#PIK3CA mutation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Präzisionsmedizin bei metastasiertem Brustkrebs
Wie moderne Testverfahren helfen können – und wie du als Patient:in sanft aktiv wirst Bei mir war in den letzen Wochen viel los, leider drehte sich viel um die Erkrankung. Ich habe viel gelernt darüber und doch war es sehr mühsam, alle Informationen zusammen zu sammeln. Den Schock habe ich bisher nicht überwunden. ❤️🩹 Derzeit erhalte ich Trodelvy am 1., 8. und 22. Tag als Infusion, schlafe…
#aktuelle Therapieoptionen Brustkrebs#bessere Entscheidungen Krebs#bewusst leben mit Krebs#Checkliste Arzttermin#FISH Test#Fortschritte Brustkrebs#Fragenkatalog Arztgespräch#genetische Tumoranalyse#HER2 low#IHC#Immunhistochemie#Informationsquellen Krebs#klinische Studien#Krebsdiagnostik#Krebsmedizin heute#Liquid Biopsy#Metastasierter Brustkrebs#metastasierter Brustkrebs verstehen#moderne Krebstherapie#molekulares Tumorboard#Mutationsanalyse#Next Generation Sequencing#NGS#Patient Empowerment#Patientenaufklärung#personalisierte Therapie#PIK3CA Mutation#Präzisionsmedizin#selbstbestimmte Patienten#Therapieanpassung
0 notes
Text
youtube
#Endometrial cancer#Gynecologic oncology#Clinical trials#Immunotherapy#Targeted therapies#Molecular classification#Precision medicine#Cancer biomarkers#GCIG#p53 mutation#Microsatellite instability-high#Checkpoint inhibitors#Oncology consensus#Therapeutic advancements#Patient stratification#Standardized outcomes#Collaborative research#PTEN mutation#PIK3CA mutation#Recurrent cancer.#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Targeted Therapy for Breast Cancer in Thrissur: Revolutionizing Precision Oncology with Dr. Bibin Francis

Breast cancer is a deeply personal and life-altering diagnosis, but medical advances are making the journey more hopeful than ever. One such advancement is targeted therapy, a precise and highly effective treatment modality transforming the outlook for breast cancer patients. In Thrissur, Kerala, this revolution in care is being led by Dr. Bibin Francis, an esteemed oncologist known for his patient-centered and research-driven approach to cancer care.
What is Targeted Therapy?
Targeted therapy is a form of cancer treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific types of cancer cells with less harm to normal cells. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which indiscriminately affects all rapidly dividing cells, targeted therapy zeroes in on molecular targets unique to cancer cells.
In breast cancer, these molecular targets often include:
Hormone receptors (ER/PR): Treatments block or suppress hormone-driven tumor growth.
HER2 receptors: HER2-positive breast cancers respond well to drugs like trastuzumab and pertuzumab.
Genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1/2, PIK3CA): These are targeted using PARP inhibitors or PI3K pathway blockers.
Thrissur: A Growing Hub for Advanced Breast Cancer Treatment
Traditionally known as Kerala's cultural capital, Thrissur is now emerging as a healthcare destination, especially in the realm of oncology. Thanks to the work of specialists like Dr. Bibin Francis, targeted therapy for breast cancer in Thrissur is becoming increasingly accessible and effective.
Dr. Francis practices at the Jubilee Mission Medical College and Research Institute in Nellikunnu, Thrissur. His clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic tools, enabling molecular profiling and personalized treatment plans for each patient.
The Role of Molecular Profiling
Personalized medicine starts with a deep understanding of each patient’s tumor. Molecular profiling analyzes tumors for:
Hormone receptor status (ER/PR)
HER2 overexpression
BRCA1/2 and PIK3CA mutations
PD-L1 levels for immunotherapy eligibility
This testing allows Dr. Francis to tailor treatments, ensuring patients receive the most effective targeted therapies while minimizing side effects.
Common Targeted Therapies Used in Thrissur
Dr. Bibin Francis employs a variety of targeted therapies based on individual tumor characteristics:
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer:
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
Pertuzumab (Perjeta)
T-DM1 and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan
Hormone Receptor-Positive Cancer:
CDK4/6 Inhibitors (Palbociclib, Ribociclib)
PI3K Inhibitors (Alpelisib)
mTOR Inhibitors (Everolimus)
BRCA-Mutated Breast Cancer:
PARP Inhibitors (Olaparib, Talazoparib)
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC):
Immunotherapy + Chemotherapy (e.g., Atezolizumab)
Patient-Centered Approach
Dr. Francis believes in empowering patients through education and shared decision-making. Each treatment plan is:
Backed by evidence-based protocols
Tailored to molecular findings
Delivered with compassion and transparency
He and his team also assist patients in navigating financial support, insurance coverage, and government healthcare schemes like KASP and Ayushman Bharat.
FAQs About Targeted Therapy in Thrissur
1. How is it different from chemotherapy? Targeted therapy acts only on cancer-specific pathways, leading to fewer side effects.
