#Machine learning (ML) for AI
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
418 notes
·
View notes
Text
Uuh… so I heard tumblr doesn’t like AI generated art so I made my own, enjoy!

(this is in fact a judgement free zone btw)
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Quantum Computing 101: What are Qubits?
Curious about quantum computing? Let's break it down!

🔍 What’s a Qubit? A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information. Unlike classical bits (0 or 1), qubits can be 0, 1, or both at the same time thanks to a phenomenon called superposition.
✨ Why Is This Cool?
Superposition: Allows qubits to explore many possibilities simultaneously.
Entanglement: Qubits can be linked, so the state of one affects the state of another, no matter the distance.
⚙️ In Action: This means quantum computers can tackle complex problems faster by processing a huge number of possibilities at once!
Follow for more insights on the future of tech! 🚀✨
Instagram: cs_learninghub YT: CS Learning Hub
#quantum computing#quantum#science#physics#computer science#bits#tumblr#aesthetic#studyblr#study#study motivation#qubits#machine learning#artificial intelligence#ai#ml#cs#learn#study blog
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
they're shaking hands honest
(ai/machine learning generated animations)
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
the good thing is that I think I finally found the final focus for my thesis. the bad thing is that it’s 2AM and I got so much adrenaline from that that I will never sleep
#also I still. somehow. after fighting it at every turn! managed to make it be partly about machine learning hOw#there’s just no escape from AI/ML/DL is there (I tried to stay away from that bc ohmg it’s everywhere and I’ve been getting increasingly#more annoyed every time I see the words AI somewhere (also often used so wildly incorrectly bc of it’s a trend rn))#but yeah it’s alright at least that’s not the sole focus#ba thesis struggle diary#2024#march 2024
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Truth speaking on the corporate obsession with AI
Hilarious. Something tells me this person's on the hellsite(affectionate)
#ai#corporate bs#late stage capitalism#funny#truth#artificial intelligence#ml#machine learning#data science#data scientist#programming#scientific programming
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
PGDM Specialization in AI & ML: Preparing for the Future of Business and Technology

#PG Diploma in AI and ML#Artificial Intelligence#Machine Learning#AI and ML in Business#AI and ML Career Opportunities#Career in Artificial Intelligence#Business and Technology#PGDM in AI and ML
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Comprehensive Guide to Web Development, Data Management, and More
Introduction
Everything today is technology driven in this digital world. There's a lot happening behind the scenes when you use your favorite apps, go to websites, and do other things with all of those zeroes and ones — or binary data. In this blog, I will be explaining what all these terminologies really means and other basics of web development, data management etc. We will be discussing them in the simplest way so that this becomes easy to understand for beginners or people who are even remotely interested about technology. JOIN US
What is Web Development?
Web development refers to the work and process of developing a website or web application that can run in a web browser. From laying out individual web page designs before we ever start coding, to how the layout will be implemented through HTML/CSS. There are two major fields of web development — front-end and back-end.
Front-End Development
Front-end development, also known as client-side development, is the part of web development that deals with what users see and interact with on their screens. It involves using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the visual elements of a website, such as buttons, forms, and images. JOIN US
HTML (HyperText Markup Language):
HTML is the foundation of all website, it helps one to organize their content on web platform. It provides the default style to basic elements such as headings, paragraphs and links.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets):
styles and formats HTML elements. It makes an attractive and user-friendly look of webpage as it controls the colors, fonts, layout.
JavaScript :
A language for adding interactivity to a website Users interact with items, like clicking a button to send in a form or viewing images within the slideshow. JOIN US
Back-End Development
The difference while front-end development is all about what the user sees, back end involves everything that happens behind. The back-end consists of a server, database and application logic that runs on the web.
Server:
A server is a computer that holds website files and provides them to the user browser when they request it. Server-Side: These are populated by back-end developers who build and maintain servers using languages like Python, PHP or Ruby.
Database:
The place where a website keeps its data, from user details to content and settings The database is maintained with services like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. JOIN US
Application Logic —
the code that links front-end and back-end It takes user input, gets data from the database and returns right informations to front-end area.

Why Proper Data Management is Absolutely Critical
Data management — Besides web development this is the most important a part of our Digital World. What Is Data Management? It includes practices, policies and procedures that are used to collect store secure data in controlled way.
