#Joan II of Burgundy
Text
Ages of French Queens at First Marriage
I have only included women whose birth dates and dates of marriage are known within at least 1-2 years, therefore, this is not a comprehensive list.
This list is composed of Queens of France until the end of the House of Bourbon; it does not include Bourbon claimants or descendants after 1792.
The average age at first marriage among these women was 20.
Ermentrude of Orléans, first wife of Charles the Bald: age 19 when she married Charles in 842 CE
Richilde of Provence, second wife of Charles the Bald: age 25 when she married Charles in 870 CE
Richardis of Swabia, wife of Charles the Fat: age 22 when she married Charles in 862 CE
Théodrate of Troyes, wife of Odo: age 14 or 15 when she married Odo in 882 or 883 CE
Frederuna, wife of Charles III: age 20 when she married Charles in 907 CE
Beatrice of Vermandois, second wife of Robert I: age 10 when she married Robert in 990 CE
Emma of France, wife of Rudolph: age 27 when she married Rudolph in 921 CE
Gerberga of Saxony, wife of Gilbert, Duke of Lorraine, and later of Louis IV: age 16 when she married Gilbert in 929 CE
Emma of Italy, wife of Lothair: age 17 when she married Lothair in 965 CE
Adelaide-Blanche of Anjou, wife of Stephen, Viscount of Gévaudan, Raymond III, Count of Toulouse, and later Louis V: age 15 when she married Stephen in 955 CE
Bertha of Burgundy, wife of Odo I, Count of Blois, and later Robert II: age 19 when she married Odo in 984 CE
Constance of Arles, third wife of Robert II: age 17 when she married Robert in 1003 CE
Anne of Kiev, wife of Henry I: age 21 when she married Henry in 1051 CE
Bertha of Holland, first wife of Philip I: age 17 when she married Philip in 1072 CE
Bertrade of Montfort, wife of Fulk IV, Count of Anjou, and second wife of Philip I: age 19 when she married Fulk in 1089 CE
Adelaide of Maurienne, second wife of Louis VI: age 23 when she married Louis in 1115 CE
Eleanor of Aquitaine, first wife of Louis VII and later Henry II of England: age 15 when she married Louis in 1137 CE
Adela of Champagne, third wife of Louis VII: age 20 when she married Louis in `1160 CE
Isabella of Hainault, first wife of Philip II: age 10 when she married Philip in 1180 CE
Ingeborg of Denmark, second wife of Philip II: age 19 when she married Philip in 1193 CE
Agnes of Merania, third wife of Philip II: age 21 when she married Philip in 1195 CE
Blanche of Castile, wife of Louis VIII: age 12 when she married Louis in 1200 CE
Margaret of Provence, wife of Louis IX: age 13 when she married Louis in 1234 CE
Isabella of Aragon, first wife of Philip III: age 14 when she married Philip in 1262 CE
Marie of Brabant, second wife of Philip III: age 20 when she married Philip in 1274 CE
Joan I of Navarre, wife of Philip IV: age 11 when she married Philip in 1284 CE
Margaret of Burgundy, wife of Louis X; age 15 when she married Louis in 1305 CE
Clementia of Hungary, second wife of Louis X: age 22 when she married Louis in 1315 CE
Joan II, Countess of Burgundy, wife of Philip V: age 15 when she married Philip in 1307 CE
Blanche of Burgundy, first wife of Charles IV: age 12 when she married Charles in 1308 CE
Marie of Luxembourg, second wife of Charles IV: age 18 when she married Charles in 1322 CE
Joan of Évreux, third wife of Charles IV: age 14 when she married Charles in 1324 CE
Bonne of Luxembourg, first wife of John II: age 17 when she married John in 1332 CE
Joan I, Countess of Auvergne, wife of Philip of Burgundy, and later John II: age 12 when she married Philip in 1338 CE
Joanna of Bourbon, wife of Charles V: age 12 when she married Charles in 1350 CE
Isabeau of Bavaria, wife of Charles VI: age 15 when she married Charles in 1385 CE
Marie of Anjou, wife of Charles VII: age 18 when she married Charles in 1422 CE
Charlotte of Savoy, second wife of Louis XI: age 9 when she married Louis in 1451 CE
Anne of Brittany, wife of Maximilian I, HRE, Charles VIII and later Louis XII: age 13 when she married Maximilian in 1490 CE
Joan of France, first wife of Louis XII: age 12 when she married Louis in 1476 CE
Mary Tudor, third wife of Louis XII: age 18 when she married Louis in 1514 CE
Claude of France, first wife of Francis I: age 15 when she married Francis in 1514 CE
Eleanor of Austria, wife of Manuel I of Portugal and later second wife of Francis I: age 20 when she married Manuel in 1518 CE
Catherine de' Medici, wife of Henry II: age 14 when she married Henry in 1533 CE
Mary, Queen of Scots, wife of Francis II: age 16 when she married Francis in 1558 CE
Elisabeth of Austria, wife of Charles IX: age 16 when she married Charles in 1570 CE
Louise of Lorraine, wife of Henry III: age 22 when she married Henry in 1575 CE
Margaret of Valois, first wife of Henry IV: age 19 when she married Henry in 1572 CE
Marie de' Medici, second wife of Henry IV: age 25 when she married Henry in 1600 CE
Anne of Austria, wife of Louis XIII: age 14 when she married Louis in 1615 CE
Maria Theresa of Spain, wife of Louis XIV: age 22 when she married Louis in 1660 CE
Marie Leszczyńska, wife of Louis XV: age 22 when she married Louis in 1725 CE
Marie Antoinette, wife of Louis XVI: age 15 when she married Louis in 1770 CE
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ramon Llull with his disciple Thomas le Myesier presenting three anthologies (philosophical compilations) to the Queen of France and Navarre, Joan II of Burgundy (wife of King Philip V of France) Miniature from "Breviculum seu electorium parvum" of Thomas le Myésier, Karlsruhe, Badische Landesbibliothek, St. Peter perg. 92, fol. 12r, French, ca. 1325

7 notes
·
View notes
Text
MARGARET OF BURGUNDY
MARGARET OF BURGUNDY, QUEEN OF FRANCE
c.1290-1315
Les Rois Maudits (The Accursed Kings)
Margaret of Burgundy was the Queen of France and Navarre, and was the first wife of King Louis X and I. She was a princess of the House of Burgundy, the oldest daughter of Robert II Duke of Burgundy an Anges of France (who was the youngest daughter of Louis IX of France). In 1305, Margaret married her cousin Louis I and had their daughter Joan.
