#Matilda of Flanders
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text






First look at the upcoming series “King and Conqueror” which will be about the invasion of William of Normandy and the subsequent conquest of England. Coming in 2025 on BBC, with Nikolaj Coster-Waldau and Clémence Poésy as William I and Matilda of Flanders.
#king and conqueror#bbc#William I of Normandy#Matilda of Flanders#William I of England#William the Conqueror#House of Normandy#nikolaj coster waldau#clémence poésy
310 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alfred Guillard, La Reine Mathilde travaillant à la Telle du Conquest, 1848. Museum of Art and History Baron Gérard, Bayeux, France.
#alfred guillard#matilda of flanders#art#paintings#women in history#medieval women#history painting#*#i know this very much Did Not Happen but its a pretty painting i like the details of the tapestry. happy coronation day matilda
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
who is matilda of flanders and also where is flanders
Holy shit someone actually asked me about Matilda of Flanders
Flanders is a region in modern day Belgium
Matilda of Flanders was the wife of William the conqueror aka William the bastard aka the first Norman king of England which makes Matilda the first Norman-Flemish queen of England + the Duchess of Flanders.
Matilda was born into a pretty prestigious family around 1031-1032. Her father was Count Baldwin V of Flanders and Adéle of France (who was the daughter of Robert II of France). So she’s of pretty high birth, especially comparing her to her husband who was a bastard. She was also considered to be both intelligent and beautiful.
There’s also a pretty dramatic tale about how she was wooed by William. One version of the story goes like this: William proposes to Matilda around 1051 to form an alliance but Matilda refuses because he is of lower birth. This enrages William so much that he pursues her all the way to Bruges and, when she’s leaving church, grabs her by her braids and throws her down into the mud (some versions says that he beat her in her own home). After recovering from this attack, she decided that she was going to marry William and nobody else.
So uh, really lovely and romantic.
But in reality, she and William had a pretty good marriage and they both genuinely liked each other. When they asked the pope to approve of their marriage, the pope refused on the grounds of consanguinity as they were 3rd cousins once removed but they decided to ignore the pope and got married anyways around 1051-1052 (and both got excommunicated from the church for a while until 1059). She was 19-20 and he was 23-24. (There’s this belief that, in the medieval era, women were married extremely young, and while there are some exceptions, it was not the case for all marriages.)
Matilda had 2 kids by the time William invaded England for the crown in the 1060s. Matilda was extremely important as she acted as regent in Williams absence from the English court and was William’s regent in Normandy during his invasion of England. She held this role 6 times over the course of 10 years. She was a pretty competent ruler as well. She was also interested in the education of her 10 children who were well educated for the time, even in comparison to other royal children.
She died in Normandy at age 52 on Nov. 2, 1083.
Bonus fact: There were rumors and report of Matilda having a crush on a wealthy English noble named Brihtric Mau when she was around 15-18 years old. She was so enamored with him that she sent him a messenger asking for his hand in marriage (A woman proposing in the medieval era??? How scandalous!!). He refused her proposal though and she was quite embarrassed although 20 years later when William conquered England, Matilda claimed one of Mau’s manors and deprived Gloucester which significantly reduced his income. William also threw Mau in prison for some reason, some ppl believe that Matilda convinced William to do so. 2 days after his arrest, Mau was found dead. Some ppl think that it was Matilda who ordered his murder.
She was also short. Around 5’0 while William was 5’10.
Ok yapping over i got hyperfixated on her in middle school and it was so fun to do all this research again! Tysm for asking!!
#long post#matilda of flanders#sorry for yapping guys it will happen again#also#PLEASEEEE ASK ME ABOUT YE OLDE ROYAL WOMEN
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Currently, doing Natalie Grueninger's Series 365 Days of Medieval and Renaissance Wonder Women. We've done Matilda of Flanders, Christine de Pizan and Eleanor of Aquitaine. Had a great talk with Matthew Lewis today about her. I thought I knew a lot about Eleanor already but was so glad to learn more. She led an incredible life and left quite the legacy for her descendants. One of the first female rulers in Europe in her own right.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Some beta sketches of Matilda of Flanders for my animated series.

Close up of her face.