Data Storage –
data after being collected needs to be stored securely such data can be stored in relational databases or cloud storage solutions. The most important aspect here is that the data should never be accessed by an unauthorized source or breached. JOIN US
Data processing:
Right from storing the data, with Big Data you further move on to process it in order to make sense out of hordes of raw information. This includes cleansing the data (removing errors or redundancies), finding patterns among it, and producing ideas that could be useful for decision-making.
Data Security:
Another important part of data management is the security of it. It refers to defending data against unauthorized access, breaches or other potential vulnerabilities. You can do this with some basic security methods, mostly encryption and access controls as well as regular auditing of your systems.
Other Critical Tech Landmarks
There are a lot of disciplines in the tech world that go beyond web development and data management. Here are a few of them:
Cloud Computing
Leading by example, AWS had established cloud computing as the on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications via web services/Internet over a decade considering all layers to make it easy from servers up to top most layer. This will enable organizations to consume technology resources in the form of pay-as-you-go model without having to purchase, own and feed that infrastructure. JOIN US
Cloud Computing Advantages:
Main advantages are cost savings, scalability, flexibility and disaster recovery. Resources can be scaled based on usage, which means companies only pay for what they are using and have the data backed up in case of an emergency.
Examples of Cloud Services:
Few popular cloud services are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These provide a plethora of services that helps to Develop and Manage App, Store Data etc.
Cybersecurity
As the world continues to rely more heavily on digital technologies, cybersecurity has never been a bigger issue. Protecting computer systems, networks and data from cyber attacks is called Cyber security.
Phishing attacks, Malware, Ransomware and Data breaches:
This is common cybersecurity threats. These threats can bear substantial ramifications, from financial damages to reputation harm for any corporation.
Cybersecurity Best Practices:
In order to safeguard against cybersecurity threats, it is necessary to follow best-practices including using strong passwords and two-factor authorization, updating software as required, training employees on security risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) represent the fastest-growing fields of creating systems that learn from data, identifying patterns in them. These are applied to several use-cases like self driving cars, personalization in Netflix.
AI vs ML —
AI is the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way we would consider “smart”. Machine learning is a type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. JOIN US
Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: some common applications include Image recognition, Speech to text, Natural language processing, Predictive analytics Robotics.
Web Development meets Data Management etc.
We need so many things like web development, data management and cloud computing plus cybersecurity etc.. but some of them are most important aspects i.e. AI/ML yet more fascinating is where these fields converge or play off each other.
Web Development and Data Management
Web Development and Data Management goes hand in hand. The large number of websites and web-based applications in the world generate enormous amounts of data — from user interactions, to transaction records. Being able to manage this data is key in providing a fantastic user experience and enabling you to make decisions based on the right kind of information.
E.g. E-commerce Website, products data need to be saved on server also customers data should save in a database loosely coupled with orders and payments. This data is necessary for customization of the shopping experience as well as inventory management and fraud prevention.
Cloud Computing and Web Development
The development of the web has been revolutionized by cloud computing which gives developers a way to allocate, deploy and scale applications more or less without service friction. Developers now can host applications and data in cloud services instead of investing for physical servers.
E.g. A start-up company can use cloud services to roll out the web application globally in order for all users worldwide could browse it without waiting due unavailability of geolocation prohibited access.
The Future of Cybersecurity and Data Management
Which makes Cybersecurity a very important part of the Data management. The more data collected and stored by an organization, the greater a target it becomes for cyber threats. It is important to secure this data using robust cybersecurity measures, so that sensitive information remains intact and customer trust does not weaken. JOIN US
Ex: A healthcare provider would have to protect patient data in order to be compliant with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) that is also responsible for ensuring a degree of confidentiality between a provider and their patients.
Conclusion
Well, in a nutshell web-developer or Data manager etc are some of the integral parts for digital world.
As a Business Owner, Tech Enthusiast or even if you are just planning to make your Career in tech — it is important that you understand these. With the progress of technology never slowing down, these intersections are perhaps only going to come together more strongly and develop into cornerstones that define how we live in a digital world tomorrow.