In 1314, the Tour de Nesle affair was revealed, it was a well-known scandal for the French royal family. The daughters-in-law of King Philip IV, Margaret, Blanche, and Joan were all accused of adultery. The three women were said to have conducted their affairs with Norman knights in a tower in Paris.
It was Isabella of France (wife of King Edward II of England) who became a witness against those involved in the affair. Isabella had given her sisters-in-law a purse, the Norman knights were found in possession of them after the three ladies had given it to them as a gift The affair was exposed and the knights were tortured and then executed.
Margaret, Blanche, and Joan were found guilty and imprisoned. Margaret spent the last two years of her life in prison. The women were imprisoned in poor conditions and mistreated, which resulted Margaret catching a virus and passing away. She died aged 24 or 25. Joan’s paternity became in doubt after the affair.
Margaret of Burgundy is one of the characters in Les Rois Maudits (The Accursed Kings) by Maurice Druon and was portrayed in the miniseries 1972 and 2005.

#margaretofburgundyqueenoffrance #margaretofburgundy #lesroismaudits #theaccursedkings #mauricedruon
#margaret of burgundy queen of france#margaret of burgundy#margaretofburgundy#les rois maudits#the accursed kings#maurice druon
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 6: Yolande of Aragon
Yolande of Aragon (also known as Yolanda de Aragón and Violant d'Aragó.)
Born: 11 August 1381
Died: 14 November 1442
Parents: John I of Aragon and Violant of Bar
Duchess of Anjou and Countess of Provence
Children: Louis III, Duke of Anjou
Marie, Queen of France
René, King of Naples
Yolande, Countess of Montfort l'Amaury
Charles, Count of Maine
Yolande was born in Zaragoza, Aragon as the eldest daughter of John I of Aragon and his second wife Violant of Bar, granddaughter of John II of France.
In 1387 a marriage offer came through the mother of the King of Naples, Louis II.
At 11 years old she signed a document that disallowed any marriage promises made by ambassadors.
In 1395 another marriage offer came from Richard II of England.
After her father’s death, her uncle was convinced to marry Yolande to Louis. She was forced to retract her protest to the marriage.
Yolande and Louis were married on December 2, 1400 in Arles.
Despite her initial rejection and her husband’s illness, they had 5 children.
As a daughter of a king, she had a claim to the throne of Aragon after her uncle’s death without an heir. The laws at the time favored male heirs, thus after two years without a king they chose Ferdinand the son of Eleanor of Aragon and John I of Castile.
Yolande’s son, Louis, was the Anjou claimant to the throne, although his claim was excluded by the Pact of Caspe..
In the second phase of the Hundred Years' War, Yolande supported the French, particularly the Armagnacs. After the attack on the Dauphin of France by the duke of Burgundy, she and her husband refused the marriage of their son Louis to the duke’s daughter.
She met with the Queen of France to arrange the marriage of her daughter and the third son of the queen, Charles.
When Charles became the Dauphin and his mother worked against his claim, Yolande became a substitute mother for the teenager. She protected him against plots, funded and helped his cause. Yolande removed Charles from his parents' court and took him to her residence where he received Joan of Arc. After his marriage to her daughter Marie she became his mother-in-law and was heavily involved in the conflict of the House of Valois.
She succeeded in having him crowned.
As her husband was often away fighting in Italy, Yolande preferred to hold court in Angers and Saumur..
After the Battle of Agincourt in 1415, the Duchy of Anjou was threatened and Louis II had Yolande, their children and Charles moved to Provence.
On 29 April 1417, Louis II died leaving Yolande, aged 33, in control of the House of Anjou. Yolande acted as regent for her young son.
Yolande not only took care of the House of Anjou but also of Charles’s cause. Yolande supported Joan of Arc from the beginning and practiced political moves to ensure the success of Charles.
She retired to Angers and then to Saumur, where she continued to play a role in politics.
From at least 1439 onwards Yolande took care and prepared her granddaughter Margaret of Anjou for marriage.
She died on 14 November 1442 at the town house of the Seigneur de Tucé in Saumur.
She is described as "the prettiest woman in the kingdom", a wise and beautiful woman and her grandson Louis XI of France described her as "a man's heart in a woman's body”.
