#Small-Scale Farmers
Text
Agricultural Extension Services: The Missing Link in Kenya’s Economic Transformation
Discover how investing in agricultural extension services can drive sustainable economic growth in Kenya, enhance food security, and empower small-scale farmers to thrive.
Learn why strengthening agricultural extension services is crucial for revitalizing Kenya’s farming sector and achieving the goals of the Bottom-Up Economic Transformation Agenda.
Explore the role of agricultural extension…
#agricultural best practices#Agricultural Education.#Agricultural Innovation#agricultural productivity#agricultural reforms#agricultural sustainability#Agricultural technology#agriculture extension services#Bottom-Up Economic Transformation Agenda#community development#crop production#economic growth.#extension programs#extension service challenges#farmer empowerment.#farmer extension officers#Farmer Support#farmer training#Food security#government policies#government support for farmers#investment in agriculture#Kenya Agriculture#Kenya dairy sector#Livestock Management#local consumption#local food systems#Rural development#rural economy#Small-scale farmers
0 notes
Text
Livelihood Security for Small-Scale Farmers
Small farmers play a crucial role in the agricultural landscape, but they often encounter obstacles when it comes to sustaining their livelihoods. However, amidst these challenges, there are ample opportunities for small-scale producers to thrive as entrepreneurs. By bypassing traditional market routes and selling their products directly to customers, such as vegetables or even transforming…

View On WordPress
#Agribusiness#Agriculture#dailyprompt#dailyprompt-2169#farming#Farming Communities#small farmers#Small-Scale Farmers
0 notes
Text
youtube
youtube
youtube
1 SELF SUFFICIENT ME: FARMERS UNDER ATTACK
2 GARDENING IN CANADA: ATTACK ON GARDENS
3 REDACTED: HANG ON, NOW BILL GATES IS COMING FOR YOUR GARDEN
Check out Jojo Mehta, founder of Stop Ecoside Now, actually talking with a straight face, about punishing people for farming. Another one wants people to adjust to Artificial Intelligence Food. All of this shite and very, very likely, billionaire-backed studies, slanted against independent food production. This is all coming from the same plague, that JUST unleashed Paganistic beliefs about Gender and sprayed the whole planet with those dangerous beliefs: the World Economic Forum. Davos. Israel. I will remind people that besides being a shady pervert, Bill Gates ' father was a lawyer for the MOSSAD.
"I call bullshit. I think this "story" is about corporate influence, control, and the continuing war on freedom, privacy, autonomy, self sufficiency and entrepreneurship. Homegrown food is just one of the examples of things that lunatics like Klaus Schwab and Bill Gates, hate." Twitter
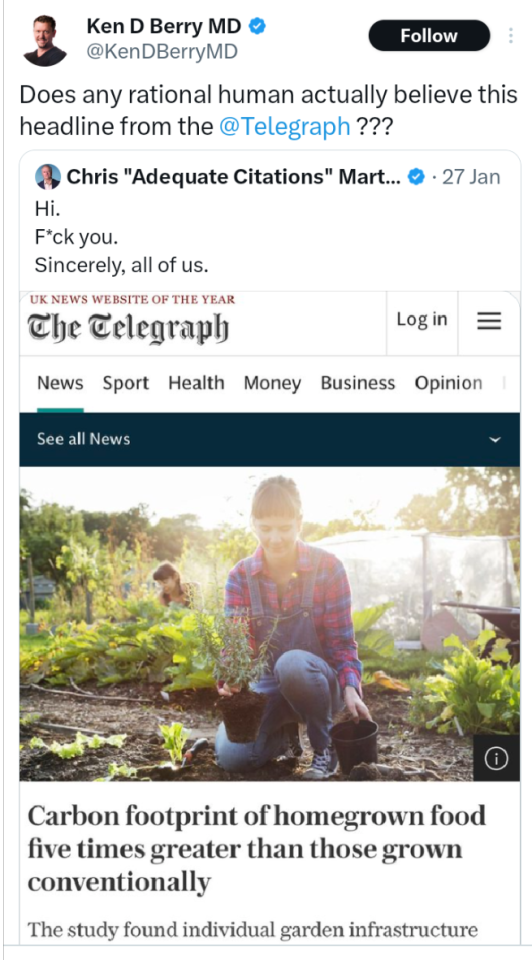
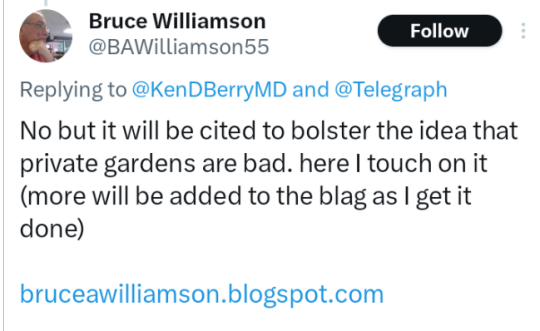
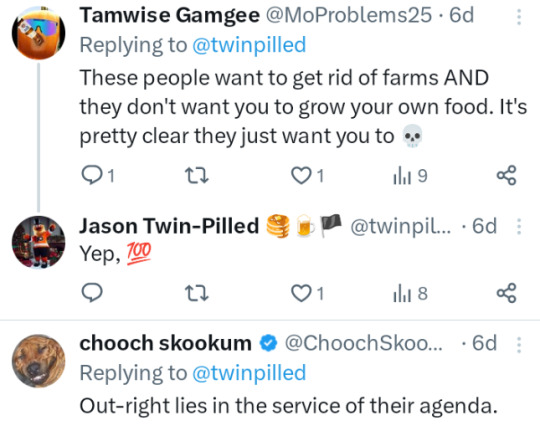






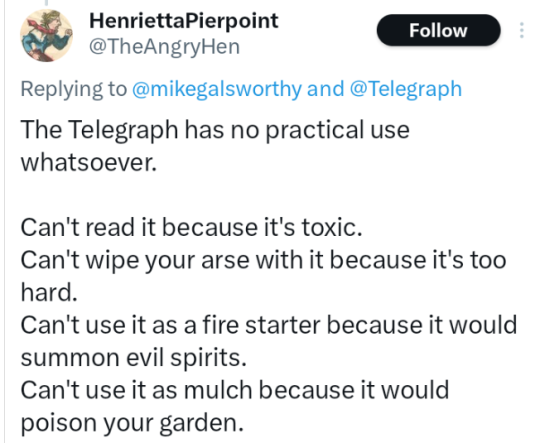
Wednesday, January 24, 2024
Hello, Nice to Meet Control You
Hello, Nice to Meet Control You: Introduction
Control. Control of others in one form or another has pervaded human history. Control has been exercised by individuals and groups over other individuals and groups. Thank you captain obvious.
This is a cursory look at various forms of control exercised over people. Both actual and possible forms are discussed. I do not pretend to be knowledgeable in the subject and are simply writing my thoughts. The footnotes and end notes are similar to references that I remember reading but not the actual reference. But I assume you know how to use a search engine. Also any typos and misspellings are due to my new gaming keyboard (not really but I need something to blame for my inability to type). Also I am using Libre Office to write this document and it has some issues with footnotes and endnotes or I just can’t use it as well as I use MS Word.
Humans have basic needs which are food, water, livelihood, and shelter. Control any one of these and you control the person. A newer and more effective route for control of others is media. Each of these topics will be discussed in turn. Additionally, the secondary means for controlling these needs will be examined.
I am not an expert in any field related to the topics nor am I any sort of revolutionary for pointing out these areas of control. I am exactly the opposite by discussing them I bring them to light so that they aren’t a problem.
The topics in this document are quickly developing. It may be obsolete before it is finished. I am not a writer. I am more verbally oriented.
Hello, Nice to Meet Control You: Food
We all eat food, all 8 billion of us. Think about that 8 billion people to feed. Most people do not realize that food distribution centers in major cities only have about three days of supply. The food supply is an attack surface for anyone wanting to control a populace. We have seen how easily the supply, among non-food things like TP, is disrupted by the Covid “pandemic”. As an example, the price of eggs rose to $5 per dozen from about $1.30.