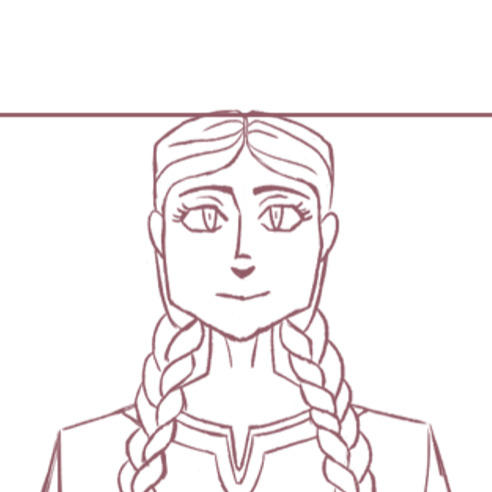
#sitbogold#matilda of flanders#digital art#concept art#sketch#artists on tumblr#11th century#medieval#flanders#house of flanders
1 note
·
View note
Text
A central element of the myth of [Eleanor of Aquitaine] is that of her exceptionalism. Historians and Eleanor biographers have tended to take literally Richard of Devizes’s conventional panegyric of her as ‘an incomparable woman’. She is assumed to be a woman out of her time. […] Amazement at Eleanor’s power and independence is born from a presentism that assumes generally that the Middle Ages were a backward age, and specifically that medieval women were all downtrodden and marginalized. Eleanor’s career can, from such a perspective, only be explained by assuming that she was an exception who rose by sheer force of personality above the restrictions placed upon twelfth-century women.
— Michael R. Evans, Inventing Eleanor: The Medieval and Post-Medieval Image of Eleanor of Aquitaine
The idea of Eleanor’s exceptionalism rests on an assumption that women of her age were powerless. On the contrary, in Western Europe before the twelfth century there were ‘no really effective barriers to the capacity of women to exercise power; they appear as military leaders, judges, castellans, controllers of property’. […] In an important article published in 1992, Jane Martindale sought to locate Eleanor in context, stripping away much of the conjecture that had grown up around her, and returning to primary sources, including her charters. Martindale also demonstrated how Eleanor was not out of the ordinary for a twelfth-century queen either in the extent of her power or in the criticisms levelled against her.
If we look at Eleanor’s predecessors as Anglo-Norman queens of England, we find many examples of women wielding political power. Matilda of Flanders (wife of William the Conqueror) acted as regent in Normandy during his frequent absences in England following the Conquest, and [the first wife of Henry I, Matilda of Scotland, played some role in governing England during her husband's absences], while during the civil war of Stephen’s reign Matilda of Boulogne led the fight for a time on behalf of her royal husband, who had been captured by the forces of the empress. And if we wish to seek a rebel woman, we need look no further than Juliana, illegitimate daughter of Henry I, who attempted to assassinate him with a crossbow, or Adèle of Champagne, the third wife of Louis VII, who ‘[a]t the moment when Henry II held Eleanor of Aquitaine in jail for her revolt … led a revolt with her brothers against her son, Philip II'.
Eleanor is, therefore, less the exception than the rule – albeit an extreme example of that rule. This can be illustrated by comparing her with a twelfth century woman who has attracted less literary and historical attention. Adela of Blois died in 1137, the year of Eleanor’s marriage to Louis VII. […] The chronicle and charter evidence reveals Adela to have ‘legitimately exercised the powers of comital lordship’ in the domains of Blois-Champagne, both in consort with her husband and alone during his absence on crusade and after his death. […] There was, however, nothing atypical about the nature of Adela’s power. In the words of her biographer Kimberley LoPrete, ‘while the extent of Adela’s powers and the political impact of her actions were exceptional for a woman of her day (and indeed for most men), the sources of her powers and the activities she engaged in were not fundamentally different from those of other women of lordly rank’. These words could equally apply to Eleanor; the extent of her power, as heiress to the richest lordship in France, wife of two kings and mother of two or three more, was remarkable, but the nature of her power was not exceptional. Other noble or royal women governed, arranged marriages and alliances, and were patrons of the church. Eleanor represents one end of a continuum, not an isolated outlier.
