses. By understanding their tactics and adopting a multi-layered approach that combines strong MFA implementations with continuous user education, robust endpoint security, and vigilant monitoring, we can collectively make it significantly harder for attackers to breach our digital fortresses. Stay informed, stay skeptical, and stay secure.
0 notes
Text
From Beginner to Pro: The 5 Best Ethical Hacking Books to Read In an era where cybersecurity threats are increasing daily, ethical hackers play a crucial role in safeguarding digital systems. If you're an aspiring ethical hacker, reading the right books can provide the foundation you need to build strong hacking and penetration testing skills. We've curated a list of the 5 best books for ethical hacking, offering everything from beginner-friendly concepts to advanced hacking techniques. Whether you're new to cybersecurity or looking to sharpen your hacking skills, these books will set you on the right path. 1. Ethical Hacking: A Hands-on Introduction to Breaking In Author: Daniel Graham Level: Beginner to Intermediate This book is a perfect starting point for ethical hacking enthusiasts. It provides practical hands-on lessons in penetration testing, guiding you through real-world hacking scenarios. Key Highlights: ✅ Step-by-step guidance on penetration testing ✅ Learn to break into computers and networks ethically ✅ Covers fundamental hacking techniques and tools If you’re looking to get started with ethical hacking and understand the mindset of a hacker, this book is a great investment. 2. Gray Hat Hacking: The Ethical Hacker's Handbook Authors: Allen Harper, Daniel Regalado, and others Level: Intermediate to Advanced "Gray Hat Hacking" is one of the most comprehensive books on ethical hacking. It goes beyond the basics, introducing advanced security tools, reverse engineering, and fuzzing techniques. Key Highlights: ✅ In-depth coverage of zero-day vulnerabilities ✅ Learn binary scanning and advanced exploitation techniques ✅ Covers topics such as malware analysis and vulnerability discovery If you want to go beyond beginner-level hacking and explore advanced cybersecurity concepts, this book is a must-read. 3. Learn Ethical Hacking from Scratch Author: Zaid Sabih Level: Beginner This book is one of the best beginner-friendly ethical hacking books available. It takes you from zero to hero, covering ethical hacking concepts, penetration testing techniques, and using Kali Linux. Key Highlights: ✅ Covers basic to intermediate ethical hacking techniques ✅ Hands-on practical exercises using real-world examples ✅ Teaches penetration testing using Kali Linux If you want to learn ethical hacking from scratch and gain hands-on experience, this book is an excellent choice. 4. Hacking: The Art of Exploitation Author: Jon Erickson Level: Intermediate Unlike other books that focus only on penetration testing, this book goes deep into the core principles of hacking and exploitation techniques. It includes a Linux programming crash course, making it a perfect read for aspiring hackers who want to understand the fundamentals of cybersecurity. Key Highlights: ✅ Deep dive into exploitation techniques and vulnerabilities ✅ Learn how programs and network security actually work ✅ Covers buffer overflows, cryptography, and shellcode writing If you're interested in learning how exploits work under the hood, this book is a must-read. 5. The Web Application Hacker’s Handbook Authors: Dafydd Stuttard & Marcus Pinto Level: Intermediate to Advanced With web applications being a prime target for hackers, this book focuses on web security and penetration testing techniques. It’s an essential read for ethical hackers who want to specialize in web security testing. Key Highlights: ✅ Covers SQL injection, XSS, CSRF, and other web attacks ✅ Learn how to test web applications for security flaws ✅ A must-read for bug bounty hunters and penetration testers If you're aiming to become a web security expert, this book will help you master web application penetration testing. Conclusion Ethical hacking is a rapidly growing field, and reading the right books can give you a competitive edge. Whether you're just starting or looking to specialize in advanced penetration testing techniques, these books will provide valuable insights.