This leads me to believe the food supply is a very frail and effective attack surface. Certainly anyone wishing to control a populations only need control the food supply chain.
The first obvious link in the food supply chain is production. Control how much food is produced and any condition from plentiful to famine can be realized. We have seen the direct attack on farmers using the specter of climate change. First in the Netherlands1 and subsequently in Germany2. The US isn’t safe from the assault on food as several animal rights and climate activist organizations have used climate change to to bolster their cause3. Claims of animal farming as being harmful to the environment is aiding the development of plant based “meat” produced in factories. This removes the production from a method that anyone could employ to one that is controlled completely by industry. The control of production is then complete once the end of animal farming is accomplished4. It is interesting that some of the very rich are buying farmland. I assume it is to provide raw materials to the food factories. Next stop distribution.
The dress rehearsal called the Covid-19 epidemic caused major disruptions in distribution of food and other comsumable products produced out side the US5. The most notable shortage was of paper products such as toilet paper. While it is true there were major supply chain issues the ultimate cause was a demand fueled by fear of shortage. In this way shortages are self fulfilling prophecies.
Controlling the food supply is a way to control the population. You can’t protest or fight back if you’re starving. Such bad behavior will be yield no food whereas good behavior will be rewarded with just enough to keep you alive.
Countermeasures
Grow some of your own food.
Eat nutritionally dense food if it is available. So that you require less food.
Source your food locally.
Counter-counter Measures
It will be made illegal to grow your own food. The argument will be the small farms produce too much greenhouse gases. Now we all know this is silly as home gardens do not require the burning of thousands of gallons of diesel fuel. You will also be accused of being selfish and an enemy of society. And someone named Greta will come to your house and punch you in the nuts (just checking to see if you’re actually reading this).
Doug Williamson Blogspot
1https://www.euronews.com/green/2023/11/30/dutch-farmers-could-be-paid-to-close-their-livestock-farms-under-new-scheme
2https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2024/01/15/germany-farmers-protests-berlin/
3https://worldanimalnews.com/250-groups-urge-the-usda-to-address-the-reduction-of-meat-dairy-to-reduce-greenhouse-gas-emissions/
4Interesting that no one is complaining about Mark Zuckerberg’s herd. He feeds his cattle beer.Yet fermentation produces a lot of CO2. https://nypost.com/2024/01/11/news/mark-zuckerberg-to-raise-cows-on-beer-and-macadamia-nuts-on-hawaii-ranch/
5https://www.freightwaves.com/news/disrupted-supply-chains-strain-trade-among-us-mexico-and-canada
1https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2024/01/22/carbon-footprint-homegrown-food-allotment-increase
The Netherlands will be the center for global food innovation with the Global Coordinating Secretariat (GCS)
On January 27, 2021, the Government of the Netherlands, the World Economic Forum (WEF) and several public and private sector partners launched Food Innovation Hubs at the Davos Agenda 2021 meeting. The Food Innovation Hubs will be a key multistakeholder platform that will leverage technology and broader innovations to strengthen local innovation ecosystems for food systems transformation. Supported by multi-year funding from the Government of Netherlands, the initiative will feature a Global Coordinating Secretariat (GCS) based in the Netherlands.
https://investinholland.com/news/the-netherlands-and-the-world-economic-forum-launch-food-innovation-hubs-initiative/The Netherlands and the World Economic Forum Launch Food Innovation Hubs Initiative
“Global food insecurity has been rising again. This stresses the need to redesign how we produce and consume food. The Netherlands is committed to forming partnerships that will catalyze the innovations that are needed to address the food system challenges. I am therefore proud to announce that the Netherlands will host the Global Coordinating Secretariat of the Food Innovation Hubs,” said Mark Rutte, Prime Minister of the Netherlands.
With the arrival of the GCS, the Netherlands will leverage its innovation-driven economy to help advance global food security. Boasting an extensive ecosystem of companies and knowledge institutions in agrifood, horticulture, breeding, high-tech and ICT, the Dutch are ideally positioned to play a leading role in shaping our planet’s food system.
The Food Innovation Hubs will be a flagship initiative of WEF’s Food Action Alliance leading to the UN Food Systems Summit 2021, and beyond. The role of the GCS will be to coordinate the efforts of the regional Hubs as well as align with global processes and initiatives such as the UN Food Systems Summit.
Global center for food innovation comes to the Netherlands
The Food Innovation Hubs initiative places the Netherlands at the center of global food innovation and sustainability. Located in Wageningen at the heart of the Dutch agrifood ecosystem, the GCS will direct the further development of global regional Food Innovation Hubs from the Netherlands. The work of these regional Hubs is already underway, with more than 20 organizations leading the initiative across Africa, ASEAN, Colombia, India and the European hub in Foodvalley Wageningen. Oost NL, a regional partner in the Invest in Holland Network, will support the GCS in starting this work.
“Food sustains life and is at the heart of our planet. But if we are to feed 10 billion people by 2050 within planetary boundaries, the way the world produces and consumes food needs to change. Innovation is critical in enabling this systemic transformation,” said Dominic Waughray, Managing Director of WEF.
“As progress is accelerated towards meeting the Sustainable Development Goals, the World Economic Forum is committed to supporting collective action and promoting country led agendas through the Food Innovation Hubs in this pivotal year for food systems,” added Waughray.
With country-led approaches, the Hubs will drive both high-end and low-cost grassroots and other innovations that could have scalable impact, as well as innovations encompassing supply chains, partnerships and business models that can enable systemic change.
Source: World Economic Forum
28 January 2021
#Youtube#FARMERS UNDER ATTACK FROM WEF GLOBALISTS#GARDENING IS UNDER ATTACK#INDEPENDENT FOOD PRODUCTION#JOJO MEHTA#STOP ECOSIDE NOW PUSHES FOR PUNISHMENT OF FARMERS#WORLD ECONOMIC FORUM PUSHES FOR ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOOD#BILL GATES IS AN ECO TERRORIST#FATHER LAWYER FOR MOSSAD#CANADA#GERMANY#AMERICA#AUSTRALIA#GET SERIOUS ABOUT LOCAL GOVERNMENTS AND THEIR RULES FOR SMALL SCALE FARMING#World Economic Forum#World Food Supply Initiative#Small Farming#Urban Farming#Food Autonomy#Carbom Footprints#USDA#People's Garden Initiative#Track American Gardens
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#social media#travel#vacation#nature#farmacia#small scale farming#urban farming#organic farming#farming#farmlife#farmers#farm#dairyequipments#dairy cows#ed dairy#cattle#cowboy#cowboys#fat cow#cowgirl#cow#cow milk#milk#villagelife#tamilnet#tamilnadu#viral news#viraltopic#video viral
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
vayalfoods ulutham paruppu providing plant-based protein, fiber, and antioxidants. Our Urad dhal are carefully selected and processed to ensure maximum nutrition and flavor, and are ideal for use in a variety of Asian dishes. Vayal Foods offers high-quality Urad Dhal, also known as ulutham paruppu, Uddina Bele / Uddhi parppu, that are sustainably sourced from small-scale farmers in India.
#vayalfoods ulutham paruppu providing plant-based protein#fiber#and antioxidants. Our Urad dhal are carefully selected and processed to ensure maximum nutrition and flavor#and are ideal for use in a variety of Asian dishes. Vayal Foods offers high-quality Urad Dhal#also known as ulutham paruppu#Uddina Bele / Uddhi parppu#that are sustainably sourced from small-scale farmers in India.
0 notes
Text
Women throughout (American and English) history worked. The idea that in the past the sole responsibility of women was domestic labor and childrearing is largely inaccurate for the majority of women in these societies. Women were expected to do domestic labor like cooking and cleaning and raising children AND work to bring income to their family, this was true for the average woman, excluding the upper middle class/wealthy. If a woman’s husband owned a tavern or restaurant, she also cooked and kept bar and did the duties associated with the business. If a woman’s husband was a (small scale/subsistence/tenant) farmer, the woman did farm labor. Often a woman was expected to do labor related to her husband’s job.