With the fundamental knowledge of web development, data management, automation and ML you will manage to catch up with digital movements. Whether you have a site to build, ideas data to manage or simply interested in what’s hot these days, skills and knowledge around the above will stand good for changing tech world. JOIN US
#Technology#Web Development#Front-End Development#Back-End Development#HTML#CSS#JavaScript#Data Management#Data Security#Cloud Computing#AWS (Amazon Web Services)#Cybersecurity#Artificial Intelligence (AI)#Machine Learning (ML)#Digital World#Tech Trends#IT Basics#Beginners Guide#Web Development Basics#Tech Enthusiast#Tech Career#america
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
AKA: How to cut through the AI news reporting PR BS

Link: https://www.cjr.org/analysis/how-to-report-better-on-artificial-intelligence.php This is an excellent article for journalists, and the public alike, to better scrutinise the claims of large AI companies and their models. There’s an awful lot of fawning, non-critical, reporting on this topic and the moment and it’s really pissing me off. We need to hold companies accountable so that we aren’t suckered into making bad decisions based on their public relations department’s claims. 100% a lot of AI progress is highly impressive, and deserves a lot of attention and praise, but we need journalists to cut through to the cold, hard, facts. Hopefully this will help you personally when reading articles and determining whether they’re fan-wank or critical reporting.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
The surprising truth about data-driven dictatorships

Here’s the “dictator’s dilemma”: they want to block their country’s frustrated elites from mobilizing against them, so they censor public communications; but they also want to know what their people truly believe, so they can head off simmering resentments before they boil over into regime-toppling revolutions.
These two strategies are in tension: the more you censor, the less you know about the true feelings of your citizens and the easier it will be to miss serious problems until they spill over into the streets (think: the fall of the Berlin Wall or Tunisia before the Arab Spring). Dictators try to square this circle with things like private opinion polling or petition systems, but these capture a small slice of the potentially destabiziling moods circulating in the body politic.
Enter AI: back in 2018, Yuval Harari proposed that AI would supercharge dictatorships by mining and summarizing the public mood — as captured on social media — allowing dictators to tack into serious discontent and diffuse it before it erupted into unequenchable wildfire:
https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2018/10/yuval-noah-harari-technology-tyranny/568330/
Harari wrote that “the desire to concentrate all information and power in one place may become [dictators] decisive advantage in the 21st century.” But other political scientists sharply disagreed. Last year, Henry Farrell, Jeremy Wallace and Abraham Newman published a thoroughgoing rebuttal to Harari in Foreign Affairs:
https://www.foreignaffairs.com/world/spirals-delusion-artificial-intelligence-decision-making
They argued that — like everyone who gets excited about AI, only to have their hopes dashed — dictators seeking to use AI to understand the public mood would run into serious training data bias problems. After all, people living under dictatorships know that spouting off about their discontent and desire for change is a risky business, so they will self-censor on social media. That’s true even if a person isn’t afraid of retaliation: if you know that using certain words or phrases in a post will get it autoblocked by a censorbot, what’s the point of trying to use those words?
The phrase “Garbage In, Garbage Out” dates back to 1957. That’s how long we’ve known that a computer that operates on bad data will barf up bad conclusions. But this is a very inconvenient truth for AI weirdos: having given up on manually assembling training data based on careful human judgment with multiple review steps, the AI industry “pivoted” to mass ingestion of scraped data from the whole internet.
But adding more unreliable data to an unreliable dataset doesn’t improve its reliability. GIGO is the iron law of computing, and you can’t repeal it by shoveling more garbage into the top of the training funnel:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/05/29/garbage-in-garbage-out-machine-learning-has-not-repealed-the-iron-law-of-computer-science/
When it comes to “AI” that’s used for decision support — that is, when an algorithm tells humans what to do and they do it — then you get something worse than Garbage In, Garbage Out — you get Garbage In, Garbage Out, Garbage Back In Again. That’s when the AI spits out something wrong, and then another AI sucks up that wrong conclusion and uses it to generate more conclusions.
To see this in action, consider the deeply flawed predictive policing systems that cities around the world rely on. These systems suck up crime data from the cops, then predict where crime is going to be, and send cops to those “hotspots” to do things like throw Black kids up against a wall and make them turn out their pockets, or pull over drivers and search their cars after pretending to have smelled cannabis.
