#Removing duplicates from a String in Java
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Exploring Java Streams API for Functional Programming
Exploring Java Streams API for Functional Programming
The Java Streams API, introduced in Java 8, provides a functional approach to processing collections of data. It allows developers to write concise, readable, and efficient code using declarative programming rather than imperative loops.
1. What is the Java Streams API?
A Stream in Java is a sequence of elements that supports various functional operations such as filtering, mapping, and reducing. It enables a lazy evaluation approach, meaning elements are processed only when needed.
Key Features: ✔ Supports functional programming concepts. ✔ Works with Collections, Arrays, and I/O sources. ✔ Uses internal iteration, improving performance. ✔ Supports parallel processing for efficiency.
2. Creating a Stream
A stream can be created from collections, arrays, or other data sources.
Example 1: Creating a Stream from a List
import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Stream;public class StreamExample { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> names = List.of("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"); Stream<String> nameStream = names.stream(); nameStream.forEach(System.out::println); } }
Example 2: Creating a Stream from an Arra
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.stream.Stream;public class ArrayStreamExample { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] arr = {"Java", "Python", "C++"}; Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(arr); stream.forEach(System.out::println); } }
3. Stream Operations
Java Streams API provides various methods for functional-style programming.
Intermediate Operations (Return another Stream)
OperationDescriptionfilter(Predicate<T>)Filters elements based on a conditionmap(Function<T,R>)Transforms each elementsorted()Sorts elements in natural orderdistinct()Removes duplicate elementslimit(n)Limits the number of elements
Terminal Operations (End the Stream)
OperationDescriptioncollect(Collectors.toList())Collects elements into a listforEach(Consumer<T>)Iterates over elementsreduce(BinaryOperator<T>)Reduces elements to a single valuecount()Returns the number of elementsanyMatch(Predicate<T>)Checks if any element matches a condition
4. Functional Programming with Streams
Example 1: Filtering a List
import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class FilterExample { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> names = List.of("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "Amanda"); List<String> filteredNames = names.stream() .filter(name -> name.startsWith("A")) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(filteredNames); // Output: [Alice, Amanda] } }
Example 2: Mapping Elements
import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class MapExample { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> names = List.of("alice", "bob", "charlie"); List<String> upperCaseNames = names.stream() .map(String::toUpperCase) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(upperCaseNames); // Output: [ALICE, BOB, CHARLIE] } }
Example 3: Reducing Elements
import java.util.List;public class ReduceExample { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> numbers = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); int sum = numbers.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum); System.out.println("Sum: " + sum); // Output: Sum: 15 } }
5. Parallel Streams for Performance
Java Streams API supports parallel execution to improve performance.import java.util.List;public class ParallelStreamExample { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> numbers = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); int sum = numbers.parallelStream().reduce(0, Integer::sum); System.out.println("Sum: " + sum); } }
Parallel streams can speed up processing for large datasets by using multi-core processors.
6. When to Use Streams API?
✔ When you need to process large datasets efficiently. ✔ When functional programming improves readability and conciseness. ✔ When you want to leverage parallel processing for performance gains.
⚠ Avoid Streams when: ❌ The operation is very simple (e.g., a single loop is sufficient). ❌ The operation modifies the underlying collection.
Conclusion
The Java Streams API enables developers to write clean, declarative, and functional-style code. By using operations like filter, map, reduce, and parallel processing, we can handle complex data transformations efficiently.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/core-java-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
hi
Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters Problem: Find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters. Link: Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Median of Two Sorted Arrays Problem: Find the median of two sorted arrays. Link: Median of Two Sorted Arrays
Longest Palindromic Substring Problem: Find the longest palindromic substring in a given string. Link: Longest Palindromic Substring
Zigzag Conversion Problem: Convert a string to a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows. Link: Zigzag Conversion
Three Sum LeetCode #15: Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
Container With Most Water LeetCode #11: Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container that holds the most water.
Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters LeetCode #3: Find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Product of Array Except Self LeetCode #238: Return an array such that each element is the product of all the other elements.
Valid Anagram LeetCode #242: Determine if two strings are anagrams.
Linked Lists Reverse Linked List LeetCode #206: Reverse a singly linked list.
Merge Two Sorted Lists LeetCode #21: Merge two sorted linked lists into a single sorted linked list.
Linked List Cycle LeetCode #141: Detect if a linked list has a cycle in it.
Remove Nth Node From End of List LeetCode #19: Remove the nth node from the end of a linked list.
Palindrome Linked List LeetCode #234: Check if a linked list is a palindrome.
Trees and Graphs Binary Tree Inorder Traversal LeetCode #94: Perform an inorder traversal of a binary tree.
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree LeetCode #235: Find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes in a BST.
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal LeetCode #102: Traverse a binary tree level by level.
Validate Binary Search Tree LeetCode #98: Check if a binary tree is a valid BST.
Symmetric Tree LeetCode #101: Determine if a tree is symmetric.
Dynamic Programming Climbing Stairs LeetCode #70: Count the number of ways to reach the top of a staircase.
Longest Increasing Subsequence LeetCode #300: Find the length of the longest increasing subsequence.
Coin Change LeetCode #322: Given a set of coins, find the minimum number of coins to make a given amount.
Maximum Subarray LeetCode #53: Find the contiguous subarray with the maximum sum.
House Robber LeetCode #198: Maximize the amount of money you can rob without robbing two adjacent houses.
Collections and Hashing Group Anagrams LeetCode #49: Group anagrams together using Java Collections.
Top K Frequent Elements LeetCode #347: Find the k most frequent elements in an array.
Intersection of Two Arrays II LeetCode #350: Find the intersection of two arrays, allowing for duplicates.
LRU Cache LeetCode #146: Implement a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache.
Valid Parentheses LeetCode #20: Check if a string of parentheses is valid using a stack.
Sorting and Searching Merge Intervals LeetCode #56: Merge overlapping intervals.
Search in Rotated Sorted Array LeetCode #33: Search for a target value in a rotated sorted array.
Kth Largest Element in an Array LeetCode #215: Find the kth largest element in an array.
Median of Two Sorted Arrays LeetCode #4: Find the median of two sorted arrays.
0 notes
Text
Leveraging Kotlin Collections in Android Development
Kotlin has gradually replaced Java as the lingua franca of Android programming. It’s a more concise language than Java, meaning your code works harder and you can build leaner applications. And Kotlin Collections are fundamental.
These collections play a fundamental role in our work as programmers by simplifying the organization and management of data. Whether it’s a list, set, map or other data structure, they allow us to categorize and store data logically. So we can save, retrieve and manipulate information, and manage a range of tasks from simple data presentation to complex algorithm implementation.
Collections also facilitate code reusability, enabling us to utilize their existing functions and methods rather than developing individual data-handling mechanisms for every task This streamlines development, reduces errors and enhances code maintainability.
At a granular level, collections enable us to perform operations like sorting, filtering, and aggregation efficiently, improving the overall quality of our products.
Overview of Kotlin Collections
Kotlin Collections come in three primary forms: Lists, Maps, and Sets. Each is a distinct type, with its unique characteristics and use cases. Here they are:
Kotlin Lists
A Kotlin List is a sequential arrangement of elements that permit duplicate values, preserving the order in which they are added.
Elements in a list are accessed by their index, and you can have multiple elements with the same value.
Lists are a great help when storing a collection of items whose order needs to be maintained – for example, a to-do list – and storing duplicate values.
Kotlin Maps
Kotlin Maps are collections of key-value pairs. In lightweight markdown language, a method allows us to link values with distinct keys, facilitating effortless retrieval of values using their corresponding keys.
The keys are also ideal for efficient data retrieval and mapping relationships between entities.
Common use cases of Kotlin Maps include building dictionaries, storing settings, and representing relationships between objects.
Kotlin Set
A Kotlin Set is an unordered collection of distinct elements, meaning it does not allow duplicate values.
Sets are useful when you need to maintain a unique set of elements and do not require a specific order for those elements.
Common use cases of Kotlin Sets include tracking unique items, such as unique user IDs, or filtering out duplicates from a list.
The choice between lists, maps, and sets depends on your specific data requirements. Lists are suitable for ordered collections with potential duplicates, maps are ideal for key-value associations, and sets are perfect for maintaining unique, unordered elements.
Kotlin Immutable vs Mutable Collections
Kotlin provides support for both immutable and mutable collections, giving you flexibility when managing data.
Immutable Collections
Immutable collections cannot be modified once they are created. They provide both general safety and specific thread safety, making them ideal for scenarios where you want to keep the data constant. Immutable collections are created using functions like listOf() , mapOf() , and setOf() .
Mutable Collections
A mutable collection can be modified after creation. These collections are more flexible and versatile, allowing you to add, remove or modify individual elements. Mutable collections are created using functions like mutableListOf() , mutableMapOf(), and mutableSetOf().
Now that we have a foundational understanding of Kotlin collections, let’s dive deeper into each type.
Using Kotlin List
How to create a list in Kotlin
Creating a Kotlin list is straightforward. Here are two great ways to get started.
Create an immutable list
To create an immutable list we can use listOf(). Check out the following example:// Example Of listOf function fun main(args: Array<String>) { //initialize list var listA = listOf<String>("Anupam", "Singh", "Developer") //accessing elements using square brackets println(listA[0]) //accessing elements using get() println(listA.get(2)) }
In the Kotlin console, you will see the following output:[Anupam, native, android, developer]
Create a mutable list
If you want to create a mutable list, we should use the mutableListOf() method. Here is an example:// Example of mutableListOf function fun main(args: Array<String>) { //initialize a mutable list var listA = mutableListOf("Anupam", "Is", "Native") //add item to the list listA.add("Developer") //print the list println(listA) }
And this is the output :[Anupam, Is, Native, Developer]
Working with a Kotlin List
Now, we’ll look at working with list items.
Accessing elements from the List
We can reach a list item using its place or index. Here’s the first item from the cantChangeList.// get first item from list var cantChangeList = listOf<Int>(1, 2, 3) val firstItem = cantChangeList[0] println(firstItem) //Output: 1
Iterating over a list
There are multiple ways to traverse a list effectively, leveraging higher-order functions such as *forEach* or utilizing for loops. This enables you to handle the list’s elements one after the other, in sequence. For example:var MyList = listOf<Int>(1, 2, 3) // print each item from list using for loop for (element in myList) { println(element) } //output: //1 //2 //3 // print each item from list using forEach loop MyList.forEach { println(it) } // Output: // 1 // 2 // 3
Adding elements from a list
Modifying a Kotlin List is a great option for mutable lists that harness functions like *add()* , **remove()** , and set(). If we want to add an element to a list, we will simply use the add()method.// Example of add() function in list val numberAdd = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3, 4) numberAdd.add(5) println(numberAdd) //Output : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Removing elements from a list
Removing elements is also a straightforward process. Here’s a coding example:// Example of remove() function in list val numberRemove = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3, 4) numberRemove.remove(3) println(numberRemove) //Output: [1, 2, 4]
Modifying List Items
Altering list items is simple. You can swap them directly with new data via their indices or by using the set commands. Here we have an example of changing an item value, either through its place marker or by using the setmethod:var myList = mutableListOf<String>("Anupam","five", "test", "change") // Changing value via index access myList[0] = "FreshValue" println(myList[0]) // Ouput: // FreshValue // Changing value using set method myList.set(0, "SetValue") println(myList[0]) // Ouput: // SetValue
Other list functions and operations
In Kotlin, list methods are essential tools when we work with collections. While there are numerous methods available, we’ll limit our focus to the most commonly used ones today.