Women also had vocations and forms of income unrelated to their husband. The nature of these jobs changed over time but many women did things like weaving, embroidery, crafting, beer brewing, chicken tending and laundress work to bring income. Women with skills were seen as better marriage candidates because they’d make money for their husband.
My great-great-great-great grandmother told fortunes and did farm labor, my great-great-great grandmother was a midwife, my great-great grandmother worked in a textile factory for most of her adult life and my great grandmother was a school lunch lady.
This is why it makes me irate when women on the right say things like “feminism forced me to get a job instead of being allowed to stay home with my children” before feminism you would have had to tend house, raise your children and bring income to your husband. Now, at the very least, the money is hopefully your own. Women were always in the workforce, their work was not recognized.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Pursuit of Zero Hunger: Unlocking a World Without Hunger

Introduction
Hunger is a persistent global issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a fundamental human right to have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food, yet achieving this goal remains a challenge. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) include Goal 2: Zero Hunger, which aims to end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture by 2030. This article explores the significance of Goal 2, the current state of global hunger, and the steps being taken to eradicate hunger and ensure food security for all.
The Scope of Global Hunger
Hunger is a multifaceted issue that extends far beyond the simple absence of food on one's plate. It encompasses a range of factors that contribute to individuals, communities, and entire nations being deprived of regular access to sufficient and nutritious food. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the alarming statistic of more than 690 million people, approximately 8.9% of the global population, suffering from chronic hunger serves as a stark reminder of the challenges we face in achieving zero hunger.
Poverty is undoubtedly one of the primary drivers of hunger. Insufficient income and resources leave individuals and families unable to afford an adequate quantity and quality of food. Poverty often leads to a cycle of hunger and malnutrition, as individuals struggle to break free from the grip of poverty, which further perpetuates food insecurity. Breaking this cycle requires comprehensive poverty alleviation strategies that address the root causes of poverty and provide opportunities for economic empowerment.
Inadequate access to nutritious food is another critical aspect of the hunger problem. Even when food is available, it may lack the necessary nutrients for individuals to lead healthy and active lives. Malnutrition, both undernutrition and overnutrition, poses significant health risks and hinders proper physical and cognitive development. Access to a diverse range of nutritious food, including fruits, vegetables, proteins, and essential vitamins and minerals, is essential for combating malnutrition and achieving food security.
Climate change poses a formidable threat to global food security. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt agricultural systems, leading to reduced crop yields and food shortages. Small-scale farmers, who are often the most vulnerable, bear the brunt of these climate impacts. Droughts, floods, and unpredictable growing seasons further exacerbate the challenges they face in producing enough food to sustain themselves and their communities. Addressing climate change and implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices are critical components of the zero hunger agenda.
Conflict and political instability also contribute to hunger and food insecurity. In regions affected by armed conflicts or political crises, food production and distribution systems are disrupted, and access to food becomes limited. Civil unrest, displacement, and the destruction of infrastructure further compound the problem, leaving populations in desperate need of assistance. Resolving conflicts, promoting peace, and ensuring humanitarian access to affected areas are essential steps towards achieving zero hunger.
Unequal distribution of resources exacerbates hunger within and between countries. Concentration of wealth, land ownership, and access to markets and resources in the hands of a few can perpetuate a vicious cycle of food insecurity. Reducing inequality and promoting equitable distribution of resources and opportunities are crucial for creating a fair and just food system that leaves no one behind.
Addressing the complexity of hunger requires a multi-dimensional and holistic approach. It involves not only increasing food production but also improving access to nutritious food, addressing poverty, mitigating climate change, promoting peace and stability, and advocating for equitable resource distribution. Governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector must collaborate and work together to implement comprehensive strategies and policies that tackle the root causes of hunger.
Efforts to combat hunger must also prioritize the empowerment of marginalized and vulnerable groups, including women, indigenous communities, and rural populations. These groups often face additional barriers to accessing food and resources, and their voices and needs must be central to any hunger eradication initiatives. By empowering these groups and ensuring their active participation in decision-making processes, we can foster more inclusive and sustainable solutions.
Hunger is a complex issue intertwined with poverty, inadequate access to nutritious food, climate change, conflict, and unequal distribution of resources. Achieving zero hunger requires addressing these interconnected challenges through comprehensive strategies that encompass poverty alleviation, sustainable agriculture, nutrition education, climate resilience, peacebuilding, and equitable resource distribution. By recognizing the multifaceted nature of hunger and taking collective action, we can pave the way towards a world where every individual has access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food, and where hunger is no longer a harsh reality.
Understanding Food Insecurity
Food insecurity is a complex and multifaceted issue that extends beyond the simple concept of hunger. While hunger specifically refers to the sensation of not having enough food to eat, food insecurity encompasses a broader set of circumstances that prevent individuals, communities, and entire nations from accessing a consistent supply of nutritious food necessary for a healthy and active lifestyle.
At its core, food insecurity is characterized by a lack of regular access to sufficient and nutritious food. It encompasses both the quantity and quality of food available to individuals and communities. It means not having enough food to meet basic dietary needs and not having access to a variety of foods that are essential for a balanced and nutritious diet. Without adequate access to nutritious food, individuals and communities face numerous challenges that can have detrimental effects on their health, well-being, and overall development.
Food insecurity affects individuals, communities, and entire nations. On an individual level, it can lead to undernutrition or malnutrition, compromising physical and cognitive development, and increasing the risk of disease and mortality. Communities and nations grappling with food insecurity face significant socio-economic challenges, hindering their progress and development.
Several factors contribute to food insecurity, including income inequality, limited agricultural productivity, and unstable food systems. Income inequality is a critical driver of food insecurity, as it affects individuals' purchasing power to access food. In societies with wide income disparities, those with lower incomes often struggle to afford an adequate and nutritious diet, leading to food insecurity. Addressing income inequality is essential to reduce food insecurity and ensure equal access to food for all.
Limited agricultural productivity is another key factor contributing to food insecurity. Insufficient agricultural production, whether due to environmental factors, inadequate access to resources, or outdated farming practices, can result in insufficient food supply. This directly affects food availability and affordability, particularly in regions heavily dependent on agriculture for sustenance. Enhancing agricultural productivity through sustainable farming practices, technology adoption, and investments in rural infrastructure is crucial to achieving food security.
Unstable food systems, including volatile food prices, inadequate storage facilities, and unreliable supply chains, also contribute to food insecurity. Fluctuations in food prices can make nutritious food unaffordable for vulnerable populations, pushing them further into food insecurity. Weak supply chains and insufficient infrastructure can lead to food losses and wastage, exacerbating the problem. Strengthening food systems and improving their resilience is vital for reducing food insecurity.
Achieving zero hunger requires addressing these underlying issues comprehensively. It necessitates a multi-faceted approach that encompasses not only increasing food production but also improving access to nutritious food, promoting income equality, and building sustainable and resilient food systems.
To address income inequality and improve access to food, efforts should focus on creating employment opportunities, implementing social protection programs, and promoting inclusive economic growth. Policies and initiatives that aim to reduce poverty, increase access to education, and empower marginalized communities can significantly contribute to reducing food insecurity.
Investments in agricultural research and development, modern farming techniques, and sustainable farming practices can enhance agricultural productivity and ensure a stable food supply. Support for small-scale farmers, including access to credit, technology, and markets, is crucial for their productivity and income generation, ultimately contributing to food security.
Strengthening food systems involves improving infrastructure, storage facilities, and transportation networks to reduce post-harvest losses and ensure efficient distribution of food. It also requires promoting market transparency, fair trade practices, and reducing food waste along the supply chain. International cooperation and partnerships are vital to sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices to build resilient and sustainable food systems globally.