#It had to be said!#eleanor of aquitaine#historicwomendaily#angevins#my post#12th century#gender tag#adela of blois#I think Eleanor's prominent role as dowager queen during her sons' reigns may have contributed to her image of exceptionalism#Especially since she ended up overshadowing both her sons' wives (Berengaria of Navarre and Isabella of Angouleme)#But once again if we examine Eleanor in the context of her predecessors and contemporaries there was nothing exceptional about her role#Anglo-Saxon consorts before the Norman Conquest (Eadgifu; Aelfthryth; Emma of Normandy) were very prominent during their sons' reigns#Post-Norman queens were initially never kings' mothers because of the circumstances (Matilda of Flanders; Edith-Matilda; and#Matilda of Boulogne all predeceased their husbands; Adeliza of Louvain never had any royal children)#But Eleanor's mother-in-law Empress Matilda was very powerful and acted as regent of Normandy during Henry I's reign#Which was a particularly important precedent because Matilda's son - like Eleanor's sons after him - was an *adult* when he became King.#and in France Louis VII's mother Adelaide of Maurienne was certainly very powerful and prominent during Eleanor's own queenship#Eleanor's daughter Joan's mother-in-law Margaret of Navarre had also been a very powerful regent of Sicily#(etc etc)#So yeah - in itself I don't think Eleanor's central role during her own sons' reigns is particularly surprising or 'exceptional'#Its impact may have been but her role in itself was more or less the norm
433 notes
·
View notes
Text
@spaceymaseyy @vaderdala1541
Yeah, though let's hope that this movie doesn't go by those crazy (and thankfully unproven) legends about William throwing Matilda out on the street and beating her into accepting his proposal because she snubbed him for being an illegitimate child. That wouldn't be so romantic.
so it’s rumored that hayden might be cast in a period film and play william the conqueror and as a history buff, MATILDA (his wife) AND WILLIAM WERE ACTUALLY HELLA ROMANTIC FOR THE TIME PERIOD, LIKE WILLIAM WAS A SIMP, AND I AM DELUSIONAL ASF, BUT THEIR RELATIONSHIP IS HOW VADERDALA COULDVE BEEN AND NOW IM GOING CRAZY
#star wars#anidala#vaderdala#history#politics#william the conqueror#matilda of flanders#english royalty#king william i
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
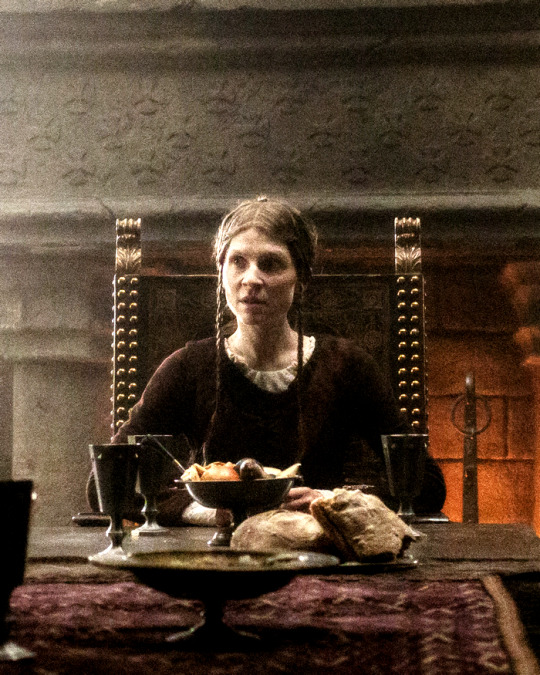
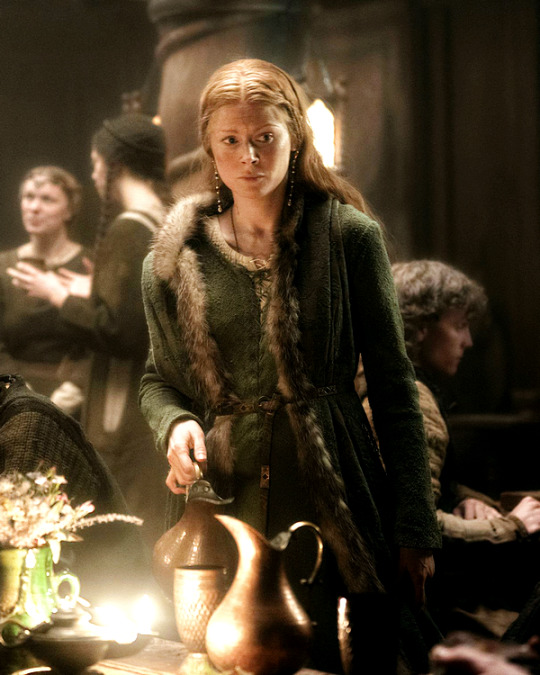


Clémence Poésy as Matilda of Flanders, wife of William, Duke of Normandy Emily Beecham as Edith the Fair aka Edith Swanneck, wife of Harold Godwinson
[BBC’s and CBS' King and Conqueror Promotional Material]