Each of these methods brings its own unique power and utility to a Kotlin collection. Now let’s explore them in detail.
sorted() : Returns a new List with elements sorted in natural order.
sortedDescending() : Returns a new List with elements sorted in descending order.
filter() : Returns a new List containing elements that satisfy a given condition.
map() : Transforms each element of the List, based on a given predicate.
isEmpty() : Checks whether the List is empty.
Here are some key examples of these methods:
Sort a Kotlin list
This collection includes the following elements (3, 1, 7, 2, 8, 6).
Here they are in ascending order:// Ascending Sort val numbs = mutableListOf(3, 1, 7, 2, 8, 6) println(numbs) val sortedNumbs = numbs.sorted() println(sortedNumbs) //Output: // Before Sort : [3, 1, 7, 2, 8, 6] // After Sort : [1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8]
Now, here’s an example of sorting in descending order:// Descending Sort val numbs = mutableListOf(3, 1, 7, 2, 8, 6) println(numbs) val sortedDesNumbs = numbs.sortedDescending() println(sortedDesNumbs) //Output: // Before Sort : [3, 1, 7, 2, 8, 6] // After Sort : [8, 7, 6, 3, 2, 1]
Filtering a Kotlin list
If you want to filter a Kotlin list, you can use the filter function. This allows you to specify a condition that each element of the list must satisfy in order to be included in the filtered list. Here’s an example:val listOfData = listOf("Anupam","is","native","android","developer") val longerThan5 = listOfData.filter { it.length > 5 } println(longerThan5)
In this example, we have a list of strings under the heading listOfData. We use the filter function to create a new list, longerThan5 , that contains only the strings from listOfData with a length greater than five characters.
Finally, we print the filtered list. The output will be:[Anupam, native, android, developer]
Check whether a Kotlin list is empty
Here you can use the isEmpty() function, as you can see in this example:val myList = listOf<Int>() if (myList.isEmpty()) { println("The list is empty.") } else { println("The list is not empty.") } // Output: // The list is empty.
In the following example we’ll create a list, myList , with values using the listOf() function, so the isEmpty will return false:// example of isEmpty() return false var list = listOf<String>("Anupam") if (list.isEmpty()) { println("Its empty.") } else { println("Its not empty.") } // Output: // Its not empty.
Transforming a list using map
As we mentioned earlier, the Kotlin map function is a powerful tool for transforming each element of a list into a new form. It applies a specified transformation function to each element and returns a new list with the results. This gives us a concise way to modify the elements in a list, without mutating the original collection.val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) val squaredNumbers = numbers.map { it * it } println(squaredNumbers) // Output: // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
In this example, we have a list called numbers, containing integers. We apply the map function to numbers and provide a lambda expression as the transformation function. The lambda expression takes each element in the numbers list and returns its square. The map function applies this transformation to each element of the list and creates a new list, squaredNumbers, with the squared values.
Searching elements in a List
Check whether element exists in the list
To search for an element in a Kotlin list, you can utilize the various methods available in the Kotlin standard library. One widely used method is the contains() function, which allows you to check whether a list contains a specific element.
Here’s an example of how you can use the contains() function in Kotlin:val myList = listOf("apple", "banana", "orange") val isElementFound = myList.contains("banana") if (isElementFound) { println("Element found!") } else { println("Element not found!") } // Output: // banana
You can also use the filter() method we mentioned earlier to filter all the elements that match a given criteria.
Search the element and get its index
Another option is to use the indexOf() method, which returns the specific position of an element in the list.val myList = listOf("apple", "banana", "orange") val index = myList.indexOf("banana") if (index != -1) { println("Element found at index $index") } else { println("Element not found in the list") } // Output: // Element found at index 1
Working with Kotlin Map
Accessing and modifying a Kotlin Map
Creating and initializing a map in Kotlin
In Kotlin, you can create and initialize a map by utilizing either the mapOf() function for immutable maps or the mutableMapOf() function for mutable maps. Here is an example of how you can create a map containing names and ages:// Immutable Map Example. Syntax is mapOf<key,value> val myImmuMap = mapOf<Int,String>(1 to "Anupam", 2 to "Singh", 3 to "Developer") for(key in myImmuMap.keys){ println(myImmuMap[key]) } // Output : // Anupam // Singh // Developer
The mapOf() function allows you to create an immutable map, ensuring that its content cannot be altered once initialized. Conversely, the **mutableMapOf()** function enables you to modify the map, transforming it into a mutable map.
In the example provided, the map contains pairs of names and ages. Each pair is created using the ‘to’ keyword, where the name is associated with its corresponding age. The map’s content is enclosed in curly brackets which look like {}.
By utilizing these functions, you can easily create and initialize maps in Kotlin according to your specific needs.
Retrieving map values
To access values in a Map, you use the associated key. For example, to get the value of “Anupam” in ‘immutable map’, you can do the:val myImmuMap = mapOf<Int,String>(1 to "Anupam", 2 to "Singh", 3 to "Developer") val valueOfAnupam = myImmuMap["Anupam"] // valueOfAnupam will be 1
Modify a map entry
You can also modify the values in a mutable Map, using keys:val myImmuMap = mapOf<Int,String>(1 to "Anupam", 2 to "Singh", 3 to "Developer") myImmuMap["Anupam"] = 5 // Update Anupam value from 1 to 5
Iterating over map entries via the map keys
You can use a for loop to iterate over a map. In this case we are iterating the map using the keys property, which contains all the keys present in the Map:val myImmuMap = mapOf<Int,String>(1 to "Anupam", 2 to "Singh", 3 to "Developer") for(key in myImmuMap.keys){ println(myImmuMap[key]) } // Output: // Anupam // Singh // Developer
Iterating over map values
We can also use a for loop to iterate over a map’s values, ignoring the map keys:val myImmuMap = mapOf<Int,String>(1 to "Anupam", 2 to "Singh", 3 to "Developer") for(value in myImmuMap.values){ println(value) } // Output: // Anupam // Singh // Developer
Other map functions and operations
Kotlin provides several useful functions and operations for working with maps. Some common ones include:
keys : This method retrieves a set, comprising all the keys present in the map.
values : The values function ensures retrieval of a collection, containing all the values stored in the map.
containsKey(key) : Determines whether a key exists in the map.
containsValue(value) : Checks whether a value exists in the map.
We have seen keys and values in the previous examples. Now let’s see the other methods in action.
Checking the existence of keys or values in the map
As we have mentioned, you can use the containsKey(key) function to check whether a specific key exists in the map, or the containsValue(value) function to determine whether a particular value is present in the map.val myImmuMap = mapOf<Int,String>(1 to "Anupam", 2 to "Singh", 3 to "Developer") // example of ***containsKey(key)*** println(myImmuMap.containsKey(2)) // exists so will print true println(myImmuMap.containsKey(4)) // not exists so will print false // Output: // true // false // example of ***containsValue(value)*** println(myImmuMap.***containsValue***("Ajay")) // not exists so print false println(myImmuMap.***containsValue***("Anupam")) // exists so print true // Output : // false // true
Working with Kotlin Set
Creating and manipulating sets in Kotlin
Creating a Kotlin Set is similar to other collections. You can use setOf() for an immutable set and mutableSetOf() for a mutable set. Here’s an example:// Immutable Set val intImmutableSet = setOf(1, 2, 3) for(element in intImmutableSet){ println(element) } // Output: // 1 // 2 // 3 // Mutable Set val intMutableSet = mutableSetOf(14, 24, 35) for(element in intMutableSet){ println(element) } // Output: // 14 // 24 // 35
Other useful Kotlin set operations and functions
Sets have unique characteristics that make them useful in certain scenarios. Common set operations include:
union() : Returns a new set that is the union of two sets.
intersect() : Returns a new set that is the intersection of two sets.
add(element) : A new element is added to enhance the set.
remove(element) : Removes an element from the set.
In the following example we show how to use the union() function:// Example of Union function val firstNum = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4,5) val secondNum = setOf(3, 4, 5,6,7,8,9) val finalUnionNums = firstNum.union(secondNum) println(finalUnionNums) // Output : // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
And here we have an example of intersect()// Example of Intersect function val fArray = arrayOf(1,2,3,4,5) val sArray = arrayOf(2,5,6,7) val iArray = fArray.intersect(sArray.toList()).toIntArray() println(Arrays.toString(iArray)) // Output: // [2, 5]
Iterating over Kotlin Set elements
Iterating through a set bears resemblance to iterating through a list. You can use a ‘for’ loop, or other iterable operations, to process each element.val intImmutableSet = setOf(1, 2, 3) for(element in intImmutableSet){ println(element) } // Output: // 1 // 2 // 3
Use cases and examples of sets in Kotlin
Sets are particularly useful when you need to maintain a collection of unique elements. For example:
Keep track of unique user IDs in a chat application.
Ensure that a shopping cart contains only distinct items.
Manage tags or categories without duplicates in a content management system.
Sets also simplify the process of checking for duplicates and ensuring data integrity.
FAQs
How do I filter strings from a Kotlin list?
To extract only strings, which can contain elements of any type, utilize the filterIsInstance() method. This method should be invoked on the kist, specifying the type T as String within the filterIsInstance() function.
The appropriate syntax for filtering only string elements within a list is:var myList: List<Any> = listOf(41, false, "Anupam", 0.4 ,"five", 8, 3) var filteredList = myList.filterIsInstance<String>() println("Original List : ${myList}") println("Filtered List : ${filteredList}") // Output : // Original List : [41, false, Anupam, 0.4, five, 8, 3] // Filtered List : [Anupam,five]
Executing filterIsInstance() will yield a list consisting solely of the String elements present within the original list, if any are found.
How do I define a list of lists in Kotlin?
The Kotlin list function listOf() is employed to generate an unchangeable list of elements. This function accepts multiple arguments and promptly furnishes a fresh list incorporating the provided arguments.val listOfLists = listOf( listOf(1, 2, 3), listOf("Anupam", "Singh", "Developer") ) print(listOfLists) Output: [[1, 2, 3], [Anupam, Singh, Developer]]
How do I filter only integers from a Kotlin list?
To extract only integers, which can contain elements of any type, you should utilize the filterIsInstance() method. This method should be invoked on the list, specifying the type T as Int within the filterIsInstance() function.