💡 Pro Tip: Combine your reading with hands-on practice in virtual labs like Hack The Box, TryHackMe, and Kali Linux to build real-world experience! Which book are you planning to read first? Let us know in the comments! 🚀
0 notes
Text
Web App Penetration Testing: Your First Line of Defense Against Cyber Attacks

In today’s hyper-connected digital world, your web applications are often the first point of contact between your business and the outside world—and that includes cybercriminals. Whether you’re an e-commerce platform, a SaaS provider, or a government portal, your web app isn’t just a business tool—it’s a potential attack surface. If you’re not proactively testing its security, you’re leaving your digital doors wide open.
Web application penetration testing (often referred to as web app pen testing) is no longer optional—it's a critical first line of defense against data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. In this article, we explore why penetration testing is essential, how it works, and how it empowers your organization to detect, fix, and prevent security issues before attackers can exploit them.
What Is Web Application Penetration Testing?
Web application penetration testing is a simulated cyberattack conducted by ethical hackers to evaluate the security of a web application. Unlike vulnerability scanners that merely identify weaknesses, penetration testers actively exploit them to understand how deep the damage could go if a real attacker gained access.
This isn’t just a scan—it’s a strategic, targeted approach that uncovers how secure your application truly is against modern-day threats like:
SQL injection
Cross-site scripting (XSS)
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
Insecure authentication and session management
Security misconfigurations
Broken access controls
And more
Think of pen testing as hiring a locksmith to try every possible way to break into your home—then fix those flaws before burglars even get the chance.
Why Web Applications Are Prime Targets
Web applications are attractive to hackers because they often store and process sensitive user data such as:
Login credentials
Financial information
Customer records
Health data
Proprietary business content
They’re also accessible 24/7 from anywhere in the world, making them ideal entry points for opportunistic cybercriminals. Combine that with the speed at which apps are deployed and updated—and often the lack of security oversight—and you’ve got the perfect storm for exploitation.
According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, web applications have been the most common vector for data breaches in recent years. Without proactive testing, you’re essentially gambling with your company’s reputation and customer trust.
The Business Case for Web App Penetration Testing
1. Prevent Costly Breaches
Data breaches are expensive. Between legal fees, customer notification, lost business, regulatory fines, and remediation, the cost can soar into millions. Pen testing helps you identify vulnerabilities before attackers do—dramatically reducing the risk and cost of a potential breach.
2. Meet Compliance Requirements
Many industries are governed by data protection and cybersecurity regulations such as:
GDPR
PCI-DSS
HIPAA
ISO 27001
These frameworks often require or strongly recommend regular penetration testing as part of a robust security program. Failing to comply can lead to stiff penalties and reputational fallout.
3. Protect Brand Reputation
Customers are more aware of data privacy than ever before. A single security incident can erode years of brand trust. Demonstrating that you conduct regular penetration testing signals to your customers and partners that you take security seriously.
4. Stay Ahead of Evolving Threats
Cyber threats evolve quickly. Automated scanners may miss new or complex attack techniques. Human-led penetration testing adapts to the latest exploits, mimicking real-world tactics to expose vulnerabilities you didn’t know existed.
What Does a Web App Pen Test Involve?
A comprehensive web application penetration test typically follows a multi-phase process:
Phase 1: Reconnaissance
The tester gathers information about the application, such as its domain structure, technologies used, entry points, and public-facing assets.
Phase 2: Threat Modeling
Next, the tester identifies potential vulnerabilities based on the app’s functionality, business logic, and user roles—this helps prioritize attack vectors.
Phase 3: Vulnerability Analysis
Automated tools and manual techniques are used to find known vulnerabilities. This includes outdated libraries, insecure code patterns, and improper error handling.
Phase 4: Exploitation
Here’s where the magic happens. The tester actively attempts to exploit the vulnerabilities found, just like a real hacker would—accessing sensitive data, bypassing login forms, or manipulating application logic.
Phase 5: Post-Exploitation and Reporting
Once access is gained, testers assess the damage that could be done. Then, they provide a detailed report including:
Vulnerabilities found
Evidence of exploitation
Risk levels
Recommendations for remediation
Some providers even offer retesting to verify fixes.
Common Web App Vulnerabilities Uncovered by Pen Testing
SQL Injection
Attackers manipulate database queries to gain unauthorized access to data.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Malicious scripts are injected into pages viewed by other users, often used to steal session cookies.