Education and awareness play a critical role in addressing food insecurity. Nutrition education programs can empower individuals and communities to make informed choices about their diets, promote healthy eating habits, and maximize the nutritional value of available resources. Education on sustainable agricultural practices can also promote environmentally friendly farming methods, improve resource management, and enhance long-term food security.
Achieving zero hunger requires collaborative efforts and strong governance at various levels. Governments, civil society organizations, international institutions, and the private sector must work together to develop and implement comprehensive policies, programs, and initiatives that address the underlying causes of food insecurity. International cooperation and partnerships are vital for sharing knowledge, expertise, and resources to build a sustainable and inclusive global food system.
Food insecurity is a complex issue that encompasses more than just hunger. It refers to the lack of regular access to sufficient, nutritious food necessary for a healthy and active life. Factors such as income inequality, limited agricultural productivity, and unstable food systems contribute to food insecurity. Achieving zero hunger requires addressing these underlying issues through a comprehensive approach that includes promoting income equality, improving agricultural productivity, strengthening food systems, and raising awareness through education and collaboration. Only through concerted efforts can we create a world where everyone has access to adequate and nutritious food, thereby achieving the goal of zero hunger.
Tackling Hunger through Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture serves as a critical pillar in the global effort to combat hunger and achieve food security. It focuses on promoting farming practices that not only increase food production but also ensure the long-term preservation of natural resources and the environment. By adopting sustainable agricultural techniques, we can address the challenges of food security while mitigating the negative impacts of agriculture on ecosystems and climate change.
Investing in research and innovation is essential for advancing sustainable agriculture. By developing and disseminating improved crop varieties and farming methods, we can enhance productivity and resilience in agricultural systems. This includes investing in agricultural research to create crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and adverse weather conditions. Furthermore, innovation in farming techniques, such as precision agriculture and vertical farming, can optimize resource use and maximize yields.
Crop diversity is a fundamental aspect of sustainable agriculture. By promoting a variety of crops, farmers can reduce the risks associated with relying on a single crop. Diversification enhances resilience to pests, diseases, and climate variability. It also contributes to a more balanced and nutritious diet, as diverse crops provide a broader range of essential nutrients. Encouraging farmers to grow a variety of crops through training, access to seeds, and market incentives can enhance both their livelihoods and the overall food security of a region.
Efficient irrigation techniques are crucial in sustainable agriculture, particularly in regions facing water scarcity. Practices such as drip irrigation and precision water management minimize water waste and ensure that water resources are used optimally. By improving irrigation infrastructure and promoting water-saving practices, we can maximize agricultural productivity while conserving water for other essential needs.
Empowering small-scale farmers is vital for achieving sustainable agriculture and food security. Smallholder farmers constitute a significant portion of the world's food producers, particularly in developing countries. Enhancing their access to resources, including land, credit, seeds, and technology, can significantly improve their productivity and livelihoods. Supporting farmers' cooperatives, providing training on sustainable practices, and facilitating access to markets can help small-scale farmers overcome barriers and strengthen their position in the agricultural value chain.
Improving access to markets and financial resources is crucial for small-scale farmers. Limited market access often hinders their ability to sell their produce at fair prices and take advantage of economic opportunities. By improving infrastructure, connecting farmers to markets, and promoting fair trade practices, we can ensure that farmers receive equitable returns for their products. Additionally, providing financial services tailored to the needs of farmers, such as microcredit and crop insurance, can enhance their resilience and enable investment in sustainable agricultural practices.
Sustainable agriculture also embraces practices that minimize the use of harmful agrochemicals and promote organic farming methods. By reducing reliance on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, sustainable agriculture protects soil health, biodiversity, and water quality. Organic farming practices prioritize natural inputs, such as compost, crop rotation, and biological pest control, to maintain soil fertility and minimize environmental impacts. Encouraging the adoption of organic farming practices through training, certification programs, and market incentives can contribute to sustainable agricultural systems.
Sustainable agriculture plays a crucial role in combating hunger and achieving food security. By promoting environmentally friendly farming practices, investing in research and innovation, encouraging crop diversity, adopting efficient irrigation techniques, empowering small-scale farmers, and improving market access, we can increase food production while preserving natural resources for future generations. Sustainable agriculture not only addresses the immediate challenge of hunger but also contributes to building resilient and sustainable food systems that can sustainably nourish the world's population.
Nutrition: Beyond Calorie Intake
Ensuring access to nutritious food is a fundamental component of achieving the goal of zero hunger. While addressing calorie intake is important, it is equally crucial to emphasize the quality and diversity of food consumed. Malnutrition, which encompasses both undernutrition and overnutrition, remains a significant global concern. To tackle this issue effectively, efforts must focus on promoting balanced diets, improving access to essential nutrients, and educating communities about healthy eating habits.
One of the key aspects of addressing malnutrition is promoting balanced diets. A balanced diet includes a variety of foods from different food groups, providing essential nutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. It is essential to ensure that individuals have access to a diverse range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Promoting dietary diversity can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote overall health and well-being.
Improving access to essential nutrients is another critical element of addressing malnutrition. This includes enhancing the availability and affordability of nutrient-rich foods, particularly for vulnerable populations. It involves strategies such as promoting local food production, supporting small-scale farmers, and strengthening food supply chains. By ensuring that nutritious foods are accessible and affordable, individuals and communities can have a greater opportunity to meet their nutritional needs.
Education and awareness play a vital role in promoting healthy eating habits and preventing malnutrition. Nutrition education programs can provide information on the importance of balanced diets, the benefits of consuming different food groups, and the risks associated with poor nutrition. These programs can also teach practical skills, such as meal planning, food preparation, and cooking techniques, to empower individuals to make healthier food choices. By promoting nutrition education at schools, healthcare facilities, and community centers, we can foster a culture of healthy eating and long-term behavior change.
Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and the private sector is crucial for implementing effective interventions and policies to address malnutrition. Governments should prioritize nutrition in their national agendas and develop comprehensive strategies that encompass food security, health, and education. They can implement policies that support sustainable agriculture, regulate food labeling and advertising, and provide incentives for the production and consumption of nutritious foods. NGOs and the private sector can contribute by partnering with communities, implementing nutrition programs, and promoting corporate social responsibility initiatives that address malnutrition.
Efforts should also focus on addressing specific nutritional needs in different population groups. For instance, targeting maternal and child nutrition is essential for breaking the intergenerational cycle of malnutrition. Providing adequate nutrition during pregnancy and early childhood is crucial for healthy growth and development. Additionally, addressing micronutrient deficiencies, such as iron, vitamin A, and iodine, is vital in reducing the prevalence of nutrient-related disorders and improving overall health.
Furthermore, innovative approaches can be utilized to improve access to nutritious food. For example, initiatives such as school feeding programs, community gardens, and urban farming can increase the availability of fresh and locally sourced produce. These approaches not only provide nutritious food but also promote community engagement, sustainability, and economic empowerment.
Ensuring access to nutritious food is a key aspect of achieving zero hunger. Efforts should go beyond addressing calorie intake alone and focus on the quality and diversity of food consumed. By promoting balanced diets, improving access to essential nutrients, and educating communities about healthy eating habits, we can effectively address malnutrition. Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and the private sector is crucial for implementing effective interventions and policies. By prioritizing nutrition and implementing comprehensive strategies, we can pave the way for a healthier and more food-secure future for all.
Building Resilience and Adaptation
Climate change presents a formidable challenge to global food security. As temperatures rise, extreme weather events become more frequent, and precipitation patterns shift, the agricultural sector faces disruptions that exacerbate hunger and threaten the livelihoods of millions of people. To address these challenges, it is crucial to build resilience and implement adaptation strategies that can mitigate the impact of climate change on food systems.
One of the key approaches to combat the effects of climate change on food security is through the development and implementation of climate-smart agriculture practices. Climate-smart agriculture encompasses a range of techniques and methods that aim to increase agricultural productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing the resilience of farming systems, and promoting sustainable land and water management. These practices include conservation agriculture, agroforestry, precision farming, and integrated pest management. By adopting climate-smart agriculture, farmers can better cope with the changing climatic conditions and maintain or increase their agricultural productivity.