#king and conqueror#kingandconqueroredit#perioddramaedit#clemence poesy#Clémence Poésy#emily beecham#maltida of flanders#edith the fair#edith swanneck#my edits#stills#they did have another woman in the stills called margaret but for the life of me I couldn't find which margaret she was supposed to be
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Below the cut I have made a list of each English and British monarch, the age of their mothers at their births, and which number pregnancy they were the result of. Particularly before the early modern era, the perception of Queens and childbearing is quite skewed, which prompted me to make this list. I started with William I as the Anglo-Saxon kings didn’t have enough information for this list.
House of Normandy
William I (b. c.1028)
Son of Herleva (b. c.1003)
First pregnancy.
Approx age 25 at birth.
William II (b. c.1057/60)
Son of Matilda of Flanders (b. c.1031)
Third pregnancy at minimum, although exact birth order is unclear.
Approx age 26/29 at birth.
Henry I (b. c.1068)
Son of Matilda of Flanders (b. c.1031)
Fourth pregnancy at minimum, more likely eighth or ninth, although exact birth order is unclear.
Approx age 37 at birth.
Matilda (b. 7 Feb 1102)
Daughter of Matilda of Scotland (b. c.1080)
First pregnancy, possibly second.
Approx age 22 at birth.
Stephen (b. c.1092/6)
Son of Adela of Normandy (b. c.1067)
Fifth pregnancy, although exact birth order is uncertain.
Approx age 25/29 at birth.
Henry II (b. 5 Mar 1133)
Son of Empress Matilda (b. 7 Feb 1102)
First pregnancy.
Age 31 at birth.
Richard I (b. 8 Sep 1157)
Son of Eleanor of Aquitaine (b. c.1122)
Sixth pregnancy.
Approx age 35 at birth.
John (b. 24 Dec 1166)
Son of Eleanor of Aquitaine (b. c.1122)
Tenth pregnancy.
Approx age 44 at birth.
House of Plantagenet
Henry III (b. 1 Oct 1207)
Son of Isabella of Angoulême (b. c.1186/88)
First pregnancy.
Approx age 19/21 at birth.
Edward I (b. 17 Jun 1239)
Son of Eleanor of Provence (b. c.1223)
First pregnancy.
Age approx 16 at birth.
Edward II (b. 25 Apr 1284)
Son of Eleanor of Castile (b. c.1241)
Sixteenth pregnancy.
Approx age 43 at birth.
Edward III (b. 13 Nov 1312)
Son of Isabella of France (b. c.1295)
First pregnancy.
Approx age 17 at birth.
Richard II (b. 6 Jan 1367)
Son of Joan of Kent (b. 29 Sep 1326/7)
Seventh pregnancy.
Approx age 39/40 at birth.
House of Lancaster
Henry IV (b. c.Apr 1367)
Son of Blanche of Lancaster (b. 25 Mar 1342)
Sixth pregnancy.
Approx age 25 at birth.
Henry V (b. 16 Sep 1386)
Son of Mary de Bohun (b. c.1369/70)
First pregnancy.
Approx age 16/17 at birth.
Henry VI (b. 6 Dec 1421)
Son of Catherine of Valois (b. 27 Oct 1401)
First pregnancy.
Age 20 at birth.
House of York
Edward IV (b. 28 Apr 1442)
Son of Cecily Neville (b. 3 May 1415)
Third pregnancy.