Authentication Flaws
Weak or broken login systems allow unauthorized users to gain access.
Broken Access Control
Users can access data or actions they shouldn’t be able to—like regular users viewing admin panels.
Security Misconfigurations
Default credentials, exposed debug tools, or misconfigured servers provide easy entry.
Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards
Users can be redirected to malicious sites via the application.
These vulnerabilities may seem small—but each one can be the start of a catastrophic breach.
How Often Should You Conduct a Pen Test?
There's no one-size-fits-all answer, but here are general guidelines:
Annually – At a minimum, once a year
After Major Updates – Any time you launch a new feature or app version
After Security Incidents – To assess how vulnerabilities were exploited
Before Going Live – For new applications or systems
The frequency should reflect your app’s complexity, exposure, and regulatory requirements.
Choosing the Right Penetration Testing Provider
Not all pen tests are created equal. When selecting a provider, look for:
Certified professionals (e.g., OSCP, CEH, CISSP)
Experience with web app technologies and frameworks
Detailed reporting with actionable recommendations
Manual testing focus, not just automated scans
Clear scoping and transparent pricing
Retesting options to confirm remediation
Remember, you’re not just buying a test—you’re investing in expertise and insight.
Final Thoughts
Your web application is more than just code—it’s the public face of your business, a key revenue driver, and often, a data goldmine. If it’s exposed to the internet, it’s exposed to threats.
Web application penetration testing is your first line of defense in an increasingly hostile digital landscape. It helps you identify and fix vulnerabilities before they become breaches, comply with regulations, and—most importantly—protect your customers, your brand, and your bottom line.
Cybersecurity isn’t a one-time checkbox. It’s an ongoing strategy. And web app pen testing should be at the core of that strategy.
#penetration testing#penetration testing service#web application penetration testing#application penetration testing#penetration testing consultant
0 notes
Text
Cyber Security Summer Internship | Top Skills You’ll Learn

As the digital world grows, so does the need for skilled cybersecurity professionals. Organizations constantly seek individuals who can effectively protect their systems, detect vulnerabilities, and respond to cyber threats. For students and fresh graduates, enrolling in a Cyber Security Summer Internship is one of the best ways to build a strong foundation in this field.
At WebAsha Technologies, the Cyber Security Summer Internship program in Pune is designed to equip participants with the practical skills and knowledge needed to succeed in today’s cybersecurity landscape. In this article, we highlight the top skills you will learn during the internship.
Network Security Basics
One of the first areas you will explore is network security. This involves understanding how data moves across networks and learning to protect it from interception and attacks.
Learn the fundamentals of network architecture and protocols.
Understand how firewalls, routers, and switches function to secure networks.
Identify common network vulnerabilities and how to mitigate them.
Study intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS).
Ethical Hacking Techniques
Ethical hacking teaches you to think like a hacker, but to strengthen system security. This skill is critical for finding and fixing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Get familiar with various hacking methodologies and tools.
Learn reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, and covering tracks.
Practice using tools such as Nmap, Metasploit, and Burp Suite.
Explore real-world hacking scenarios and practice ethical response methods.
Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT)
VAPT is a key component of any cybersecurity strategy. It helps organizations identify weaknesses in their systems through systematic testing.
Learn to conduct vulnerability assessments to discover security gaps.
Perform penetration tests to simulate real-world attacks.
Understand the phases of VAPT: planning, scanning, exploitation, and reporting.
Gain experience in documenting findings and suggesting remediation steps.
Web Application Security
With web applications being a major target for attackers, web security is a crucial skill.
Study common web application vulnerabilities, including SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Learn how to test web apps for security flaws using automated and manual techniques.
Understand how to secure APIs and manage user authentication securely.
Get hands-on practice in identifying and mitigating web security risks.
Malware Analysis and Threat Detection
Another essential skill is the ability to analyze malware and detect potential threats before they cause damage.
Learn about different types of malware: viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
Understand how malware behaves and propagates.
