#Northern Wei dynasty
Photo








Ancient Tombs Discovered in China's Henan
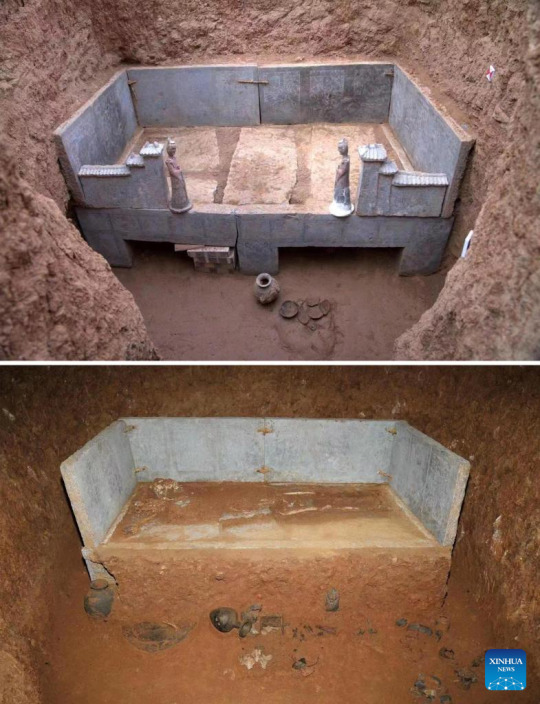
A cemetery found in Zhucang Village in Mengjin District of Luoyang City, central China's Henan Province. A cemetery consisting of three tombs was recently listed as one of the five key archaeological discoveries in Henan Province in 2022. In the tombs probably built between the late period of the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) and the Eastern Wei Dynasty (534-550), large-scale and well-organized stone beds with stone folding screens were found. This is the first time that stone beds dating back to this period have been unearthed in Luoyang City.
#Ancient Tombs Discovered in China's Henan#ancient tombs#ancient graves#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient china#chinese history#northern wei dynasty#eastern wei dynasty
58 notes
·
View notes
Text

What I love about Mulan is how her motivations are heavily feminine, yet they aren’t treated as a weakness but instead what makes her strong!
🇨🇳⚔️🐴
#history#mulan#china#disney princess#womens history#folklore#hua mulan#femininity#northern wei dynasty#chinese history#disney#girl power#feminine#trans women are women#strong women#disney movie#female character#disney world#military#girly things#feminine history#chinese folklore#grl pwr#feminine power#women empowerment#nickys facts
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
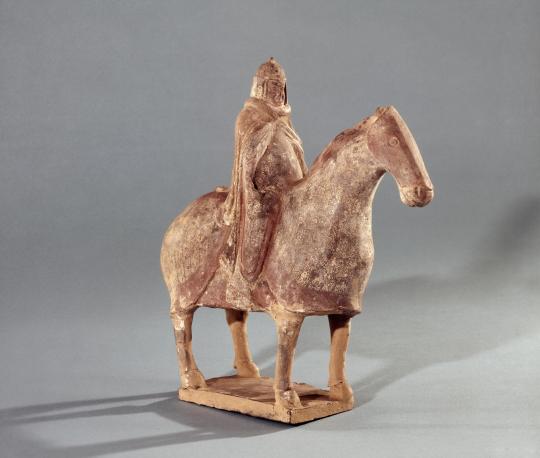

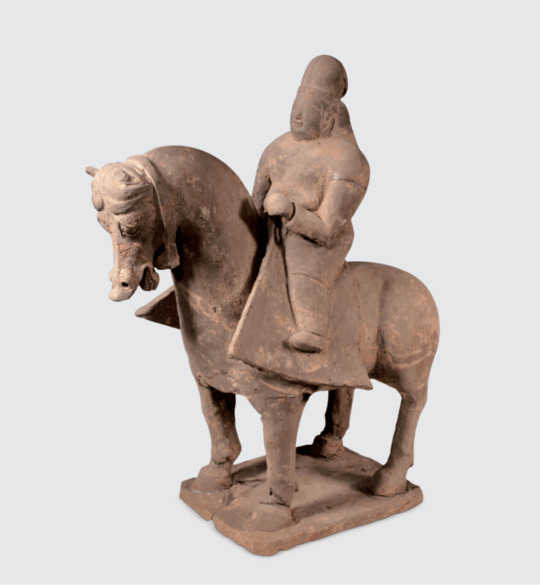
earthenware figure of horse with rider. northern wei dynasty, 386-534.
the british museum only notes that the figure was purchased from private collector george eumorfopoulos; it might have been originally taken from a tomb.
#china#northern and southern dynasties#northern wei dynasty#decorative arts#funereal arts#museum trawling#image source: british museum
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Art from November 2023.

Her name is Jingyi and she's a journalist with a little blog.