Investing in the development and dissemination of climate-resistant crop varieties is another essential strategy. Plant breeding programs can focus on developing crop varieties that are more tolerant to heat, drought, flooding, and pests. These climate-resistant varieties have the potential to withstand extreme weather events and produce higher yields under challenging conditions. Additionally, promoting crop diversity and utilizing traditional and local crop varieties that are adapted to specific climate conditions can contribute to enhancing the resilience of agricultural systems.
Implementing early warning systems is crucial for anticipating and responding to weather-related risks. Timely and accurate information about weather patterns, such as rainfall, temperature, and extreme events, allows farmers to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to protect their crops and livelihoods. Early warning systems enable farmers to adjust their planting and harvesting schedules, implement protective measures, and access support and resources in advance of potential disasters. These systems can be enhanced through the use of technology, including weather monitoring tools, satellite data, and mobile communication networks.
In addition to on-farm strategies, addressing climate change and food security requires collaborative efforts at regional, national, and international levels. Governments, international organizations, research institutions, and civil society must work together to develop and implement policies and initiatives that promote climate resilience in the agricultural sector. This includes investing in climate-smart infrastructure, improving access to climate information and resources for farmers, and supporting sustainable land and water management practices.
Promoting climate-smart agriculture also involves integrating climate change considerations into broader development strategies. This includes incorporating climate resilience and adaptation measures into national agricultural policies, land-use planning, and disaster risk reduction frameworks. It also requires supporting small-scale farmers, particularly in vulnerable regions, by providing access to financial services, agricultural inputs, and capacity-building programs that equip them with the knowledge and tools to adapt to changing climate conditions.
Furthermore, international cooperation and financial support are essential to help developing countries build resilience and adapt to climate change. Industrialized nations, as major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, should fulfill their commitments to provide financial resources and technology transfer to support climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts in developing countries. This includes funding for research and development, capacity-building programs, and infrastructure improvements that enhance climate resilience in agriculture.
Climate change poses significant challenges to food security by disrupting agricultural production and exacerbating hunger. Building resilience and implementing adaptation strategies are crucial to mitigate the impact of climate change on food systems. This involves developing and promoting climate-smart agriculture practices, investing in climate-resistant crop varieties, implementing early warning systems, and integrating climate considerations into broader development strategies. Through collaborative efforts at all levels, we can work towards ensuring a sustainable and secure food supply in the face of a changing climate.
Promoting Gender Equality
Achieving zero hunger is intricately linked to addressing gender inequality, as women play a pivotal role in agriculture and food production worldwide. However, they often face significant barriers that limit their access to resources, land, credit, and decision-making power. Empowering women and promoting gender equality in agriculture and food systems is crucial for enhancing agricultural productivity, improving food security, and ultimately achieving the goal of zero hunger.
Women make up a substantial portion of the agricultural labor force, particularly in developing countries. They are involved in various stages of food production, from planting and harvesting to processing and marketing. Despite their significant contributions, women face systemic challenges that hinder their productivity and restrict their ability to access resources. Gender norms and discriminatory practices often result in unequal access to land ownership, credit facilities, agricultural inputs, and extension services. This inequality not only undermines women's economic empowerment but also hampers overall agricultural productivity and food production.
Empowering women in agriculture involves dismantling the barriers that hinder their full participation and addressing gender-based inequalities. Providing women with secure land rights and access to productive resources is a crucial step towards ensuring their equal participation. This can be achieved through legal reforms, awareness campaigns, and support for women's land rights organizations. By enabling women to have control over land and other productive assets, they gain the autonomy and resources necessary to make decisions about agricultural practices and investments.
Access to credit is another critical factor in empowering women in agriculture. Financial institutions and development programs should prioritize providing women with access to affordable credit and financial services. By ensuring equal access to credit facilities, women can invest in agricultural inputs, machinery, and technology, thereby enhancing their productivity and contributing to food security. Moreover, targeted financial literacy programs can equip women with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively manage their finances and make informed decisions regarding agricultural investments.
Gender-responsive extension services and training programs play a vital role in empowering women farmers. These programs should address the specific needs and priorities of women, providing them with the necessary knowledge and skills to adopt sustainable farming practices, improve crop productivity, and manage post-harvest activities. Furthermore, mentorship programs and networking opportunities can facilitate the exchange of experiences and knowledge-sharing among women farmers, enabling them to learn from each other and strengthen their capacities.
Promoting women's participation in decision-making processes is essential for achieving gender equality in agriculture and food systems. Women's voices and perspectives need to be heard and considered in the development and implementation of policies, programs, and initiatives related to agriculture and food security. This requires creating inclusive spaces for women to engage in decision-making at all levels, from local communities to national and international platforms. Strengthening women's leadership and representation in farmer organizations, cooperatives, and agricultural institutions can contribute to more equitable and effective decision-making processes.
Recognizing and valuing the unpaid care and domestic work performed by women is also crucial for achieving gender equality in agriculture. The burden of household chores and caregiving responsibilities often falls disproportionately on women, limiting their time and energy for productive activities. Investing in infrastructure, such as water and sanitation facilities, energy sources, and transportation, can alleviate the burden of unpaid care work, reduce drudgery, and create opportunities for women to engage in income-generating activities.
Promoting gender equality in agriculture and food systems is not only a matter of social justice but also a strategic imperative. Studies have shown that closing the gender gap in agriculture could increase agricultural productivity and contribute to global food security. When women have equal access to resources and decision-making power, they are more likely to invest in the well-being of their families, improve farming practices, and adopt sustainable agricultural technologies. Moreover, empowering women in agriculture can have a multiplier effect, as they tend to invest a significant portion of their income in education, health, and nutrition, benefiting their households and communities.
Achieving zero hunger requires addressing gender inequality in agriculture and food systems. Empowering women, ensuring their equal access to resources, land, credit, and decision-making, is essential for enhancing agricultural productivity, improving food security, and promoting sustainable development. By promoting gender equality, we unlock the full potential of women as agents of change in the fight against hunger. Investing in women farmers and recognizing their invaluable contributions can pave the way for a more equitable and food-secure future for all.
Collaboration and Partnerships
The journey towards achieving zero hunger is a complex and multifaceted task that requires collaboration and partnerships among various stakeholders. No single entity can tackle this challenge alone. Governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector must come together, pooling their resources, sharing knowledge, and coordinating efforts to implement effective policies, programs, and initiatives that address the underlying causes of hunger and achieve sustainable development.
Governments play a central role in driving the efforts to eradicate hunger. They have the responsibility to establish and implement national policies and strategies that prioritize food security and nutrition. This includes allocating sufficient resources, developing sustainable agricultural practices, investing in rural infrastructure, and ensuring access to social protection programs for vulnerable populations. Governments should also create an enabling environment that encourages private sector investments in agriculture and promotes the engagement of civil society organizations in hunger alleviation initiatives.
International organizations, such as the United Nations agencies, the World Bank, and regional development banks, have a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to combat hunger. These organizations provide technical expertise, policy guidance, and financial support to countries in their efforts to achieve food security and nutrition goals. They facilitate knowledge exchange, promote best practices, and coordinate international partnerships for sustainable development. Additionally, they monitor progress, assess the impact of interventions, and advocate for policy changes at the global level to address systemic issues related to hunger.
Civil society organizations, including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community-based organizations, and grassroots movements, are instrumental in mobilizing communities, raising awareness, and implementing on-the-ground interventions to address hunger. They work closely with local communities, advocating for their rights and empowering them to actively participate in decision-making processes related to food security and nutrition. Civil society organizations also play a crucial role in monitoring and holding governments accountable for their commitments to achieving zero hunger.