Age 26 at birth.
Edward V (b. 2 Nov 1470)
Son of Elizabeth Woodville (b. c.1437)
Sixth pregnancy.
Approx age 33 at birth.
Richard III (b. 2 Oct 1452)
Son of Cecily Neville (b. 3 May 1415)
Eleventh pregnancy.
Age 37 at birth.
House of Tudor
Henry VII (b. 28 Jan 1457)
Son of Margaret Beaufort (b. 31 May 1443)
First pregnancy.
Age 13 at birth.
Henry VIII (b. 28 Jun 1491)
Son of Elizabeth of York (b. 11 Feb 1466)
Third pregnancy.
Age 25 at birth.
Edward VI (b. 12 Oct 1537)
Son of Jane Seymour (b. c.1509)
First pregnancy.
Approx age 28 at birth.
Jane (b. c.1537)
Daughter of Frances Brandon (b. 16 Jul 1517)
Third pregnancy.
Approx age 20 at birth.
Mary I (b. 18 Feb 1516)
Daughter of Catherine of Aragon (b. 16 Dec 1485)
Fifth pregnancy.
Age 30 at birth.
Elizabeth I (b. 7 Sep 1533)
Daughter of Anne Boleyn (b. c.1501/7)
First pregnancy.
Approx age 26/32 at birth.
House of Stuart
James I (b. 19 Jun 1566)
Son of Mary I of Scotland (b. 8 Dec 1542)
First pregnancy.
Age 23 at birth.
Charles I (b. 19 Nov 1600)
Son of Anne of Denmark (b. 12 Dec 1574)
Fifth pregnancy.
Age 25 at birth.
Charles II (b. 29 May 1630)
Son of Henrietta Maria of France (b. 25 Nov 1609)
Second pregnancy.
Age 20 at birth.
James II (14 Oct 1633)
Son of Henrietta Maria of France (b. 25 Nov 1609)
Fourth pregnancy.
Age 23 at birth.
William III (b. 4 Nov 1650)
Son of Mary, Princess Royal (b. 4 Nov 1631)
Second pregnancy.
Age 19 at birth.
Mary II (b. 30 Apr 1662)
Daughter of Anne Hyde (b. 12 Mar 1637)
Second pregnancy.
Age 25 at birth.
Anne (b. 6 Feb 1665)
Daughter of Anne Hyde (b. 12 Mar 1637)
Fourth pregnancy.
Age 27 at birth.
House of Hanover
George I (b. 28 May 1660)
Son of Sophia of the Palatinate (b. 14 Oct 1630)
First pregnancy.
Age 30 at birth.
George II (b. 9 Nov 1683)
Son of Sophia Dorothea of Celle (b. 15 Sep 1666)
First pregnancy.
Age 17 at birth.
George III (b. 4 Jun 1738)
Son of Augusta of Saxe-Gotha (b. 30 Nov 1719)
Second pregnancy.
Age 18 at birth.
George IV (b. 12 Aug 1762)
Son of Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (b. 19 May 1744)
First pregnancy.
Age 18 at birth.
William IV (b. 21 Aug 1765)
Son of Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (b. 19 May 1744)
Third pregnancy.
Age 21 at birth.
Victoria (b. 24 May 1819)
Daughter of Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saafield (b. 17 Aug 1786)
Third pregnancy.
Age 32 at birth.
Edward VII (b. 9 Nov 1841)
Daughter of Victoria of the United Kingdom (b. 24 May 1819)
Second pregnancy.
Age 22 at birth.
House of Windsor
George V (b. 3 Jun 1865)
Son of Alexandra of Denmark (b. 1 Dec 1844)
Second pregnancy.
Age 20 at birth.
Edward VIII (b. 23 Jun 1894)
Son of Mary of Teck (b. 26 May 1867)
First pregnancy.
Age 27 at birth.
George VI (b. 14 Dec 1895)
Son of Mary of Teck (b. 26 May 1867)
Second pregnancy.
Age 28 at birth.
Elizabeth II (b. 21 Apr 1926)
Daughter of Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon (b. 4 Aug 1900)
First pregnancy.
Age 25 at birth.