The appropriate syntax for filtering solely integer elements within a list is:var myList: List<Any> = listOf(5, false, "Anupam", 0.4 ,"five", 8, 3) var filteredList = myList.filterIsInstance<Int>() println("Original List : ${myList}") println("Filtered List : ${filteredList}") // Output : // Original List : [5, false, Anupam, 0.4, five, 8, 3] // Filtered List : [5, 8, 3]
Executing filterIsInstance() will yield a list consisting solely of the Int elements present within the original list, if any are found.
What are the different types of Kotlin Collections?
Kotlin’s official docs provide an overview of collection types in the Kotlin Standard Library, including sets, lists, and maps. For each collection type, there are two interfaces available: a read-only interface that allows accessing collection elements and provides some operations and then a mutable interface collections where you can modify the items. The most common collections are:
List
Set
Map (or dictionary)
How do I find out the length a Kotlin list?
To find out the length of a Kotlin list, you can use the size property. Here is an example:val myList = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) val length = myList.size println("The length of the list is $length")
Output:The length of the list is 5
What is List<*> in Kotlin?
In Kotlin, you can create a generic list with an unspecified type. When you use a generic list, you’re essentially saying, “I want a list of something, but I don’t care what type of things are in it”. This can be useful when you are writing generic code that can work with any type of list.fun printList(list: List<*>) { for (item in list) { println(item) } } val intList = listOf(1, 2, 3) val stringList = listOf("a", "b", "c") printList(intList) // This will print 1, 2, 3 printList(stringList) // This will print a, b, c
Can we use iterators to iterate a Koltin collection?
Yes, you can use iterators in Kotlin. In the previous examples we have seen how to iterate a Kotlin collection using for or forEach. In case you want to use iterators, here you can see an example of iterating a Kotlin list with an iterator.val myList = listOf("apple", "banana", "orange") val iterator = myList.iterator() while (iterator.hasNext()) { val value = iterator.next() println(value) }
In the example, we call iterator() on the list to get the iterator for the list. The while loop then uses hasNext() to check if there is another item in the list and next() to get the value of the current item.
0 notes
Text
Remove Duplicate Characters From a String In C#
Remove Duplicate Characters From a String In C#
Remove Duplicate Characters From a String In C# Console.Write(“Enter a String : “);string inputString = Console.ReadLine();string resultString = string.Empty;for (int i = 0; i < inputString.Length; i++){if (!resultString.Contains(inputString[i])){resultString += inputString[i];}}Console.WriteLine(resultString);Console.ReadKey(); Happy Programming!!! -Ravi Kumar Gupta.

View On WordPress
#.NET#c#Coding#java#Program#program in c#Programming#Remove Duplicate Characters From a String#Remove Duplicate Characters From a String In C#Technology
0 notes
Link
Data Structures and Algorithms from Zero to Hero and Crack Top Companies 100+ Interview questions (Java Coding)
What you’ll learn
Java Data Structures and Algorithms Masterclass
Learn, implement, and use different Data Structures
Learn, implement and use different Algorithms
Become a better developer by mastering computer science fundamentals
Learn everything you need to ace difficult coding interviews
Cracking the Coding Interview with 100+ questions with explanations
Time and Space Complexity of Data Structures and Algorithms
Recursion
Big O
Dynamic Programming
Divide and Conquer Algorithms
Graph Algorithms
Greedy Algorithms
Requirements
Basic Java Programming skills
Description
Welcome to the Java Data Structures and Algorithms Masterclass, the most modern, and the most complete Data Structures and Algorithms in Java course on the internet.
At 44+ hours, this is the most comprehensive course online to help you ace your coding interviews and learn about Data Structures and Algorithms in Java. You will see 100+ Interview Questions done at the top technology companies such as Apple, Amazon, Google, and Microsoft and how-to face Interviews with comprehensive visual explanatory video materials which will bring you closer to landing the tech job of your dreams!
Learning Java is one of the fastest ways to improve your career prospects as it is one of the most in-demand tech skills! This course will help you in better understanding every detail of Data Structures and how algorithms are implemented in high-level programming languages.
We’ll take you step-by-step through engaging video tutorials and teach you everything you need to succeed as a professional programmer.
After finishing this course, you will be able to:
Learn basic algorithmic techniques such as greedy algorithms, binary search, sorting, and dynamic programming to solve programming challenges.
Learn the strengths and weaknesses of a variety of data structures, so you can choose the best data structure for your data and applications
Learn many of the algorithms commonly used to sort data, so your applications will perform efficiently when sorting large datasets
Learn how to apply graph and string algorithms to solve real-world challenges: finding shortest paths on huge maps and assembling genomes from millions of pieces.
Why this course is so special and different from any other resource available online?
This course will take you from the very beginning to very complex and advanced topics in understanding Data Structures and Algorithms!
You will get video lectures explaining concepts clearly with comprehensive visual explanations throughout the course.
You will also see Interview Questions done at the top technology companies such as Apple, Amazon, Google, and Microsoft.
I cover everything you need to know about the technical interview process!
So whether you are interested in learning the top programming language in the world in-depth and interested in learning the fundamental Algorithms, Data Structures, and performance analysis that make up the core foundational skillset of every accomplished programmer/designer or software architect and is excited to ace your next technical interview this is the course for you!
And this is what you get by signing up today:
Lifetime access to 44+ hours of HD quality videos. No monthly subscription. Learn at your own pace, whenever you want
Friendly and fast support in the course Q&A whenever you have questions or get stuck
FULL money-back guarantee for 30 days!
This course is designed to help you to achieve your career goals. Whether you are looking to get more into Data Structures and Algorithms, increase your earning potential, or just want a job with more freedom, this is the right course for you!
The topics that are covered in this course.
Section 1 – Introduction
What are Data Structures?
What is an algorithm?
Why are Data Structures And Algorithms important?
Types of Data Structures
Types of Algorithms
Section 2 – Recursion
What is Recursion?
Why do we need recursion?
How does Recursion work?
Recursive vs Iterative Solutions
When to use/avoid Recursion?
How to write Recursion in 3 steps?
How to find Fibonacci numbers using Recursion?
Section 3 – Cracking Recursion Interview Questions
Question 1 – Sum of Digits
Question 2 – Power
Question 3 – Greatest Common Divisor
Question 4 – Decimal To Binary
Section 4 – Bonus CHALLENGING Recursion Problems (Exercises)
power
factorial
products array
recursiveRange
fib
reverse
palindrome
some recursive
flatten
capitalize first
nestedEvenSum
capitalize words
stringifyNumbers
collects things
Section 5 – Big O Notation
Analogy and Time Complexity
Big O, Big Theta, and Big Omega
Time complexity examples
Space Complexity
Drop the Constants and the nondominant terms
Add vs Multiply
How to measure the codes using Big O?
How to find time complexity for Recursive calls?
How to measure Recursive Algorithms that make multiple calls?
Section 6 – Top 10 Big O Interview Questions (Amazon, Facebook, Apple, and Microsoft)
Product and Sum
Print Pairs
Print Unordered Pairs
Print Unordered Pairs 2 Arrays
Print Unordered Pairs 2 Arrays 100000 Units
Reverse
O(N) Equivalents
Factorial Complexity
Fibonacci Complexity
Powers of 2
Section 7 – Arrays
What is an Array?
Types of Array
Arrays in Memory
Create an Array
Insertion Operation
Traversal Operation
Accessing an element of Array
Searching for an element in Array
Deleting an element from Array
Time and Space complexity of One Dimensional Array
One Dimensional Array Practice
Create Two Dimensional Array
Insertion – Two Dimensional Array
Accessing an element of Two Dimensional Array
Traversal – Two Dimensional Array
Searching for an element in Two Dimensional Array
Deletion – Two Dimensional Array
Time and Space complexity of Two Dimensional Array
When to use/avoid array
Section 8 – Cracking Array Interview Questions (Amazon, Facebook, Apple, and Microsoft)
Question 1 – Missing Number
Question 2 – Pairs
Question 3 – Finding a number in an Array
Question 4 – Max product of two int
Question 5 – Is Unique
Question 6 – Permutation
Question 7 – Rotate Matrix
Section 9 – CHALLENGING Array Problems (Exercises)
Middle Function
2D Lists
Best Score
Missing Number
Duplicate Number
Pairs
Section 10 – Linked List
What is a Linked List?
Linked List vs Arrays
Types of Linked List
Linked List in the Memory
Creation of Singly Linked List
Insertion in Singly Linked List in Memory
Insertion in Singly Linked List Algorithm
Insertion Method in Singly Linked List
Traversal of Singly Linked List
Search for a value in Single Linked List
Deletion of a node from Singly Linked List
Deletion Method in Singly Linked List
Deletion of entire Singly Linked List
Time and Space Complexity of Singly Linked List
Section 11 – Circular Singly Linked List
Creation of Circular Singly Linked List
Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List
Insertion Algorithm in Circular Singly Linked List
Insertion method in Circular Singly Linked List
Traversal of Circular Singly Linked List
Searching a node in Circular Singly Linked List
Deletion of a node from Circular Singly Linked List
Deletion Algorithm in Circular Singly Linked List
A method in Circular Singly Linked List
Deletion of entire Circular Singly Linked List
Time and Space Complexity of Circular Singly Linked List
Section 12 – Doubly Linked List
Creation of Doubly Linked List
Insertion in Doubly Linked List
Insertion Algorithm in Doubly Linked List
Insertion Method in Doubly Linked List
Traversal of Doubly Linked List
Reverse Traversal of Doubly Linked List
Searching for a node in Doubly Linked List
Deletion of a node in Doubly Linked List
Deletion Algorithm in Doubly Linked List
Deletion Method in Doubly Linked List
Deletion of entire Doubly Linked List
Time and Space Complexity of Doubly Linked List
Section 13 – Circular Doubly Linked List
Creation of Circular Doubly Linked List
Insertion in Circular Doubly Linked List
Insertion Algorithm in Circular Doubly Linked List
Insertion Method in Circular Doubly Linked List
Traversal of Circular Doubly Linked List
Reverse Traversal of Circular Doubly Linked List
Search for a node in Circular Doubly Linked List
Delete a node from Circular Doubly Linked List
Deletion Algorithm in Circular Doubly Linked List
Deletion Method in Circular Doubly Linked List
Entire Circular Doubly Linked List
Time and Space Complexity of Circular Doubly Linked List
Time Complexity of Linked List vs Arrays
Section 14 – Cracking Linked List Interview Questions (Amazon, Facebook, Apple, and Microsoft)
Linked List Class
Question 1 – Remove Dups
Question 2 – Return Kth to Last
Question 3 – Partition
Question 4 – Sum Linked Lists
Question 5 – Intersection
Section 15 – Stack
What is a Stack?
What and Why of Stack?