#my art#ffvii oc#final fantasy vii#final fantasy vii oc#northern wei dynasty#hanfu#just a one off oc#original character
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Emperor Xiaowen and his entourage worshipping the Buddha, ca.522-23
Northern Wei dynasty, China
From the Central Binyang Cave, Longmen, Henan province
Limestone with traces of pigment
H. 82 in. (208.3 cm); W. 12 ft. 11 in. (393.7 cm)
Together with a companion piece showing an empress and her attendants (now in the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, Kansas City), this depiction of an emperor and his entourage once adorned the Central Binyang Cave (also known as Cave 3) in the Longmen complex, near Luoyang, in Henan province. It was positioned centrally on the northeast wall between a group of protective semidivinities above and a narrative debate scene below. Xuanwu commissioned the construction of the Central Binyang Cave in honor of his father, the emperor Xiaowen (r. 471–99), and his mother, the dowager Wenzhou (d. 494); the emperor and empress in the reliefs are therefore believed to refer to his parents. A figure wearing court garments and holding a tasseled baton leads the procession. He is followed by a smaller figure wearing armor and another who stands before the emperor, holding an incense burner. The trees originally indicated the point at which the procession moved around a corner, from the north to the east wall. Several of the attendants hold lotuses or other flowers and offerings, and the entire procession can be understood as making offerings to the Buddhas in the cave, an act of merit making that would continue in perpetuity and improve the future lives of the participants.
Collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art
#The Met#Metropolitan Museum of Art#Northern Wei dynasty#Northern and Southern dynasties#6th century#relief#religion#art#art history#Chinese#Binyang Caves#Longmen Grottoes#Henan#Xuanwu era#period dress#stone#limestone#portrait
1 note
·
View note
Text
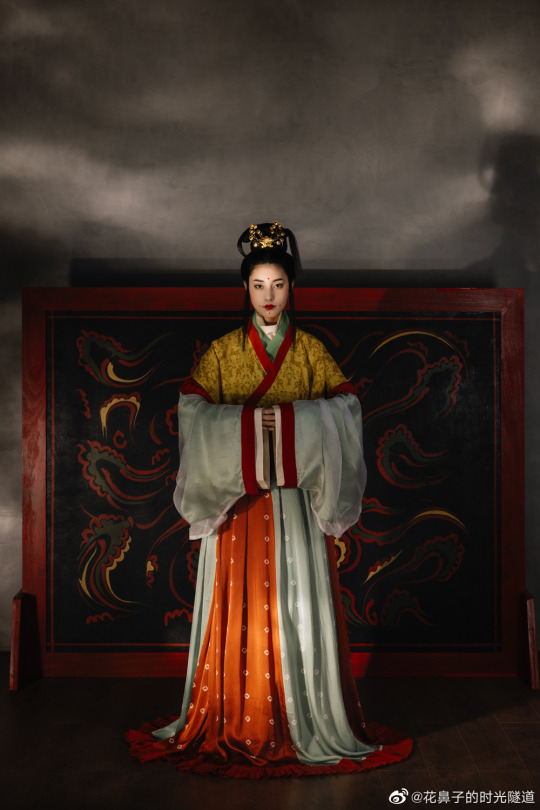
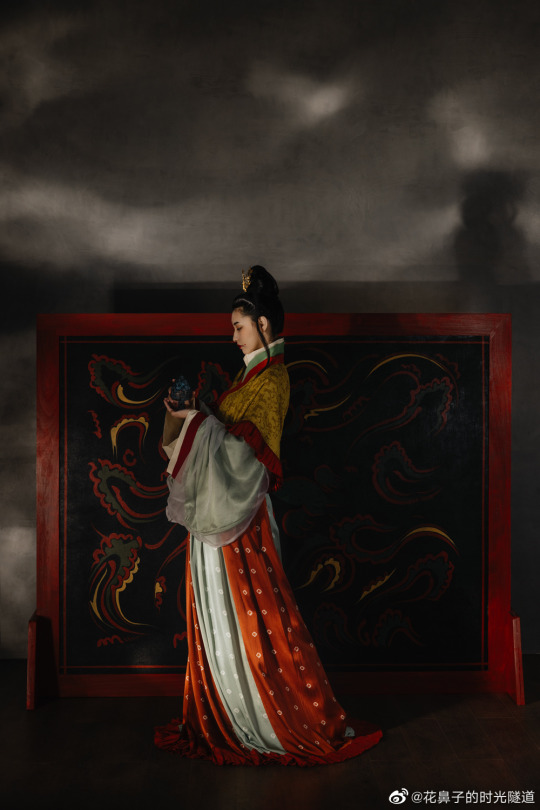








【Historical Reference Artifacts】:
China Jin Dynasty PaintingBy Gu Kaizhi (顾恺之)

・ Wei, Jin, Southern and Northern Dynasties Female Figurines showing woman makeup at the time:
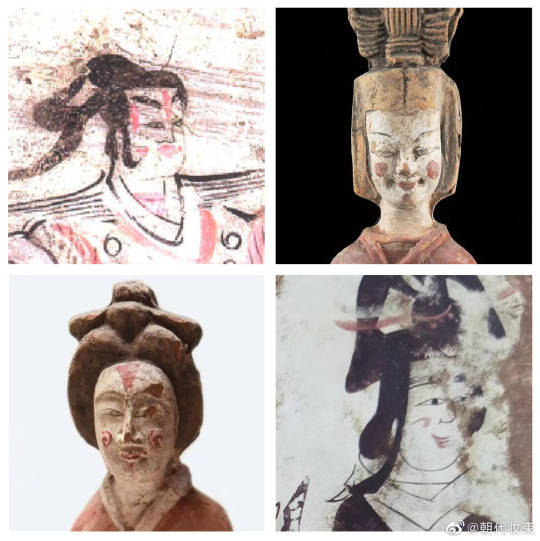


[Hanfu・漢服]Chinese Wei and Jin Dynasty-Northern and Southern Dynasties(220—589)Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
————————
📷Photo:@realyn
💄Stylist:@仰望的花鼻子
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/5541803701/N77vXcOBE
————————
#chinese hanfu#Wei and Jin Dynasty-Northern and Southern Dynasties(220—589)#hanfu#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#chinese history'#historical fashion#historical makeup#Wise and Benevolent Women (列女仁智圖)#chinese history#ancient china#chinese fashion#hanfu art#漢服#汉服#chinese style#中華風#魏晋南北朝
