#Institute of professional Banking
Text
institute of professional banking Offers: Bank course online
One of the Most Trusted Professional Banking Institute Helping Unemployed Graduates to be Professionally Qualified & Competent Banking Professionals 7000+ placements in leading private sector banks.
The rapidly growing business in India is turning to Banks for their credit needs; which suggests that the country’s banking sector is also poised for strong growth. This growth is paving way for many career opportunities in the banking sector such as in retail banking for well-educated manpower.
Post Graduate Certificate in Retail Banking (PGCRB) program is the flagship course for fresh graduates & postgraduates to make them “Smart Banker” by undergoing an intensive training program of 3 Months by bankers having domain specialization.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Institute of Professional Banking (IPB India)
Branches
IPB Partners
Subhas Yadav @The Best Career Coach Award by IPB Head Office
Success Stories
Akanshi Singh (Ballia, Uttar Pradesh) Bandhan Bank
Pragati Singh (Mau, Uttar Pradesh) HDFC Bank
Khushali Gujrati (Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh) HDFC BANK
Riya Gupta (Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh) Bandhan Bank
Akansha Singh (Mau, Uttar Pradesh) Bandhan Bank
Himanshu Gupta (Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh)…

View On WordPress
#bank jobs in 2024#Banking careers vacancy#Banking employment opportunities#Banking industry jobs#Banking jobs#Banking positions#Finance career paths#Finance jobs in India#Financial institutions careers#Financial services careers opportunities#Institute of Professional Banking#Investment banking opportunities#IPB India#Ipb Varanasi branch
0 notes
Photo

Learn banking terminology with 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐭𝐮𝐭𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐟𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐚𝐥 𝐁𝐚𝐧𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 (𝐈𝐏𝐁)
0 notes
Text
Also re:necropolitics of israel (click)
A few days ago there were reports of Israeli soldiers "returning" bodies of martyrs they took like just straight up from Gaza. Here is a report about bodies being stolen from al-Shifa (click).
The director of Al-Shifa had reported the bodies being stolen back in November (click) before his arrest. The hospital workers mentioned not knowing why the soldiers would do that. The speculation of the photo-op arose because the photo-op of October 7th within Israel happened a month and a half after October 7th, after the Al-Shifa raid. People (Palestinians) noted that the level of violence done to the bodies seemed similar to what they had been seeing with the bombs in Gaza, and found it hard to believe that Hamas could inflict that much damage. There was a thread that was examining this idea but I haven't found it as it's been a bit. If I find it, I'll comment on this post.
But even then, Israel routinely makes corpses serve out their sentences or even outright steals them for the sake of enacting psychological torture onto the relatives of the martyr (click). The burial process is an essential step in mourning and grief, which means by withholding the bodies, they ensure that the family is unable to recover emotionally from the death of their loved one nor are they allowed to move on. This is essentially a form of ensuring that people are unable to resist as the emotional toll this takes on them is quite high.
A variety of reports and testimonies are linked in this article regarding the harvesting and removal of organs throughout the years by Israel (click). The most damning of the evidence is a testimony by Dr. Meira Weiss in her book "Over Their Dead Bodies." The article has a translated passage from Hebrew about the period at the turn of the century and their practices then (roughly 1996-2002):
“They would take corneas, skin, and heart valves, while noting that non-professionals would not notice the absence of these organs as they would place something plastic in place of the corneas and ‘take’ the skin from the back so that the family wouldn’t see it. In addition, the bodies of detained martyrs are used in medical colleges at Israeli universities for research purposes.” Weiss confirmed that “in the first Intifada, the army effectively allowed the institute to extract organs from Palestinians under a military procedure that required the autopsy of a Palestinian prisoner. The autopsy procedure was accompanied by organ removal, which was used by the Israeli Skin Bank established in 1985 to treat burns suffered by Israeli soldiers. This was after the Chief Rabbinate Council issued a ruling legitimizing it, which led to saving the lives of many Israelis who were injured during attacks on Palestinian citizens, continuous assaults, and wars — at the expense of Palestinian martyrs, according to specialized Israeli medical sources for burn treatment.”
It's worthy to note: as an occupying force especially, Israel should not be doing ANYTHING with these bodies and just returning them to the families. I've seen some people say "they didn't JUST harvest Palestinians' organs, they also harvested Israeli organs." It doesn't matter. They are an occupying force that enacts systematic violence on Palestinians especially and within this context, anything Israel does towards Palestinians is a targeted, racialized violence. It is widely known that Israel denies crimes it has committed until many, many years, especially from during the Nakba, such as well poisoning.
People provide evidence that organs can't be used after a certain point in time.... in this context (October 2023-December 2023), it's not about whether or not the organs were used for anything. It is specifically for the purpose of body desecration which Israeli soldiers especially have not been shy about. Here is a report during the bulldozer massacre in which people report that Israeli soldiers run over bodies for no other reason than desecration (click).
Also, remember the grave desecration that happened a few days ago? It was reported that they had stolen bodies believed to belong to young Palestinian activists then (click). This is widely known as 'necroviolence' on Palestinian bodies in order to humiliate them (click).
You cannot remove the context of an oppressive force (Israel) that is documented to have disrespected graves and bodies. You must analyze it within this context, not any others. Withholding bodies of Palestinians, no matter what they did while they were alive, is a form of disrespect and oppression on a subjugated population. To deny that this happens and to attribute it to antisemitism is not only disrespectful of Palestinians' mourning rights, but also an effort to remold the narrative into one of "Jewish people against Palestinians" by emphasizing the Jewishness of the occupying force rather than focusing on... you know... the fact that they're an occupying force known to enact violence on Palestinian martyrs.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
since we now know that all those "my blog is safe for Jewish people" posts are bullshit, here are some Jewish organizations you can donate to if you actually want to prove you support Jews. put up or shut up
FIGHTING HUNGER
Masbia - Kosher soup kitchens in New York
MAZON - Practices and promotes a multifaceted approach to hunger relief, recognizing the importance of responding to hungry peoples' immediate need for nutrition and sustenance while also working to advance long-term solutions
Tomchei Shabbos - Provides food and other supplies so that poor Jews can celebrate the Sabbath and the Jewish holidays
FINANCIAL AID
Ahavas Yisrael - Providing aid for low-income Jews in Baltimore
Hebrew Free Loan Society - Provides interest-free loans to low-income Jews in New York and more
GLOBAL AID
American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee - Offers aid to Jewish populations in Central and Eastern Europe as well as in the Middle East through a network of social and community assistance programs. In addition, the JDC contributes millions of dollars in disaster relief and development assistance to non-Jewish communities
American Jewish World Service - Fighting poverty and advancing human rights around the world
Hebrew Immigrant Aid Society - Providing aid to immigrants and refugees around the world
Jewish World Watch - Dedicated to fighting genocides around the world
MEDICAL AID
Sharsheret - Support for cancer patients, especially breast cancer
SOCIAL SERVICES
The Aleph Institute - Provides support and supplies for Jews in prison and their families, and helps Jewish convicts reintegrate into society
Bet Tzedek - Free legal services in LA
Bikur Cholim - Providing support including kosher food for Jews who have been hospitalized in the US, Australia, Canada, Brazil, and Israel
Blue Card Fund - Critical aid for holocaust survivors
Chai Lifeline - An org that's very close to my heart. They help families with members with disabilities in Baltimore
Chana - Support network for Jews in Baltimore facing domestic violence, sexual abuse, and elder abuse
Community Alliance for Jewish-Affiliated Cemetaries - Care of abandoned and at-risk Jewish cemetaries
Crown Heights Central Jewish Community Council - Provides services to community residents including assistance to the elderly, housing, employment and job training, youth services, and a food bank
Hands On Tzedakah - Supports essential safety-net programs addressing hunger, poverty, health care and disaster relief, as well as scholarship support to students in need
Hebrew Free Burial Association
Jewish Board of Family and Children's Services - Programs include early childhood and learning, children and adolescent services, mental health outpatient clinics for teenagers, people living with developmental disabilities, adults living with mental illness, domestic violence and preventive services, housing, Jewish community services, counseling, volunteering, and professional and leadership development
Jewish Caring Network - Providing aid for families facing serious illnesses
Jewish Family Service - Food security, housing stability, mental health counseling, aging care, employment support, refugee resettlement, chaplaincy, and disability services
Jewish Relief Agency - Serving low-income families in Philadelphia
Jewish Social Services Agency - Supporting people’s mental health, helping people with disabilities find meaningful jobs, caring for older adults so they can safely age at home, and offering dignity and comfort to hospice patients
Jewish Women's Foundation Metropolitan Chicago - Aiding Jewish women in Chicago
Metropolitan Council on Jewish Poverty - Crisis intervention and family violence services, housing development funds, food programs, career services, and home services
Misaskim - Jewish death and burial services
Our Place - Mentoring troubled Jewish adolescents and to bring awareness of substance abuse to teens and children
Tiferes Golda - Special education for Jewish girls in Baltimore
Yachad - Support for Jews with disabilities
#atlas entry#please add any more you know of an especially add fundraisers for you or people you know#if there are any fundraisers for synagogues please add those as well#jew#jewish#judaism#jumblr#punch nazis
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
What then is the explanation? Why do workers typically push for more consumption rather than for shorter hours? Here I think Cohen’s argument is untypically unclear. He tells us that workers do indeed want more goods (other things being equal) but it is also plain that they dislike the toil then need to engage in to get those goods and evidences that claim by making the point that if workers were granted money such that they didn’t need to work at their jobs, very few of them would choose to do so gratis, and there would be a dramatic decline in the amount of work done. His suggestion seems to be that since there is a permanent propaganda campaign in support of people getting more stuff and no corresponding campaign in favour of free time of the kind one can enjoy without extra spending, extra consumption always has a salience for people that additional leisure lacks.
I think Cohen’s uncharacteristically feeble discussion of this point can be explained in part by a blindspot in his thinking. First of all, he neglects the way in which states support and encourage consumer spending and simultaneously encourage a culture of work and effort through moralizing campaigns, stigmatization of “shirkers” and the like. Take the first of these elements: states help establish and support structures of lending to help people to do things like buy their own homes and then furnish their homes. They do this in a variety of ways, by providing support to banks and other financial institutions but also by giving borrowers all kinds of tax breaks. In order to buy the things they want, consumers have little choice but to borrow, but once they have borrowed they have to repay and repaying requires income, which requires work. Now perhaps workers could simply refuse the blandishments of capital and refuse to borrow in order to consume and then the option to work less would be more available to them. But I think this neglects the competitive and social aspects of consumption that Cohen rather dismissively refers to as “keeping up with the Joneses”. One need not be of a particularly competitive or comparative disposition to be caught up in social standards of self-presentation that are inherently comparative in nature, as Adam Smith knew in that famous passage about labourers being ashamed to appear in public without a linen shirt or, in some countries, leather shoes.
Still feels like everyone's discourse on consumerism & capitalism is stuck in the 1960s, he criticizes Cohen's view and maybe I'm out of touch but this doesn't feel much better. Maybe because the only people who write on consumerism are petite-bourgeoisie who unlike most people do live like this.
Speaking as a member of the salaried class, while I do appreciate the gee-gaws I am able to purchase with my full-time job, speaking as I believe a somewhat representative member of the professional-managerial class I am more concerned with rent, health insurance, and the ability to hopefully retire at some point, and these guide my financial decisions. I purchase some fun stuff I didn't choose my career to be able to afford a fancier grill. I crave the respectability of not living in a van.
Now there Is perhaps a discussion of how I could move to somewhere cheaper like Montana or Spain and why I don't do that but if you're going to discuss this issue I think you gotta address issues like that directly
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
Confirmation Signs To Determine Your Future Spouse