Stack Operations
Stack using Array vs Linked List
Stack Operations using Array (Create, isEmpty, isFull)
Stack Operations using Array (Push, Pop, Peek, Delete)
Time and Space Complexity of Stack using Array
Stack Operations using Linked List
Stack methods – Push, Pop, Peek, Delete, and isEmpty using Linked List
Time and Space Complexity of Stack using Linked List
When to Use/Avoid Stack
Stack Quiz
Section 16 – Queue
What is a Queue?
Linear Queue Operations using Array
Create, isFull, isEmpty, and enQueue methods using Linear Queue Array
Dequeue, Peek and Delete Methods using Linear Queue Array
Time and Space Complexity of Linear Queue using Array
Why Circular Queue?
Circular Queue Operations using Array
Create, Enqueue, isFull and isEmpty Methods in Circular Queue using Array
Dequeue, Peek and Delete Methods in Circular Queue using Array
Time and Space Complexity of Circular Queue using Array
Queue Operations using Linked List
Create, Enqueue and isEmpty Methods in Queue using Linked List
Dequeue, Peek and Delete Methods in Queue using Linked List
Time and Space Complexity of Queue using Linked List
Array vs Linked List Implementation
When to Use/Avoid Queue?
Section 17 – Cracking Stack and Queue Interview Questions (Amazon, Facebook, Apple, Microsoft)
Question 1 – Three in One
Question 2 – Stack Minimum
Question 3 – Stack of Plates
Question 4 – Queue via Stacks
Question 5 – Animal Shelter
Section 18 – Tree / Binary Tree
What is a Tree?
Why Tree?
Tree Terminology
How to create a basic tree in Java?
Binary Tree
Types of Binary Tree
Binary Tree Representation
Create Binary Tree (Linked List)
PreOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Linked List)
InOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Linked List)
PostOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Linked List)
LevelOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Linked List)
Searching for a node in Binary Tree (Linked List)
Inserting a node in Binary Tree (Linked List)
Delete a node from Binary Tree (Linked List)
Delete entire Binary Tree (Linked List)
Create Binary Tree (Array)
Insert a value Binary Tree (Array)
Search for a node in Binary Tree (Array)
PreOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Array)
InOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Array)
PostOrder Traversal Binary Tree (Array)
Level Order Traversal Binary Tree (Array)
Delete a node from Binary Tree (Array)
Entire Binary Tree (Array)
Linked List vs Python List Binary Tree
Section 19 – Binary Search Tree
What is a Binary Search Tree? Why do we need it?
Create a Binary Search Tree
Insert a node to BST
Traverse BST
Search in BST
Delete a node from BST
Delete entire BST
Time and Space complexity of BST
Section 20 – AVL Tree
What is an AVL Tree?
Why AVL Tree?
Common Operations on AVL Trees
Insert a node in AVL (Left Left Condition)
Insert a node in AVL (Left-Right Condition)
Insert a node in AVL (Right Right Condition)
Insert a node in AVL (Right Left Condition)
Insert a node in AVL (all together)
Insert a node in AVL (method)
Delete a node from AVL (LL, LR, RR, RL)
Delete a node from AVL (all together)
Delete a node from AVL (method)
Delete entire AVL
Time and Space complexity of AVL Tree
Section 21 – Binary Heap
What is Binary Heap? Why do we need it?
Common operations (Creation, Peek, sizeofheap) on Binary Heap
Insert a node in Binary Heap
Extract a node from Binary Heap
Delete entire Binary Heap
Time and space complexity of Binary Heap
Section 22 – Trie
What is a Trie? Why do we need it?
Common Operations on Trie (Creation)
Insert a string in Trie
Search for a string in Trie
Delete a string from Trie
Practical use of Trie
Section 23 – Hashing
What is Hashing? Why do we need it?
Hashing Terminology
Hash Functions
Types of Collision Resolution Techniques
Hash Table is Full
Pros and Cons of Resolution Techniques
Practical Use of Hashing
Hashing vs Other Data structures
Section 24 – Sort Algorithms
What is Sorting?
Types of Sorting
Sorting Terminologies
Bubble Sort
Selection Sort
Insertion Sort
Bucket Sort
Merge Sort
Quick Sort
Heap Sort
Comparison of Sorting Algorithms
Section 25 – Searching Algorithms
Introduction to Searching Algorithms
Linear Search
Linear Search in Python
Binary Search
Binary Search in Python
Time Complexity of Binary Search
Section 26 – Graph Algorithms
What is a Graph? Why Graph?
Graph Terminology
Types of Graph
Graph Representation
The graph in Java using Adjacency Matrix
The graph in Java using Adjacency List
Section 27 – Graph Traversal
Breadth-First Search Algorithm (BFS)
Breadth-First Search Algorithm (BFS) in Java – Adjacency Matrix
Breadth-First Search Algorithm (BFS) in Java – Adjacency List
Time Complexity of Breadth-First Search (BFS) Algorithm
Depth First Search (DFS) Algorithm
Depth First Search (DFS) Algorithm in Java – Adjacency List
Depth First Search (DFS) Algorithm in Java – Adjacency Matrix
Time Complexity of Depth First Search (DFS) Algorithm
BFS Traversal vs DFS Traversal
Section 28 – Topological Sort
What is Topological Sort?
Topological Sort Algorithm
Topological Sort using Adjacency List
Topological Sort using Adjacency Matrix
Time and Space Complexity of Topological Sort
Section 29 – Single Source Shortest Path Problem
what is Single Source Shortest Path Problem?
Breadth-First Search (BFS) for Single Source Shortest Path Problem (SSSPP)
BFS for SSSPP in Java using Adjacency List
BFS for SSSPP in Java using Adjacency Matrix
Time and Space Complexity of BFS for SSSPP
Why does BFS not work with Weighted Graph?
Why does DFS not work for SSSP?
Section 30 – Dijkstra’s Algorithm
Dijkstra’s Algorithm for SSSPP
Dijkstra’s Algorithm in Java – 1
Dijkstra’s Algorithm in Java – 2
Dijkstra’s Algorithm with Negative Cycle
Section 31 – Bellman-Ford Algorithm
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
Bellman-Ford Algorithm with negative cycle
Why does Bellman-Ford run V-1 times?
Bellman-Ford in Python
BFS vs Dijkstra vs Bellman Ford
Section 32 – All Pairs Shortest Path Problem
All pairs shortest path problem
Dry run for All pair shortest path
Section 33 – Floyd Warshall
Floyd Warshall Algorithm
Why Floyd Warshall?
Floyd Warshall with negative cycle,
Floyd Warshall in Java,
BFS vs Dijkstra vs Bellman Ford vs Floyd Warshall,
Section 34 – Minimum Spanning Tree
Minimum Spanning Tree,
Disjoint Set,
Disjoint Set in Java,
Section 35 – Kruskal’s and Prim’s Algorithms
Kruskal Algorithm,
Kruskal Algorithm in Python,
Prim’s Algorithm,
Prim’s Algorithm in Python,
Prim’s vs Kruskal
Section 36 – Cracking Graph and Tree Interview Questions (Amazon, Facebook, Apple, Microsoft)
Section 37 – Greedy Algorithms
What is a Greedy Algorithm?
Well known Greedy Algorithms
Activity Selection Problem
Activity Selection Problem in Python
Coin Change Problem
Coin Change Problem in Python
Fractional Knapsack Problem
Fractional Knapsack Problem in Python
Section 38 – Divide and Conquer Algorithms
What is a Divide and Conquer Algorithm?
Common Divide and Conquer algorithms
How to solve the Fibonacci series using the Divide and Conquer approach?
Number Factor
Number Factor in Java
House Robber
House Robber Problem in Java
Convert one string to another
Convert One String to another in Java
Zero One Knapsack problem
Zero One Knapsack problem in Java
Longest Common Sequence Problem
Longest Common Subsequence in Java
Longest Palindromic Subsequence Problem
Longest Palindromic Subsequence in Java
Minimum cost to reach the Last cell problem
Minimum Cost to reach the Last Cell in 2D array using Java
Number of Ways to reach the Last Cell with given Cost
Number of Ways to reach the Last Cell with given Cost in Java
Section 39 – Dynamic Programming
What is Dynamic Programming? (Overlapping property)
Where does the name of DC come from?
Top-Down with Memoization
Bottom-Up with Tabulation
Top-Down vs Bottom Up
Is Merge Sort Dynamic Programming?
Number Factor Problem using Dynamic Programming
Number Factor: Top-Down and Bottom-Up
House Robber Problem using Dynamic Programming
House Robber: Top-Down and Bottom-Up
Convert one string to another using Dynamic Programming
Convert String using Bottom Up
Zero One Knapsack using Dynamic Programming
Zero One Knapsack – Top Down
Zero One Knapsack – Bottom Up
Section 40 – CHALLENGING Dynamic Programming Problems
Longest repeated Subsequence Length problem
Longest Common Subsequence Length problem
Longest Common Subsequence problem
Diff Utility
Shortest Common Subsequence problem
Length of Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Subset Sum Problem
Egg Dropping Puzzle
Maximum Length Chain of Pairs
Section 41 – A Recipe for Problem Solving
Introduction
Step 1 – Understand the problem
Step 2 – Examples
Step 3 – Break it Down
Step 4 – Solve or Simplify
Step 5 – Look Back and Refactor
Section 41 – Wild West
Download
To download more paid courses for free visit course catalog where 1000+ paid courses available for free. You can get the full course into your device with just a single click. Follow the link above to download this course for free.