2. Who is eligible? Eligibility is based on molecular profiling and receptor testing.
3. How are treatments given? Orally or via IV, depending on the drug type.
4. What about cost? Costs can vary, but Dr. Francis's clinic works with patients to access support programs.
5. Are male breast cancer patients eligible? Yes, if their cancer shows targetable biomarkers.
0 notes
Link
Positive recommendation based on phase III INAVO120 data showing ItovebiTM (inavolisib) in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant more than doubled progression-free survival in the first-line setting1The Itovebi-based regimen also demonstrated #BioTech #science
0 notes
Text
Lung Cancer Research in gene therapy and improvements in radiation therapy have provided a new ray of hope for lung cancer patients. Management of symptoms and improving the quality of life is one of the most important features of cancer care and the cancer nurse plays a large role in this by providing proactive and treatment centric nursing interventions for symptoms palliation. Lung cancer is one of the most lethal diseases in the United States with more deaths compared with any other form of cancer. With 160,390 deaths in 2007, lung cancer represents the single most threatening form of the disease exceeding causalities for breast cancer, colon cancer and prostrate cancer put together. in England, lung cancer accounts for 5% of all deaths every year. Patients with lung cancer also present with higher levels of symptom distress compared with other forms of cancer. Further, lung cancer patients also experience multiple symptoms, which vary with different treatment modalities. Poor symptoms management not only leaves the patient severely dysfunctional but also psychologically distressed. New developments in cancer treatment such as gene therapy and radiotherapy also impact care provision. Providing Symptoms management is a vital aspect and oncology nurses have a large role to play in alleviating the distress of the patients. Let us briefly examine the new developments in cancer care with the impacts on the professional practice of the cancer care nurse. Genetic and Molecular Biology of cancer Our understanding of cancer has advanced much over the last two decades. Researchers have made great strides in the study of the genetic and the molecular biology of cancer. The genetic abnormalities that lead to cancer are more clearly illustrated by the vast amount of research conducted on colorectal carcinoma. It has been found that the genetic precursors for cancer include suppression of the tumor suppression gene APC leading to the transformation of the normal somatic cell into an adenomatous polyp. This is followed by mutations in other tumor suppression genes such as P53, DCC and K-Ras resulting in the formation of adenoma with a great propensity for developing into carcinoma. Most cases of cancer are caused by loss of cell regulation due to suppression of P53 or abnormalities in P53 gene affecting natural cellular apoptosis leading to uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells. Some of the genes like: PTEN/MMAC1, DMBT1 (deleted in malignant brain tumor-1), EGFR, TP53, P16, PDGFR, are implicated in lung cancer and brain tumors. Today, though we know about the alterations in these genes, we are yet without a clue as to the cause for these abnormal gene alterations. Several studies have revealed that P53 mutations are the most common among humans and therefore carry a high risk potential for developing cancers. Since the P53 gene is directly responsible for cell cycle regulation, including the initiation of apoptosis, aberration in the gene results in uncontrolled cell growth. Other studies have shown that the P. I3 kinase (phosphoinositide-3-kinase has an important role in regulating the number and size of the cells. a recent study by Massion et. al (2004) also observed a distinct increase in PIK3CA in 70% of squamous carcinomas and in 38% of large cell carcinomas. Thus, APC gene, p53, Ras and several other biological markers have already been identified and are currently the focus of the development of more effective pharmacogenetic interventions. Lung Cancer Treatment Methods There are a variety of treatment methods for lung cancer including, Surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, Photodynamic therapy, gene therapy, etc. While chemotherapy and radiation therapy are traditional, they have not proved to be totally effective. The rapid advancements in gene therapy seem to offer a new ray of hope for lung cancer patients. One of the successful pilot studies was conducted by Dr. David P. Carbone, Phd, in early 2000. The primary purpose of this gene therapy was to trigger the expression of P53 and to suppress the oncogenes by injecting normal genes into the cancerous cells using recombinant adenovirus as a vector. This trial was administered on patients with bronchioloalveolar lung carcinoma, a condition which is typically non-responsive to radiation and chemotherapy. Four of the 11 subjects showed considerable improvements in symptoms management and four out of 9 subjects who were evaluated for DLCO showed 20% increase in gaseous absorption (from air into blood). More recently gene therapy has focused on chaperone heat shock protein 90 (HSP90), which is responsible in several cellular signaling mechanisms for a number of oncogenic client proteins such as ERBB2, C-RAF, CDK4, AKT/PKB, mutant P53 etc. Thus, by targeting and modulating the HSP90 it is possible to inhibit the development of malignant phenotypes. Successful clinical trials have been reported for drugs such as geldanamycin analogue and 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin offering a new promise for cancer patients. The development of effective