ꕀ ׅ࣪ ꒰ ✮ ꒱ links : navigation. send love.
pacs. paid services.

one
wishing well, a fountain, throwing coin and wishing in fountain, unexpected meeting, receiving the most special gift from someone, a lost purse/wallet, climbing alone in mountain to reduce stress/ hangout, being alone without feeling lonely, a dog coming towards you, small home in forest, cross roads, being happy in other people relationship, going to building/institutions to fix legal documents, a friends to lovers trope, visioning your past life, a gallantry from someone, aiming financial achievement, lucky money wins, a nest eggs, flames, mutual feelings with someone, being flirt, co-worker, a new friend, ships, a little home/cottage, new house/places, moving to a new place, soulmate connection, meeting perfect person/ ideal lover, seeing lots of abiding love, wedding, wedding rings, hurt/painful feeling, hospital/doctor, unrequited love
⋆ feel free to ask question you didn't understand in this reading
‹𝟹 leave like or re-blog when you love it !
two
changing location whether it is for work or residency, when you heal from the past, starting a new, stork, a invitation for a event, gifts ( receive or give ), helpful advice from someone, receiving lots of good news, a clock/time, your hate and fear towards someone, a handshake, a journey ( travel ), birds, sharing ( partnership), food, restaurant/ fast-food places, notice of correspondence from important bills, writer/ journalist, financial loans/help, being at your lowest point such as feeling trapped/tired/staying at home/unhealthy situation, a friend betrayal, older than you, foreign, lawyer/authority, being attack, an enemy, invitation in weddings or engagements, church, cemetery, thinking negative/ having negative thoughts, a large body of water such as beaches, pools, fountains etc, night, cold weather/winter, locks, fishes, physical union with someone, a mending of broken friendship/ex love, party, clubs
⋆ feel free to ask questions you didn't understand in this reading
‹𝟹 leave like or re-blog when you love it !
three
younger, foreign / leader, bad girl & boy image/personality, unexpected kiss, feeling lonely, a new lover/person, family oriented, lady and moody, soulmates connection, unexpected friendship with someone, horse/sagittarius, a good news coming, an artist/poet, student of arts, athletic body or an athlete, lack of focus in commitment, receive or give gifts, fountains, generous, wears uniform that symbolize their position at work, a friend, co-worker, a peer, taking time to heal the wounds of the past, in park, in forest, walking around and meeting someone new, having time alone, wandering in woods, in the big trees, travel, achievement, lucky breaks, successful moving up ( at work or something), the space, distance, someone is far away, delay, receiving love letters and bouquet of flowers, country side, simple life, money surrounds them, professional person, workaholic and less focus on love, a bank; good at handling finances, provides good advice in finance, a happy family, fire/burning, summer, evening, warm weather country, good judgement, social
⋆ feel free to ask questions you didn't understand in this reading
‹𝟹 leave like 🙵 re-blog when you love it !
four
authority, can be foreign, arrogant, weddings, older, negative emotions, large body of water such as beaches, pool, fountains, lake, pond etc, night, cold weather/winter, a dog, a friend, a church, a purse, money, financially stable/ wealthy, office, jewelry box, a social butterfly, enjoy clubs and socializing, likes to be busy and active, wine, travel, trips via water, clouds, heavy rains, good partner, sensual, good at financial advice, an expensive wedding of a friend, children, financially secure, fixing cars, lily, workaholic, trying their best at difficult situation, lion, a Leo sign, quite, electric, jealous and possessive, like to give great advice, streets of gold
⋆ feel free to ask questions you didn't understand in this reading
‹𝟹 leave like 🙵 re-blog when you love it !
© thedivineart. do not plagiarize any of my work, translate or repost it on other social media platform.
#pick a card#divination#tarot community#tarot#oracle reading#spirituality#witchblr#witches of tumblr#witch#witch community#tarot witch#beginner witch#tarotblr#pick a pile#pick a picture#pick a photo#pick a deck#pick an image#future spouse reading#future spouse#love reading#psychic readings#psychic reading#intuition#intuitive tarot reading#intuitive#future lovers#cartomancy#oracle card readings#oracle
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
ok ok slightly feral post as promised.
first, some context setting: I think it's really interesting to analyse texts in terms of both what the author was trying to do (and whether they succeeded) and what they ended up doing (intentionally or not) and I think their cultural/historical context is vital if you want to do this. I'm not interested in whether Robert Jordan or the Wheel of Time are, like, morally correct in their politics or whatever. I'm interested in what the art is trying to do.
and the thing about Jordan, see, is that he projected this image during his lifetime of a Genial Older Man (see: beard and pipe) but he...wasn't actually that old! He was 42 when EoTW was published. He died at 58. He was a Baby Boomer publishing books at a time when Baby Boomers were the hip young generation taking over from stodgy WWII veterans (Gen Z: It Will Happen To You Too).
What this means is that he was a child and adolescent during the Civil Rights movement, in a then-majority Black city in the Jim Crow South*. He would have gone to segregated schools. The tertiary institutions he attended had only started to desegregate a year or two before he attended each of them. I think his war trauma in Vietnam gets a lot of attention because he did talk about it and also because that's a narrative we understand for white men, but I think we...skim over the impact on white men of growing up at this time because? Civil Rights only happened to Black Americans I guess? but it's his context too. Similarly, he was an adolescent and young man at the time the (white) feminist movement was really kicking off in the US. he was in his mid-20s when banks were first legally *required* to allow women to open accounts and have credit cards in their own names. he went on to marry a woman a decade older than him, who had left her husband to raise her son as a single mother while continuing a professional career in the early 70s; these were issues that must have been incredibly relevant for her.
and what we see in his writing is attempts to grapple with gender and race that are self-evidently of mixed success, but I think have to be contextualised in light of this period of immense change he grew up in. Think about the predominance of women as merchants and bankers in WoT, in the context of how recent their rights to even control their own money were in the US. The...everything...he was trying to do with the Seanchan, making them extra-canonically Southern American-coded. The Whitecloaks as the KKK (among other things, of course).
As an example, I think there's also something probably unintentional but fascinating in the way he presents the pre-Breaking Aiel: bluntly, they are a distinct ethnic group in hereditary servitude (always thinking about how that ancestor of Rand's in the Rhuidean sequence had to get permission from Mierin Sedai to switch to someone else's service so he could marry his girlfriend, this is...uh...super cognate to issues enslaved Black people faced). They're associated with agriculture through the Song sequence. And they're pretty much the ideal of what slave-owning Southern American culture WANTED enslaved Black people to be: completely happy to serve. Then, as the post-breaking Aiel, they become feared as a source of violence, which resonates with the way that enslaved people were feared by their slavers.
I don't think for a second that the intention here was to depict the AoL as a Secret Slavery Dystopia, I think we're meant to take the Rhuidean flashback sections pretty much as they read on the page. But I also think putting Jordan in his historical and cultural context does pose the comparison. Similarly, I find it really interesting that he positions Seanchan as riven by constant revolts and uprisings (because it's a fascist slaver regime) but he never ever goes so far as to link enslaved people in Seanchan (damane and da'covale) to those revolts and uprisings, even though that is fundamentally the deep fear *for real and obvious reasons* of all slavery-based societies.
Or then there's the changes to the Two Rivers in the books - like, both then and now I think it's actually pretty radical to present an influx of Muslim-coded refugees of colour as a thing that enriches the Two Rivers both socially and economically. Various characters are wistful that it's changed, but they don't think it's bad. The text here is really clear that welcoming the Domani and Almoth Plain refugees is both morally right and beneficial. And this is in a book being written and published shortly after the first Gulf War.
There's so many more things like this where I just have no real idea what he was trying to do on purpose and what was accidental and what was fun for him in fiction but did not necessarily link at all to his real-world political beliefs. but gosh it's interesting to turn over and poke at.
#wheel of time#wot book spoilers#robert jordan#and then there's things like...IIRC some stuff about Gareth Bryne is referencing General Lee#and I know a lot of you are Bryne haters but the point here is not#that that means Bryne is bad#it's: how hard was RJ thinking about that and why did he do it at all?
282 notes
·
View notes
Text
When parties fail, movements step up