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Datatypes in python :: 1. Numeric datatypes:: Integer( for real numbers) Complex( for inputting the complex numbers) Float( for decimal numbers) 2. Dictionary:: dictionary is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. In Python dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and they have keys and values Eg:: thisdict = { "brand": "Ford", "model": "Mustang", "year": 1964 } print(thisdict) 3. Boolean:: In programming you often need to know if an expression is True or False. You can evaluate any expression in Python, and get one of two answers, True or False. When you compare two values, the expression is evaluated and Python returns the Boolean answer 4. Set:: set is an unordered collection of items. Every set element is unique (no duplicates) and must be immutable (cannot be changed). However, a set itself is mutable. We can add or remove items from it. Sets can also be used to perform mathematical set operations like union, intersection, symmetric difference, etc. 5. Strings:: String literals in python are surrounded by either single quotation marks, or double quotation marks. Enjoy the post ? Drop a like and comment If you like the content Do Like comment share save 🤍 💬 📲 📁 _____________________LIKE___ ------------------COMMENT----- ------------SHARE--------- ______SAVE ____________________________ For more updates Follow us Facebook :: https://m.facebook.com/Coding_basics-109490784148247/?ref=bookmarks Instagram :: https://www.instagram.com/coding_basics/ YouTube :: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLx9JC9ithJllNRyIBuUGnurkvLZ2MHCgs ______________________________________________ ************************************************** #programming #code #c #c++ #java #javaprogramming #c_basics #python #pythonprogramming #coding #program #progress #coding_with_chakri #c_programming_language #c++_programming_language #java_programming_language #input #output #input_statements #input #LEARN_APPLY_GROW #learn #apply #grow #basics #basictraining #codingbootcamp #suray #chakri #local #global ______________________________________________ *************************************************** https://www.instagram.com/p/CDJN7OwH5Du/?igshid=xhpxjrmyccen
#programming#code#c#java#javaprogramming#c_basics#python#pythonprogramming#coding#program#progress#coding_with_chakri#c_programming_language#java_programming_language#input#output#input_statements#learn_apply_grow#learn#apply#grow#basics#basictraining#codingbootcamp#suray#chakri#local#global
1 note
·
View note
Text
Java program to remove duplicate characters from a String
Java program to remove duplicate characters from a String
In this article, we will discuss how to remove duplicate characters from a String. Here is the expected output for some given inputs : Input : topjavatutorial Output : topjavuril Input : hello Output : helo The below program that loops through each character of the String checking if it has already been encountered and ignoring it if the condition is true. package com.topjavatutorial; public…
View On WordPress
#delete duplicate characters in a string#How to remove duplicate characters from a string in java#java - function to remove duplicate characters in a string#Java - Remove duplicates from a string#java LinkedHashSet#java remove duplicate characters#java remove duplicate characters preserving order#java remove duplicate chars from String#java remove duplicates#Remove all duplicates from a given string#Remove duplicate values from a string in java#remove duplicates from String in java#Removing duplicates from a String in Java
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Queue in java

Hierarchy of interfaces in Java Collection Framework: Relationship between. Next we are adding 5 strings in random order into the priority queue.
See Ĭopyright © 2000–2019, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. Queue is a Collection that allows duplicate elements but not null elements. The first line tells us that we are creating a priority queue: Queue testStringsPQ new PriorityQueue () PriorityQueue is available in java.util package.
Chronicle Queue is a persisted low-latency messaging framework for high performance and critical. However, there's one exception that we'll touch upon later. This project covers the Java version of Chronicle Queue. Each of these methods exists in two forms: one throws an exception if the operation fails, the other returns a special value (either null or false, depending on the. Besides basic Collection operations, queues provide additional insertion, extraction, and inspection operations. In fact, most Queues we'll encounter in Java work in this first in, first out manner often abbreviated to FIFO. A collection designed for holding elements prior to processing. * * This implementation uses a singly linked list with a static nested class for * linked-list nodes. After we declare our Queue, we can add new elements to the back, and remove them from the front. Recommended Articles This is a guide to Queue in Java. We have seen examples of the most commonly used methods in queue operation. There are alternative methods available for all the methods. It supports operations like insertion, retrieval, and removal. Hence we create the instance of the LinkedList and the PriorityQueue class and assign it to the queue interface. Since the Queue is an interface, we cannot create an instance of it. ****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac Queue.java * Execution: java Queue enqueue and dequeue * operations, along with methods for peeking at the first item, * testing if the queue is empty, and iterating through * the items in FIFO order. The Queue is a special interface in Java that is used to hold the elements in insertion order. Queue interface is a part of Java Collections that consists of two implementations: LinkedList and PriorityQueue are the two classes that implement the Queue interface. Below is the syntax highlighted version of Queue.java The Queue interface of the Java collections framework provides the functionality of the queue data structure.

0 notes
Text
Step by step instructions to Generate and Extract APK Files
In Google, I/O 2018, Android App Bundle, another record design was acquainted with dispersing Android applications through Google Play. Later in 2019, Google began prescribing designers to transfer new applications/refreshes in .aab design rather than customary .apk. The primary target of the Android App Bundle is diminishing the size of the application you download from Play Store. It is an assortment of various APKs created progressively for different gadget setups. Assuming you need to introduce .aab record outside of Play Store, you wanted to initially extricate APK documents from AAB and introduce them physically on your Android gadget.

For instance, if an Android application has numerous strings .vcf files for various dialects and your gadget default language is set to English. A .apk record will be created powerfully for your gadget barring any remaining language documents to lessen the .apk size.
This component comes handy according to a client perspective yet for engineers and analyzers, it added more migraine. Since it is unimaginable to expect to introduce a .aab document like APKs, you wanted to either first transfer it to Play Store for testing or physically create APK records from Android App Bundle (.aab). When various APKs or widespread APK record is removed from .aab, you can introduce the application on various gadget setups.
Changing over torrent App error (.aab) to APK File
In the wake of creating the Android App Bundle from Android Studio or your beloved IDE, you wanted to initially test how the produced APKs act when sent on nearby mobiles. The speediest way of doing this is changing over the .aab document to APK and introducing it conventionally.
To separate APK records from Android App Bundle, we're utilizing the bundle tool, which is an open-source order line apparatus accessible on GitHub. This instrument is for controlling the Android App Bundle to produce APK set chronicle (.apks) document. Once the ".apks" record is produced utilizing the bundle tool, we can remove the APK documents by changing the document to a .zip design.
Here is how you can utilize the bundle tool to produce .apks document record from Android App Bundle and concentrate .apk documents:
Stage 1: Download bundle tool order line device
First of all, download the most recent rendition of the bundle tool container record from GitHub and save it inside an organizer on the Desktop. At the hour of composing this article, the most recent rendition of the bundle tool is 0.10.2 and for straightforwardness, change the record name from bundle tool-all-0.10.2.jar to bundletool.jar
Stage 2: Generate APK Set Archive tmp file from .aab
Duplicate your Android App Bundle (.aab) record to a similar envelope where you have downloaded the bundletool.jar in past advances. This is vital and you should ensure both bundletool.jar and .aab documents are in a similar envelope each time you run the bundle tool order.
As displayed in the screen capture, the name of my Android App Bundle is NHL.aab and both "bundletool.jar" and "NHL. aab" documents are in a similar organizer. For this instructional exercise, we are utilizing the AAB document of our Notification History application.
Presently open the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac) and change the catalog to your Desktop envelope utilizing the CD order. To create an APK set document (.apks) record containing diverse APK documents of all gadgets setups your application upholds, run the form asks order as displayed beneath.
java - container bundletool.jar assemble apks - bundle=nhl.aab - output=nhl.apks
· bundletool.jar – The name of .container record you downloaded from GitHub
· NHL.aab – Your Android App Bundle record name
· NHL. apks – The name of the yield record. It is a .apks record. Try not to mistake it for the customary .apk document.

Stage 3: Extract APK Files
Once the "NHL. asks" record is produced, it is exceptionally simple to remove APK documents from it. You should simply, rename the "NHL.apks" document to "nhl.zip" and separate it typically utilizing a ZIP record extractor. You will presently discover a ton of APK documents in parts and independent elements envelopes.
Presently you have effectively changed over the .aab document to .apk records and you can introduce them on your gadget ordinarily. This is how you can introduce the .aab document on an Android gadget.
Stand by it's not finished at this point. Did you see any issue with the above order? Indeed, it is producing a lot of Debug APK records and you don't know concerning which one you wanted to introduce? Imagine a scenario in which you need marked APKs or an all-inclusive marked APK from Android App Bundle. Luckily, the bundle tool accompanies various banners for extricating the required APK from the .aab document.
Creating Signed APKs utilizing your Keystore
To create marked APK documents with your Keystore record, run the underneath order.
java - container bundletool.jar fabricate apks - bundle=nhl.adb - output=nhl.apks - ks=keystore.jks - ks-pass=pass:your_keystore_password - ks-key-alias=your_key_alias - key-pass=pass:your_key_password
This will again create an "NHL. asks" document and you wanted to rename it to "nhl.zip" and extricate the compress record to see marked apks in the two parts and independent organizers.
Creating a Universal APK from Android App Bundle
Assuming you need to produce just one single APK from your .aab document, run the underneath order.
java - container bundletool.jar construct apks - bundle=nhl.aab - output=nhl.apks - mode=universal
This order will create the NHL. apks document and again you wanted to rename it to nhl.zip and separate it to get a universnal.apk record.
Overwriting existing .apks record
Assuming you need to overwrite the old .apks record with the upgraded one, you wanted to simply add the – overwrite banner to your order as displayed underneath.
java - container bundletool.jar construct apks - bundle=nhl.aab - output=nhl.apks - overwrite
Separating Signed Universal APK record from Android App Bundle
Presently how about we join all the above banners to create a solitary general APK document and overwrite the current APK chronicle if currently accessible.
java - container bundletool.jar assemble apks - bundle=nhl.aab - output=nhl.apks - overwrite - mode=universal - ks=keystore.jks - ks-pass=pass:your_keystore_password - ks-key-alias=your_key_alias - key-pass=pass:your_key_password
After running this order, you should rename the created "NHL.apks" record to "nhl.zip" and extricate it to track down the marked "universal.apk" document.
There are not many further developed banners like - gadget spec, - an associated gadget, - gadget id to create APK and introduce Android App Bundle on associated or explicit gadget setups. Aside from them you additionally have to remove apks and get-size complete orders for more use-cases.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Write a program in java to demonstrate remove duplication from ArrayList to TreeSet?
Write a program in java to demonstrate remove duplication from ArrayList to TreeSet?
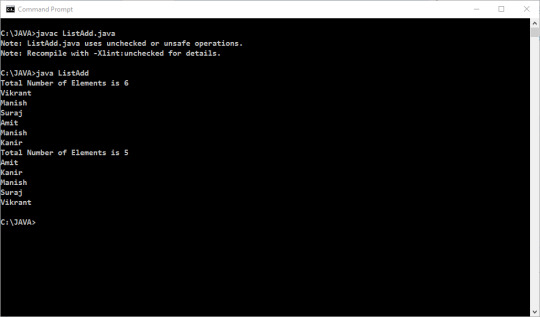
import java.util.*; public class ListAdd { public static void main(String arg[]) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); ArrayList ls=new ArrayList(); TreeSet set=newTreeSet(); ls.add("Vikrant"); ls.add("Manish"); ls.add("Suraj"); ls.add(3,"Amit"); ls.add("Manish"); …
View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
android copy project
https://stackoverflow.com/a/57102685/3151712
(Not in Android Studio) Make a copy / duplicate the existing 'OldProject' directory.
(Not in Android Studio) Rename the copied directory to 'NewProject'.
Start Android Studio 3.4.
Select 'Open an existing Android Studio project'.
Navigate to the 'NewProject' directory, select it and click 'Open'.
Build -> Clean project.
File -> Sync project with gradle file.
Click the '1:Project' side tab and choose Android from the drop-down menu.
Expand the app -> java folder.
Right-click com.example.android.oldproject and select Refactor -> Rename.
Give a new name to the new project in the Rename dialog.
Select 'Search in comments and strings' and 'Search for text occurrences'. Click Refactor.
The 'Find: Refactoring Preview' pane appears, click 'Do Refactor'.