229 notes
·
View notes
Text

#mdzs#dungeon meshi#wei wuxian#marcille donato#i know mdzs has no specific canonical time period#but mxtx has mentioned her main inspirations were the wei-jin and northern and southern dynasties#so putting wwx's death in 451- 13 years before marcille's birth- isn't much of a stretch#anyway necromancy blorbos go brrrrr
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ugh. Why is it so difficult to find info on men's clothing? 90% of the websites I visit are about women's clothing only. Sometimes with a very small paragraph or two on men's clothing. Ugh. Whyyyyyyy.
#hanfu#chinese history#historical fashion#chinese fashion#sui dynasty#tang dynasty#northern and southern dynasties#wei and jin dynasties#history of hanfu
15 notes
·
View notes
Photo








Hua Mulan (2009) - Mulan: Rise of a Warrior
Don’t do martial arts anymore. You are a girl...
#hua mulan#cmovie#perioddramaedit#filmedit#movieedit#花木兰#mulan rise of a warrior#zhao wei#vicki zhao#northern and southern dynasties#gzh#gifshistorical#filmtv#filmgifs#cinemapix#moviegifs#tvfilmedit#tvfilmdaily
100 notes
·
View notes
Text
Imperial Chinese Harem Systems part 3
Western Han
Empress (皇后 ; huáng hòu)
Lady of Bright Deportment (昭儀; zhāo yí)
Lady of Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú), created by Emperor Wu
Lady of Graceful Beauty (娙娥; xíng é), created by Emperor Wu
Lady of Lovely Countenance (容華; róng huá), created by Emperor Wu
Lady of Complete Deportment (充衣; chōng yī), created by Emperor Wu
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Virtuous Lady (良人; liáng rén)
Consort (八子; bā zi)
Lady (七子; qī zi)
Senior Palace Woman (長使; zhǎng shǐ)
Junior Palace Woman (少使; shǎo shǐ)
Lady for Miscellaneous Uses (五官; wǔ guān)
Lady of Complaisant Constancy (順常; shùn cháng)
Lady Without Impurity (舞涓; wǔ juān), Lady of Reverent Gentleness (共和; gòng hé), Lady who Pleases the Spirit (娛靈; yú líng), Lady who Could Comfort a Multitude (保林; bǎo lín), Lady of Excellent Employment (良使; liáng shǐ), Lady for Night Attendance (夜者; yè zhě)
The principal wife of the Crown Prince was called (妃; fēi). There also exists a sub-ranking system for concubines; they were called Ladies of Excellence (良娣; liáng dì) and (孺人; rú rén). For grandchildren of the Emperor, their principal wives were called Madame (夫人; fū rén). Concubines for these people have no titles, and were simple called (家人子; jiā rén zǐ).
Eastern Han
Empress (皇后; huáng hòu)
Noble Lady (貴人; guì rén)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Courtier (宮人; gōng rén)
Talented Lady (才女; cǎi nǚ
No limits were set for these consorts. This later created situations when more than 20,000 women were living in the palace during the reigns of Emperor Huan and Emperor Ling.