#women history#women in history#french history#joan of arc#margaret of anjou#anjou#15th century#medieval#medieval history#1400s#france
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Partial List of Royal Saints
Saint Abgar (died c. AD 50) - King of Edessa, first known Christian monarch
Saint Adelaide of Italy (931 - 999) - Holy Roman Empress as wife of Otto the Great
Saint Ælfgifu of Shaftesbury (died 944) - Queen of the English as wife of King Edmund I
Saint Æthelberht of Kent (c. 550 - 616) - King of Kent
Saint Æthelberht of East Anglia (died 794) - King of East Anglia
Saint Agnes of Bohemia (1211 - 1282) - Bohemian Princess, descendant of Saint Ludmila and Saint Wenceslaus, first cousin of Saint Elizabeth of Hungary
Saint Bertha of Kent (c. 565 - c. 601) - Frankish Princess and Queen of Kent as wife of Saint Æthelberht
Saint Canute (c. 1042 - 1086) - King of Denmark
Saint Canute Lavard (1096 - 1131) - Danish Prince
Saint Casimir Jagiellon (1458 - 1484) - Polish Prince
Saint Cormac (died 908) - King of Munster
Saint Clotilde (c. 474 - 545) - Queen of the Franks as wife of Clovis I
Saint Cunigunde of Luxembourg (c. 975 - 1033) - Holy Roman Empress as wife of Saint Henry II
Saint Edmund the Martyr (died 869) - King of East Anglia
Saint Edward the Confessor (c. 1003 - 1066) - King of England
Saint Edward the Martyr (c. 962 - 978) - King of the English
Saint Elesbaan (Kaleb of Axum) (6th century) - King of Axum
Saint Elizabeth of Hungary (1207 - 1231) - Princess of Hungary and Landgravine of Thuringia
Saint Elizabeth of Portugal (1271 - 1336) - Princess of Aragon and Queen Consort of Portugal
Saint Emeric (c. 1007 - 1031) - Prince of Hungary and son of Saint Stephen of Hungary
Saint Eric IX (died 1160) - King of Sweden
Saint Ferdinand (c. 1199 - 1252) - King of Castile and Toledo
Blessed Gisela of Hungary (c. 985 - 1065) - Queen Consort of Hungary as wife of Saint Stephen of Hungary
Saint Helena (c. 246 - c. 330) - Roman Empress and mother of Constantine the Great
Saint Henry II (973 - 1024) - Holy Roman Emperor
Saint Isabelle of France (1224 - 1270) - Princess of France and younger sister of Saint Louis IX
Saint Jadwiga (Hedwig) (c. 1373 - 1399) - Queen of Poland
Saint Joan of Valois (1464 - 1505) - French Princess and briefly Queen Consort as wife of Louis XII
Blessed Joanna of Portugal (1452 - 1490) - Portuguese princess who served as temporary regent for her father King Alfonso V
Blessed Karl of Austria (1887 - 1922) - Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, King of Croatia, and King of Bohemia
Saint Kinga of Poland (1224 - 1292) - Hungarian Princess, wife of Bolesław V of Poland and niece of Saint Elizabeth of Hungary
Saint Ladislaus (c. 1040 - 1095) - King of Hungary and King of Croatia
Saint Louis IX (1214 - 1270) - King of France
Saint Ludmila (c. 860 - 921) - Czech Princess and grandmother of Saint Wenceslaus, Duke of Bohemia
Blessed Mafalda of Portugal (c. 1195 - 1256) - Portuguese Princess and Queen Consort of Castile, sister of Blessed Theresa of Portugal
Saint Margaret of Hungary (1242 - 1270) - Hungarian Princess, younger sister of Saint Kinga of Poland and niece of Saint Elizabeth of Hungary
Saint Margaret of Scotland (c. 1045 - 1093) - English Princess and Queen Consort of Scotland
Blessed Maria Cristina of Savoy (1812 - 1836) - Sardinian Princess and Queen Consort of the Two Sicilies
Saint Matilda of Ringelheim (c. 892 - 968) - Saxon noblewoman and Queen of East Francia as wife of Henry I
Saint Olaf (c. 995 - 1030) - King of Norway
Saint Olga of Kiev (c. 900 - 969) - Grand Princess of Kiev and regent for her son Sviatoslav I, grandmother of Saint Vladimir the Great
Saint Oswald (c. 604 - 642) - King of Northumbria
Saint Radegund (c. 520 - 587) - Thuringian Princess and Frankish Queen
Saint Sigismund of Burgundy (died 524) - King of the Burgundians
Saint Stephen of Hungary (c. 975 - 1038) - King of Hungary
Blessed Theresa of Portugal (1176 - 1250) - Portuguese Princess and Queen of León as wife of King Alfonso IX, sister of Blessed Mafalda
Saint Vladimir the Great (c. 958 - 1015) - Grand Prince of Kiev and grandson of Saint Olga of Kiev
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
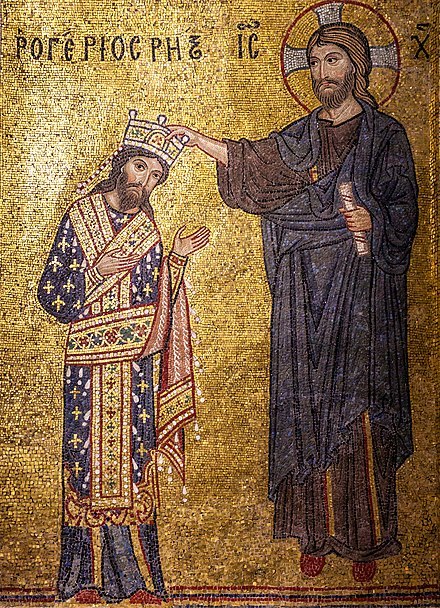
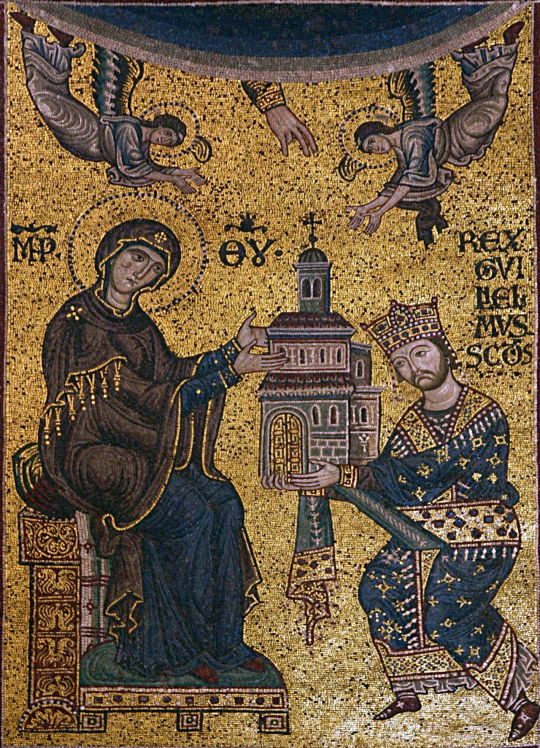









The Bastard Kings and their families
This is series of posts are complementary to this historical parallels post from the JON SNOW FORTNIGHT EVENT, and it's purpouse to discover the lives of medieval bastard kings, and the following posts are meant to collect portraits of those kings and their close relatives.
In many cases it's difficult to find contemporary art of their period, so some of the portrayals are subsequent.