Expand the res -> values folder and double-click the strings.xml file.
Change the app_name string value to "New Project".
Check the file and sync the project with the Gradle file:
In Android Studio Project pane, expand Gradle Scripts and open build.gradle (Module: app).
In android -> defaultConfig -> applicationId check that the value of the applicationID key is "com.example.android.newproject". If the value isn't correct, change it manually.
File -> Sync project with gradle file
Make sure that the app and package names are correct in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
Expand the app -> manifests folder and double click AndroidManifest.xml.
Check that the 'package' name is correct. It should be "com.example.android.newproject". If not, change it manually.
ㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡ
위 작업후에도 firebase를 사용한 경우
https://stackoverflow.com/a/34923311/3151712
You have added the Google Play Services plugin to the project, which reads from the google-services.json found in your app module.
The google-services.json contains service configuration data, such as Google Project ID, application package name, etc..
Since the application package name is also stored in that json, it will not match anymore, so you have to create a new application in your Firebase console, and export the new configuration json.
Then replace the google-services.json in your project with the one you have generated.
위 작업을 해주어야 한다.
.
.
우선 firebase 페이지에가서 새로운 프로젝트를 만든다.
그리고 setting페이지 하단을 보면 아래와 같은에 여기서 android icon 선택
google-services.json만드는 과정


gradle화일 둘다 수정
아래) android studio 왼쪽편에 있는 화일매니저에서 android 를 project 로 바꾸고 app안에 google-services.json이 있는 것을 확인할수 있다.
새로 생성된 화일 붙여넣기
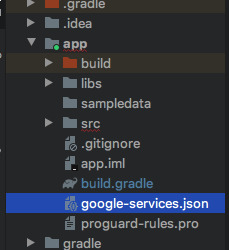

ㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡ
이렇게 하고도 navigation args관련해서 navigation화일에 들어가 각각 argument의 class를 새로 고쳐주어야 했다. 또 몇몇 에러나는 부분을 손수 수정해줘야 했다.(extension func 도 그 한예에 속한다.)
=====================================================
git을 사용하는 경우 기존의 git을 없애고 새로 시작해야한다.
https://stackoverflow.com/a/31991358
In order to drop the current git repository and create a new one you need to:
Go to the project's directory: cd PROJECT_DIRECTORY
Remove all the git specific files: rm -rf $(find . -name ".git*")
Initialize a new git repository: git init
This doesn't remove your project's files, only git configs
참고로 macos에서 숨겨진 화일도 보고 싶은경우
command + shift + . 을 하면 된다.
0 notes
Text
Python Tutorial: Nail PYTHON LIST In 10 Min, List trick.

Introduction to Python Lists.
Hola and welcome to today's Python Tutorial on "Python lists and its functions". In this, tutorial you'll learn the basics of python lists and its various function with example. Python lists are similar to an array of programming language but "Lists in Python" are more powerful in terms of functionality and are flexible in usage.
Lists in Python.
All programming language used data structure to store and manipulate data. The List data type in python is similar to array in C++ or Java or Python or Tables in COBOL. A Python Lists can be used to store, manipulate and retrieve data element as per business requirements. You can store different types (i.e. string and integer data) of data elements in the lists and lists can grow dynamically in memory. In laymen term, A list is similar to an array that consists of a group of elements or items. Just like an array, a list can store elements. But, there is one major difference between an array and a Python List. An array can store one kind of data whereas a list can store different type of the data. Thus, Python Lists are more versatile abd useful than array. List in Python are most widely used datatypes in Python program. Python Lists are easy to define and flexible to use in Python programs. In order to define a list in python, you need to enclosed data items in between square brackets. You can also use various list function to add, append, remove, update, search and delete data items from the Python Lists. Python Lists can grow dynamically in memory. But the size of any array is fixed and they cannot expand during the run time.Python Lists can store different types of data i.e. (String or Numeric), but in the array you can only store a single type of data at a time.
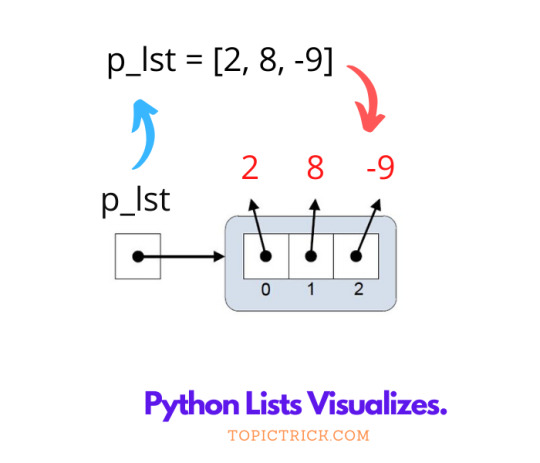
Python Lists Visualization.
How Python Lists Works?
Imagine you went to a shopping mall for shopping grocery items. Each time you pick an item from the shelf you scan it with the scanner before placing the item into your basket. The scanning machine stores the scanned item into machine memory. It also displays the list of items on the screen in the order in which item was scanned. You can visualize this scanner machine as a 'Python list' which is storing items in a sequence after being scanned on the machine. In the following example, shp_lst is a Python List which will store the name of purchase items, every time you scan an item with scanning machine, the item is added/appended to list shp_lst and index is updated. You can access these store items from shp_lst list by using python for .. loop or by other python functions and accessing list item is pretty simple and straight forward. You will learn to perform various operation on lists in later part of the Python Tutorial
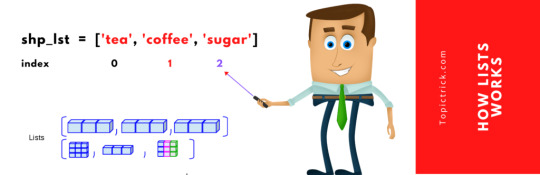
How list in python works.
Python Lists and List functions.
Lists in Python are primarily used to store data in a sequence. A list is a list in itself and it can store different type of data. Lists in python are defined by square brackets and each data item is separated by ',' comma-delimited. Python list provides many in-build functions that can be used to manipulate data in the lists. Now, let's discuss all lists function in details: Example 1: How to create lists in Python? # Define an empty Lists in Python. shp_lst = # Define Lists in Python with integer items only. shp_lst = # Define Lists in Python with strings items only. shp_lst = # Define Lists in Python with mixed items. shp_lst = # Print Python Lists elements. print(shp_lst) Example 2: Python range() Function to create lists. # Python range() function. num_lst = list(range(1,10,1)) num_lst Example 3: For loop to create Python lists. # Python for loop function. a = for i in range(1,10,1): a.append(i) print ('Print List Value:' a) Example 4: Update the elements of lists. # Update first element of the lists. a = a = 2 Example 5: Concatenate two python lists. # Concatinate two Python lists. a = b = print ('Concatinate List :', (a+b)) Concatinate List : How to get individual items in a the list with Indexes and Slicing? By now you have understood that list in python is a sequence data sets. You can store a similar value of different values as per requirements and you know that each item has an associated index. You can use this index to access lists values. Python Lists start with zero and index is incremented by one every time an item is added or appended to the list. The process of creating a new python list from an existing list is termed as slicing operations. Slicing represents extracting a piece of the list by mentioning starting and ending position numbers.Syntax :: list_name list_name - Name of existing list variable. start_position - starting index position. end_position - end of index position.step size - the gap between items, the default step size is 1. Example 2: Python Lists Indexing and Slicing. # Create shp_lst shopping Lists in Python. shp_lst = # Print third element of the shp_lst list. shp_lst 'salt' # Print the second and third element of the shp_lst list. shp_lst # Create a new List from the existing shp_lst List. shp_lst_sl = shp_lst shp_lst_sl # Print last 2 items of the shp_lst List using negative indexes. shp_lst

Lists in Python with additional methods/functions.
Python Lists and Function.
As you know, Lists in Python are a powerful data set and are equally flexible to use. Python Lists provides many additional function/methods that can be used to perform many data manipulation operations on the lists. Let's discuss all these functions one by one with examples: Python List Append Method. The Python List append method is used to append items at the end of the list. In the following example, a new item would be added to the list.list.append(x)# Create shopping shp_lst Lists in Python. shp_lst = # Append jam item to the shp_lst Lists. shp_lst.append('jam') # Print the items of the lists. shp_lst Python List Extend Method. The Python List extends method is used to append all items from another list. In the following example, all items from shp_ext_lst will be added to the existing shopping list. list.extend(iterable)# Create shp_lst Lists in Python. shp_lst = # Append items from shp_ext_lst List to the shp_lst List. shp_ext_lst = shp_lst.extend(shp_ext_lst) # Print the List (shp_lst). shp_lst Python List Insert Method. The Python List insert method is used to insert an item at a specific location in the list. You need to specify the position where you want to insert value in the list. list.insert(i, x)# Create shp_lst shopping Lists in Python. shp_lst = # Insert a new item at the second position. shp_lst.insert(1,'jam') # Print the shopping list (shp_lst). shp_lst Python List Remove Method. The Python List Remove method is used to remove the item from the Python list. You need to specify the value that you want to drop from the list. Also, if your list has duplicate value then remove method will only remove first value and will retain second value. If the value is not present in the list then it will throw an error (i.e. list.remove(x): x not in list). list.remove(x)# Create Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Remove item from the pgm_lst list. pgm_lst.remove('CICS') # Print the programming language list (pgm_lst). pgm_lst # Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Remove an item from the list. pgm_lst.remove('JAVA') # Print the programming language list (pgm_lst). pgm_lst Python List Pop Method. The Python List POP method is to remove the specific item from the list. You are required to specify the position of the item as a parameter. list.pop()# Create programming language pgm_lst Lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Drop list last data item. pgm_lst.pop() # Print the programming list (pgm_lst). pgm_lst # Programming language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Remove specific item from the list. pgm_lst.pop(3) # Print the programming language list (pgm_lst). pgm_lst Python List Clear Method. The Python List clear method is used to clear items from the lists. list.clear()# Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Clear item from the list. pgm_lst.clear() # Print the programming list (pgm_lst). pgm_lst Python List Index Method. The Python List Index method is used to get the index of the item. You are required to specify the item name as a parameter. If the item is not present in the list then it will throw an error message.list.index(x])# Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Get index of the item from the list. pgm_lst.index('CICS') 1 Python List Count Method. The Python List Count method is used to get the count of specific items in the list. You need to specify the item as an argument. list.count(x)# Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Clear item from the list. pgm_lst.count('COBOL') 1 Python List Sort Method. The Python List Sort method is used to arrange items in the list. Python list sort has two parameters i.e. Key=None and reverse=False. list.sort(key=None, reverse=False)# Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Sort item in the list. pgm_lst.sort() pgm_lst # Sort item in the list. pgm_lst.sort(key=None,reverse=True) pgm_lst Python List Reverse Method. The Python List Reverse method is used to reverse the order of items in the list. list.reverse()# Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Reverse the order of items in the list. pgm_lst.reverse() pgm_lst Python List Copy Method. The Python Lists copy method is used to copy an item from one list to others.list.copy()# Programming Language lists in Python. pgm_lst = # Reverse the items sequence in the list. a = pgm_lst.copy() a Python List Sum Function. The Python Lists sum method is used to retrieve the sum of all elements of the list.list.sum()# Programming Language lists in Python. a_lst = # Get sum of all items. print('The sum of all list items :', sum(a_lst))
Lists in Python Live Coding Demo.
https://youtu.be/dyZyHaXZb-8
Conclusion.