HSP90 inhibitors is currently the focus of pharmacogentic researchers. The downside of gene therapy is that it is still a new therapy and in most cases in the trial phase in which patients willingly consent after being informed of the potential risk factors. Research nurses have an important role to play in identifying appropriate candidates for gene therapy in consultation with the doctor and in constant monitoring of the patients for any abnormal reactions to gene therapy. Also, since some of the adverse effects may not manifest immediately, nurses who care for patients who underwent gene therapy have to be aware of the possible immediate side effects and the management of long-term effects, which may not be listed within the gene therapy protocol at the time of the therapy. Oncology nurses have to educate the patients and their families as to the potentials of gene therapy, train other nursing staff and also participate in the research programs for gene therapy as they have the first hand information about patients reaction to genetic therapy. Since gene therapy is very much in the trial phase now, cancer nurses have a significant role in terms of their valuable input into research, as they are the direct caregivers for patients in clinical trials. Radiotherapy Radiotherapy has been one of the mainstay treatments for cancer. However, conventional radiotherapy has not been very effective and so more effective forms of non-conventional interventions such as hyperfractionated, accelerated and combined hyperfractionated / accelerated radiotherapy regimens have begun to be tested. A recent study by Lester et.al (2006) showed that conventional radiotherapy is not very effective in terms of treatment outcome even with higher dosages and that it only resulted in increased side effects including oesophagitis, anemia, etc. Of the fourteen trials which were reviewed for the study, it was found that even with high dosage RT there was only very little improvement in terms of survival with 5% at one year and 3% at 2 years. The study also found that for those patients with higher PS (performance status), increasing the radiation dosage to as 36Gy/12F would offer better survival chances though the risk for oesophagitis and other radiation side effects are also increased. An extensive British study has found that hyperfractioned and accelerated forms of radiotherapy have both proven to be cost effective as well as more positive in terms of treatment outcome. The idea behind accelerated radiotherapy is to exploit the fast repair capacity of normal cells compared with cancer cells by using frequent dosage. Thus, while the healthy repair mechanism of normal cells enables them to recover swiftly cancer cells are less likely to survive the radiation exposure. Researchers believe that Continuous Hyperfractionated Accelerated Radiotherapy (CHART) offers better survival chances over conventional radiotherapy. However, such a change in treatment regimen involves "out of hours" working by nursing staff or alternatively more nursing staff which is a problem with the existing nursing shortage. Also, the quality of life factor is an issue as there would be considerable disadvantages during the frequent and intensive treatment period. However, the long-term effects override the temporary discomfort and most patients are willing to undergo the regimen for better survival chances. It is important that the cancer nurse understands and explains the implications of these new radiation-based treatment methods so the patient would be better prepared for the treatment course. Conclusion Symptoms management is most important for lung cancer patients. Asides the multiple symptoms associated with lung cancer, new symptoms also develop with respect to the nature of treatment. Providing ventilatory care, anemia care, and pain management are some of the common symptomatic interventions on the part of the nurse. Thus, continuous monitoring of symptoms is necessary during the course of the treatment in order to provide more effective clinical interventions for better symptoms management. From the cancer nursing perspective the integration of therapy and symptoms management is most important to provide vital relief for patients. New therapies based on the specific biological process of lung cancer are being developed. Cancer nurses with sufficient knowledge of the biological basis of these therapies would be better equipped to deal with the practical clinical implications and provide better symptoms management. The technical understanding of the nurses is also crucial in educating and in enabling the patients to take care of themselves. Further, it also goes without saying that nurses, as the primary caregivers are responsible for the emotional well being of the patients. Improving the quality of life is one of the most important features of cancer care and the cancer nurse plays a large role in this by providing proactive and treatment centric nursing interventions for symptoms palliation. Bibliography CDC, "Lung Cancer: Statistics," Accessed!4th Dec 2007, available at http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/lung/statistics/ Caldas, C. (1998) "Science, medicine and the future - Molecular assessment of cancer': British Medical Journal: No.316 pp. 1360-1363, Available online at, http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1113070 3) Nobuaki Ishii and N. de Tribolet, "Are p53 mutations and p53 over expression prognostic factors for astrocytic tumors? Critical reviews in Neurosurgery, vol 8 / no 5, Sept 1998. Massion, Pierre P, Taflan, Et, al (Nov 2004), "Early Involvement of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway in Lung Cancer Progression," American Journal of Respiratory and Critical care