Charles III (b. 14 Nov 1948)
Son of Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom (b. 21 Apr 1926)
First pregnancy.
Age 22 at birth.
381 notes
·
View notes
Text









Medieval Women Week || Favorite woman writer ↬ Marie de France
Who was this versatile author, the first woman of her times to have written successfully in the vernacular? She was definitely not Marie de Champagne, daughter of Eleanor of Aquitaine and patroness of Chrétien de Troyes, as Winkler suggested. A tempting, but by no means fully convincing, identification is with Marie, abbess of Shaftesbury in Dorset, illegitimate daughter of Geoffrey Plantagenet and half-sister to Henry II. … A claim has been made, albeit somewhat thin, for Mary, abbess of Reading. This abbey was well known as a centre of literary activity and had in its possession the Harley manuscript containing, as we have seen, both the Fables and the Lais. There is no clear-cut reason why either work could not have been written by an abbess or a nun, and there is some slight evidence of experience of monastic life in Le Fresne, Yonec and Eliduc. But the prominence of the motif of adultery in the Lais (see also fables 44 and 45), Marie’s attitude towards the dissolution of marriage in Le Fresne and Eliduc, and her evident interest in the chivalric life suggest that these love poems were not written by someone steeped in ecclesiastical ideology. … Marie de France was certainly an educated lady of good family, who knew Latin well enough to have contemplated translating a Latin work into French (Lais, Prologue, vv. 28–32) and to have done so in the case of the Espurgatoire. She was obviously a good linguist and acquired a sound knowledge of English before translating the fables. She was also fully conversant with the life and aspirations of the nobility of her time. Her education could well have been obtained in a convent and her knowledge of court life from her upbringing and personal experiences in England. Was she Marie, the eighth child of Waleran de Meulan (also called Waleran de Beaumont), a member of one of the greatest of the Norman houses? Waleran’s fief was in the French Vexin, which would tally with Marie’s statement that she comes from France and explain her evident local knowledge of the town of Pitres in the Norman Vexin… Marie de Meulan married Hugh Talbot, baron of Cleuville, owner of lands in Herefordshire and Buckinghamshire, as well as in Normandy, and a member of a family prominent in several English counties including Devonshire, Gloucestershire and Kent. Marie’s father is an interesting figure – a loyal and courageous soldier, but also a well-educated man who may have written Latin verse. Moreover, several of the manuscripts of the Historia Regum Britanniae of Geoffrey of Monmouth are dedicated to him. It is tempting to think that his daughter may have known William of Gloucester, a possible Count William, as his father was also one of Geoffrey’s dedicatees. Marie de Meulan may, however, have been too young to be Marie de France, as her birth seems to date from the 1140s, perhaps as late as 1150. The most recent identification has been as Marie, countess of Boulogne after 1154, daughter of Stephen of Blois (King of England, 1135–54) and of Matilda of Boulogne. Educated in a convent, Marie de Boulogne became abbess of Romsey in Hampshire, but was removed from her convent by Henry II, who wanted to keep Boulogne in his sway. She was married off to Matthew of Flanders and thus became the sister-in-law of Hervé II, son of Guiomar of Léon... Eventually, at some time between 1168 and 1180, Marie de Boulogne returned to a convent, perhaps that of Sainte Austreberthe at Montreuil-sur-Mer in her own county. Her Count William could have been William of Mandeville, a crusade companion of Philip of Flanders, her husband’s brother. The ‘noble king’ would probably have been the Young King, as Philip and Matthew, originally supporters of Henry II, changed sides in 1173. Marie herself may have already been a supporter of the Young King, as in 1168 she sent Louis clandestine information about the secret negotiations between Henry and the Emperor Frederick. — The Lais of Marie de France translated with an introduction by Glyn S. Burgess and Keith Busby
#medievalwomenweek#marie de france#english history#french history#european history#women's history#medieval#history#nanshe's graphics
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Characterization and Enneagram Type 2: The Mother
The Enneagram of Personality is a tool that categorizes human behavior into nine types based on motivations, fears, and desires.
This is also a useful tool for characterization, mapping your characters into one of the enneagram types to further flesh them out.
Type 2 is formally known as The Helper
Below are remixed/flanderized characteristics of this type.