The problem here is that “crime the police detected” isn’t the same as “crime.” You only find crime where you look for it. For example, there are far more incidents of domestic abuse reported in apartment buildings than in fully detached homes. That’s not because apartment dwellers are more likely to be wife-beaters: it’s because domestic abuse is most often reported by a neighbor who hears it through the walls.
So if your cops practice racially biased policing (I know, this is hard to imagine, but stay with me /s), then the crime they detect will already be a function of bias. If you only ever throw Black kids up against a wall and turn out their pockets, then every knife and dime-bag you find in someone’s pockets will come from some Black kid the cops decided to harass.
That’s life without AI. But now let’s throw in predictive policing: feed your “knives found in pockets” data to an algorithm and ask it to predict where there are more knives in pockets, and it will send you back to that Black neighborhood and tell you do throw even more Black kids up against a wall and search their pockets. The more you do this, the more knives you’ll find, and the more you’ll go back and do it again.
This is what Patrick Ball from the Human Rights Data Analysis Group calls “empiricism washing”: take a biased procedure and feed it to an algorithm, and then you get to go and do more biased procedures, and whenever anyone accuses you of bias, you can insist that you’re just following an empirical conclusion of a neutral algorithm, because “math can’t be racist.”
HRDAG has done excellent work on this, finding a natural experiment that makes the problem of GIGOGBI crystal clear. The National Survey On Drug Use and Health produces the gold standard snapshot of drug use in America. Kristian Lum and William Isaac took Oakland’s drug arrest data from 2010 and asked Predpol, a leading predictive policing product, to predict where Oakland’s 2011 drug use would take place.
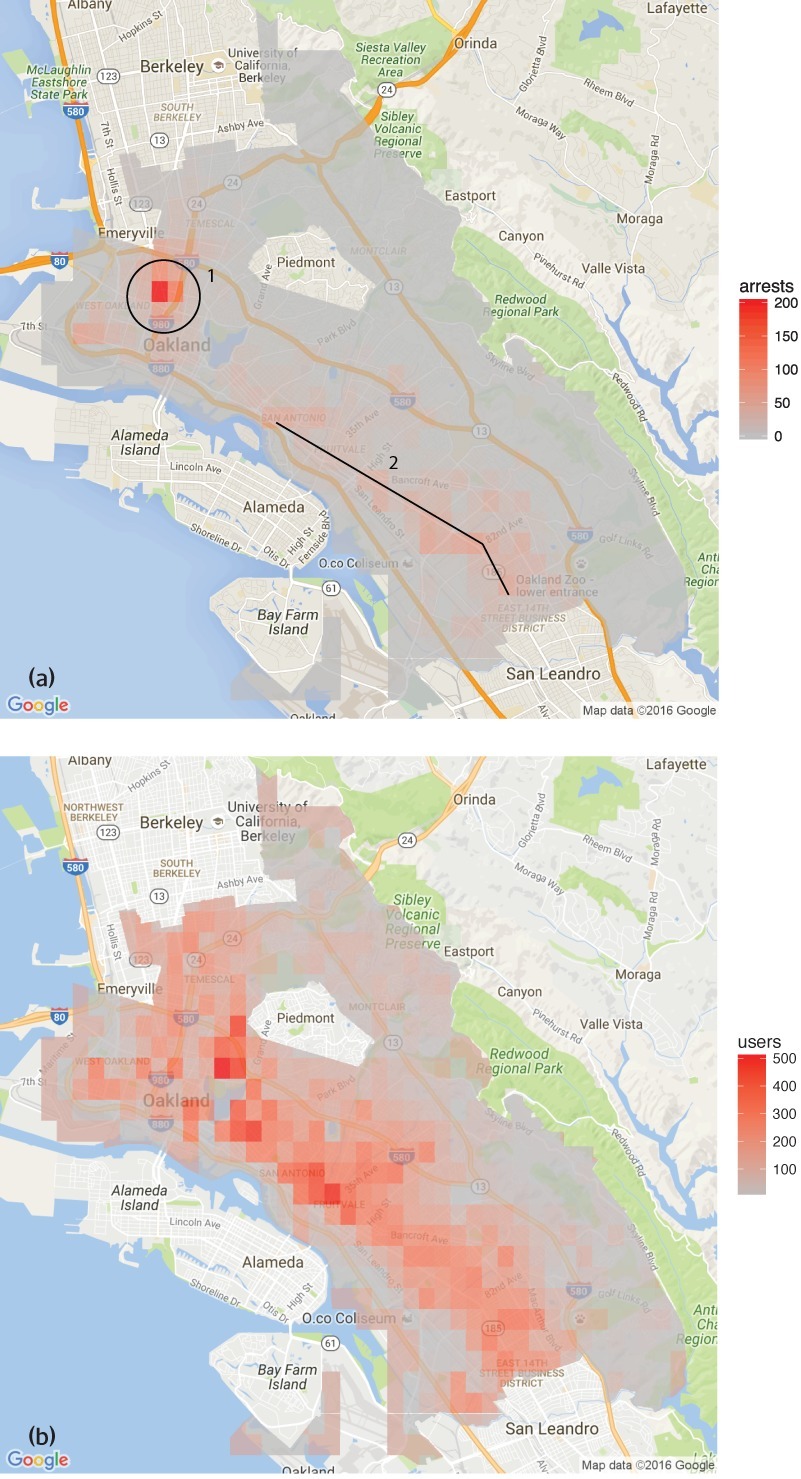
[Image ID: (a) Number of drug arrests made by Oakland police department, 2010. (1) West Oakland, (2) International Boulevard. (b) Estimated number of drug users, based on 2011 National Survey on Drug Use and Health]
Then, they compared those predictions to the outcomes of the 2011 survey, which shows where actual drug use took place. The two maps couldn’t be more different:
https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1740-9713.2016.00960.x
Predpol told cops to go and look for drug use in a predominantly Black, working class neighborhood. Meanwhile the NSDUH survey showed the actual drug use took place all over Oakland, with a higher concentration in the Berkeley-neighboring student neighborhood.