Finally, we reach an end of today's tutorial on List in Python. By now, you have understood the basics of Lists in Python. You've also learned about various inbuilt function for performing various data manipulation operations. In our next python tutorial, you will learn more about Tuple. If you like our tutorial, please don't forget to share with your friend and family and do leave your valuable feedback. Your comments are valuable to us. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ FRESHERS JAVA Interview Questions and Answers
java Interview Questions for freshers :-
1. What is Java? Java is a object-oriented programming language originally developed by Sun Micro systems and released in 1995. Java runs on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and the various versions of UNIX. 2. What is serialization? Serialization converts an object to a stream of bytes for safety purposes. We can save it as a file, store in DB or send it by the network. We can also recreate the state of an item when needed. 3. What is a Java virtual machine? JVM helps the computer to run the Java program or other languages. It acts as a run-time engine. Java code is compiled into bytecode to run on any computer. 4. What is constructor? It is an instant and special method having the same name as the class. A constructor can be overloaded and a section of code to load newly created objects. If a constructor is created with a parameter then another constructor can be created without a parameter. 5. Describe variables? Name them A name for a memory location is variable. And it is called a basic unit of storage in a program. You can change the stored value during the program execution. Local variables Instant variables Static variables 6. What is the classloader? Classloader is a Java runtime environment to load Java classes into Java virtual machine. It loads class files from the network, file system, and other sources. In java, there is 3 built-in classloader. Extension System/application Bootstrap 7. What are the wrapper class? A wrapper class wraps or contains primitive data types. The Java primitives change into the reference types. It contains a field when we create an object. Primitive data types are stored in this field. Thus a primitive value is also be wrapped. 8. Define a package and its advantages? The collection of classes, sub-packages, and interfaces are bundled together is called packages. We can modularize the code and optimize its reuse. The code can also be imported by other classes and reused. It helps to remove name clashes. Provide access protection to manage the code. The classes and interfaces are easily maintained because of proper structure. It contains hidden classes to use within the packages. 9. What is the JIT compiler? JIT is a program to help in changing the Java bytecode into instructions. It improves the performance of Java applications at the run time and known as the integral parts of the Java Runtime Environment. 10. What are the special keywords in Java? Name them The special keywords in Java are access modifiers. Constructor, variable, scope of a class, data member or method is restricted. Default, private, protected and the public are four types of access modifiers.

java Interview Questions for freshers 11. What are garbage collectors? and types. It implicit memory management and destroy the unused objects to relieve the memory. It automatically removes the unreferenced objects to make the memory efficient. There are 4 types of garbage collectors. Serial garbage G1 garbage CMS garbage Parallel garbage 12. Tell the smallest piece of programmed instructions? How does it create? A thread, A scheduler executes independently. All programs having one thread is called the main thread. JVM creates the main thread when the program starts its execution. The main ( ) of the program is invoked by the main thread. Thread is created – By implementing the Runnable interface and extending the thread. 13. What executes a set of statements? Finally block always executes a set of statements. It is with a try block of any exception occurs or not. It does not execute the program by calling System.exit( ) or by a fatal error. 14. What refers to Multi-threading? Synchronization, it keeps all concurrent threads in execution. Memory consistency errors are avoided by synchronization. Execution of multiple threads accesses the same objects and fields. The thread holds the monitor when the method is considered as synchronized. 15. Tell the purpose of final, finally and finalize? Final cannot be overridden, inherited or change. For restrict the class, variable and method. Finally, is used for putting important code and executed the exception is handled or not. Finalize is for cleaning up processing before the object is collected in the garbage. 16. Where we use a different signature? In method overloading signature must be different. The same class method shares the same name. Every single method should be the indifferent number of parameters or different orders or types of parameters. For “adding” or “extending” and known as a compile-time polymorphism. 17. What is Run-time polymorphism? Method Overriding is run-time polymorphism having the same signature. Inheritance is required in Method Overriding. It is used to change existing behavior. The subclass has the same method od same number, name, parameters, return type. 18. Name the method that belongs to the class? In Java, the static method belongs to the class and access only static data. It calls only other static methods and directly accessed by the class name. To define variables, static is used. 19. Describe Object-oriented paradigm? The programming paradigm based on data and methods is called object-oriented programming. Paradigm incorporates the advantages of reusability and modularity. Objects are instances of classes to interact with one another. It designs programs and applications. 20. In Java, what is an object? A real-time entity of some behavior and state is called an object. It is an instance of a class with instance variables. The new keyword is for creating the object of the class. 21. What is an object-based programming language? JavaScript, VBScript is an object-based language and has in-built objects. All the concepts of OOPs such as polymorphism and inheritance are not followed by object-based languages. 22. Name the constructor used in Java? Default constructor – It is used to perform the task on object creation and to initialize the instance variable with default values. The constructor does not accept any value. If no constructor is defined in the class, then a default constructor is invoked implicitly by the compiler. Parameterized constructor – This constructor accepts the arguments. It initializes the instance variables with the given values. 23. How to copy the values of the item to others in Java? We can print the values by using the constructor, to allow the values of one object to other and the design of clone. In Java, there is no copy constructor. 24. Explain the Java method? The Java method is invoked explicitly and is to disclose the nature of an item, it has an entry. Its name is not the same as the class name. It is not given by the finder. 25. Describe the static variables? The static variable belongs to the class and makes the memory-efficient of the program. It refers to the common property of all objects. At the moment when class is loading, it gets the memory in the department field. 26. What is aggregation? Aggregation is described as a has-a relationship and has an entity reference. And having a relationship between two classes. The weak relationship is represented by aggregation. 27. What is a super keyword? Mention its uses. The Super keyword is a hint variable is to mention at once parent class item with the concept of inheritance, the keyword comes into the picture. It appeals soon the parent class technique and constructor. Refers directly parent class instance variable. It is used to initialize the base class variables. 28. What is method overriding? Name the rules and use them. In Java method overriding is when a subclass has the specific implementation or the same method as in the parent class. Rules : It should have the same name and signature as in the parent class. IS-A relationship should be in between two classes. Uses : For runtime polymorphism To give the specific implementation already provided by its superclass. 29. What are polymorphism and its types? Polymorphism is used in a different context and define the situations. When a single object refers to the super or sub-class depends on the reference type is polymorphism. Many forms are considered as polymorphism. 30. Explain the OOPs concepts in Java? For programmers to create the components for re-using in different ways. OOPs is known as programming style. The four concepts are Abstraction Inheritance Polymorphism Encapsulation Interface 31. What is stored in a heap memory? Java String pool is a collection of Strings are stored. If you create a new object, the string pool confirms the object is in the pool or not. The same reference is returned to the variable if it is already in the pool. 32. How to call one constructor to another to the current object? By constructor chaining. It is occurred by inheritance. The task of a subclass constructor is to call the superclass constructor. There are two ways to do constructor chaining. Within the same class using the keyword “this” ( ) From base class using the keyword “super” ( ) 33. Tell the nature of Java strings? The nature of string objects are immutable which is cached in the string pool. The state of string object cannot be modified after the creation. Java creates a new string object if you update the value of the particular object. 34. What is the interface of the Util package? It’s characteristics. Map in Java is the interface of the Util package. It is used to map a key and a value. It is different from other collection types. And it is not the subset of the main collection interface. Duplicate keys are not contained The order of a map is depending upon the specific implementation 35. Describe Java Stack memory? Stack memory is in the Last-In-First-Out order to free memory. It is used for the execution of a thread. It contains local primitives and reference to other objects. To define the stack memory, we use –Xss. The memory of the stack is considered short-lived. 36. Why Runnable Interface is used in Java? Runnable interface is used in java for implementing multi threaded applications. Java.Lang.Runnable interface is implemented by a class to support multi threading. 37. What are the two ways of implementing multi-threading in Java? Multi threaded applications can be developed in Java by using any of the following two methodologies: By using Java.Lang.Runnable Interface. Classes implement this interface to enable multi threading. There is a Run() method in this interface which is implemented. By writing a class that extend Java.Lang.Thread class. 38. When a lot of changes are required in data, which one should be a preference to be used? String or StringBuffer? Since StringBuffers are dynamic in nature and we can change the values of StringBuffer objects unlike String which is immutable, it's always a good choice to use StringBuffer when data is being changed too much. If we use String in such a case, for every data change a new String object will be created which will be an extra overhead. 39. What's the purpose of using Break in each case of Switch Statement? Break is used after each case (except the last one) in a switch so that code breaks after the valid case and doesn't flow in the proceeding cases too. If break isn't used after each case, all cases after the valid case also get executed resulting in wrong results. 40. How garbage collection is done in Java? In java, when an object is not referenced any more, garbage collection takes place and the object is destroyed automatically. For automatic garbage collection java calls either System.gc() method or Runtime.gc() method. 41. How we can execute any code even before main method? If we want to execute any statements before even creation of objects at load time of class, we can use a static block of code in the class. Any statements inside this static block of code will get executed once at the time of loading the class even before creation of objects in the main method. 42. Can a class be a super class and a sub-class at the same time? Give example. If there is a hierarchy of inheritance used, a class can be a super class for another class and a sub-class for another one at the same time. In the example below, continent class is sub-class of world class and it's super class of country class. public class world { .......... } public class continenet extends world { ............ } public class country extends continent { ...................... } 43. How objects of a class are created if no constructor is defined in the class? Even if no explicit constructor is defined in a java class, objects get created successfully as a default constructor is implicitly used for object creation. This constructor has no parameters. 44. In multi-threading how can we ensure that a resource isn't used by multiple threads simultaneously? In multi-threading, access to the resources which are shared among multiple threads can be controlled by using the concept of synchronization. Using synchronized keyword, we can ensure that only one thread can use shared resource at a time and others can get control of the resource only once it has become free from the other one using it. 45. Can we call the constructor of a class more than once for an object? Constructor is called automatically when we create an object using new keyword. It's called only once for an object at the time of object creation and hence, we can't invoke the constructor again for an object after its creation. 46. There are two classes named classA and classB. Both classes are in the same package. Can a private member of classA can be accessed by an object of classB? Private members of a class aren't accessible outside the scope of that class and any other class even in the same package can't access them. 47. Can we have two methods in a class with the same name? We can define two methods in a class with the same name but with different number/type of parameters. Which method is to get invoked will depend upon the parameters passed. For example in the class below we have two print methods with same name but different parameters. Depending upon the parameters, appropriate one will be called: public class methodExample { public void print() { system.out.println("Print method without parameters."); } public void print(String name) { system.out.println("Print method with parameter"); } public static void main(String args) { methodExample obj1 = new methodExample(); obj1.print(); obj1.print("xx"); } } 48. How can we make copy of a java object? We can use the concept of cloning to create copy of an object. Using clone, we create copies with the actual state of an object. Clone() is a method of Cloneable interface and hence, Cloneable interface needs to be implemented for making object copies. 49. What's the benefit of using inheritance? Key benefit of using inheritance is reusability of code as inheritance enables sub-classes to reuse the code of its super class. Polymorphism (Extensibility ) is another great benefit which allow new functionality to be introduced without effecting existing derived classes. 50. What's the default access specifier for variables and methods of a class? Default access specifier for variables and method is package protected i.e variables and class is available to any other class but in the same package,not outside the package. 51. Give an example of use of Pointers in Java class. There are no pointers in Java. So we can't use concept of pointers in Java. 52. How can we restrict inheritance for a class so that no class can be inherited from it? If we want a class not to be extended further by any class, we can use the keyword Final with the class name. In the following example, Stone class is Final and can't be extend public Final Class Stone { // Class methods and Variables } 53. What is Java? and how does Java enables high performance? Java is a platform-independent, object-oriented, portable, multi-thread, high-level programming language. The collection of objects is considering as Java. We use Java for developing lots of websites, games and mobile applications. For high performance, Java uses Just in time compiler. java Interview Questions and Answers for freshers Pdf free Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
13 of the Best SEO Tools for Auditing and Monitoring Website Performance

There's nothing quite like a sudden Google algorithm update to leave marketers feeling equal parts confused and concerned. It seems like they wait for you to get all of your ducks in a row and then unleash an update that makes your efforts instantly obsolete.