Quote: “I am worth something.”
Background: Grew up in a place where they must please others to survive.
Personality: Mothering and smothering. They show care and concern because they need it back.
Positive Arc: Finds affirmation inside of themselves, rather than outside.
Negative Arc: They keep people in a state of needing them. They become resentful and deranged from lack of appreciation of their love.
Examples in fiction:
Samwise Gamgee (The Lord of the Rings)
Miss Honey (Matilda)
#enneagram#type 2#the helper#writing characters#characterization#writeblr#writing tips#samwise gamgee
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ages of English Queens at First Marriage
I have only included women whose birth dates and dates of marriage are known within at least 1-2 years, therefore, this is not a comprehensive list. For this reason, women such as Philippa of Hainault and Anne Boleyn have been omitted.
This list is composed of Queens of England when it was a sovereign state, prior to the Acts of Union in 1707. Using the youngest possible age for each woman, the average age at first marriage was 17.
Eadgifu (Edgiva/Ediva) of Kent, third and final wife of Edward the Elder: age 17 when she married in 919 CE
Ælfthryth (Alfrida/Elfrida), second wife of Edgar the Peaceful: age 19/20 when she married in 964/965 CE
Emma of Normandy, second wife of Æthelred the Unready: age 18 when she married in 1002 CE
Ælfgifu of Northampton, first wife of Cnut the Great: age 23/24 when she married in 1013/1014 CE
Edith of Wessex, wife of Edward the Confessor: age 20 when she married in 1045 CE
Matilda of Flanders, wife of William the Conqueror: age 20/21 when she married in 1031/1032 CE
Matilda of Scotland, first wife of Henry I: age 20 when she married in 1100 CE
Adeliza of Louvain, second wife of Henry I: age 18 when she married in 1121 CE
Matilda of Boulogne, wife of Stephen: age 20 when she married in 1125 CE
Empress Matilda, wife of Henry V, HRE, and later Geoffrey V of Anjou: age 12 when she married Henry in 1114 CE
Eleanor of Aquitaine, first wife of Louis VII of France and later Henry II of England: age 15 when she married Louis in 1137 CE
Isabella of Gloucester, first wife of John Lackland: age 15/16 when she married John in 1189 CE
Isabella of Angoulême, second wife of John Lackland: between the ages of 12-14 when she married John in 1200 CE
Eleanor of Provence, wife of Henry III: age 13 when she married Henry in 1236 CE
Eleanor of Castile, first wife of Edward I: age 13 when she married Edward in 1254 CE
Margaret of France, second wife of Edward I: age 20 when she married Edward in 1299 CE
Isabella of France, wife of Edward II: age 13 when she married Edward in 1308 CE
Anne of Bohemia, first wife of Richard II: age 16 when she married Richard in 1382 CE
Isabella of Valois, second wife of Richard II: age 6 when she married Richard in 1396 CE
Joanna of Navarre, wife of John IV of Brittany, second wife of Henry IV: age 18 when she married John in 1386 CE
Catherine of Valois, wife of Henry V: age 19 when she married Henry in 1420 CE
Margaret of Anjou, wife of Henry VI: age 15 when she married Henry in 1445 CE
Elizabeth Woodville, wife of Sir John Grey and later Edward IV: age 15 when she married John in 1452 CE
Anne Neville, wife of Edward of Lancaster and later Richard III: age 14 when she married Edward in 1470 CE
Elizabeth of York, wife of Henry VII: age 20 when she married Henry in 1486 CE
Catherine of Aragon, wife of Arthur Tudor and later Henry VIII: age 15 when she married Arthur in 1501 CE
Jane Seymour, third wife of Henry VIII: age 24 when she married Henry in 1536 CE
Anne of Cleves, fourth wife of Henry VIII: age 25 when she married Henry in 1540 CE
Catherine Howard, fifth wife of Henry VIII: age 17 when she married Henry in 1540 CE
Jane Grey, wife of Guildford Dudley: age 16/17 when she married Guildford in 1553 CE
Mary I, wife of Philip II of Spain: age 38 when she married Philip in 1554 CE
Anne of Denmark, wife of James VI & I: age 15 when she married James in 1589 CE
Henrietta Maria of France, wife of Charles I: age 16 when she married Charles in 1625 CE
Catherine of Braganza, wife of Charles II: age 24 when she married Charles in 1662 CE
Anne Hyde, first wife of James II & VII: age 23 when she married James in 1660 CE
Mary of Modena, second wife of James II & VII: age 15 when she married James in 1673 CE
Mary II of England, wife of William III: age 15 when she married William in 1677 CE
118 notes
·
View notes
Text

The picturesque harbour village of Clovelly in Devon was once owned by William the Conqueror.