Three Kingdoms
Cao Wei
During the reign of Cao Cao (who was not an emperor but a king):
Queen (王后; wáng hòu)
Madame (夫人; fū rén)
Lady of Bright Deportment (昭儀; zhāo yí)
Lady of Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú)
Lady of Lovely Countenance (容華; róng huá)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
During the reign of Emperor Wen:
Empress (皇后; huáng hòu)
Madame (夫人; fū rén)
Noble Imperial Concubines (貴嬪; guì pín)
Lady of Pure Beauty (淑媛; shū yuàn)
Lady of Bright Deportment (昭儀; zhāo yí)
Lady of Cultivated Countenance (修容; xiū róng)
Lady of Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú)
Lady of Lovely Countenance (容華; róng huá)
Lady of Humble Capability (順成; shùn chéng)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Virtuous Lady (良人; liáng rén)
During the reign of Emperor Ming:
Empress (皇后; huáng hòu)
Madame (夫人; fū rén)
Noble Imperial Concubines (貴嬪; guì pín)
Pure Consort (淑妃; shū fēi)
Lady of Pure Beauty (淑媛; shū yuàn)
Lady of Bright Deportment (昭儀; zhāo yí)
Lady of Bright Magnificence (昭華; zhāo huá)
Lady of Cultivated Countenance (修容; xiū róng)
Lady of Cultivated Deportment (修儀; xiū yí)
Lady of Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú)
Lady of Lovely Countenance (傛華; rǒng huá)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Virtuous Lady (良人; liáng rén)
Northern & Southern Dynasties
Liu Song
1 Empress (皇后; huáng hòu)
3 Madames (夫人; fū rén) Noble Imperial Concubines (貴嬪; guì pín), Consort (夫人; fū rén), and Noble Lady (貴人; guì rén)
9 Imperial Concubines (嬪; pín) Pure Consort (淑妃; shū fēi), Lady of Pure Beauty (淑媛; shū yuàn), Lady of Warm Ceremony (淑儀; shū yí), Lady of Cultivated Splendidness (修華; xiū huá), Lady of Cultivated Countenance (修容; xiū róng), Lady of Cultivated Deportment (修儀; xiū yí), Lady of Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú), Lady of Everlasting Splendidness (傛華; yǒng huá), and Lady of Sufficient Splendidness (充華; chōng huá)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
From 456, during the reign of Emperor Xiaowu:
1 Empress (皇后; huáng hòu)
3 Madames (夫人; fū rén) Noble Consort (貴妃; guì fēi), Noble Imperial Concubines (貴嬪; guì pín), and Noble Lady (貴人; guì rén)
9 Imperial Concubines (嬪; pín) Pure Consort (淑妃; shū fēi), Lady of Pure Beauty (淑媛; shū yuàn), Lady of Warm Ceremony (淑儀; shū yí), Lady of Bright Deportment (昭儀; zhāo yí), Lady of Bright Countenance (昭容; zhāo róng), Lady of Bright Splendidness (昭華; zhāo huá), Lady of Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú), Lady of Lovely Countenance (容華; róng huá), and Lady of Sufficient Splendidness (充華; chōng huá)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Lady of Regular Talents (中才人; zhōng cái rén)
Lady of Complete Deportment (充衣; chōng yī)
From the reign of Emperor Ming:
1 Empress (皇后; huáng hòu)
3 Madames (夫人; fū rén) Noble Consort (貴妃; guì fēi), Noble Imperial Concubines (貴嬪; guì pín), and Noble Concubine (貴姬; guì jī)
9 Imperial Concubines (嬪; pín) Lady of Pure Beauty (淑媛; shū yuàn), Lady of Pure Deportment (淑儀; shū yí), Lady of Pure Countenance (淑容; shū róng), Lady of Bright Splendidness (昭華; zhāo huá), Lady of Bright Deportment (昭儀; zhāo yí), Lady of Bright Countenance (昭容; zhāo róng), Lady of Cultivated Splendidness (修華; xiū huá), Lady of Cultivated Deportment (修儀; xiū yí), and Lady of Cultivated Countenance (修容; xiū róng)
5 (職; zhí)
Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú)
Lady of Lovely Countenance (容華; róng huá)
Lady of Sufficient Countenance (充華; chōng huá)
Lady of Inherit Honor (承徽; chéng huī)
Lady of Kind Honor (列榮; liè róng)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Lady of Regular Talents (中才人; zhōng cái rén)
Lady of Talents (才人; cái rén)
Lady of Virtue (良人; liáng rén)
Lady of Complete Deportment (充衣; chōng yī)) Handsome Fairness (婕妤; jié yú)Lady of Lovely Countenance (容華; róng huá), Lady of Sufficient Countenance (充華; chōng huá), Lady of Inherit Honor (承徽; chéng huī), and Lady of Kind Honor (列榮; liè róng)
Beauty (美人; měi rén)
Lady of Regular Talents (中才人; zhōng cái rén)
Lady of Talents (才人; cái rén)
Lady of Virtue (良人; liáng rén)
Lady of Complete Deportment (充衣; chōng yī)
#historical chinese harem system#western han#eastern han#three kingdoms#cao wei#northern and southern dynasties#liu song
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tuoba Tao: Ok, maybe playing ‘whose family is most dysfunctional’ wasn’t the best idea we’ve had. Tuoba Huang's been crying in the bathroom for an hour. We can’t get him out...