What’s even more vivid is what happens when you simulate running Predpol on the new arrest data that would be generated by cops following its recommendations. If the cops went to that Black neighborhood and found more drugs there and told Predpol about it, the recommendation gets stronger and more confident.
In other words, GIGOGBI is a system for concentrating bias. Even trace amounts of bias in the original training data get refined and magnified when they are output though a decision support system that directs humans to go an act on that output. Algorithms are to bias what centrifuges are to radioactive ore: a way to turn minute amounts of bias into pluripotent, indestructible toxic waste.
There’s a great name for an AI that’s trained on an AI’s output, courtesy of Jathan Sadowski: “Habsburg AI.”
And that brings me back to the Dictator’s Dilemma. If your citizens are self-censoring in order to avoid retaliation or algorithmic shadowbanning, then the AI you train on their posts in order to find out what they’re really thinking will steer you in the opposite direction, so you make bad policies that make people angrier and destabilize things more.
Or at least, that was Farrell(et al)’s theory. And for many years, that’s where the debate over AI and dictatorship has stalled: theory vs theory. But now, there’s some empirical data on this, thanks to the “The Digital Dictator’s Dilemma,” a new paper from UCSD PhD candidate Eddie Yang:
https://www.eddieyang.net/research/DDD.pdf
Yang figured out a way to test these dueling hypotheses. He got 10 million Chinese social media posts from the start of the pandemic, before companies like Weibo were required to censor certain pandemic-related posts as politically sensitive. Yang treats these posts as a robust snapshot of public opinion: because there was no censorship of pandemic-related chatter, Chinese users were free to post anything they wanted without having to self-censor for fear of retaliation or deletion.
Next, Yang acquired the censorship model used by a real Chinese social media company to decide which posts should be blocked. Using this, he was able to determine which of the posts in the original set would be censored today in China.
That means that Yang knows that the “real” sentiment in the Chinese social media snapshot is, and what Chinese authorities would believe it to be if Chinese users were self-censoring all the posts that would be flagged by censorware today.
From here, Yang was able to play with the knobs, and determine how “preference-falsification” (when users lie about their feelings) and self-censorship would give a dictatorship a misleading view of public sentiment. What he finds is that the more repressive a regime is — the more people are incentivized to falsify or censor their views — the worse the system gets at uncovering the true public mood.