Sure, they're pretty open about that fact that they're doing this for everyone's own good -- each algorithm tweak brings us one step closer to more relevant search results, after all. However, there is still some secrecy behind exactly how Google evaluates a website and ultimately determines which sites to show for which search queries.
That said, there are a number of tools out there -- some free, some paid -- that help you to look at your own site the way that Google sees it.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, '1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e', {});
These tools are critical to your organic search strategy because they allow you to focus on the elements of your site that Google deems important. In this post, we'll walk through 13 such tools that all help you run a site analysis like a marketer ... and a Google bot.
SEO Tools
1. Google's Webmaster Tools
Perhaps the best way to understand the way Google sees your site is to ask Google. Google's Webmaster Tools are novice-friendly resources that explain the fundamentals of Google search.
For example, Google's Fetch as Google tool allows you to see a particular URL as Google sees it, which is critical when troubleshooting for poor SEO performance. The information returned can help you modify the page in question for better results, and can even help you isolate problematic code when you believe your site's been hacked.
Another great feature of Google Webmaster Tools is PageSpeed Insights. This SEO tool measures the performance of both your desktop and mobile site in terms of speed. With mobile search queries surpassing desktop searches, page speed is becoming increasingly important to businesses that want to hold on to their visitors.
"PageSpeed Insights evaluates how well a page follows common performance best practices and computes a score from 1-100 that estimates its performance headroom," according to Google Developers. That score can be Good, as in 80 or above; Medium, as in 60 to 79; or Low, as in 0 to 59.
2. Ahrefs
Cost: $99/mo for Lite Plan
Purpose: Keyword Research
Ahrefs is an advanced SEO resource that examines your website property and produces keyword, link, and ranking profiles to help you make better decisions on your content. Three of its main tools are:
When using the Keyword Explorer, Ahrefs will also produce the "parent topic" of the keyword you looked up, as you can see in the screenshot above, underneath the Keyword Difficulty meter. A keyword's parent topic is a broader keyword with higher search volume than your intended keyword, but likely has the same audience and ranking potential -- giving you more a valuable SEO opportunity when optimizing a particular blog post or webpage.
3. HubSpot's Website Grader
Back in 2007, HubSpot released a tool called Website Grader that helped businesses uncover search engine optimization opportunities. Because a lot has changed since then, the company has released a new and improved version of the tool.
Website Grader is an online tool that generates personalized reports based on the following key metrics:
All you need is your website URL and an email address to get started. Simply plug in your information and you can expect a score (1-100) as well as a detailed report in a matter of seconds.
Aside from Website Grader, HubSpot also has a handful of paid SEO tools to help you better direct your efforts.
For example, within the HubSpot Blogging App, users will find as-you-type SEO suggestions. This helpful inclusion serves as a checklist for content creators of all skill levels. HubSpot customers also have access to the Page Performance App, Sources Report, and the Keyword App. The HubSpot Marketing Platform will provide you with the tools you need to research keywords, monitor their performance, track organic search growth, and diagnose pages that may not be fully optimized.
4. Check My Links
To ensure that your links on a webpage -- whether external or internal -- actually work, consider Check My Links.
This broken-link checker makes it easy for a publisher or editor to make corrections before a page is live. Think about a site like Wikipedia, for example. The Wikipedia page for the term "marketing" contains a whopping 711 links. Not only was Check My Links able to detect this number in a matter of seconds, but it also found (and highlighted) seven broken links.
The tool highlights all the good links in green, and those that are broken in red, making it easy to spot the ones that don't work or are no longer active.
5. BuzzStream
Cost: Free 14-day trial, then paid plans from $24/mo
Purpose: Link Building
BuzzStream might be the most inexpensive way to manage your outreach to the people who can provide inbound links to your website.
Although backlinks to your website are critical to ranking well on Google, the outreach you do while link building can feel a lot like cold calling. BuzzStream makes it easy to research the appropriate people, come up with effective email messages, and track who's accepted each link request. Your link building queue looks like this:

Image via BuzzStream
BuzzStream helps you identify candidates for outreach based on their industry and how engaged they are across various social networks -- so you know who will be most receptive to your backlink request and boost your ranking on Google.
6. Moz's Pro Tools
Cost: Free 30-day trial, then paid plans from $99/mo
Purpose: Website Analysis
The Moz Pro subscription serves as an all-in-one tool for increasing your business' search ranking. Moz's collection of research tools provides subscribers with the resources they need to identify SEO opportunities, track growth, build reports, and optimize their overall efforts.
For example, the Crawl Test tool employs Moz's own web crawler, RogerBot, to analyze up to 3,000 links on a given URL. Once completed, users then receive an email report that details the data for each page the site links to.

Image via Moz
This is super helpful if you're looking to identify "crawlability" factors, such as duplicate content and redirects that could be influencing your SEO performance.
7. UpCity's SEO Report Card
SEO Report Card by UpCity lets you analyze your website to determine how it stacks up against your competitors.
In exchange for a bit of your contact information, SEO Report Card will serve up a report that covers the following:
8. Woorank
Cost: Free 14-day trial, then $49/mo for a Pro Plan or $149/mo for a Premium Plan
Purpose: Website Analysis
Woorank's in-depth site analysis helps marketers reveal opportunities for optimization and improvement. This analysis takes into account the performance of existing SEO initiatives, social media, usability, and more.
Each report is divided into eight sections:
Spanning 70+ metrics, it would be hard -- if not impossible -- to not uncover opportunities for improvement.
As a bonus, Woorank makes it easy for users to download their reviews as branded PDFs. This makes company-wide distribution and presentation more streamlined than ever.
SEMrush is a super elaborate dashboard that reports on the performance of domains as a whole and their specific pages. The website offers numerous toolkits, one of which is an SEO toolkit.
Below is one of the toolkit's flagship features, allowing you to plug in a website page to see for what keywords it's ranking, what the page's rank is for that keyword, the keyword's monthly search volume, and more.
The rest of the SEO toolkit allows you to compare your page performance to competition, analyze backlinks from other websites to your site (also known as link building), research appropriate keywords, and take advantage of similar on-page SEO opportunities.
10. Screaming Frog's SEO Spider
Cost: The LITE version is free (with limitations*), and the paid plan is $160/year
Purpose: Website Analysis
The Screaming Frog SEO Spider is a search marketer's best friend.
Designed specifically for the SEO-minded, this program crawls the websites you specify, examining the URLs for common SEO issues. This program simplifies and expedites an otherwise time-consuming process -- especially for larger websites. It could take hours or days to manually evaluate the same URLs.
Take a closer look at how it works:
The Java program is fairly intuitive, with easy-to-navigate tabs. Additionally, you can export any or all of the data into Excel for further analysis. So say you're using Optify, Moz, or RavenSEO to monitor your links or rankings for specific keywords -- you could simply create a .csv file from your spreadsheet, make a few adjustments for the proper formatting, and upload it to those tools.
*Pricing limitations include: You can only scan 500 URLs per website, and you don't have full access to configuration options and source code features. To remove these limitations, users can purchase a 12-month license for around $160/year.
11. Found's SEO Audit Tool
Want to rise above your competitors on search engine results pages?
(Who doesn't?)
The SEO Audit Tool by Found is an easy-to-use tool for marketers looking to identify (and solve) common SEO errors on a website.
Simply enter your URL and receive an instant automated SEO audit of your site. Found's SEO Audit Tool is broken down into three main parts:
Similar to Woorank, once you run a report, the tool makes it easy for you to download the results as a PDF to be easily shared within your organization.
12. Remove'em
Cost: $249 per domain or a subscription option starting at $99/mo
Purpose: Link Building
Have you ever purchased links? Spammed the comments section on a string of blogs using the same message and link? If so, we'll forgive your bad judgment just this once ... but Google won't.
Artificial or unnatural links have the potential to seriously hurt your search ranking. To clean them up, check out Remove'em:
This helpful tool scans your backlink profile and turns up a list of contact information for the links and domains you'll need to reach out to for removal. Alternatively, the tool also allows you to export the list if you wish to disavow them using Google's tool. (Essentially, this tool tells Google not to take these links into account when crawling your site.)
13. Varvy's SEO Overview Tool
This SEO auditing tool provides users with information regarding their domain strength, links, image SEO, social counts and mentions, page/technical SEO, page speed, and more.
The comprehensive report is prepared in less than a minute, and dives deep into different aspects of your website's performance. You'll notice that the tool employs green checks, red Xs, and yellow exclamation points to denote the severity of the issue.
One the our favorite features is the detailed image overview:
This section of the report focuses on the strength of the images your website employs by analyzing the alt text. If you're using too many words, missing alt text, or the alt text appears weak, the tool will notify you so that you can make any necessary changes.
You'll never get a look behind the Google curtain to learn everything they know (or don't know) about your site. But by leveraging SEO best practices and getting the most out of tools like those listed here, you can greatly increase the chances that your website will show up in response to the right search queries.
This content was originally published here.
0 notes