Use tools to detect, analyze, and remove malicious code.
Study case examples of high-profile malware attacks and their impacts.
Cryptography and Data Protection
Protecting sensitive data is a critical part of cybersecurity. You will gain an understanding of cryptography and how it ensures data security.
Learn the basics of encryption and decryption.
Understand the differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
Explore digital signatures, certificates, and secure key management.
Study how cryptography is used in securing communications and transactions.
Incident Response and Handling
Responding quickly and effectively to a cyber incident is vital in minimizing damage.
Learn the stages of incident response: preparation, detection, containment, eradication, and recovery.
Practice creating incident response plans.
Understand how to preserve evidence and maintain the chain of custody.
Study real-world case studies to learn best practices.
Security Compliance and Best Practices
In addition to technical skills, understanding security standards and compliance is essential.
Get familiar with key standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, and PCI-DSS.
Learn best practices for creating security policies and procedures.
Understand the role of audits and risk assessments in maintaining compliance.
Final Thoughts
The Cyber Security Summer Internship at WebAsha Technologies is more than just a learning opportunity—it’s a stepping stone to a successful career in cybersecurity. By the end of the program, participants will have hands-on experience, a deep understanding of essential security practices, and the confidence to tackle real-world security challenges.
For students and IT enthusiasts looking to build a strong career foundation, this internship provides everything needed to get started. Enroll today and take the first step toward becoming a skilled cybersecurity professional.
#Cyber Security Summer Internship#Ethical Hacking Summer Training#VAPT Internship#Cyber Security Summer Course#Cyber Security Internship with Placement#Cyber Security Summer Bootcamp#Summer Internship in Cyber Security
0 notes
Text
How Drupal Ensures Compliance and Data Security in 2025
In today's age of the internet, where data breaches and compliance issues are making headlines daily, organizations require a content management system (CMS) that, in addition to being robust and scalable, is secure and compliant too. Drupal, the most trusted open-source CMS platform globally, has raised the bar at every turn. In 2025, Drupal raises the bar again with improved data protection and adherence to international standards.
This is why more and more, businesses are partnering with a good Drupal development firm or hiring best Drupal development services to create, host, and protect their websites.
Here we talk about how Drupal has been made compliant and secure for the data in 2025 by highlighting the most important features, improvements, and best practices of the platform making it one of the highly chosen platforms for government organizations, banks and financial institutions, healthcare providers, and companies handling sensitive data.

1. Security Architecture at its Core
Fundamentally, Drupal is designed to be secure. The system runs on a strong security-first architecture that includes:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Drupal supports fine-grained user access rights down to where users are only able to view content and operate functions.
Database Abstraction: Prevents SQL injection by running on the basis of a layer of abstraction to sanitize input. It.
CSRF and XSS Protection: Drupal comes with built-in protection against Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), two common web application vulnerabilities.
Secure Coding Standards: Drupal has strict coding standards and peer-reviewed contributions, so it is less likely that insecure code will be released.
When you are outsourcing the service of a Drupal web development agency, such foundational security features are a part of the package as the company forms its work upon the basis of a secure and compliant digital experience.
2. Security Team and Continuous Updates
Drupal's dedicated Security Team monitors and resolves vulnerabilities 24/7. In 2025, the community has further strengthened with faster response times and proactive measures that patch vulnerabilities well before they can be exploited.
Secondly, Drupal 10.x (and subsequent versions in 2025) is updated periodically, and security advisories are released openly. This alerts developers and site administrators to it and gives them a chance to move quickly. Top-class Drupal development service ensures that client sites are kept current and secure with zero downtime.
3. Compliance-Ready Architecture
The flexibility of Drupal makes it possible to use it with almost any compliance framework. In 2025, organizations leverage Drupal to become compliant with some of the globe's most significant international standards:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
SOC 2
ISO/IEC 27001
How Drupal Ensures Compliance
Data Anonymization & Export: With GDPR fully in effect, Drupal makes anonymizing, deleting, or exporting personal data on demand for users easy.
Audit Logs: Track user actions and system changes for traceability and accountability.