This Saturday (19 Aug), I'm appearing at the San Diego Union-Tribune Festival of Books. I'm on a 2:30PM panel called "Return From Retirement," followed by a signing:
https://www.sandiegouniontribune.com/festivalofbooks

Does anyone like the American two party system? The parties are opaque, private organizations, weak institutions that are prone to capture and corruption, and gerrymandering's "safe seats" means that the real election often takes place in the party's smoke-filled rooms, when a sure-thing candidate is selected:
https://doctorow.medium.com/weak-institutions-a26a20927b27
But there doesn't seem to be any way to fix it. For one thing, the two parties are in charge of any reform, and they're in no hurry to put themselves out of business. It's effectively impossible for a third party to gain any serious power in the USA, and that's by design. After the leftist Populists party came within a spitting distance of power in the 1890s, the Dems and Repubs got together and cooked the system, banning fusion voting and erecting other structural barriers.
The Nader and Perot campaigns were doomed from the outset, in other words. Either candidate could have been far more popular than the D and R on the ballot, and they still would have lost. It's how the deck is stacked, and to unstack it, reformers would need to take charge of at least one – and probably both – of the parties.
But that's not cause for surrender – it's a call to action. In an interview with Seymour Hersh, Thomas Frank (Listen, Liberal) sets out another locus of power, one with the potential to deliver control over the party to its base: social movements:
https://seymourhersh.substack.com/p/ordinary-people-by-the-millions
It's been done before. The parties are routinely transformed by power-shifts within their internal coalitions: since 1970, corporate Dems have consistently pushed the party to the right, making it the power of white-collar professionals and relying on working people showing up and marking their ballots with a D because they have "nowhere else to go."
Bill Clinton was the most successful of these corporate raiders, delivering the parts of the Reagan Revolution that Reagan himself could never have managed: dismantling tariffs and bank regulations, passing the crime bill and welfare "reform." He came within a whisper of (partially) privatizing Social Security.
This set in motion the forces that made Trumpism possible: when Dems told deindustrialized workers to "learn to code" and blamed them for the destruction of their communities, it opened a space for Make America Great Again, the (empty) workerist rhetoric of the GOP. The Dems' plan of putting "really smart people" in charge and letting them run things was a (predictable) disaster. "Really smart" isn't the same as "infallible" and really smart people can be spooked or bulled into doing the wrong thing – like Obama "foaming the runways" for the banks with the houses of mortgage holders, and leaving the bankers responsible for the Great Financial Crisis unscathed:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/15/mon-dieu-les-guillotines/#ceci-nes-pas-une-bailout
"Really smart people" can't get us out of this mess. Instead, we need the kind of muscular political action – the "whirlwind" – that characterized FDR's New Deal: "complete reformation of the banking industry.. just about every other industry as well. Regulation. Social Security. Public works. Antitrust. Soil conservation."
FDR got there by alienating his former classmates and refusing the go-slow entreaties of his cronies. He got there because there was a mass social movement that made him do it ("I want to do it, now make me do it"):
https://humanizingthevacuum.wordpress.com/2014/09/16/i-agree-with-you-i-want-to-do-it-now-make-me-do-it/
Every time in US history where one of the political party duopoly listened to its base, it was because of a mass social movement: the farmers' movement (1890s), labor (1930s), civil rights and antiwar (1960s). As Frank says:
Social movements succeed. They build and they change the intellectual climate and then, when the crisis comes, they make possible things like agrarian reform or the New Deal or the Civil Rights acts of the 1960s.
Today, we see the seeds of those social movements: the new union movement. Black Lives Matter. Neobrandeisians with their "hipster antitrust." These are the movements that are creating "ideas lying around": ideas that, in time of crisis, can move from the fringe to the center in an eyeblink:
https://doctorow.medium.com/ideas-lying-around-33a28901a7ae
They are setting in motion another transformation of the Democratic Party, from its top-down, "really smart people" model to a bottom-up, people-powered one, kept in check by movements, not party bosses. As Frank says, "They require the mass participation of ordinary people. Without that, I am afraid that nothing is possible."


I'm kickstarting the audiobook for "The Internet Con: How To Seize the Means of Computation," a Big Tech disassembly manual to disenshittify the web and make a new, good internet to succeed the old, good internet. It's a DRM-free book, which means Audible won't carry it, so this crowdfunder is essential. Back now to get the audio, Verso hardcover and ebook:
http://seizethemeansofcomputation.org

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/17/popular-front-of-judea/#speaking-frankly
#pluralistic#sy hersh#theories of change#third parties#us politics#thomas frank#unions#labor#organized labor#civil rights movement#black lives matter#dinos#entryism#occupy democrats
272 notes
·
View notes
Text
"It seems to me that we now have critical tools to track and condemn the destabilization of the juridico-political category of the civilian, a destabilization that has enabled the killing of innocent, blameless subjects, whether in Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria, or Yemen, to mention only a few recent examples. But perhaps we need to think more about the making of the figure of the civilian and the notion of civilian normalcy, the territorial and discursive conditions that go into cultivating civilian lives, and their unequal distribution. I propose that the settler-colonial conquest and territorialization of the land are not merely the context of the current events but forces that produce and stabilize specific categories, including that of the civilian. There is power involved in the making and unmaking of the civilian, not only in her being the target of violence. In Palestine, this power is an exercise of settler-colonial territorialization as it has been intertwined with the ongoing removal, killing, and enclosure of Palestinians.
Once the Zionist state was able to mark its borders, to fortify them with settlements and armed settlers, once it was able to territorialize itself by depopulating Palestinian villages and cities, destroying them, preventing the return of Palestinian refugees, and conscripting Jews from all the over world to populate the new settlements, once it did everything that was becoming illegitimate elsewhere in the decolonizing world, then it could begin to both materialize the figure of the civilian and the notion of civilized normalcy and weaponize them as conditions on the ground to be defended. In the civilian’s name and for its protection, atrocities could be carried out.
Key to this notion of civilian normalcy is its institutional-territorial condition of possibility: a strong state form with continuous territory and fortified borders. Israel has it. It acquired this state form by force from the Palestinians. This state form has institutions: a professional standing military, a police force, an interior ministry, a registry of citizens, and a defense ministry. These are but select institutions that produce and reproduce the distinction between civilian and combatant, even as national military service is mandatory for all Jewish, Israeli citizens, with only some exceptions. The condition of possibility for these institutions is the exclusion of the Palestinians — in terms of entry to the country, residency rights, family unification, access to land, and so on — their suppression, removal, policing, and enclosure. These institutions have fostered an Israeli civil society, civil posture, civil plurality—and civilian normalcy. The settler, the precise figure through which proceeded both the territorialization of the Zionist state of Israel and the dispossession and removal of Palestinians, has also morphed into a civilian.
The occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip in 1967 was central to the making of Israeli civilian normalcy. The “occupied territories” have always been the terrain for unleashing Israeli military power, thereby preventing the violence of the occupation from intruding into normalized Israeli civilian life. There, behind the green line, Israel has conducted the “conflict.” The more settler-military violence there is in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, the more civilian normalcy there is in Israel, and the more the notion of civilian normalcy can be weaponized to justify more violence in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. But the purifying and normalizing operations of the green line did not always go unchallenged. Palestinians have always understood that the condition of possibility for this civilian normalcy, inside the green line, was the destruction of Palestinian existence on the land and the ban on their return to the land. Hence, there have always been breaches of the enclosure and operations to undo the frontier: what Palestinians call “return.”
Meanwhile, a Palestinian claim for civilian status or civilian normalcy has met many challenges. Palestinian society was destroyed in 1948. The territories occupied in 1967 have been purposefully fragmented, disconnected, and separated by settlements. There is no state form, standing military, depth of territory, or civilian posture. Instead, there are many refugee camps, dispossessed families, and subjects-in-struggle. Everything that could cultivate civilian normalcy is already targeted by the Israeli Occupation, from homes and schools to NGOs, cultural centers, and universities. When compared to the other side of the green line, life in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, the containers of Israel’s violence against Palestinians, cannot manifest civilian normalcy.
But there is more. The civilian ethos, as a matter of liberal sensibility, requires innocence, political passivity, lack of movement, and fixity. In the eyes of the liberal, civilized West, the civilian must be pacified, passive, and blameless and must reject rebellion. The Palestinians, as refugees, as politically engaged resistant subjects, as subjects who look in the direction of the land from which they were expelled and aspire to move in its direction, and as persons who wish not to settle in an enclosure, do not pass the test of this ethos. Their just refusal of confinement, steadfast rejection of enclosure, and non-despairing hope to return to the land from which they were expelled violates this liberal ethos. Their dreams and aspirations render them, in the eyes of those who value civilian normalcy despite its heavy toll on others, obliterable. Therefore, no emotion can be allowed to arise in the face of their extermination. Quite to the contrary. In the name of civilian normalcy, the a-civilian must be obliterated."
#samera esmeir#palestine#if you read only one political essay on the current palestinian situation make it this one
135 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cosplay the Classics: Nazimova in Salomé (1922)—Part 2
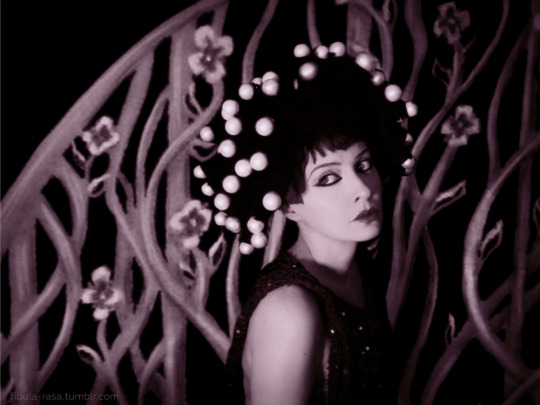