Medicine, Heike Allgayer, MD, PHd,(2003), "Molecular Staging of Cancer: Concepts of Today, Therapies of Tomorrow," Journal of Surgical Oncology, 82, 217-223 Karen T. Barker and Richard S. Houlston, "Overgrowth syndromes: Is dysfunctional P. 13 Kinase signalling a Unifying mechanism," European Journal of Human Genetics (2003) 11, 665-670. Available online at, http://www.nature.com/ejhg/journal/v11/n9/full/5201026a.html Richard C. Duke, David M. Ojcius and John Ding-E Young, (Dec 1996) "Cell Suicide in Health and Disease," Scientific American. Marissa V Powers and Paul Workman, "Targeting of multiple signaling pathways by heat shock protein 90 molecular chaperone inhibitors," Endocrine-Related Cancer 13, S125-135 ACS, "Gene Therapy for Lung Cancer," Accessed Dec 15th 2007, available at http://www.cancer.org/docroot/NWS/content/NWS_1_1x_Gene_Therapy_for_Lung_Cancer.asp Wake B.L., Taylor, R.S., Sandercock, J. 'Hyperfractionated/accelerated radiotherapy regimens for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. A systematic review of clinical and cost-effectiveness'. Birmingham: University of Birmingham, Department of Public Health and Epidemiology, January 2002. Lester JF, Macbeth FR, Toy E, Coles B. (2006), "Palliative radiotherapy regimens for non-small cell lung cancer." Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD002143. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002143.pub2. Connie Henke Yarbro, Margaret Hansen & Michelle Goodman, "Cancer Nursing: Principles and Practices," Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Sixth edition Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Alpelisib
Alpelisib is a medication used in the treatment of certain types of advanced or metastatic breast cancers. It is a selective inhibitor of the enzyme PI3-kinase (phosphoinositide 3-kinase), specifically targeting the alpha isoform. The PI3-kinase pathway is involved in cellular signaling related to cell growth, proliferation, and survival. Mutations in the PIK3CA gene, leading to overactivation of the PI3-kinase pathway, are found in some breast cancers. By inhibiting the alpha isoform of PI3-kinase, alpelisib helps control the growth of cancer cells in these cases. Alpelisib is often used in combination with other medications, such as endocrine therapies, to provide a comprehensive treatment approach. Buy high quality Alpelisib from Chemicea Pharmaceuticals. Chemicea Pharmaceuticals is one of the leading manufacturer and exporter of Alpelisib
#N Nitroso Aceclofenac#N Nitroso Atenolol#N Nitroso Atomoxetine#N Nitroso Benazepril#N Nitroso Betahistine#N Nitroso Bisoprolol#N Nitroso Brinzolamide#N Nitroso Bupropion#N Nitroso Ciprofloxacin#N Nitroso Dabigatran Etexilate#N Nitroso Desloratadine#N Nitroso Diclofenac#N Nitroso Elagolix#N Nitroso Enalapril#N Nitroso Safinamide#N Nitroso Prilocaine#N Nitroso Vonoprazan#N Nitroso Silodosin#N Nitroso Duloxetine#N Nitroso Folic acid#N Nitroso Propranolol#N Nitroso Paroxetine#N Nitroso Perindopril#N Nitroso Vortioxetine#N Nitroso Meglumine#N Nitroso Nortriptyline#N Nitroso Rasagiline
0 notes
Text
“Cowden Syndrome”, Victor McKusick, Mendelian Inheritance in Man, 1966. 考登綜合症。(PIK3CA).
Here I present: “Cowden Syndrome”, Victor McKusick, Mendelian Inheritance in Man’, 1966. 考登綜合症。(PIK3CA). INTRODUCTION. Cowden syndrome is a hamartomatous disorder characterized by macrocephaly, facial trichilemmomas, acral keratoses, papillomatous papules, and an increased risk for the development of breast, thyroid, and endometrial carcinoma. While there is association with mutation in the…
0 notes
Text
BioAdvisers said on Biotech Advisers
Loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines significantly correlates with AZD8186 sensitivity
Ocosu-Brackett et al.’S Figure 6 “Effect of the combination of AZD8186 and anti-PD1 on isogenic models” is featured on the cover of “Oncotarget” issue 11.
In vitro cell viability assays and immunoblots showed that loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines was significantly associated with AZD8186 sensitivity.
AZD8186 combined with paclitaxel and eribulin has a synergistic effect on the growth inhibition of PTEN-losing cells.
AZD8186 significantly enhanced the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 antibodies in a melanoma xenograft model of PTEN-deficient BP mice, but not in a PTEN wild-type CT26 xenograft model.
In vitro, cell proliferation and colony formation assays were performed to determine the sensitivity of the cells to AZD8186.
AZD8186 has single-agent efficacy in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN, but has limited single-agent efficacy in vivo.
“Phosphatidylinositol,” said the University of Texas Medical Anderson Cancer Center’s Department of Surgical Oncology, the Department of Research Cancer Therapy, the Department of Breast Cancer Surgery, and the Dr. Franka Meric-Bernstam Research Center in Houston, Texas, USA The 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cellular processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival. ”
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cell processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival.
——Dr. Funda Meric-Bernstam, Department of Cancer Therapy, Department of Breast Surgery, Oncology and Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Personalized Cancer Therapy Institute
MiRNA mutation, loss of copy number, epigenetic silencing, and downregulation of PTEN protein can lead to inactivation of PTEN function, leading to activation of the PI3K / AKT / mTOR pathway, which in turn increases tumor growth in a variety of solids, invades and metastases tumors including the breast Cancer, endometrial cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, glioblastoma and colorectal cancer.