Data Encryption: Drupal supports database encryption at rest and SSL/TLS for encrypted data in transit, which is industry best practice.
Most organizations outsource the installation of such compliance aspects to a professional Drupal development company that they entrust to abide by their industry-specific requirements.
4. Modular Security Improvements
The largest strength of Drupal is its modularity. Scores of contributed modules in 2025 are very commonly used to secure and comply sites. A few of them are:
Secure Login Module: Enforces 2FA (two-factor authentication) and CAPTCHA-based protection.
Password Policy Module: Enforces strict password policies and expiry dates.
Encrypt Module: Enables encryption of sensitive fields or entire database tables.
Security Kit Module: Offers a customizable security hardening solution for headers and content protection.
These modules are typically packaged by top Drupal web development companies to create customized solutions based on the specific security needs of each client.
5. Privacy by Design
Drupal encourages Privacy by Design, a philosophy that has become the norm of data protection policies in 2025. Whether creating a personal blog or an eCommerce site globally, developers can include privacy principles from the start: Minimal Data Collection: Form and API developers can configure forms and APIs to capture minimal user information.
Explicit Consent Mechanisms: Easy integration opt-in checkboxes, cookie banners, and preference centers ensure user consent.
Customizable Data Retention Policies: Automatically delete or archive the data after a while.
These features can be implemented by businesses easily without compromising quality user experience with the help of an experienced Drupal development company.
6. Third-Party Integrations with Security Controls
In today's tech stack, third-party system integration with CRMs, ERPs, and marketing systems is inevitable. Drupal's API-first nature makes interactions with such services secure:
Firewall and Access Control Layers: Secures so that APIs are accessed from trusted places only.
Rate Limiting and Throttling: Protects from brute-force attacks and abuse of public endpoints.
Professional Drupal web development companies integrate these features in a way that is both user-friendly and compliant.
7. Alignment of Cloud and DevOps Security
The native integration of the newest DevOps trends and cloud platforms within Drupal in 2025 provides additional security:
CI/CD Pipelines: Static security checking and code scan features like SonarQube and Snyk are applied in Drupal CI/CD pipelines.
Containerization with Docker/Kubernetes: Docker/Kubernetes with secure container deployment isolates apps and reduces the attack surface.
Drupal on Acquia, Pantheon, and Platform.sh: These solutions feature enterprise-grade security features such as WAF (Web Application Firewalls), DDoS protection, and compliance certification.
Through collaboration with a Drupal development company, businesses can host secure and scalable cloud applications and remain regulatory compliant.
8. Accessibility and Inclusivity in Security
Security and compliance are not just technical issues; they're also ethical responsibilities. Drupal, with its inclusiveness-oriented nature, ensures that:
WCAG 2.2 Compliance: Drupal websites are disability accessible to users, as per ADA and Section 508 compliance.
Multilingual Privacy Policies: Drupal has multilingual support that ensures the provision of privacy and security alerts to all users.
Top Drupal development services encompass accessibility testing and best practices in all levels of development.
9. Drupal Community and Documentation
Lastly, Drupal's worldwide active community ensures a secure environment. Thousands of developers contribute to code reviews, security scans, and knowledge sharing. Documentation on Drupal.org, webinars, and security guides make deployment and maintenance of compliant systems easier than ever.
In 2025, functionalities like Project Browser and Automatic Updates further make the platform secure by simplifying module discovery and patch application, respectively.
A quality Drupal web development company will always be at the forefront of these advancements to create the optimal result.
Conclusion
With changing data privacy regulations and increasingly advanced cyber attacks, a secure, compliant CMS has never been more critical. Drupal's robust architecture, dedicated security team, upgradable modularity, and adherence to international compliance standards make it a leading-edge solution for 2025.
Businesses that are looking to future-proof their web assets are not only betting on Drupal development services to build a website, but to develop an enterprise-grade compliance and data security policy. Through partnership with an experienced Drupal development company, businesses can be assured that their websites are not only beautiful and functional but robust and regulation-friendly as well.
0 notes