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
As the studio system emerged in the American film industry at the start of the 1920s, many of the biggest stars in Hollywood chose independence. Alla Nazimova, an import from the stage, was one of them. In 1922, she made a series of professional and creative decisions that would completely change the trajectory of her career.
In part one of CtC: Nazimova in Salomé, I described how Nazimova’s independent productions were shaped in response to trends and ideas surrounding young/independent womanhood in America after World War I and the influenza pandemic. Here in part two, I’ll fit these productions, A Doll’s House and Salomé, into the broader context of the big-money business of film becoming legitimate in America.
While the full essay and photo set are available below the jump, you may find it easier to read (formatting-wise) on the wordpress site. Either way, I hope you enjoy the read! Oh and Happy Bi Visibility Day to all those who celebrate!
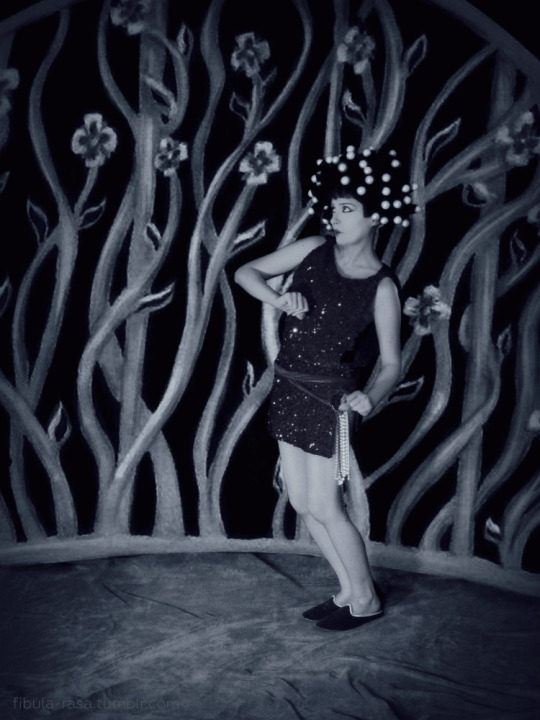

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
Artists United? Allied Artists and the Release of Salomé
When Nazimova made her screen debut in War Brides (1916), the American film industry was undergoing a series of formative changes. Southern California became the center of professional filmmaking in the US—fleeing New Jersey (where War Brides was filmed) largely because of Thomas Edison’s attempts to monopolize the business. Preferences of audiences and exhibitors shifted away from one and two-reel films and towards feature-length films. The Star System emerged in full force. Nazimova soon relocated to Hollywood, signed a contract with Metro, and reaped the benefits of this boom period for American film artists.
The focus on feature-film production and the marketing of films based on the reputations of specific filmmakers or stars required a greater initial outlay of resources—time, money, and labor. But, it also paid dividends—the industry quickly grew into a big-money business. The underlying implication of that is that a larger share of the profits were shifted from the people doing the creating (artists and technicians) and towards other figures (capitalists). In practice, this also meant film companies would become eligible for listing on the stock exchange and could secure funding from banks and financial institutions, both of which were rare or impossible before the mid-1920s. The major players on the business end of production, distribution, and exhibition, therefore, wanted to consolidate their power and reduce the power and influence of the filmmakers.
To illustrate how momentous this handful of years was in the history of the US film industry, allow me to highlight a few key events. Will Hayes’ office was set up in 1922 to make official Hollywood’s commitment to self-censorship. Eastman Kodak introduced 16 mm film in 1923, a move which, while making filmmaking more accessible and affordable, also widened and formalized the division between the professional industry and amateur filmmaking. Dudley Murphy’s “visual symphony” Danse Macabre[1] was released in 1922—considered America’s first avant-garde film. Nazimova’s Salomé was considered America’s first art film from its initial release in 1923. That these labels were deemed relevant in this period illustrates the line being drawn between those films and film as a conventional, commercial product. The concept of art cinemas in the US was first proposed in 1922 spurring on the Little Cinema movement later in the decade.

from Danse Macabre

from Salomé
As any industry matures, both the roles within it and its output become more starkly delineated. That is to say that, as the US industry began differentiating between art/avant-garde/experimental film and commercial film, the jobs within professional filmmaking also became more firmly defined. Filmmaking has always been a collaborative art, but in the period prior to the 1920s, it was common for people in film to do a little of everything. As a result, what sparse credits made it onto the final film didn’t necessarily reflect all of the work that was done. To illustrate this using Nazimova,[2] at Metro, she had her own production unit under the Metro umbrella. While her films were “Nazimova Productions,” she didn’t have full creative control of her films. However, Nazimova did choose her own projects, develop said projects, and contribute to their writing, directing, and editing. When those films were released, aside from the “Nazimova Productions” banner, her only credit would usually be for her acting. Despite that impressive level of creative power, the studio still had the ultimate say on whether a film got made, and how it would be released. As studios grew and tightened control of their productions, this looser filmmaking style became much less common.
The structure of the industry at this time was roughly tripartite—production, distribution, and exhibition. Generally speaking, the way studio-made films traveled from studio to theatre—before full vertical integration—was that the production company would make available a slate of films of different scales. (Bigger productions with bigger names attached would have a special designation and come with higher rental fees.) Famous Players-Lasky was the biggest production house at the time, though other studios, like Metro, were quickly catching up. Distribution companies would then place this slate of films on regional exchanges, centered in the biggest cities in a given region. Exhibitors (this could be owners of chains like Loew’s in the Midwest and Northeast, the Saengers around the gulf coast, or individual theatre owners) could then rent films through their local exchanges. (This was an ever-shifting industry, so this process was not true for every single film. This is only meant as a quick overview of the system.) As the 1920s wore on, exhibitors began entering the production arena and producers further merged with distribution companies and exhibition chains. Merger-mania was the rule of the day.
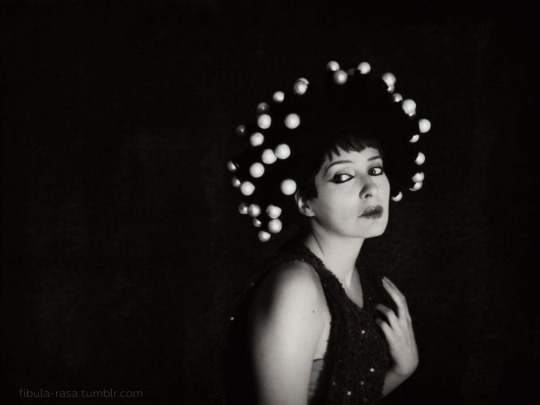

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
As merger upon merger took place and a handful of businessmen tried to monopolize the industry, American filmmakers responded by championing the artistic legitimacy of filmmaking in the US. Leading this charge were the very filmmakers on whose backs the big business of film had been built. As noted in Tino T. Balio’s expansive history of United Artists, The Company Built by the Stars:
…Richard A. Rowland, president of Metro Pictures, proclaimed that ‘motion pictures must cease to be a game and become a business.’ What he wanted was to supplant the star system, which forced companies to compete for big names and pay out-of-this-world salaries for their services. Metro, he said, would thenceforth decline from ‘competitive bidding for billion-dollar stars’ and devote its energies to making big pictures based on ‘play value and excellence of production.’”
It’s notable for us that these ideas were espoused by Rowland, head of the studio where Nazimova was currently one of those “billion-dollar stars.” (“Billion-dollar” is obviously a massive overstatement.) It was a precarious time for any filmmaker who cared about the quality and artistry of their work. It was this environment that birthed United Artists, a new production company built around the prestige and reputation of its filmmakers, Douglas Fairbanks, Mary Pickford, Charlie Chaplin, and D.W. Griffith. As the statement announcing the formation of UA detailed:
“We also think that this step is positively and absolutely necessary to protect the great motion picture public from threatening combinations and trusts that would force upon them mediocre productions and machine-made entertainment.”
It’s an accurate assessment of industry trends at the time. If the desired product is a high-quality feature-length film, production is necessarily more expensive. As the UA statement intimates, monopolizing the entire industry and sacrificing quality for quantity to fill the exchanges and theatrical bills was the studio heads’ solution to rising costs. Not a great signal for filmmaking as art in America.
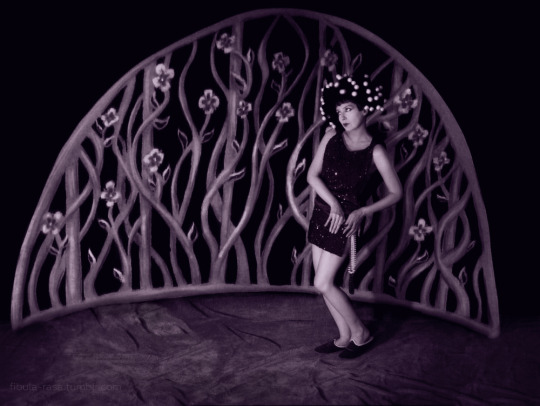