What’s more, adding additional (bad) data to the system doesn’t fix this “missing data” problem. GIGO remains an iron law of computing in this context, too.
But it gets better (or worse, I guess): Yang models a “crisis” scenario in which users stop self-censoring and start articulating their true views (because they’ve run out of fucks to give). This is the most dangerous moment for a dictator, and depending on the dictatorship handles it, they either get another decade or rule, or they wake up with guillotines on their lawns.
But “crisis” is where AI performs the worst. Trained on the “status quo” data where users are continuously self-censoring and preference-falsifying, AI has no clue how to handle the unvarnished truth. Both its recommendations about what to censor and its summaries of public sentiment are the least accurate when crisis erupts.
But here’s an interesting wrinkle: Yang scraped a bunch of Chinese users’ posts from Twitter — which the Chinese government doesn’t get to censor (yet) or spy on (yet) — and fed them to the model. He hypothesized that when Chinese users post to American social media, they don’t self-censor or preference-falsify, so this data should help the model improve its accuracy.
He was right — the model got significantly better once it ingested data from Twitter than when it was working solely from Weibo posts. And Yang notes that dictatorships all over the world are widely understood to be scraping western/northern social media.
But even though Twitter data improved the model’s accuracy, it was still wildly inaccurate, compared to the same model trained on a full set of un-self-censored, un-falsified data. GIGO is not an option, it’s the law (of computing).
Writing about the study on Crooked Timber, Farrell notes that as the world fills up with “garbage and noise” (he invokes Philip K Dick’s delighted coinage “gubbish”), “approximately correct knowledge becomes the scarce and valuable resource.”
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/07/25/51610/
This “probably approximately correct knowledge” comes from humans, not LLMs or AI, and so “the social applications of machine learning in non-authoritarian societies are just as parasitic on these forms of human knowledge production as authoritarian governments.”

The Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers’ Workshop summer fundraiser is almost over! I am an alum, instructor and volunteer board member for this nonprofit workshop whose alums include Octavia Butler, Kim Stanley Robinson, Bruce Sterling, Nalo Hopkinson, Kameron Hurley, Nnedi Okorafor, Lucius Shepard, and Ted Chiang! Your donations will help us subsidize tuition for students, making Clarion — and sf/f — more accessible for all kinds of writers.

Libro.fm is the indie-bookstore-friendly, DRM-free audiobook alternative to Audible, the Amazon-owned monopolist that locks every book you buy to Amazon forever. When you buy a book on Libro, they share some of the purchase price with a local indie bookstore of your choosing (Libro is the best partner I have in selling my own DRM-free audiobooks!). As of today, Libro is even better, because it’s available in five new territories and currencies: Canada, the UK, the EU, Australia and New Zealand!

[Image ID: An altered image of the Nuremberg rally, with ranked lines of soldiers facing a towering figure in a many-ribboned soldier's coat. He wears a high-peaked cap with a microchip in place of insignia. His head has been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.' The sky behind him is filled with a 'code waterfall' from 'The Matrix.']

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Raimond Spekking (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acer_Extensa_5220_-_Columbia_MB_06236-1N_-_Intel_Celeron_M_530_-_SLA2G_-_in_Socket_479-5029.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
—
Russian Airborne Troops (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vladislav_Achalov_at_the_Airborne_Troops_Day_in_Moscow_%E2%80%93_August_2,_2008.jpg
“Soldiers of Russia” Cultural Center (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Col._Leonid_Khabarov_in_an_everyday_service_uniform.JPG
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#habsburg ai#self censorship#henry farrell#digital dictatorships#machine learning#dictator's dilemma#eddie yang#preference falsification#political science#training bias#scholarship#spirals of delusion#algorithmic bias#ml#Fully automated data driven authoritarianism#authoritarianism#gigo#garbage in garbage out garbage back in#gigogbi#yuval noah harari#gubbish#pkd#philip k dick#phildickian
833 notes
·
View notes
Text
Boost E-commerce in Saudi Arabia with ML-Powered Apps

In today's digital era, the e-commerce industry in Saudi Arabia is rapidly expanding, fueled by increasing internet penetration and a tech-savvy population. To stay competitive, businesses are turning to advanced technologies, particularly Machine Learning (ML), to enhance user experiences, optimize operations, and drive growth. This article explores how ML is transforming the e-commerce landscape in Saudi Arabia and how businesses can leverage this technology to boost their success.