1) Tancred I of Sicily ( 1138 – 1194), son of Roger III of Apulia and Emma of Lecce; with his sons Roger III of Sicily (1175 –1193) and William III of Sicily (c. 1186 – c. 1198)
2) His wife, Sibylla of Acerra (1153–1205), mother of Roger III and William III
3) His brother-in-law, Richard of Acerra (d. 1196)
4)His father, Roger III of Apulia (1118 – 1148), son of Roger II of Sicily and his wife Elvira of Castile
5) His grandfather, Roger II of Sicily (1095– 1154), son of Roger I of Sicily and his wife Adelaide del Vasto
6) His uncle, William I of Sicily (1120/1121 – 1166), son of Roger II of Sicily and his wife Elvira of Castile
7) His cousin, William II of Sicily (1153 – 1189), son of William I of Sicily and his wife Joan of England
8) His aunt, Constance I of Sicily (1154–1198), daughter of Roger II of Sicily and his wife Beatrice of Rethel
9) His uncle, Holy Roman Emperor Henry VI (1165 – 1197), son of Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I and his wife Beatrice I of Burgundy; and Constance I of Sicily's husband
10) His cousin, Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II (1194 – 1250), son of Constance I of Sicily and Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I
#jonsnowfortnightevent2023#asoiaf#a song of ice and fire#day 10#echoes of the past#historical parallels#medieval bastard kings#bastard kings and their families#tancred i of sicily#roger iii of sicily#william iii of sicily#sibylla of acerra#richard of acerra#roger iii of apulia#roger ii of sicily#william i of sicily#william ii of sicily#constance i of sicily#holy roman emperor henry vi#holy roman emperor frederick ii#canonjonsnow
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Christine de Pizan with Queen Isabeau.
Master of the Cité des Dames, c. 1410–1414.
Picturing a scene of Queen Isabeau receiving Christine de Pizan's 'Le Livre de la Cité des Dames' (which begs the question, did they meet in real life? Answer: Probably).
Illumination on parchment, from Christine de Pizan's 'Book of the Queen', stored at the British Library.
It's time to refresh my memory on Isabeau of Bavaria, of whom I've written about before on this blog (link here). The notes in one of my old notebooks tell me she was the mother-in-law to two Plantagenet kings. Her eldest daughter, Isabella of Valois, married Richard II of England (she was six years old and Henry, a widower, was 22 years her senior; it was agreed that consummation of the marriage would not take place until she was at least 12 years old), while Isabeau's youngest, Catherine of Valois, married Henry V (she was 19, and following Henry's death she went on marry Owen Tudor, remember, grandfather of the man who would become Henry VII and begin the Tudor dynasty).
Isabeau herself was only 15 years old when she married Charles VI of France. My notes are as follows:
History wasn't kind to her and she stands condemned as a spendthrift and sexually promisicuous, but was this propaganda? She denied her own son, [the Dauphin Charles who eventually went on to become Charles VII of France], as heir to the throne by saying he was illegitimate. Why? Her husband was known as Charles the Mad on account of bouts of mental illness (Is he the one who thought he was made entirely of glass? ANSWER: YES.) Isabeau stood in as regent during these periods. She lived between c. 1370-1435 and gave birth to twelve children - eight survived to adulthood.
So, more to explore. A quick scan of the young Isabella's history on Wikipedia says Richard died in 1400, so she would have been about ten years old and had a lucky escape there. She then went on to marry her cousin when she was 16 and he a mere 11 years old. At the age of 19 she died in childbirth, presumably with their child. What a life.
NOTE: I need to gen up on the Treaty of Troyes (1420). [Not to be confused with the Treaty of Troyes (1564) or the Treaty of Troyes (1814)]. It must have been drawn up while Charles VI was incapacitated; did he ever become aware of the terms? Essentially, his son, the Dauphin Charles, was disinherited from the succession (hence my earlier notes that Isabeau "denied her own son, Charles VIII, as heir to the throne by saying he was illegitimate. Why?"), and marriage was arranged between Charles' and Isabeau's daughter, Catherine, and Henry V of England. Henry was made regent of France and was acknowledged (along with his future sons) as successor to the French throne.
Pilfered from Wikipedia:
The treaty was undermined by the deaths of both Charles VI and Henry V within two months of each other in 1422. The infant Henry VI of England [Henry's son with Catherine] became King of both England and France, but the Dauphin Charles also claimed the throne of France upon the death of his father.
Henry died of a serious, undiagnosed illness in 1422 aged 35 and consequently did not live to be crowned King of France. I haven't yet ascertained the cause of death for his father-in-law, who died shortly afterwards aged 53. Events became even more complicated; Isabeau was imprisoned by her son, rescued by John the Fearless, duke of Burgundy, but then deserted by him when he went to join the new French king fight against the English. Somewhere along the line, Joan of Arc got involved.
0 notes
Photo

Joan of Geneva (born c. 1040; died 1095) was a Countess Consort of Savoy; married to Amadeus II, Count of Savoy.
According to the much later Chronicles of Savoy, Amadeus married Joan, daughter of "Girard, Count of Burgundy", which scholars have surmised to have been Count Gerold of Geneva. The Chronicon Altacumbae says only that "the wife of Amadeus [was] from Burgundy", which might refer to Amadeus I. If his wife were Genevan, it would explain how the house of Savoy came so early to possess a large portion of the Genevois. His wife, whatever her name and origins, bore Amadeus II several children, although there is some uncertainty about how many.