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
So, Nazimova was in good company when she chose to go independent, believing in film as art and that American moviegoers deserved better than derivative, studio-conceived films. Some of the other artists who went independent included George Fitzmaurice (one of the most revered directors of the silent era, though most of his films are now sadly lost), Charles Ray, Max Linder, Norma Talmadge (in alliance with Sam Goldwyn), and Ferdinand Pinney Earle (whose massive mostly-lost artistic experiment Omar Khayyam, I profiled in LBnF). If these filmmakers shared the motivation of UA to create higher-calibre productions, where would the money come from? For Nazimova, the answer was her own bank account.
In 1922, Nazimova’s final film for Metro, Camille (1921), was still circulating widely due to the rising popularity of her co-star, Rudolph Valentino, after the release of Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse (1921) and The Sheik (1921). While Nazimova had the funds to complete A Doll’s House and Salomé, there was no sure bet for the films’ releases. Nazimova’s initial concept for her independent productions was the “repertoire” film. This scheme would have seen A Doll’s House released as a shorter film with Salomé as a feature and the two could be rented as a package by exhibitors. It was a creative response to growing tensions between producers and exhibitors over a practice called block booking. Block booking was a strategy studios employed to leverage the Star System to its fullest. They would take the most in-demand films associated with the biggest drawing stars and only make them available in a package deal with productions that were perceived as less marketable. Nazimova was aware that her films at Metro had been rented this way (as the special feature). It’s not completely clear from my research if the decision to release Salomé and A Doll’s House as two features was creative, practical, or a combination of the two. The “repertoire” concept may not have gone according to plan, but it was an early indication that Nazimova was well-informed of the nuances of distribution and exhibition.
Nazimova’s need for proper distribution was met by United Artists’ distribution subsidiary, Allied Artists. United Artists’ first few years were a struggle. Fairbanks, Pickford, and Griffith[3] needed significant time and money to finish the high-quality productions that they promised and Allied was their solution. This distribution arm would release the work of other independent talent using the same exchanges as UA, but under a different banner. Though Allied used UA’s exchanges for distribution, the subsidiary had its own staff. Allied having different branding would also protect the prestige of the UA name. (An unkind, but not entirely inaccurate summary: the money your work brings in is good enough for us, but your work is not.) Allied would have a full release slate to generate the revenue that UA needed to remain in operation.
Nazimova was one of the filmmakers who signed a distribution deal with Allied and had reason to regret it—though she and Charles Bryant didn’t openly rag on UA/Allied.[4] Notably, Mack Sennett had arranged the release of Suzanna (1923) through Allied and was vocal about the company bungling its release. Differences over distribution and exhibition would also lead to Griffith’s exit from the company and a major rift between Chaplin and Pickford-Fairbanks. After 1923, Allied reduced its operation, at least in part because of the bad reputation they were garnering with other filmmakers. Despite numerous independents losing money on productions released through Allied, by 1923, Allied had netted UA 51 million dollars in revenue!

Trade ad for Salomé from Motion Picture News, 10 March 1923
The questionable deals that these independent filmmakers received with Allied are often mentioned in discourse about the period, but very, very rarely does anyone offer details of what Allied’s inadequate distribution looked like. Using the information available to me via Lantern, I collected and analyzed data regarding the release and exhibition of Nazimova’s final two Metro films and both of her Allied films.[5] Looking at the trade publications Exhibitor’s Trade Review, Moving Picture World, Motion Picture News, and Exhibitors Herald, I categorized every item I found about the release or exhibition of Billions (1920),[6] Camille, A Doll’s House, and Salomé. The “release” items are primarily advertisements, reviews, and news items about release dates or pre-release screenings. The number of these items for all four films were comparable.
The items in the “exhibition” category, however, reveal a marked difference between the Metro and Allied releases. This category includes items like first-run theatre listings, exhibitor feedback, and advertising advice for theatre owners. Only counting exhibition items from the first two years (24 months) from the initial release of each film, Billions and Camille had twice as many items as A Doll’s House and Salomé!
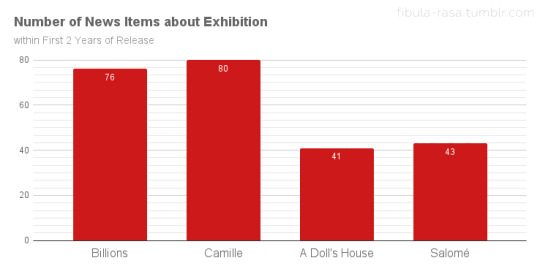
While this isn’t necessarily hard data on how many theatres ran each film, it is a rough indicator of how well the films circulated. This data suggests that neither A Doll’s House or Salomé had distribution comparable to the Metro films. In order to compensate for the Rudy factor—Valentino’s major rise to stardom in 1921—which could have affected Camille’s numbers in a big way, I included Billions as well. Billions was sold as a special (a bigger production with premium rental fees) on Nazimova’s name alone. It was not especially well received. Exhibitors/theatre owners had mixed feelings on the film because Nazimova’s previous film, Madame Peacock (1920), had underperformed. Many exhibitors viewed Billions as an improvement, though it still did not meet their perception of Nazimova’s standard of quality. Despite that, Billions had 76 exhibition-related items across its first 24 months of availability to Camille’s 80.
To get a little deeper into this data, I wanted to see how the feedback from exhibitors and theatre owners compared. I broke down the exhibitor feedback for each film as positive, middling, or negative based on how the exhibitors assessed audience response and/or box office receipts. (I discounted feedback that only reflected theatre owners’ own personal assessment of the films without mention of their patrons or receipts.) Positive feedback could be good reception and/or good receipts, middling suggests only average business and no noteworthy reception, and negative indicates poor response and/or poor ticket sales. Since there are so many more items about Camille and Billions than A Doll’s House and Salomé, I compared ratios as an indicator of exhibitor satisfaction. The results were truly surprising.
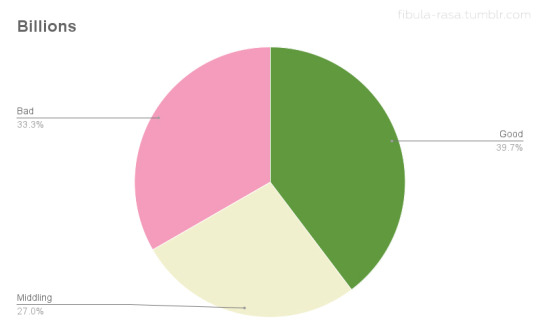
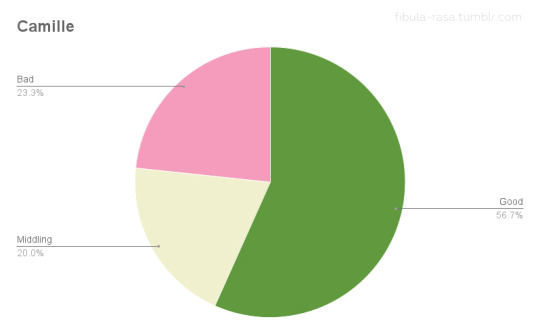
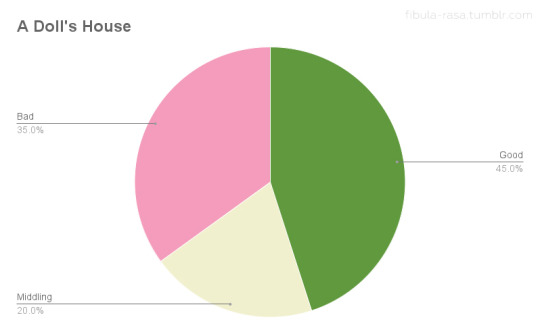
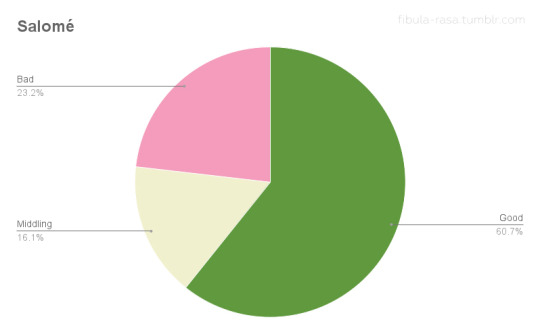
Theatre owners who rented Salomé may have been in significantly smaller numbers than those who ran Camille, but their satisfaction with ticket sales and audience feedback was roughly equivalent. (Though slightly more positive for Salomé!) The numbers for Billions line up with the qualitative assessment I summarized above, displaying a roughly equal 3-way split. A Doll’s House was the most divisive with the highest proportion of negative feedback of the four films, yet with a higher proportion of positive feedback than Billions.
Taking all of this into account, it’s clear that Salomé did not flop because it was too artsy or esoteric for the American moviegoing public. Such assumptions are obviously not very thoughtful or informed by reliable data.[7] A more historically sound reading is that, as professional filmmaking matured into a “legitimate” industry in the US, the various arms of the business were rigidly formed to fit conventional output. The conservatism that this engendered made the American industry ill-equipped at marketing anything too unconventional or experimental. While Hollywood insiders were lamenting European filmmakers artistically outdoing Americans—especially following the US release of The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari (1920)—very few people with the power to shape the industry did anything to support experimentation. Given this environment, Salomé could only have been produced independently, but the quickly ossifying distribution and promotional systems didn’t have the range to give it a proper release. Two films contemporary to Salomé, Beggar on Horseback (1925) and The Old Swimmin’ Hole (1921) offer further evidence of the industry’s limitations.
The Old Swimmin’ Hole is a feature-length production by Charles Ray, experimental in that it uses no intertitles. The story is simple and familiar with Ray playing the Huck-Finn-type character he was well known for. Ray’s experiment was not an expensive one and the film was successful. However, decision makers at First National, the film’s distributors, felt that The Old Swimmin’ Hole was simply too complex for small-town Americans to comprehend and it wasn’t released outside of cities. To put it plainly, the distributor’s unfounded concept of ignorant yokels meant that a film about country living was largely inaccessible to anyone actually living in the country. Though the film was well received and turned a profit, this distribution decision likely limited its audience as well as possible revenue from small-town exhibition.