The Current E-commerce Landscape in Saudi Arabia
The e-commerce market in Saudi Arabia has seen exponential growth over the past few years. With a young population, widespread smartphone usage, and supportive government policies, the Kingdom is poised to become a leading e-commerce hub in the Middle East. Key players like Noon, Souq, and Jarir have set the stage, but the market is ripe for innovation, especially with the integration of Machine Learning.
The Role of Machine Learning in E-commerce
Machine Learning, a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI), involves the use of algorithms to analyze data, learn from it, and make informed decisions. In e-commerce, ML enhances various aspects, from personalization to fraud detection. Machine Learning’s ability to analyze large datasets and identify trends is crucial for businesses aiming to stay ahead in a competitive market.
Personalized Shopping Experiences
Personalization is crucial in today’s e-commerce environment. ML algorithms analyze user data, such as browsing history and purchase behavior, to recommend products that align with individual preferences. This not only elevates the customer experience but also drives higher conversion rates. For example, platforms that leverage ML for personalization have seen significant boosts in sales, as users are more likely to purchase items that resonate with their interests.
Optimizing Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is critical for e-commerce success. ML-driven predictive analytics can forecast demand with high accuracy, helping businesses maintain optimal inventory levels. This minimizes the chances of overstocking or running out of products, ensuring timely availability for customers. E-commerce giants like Amazon have successfully implemented ML to streamline their inventory management processes, setting a benchmark for others to follow.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Price is a major factor influencing consumer decisions. Machine Learning enables real-time dynamic pricing by assessing market trends, competitor rates, and customer demand. This allows businesses to adjust their prices to maximize revenue while remaining competitive. Dynamic pricing, powered by ML, has proven effective in attracting price-sensitive customers and increasing overall profitability.
Enhanced Customer Support
Customer support is another area where ML shines. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle a large volume of customer inquiries, providing instant responses and resolving issues efficiently. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces the operational costs associated with maintaining a large support team. E-commerce businesses in Saudi Arabia can greatly benefit from incorporating ML into their customer service strategies.
Fraud Detection and Security
With the rise of online transactions, ensuring the security of customer data and payments is paramount. ML algorithms can detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns and identifying anomalies. By implementing ML-driven security measures, e-commerce businesses can protect their customers and build trust, which is essential for long-term success.
Improving Marketing Campaigns
Effective marketing is key to driving e-commerce success. ML can analyze customer data to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific audiences. It enhances the impact of marketing efforts, leading to improved customer engagement and higher conversion rates. Successful e-commerce platforms use ML to fine-tune their marketing strategies, ensuring that their messages reach the right people at the right time.
Case Study: Successful E-commerce Companies in Saudi Arabia Using ML
Several e-commerce companies in Saudi Arabia have already begun leveraging ML to drive growth. For example, Noon uses ML to personalize the shopping experience and optimize its supply chain, leading to increased customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. These companies serve as examples of how ML can be a game-changer in the competitive e-commerce market.
Challenges of Implementing Machine Learning in E-commerce
While the benefits of ML are clear, implementing this technology in e-commerce is not without challenges. Technical hurdles, such as integrating ML with existing systems, can be daunting. Additionally, there are concerns about data privacy, particularly in handling sensitive customer information. Businesses must address these challenges to fully harness the power of ML.
Future Trends in Machine Learning and E-commerce
As ML continues to evolve, new trends are emerging that will shape the future of e-commerce. For instance, the integration of ML with augmented reality (AR) offers exciting possibilities, such as virtual try-ons for products. Businesses that stay ahead of these trends will be well-positioned to lead the market in the coming years.
Influence of Machine Learning on Consumer Behavior in Saudi Arabia
ML is already influencing consumer behavior in Saudi Arabia, with personalized experiences leading to increased customer loyalty. As more businesses adopt ML, consumers can expect even more tailored shopping experiences, further enhancing their satisfaction and engagement.