0 notes
Text










Philip V of France and his wife Joan of Burgundy being extremely cute :)
#Philip V of France#Joan II of Burgundy#Philip the tall#Les rois maudits#les rois maudits 2005#maurice druon#Philippe V#Philippe le long#Julie depardieu#They're so cute#period drama#period drama edit#the accursed kings
22 notes
·
View notes
Photo










Medieval/Renaissance playing cards
from: http://www.laurainksetter.com
#playing cards#history#isabella i of castile#ferdinand ii of aragon#joan of arc#juana i of castile#eleanor of viseu#john ii of portugal#mary of burgundy#maximilian i#anne boleyn#henry viii#women in history#men in history
621 notes
·
View notes
Text






Every Queen of France Ever
Other posts in this series: Every Queen of England ever, Every English Princess ever
Richilde of Provence - Queen consort of West Francia from 870 to 877 (wife of Charles the Bald)
Adelaide of Paris - Queen consort of West Francia from October 6th 877 to April 10th 879 (wife of Louis the Stammerer)
Richardis of Swabia - Queen consort of West Francis from 884 to 887 (wife of Charles the Fat)
Richardis of Swabia - Queen consort of West Francis from 884 to 887 (wife of Charles the Fat)
Théodrate of Troyes - Queen consort of West Francia from 888 to 898 (wife of Odo of France)
Frederuna - Queen consort of West Francia from 907 to 917 (wife of Charles the Simple)
Eadgifu of Wessex - Queen consort of West Francia from 919 to 922 (wife of Charles the Simple)
Beatrice of Vermandois - Queen consort of West Francia from 922 to 923 (wife of Robert I)
Emma of France - Queen consort of West Francia from 923 to 935 (wife of Rudolph of France)
Gerberga of Saxony - Queen consort of West Francia from 939 to 954 (wife of Louis IV)
Emma of Italy - Queen consort of West Francia from 965 to 986 (wife of Lothair of France)
Adelaide of Aquitaine - Queen consort of the Franks from 987 to 996 (wife of Hugh Capet)
Rozala of Italy - Queen consort of the Franks from 996 to 996 (wife of Robert II)
Bertha of Burgundy - Queen consort of the Franks from 996 to 1000 (wife of Robert II)
Constance of Arles - Queen consort of the Franks from 1001 to 1031 (wife of Robert II)
Matilda of Frisia - Queen consort of the Franks from 1034 to 1044 (wife of Henry I)
Anne of Kiev - Queen consort of the Franks from May 19th 1051 to August 4th 1060 (wife of Henry I)
Bertha of Holland - Queen consort of the Franks from 1072 to 1092 (wife of Philip I)
Bertrade de Montfort - Queen consort of the Franks from May 15th 1092 to July 29th 1108 (wife of Philip I)
Adelaide of Maurienne - Queen consort of the Franks from 1115 to August 1st 1137 (wife of Louis VI)
Eleanor of Aquitaine - Queen consort of the Franks from August 1st 1137 to March 21st 1152 (wife of Louis VII)
Constance of Castile - Queen consort of the Franks from 1154 to October 4th 1160 (wife of Louis VII)
Adela of Champagne - Queen consort of the Franks from November 13th 1160 to September 18th 1180 (wife of Louis VII)
Isabella of Hainault - Queen consort of France from April 28th 1180 to March 15th 1190 (wife of Philip II)
Ingeborg of Denmark - Queen consort of France from August 15th 1193 to November 5th 1193 (wife of Philip II
Agnes of Merania - Queen consort of France from 1196 to 1200 (wife of Philip II)
Ingeborg of Denmark - Queen consort of France from 1200 to July 14th 1223 (wife of Philip II)
Blanche of Castile - Queen consort of France from July 14th 1223 to November 1226 (wife of Louis VIII)
Margaret of Provence - Queen consort of France from May 27th 1234 to August 25th 1270 (wife of Louis IX)
Isabella of Aragon - Queen consort of France from August 25th 1270 to January 28th 1271 (wife of Philip III)
Marie of Brabant - Queen consort of France from August 21st 1274 to October 5th 1285 (wife of Philip III)
Joan I of Navarre - Queen consort of France from October 5th 1285 to April 2nd 1305 (wife of Philip IV)
Margaret of Burgundy - Queen consort of France from 1314 to 1315 (wife of Louis X)
Clementia of Hungary - Queen consort of France from August 19th 1315 to June 5th 1316 (wife of Louis X)
Joan II of Burgundy - Queen consort of France from 1316 to 1322 (wife of Philip V)
Blanche of Burgundy - Queen consort of France from January 3rd 1322 to May 19th 1322 (wife of Charles IV)
Marie of Luxembourg - Queen consort of France from September 21st 1322 to March 26th 1324 (wife of Charles IV)
Joan of Évreux - Queen consort of France from July 5th 1324 to February 1st 1328 (wife of Charles IV)
Joan of Burgundy - Queen consort of France from April 1st 1328 to December 12th 1349 (wife of Philip VI)
Blanche of Navarre - Queen consort of France from January 29th 1350 to August 22nd 1350 (wife of Philip VI)
Joan I of Auvergne - Queen consort of France from 1350 to 1360 (wife of John II)
Joanna of Bourbon - Queen consort of France from April 8th 1364 to February 6th 1378 (wife of Charles V)
Isabeau of Bavaria - Queen consort of France from July 17th 1385 to October 21st 1422 (wife of Charles VI)
Marie of Anjou - Queen consort of France from December 18th 1422 to July 14th 1461 (wife of Charles VII)
Charlotte of Savoy - Queen consort of France from July 22nd 1461 to August 30th 1483 (wife of Louis XI)
Anne of Brittany - Queen consort of France from December 6th 1491 to April 7th 1498 (wife of Charles VIII)
Joan of France - Queen consort of France from April 1498 to December 15th 1498 (wife of Louis XII)
Anne of Brittany - Queen consort of France from January 8th 1499 to January 9th 1515 (wife of Louis XII)
Mary Tudor - Queen consort of France from October 9th 1514 to January 1st 1515 (wife of Louis XII)
Claude of France - Queen consort of France from January 1st 1515 to July 20th 1524 (wife of Francis I)
Eleanor of Austria - Queen consort of France from July 4th 1530 to March 31st 1547 (wife of Francis I)
Catherine de' Medici - Queen consort of France from March 31st 1547 to July 10th 1559 (wife of Henry II)
Mary Stuart - Queen consort of France from July 10th 1559 to December 5th 1560 (wife of Francis II)
Elisabeth of Austria - Queen consort of France from November 26th 1570 um May 30th 1574 (wife of Charles IX)
Louise of Lorraine - Queen consort of France from February 15th 1575 to August 2nd 1589 (wife of Henry III)
Margaret of Valois - Queen consort of France from August 2nd 1589 to 1599 (wife of Henry IV)
Marie de' Medici - Queen consort of France from December 17th 1600 to May 14th 1610 (wife of Henry IV)
Anne of Austria - Queen consort of France from November 24th 1615 to May 14th 1643 (wife of Louis XIII)
Maria Theresa of Spain - Queen consort of France from June 9th 1660 to July 30th 1683 (wife of Louis XIV)
Marie Leszczyńska - Queen consort of France from September 4th 1725 to June 24th 1768 (wife of Louis XV)
Marie Antoinette - Queen consort of France from May 10th 1774 to September 21st 1792 (wife of Louis XVI)
Maria Amalia of Naples and Sicily - Queen consort of the French from August 9th 1830 to February 24th 1848 (wife of Louis Philippe I)
#historical women#french history#anne of brittany#mary tudor queen of france#claude of france#eleanor of austria#eleanor of aquitaine#catherine de medici#mary queen of scots#marie antoinette
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ages of French Princesses at First Marriage
I have only included women whose birth dates and dates of marriage are known within at least 1-2 years, therefore, this is not a comprehensive list.