Stills from The Old Swimmin’ Hole from Motion Picture Magazine, April 1921
Beggar on Horseback was produced by one of the biggest studios in Hollywood, Famous Players-Lasky, and distributed by Paramount. Starring comedian Edward Everett Horton, Beggar was an expressionist comedy based on a popular play. The film had a popular star, popular source material, and was made and released by a major company, but Beggar was apparently too unconventional for that major company to adequately market it. (Unfortunately, only a few minutes of the film survive, so we can’t fully reassess it unless more is found/identified!)

Stills from Beggar on Horseback from Picture-Play Magazine, August 1925
With all these complicating factors at play, how might have Salomé found its audience in 1922-3? Nazimova and Charles Bryant had innovative ideas for the film’s release that might have done the trick, if they had been able to act on them. Nazimova and Sam Zimbalist had finished cutting Salomé in late-spring 1922. Having spent practically all of her money to finish the film, and following A Doll’s House’s disappointing results, Nazimova was eager for Salomé to hit theatres. Though the film was in the can and private preview screenings had been held by Bryant by summer ‘22, Salomé wouldn’t be released until February of 1923. In studio filmmaking, holding a film in extended abeyance wasn’t ideal but it was not disastrous. Studios had significantly more resources and revenue streams than independent producers. If, for example, the release of Billions had been delayed for seven months, Nazimova still had two films on the Metro exchanges (and therefore in theatres) and Camille would have entered production in the meantime. But for Nazimova as an independent producer, this situation was wholly untenable. (In fact, Pickford, Fairbanks, and Griffith were in a similar untenable situation when they founded Allied.)
Initially, Bryant proposed roadshowing Salomé. Roadshowing is a release strategy for notable film productions where a film is toured around major cities, often with in-person engagements by stars, writers, and/or directors. Nazimova expanded the idea of touring with Salomé not simply as a roadshow, but paired with a short play in which she would star. Double the Alla, double the fun. As far as I can tell, there isn’t publicly available information about why Salomé wasn’t roadshowed. However, we do know that Griffith, as the only non-performer in UA, wanted to utilize different approaches for the release of his films—like roadshowing—and it became one of the major points of disagreement with his fellow UA decision makers. That could be taken as an indication that something similar might have occurred with Nazimova and Allied.
As time dragged on without a release date for Salomé and Nazimova returned to theatrical work—openly admitting to audiences that she was broke—Bryant took matters into his own hands. At the end of December 1922, Bryant negotiated with the owner of the Criterion Theatre in New York City for Salomé to run on New Year’s as a special presentation. In two days, Salomé grossed $2,630, setting records for the theatre. Adjusted for inflation, that’s $48,988.96. It was successful enough that the owner of the Criterion opted to hold the film over. This bold move must have lit a fire under Allied’s tuckuses, as Salomé finally had its first-run release a little over a month later.
In the 1920s, the first-run booking of a film was a crucial part of its further success. Concurrent nationwide release of films wasn’t the norm yet, and if a film was a big production, getting booked at high-capacity motion picture houses in major cities was a necessity. These big city releases would, in theory, generate interest in the film with exhibitors across the country and internationally. Basically, if you spent a lot on a movie but couldn’t land a first-run release, you weren’t likely to turn a profit or even break even. Salomé had a handful of first-run bookings and local reviewers from those cities believed the film would succeed. A reviewer from the Boston Transcript in February 1923 wrote:
“…this newest Salome is something far better than a photographed play. Considered both as picture acting, and as an interesting experiment in design, “Salome” is a notable production. It will have a far and wide reaching influence on future films in this country.”
But, as I mentioned, only a handful of first-run theatres played Salomé, and, taken collectively, the notices I analyzed from contemporary trades imply that it didn’t gain traction once it was made available beyond its initial run.
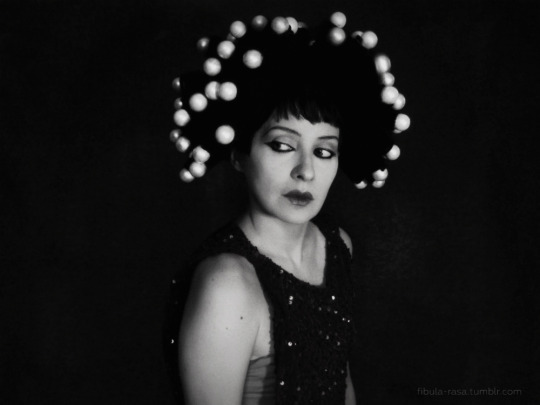

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
During this regrettably short theatrical run, exhibitors and reviewers from trade publications advised that Salomé was a unique film that called for unique promotion. The overall assumption was that theatre owners knew their patrons and recognised whether out-of-the-ordinary movies were popular with them. Rather than purely judging a film’s quality, exhibitors and trade reviewers had concerns specific to exhibition when providing feedback. These concerns cannot be overlooked if you want to understand their assessments. For example, exhibitor feedback was very often informed by how high the rental fees were for a film, even if exhibitors don’t directly mention said fees. That is to say, a mediocre film might be rated highly if the rental fees were modest (and if block booking wasn’t an issue). Reviewers in the early 1920s, both for popular magazines and trade publications, were already accustomed to the formulaic nature of most studio output. Their reviews commonly expressed fatigue with studio films’ lack of originality. And, perhaps surprisingly, this sentiment was shared among theatre owners as well—particularly when a run-of-the-mill film was sold to them as anything other than a “programmer” (a precursor to B-movies).
What I have learned, not just by analyzing feedback for Salomé, but also for all of the films in my LBnF series, is that when a 1920s reviewer calls out bizarreness in a film, it’s not always a negative quality, even when the review isn’t positive. In the case of reviews written for exhibitors/theatre owners, focussing on what makes a movie different is purely pragmatic. It guides how exhibitors might market films to patrons and helps exhibitors judge if a film would be suitable for their audiences. And, from that same research, I’ve found significant indications there were numerous markets throughout the US that were hungry for novelty—contrary to what studio apparatchiks wanted to admit. So, pointing out Salomé’s bizarreness was a recommendation for those markets to consider renting it as much as it was a warning against renting for theatre owners who only had success with more conventional films.

Cover of the Campaign Book for Salomé reproduced in Exhibitors Herald, 9 February 1924
In the case of Salomé, reviews and feedback upon its release focused on two major points:
The film isn’t “adult” in nature. Well-known productions of Strauss’ opera and the 1918 Theda Bara film of the same name led to a presumption of salaciousness. (I talked a bit about that in Part One!)
The film deserves/requires a build up as an artistic event film.
Nazimova’s company helped exhibitors with the latter point in a few ways. The company provided Aubrey Beardsley inspired art posters conceived by Natacha Rambova and executed by Eugene Gise. They printed a book to guide promotion of an artistic spectacle. (So far, I haven’t been able to find a physical or digital copy, so I can’t assess how good the advice was!) Salomé was also distributed with an official musical score, apparently written for a full orchestra.