The private sector has a significant role to play in advancing the goal of zero hunger. Companies involved in agriculture, food processing, and distribution can contribute through sustainable business practices, innovation, and investment in agricultural value chains. Public-private partnerships can be formed to leverage the expertise, technology, and resources of the private sector in addressing the challenges of food security and nutrition. Engaging the private sector can lead to increased productivity, improved market access for smallholder farmers, and the development of innovative solutions to reduce post-harvest losses and improve food distribution systems.
Collaboration and partnerships among these stakeholders are crucial for maximizing the impact of interventions and addressing the root causes of hunger. By pooling resources and expertise, stakeholders can achieve greater efficiency, avoid duplication of efforts, and scale up successful initiatives. Collaboration also allows for the sharing of knowledge and best practices, facilitating innovation and learning from each other's experiences. Through coordinated efforts, stakeholders can identify gaps, develop comprehensive strategies, and implement integrated approaches that address the complex and interconnected challenges of hunger.
Multi-stakeholder partnerships should be based on principles of inclusivity, transparency, and accountability. All stakeholders, including marginalized groups, small-scale farmers, women, and youth, should have a seat at the table and actively participate in decision-making processes. Partnerships should prioritize the needs and priorities of those most affected by hunger and ensure that interventions are context-specific and culturally appropriate.
Achieving zero hunger requires collaboration and partnerships among governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector. By working together, stakeholders can pool their resources, share knowledge, and coordinate efforts to implement effective policies, programs, and initiatives that address the underlying causes of hunger and achieve sustainable development. With collective action and a shared commitment, we can create a world where everyone has access to sufficient, nutritious food and no one goes to bed hungry.
Conclusion
Goal 2: Zero Hunger stands as a testament to our collective commitment to eradicating hunger and achieving food security for all. While the challenges are immense, significant progress has been made in recent years. However, there is still a long way to go. By addressing the root causes of hunger, promoting sustainable agriculture, improving nutrition, building resilience, empowering women, and fostering collaboration, we can unlock a future where hunger is nothing but a distant memory. The pursuit of zero hunger is not just a noble aspiration; it is a moral imperative that demands our unwavering dedication and concerted action. Together, we can create a world where no one goes to bed hungry, where food becomes a basic right rather than a luxury, and where the potential of every individual is unleashed.
#How to achieve zero hunger through sustainable agriculture#Addressing food insecurity: a comprehensive approach to zero hunger#Empowering women in agriculture for zero hunger#Climate change and its impact on food security#The role of partnerships in achieving zero hunger#Achieving zero hunger through collaborative efforts#Promoting gender equality for sustainable food systems#Climate-smart agriculture: a solution for food security#Strategies to combat hunger and promote sustainable development#The importance of access to nutritious food in achieving zero hunger#Tackling food insecurity: a global priority for sustainable development#Addressing the root causes of hunger for long-term solutions#The role of governments in achieving zero hunger#Building resilience in agriculture to mitigate the impact of climate change on food security#Harnessing the potential of small-scale farmers for zero hunger#Innovative approaches to promote food security and nutrition#Ensuring equal access to resources for sustainable food production#Strengthening agricultural value chains for zero hunger#The role of education in promoting sustainable food systems and zero hunger#Integrating gender equality into agricultural policies for food security#Sustainable farming practices for achieving zero hunger#Leveraging technology to enhance food production and reduce hunger#Overcoming barriers to food access and nutrition for vulnerable populations#Promoting sustainable land and water management for food security#The impact of income inequality on hunger and food insecurity#Investing in agricultural research and innovation for zero hunger#Advocating for policy changes to address hunger and promote sustainable agriculture#Strategies to improve market access for smallholder farmers and reduce hunger#Strengthening early warning systems for climate-related risks and food security#Creating a roadmap for achieving zero hunger: lessons learned and best practices
0 notes
Text
‘Farm Didi’: She Quits Her Job To Help Rural Women Scaling Up Their Businesses
How Manjari Sharma Helped The Rural Women Earning Decent Income
Manjari Sharma, an IIM graduate was working as a corporate when visited the remote villages of Bihar. It was volunteer work and she spent 15 days there. To her astonishment, she found the women of the villages very skilful. She was amazed to see how those villagers women took out time for their household chores and invested…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Please come and see me because I’ll be dead soon’: how Michael Sheen got sucked into a forever chemicals exposé
An opera-loving member of high society turned eco-activist who was forced into police protection with a panic button round his neck. A Hollywood actor who recorded said activist’s life story as he was dying from exposure to the very chemicals he was investigating. Throw in two investigative journalists who realise not everything is as it seems, then uncover some startling truths, and you have “podcasting’s strangest team” on Buried: The Last Witness.
On their award-winning 2023 podcast Buried, the husband and wife duo Dan Ashby and Lucy Taylor dug into illegal toxic waste dumping in the UK and its links to organised crime. This time, they focus on “forever chemicals”, specifically polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and set out to discover whether one whistleblower may have been decades ahead of his time in reporting on their harmful impact.
“It’s amazing how big the scale of this story is,” says Ashby, as we sit backstage at the Crucible theatre, where they are doing a live discussion as part of Sheffield DocFest. “With this series, we don’t just want it to make your blood turn cold, we want it to make you question your own blood itself.”
It all started when Taylor and Ashby were sent a lead about the work of former farmer’s representative Douglas Gowan. In 1967, he discovered a deformed calf in a field and began to investigate strange goings on with animals close to the Brofiscin and Maendy quarries in south Wales. He linked them to the dumping of waste by companies including the nearby Monsanto chemical plant, which was producing PCBs.
PCBs were used in products such as paint and paper to act as a fire retardant, but they were discovered to be harmful and have been banned since 1981 in the UK. However, due to their inability to break down – hence the term forever chemical – Gowan predicted their legacy would be a troubling one. “I expect there to be a raft of chronic illness,” he said. He even claimed that his own exposure to PCBs (a result of years of testing polluted grounds) led his pancreas and immune system to stop working. “I’m a mess and I think it can all be attributed to PCBs,” he said.
However, Gowan wasn’t a typical environmentalist. “A blue-blood high-society Tory and a trained lawyer who could out-Mozart anyone,” is how Taylor describes him in the series. He would even borrow helicopters from friends in high places to travel to investigate farmers’ fields. Gowan died in 2018 but the pair managed to get hold of his life’s work – confidential reports, testing and years of evidence. “I’m interested in environmental heroes that aren’t cliche,” says Ashby. “So I was fascinated by him. But then we started to see his flaws and really had to weigh them up. My goodness it’s a murky world we went into.”
The reason they were able to delve even deeper into this murky world is because of the award-winning actor Michael Sheen who, in 2017, came across Gowan’s work in a story he read. He was so blown away by it, and the lack of broader coverage, that he tracked him down. “I got a message back from him saying: ‘Please come and see me because I’ll be dead soon,’” says Sheen. “I took a camera with me and spent a couple of days with him and just heard this extraordinary story.”
What Gowan had been trying to prove for years gained some traction in 2007, with pieces in the Ecologist and a Guardian article exploring how “Monsanto helped to create one of the most contaminated sites in Britain”. One was described as smelling “of sick when it rains and the small brook that flows from it gushes a vivid orange.” But then momentum stalled.
Years later, in 2023, Ashby and Taylor stumbled on a recording of Sheen giving the 2017 Raymond Williams memorial lecture, which referenced Gowan and his work. Before they knew it, they were in the actor’s kitchen drinking tea and learning he had conducted a life-spanning seven-hour interview with Gowan before his death. So they joined forces. Sheen isn’t just a token celebrity name added for clout on this podcast; he is invested. For him, it’s personal as well as political. “Once you dig into it, you realise there’s a pattern,” he says. “All the places where this seems to have happened are poor working-class areas. There’s a sense that areas like the one I come from are being exploited.”