#tuoba tao#tuoba huang#incorrect northern wei#this could be any dynasty#or tuoba gui and tuoba si#there was so much daddy issues in northern wei
0 notes
Photo
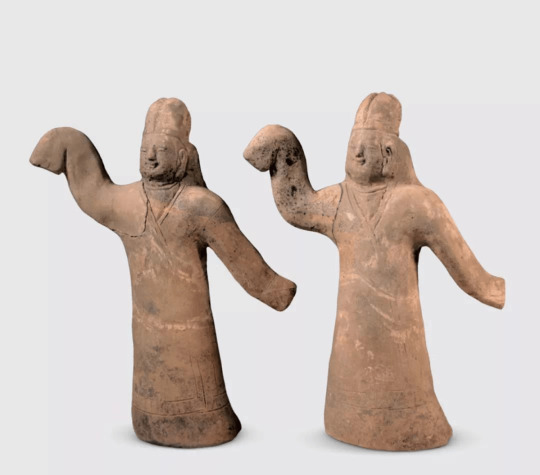
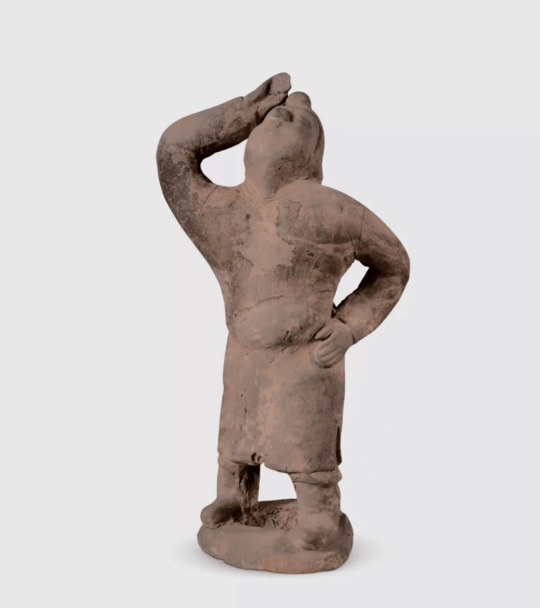
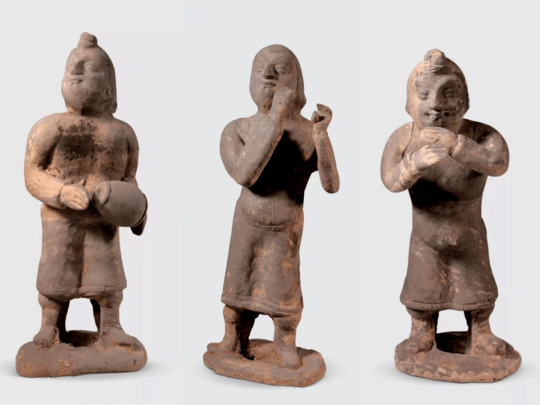
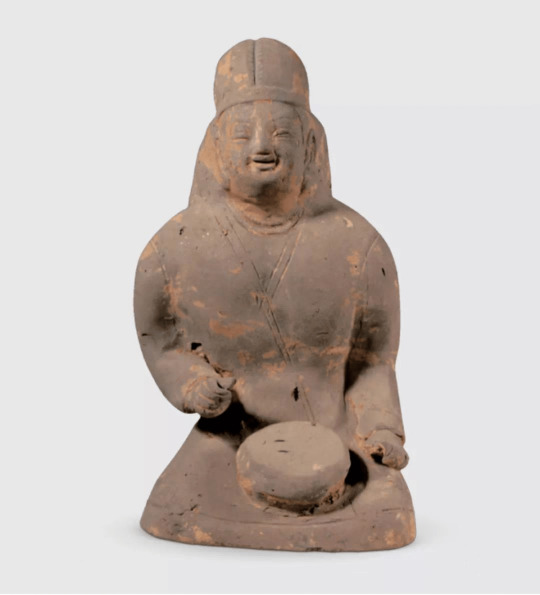






Ancient Terracotta Figurines Unearthed in Shanxi
Archaeologists from the Datong Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology recently unearthed a large group of terracotta figurines from a tomb in a group dating to the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) in Datong, Shanxi province.
Experts said the new archaeological discovery provides new materials for the study of funeral culture, ethnic costumes and social life of the dynasty.
Various patterns can be seen in the figurines, including musicians, dancers, servants, laborers, animals and vessels.
The relics show that the tomb owners were members of the upper class. Costumes of the female musicians show the integration of national culture and costume development during the period.