He then gifted the estate to his wife Matilda of Flanders, and it has been a settlement since the 13th century.
Built into a 400ft cliff, the village has no vehicular access so residents rely on using sledges, largely replacing Donkeys, to transport goods from the bay.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text


The 1st May marks the anniversary of the death of a remarkable Scottish born woman.
She is known to us by the Norman-French title “Matilda of Scotland” born around 1080 at Dunfermline and Christened with the name Edith,one of the eight children of King Malcolm III of Scotland and his second wife Saint Margaret. At her christening were her godfather Robert Curthose, Duke of Normandy and the eldest son of King William I of England (the Conqueror) and her godmother, Matilda of Flanders, the wife of King William I of England (the Conqueror). The infant Matilda pulled at Queen Matilda’s headdress, which was seen as an omen that the younger Matilda would be a queen one day. In fact, she would marry Queen Matilda’ s son and Robert Curthose’s brother, King Henry I of England.
Thus with links to three different cultures, Anglo-Saxon, Scottish and Norman French, Edith was a marriageable prospect, but her eventual betrothal to Henry I of England seems, by all accounts, to have been a love match as much as a dynastic union. She was free to marry only after a court case at which she had to prove that her stay in a convent was for purposes of protection and that she never formally took the veil of a nun, such were the religious complexities at the time.
The character, education and birthright of Matilda of Scotland seem to have given her a high degree of autonomy at Henry’s court. She also had her separate sources of income, her own retinue of staff and was frequently left in virtual charge of the realm during his regular absences in Normandy. Her charters cover a wide range of issues and she was particularly interested in architecture, being responsible for several abbey building projects as well as bridge construction and the provision of England’s first public toilets, attached to a bath complex near at Queenhithe, a small and ancient ward of the City of London.
It is possible that in 1114 she sent masons north with her brother Alexander when he returned to Scotland after fighting alongside Henry in Wales. She herself was said to have “fluent honeyed speech” by Marbodius of Rennes and she filled her court with poets and musicians. She was responsible for commissioning a biography of her mother Margaret who was also renowned in Scotland for bringing light and colour to the Scottish Royal Court.
It is believed that Matilda (Edith) only returned once to Scotland during her lifetime and, due to the lack of surviving documentary evidence, her influence in Scotland is unknown. However, she is believed to have had a close relationship with her brothers, three of whom were kings north of the border.
Also absent from our history books, she may just possibly be better known to us as the “fair lady” in the nursery rhyme “London Bridge is falling down”. Her works of charity made her a queen beloved of all Londoners who also probably claimed her as a Wessex girl despite her Scottish birthplace.
Matilda of Scotland fulfilled her dynastic duty by giving birth to both a daughter, also called Matilda, and a son, William. William died in a tragic boat disaster shortly after Matilda’s own early death in 1118. She was only 38. Her daughter Matilda married the German Emperor Henry V and is known to us today as the Holy Roman Empress Matilda, the princess who became embroiled in a bitter English Civil War.
There is loads more about our forgotten English Queen here http://garethrussellcidevant.blogspot.com/.../daughter-of...
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
I just finished my third week of student teaching and to celebrate I decided to watch the first lecture of Natalie Grueninger's 365 Days With Medieval and Renaissance Wonder Women. The first lecture was on Matilda of Flanders wife of William the Conqueror. I didn't know very much about her before but now I feel like I've gotten to know her so well. She was such a badass. So glad I signed up for this course looking forward to learning about some more Medieval and Renaissance Women this year.
1 note
·
View note
Text

hOLY SHIT!!! IS THIS A REFERENCE TO THE HOUSE OF FLANDERS?!?!?!
0 notes