This list is composed of princesses of France until the end of the House of Bourbon; it does not include Bourbon claimants or descendants after 1792.
The average age at first marriage among these women was 15.
Judith of Flanders, daughter of Charles the Bald: age 12 when she married Æthelwulf, King of Wessex in 856 CE
Rothilde, daughter of Charles the Bald: age 19 when she married Roger, Count of Maine in 890 CE
Emma of France, daughter of Robert I: age 27 when she married Rudolph of France in 921 CE
Matilda of France, daughter of Louis IV: age 21 when she married Conrad I of Burgundy in 964 CE
Hedwig of France, daughter of Hugh Capet: age 26 when she married Reginar IV of Hainault in 996 CE
Gisela of France, daughter of Hugh Capet: age 26 when she married Hugh of Ponthieu in 994 CE
Hedwig of France, daughter of Robert II: age 13 when she married Renauld I, Count of Nevers in 1016 CE
Adela of France, daughter of Robert II: age 18 when she married Richard III of Normandy in 1027 CE
Constance of France, daughter of Philip I: age 16 when she married Hugh I, Count of Troyes in 1094 CE
Cecile of France, daughter of Philip I: age 9 when she married Tancred, Prince of Galilee in 1106 CE
Constance of France, daughter of Louis VI: age 14 when she married Eustace IV, Count of Boulogne in 1140 CE
Marie of France, daughter of Louis VII: age 14 when she married Henry I, Count of Champagne, in 1159 CE
Alice of France, daughter of Louis VII: age 14 when she married Theobald V, Count of Blois in 1164 CE
Margaret of France, daughter of Louis VII: age 14 when she married Henry the Young King in 1172 CE
Alys of France, daughter of Louis VII: age 35 when she married William IV of Ponthieu in 1195 CE
Agnes of France, daughter of Louis VII: age 8 when she married Alexios II Komnenos in 1180 CE
Marie of France, daughter of Philip II: age 13 when she married Philip I of Namur in 1211 CE
Isabella of France, daughter of Louis IX: age 14 when she married Theobald II of Navarre in 1255 CE
Blanche of France. daughter of Louis IX: age 16 when she married Ferdinand de la Cerda in 1269 CE
Margaret of France, daughter of Louis IX: age 16 when she married John I, Duke of Brabant in 1270 CE
Agnes of France, daughter of Louis IX: age 19 when she married Robert II, Duke of Burgundy in 1279 CE
Blanche of France, daughter of Philip III: age 22 when she married Rudolf III of Austria in 1300 CE
Margaret of France, daughter of Philip III: age 20 when she married Edward I of England in 1299 CE
Isabella of France, daughter of Philip IV: age 13 when she married Edward II of England in 1308 CE
Joan II of Navarre, daughter of Louis X: age 6 when she married Philip III of Navarre in 1318 CE
Joan III, daughter of Philip V: age 10 when she married Odo IV, Duke of Burgundy in 1318 CE
Margaret I, daughter of Philip V: age 10 when she married Louis I of Flanders in 1320 CE
Isabella of France, daughter of Philip V: age 11 when she married Guigues VIII of Viennois in 1323 CE
Blanche of France, daughter of Charles IV: age 17 when she married Philip, Duke of Orleans in 1345 CE
Joan of Valois, daughter of John II: age 9 when she married Charles II of Navarre in 1352 CE
Marie of France, daughter of John II: age 20 when she married Robert I, Duke of Bar in 1364 CE
Isabella, daughter of John II: age 12 when she married Gian Geleazzo Visconti in 1360 CE
Catherine of France, daughter of Charles V: age 8 when she married John of Berry, Count of Montpensier in 1386 CE
Isabella of Valois, daughter of Charles VI: age 6 when she married Richard II of England in 1396 CE
Joan of France, daughter of Charles VI: age 5 when she married John V, Duke of Brittany in 1396 CE
Michelle of Valois, daughter of Charles VI: age 14 when she married Philip III, Duke of Burgundy in 1409 CE
Catherine of Valois, daughter of Charles VI: age 19 when she married Henry V of England in 1420 CE
Catherine of France, daughter of Charles VII: age 12 when she married Charles I, Duke of Burgundy in 1440 CE
Joan of France, daughter of Charles VII: age 12 when she married John II , Duke of Bourbon in 1447 CE
Yolande of Valois, daughter of Charles VII: age 18 when she married Amadeus IX, Duke of Savoy in 1452 CE
Magdalena of Valois, daughter of Charles VII: age 18 when she married Gaston, Prince of Viana in 1461 CE
Anne of France, daughter of Louis XI: age 12 when she married Peter of Bourbon in 1473 CE
Joan of France, daughter of Louis XI: age 12 when she married Louis XII in 1476 CE
Claude of France, daughter of Louis XII: age 15 when she married Francis I in 1514 CE
Renée of France, daughter of Louis XII: age 18 when she married Ercole II d'Este in 1528 CE
Madeleine of Valois, daughter of Francis I: age 17 when she married James V of Scotland in 1537 CE
Margaret of Valois, daughter of Francis I: age 36 when she married Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy in 1559 CE
Elisabeth of Valois, daughter of Henry II: age 13 when she married Philip II of Spain in 1559 CE
Claude of Valois, daughter of Henry II: age 12 when she married Charles III, Duke of Lorraine in 1559 CE
Margaret of Valois, daughter of Henry II: age 19 when she married Henry IV in 1572 CE
Elisabeth of France, daughter of Henry IV: age 13 when she married Philip IV of Spain in 1615 CE
Christine of France, daughter of Henry IV: age 13 when she married Victor Amadeus I, Duke of Savoy in 1619 CE
Henrietta Maria of France, daughter of Henry IV: age 16 when she married Charles I of England in 1625 CE
Louise Élisabeth of France, daughter of Louis XV: age 12 when she married Philip, Duke of Parma in 1739 CE
Marie-Thérèse, daughter of Louis XVI: age 21 when she married Louis Antoine, Duke of Angoulême in 1799 CE
21 notes
·
View notes
Photo






AU: Edward, prince of Wales, becomes King Edward V of England when his father dies in 30 April 1487. Although nearly reaching majority, the new king has yet to deal with a council mounted by his father in order to govern the realm on his behalf until his 18th birthday.