#China#Datong Shanxi Province#Ancient Terracotta Figurines Unearthed in Shanxi#Northern Wei Dynasty#ancient tomb#ancient grave#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient china#chinese history
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
English added by me :)
Further Details:
In 2014, while digging ground to construct the Number 7 line for the Chengdu metro, a 2300 square meter tomb with 13 graves was dug up near Mohechi (摩诃池), the former back gardens of the Prince's mansion in Sichuan (蜀王府). Of the 13 chambers in the tomb, most were single graves, and some had been plundered or were difficult to get to. Chamber #8 was found to have its seal still closed and in decent condition, with archeologists speculating that the area had been subject to earthquakes in the past, and robbers skipped over the chamber because they were afraid of the walls collapsing if the heavy stone door was moved. Chamber #8 was also discovered to contain two rooms and the engraving of a dragon and phoenix, indicating that whoever the tomb belonged to were of relatively high status.
While the royal mausoleum of the prince of Sichuan had long been unearthed, the new joint grave was originally thought to be the tomb of an aristocratic husband and wife, as the type of tomb was typical of a husband and wife pair. The area where the new tomb had been discovered was also known long ago as 公公坟 (the eunuch graves). Other tombs of court eunuchs buried around Chengdu had been discovered in 1953, 1955, 1956, 2003, 2005, and 2008.
At the same time, experts noticed that the porcelain relics buried in the Chamber #8 all shared an unusual characteristic: the male figurines had no facial hair. This led to the realisation that the figurines depicted eunuchs. Additionally, two stone tablets were eventually located which turned out to be the epitaphs for the graves, and which allowed the archeologists to confirm that the tomb did indeed belong to two imperial eunuchs from the Ming dynasty. Moreover, the tablets revealed that the eunuchs were named Wei Yu (魏玉, b.1470) and Ruan Ying (阮英, b. 1472). Both were born from poor farming families in Tongzhou (潼州; present day northern Sichuan province).
In the fourteenth year of Chenghua, there was a huge drought in the nation, so both children were sent by their families to become eunuchs in the palace as a means to survive. Being from the same area and around the same age, they would grow to become very close.
In the Ming dynasty, imperial eunuchs had great power, such that they were in charge of many government and even military affairs. Due to this, Wei Yu and Ruan Ying did not stay in Beijing to serve the emperor but instead eventually ended up as chief eunuchs in Shuwangfu, the center of government in Sichuan. Based on the epitaph and historical materials, historians concluded that Wei Yu and Ruan Ying did not necessarily overstep their power as is often the depiction of court eunuchs of the era, and in fact, they cooperated very well with the Zhu Chun, the prince of Sichuan and Hongwu Emperor's 11th son, assisting him to repair infrastructure and bringing prosperity to the people of Chengdu.
Wei Yu was favored by the prince for being clever and witty, and was bestowed the surname Shuang, so is also referred to in records as Shuang Yu (双玉). As Wei Yu's status grew, Ruan Ying's did as well.
In the 10th year of Zhengde (1515), having experienced some rough times, Wei Yu and Ruan Ying decided they wanted to be buried together and and obtained royal permission for it to be so. As they had no children, they were able to accumulate all their earnings (imperial servants were paid) and buy a plot of land. One year later, Ruan Ying passed away and Wei Yu had a tomb built with two rooms so that they could be buried together. Ten years later, when he passed away also, Wei Yu was buried with Ruan Ying, fulfilling their desire to be entombed together.
--
Additional sources:
https://www.sohu.com/a/413776430_120795605