Government Support and Regulations
The Saudi government is proactively encouraging the integration of cutting-edge technologies, including ML, within the e-commerce industry. Through initiatives like Vision 2030, the government aims to transform the Kingdom into a global tech hub. However, businesses must also navigate regulations related to data privacy and AI to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Machine Learning is revolutionizing e-commerce in Saudi Arabia, offering businesses new ways to enhance user experiences, optimize operations, and drive growth. By embracing ML, e-commerce companies can not only stay competitive but also set new standards in the industry. The future of e-commerce in Saudi Arabia is bright, and Machine Learning will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping its success.
FAQs
How does Machine Learning contribute to the e-commerce sector? Machine Learning enhances e-commerce by improving personalization, optimizing inventory, enabling dynamic pricing, and enhancing security.
How can Machine Learning improve customer experiences in e-commerce? ML analyzes user data to provide personalized recommendations, faster customer support, and tailored marketing campaigns, improving overall satisfaction.
What are the challenges of integrating ML in e-commerce? Challenges include technical integration, data privacy concerns, and the need for skilled professionals to manage ML systems effectively.
Which Saudi e-commerce companies are successfully using ML? Companies like Noon and Souq are leveraging ML for personalized shopping experiences, inventory management, and customer support.
What is the future of e-commerce with ML in Saudi Arabia? The future looks promising with trends like ML-driven AR experiences and more personalized
#machine learning e-commerce#Saudi Arabia tech#ML-powered apps#e-commerce growth#AI in retail#customer experience Saudi Arabia#digital transformation Saudi#ML app benefits#AI-driven marketing#predictive analytics retail#Saudi digital economy#e-commerce innovation#smart retail solutions#AI tech adoption#machine learning in business
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Statistical Tools
Daily writing promptWhat was the last thing you searched for online? Why were you looking for it?View all responses Checking which has been my most recent search on Google, I found that I asked for papers, published in the last 5 years, that used a Montecarlo method to check the reliability of a mathematical method to calculate a team’s efficacy. Photo by Andrea Piacquadio on Pexels.com I was…

View On WordPress
#Adjusted R-Squared#Agile#AI#AIC#Akaike Information Criterion#Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)#Algorithm#algorithm design#Analysis#Artificial Intelligence#Bayesian Information Criterion#Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC)#BIC#Business#Coaching#consulting#Cross-Validation#dailyprompt#dailyprompt-2043#Goodness of Fit#Hypothesis Testing#inputs#Machine Learning#Mathematical Algorithm#Mathematics#Mean Squared Error#ML#Model Selection#Monte Carlo#Monte Carlo Methods
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Definition: AI refers to the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way that we would consider “smart.” It encompasses various technologies that allow machines to mimic human intelligence.
Scope: Includes machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, and more.
Machine Learning (ML):
Definition: ML is a subset of AI that focuses on the ability of machines to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
Scope: Primarily involves algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to perform specific tasks without using explicit instructions.
#coding#programming#tech updates#cool tech#software#developer#tech#artificial intelligence#machine learning#ai/ml
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
𝗥𝗲𝘃𝗼𝗹𝘂𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝗶𝘇𝗲 𝗬𝗼𝘂𝗿 𝗠𝗮𝗻𝘂𝗳𝗮𝗰𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝘄𝗶𝘁𝗵 𝗔𝗜-𝗱𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗻 𝗘𝗥𝗣 𝗦𝗼𝗹𝘂𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀!
Discover how integrating Artificial Intelligence with Enterprise Resource Planning can transform your manufacturing operations. Check out our latest blog post to explore the future of smart manufacturing:
Read more about the next wave of intelligent ERP systems and stay ahead in the digital transformation race!
https://www.codetrade.io/blog/ai-driven-erp-solutions-for-the-manufacturing-industry/
#artificial intelligence#machine learning#erp solution#manufacturing industry#ERP in AI#enterprise resource planning#intelligent ERP system#AI ML#AI-driven ERP solutions
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
In this blog, we discuss how Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) developed mobile app can reshaping homeowner associations in the coming decade of real estate.
#Artificial Intelligence#Machine Learning#AI#ML#Real Estate#Real Estate Sector#Real Estate Industry#Homeowner Associations#HOA Mobile App#HOA App Development#HOA Mobile App Development#Arizona#USA#SkyTech Mobile
3 notes
·
View notes