Sheen even goes to visit some contaminated sites in the series, coming away from one feeling sick. “That made it very real,” he says. “To be looking into a field and going: ‘Well, I’m pretty sure that’s toxic waste.’” Sheen was living a double life of sorts. “I went to rehearsals for a play on Monday and people were like, ‘What did you do this weekend?’” he says. “‘Oh, I went to the most contaminated area in the UK and I think I may be poisoned.’ People thought I was joking.” Sheen ended up being OK, but did have some temporary headaches and nausea, which was a worry. “We literally had to work out if we had poisoned Michael Sheen,” says Ashby, who also ponders in the series: “Have I just killed a national treasure?”
The story gets even knottier. Gowan’s findings turn out to be accurate and prescient, but the narrative around his journey gets muddy. As a character with a flair for drama, he turned his investigation into a juicy, riveting story filled with action, which could not always be corroborated. “If he hadn’t done that, and if he’d been a nerdy, analytical, detail-oriented person who just presented the scientific reports and kept them neatly filed, would we have made this podcast?” asks Taylor, which is a fascinating question that runs through this excellent and gripping series.
Ashby feels that Gowan understood how vital storytelling is when it comes to cutting through the noise. “We have so much science proving the scale of these problems we face and yet we don’t seem to have the stories,” he says. “I think Douglas got that. Fundamentally, he understood that stories motivate human beings to act. But then he went too far.”
However, this is not purely about Gowan’s story – it’s about evidence. The Last Witness doubles up as a groundbreaking investigation into the long-lasting impact of PCBs. “We threw the kitchen sink at this,” says Ashby. “The breakthrough for us is that the Royal Society of Chemistry came on board and funded incredibly expensive testing. So we have this commitment to go after the truth in a way that is hardly ever done.”
From shop-bought fish so toxic that it breaches official health advice to off-the-scale levels of banned chemicals found in British soil, the results are staggering. “The scientist almost fell off his chair,” says Ashby. “That reading is the highest he has ever recorded in soil – in the world. That was the moment we knew Douglas was right and we are now realising the scale of this problem. The public doesn’t realise that even a chemical that has been banned for 40 years is still really present in our environment.”
To go even deeper into just how far PCBs have got into our environment and food chain, Ashby and Taylor had their own blood tested. When Taylor found 80 different types of toxic PCB chemicals in her blood it was a sobering moment. “I was genuinely emotional because it’s so personal,” she says. “It was the thought of this thing being in me that was banned before I was even born and the thought of passing that on to my children.” Ashby adds: “We’ve managed physical risk in our life as journalists in Tanzania and with organised crime, but more scary than a gangster is this invisible threat to our health.”
In order to gauge the magnitude of what overexposure to PCBs can do, they headed to Anniston, Alabama, once home to a Monsanto factory. “As a journalist, you have an inbuilt scepticism and think it can’t be that bad,” says Ashby. “But when I got there I couldn’t believe what I was seeing. I hate to use words like dystopian, but it was. There is a whole massive school that can’t be used. There’s illnesses in children and cancers. It truly was the most powerful vignette of the worst-case example of these chemicals.”
It’s bleak stuff but instilling fear and panic is not the intention. “Obviously, we’re really concerned about it,” says Ashby. “And although the environmental crises we face do feel overwhelming, it is incredible how a movement has formed and how individuals are taking action in communities. The lesson to take from Douglas is that the response doesn’t have to be resignation. It can be agency.”
#Michael Sheen#Interview#Buried#The Last Witness#BBC Radio 4#it's interesting that with two little kids at home he went in a poisoned place anyway
757 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Macadamia Shell Controversy in Kenya
The Macadamia Shell Association of Kenya has raised concerns about the potential importation of raw macadamia nuts from other countries. The association argues that this move could negatively impact local industries that rely on macadamia shells as a fuel source.
According to the association, macadamia shells are a crucial byproduct of the macadamia processing industry in Kenya. These shells are…
#air pollution#carbon emissions#diversification#domestic industries#economic benefits#environmental impact#environmental regulations#foreign exchange earnings#fuel source#government regulation#greenhouse gases#import ban#job creation#kenya#land use#macadamia industry#macadamia nuts#macadamia shell association#macadamia shells#market risk#particulate matter#pollution control measures#quality standards#raw macadamia nuts#renewable energy#research and development#Small-scale farmers#sustainable farming practices#sustainable fuel#trade regulations
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sustainable gastronomy can help us to take care of our one and only planet.

Here are the 4 ways to practice sustainable gastronomy:
Buy from small-scale, local producers.
Try local foods.
Cook a traditional recipe with local ingredients.
Say no to Food Waste.
#Small scale farmers#local producers#Local foods#local ingredients#food waste#Sustainable Gastronomy#Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
1 note
·
View note
Text
Zuni farmers in the southwestern United States made it through long stretches of extremely low rainfall between A.D. 1200 and 1400 by embracing small-scale, decentralized irrigation systems. Farmers in Ghana coped with severe droughts from 1450 to 1650 by planting indigenous African grains, like drought-tolerant pearl millet.
Ancient practices like these are gaining new interest today. As countries face unprecedented heat waves, storms and melting glaciers, some farmers and international development organizations are reaching deep into the agricultural archives to revive these ancient solutions.
Drought-stricken farmers in Spain have reclaimed medieval Moorish irrigation technology. International companies hungry for carbon offsets have paid big money for biochar made using pre-Columbian Amazonian production techniques. Texas ranchers have turned to ancient cover cropping methods to buffer against unpredictable weather patterns.
But grasping for ancient technologies and techniques without paying attention to historical context misses one of the most important lessons ancient farmers can reveal: Agricultural sustainability is as much about power and sovereignty as it is about soil, water and crops.
380 notes
·
View notes
Note
Fletcher and foxboy malewife are my favorite but what if.... fletcher and naga malewife? I think that'd be interesting
Yan Farmer Flemish Rabbit Hybrid + Naga Reader
[No pronouns used for Reader but they are referred to as wife and intended to be male]
-
"Give it back...... Give it back...."
A stalking plague falls upon the sleepy town. Residents of a once a bustling burrow of rabbits now lock their doors soon as the sun sets over the mountains in fear of the shadow lurking down every barren alleyway. Hunger pains, yet it does not seek the flesh of these creature. It hunts each night - a restless search for the item able to free it from this place. Anger and fear rule its mind, teeth flared at any and all who answer their pleas incorrectly. Confusion replaces the fear dread in the hearts of its victims at the accusations of theft. Regardless, the beast points their claws at whomever crosses their path til what they have lost is rightfully returned.
"Give it back...."
"This what you're lookin' for?"
A chain dangles freely from the rabbit's finger - moonlight bouncing off the blood red gem tailored to the sliver band attached to the end of the chain. There's something odd about this rabbit. Why does this one smell so... familiar?
The barn.
Your sanctuary from the raging storm has been the crux of all your troubles from the very beginning. This rabbit must be is caretaker then. You've seen him in passing, but had no interest in him besides his herd so you never paid much attention to the details. One that goes without saying is how large the man is. Your tail gives you leverage now, but if you don't get your ring back soon then surely-
"It's rude to keep what isn't yours. Give it to me."
"Hey, now- I found this on my property fair and square. I even waited the first couple of nights for you to come back, but you never showed. I was starting to worry I'd never see you again."
Does he enjoy the sound of his own voice? Something catches your eye over the rabbit's shoulder. A glimmer of yellow breaking over the horizon. Panic sets in as a tingle runs through the nerves of your tail. It won't be long now. You needed to act fast. The rabbit looked to be aware of your peril as he takes several steps back into the growing sunlight. Your hand recoils as it creeps towards you.
"Been watching you for a long time now. Long enough to know a small bit about this whole... situation you got going on. I'll give you this ring back - for a price.~"
He's stalling. Sunlight blinds your sight as that accursed ball of light peeks over the buildings. Your body slowly begins to shrink - tail splitting in two as you topple over from the sudden shift in your shape. You crash to the ground - the bulk of your scales receding into your all too human flesh as you land. The rabbit whistles, turning a bashful eye away from your nude figure.
"If humiliating me is what you wanted, I'd say you got what you wished. Can I have my ring back now?"