https://m.thepaper.cn/yidian_promDetail.jsp?contid=3744568&from=yidian
https://www.toutiao.com/article/6706734279713358350/?wid=1705638571420
video (in Chinese)
video (in Chinese)
#tried to find a better douyin to introduce/summarise the topic but some of them had really annoying voice overs lol#i think there is like a cctv type documentary about the dig with actual expert talking heads but i can't find the video online atm#anyway. it's really incredible to me that they even recorded their birth and death years like bro...so often these details are lost to time#but we know all these things about these two from 600 years ago :')#chinese history#video#douyin#tiktok#long post#同志历史
580 notes
·
View notes
Text
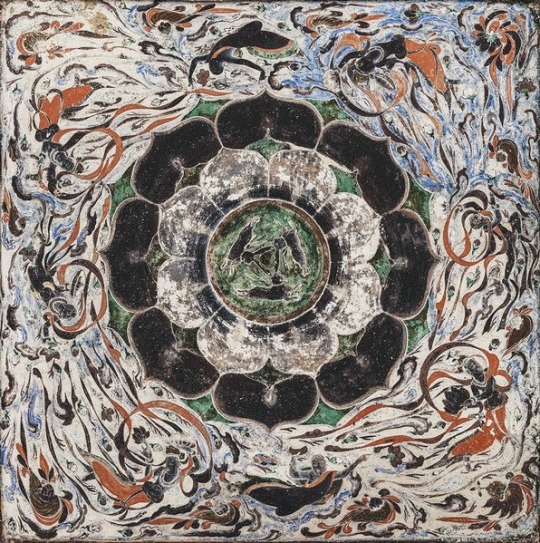







Incredible art from the Northern Wei Dynasty, Mogao Caves, 4th century
My brief experience seeing Wei Dynasty art in North China taught me it's some of the most refined in Chinese history
[Photo/Chinaculture.org]
592 notes
·
View notes
Text
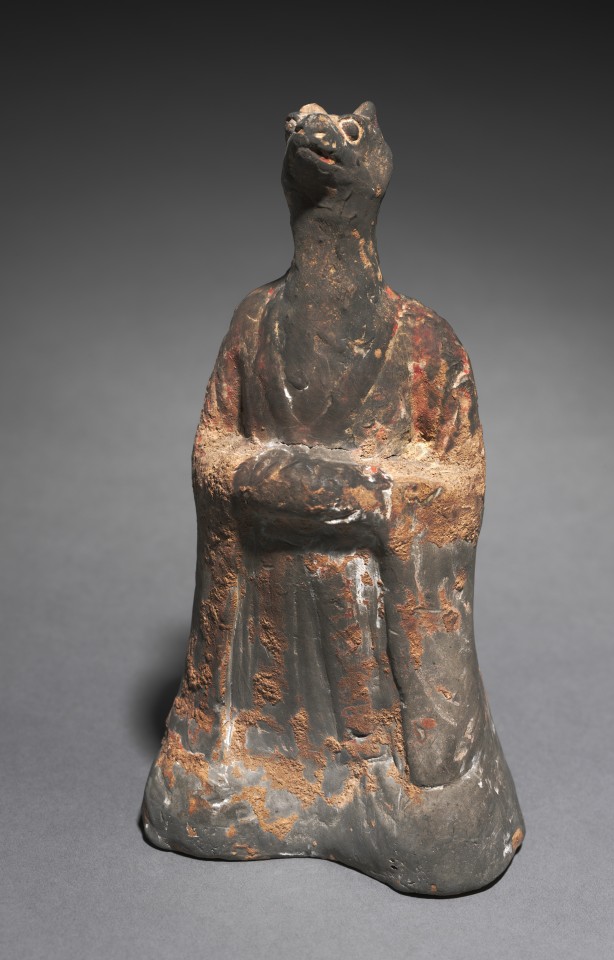

Mortuary Figure of the Zodiac Sign: Rat (Aries), 500s.
China, Northern Wei dynasty (386-534)
Gray earthenware with traces of slip; overall: 22.6 cm (8 7/8 in.)
The Cleveland Museum of Art, The Norweb Collection 1972.76.1
0 notes
Text
Dead languages and maybe Wei Ying is long-lost royalty
Today I had a discussion with @pakhnokh regarding why Wei Wuxian didn’t know the deeper layer of meaning behind the Lan forehead band. It was a long discussion on Twitter, so I figured I should just make a post here and leave this information out for anyone who might find it useful.
To start off: The reason why Wei Ying didn't know the deeper layer of meaning of the Lan forehead band was in the book. But it was written in a very opaque way, in one single throw-away line. In the book, when Wei Ying had to copy the Lan rules, he specifically complained that the rules were written in seal script.
The Useless Ye Olde’ Script
Seal script is a script that predated traditional Mandarin. It was infamous for being needlessly complex and having dozens, if not hundreds different dialects and writing methods. Some forms of seal script were entirely different languages altogether. When Qin Shi Huang united ancient China, he burned a lot of books and forced people to adopt a standard way to write, thus cementing traditional Mandarin as a singular language that is still used today, 2000 years after. A way to visualize how complex seal script was, is that there were 22 different ways to write the word 'sword'.

That is how mind-bogglingly complex it was. And worse, it was the source of much conflict in ancient times. To explain it simply, it was supposed to be one language. But if people could not even agree on how to write the same word, then how could they agree on more important things and cease warring against each other?
Language standardization was one of Qin Shi Huang’s greatest achievements, if not the greatest, as it laid the foundation for more peace and eventual unification in later dynasties.
This topic was made into an Academy Award-nominated movie, Hero by Zhang Yimou in 2002.

(the word ‘sword’ that Qin Shi Huang decided on, thus wiping out the other 20+ ways to write the same word)
Dating Mo Dao Zu Shi in real history (or, Wei Ying might actually be long-lost royalty)
In a very interesting turn of events, MXTX has confirmed in her latest interview in Subaru magazine, that the events of MDZS happened during Wei Jin, Southern and Northern Dynasties (commonly referred to as the Six Dynasties era by English-speaking historians, even though these two don’t perfectly line up).
Yes, the same Wei 魏 in Wei Ying 魏婴, Wei Wuxian 魏无羡.
So the events in MDZS took place in the era immediately after the fall of the Qin dynasty (caused by Qin Shi Huang’s death and his sons not being able to measure up). Therefore, Wei Ying’s generation is in a time after the language has standardized into a single form.