Loss of PTEN and increased PI3K signaling are related to the resistance of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab and endocrine therapy, and the poor prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer.
In vitro, they consumed PIK3CB, which encodes PI3K, to reveal the significant growth inhibitory effect of PTEN-deficient tumors, whereas in corresponding PTEN-deficient tumors, to inhibit PIK3CA or encodes PI3K respectively. For PI3K, it did not have this growth inhibitory effect.
Therefore, the PI3K subtype is a driver of abnormal proliferation in PTEN-deficient cancers, and therefore, PI3K is a promising target for the treatment of PTEN-deficient TNBC. AZD8186 is a selective and potent small molecule inhibitor of PI3K with additional activity on PI3K isoforms.
The Merrick-Bernstam research team concluded in their Oncotarget paper, “These results provide preclinical evidence for the antitumor efficacy of AZD8186 in PTEN-deficient solid tumors. AZD8186 has a single drug in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN Efficacy, with a modest single-agent effect in the body. In addition, AZD8186 enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel, but the use of this combination in an immunosuppressive model can observe stable and progressive disease. In an immune-capable model, AZD8186 Combination with anti-PD1 can lead to regression of PTEN-deficient BP tumors. We realize that although AZD8186 sensitivity is associated with PTEN loss, we can only speculate on causality. In conclusion, although further understanding of the mechanism of action of these combinations is required. ”
Abbkine specializes in the fields of proteinology and cytology, and is committed to innovating and developing various antibodies, proteins, analytical reagents and kits, with a view to becoming a key promoter in the fields of life science research and development, and drug development. We provide you with the favorite products of protein and immune research users, from basic immunological products such as protein extraction and quantification, to internal reference label antibodies, primary antibodies and secondary antibodies for immunological experiments; favorite products of cell research users, from Dyes and kits for detecting cell status, organelle extraction kits, cell substructure staining and cell metabolism detection products, and cytokine and protein detection kits for cell culture, just to help your research career !
About Abbkine
Our positioning: Serve global users of cell and protein research, and provide users with economical and technical product solutions by applying processes and product portfolios.
Our mission: to inspire our inherent creativity, provide competitive biomedical products and services, and continue to create maximum value for our customers.
Our vision: to be a respected, world-class supplier of biomedical products and services.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Wie man Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) sinnvoll bei einer Krebserkrankung nutzt – Ein Leitfaden für Patient:innen
In einer Zeit, in der sich medizinisches Wissen rasant entwickelt und die Informationsflut überwältigend scheint, kann künstliche Intelligenz (KI) eine große Hilfe sein – gerade für Menschen mit einer Krebserkrankung. Dieser Beitrag soll dir zeigen, wie du KI gezielt nutzen kannst, um dich besser zu informieren, die richtigen Fragen zu stellen und mehr Klarheit für deine persönliche Behandlung zu…
#ADC-Therapie#Arztgespräch vorbereiten#Blog Brustkrebs#Brustkrebs#brustkrebs blog#ChatGPT#digitale Unterstützung bei Krebs#HER2-low#Hormonrezeptor-positiv#Immuntherapie#Künstliche Intelligenz#Krebs verstehen#Krebsblog#Krebsdiagnose#Krebszentren#Liquid Biopsy#Medikamente bei Krebs#Metastasierter Brustkrebs#NGS-Test#Onkologie#Patient Empowerment#PIK3CA-Mutation#Studienrecherche#Therapieübersicht#Trop-2-Expression#Zweitmeinung
0 notes
Text
Bioadvisers shared on Biotech Advisers
Loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines significantly correlates with AZD8186 sensitivity
Ocosu-Brackett et al.’S Figure 6 “Effect of the combination of AZD8186 and anti-PD1 on isogenic models” is featured on the cover of “Oncotarget” issue 11.
In vitro cell viability assays and immunoblots showed that loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines was significantly associated with AZD8186 sensitivity.
AZD8186 combined with paclitaxel and eribulin has a synergistic effect on the growth inhibition of PTEN-losing cells.
AZD8186 significantly enhanced the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 antibodies in a melanoma xenograft model of PTEN-deficient BP mice, but not in a PTEN wild-type CT26 xenograft model.
In vitro, cell proliferation and colony formation assays were performed to determine the sensitivity of the cells to AZD8186.
AZD8186 has single-agent efficacy in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN, but has limited single-agent efficacy in vivo.
“Phosphatidylinositol,” said the University of Texas Medical Anderson Cancer Center’s Department of Surgical Oncology, the Department of Research Cancer Therapy, the Department of Breast Cancer Surgery, and the Dr. Franka Meric-Bernstam Research Center in Houston, Texas, USA The 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cellular processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival. ”
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cell processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival.