Led by his paternal uncle, the duke of Gloucester, the council is forced to deal with Edward’s maternal family. There are tensions between Richard of York and Anthony Wideville, but thankfully they are not materialized. Edward proves to be mature for his age and with a sharp wit. The new king is the essential key to keep things at ease, in spite of the Dowager Queen’s suspicious concerning the rule of her former brother-by-law.
Nonetheless, any shadow bet-ween the two parties is solved when Edward himself makes certain when and where he is crowned. A month after he is acknowledged as King of England, he is crowned according to the traditional rites at Westminster Abbey. But nothing is really clear until a dispute is seen between uncle and nephew. Soon, before he reaches 18 himself, Edward secures his power by deposing Richard. The duke is put on household arrest in Middleham Castle.
But Edward is careful by not delegating too much power in his maternal relatives’s hands. He tries to be just and good, hoping to emulate his ancestor and namesake Edward III. That way, Edward V’s reign is marked by domestic security and a strong sense of chivalry. Renaissance court in the models of Italy and Burgundy are thus established. Arts, literature and music flourish. Jousts are popular and never again was seen such glamour being paraded ever since Edward III’s reign. It cannot be even compared to that of his father.
However, there are some rebells to deal with. Edward defeats Henry and Jasper Tudor, but being a merciful king, does not execute neither of them. He instead marries Henry to his sister Elizabeth and Jasper to his maternal aunt, Jacquetta Wideville. He also reinstates Henry Tudor to his earldom of Pembroke. All seems settled then.
In personal affairs, Edward V marries Anne of Brittany as accorded between his father and the duke Franz II. Soon, the king of England is also the duke of Brittany. They share time between the courts of Bretagne and England. The union proves successful and to many is a great surprise that Edward is, unlike his father, faithful to his wife. By her side, they have eight children:
1. Edward, Prince of Wales. [b.1490-d.1550]. Becomes King Edward VI in 1515 and is married to Infanta Katherine of Aragon. They have issue. Edward is succeeded by his son, also named Edward, who becomes Edward VII in 1550.
2. Elizabeth, Queen of France. [b.1491-d.1548]. Marries King François I and has issue.
3. Richard, duke of Brittany. [b. 1493-d.1547]. Marries Claude de France with whom he has issue.
4. Anthony, duke of York. [b. 1495-d.1555]. Marries Lady Margaret of Clarence. Has issue.
5.Mary, Holy Roman Empress and Queen of Spain. [b. 1497-1558]. Marries Karl V, Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain. Has issue.
6. Twins: Margaret and James [b. 1498-1498]. Both died in infancy.
7.Cecily, Queen of Scots. [b. 1500-1547]. Marries James IV and has issue.
8. Joan, Countess of Pembroke. [b. 1502-1553]. Marries Arthur, son of Henry Tudor and Elizabeth of York, Earl and Countess of Pembroke.
#Alternative Universe#Edward V#King Edward V#King Edward V of England#Edward V of England#what if he survived#Anne of Brittany#i do NOT claim to own any of those gifs#found them online with the ONLY purpose to play with history#if however any of these gifs belong to anyone please let me know so I can credit them properly#plantagenet edit#house of york#jamie campbell bower#nikolaj coster waldau#lena headey#as queen anne
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
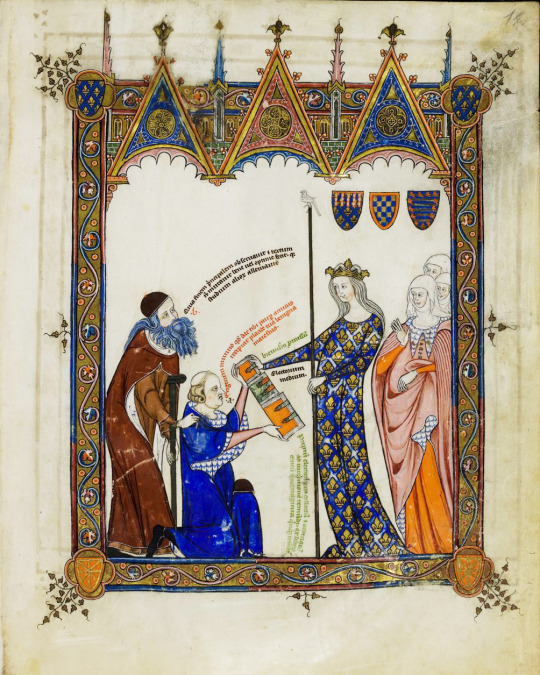

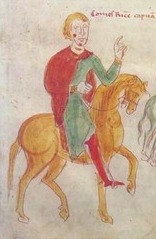
Ramon Llull presenting his book to the Queen of France and Navarre, Joan II of Burgundy Miniature from Breviculum seu electorium parvum, c. 1325
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 3: Bonne of Luxembourg
Bonne of Luxembourg (also known as Jutta/Judith)
Born: 20 May 1315
Died:11 September 1349
Parents: John of Bohemia and Elisabeth of Bohemia
Duchess of Normandy and Countess of Anjou and Maine.