Art Posters designed by Rambova and painted by Gise as reproduced in Exhibitor’s Trade Review, 10 February 1923
The exhibitors who ran Salomé—and put at least some of this advice into practice—were satisfied with the business it did. By these accounts, the American moviegoing public was attracted by the novelty of Salomé, but what chance were they given to see it?
While this evidence of Allied’s poor distribution work may be circumstantial, it certainly complicates the narratives that Salomé was an unqualified flop or that average Americans weren’t (or aren’t) receptive to artistic experimentation. Given that Nazimova was not the only independent filmmaker who suffered from Allied’s inept distribution, it does seem like the underwhelming business Salomé did was due more to a poor choice of business partners than to any quality of the film or of American moviegoers. That said, with the increasing monopolization of the industry, Nazimova did not have a wealth of options.
Though Salomé was made and released at an tumultuous period for the US film industry, it did eventually find its audience through circulation in art cinemas. As the gap between experimental/avant-garde film widened in the US and the professional industry became less and less tolerant of departures from convention, Americans concerned with film as an art form rallied around amateur filmmaking clubs and art cinemas began popping up in cities by the middle of the decade. Salomé played in these theatres even after the advent of sound—occasionally even today. This is likely the key reason that Salomé survives and we’ve been able to continue to enjoy and reevaluate it one hundred years later.
Salomé is a significant film made at a significant moment in American film history. Nazimova took a major risk in going independent and personally funding two artistic projects. These films were founded on the beliefs that American moviegoers wanted art made by human beings with unique imaginations, feelings, sensibilities and that there was an audience for more than derivative, “machine-made” film. In my opinion, through close analysis of the circumstances of Salomé‘s release, we can see that Nazimova was likely correct, but didn’t get a genuine chance to prove it in her lifetime. Additionally, it’s important to note that Nazimova’s risks did not “ruin” her as is occasionally said. The state of her finances were more greatly affected in the 1920s by her fake husband’s habit of spending her money and by getting swindled by a pair of con artists over her estate, The Garden of Alla. Soldiering on, Nazimova continued to work in both theatre and film for the rest of her life and found more stability with the partner she would meet at the end of the 1920s, Glesca Marshall.
——— ——— ———
Once I finished this “Cosplay the Classics” entry, I realized that it would way too much for me to include a section on another relevant topic to Salomé: Orientalism in Hollywood. But, I feel that the topic is too important to just edit that writing out. Look out for a shorter “postscript” entry soon!
——— ——— ———
☕Appreciate my work? Buy me a coffee! ☕
——— ——— ———
Footnotes:
[1] Danse Macabre is also thought to be a major influence on Walt Disney animating to music, as seen in “Silly Symphonies” and later Fantasia (1940) and Disney’s other musical anthology features. It was also in this period that Disney fled from his debtors in the Midwest to California with his first “Alice” movie. However, the wide-ranging effects of Disney’s business practices were not felt until much later, so that’s another story for another time!
[2] Nazimova was one of a handful of women in Hollywood at the time who held significant creative power. June Mathis and Natacha Rambova, both of whom Nazimova regularly worked with, Mary Pickford and her regular tag-team partner Frances Marion are among some of the others.
[3] Chaplin wouldn’t produce a film for UA until 1923’s A Woman of Paris, as he was fulfilling a pre-existing contract with another studio.
[4] According to Gavin Lambert’s biography of Nazimova (which I discussed as a largely unreliable source in Part One), Robert Florey supposedly advised Nazimova against signing with them, citing Max Linder and Charles Ray as artists who had been “ruined” by their deals. However, the timeline does not quite match up. Though Florey did visit the set of Salomé, Nazimova had already signed the Allied deal by then and Ray had not finished The Courtship of Miles Standish (1923) when Salomé was in production. In fact, there was almost a year and a half between the completion of Salomé and the release of Standish. Whether this was a lapse of memory by Florey or misreporting by Lambert, I can’t be sure.
[5] Originally, I wanted to include Madonna of the Streets (1924) in my comparisons but, at the moment, Lantern has gaps in their Moving Picture World archive for 1924-5. I didn’t want to draw conclusions from incomplete data.
[6] Billions was also a Rambova-Nazimova collaboration. Rambova designed a fantasy sequence for the film.
[7] A mindset that’s still common among commercial media outlets today unfortunately. I could rant and rant about “content” and “content creation” all day but that’s another story for another time.
——— ——— ———
Bibliography/Further Reading
(This isn’t an exhaustive list, but covers what’s most relevant to the essay above!)
Lost, but Not Forgotten: A Doll’s House (1922)
“Nazimova in Repertoire” in Motion Picture News, 29 October 1921
“Alla Nazimova Plans for Her New Pictures” in Moving Picture World, 29 October 1921
“Nazimova Abandons Dual Program for Latest Film” in Exhibitors Herald, 24 December 1921
“Plays and Players”in Photoplay, February 1922
“PICTORIAL SECTION” in Exhibitors Herald, 4 February 1922
“New Nazimova Film May Be Roadshowed“ in Exhibitors Herald, 15 April 1922
“Newspaper Opinions” in The Film Daily, 3 January 1923
“Splendid Production Values But No Kick in Nazimova’s ‘Salome’” in The Film Daily, 7 January 1923
“Claims “Salome” Hit New Mark at N. Y. Criterion” in Exhibitors Herald, 27 January 1923
“Salome” in Exhibitors Trade Review, 20 January 1923
“Nazimova in SALOME” in Exhibitors Herald, 27 January 1923
“Nazimova Appeals To Exhibitors In Behalf of ‘Salome’” in Exhibitor’s Trade Review, 27 January 1923
“Novelty Features Paper and Ads for ‘Salome’” in Exhibitor’s Trade Review, 10 February 1923
“SALOME’ —Class AA” from Screen Opinions, 15 February 1923
Nazimova: A Biography by Gavin Lambert (Note: I do not recommend this without caveat even though it’s the only monograph biography of Nazimova. Lambert did a commendable amount of research but his presentation of that research is ruined by misrepresentations, factual errors, and a general tendency to make unfounded assumptions about Nazimova’s motivations and personal feelings.)
Lovers of Cinema: The First American Avant-Garde 1919-1945 ed. Jan-Christopher Horak (most notably, “The First American Avant-Garde 1919-1945” by Horak, “The Limits of Experimentation in Hollywood” by Kristin Thompson, and “Startling Angles: Amateur Film and the Early Avant-Garde” by Patricia R. Zimmermann)
United Artists: The Company Built by the Stars, Vol. 1 1919-1950 by Tino Balio
#1920s#1922#Salomé#salome#nazimova#alla nazimova#film history#cosplay#queer film#silent era#classic movies#film#avant garde#experimental film#cinema#queer film history#silent cinema#1923#classic cinema#american film#women filmmakers#women in film#silent film#classic film#silent movies#bisexual visibility#cosplayers#natacha rambova#united artists#Metro
21 notes
·
View notes
Text




The distinguished architect John Burnett died on July 2nd 1938 at Colinton, Edinburgh.
Burnett designed buildings the length and breadth of the British Isles and on the continent of Europe and as far afield as South Africa.
John Burnet was born a soldier's son at Craighead House, Kirk O' Shotts, and trained initially as a carpenter. After becoming a Clerk of Works, he set up as an architect specializing in modest churches and houses in the Italianate and Classical styles, and large-scale commercial buildings and hospitals in the Italian Renaissance, Baronial and Gothic styles.
One of his first undertakings in Glasgow was the Royal Institute of the Fine Arts in Sauchiehall Street, which was won by competition. Other notable buildings there are the offices of the Clyde Trust, the Athenaeum, the Botanical Department and extension of the University, the Pathological Institute, the Barony Church.
In Edinburgh he designed the Professional and Civil Service Stores, George Street, the business premises of R. W. Forsyth in Princes Street, which later housed Burtons for many years, and in Scotland and England generally many public, ecclesiastical and domestic buildings. He was also architect for the Edinburgh International Exhibition of 1906.
Important commissions came to him from London and to London he devoted the latter part of his life, the firm, of which he was senior partner, being known as Sir John Burnet, Tait & Lorne. He had the honour in 1905 of being entrusted by the Government with the important additions to the British Museum, now known as the King Edward VII. Galleries.
Among his numerous London designs are the Institute of Chemistry in Russell Square, the Kodak building in Kingsway, Adelaide House and Vigo House, and the Second Church of Christ Scientist. He was the chief architect in Palestine and Gallipoli for the Imperial War Graves Commission.
The professional esteem with which Sir John was regarded in Britain may be expressed by the words used in connection with the conferring of the Gold Medal of the Royal Institute of British Architects in 1923, ‘‘ Few architects living can compare with him either in quantity or quality of output, and fewer still may be said to have had as pervasive an influence on the work of their own time.”
In France he had received both bronze and gold medals at the Salon and was a corresponding member of the Institute of France and of the Société central des Architectes Francais. He had the same relation with the American Institute of Architects.
Knighted in 1914, Sir John was a member of both the Royal Scottish Academy and the Royal Academy. He was an Honorary LL.D., of Glasgow and Fellow of the Royal Institute of British Architects, of the Royal Society, Edinburgh, and of the Royal Society of Antiquaries.
Though he took fewer commissions personally, Burnet worked into his late seventies – he designed the famous Unilever building on London in 1933 - before he eventually retired, spending his final years at Colinton in Edinburgh. He died at home at the age of 81 on this day, 1938, he is buried at Warriston Cemetery.
Pics are the beutiful Drumsheugh Baths in Edinburgh, the old Public Library and Museum, Capbelltown and the former Clydesdale Bank Headquarters, St Vincent Place, Glasgow.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the Services Offered Under Retail Banking by Banks
Retail banking, also known as consumer banking or personal banking, refers to the provision of banking services to individual consumers. Retail banks offer a wide range of financial products and services, including deposit accounts, loans, mortgages, credit cards, and other financial services.
The main objective of retail banking is to provide financial services to individuals and small businesses. The retail banking sector is highly competitive, with numerous players ranging from large multinational banks to smaller local banks and credit unions. Banks in the retail banking sector typically have a large branch network and offer a range of products and services through digital channels as well.
Here are some of the common services offered under retail banking
READ MORE......
#ipb#banking#ipbindia#ipb banking#ipb bank#ipb course#institute of professional banking course fees#ibp banking course#professional banking courses#bankingcourse
0 notes
Text
this is a really weird thing to complain about perhaps + has a really simple fix of "why don't you just switch banks then bc no one cares??"
but last year (maybe the year before?) my bank switched from a very conservative navy blue, berry red, and steel grey colour scheme that had a sort of feel of professional detachment to it that i've come to associate with dry corporate things like banking, to this "fun" new thing that's lime green and hot pink, with (mostly) light grey text on dark grey backgrounds, and uses exclusively black and white pictures of Attractive Diverse Youths of an Indeterminate Age Doing Fun Millennial-Appealing Non-Banking Activities to try and jazz it up, and i... i don't... hate it, but it feels... wrong?
it feels too very specifically engineered. calculated. like, you're a bank. you're a financial institution owned by a larger one that has all the money in the world and does not care to help a single soul with it, but you know it doesn't matter because we're stuck with you anyways.