The Lan rules, at least the first set and the meaning of the forehead band, were written about 500 years before Wei Ying’s generation, at the founding of House Lan. So that would put it squarely in the pre-Qin, pre-lingual-standardization era.
So by Wei Ying’s time, the Lan rules were essentially written in a dead, kinda useless, and very very hard-to-read-because-it-has-some-hundred-different-dialect language.
That’s on top of the fact that it was probably written in the highest level of 书面语 shumianyu (written language) possible. I.e. extremely condensed and truncated (with zero punctuation).
So the Lan rules are more or less a very thick law book of a different nation written in the strictest, most condensed dead language that is in no way, shape, or form still in practical use for Wei Ying (and most other people not Lan). Do you feel like reading it? I don’t.
And that is why Wei Ying never figured out the original meaning of the forehead band despite having copied the rules hundreds of times (first day in class, he was already punished and sentenced to copying the rules 100 times by Lan Qiren).
Because he was just copying the words without really reading them. This was mentioned when Wei Ying asked Lan Wangji the meaning of the Lan forehead band, and Lan Wangji replied with, you have copied the rules so many times and you still don’t know?
But isn’t Wei Ying really well-read and smart, and what about the Wen book?
1/ Wei Ying is smart and well-read. There was one throw-away line in the book that mentioned his having read all the books available to him in Lotus Pier, and that he had read all kinds of trivia (including the Thousand Sores and Hundred Holes curse that got put on Jin Zixun). But it was also stated that he favored practical things or things that interested him. Lan rules in dead, extremely hard to read language are… well… yeah…
There was never any mention in canon where he remembered specific Lan rules unless it was literally beaten into him by teenage Lan Wangji.
2/ In the novel, the Lan rules are singled out as the only materials written in seal script. The Wen books were standard issued to everyone who took part in the Wen education camp. So the chance that it was written in seal script is low to none.
Wei Ying is not the only person who doesn’t know the meaning of the Lan forehead band
Jiang Cheng didn't know either. Jin Ling didn't know either. During the Wen archery competition, when Wei Ying pulled off Lan Wangji's forehead band, he did ask Jiang Cheng what the hell was that, when Lan Wangji and other Lan members reacted like he did something shameful. Jiang Cheng replied with, how the hell would I know? Their house has so many rules. Just stop poking them.
Jin Ling didn't know until the other Lan teenagers told him. The only characters who know this in canon are all members of Lan house. The impression that Wei Ying is the only one who doesn't know is 100 percent fanon. Keep in mind both Jiang Cheng and Jin Ling are clan heirs, so their education and knowledge of other houses absolutely are not low.
In fact, the novel specifically shows that.....the rest of the cultivation world is not that clear on the actual specifics of Lan rules either. This is shown when Jin Zixun pressured Lan Xichen and Lan Wangji into drinking wine, a clear violation of Lan rules, and the rest of the cultivators in the banquet cheered him on.
These cultivators were also heads of Houses or very high-ranking members. Many of them would have studied in Cloud Recess. So again, people who have high education… still know shit all about the actual specifics of Lan rules beyond a vague, general monk-like impression.
About the only other person aside from Wei Ying (and Lan members) who knew the specific rule that Lans do not drink in that banquet was Jin Guangyao, a character whose trademark is high intelligence and extreme social savvy (plus having roomed with Lan Xichen and taken care of him for unknown amount of time right before the Sunshot campaign)
Are there secret parts of the Lan rules?
No. The Lan rules are public. The book is very clear on this. All Lan rules are carved into a massive stone placed at the foot of the mountain where Cloud Recess is, where anyone passing through or coming into House Lan can see it.
This rule stone was first mentioned when Lan Wangji and Wei Wuxian met for the first time. Wei Ying complained that he didn’t know the rules and why are there so many things forbidden in the Lan rules? Lan Wangji replied with, rules are written on the stone. Go read it yourself.
The second time it was mentioned in the book, was Lan Qiren’s first class. The first thing he did was complained that even with the stone and rules being in open space, nobody bothered to read. So he will read the rules now.
The book mentioned at least two different sets of Lan rules that both need to be obeyed: 礼则篇 Lize Pian (Book of Rites) 上义篇 Shang Yi Pian (Book of Justice). Whether the rules are separated further into more sets or not is unknown.
Why are some Lan rules better known than others?
Because Lan rules are based on 克己復禮 Keji Fuli, a real-life Confucius asceticism that calls for the restraint/purge of one’s ego and to return to the core rites. This is also newly confirmed in MXTX’s new interview, though it has been more or less heavily suggested in the book itself, with House Lan being known as the House of Gentlemen.
Gentlemen here is not the Western ideal of Gentlemen, but rather a Confucius ideal and set of values. Confucius is the person who created this ideal in the first place.
So it’s not that some rules are better known, but rather the entire image of Lan House is a huge pointer as to how they live their life: with great restraint.
648 notes
·
View notes