——Dr. Funda Meric-Bernstam, Department of Cancer Therapy, Department of Breast Surgery, Oncology and Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Personalized Cancer Therapy Institute
MiRNA mutation, loss of copy number, epigenetic silencing, and downregulation of PTEN protein can lead to inactivation of PTEN function, leading to activation of the PI3K / AKT / mTOR pathway, which in turn increases tumor growth in a variety of solids, invades and metastases tumors including the breast Cancer, endometrial cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, glioblastoma and colorectal cancer.
Loss of PTEN and increased PI3K signaling are related to the resistance of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab and endocrine therapy, and the poor prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer.
In vitro, they consumed PIK3CB, which encodes PI3K, to reveal the significant growth inhibitory effect of PTEN-deficient tumors, whereas in corresponding PTEN-deficient tumors, to inhibit PIK3CA or encodes PI3K respectively. For PI3K, it did not have this growth inhibitory effect.
Therefore, the PI3K subtype is a driver of abnormal proliferation in PTEN-deficient cancers, and therefore, PI3K is a promising target for the treatment of PTEN-deficient TNBC. AZD8186 is a selective and potent small molecule inhibitor of PI3K with additional activity on PI3K isoforms.
The Merrick-Bernstam research team concluded in their Oncotarget paper, “These results provide preclinical evidence for the antitumor efficacy of AZD8186 in PTEN-deficient solid tumors. AZD8186 has a single drug in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN Efficacy, with a modest single-agent effect in the body. In addition, AZD8186 enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel, but the use of this combination in an immunosuppressive model can observe stable and progressive disease. In an immune-capable model, AZD8186 Combination with anti-PD1 can lead to regression of PTEN-deficient BP tumors. We realize that although AZD8186 sensitivity is associated with PTEN loss, we can only speculate on causality. In conclusion, although further understanding of the mechanism of action of these combinations is required. ”
Abbkine specializes in the fields of proteinology and cytology, and is committed to innovating and developing various antibodies, proteins, analytical reagents and kits, with a view to becoming a key promoter in the fields of life science research and development, and drug development. We provide you with the favorite products of protein and immune research users, from basic immunological products such as protein extraction and quantification, to internal reference label antibodies, primary antibodies and secondary antibodies for immunological experiments; favorite products of cell research users, from Dyes and kits for detecting cell status, organelle extraction kits, cell substructure staining and cell metabolism detection products, and cytokine and protein detection kits for cell culture, just to help your research career !
About Abbkine
Our positioning: Serve global users of cell and protein research, and provide users with economical and technical product solutions by applying processes and product portfolios.
Our mission: to inspire our inherent creativity, provide competitive biomedical products and services, and continue to create maximum value for our customers.
Our vision: to be a respected, world-class supplier of biomedical products and services.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Asian Countries are witnessing an Increasing Demand for Breast Cancer Drugs
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women after lung cancer. Advancements in screening and treatment for breast cancer have improved survival rates in the last few decades. Breast cancer is a kind of cancer formed in tissues of the breast. The most common types of breast cancer are ductal carcinoma, which begins in the lining of the milk ducts and lobular carcinoma, which starts in the lobules (milk glands) of the breast.
In the US, around 12% of women develop breast cancer over the course of their lifetime. In Canada, an estimated 26,900 women were expected to be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2019 and breast cancer accounts for nearly 25% of new cases of cancer among Canadian women.
North America was leading the global breast cancer drug market with more than 45% of the revenue in 2018. The presence of standard healthcare infrastructure, increasing awareness about early disease diagnosis, and the presence of established players are among the factors that make North America a major shareholder in the market.
Product approvals, collaboration, and development of new drugs are among the strategies followed by dominant companies to strengthen their position in the market. For instance, in May 2019, Novartis announced the US FDA approval for Piqray in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of postmenopausal women and men with hormone receptor-positive, PIK3CA-mutated, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HR+/HER2-), advanced or metastatic breast cancer
Expiration of patents, high development cost of the drug, and strict regulatory guidelines are hampering the growth of the market. By considering all the above facts and figures and an in-depth analysis of the market, the market research company predicts that global breast cancer drugs market is going to reach revenue of around $36.7 billion, and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast ed period of 2019- 2025.
Read the full report summary @ breast cancer drugs market or Download sample report @ breast cancer drugs market sample report.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Molecular Testing?
Molecular testing is a laboratory method that checks a sample of tissue, blood, or other body fluid for certain genes, proteins, or other molecules that may be a sign of a disease or condition. It can be done alone or with other procedures such as biopsies to help diagnose cancer or other diseases. Molecular tests can also help plan treatment, find out how well treatment is working, and predict whether cancer will spread or return. Here is some more information about molecular testing.
Whether you have heard these terms during the COVID-19 pandemic or not, molecular diagnostics (MDx) is an important and rapidly developing area of medical laboratory science. Molecular diagnostics utilizes techniques from molecular biology, such as PCR and other nucleic acid amplification tests, to help diagnose disease.
The earliest molecular techniques were developed in the 1950s to study genetic markers, but it took decades for these methods to be applied to medical laboratory diagnosis. MDx is now the basis for many routine tests that help to identify infectious agents and guide antimicrobial therapy.