"free spirited photography" "old-fashioned competition" "energetic black-and-white imagery"
why does it feel like they're trying to convince me of something?? this is like a new wave social media app that hasn't figured out how manipulative phrasing has worked yet.
the whole thing feels disingenuous and tacky. they're an online only bank, so they're trying to appeal to millennials and younger by being Hip and Cool with the Youths, but it just feels sour. reminds me a bit of 'they live (1988)'-ish, or when you get a new job and they're like "we're a family here! 🥰" and everything is really sleek and buzzfeed/tech startup-esq and counter-productively techy in a really inhuman way and you end up getting fired over zoom by a bohemian chic hr woman wearing fashion glasses she doesn't need with bangles that jingle the entire time she gesticulates while telling you she's really-really sorry your mom has cancer, but you did break company policy by taking 10 days off this year 😢
also when i say "i don't hate it" i mean uhm. if this was the kind of colours and imagery that someone was using to promote a community-based event that involved interacting with other people, i would find it enjoyable and engaging. but there's something about it being used to encourage engagement with an app designed to take my money that makes me feel uhh well all of the above i guess.
i don't know. corporations have more access to us on a deeply personal level than ever before, so when i see things like this it makes me nervous to think about how many greedy corporate execs sat in a room workshopping the best way to seem like Your Cool Friend like some sort of shapeshifting social parasite. but maybe i'm just paranoid.
#hellooooooooooo i am reading too much into this but i can't help how i feel. it might be the hangover talking#all of this is bc i need to go by drywall to patch the hole we made in my guys wall that he's freaking out over#(RELAX i can fix it seamlessly oh my god chill out about the deposit i'm so good at this)#and i opened my banking app to shuffle money around and he went ''woah your bank is watermelon themed??''#jj stuff
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
""Moreover, it turns out that the United States is not all that tightfisted when it comes to social spending. “If you count all public benefits offered by the federal government, America’s welfare state (as a share of its gross domestic product) is the second biggest in the world, after France’s,” Desmond tells us. Why doesn’t this largesse accomplish more?
For one thing, it unduly assists the affluent. That statistic about the U.S. spending almost as much as France on social welfare, he explains, is accurate only “if you include things like government-subsidized retirement benefits provided by employers, student loans and 529 college savings plans, child tax credits, and homeowner subsidies: benefits disproportionately flowing to Americans well above the poverty line.” To enjoy most of these, you need to have a well-paying job, a home that you own, and probably an accountant (and, if you’re really in clover, a money manager).
“The American government gives the most help to those who need it least,” Desmond argues. “This is the true nature of our welfare state, and it has far-reaching implications, not only for our bank accounts and poverty levels, but also for our psychology and civic spirit.” Americans who benefit from social spending in the form of, say, a mortgage-interest tax deduction don’t see themselves as recipients of governmental generosity. The boon it offers them may be as hard for them to recognize and acknowledge as the persistence of poverty once was to Harrington’s suburban housewives and professional men. These Americans may be anti-government and vote that way. They may picture other people, poor people, as weak and dependent and themselves as hardworking and upstanding. Desmond allows that one reason for this is that tax breaks don’t feel the same as direct payments. Although they may amount to the same thing for household incomes and for the federal budget—“You can benefit a family by lowering its tax burden or by increasing its benefits, same difference”—they are associated with an obligation and a procedure that Americans, in particular, find onerous. Tax-cutting Republican lawmakers want the process to be both difficult and Swiss-cheesed with loopholes. (“Taxes should hurt,” Ronald Reagan once said.) But that’s not the only reason. What Desmond calls the “rudest explanation” is that if, for whatever reason, we get a tax break, most of us like it. That’s the case for people affluent and lucky enough to take advantage of the legitimate breaks designed for their benefit, and for the wily super-rich who game the system with expensive lawyering and ingenious use of tax shelters.
And there are other ways, Desmond points out, that government help gets thwarted or misdirected. When President Clinton instituted welfare reform, in 1996, pledging to “transform a broken system that traps too many people in a cycle of dependence,” an older model, Aid to Families with Dependent Children, or A.F.D.C., was replaced by Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, or TANF. Where most funds administered by A.F.D.C. went straight to families in the form of cash aid, TANF gave grants to states with the added directive to promote two-parent families and discourage out-of-wedlock childbirth, and let the states fund programs to achieve those goals as they saw fit. As a result, “states have come up with rather creative ways to spend TANF dollars,” Desmond writes. “Nationwide, for every dollar budgeted for TANF in 2020, poor families directly received just 22 cents. Only Kentucky and the District of Columbia spent over half of their TANF funds on basic cash assistance.” Between 1999 and 2016, Oklahoma directed more than seventy million dollars toward initiatives to promote marriage, offering couples counselling and workshops that were mostly open to people of all income levels. Arizona used some of the funds to pay for abstinence education; Pennsylvania gave some of its TANF money to anti-abortion programs. Mississippi treated its TANF funds as an unexpected Christmas present, hiring a Christian-rock singer to perform at concerts, for instance, and a former professional wrestler—the author of an autobiography titled “Every Man Has His Price”—to deliver inspirational speeches. (Much of this was revealed by assiduous investigative reporters, and by a 2020 audit of Mississippi’s Department of Human Services.) Moreover, because states don’t have to spend all their TANF funds each year, many carry over big sums. In 2020, Tennessee, which has one of the highest child-poverty rates in the nation, left seven hundred and ninety million dollars in TANF funds unspent."
- The New Yorker: "How America Manufactures Poverty" by Margaret Talbot (review of Matthew Desmond's Poverty by America).
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
Free tactical medicine learning resources
If you want to learn first aid, emergency care or tactical medical care for real, you will need to practice these skills. A lot. Regularly. There’s no way to learn them just from books. But if you’re looking to supplement your training, can’t access hands on training, are a layperson doing research for your writing or otherwise just curious, here are some free resources (some may need a free account to access them).
TCCC
The current gold standard in the field is Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC), developed by the US army but used by militaries around the world. There is also a civilian version of the system called Tactical Emergency Casualty Care (TECC). Training materials, Standards of Care, instructional videos, etc. can be accessed at deployedmedicine.com. You’ll need a free account. This should be your first and possibly only stop.
There’s also an app and a podcast if those are more your thing, although I haven’t personally tried them.
More TCCC (video) resources
STOP THE BLEED® Interactive Course
TCCC-MP Guidelines and Curriculum presentations and training videos
EURMED’s Medical Beginner's Resource List has suggested list of video materials (disclaimer: I haven’t watched the playlists, but I have been trained by nearly all of the linked systems/organisations and can vouch for them)
Tactical Medical Solutions training resource page (requires registration; some of the courses are free)
North American Rescue video downloads
Emergency medicine
WHO-ICRC Basic Emergency Care: approach to the acutely ill and injured — an open-access course workbook for basic emergency care with limited resources
Global Health Emergency Medicine — open-access, evidence-based, peer-reviewed emergency medicine modules designed for teachers and learners in low-resource health setting
AFEM Resources — curricula, lecture bank, reviews, etc.
Global Emergency Medicine Academy Resources (links to more resources)
OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology textbook
Open-access anatomy and physiology learning resources
OpenStax Pharmacology for nurses textbook
Principles of Pharmacology – Study Guide
Multiple Casualty Incidents
Management of Multiple Casualty Incidents lecture
Bombings: Injury Patterns and Care blast injuries course (scroll down on the page)
Borden Institute has medical textbooks about biological, chemical and nuclear threats
Psychological first aid: Guide for field workers
Prolonged field care
When the evac isn’t coming anytime soon.
Prolonged Field Care Basics lecture (requires registration)
Aerie 14th Edition Wilderness Medicine Manual (textbook)
Austere Emergency Medical Support (AEMS) Field Guide (textbook)
Prolonged Casualty Care (PCC) Guidelines
Wilderness Medical Society Clinical Practice Guidelines
Austere Medicine Resources: Practice Guidelines — a great resource of WMS, PFC, TCCC, etc. clinical practice guidelines in one place
The Wilderness and Environmental Medicine Journal (you can read past issues without a membership)
Prolonged Field Care Collective: Resources
National Park Services Emergency Medical Services Resources
Guerilla Medicine: An Introduction to the Concepts of Austere Medicine in Asymmetric Conflicts (article)
Mental health & PTSD
National Center for PTSD
Psychological first aid: Guide for field workers
Combat and Operational Behavioral Health (medical textbook)
Resources for doctors and medical students
Or you know, other curious people who aren’t afraid of medical jargon.
Borden Institute Military Medical Textbooks and Resources — suggestions: start with Fundamentals of Military Medicine; mechanism of injury of conventional weapons; these two volumes on medical aspects of operating in extreme environments; psychosocial aspects of military medicine; or Combat Anesthesia
Emergency War Surgery textbook and lectures
Disaster Health Core Curriculum — online course for health professionals
Médecins Sans Frontières Clinical guidelines
Pocket book of hospital care for children: Second edition — guidelines for the management of common childhood illnesses in low resource settings
Grey’s Quick Reference: Basic Protocols in Paediatrics and Internal Medicine For Resource Limited Settings
The Department of Defense Center of Excellence for Trauma: Trauma Care Resources (links to more resources)
#feel free to share and add more#tactical medicine#tactical combat casualty care#prolonged field care#austere medicine#military medicine#tccc#tecc#disaster medicine#wilderness medicine#emergency medicine#emergency medical services#learning resources#writing resources#mandalorian medics#paramedicine#medicine
30 notes
·
View notes