Children: Charles V of France (21 January 1338 – 16 September 1380)
Catherine (1338–1338)
Louis I, Duke of Anjou (23 July 1339 – 20 September 1384)
John, Duke of Berry (30 November 1340 – 15 June 1416)
Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404)
Joan (24 June 1343 – 3 November 1373)
Marie (12 September 1344 – October 1404) - the wife of Robert, Duke of Bar
Agnes (1345–1349)
Margaret (1347–1352)
Isabelle (1 October 1348 – 11 September 1372)
She was the second daughter of John of Bohemia and Elisabeth of Bohemia and the first wife of John II of France.
She was first betrothed to the future King Casimir the Great of Poland but the arrangement failed as he married someone else. She was then betrothed to Henry of Bar, an arrangement that also failed. She then married John, Duke of Normandy.
The wedding took place at the Collegiate Church of Notre-Dame, Melun on 28 July 1332. She was 17 while her husband was 13. Her name was changed to Bonne (French version) or Bona (Latin version).
She is considered a patron of the arts, one of her favorites was the composer Guillaume de Machaut.
She died of the bubonic plague in Maubuisson on 11 September 1349, aged 34.
1 note
·
View note
Photo






Favorite History Books || Conquest: The English Kingdom of France in the Hundred Years’ War by Juliet Barker ★★★☆☆
The Hundred Years’ War is defined in the popular imagination by its great battles. The roll-call of spectacular English victories over the French is a source of literary celebration and national pride and even those who know little or nothing about the period or context can usually recall the name of at least one of the most famous trilogy – Crécy, Poitiers, Agincourt. It is curious therefore that an even greater achievement has been virtually wiped from folk memory. Few people today know that for more than thirty years there was an English kingdom of France. Quite distinct from English Gascony, which had belonged to the kings of England by right of inheritance since the marriage of Eleanor of Aquitaine and Henry II in 1152, the English kingdom was acquired by conquest and was the creation of Henry V.
When he landed a great English army on the beaches of Normandy at the beginning of August 1417 Henry opened up an entirely new phase in the Hundred Years’ War. Never before had an English monarch invaded France with such ambitious plans: nothing less than the wholesale conquest and permanent annexation of Normandy. Yet, after he had achieved this in the space of just two years, the opportunity presented itself to secure a prize to which even his most illustrious ancestor, Edward III, could only aspire: the crown of France itself. On 21 May 1420 Charles VI of France formally betrothed Henry V of England to his daughter and recognised him as his heir and regent of France. In doing so he disinherited his own son and committed both countries to decades of warfare.
By a cruel twist of fate, Henry died just seven weeks before his father-in-law, so it was not the victor of Agincourt but his nine-month- old son, another and much lesser Henry, who became the first (and last) English king of France. Until he came of age and could rule in person, the task of defending his French realm fell to his father’s right-hand men. First and foremost among these was his brother John, duke of Bedford, a committed Francophile who made his home in France and for thirteen years ruled as regent on his nephew’s behalf. His determination to do justice to all, to rise above political faction and, most important of all, to protect the realm by a slow but steady expansion of its borders meant that, at its height, the English kingdom of France extended from the coast of Normandy almost down to the banks of the Loire: to the west it was bounded by Brittany, to the east by the Burgundian dominions, both of which, nominally at least, owed allegiance to the boy-king.
Bedford’s great victory at Verneuil in 1424 seemed to have secured the future of the realm – until the unexpected arrival on the scene of an illiterate seventeen-year-old village girl from the marches of Lorraine who believed she was sent by God to raise the English siege of Orléans, crown the disinherited dauphin as true king of France and drive the English out of his realm. The story of Jehanne d’Arc – better known to the English-speaking world today as Joan of Arc – is perhaps the most enduringly famous of the entire Hundred Years’ War. The fact that, against all the odds, she achieved two of her three aims in her brief career has raised her to iconic status, but it is the manner of her death, burned at the stake in Rouen by the English administration, which has brought her the crown of martyrdom and literally made her a saint in the Roman Catholic calendar. The terrible irony is that Jehanne’s dazzling achievements obscure the fact that they were of little long-term consequence: a ten-year-old Henry VI was crowned king of France just six months after her death and his kingdom endured for another twenty years.
Of far more consequence to the prosperity and longevity of the English kingdom of France was the defection of the ally who had made its existence possible. Philippe, duke of Burgundy, made his peace with Charles VII in 1435, just days after the death of Bedford. In the wake of the Treaty of Arras much of the English kingdom, including its capital, Paris, was swept away by the reunited and resurgent French but the reconquest stalled in the face of dogged resistance from Normandy and brilliant tactical military leadership from the “English Achilles”, John Talbot. For almost a decade it would be a war of attrition between the two ancient enemies, gains by each side compensating for their losses elsewhere, but no decisive actions tipping the balance of power.
Nevertheless, the years of unremitting warfare had their cost, imposing an unsustainable financial burden on England and Normandy, draining both realms of valuable resources, including men of the calibre of the earls of Salisbury and Arundel, who were both killed in action, and devastating the countryside and economy of northern France. The demands for peace became more urgent and increasingly voluble, though it was not until Henry VI came of age that anyone in England had the undisputed authority to make the concessions necessary to achieve a settlement.
The Truce of Tours, purchased by Henry’s marriage to Marguerite of Anjou, the infamous ‘she-wolf of France’, proved to be a disaster for the English. In his determination to procure peace at any price, the foolish young king secretly agreed to give up a substantial part of his inheritance: the county of Maine would return to French hands without compensation for its English settlers who had spent their lives in its defence.
Worse was to follow, for while the English took advantage of the truce to demobilise and cut taxes, Charles VII used it to rearm and reorganise his armies so that, when he found the excuse he needed to declare that the English had broken its terms, he was ready and able to invade with such overwhelming force that he swept all before him. The English kingdom of France which, against the odds, had survived for three decades, was crushed in just twelve months.
#historyedit#litedit#hundred years' war#medieval#english history#french history#european history#history#history books#nanshe's graphics
29 notes
·
View notes