A common example is the rapid detection of influenza or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) using a real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). This test can detect many different kinds of bacteria or viruses in a sample, usually within an hour. View here: https://www.jantdx.com for more details about this service.
Molecular tests are also used to diagnose some types of cancer, including mutations in the BRAF and PIK3CA genes that can increase your risk of getting a certain type of thyroid cancer. These tests can also help determine if you have a gene that makes it easier for your tumor to grow or spread.
Other molecular tests look for specific proteins or other biomarkers that can be useful in predicting how a tumor will respond to various treatments. For example, a gene expression signature that predicts benefit from tyrosine kinase inhibitors can help choose the best medication for advanced breast cancer.
Some large-scale genetic tests look at whole sections of DNA called chromosomes rather than individual genes. These include karyotypes and chromosomal microarrays. These tests can also have findings unrelated to the reason they were ordered (secondary findings).
The availability of these new tests has led some to recommend that all thyroid nodules be molecularly tested before surgery. However, prospective studies assessing the effect of molecular testing on surgical rates and outcomes are lacking. Those studies that do exist are correlative in nature and show that fewer surgeries were performed during the time period when molecular testing was introduced, but they do not prove that the tests caused this change. Learn more about the above topic by clicking this link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molecular_diagnostics.
0 notes
Link
Inavolisib in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant more than doubled progression-free survival compared to palbociclib and fulvestrant alone1The inavolisib combination has the potential to address resistance to treatment and poor prognosis a #BioTech #science
0 notes
Text
New Blood-Vessel-on-a-Chip Can Help Researchers Further Understand Vascular Malformations
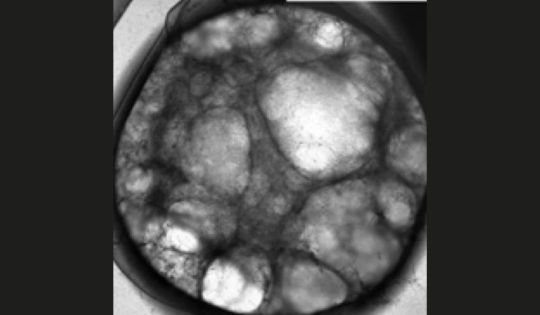
New Blood-Vessel-on-a-Chip Can Help Researchers Further Understand Vascular Malformations. A research team led by William Polacheck, Ph.D., at the UNC School of Medicine, has engineered a microfluidic model that mimics a rare genetic disorder affecting the structure of veins, arteries, capillaries, and lymphatic vessels. February 24, 2023, CHAPEL HILL, N.C. - Our bodies are made up of 60,000 miles of complex pipes that play a vital role in transporting nutrients throughout our bodies, performing waste disposal, and supplying our organs with fresh oxygen and blood. Several things can go wrong with this complex system, including vascular malformations (VMs), a group of rare genetic disorders that causes an abnormal formation of veins, arteries, capillaries, or lymphatic vessels at birth. VMs can interfere with the duties of our precious pipes by causing blockages, poor drainage, and the formation of cysts and tangles.

William Polacheck, PhD To address a need for further study, William Polacheck, Ph.D., assistant professor in the UNC-NCSU Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering and the Department of Cell Biology and Physiology, and his team from across the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, have developed a model that mimics VMs specifically caused by a mutation of PIK3CA – a gene that has been implicated in multiple types of lymphatic, capillary, and venous malformations. Their work was published in Science Advances, an open-access multidisciplinary journal from the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). “There are number of ‘chicken and the egg problems’ of the PIK3CA mutation,” said Polacheck. “Is it causing something else to go wrong? Or is there something else in the environment causing the mutation to have more severe effects? Working in a much more controlled environment, such as a microfluidic model, allows us to isolate and figure out how the genetics of the disease relate to what’s happening in the cells.” VMs are caused by mutations in the genes that direct the development of vasculature throughout the body. Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) is one of those genes. Activating mutations in PIK3CA commonly contribute to malformations of the smaller blood vessels, causing blood to pool underneath the skin. This specific type of vascular malformation is usually discovered at birth. These diseases start as the baby is developing. Since there is a multitude of changes happening at this point in the child’s development, it can be a difficult condition for researchers to study.
A Team in the Making
Julie Blatt, MD, professor of pediatric hematology-oncology in the UNC Department of Pediatrics, saw the need for a new approach to model the disease, which affects a majority of her patients. She has had a long-standing interest in the clinical management of patients with vascular malformations, as well as an interest in repurposing cancer drugs for the disease. Impressed with his prior manuscripts, Dr. Blatt picked up the phone and cold-called Polacheck, who is a biomedical engineer by trade, to ask if he could create a microfluidic model of PIK3CA-specific vascular malformations. “I think the transdisciplinary aspect keeps the possibility of application to patients at the forefront, said Dr. Blatt. “The Polacheck lab has prioritized introduction of genetic mutations that are relevant to patients and to studying drugs which we know or think will have benefit.”

Wen Yih Aw, PhD Around the same time, Wen Yih Aw, Ph.D., was working as a postdoctoral researcher at UNC Catalyst, a research group focused on understanding rare diseases in the Eshelman School of Pharmacy. Aw was collaborating with the Polacheck lab on a vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome project. Eventually, Aw joined the Polacheck lab and used her molecular biology expertise to help develop the VMs model. In addition to Dr. Blatt and Aw, the lab has an ongoing collaboration with Boyce Griffith, Ph.D. in the Department of Mathematics and the Computational Medicine Program at the UNC College of Arts and Sciences, who is helping with analyzing the structures of the networks. “All those pieces were necessary to complete the work,” said Polacheck. “It does say something about UNC-Chapel Hill because there were multiple departments across campus involved. There were no barriers whatsoever to working together on this project.”
How a Microfluidic Model Works
Microfluidic models are incredibly small – about the size of a millimeter – three-dimensional devices that can be used to control or simulate the environment within the body. In this case, a small piece of blood vessel composed of healthy human endothelial cells or endothelial cells expressing the PIK3CA mutation is centered inside of the device. From there, the researchers can look into the process of vascular formation, and introduce specific chemicals and mechanical forces to the model to simulate the conditions of the body. They observed the formation of enlarged and irregular vasculature with the introduction of PIK3CA mutation. To confirm whether or not their model accurately portrays the manifestation of the disease, the team next conducted a drug efficacy study.

Images of control (Top) and PIK3CAE542K vascular networks (Bottom). Vascular networks were labeled with fibrin (magenta), 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (white), actin (green), and endothelial cell–specific CD31 staining (cyan). There are two drugs currently used for the treatment of vascular malformations: rapamycin and alpelisib. The latter is a newly discovered PIK3CA-specific inhibitor recently approved by the FDA to treat certain types of breast cancer and PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum. So far, pre-clinical studies in mouse models and in patients have shown that alpelisib is more effective in reversing vascular malformation defects. After selecting the two drugs, Polacheck and Aw applied the treatment to their devices. The study was a success. “The blood vessels used to be really dilated and large,” said Aw, first author of the study. “By imaging the vessels before and after treating with drugs, we observed the vessels shrink and, more or less, revert it back to a normal shape and function. We were very excited to be able to replicate some of the results in vitro with the model we built.” Moving forward, Aw and Polacheck are looking to replicate the finding in tissues from vascular malformation patients, especially those who don’t have the PIK3CA mutation or don’t have clear genetic information. Their model can now be used to evaluate new medications or to perform synergistic drug studies.
Multiple Paths for Future Study
Now that they know that their model works, Aw and Polacheck plan to use it to study the behavior of the mutated cells over time, as well as how the mutation affects malformations of the lymphatic tissue. The disease initially begins with an individual cell that acquires the PIK3CA mutation. Then, much like a chain reaction, the effects of the mutation in that one cell spreads to the surrounding cells until the malformation is fully formed. As their model currently stands, the lab cannot mimic that natural process. Aw is currently working on a new and different approach for a microfluidic model. She aims to create a platform that will allow them to start with cells that are healthy, and then “flip on” the mutation, and watch it progress across the tissue of interest. Ultimately, it will help them understand how the mutation is able to affect other cells and move throughout space. Vascular malformations can also occur in lymphatic tissue. As opposed to blood vessels, lymphatic vessels have a duty to recycle excess fluid throughout the body and acts as a superhighway for immune cells to get to sites of infection. Very little is known about the basic cell biology of lymphatic endothelial cells, so Polacheck is hoping to do a study that is similar to his most recent one. “The outputs are slightly different because the function of the lymphatics is different from blood vessels,” said Polacheck. “By comparing and contrasting what happens on the blood side and the lymphatic side, we will also be able to learn something about the basic biology of those two types of tissues.” Source: UNC School of Medicine Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How a new blood-vessel-on-a-chip can help researchers further understand vascular malformations
Control cells and endothelial cells expressing PIK3CA-activating mutations cultured in 3D fibrin matrices and imaged at 0 and 168 hours after seeding. Scale bars, 1000 μm. Credit: Aw et al. Our bodies are made up of 60,000 miles of complex pipes that play a vital role in transporting nutrients throughout our bodies, performing waste disposal, and supplying our organs with fresh oxygen and…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
“Colorectal Cancer 3q”, Victor McKusick, Mendelian Inheritance in Man’, 1966. 结肠癌。(CRC).
Here I present: “Colorectal Cancer 3q”, Victor McKusick, Mendelian Inheritance in Man’, 1966. 结肠癌。(CRC). INTRODUCTION. Chromosome #3 has two different colorectal cancers located on the “3p” short-arm & “3q” long-arm. There is evidence that colorectal cancer is caused by mutation in the PIK3CA gene on cytogenetic location 3q26.32 and genomic coordinates 3:179,148,126-179,240,093. The screenshot…
0 notes