A curse passed down generation by generation. By night, you are your true self. By day, you are forced to walk this earth on two legs like the rest of animal kin. The disadvantage it puts you at is steep. Smaller, weaker, pitiful. That ring has the power to return you to your proper state even now. You have to get it back.
The rabbit appears offended by your words.
"Humiliate you? Now why on earth would I want to humiliate my wife? You'll get this ring back on our wedding day. I'd love to get you something flashy myself, but it's nicer to keep things in the family. Sooner we get married, sooner you get this back - got it?."
He.... can't be serious. You still return to your true form by sunset. You may be able to overpower him then. As things stood now, you had no chance. Not only was he bigger than you, but in the scarce chance you obtain the upper hand now the town's people are sure to come to his rescue before you can grab what's yours and flee.
"Alright. I will become your wife in exchange for what's mine."
The rabbit grins. "That's the spirit. Name's Fletcher by the way, but most folks call me Fetch. Thought you might like to know since we'll be stuck together from now on."
Fletcher pulls something from his shoulders as he approaches. A fuzzy blanket which he drapes around you as he lifts you off the cold ground. The bastard really has been watching you- Shuddering from the cold, you seek the warmth from his fur as you place your head to his chest - heart beat gone sporadic as you nestle your face deeper into the fluff. If you are to be stuck with him for now, it's better to play along than give away your true intentions so soon.
"Heh, let's get you home before you freeze out here. I'll make you something to eat and we'll get to know each other better before we start planning our special day."
That sounds.... pleasant. The food that is. You can't recall the last time you'd eaten. Hooking your arms around the rabbits neck, he carries you off in the direction of his home as the sleepy town you once terrorized wakes once more.
#Fletcher my oc#yandere x reader#yandere headcanons#yandere x you#yandere imagines#yandere blurb#yandere insert#yandere#male yandere#yandere drabble#yandere farmer#yandere hybrid#yandere scenarios
380 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: The Moon (pt. 1)
Beaver Moon - the first full moon of November
Beavers are known to build their winter homes in November to prepare for the first frost, which is why some say the November full moon is called a Beaver Moon. Other sources claim that the name comes from early Native American tribes setting beaver traps in November to use their pelts for warmth in the winter months.
Blood Moon - a full moon that coincides with a full lunar eclipse and that has an unusually reddish appearance
During a full lunar eclipse (when the full moon is completely in the darkest part of Earth's shadow) a small amount of the sun's light from around the edges of the Earth passes through the Earth's atmosphere and hits the surface of the moon. Because of the properties of the different colors of light, the moon appears red. (More dust or particles in the Earth's atmosphere will make the moon appear redder.) The red appearance of these full moons gives them their name.
Blue Moon - the second full moon in a calendar month
Because most months have more than 29.5 days, there's bound to be some months with more than one full moon. When you have two full moons in a single calendar month, the second is called a blue moon. The term blue moon is also used in the phrase "once in a blue moon" to describe something that happens very rarely.
Harvest Moon - the full moon nearest the time of the September equinox
The full moon that occurs closest to the fall equinox (approximately September 23rd) is the one called the harvest moon. Usually in September but sometimes in October, the harvest moon is so named because of the extra moonlight it provides in the evenings to farmers harvesting their summer crops. The angle of the moon's orbit relative to the horizon causes the fall full moon to rise faster than usual, which makes it seem like the moon is rising at the same time (near sunset) for several nights in a row, providing bright moonlight for harvesting.
Hunter's Moon - the full moon after the harvest moon
The term has origins from the Algonquin tribes. It is apparently called this because this is the time of year when hunters would begin to store meat for the winter months. Like the harvest moon, the hunter's moon also appears to rise faster providing extended moonlight for hunting in the evening.
Long Night Moon - the full moon that occurs nearest the winter solstice
Also known as the Moon Before Yule. The winter solstice is also the day with the fewest daylight hours and the longest night, hence this moon's name.
Strawberry Moon - June's full moon
Either the last full moon of spring or the first full moon of summer, the strawberry moon occurs in June and signals the start of the summer, when strawberries ripen in the US. The name apparently comes from the Algonquin tribes. A European name for this moon is the Rose Moon, or the Honey Moon.
Supermoon - a full moon occurring when the moon is at or near the closest point to Earth in its orbit
When the moon orbits the Earth, it is not always the same distance from the Earth. When a full moon reaches the point in its orbit that is closest to Earth, known as the perigee, it appears brighter than at other points and so we call it a supermoon. Originally, the term supermoon was used to describe either a full moon or a new moon occurring at or near perigee but later, the meaning was restricted to only a full moon at this orbital point.
Wolf Moon - the first full moon of the year
'Wolf moon' is the name for the first full moon in a calendar year, and since a full moon occurs every 29.5 days (a period known as the synodic month), the wolf moon always occurs in January.

This graphic shows the position of the Moon and the Sun during each of the Moon’s phases and the Moon as it appears from Earth during each phase. Not to scale.
Moon Phases:

Earthshine:

Though the Moon is in a crescent phase in this photograph, most of the darkened, Earth-facing side of the Moon is still dimly visible, illuminated by sunlight reflecting off our planet. This reflected light is called earthshine.
Daytime Moons:

The waxing Moon rises over a ridge in the Wasatch Mountains, Utah.
Though the Moon is often thought of as a nighttime visitor, it’s also visible during the day as a faint, pale presence. The best times to see a daytime Moon are perhaps during the first and last quarter phases, when the Moon is high enough above the horizon and at about 90 degrees from the Sun in the sky. This helps make the Sun’s reflected light bright enough to see as it reflects off of the Moon. The Moon can be seen in the daylit sky at any phase except for the new moon, when it’s invisible to us, and full moon, when it’s below the horizon during the day. The crescent through quarter phases are high in the sky during the day, but the daytime gibbous phases can be glimpsed only just before the Sun sets.
Sources: 1 2
If these writing notes helped with your poem/story, please tag me. Or leave a link in the replies. I'd love to read them!
Writing Notes: The Moon (pt. 2)
#writing notes#moon#writeblr#writing prompt#spilled ink#literature#poetry#nature#words#worldbuilding#creative writing#fiction#lit#dark academia#light academia#studyblr#langblr#writing reference#writing resources
228 notes
·
View notes
Text
Popularly known as Red Cow Peas, Thatta Payaru / Karamani in Tamil, Vanpayar in Malayalam, Alasandulu / Bobbarulu in Telugu, Bora in Hindi, Alasande / Tadagani in Kanada.
#Vayal Foods offers high-quality red beans#also known as Red Cow Peas#Thatta Payaru / Karamani#that are sustainably sourced from small-scale farmers in India. vayalfoods thatta payir providing plant-based protein#fiber#and antioxidants. Our red beans are carefully selected and processed to ensure maximum nutrition and flavor#and are ideal for use in a variety of Asian and Japanese dishes
0 notes
Text
Alright, here's my dream Stardew Valley style game, designed for my own tastes.
You come to a small town with the usual twenty to thirty people. It's in the middle of nowhere. It's a fantasy town, and no one actually farms anymore, partly because it's only questionably profitable, partly because a lot of the knowledge has been lost. Instead, everyone uses these magic doodads which are very powerful but also very limited. The tavernkeeper has a doodad that makes him a single kind of weak ale and a single variety of off-tasting wine. The clothier has basically a square mile of linen to work with, and everyone wears her drab clothes. Tools are made from a doodad that the blacksmith owns, not even made of any actual metal, just a material that wears away after a month and needs to be replaced by a new copy from the blacksmith's doodad. People get their meals from the doodads. They get their medical checkups. It's all a bit shit.
Because I'm a worldbuilder at heart, I would have this all exist in the wake of a large-scale war that depleted the town of its fighting-age population, with the doodads being a sort of government program to ensure that more of the lifeblood of the town could be drained away. And for there to be some reason for the town to continue existing, perhaps the government is harvesting some resources necessary in the creation of doodads. That's enough for a pro-doodad faction and maybe some minor drama with them, though I do like the idea that the only reason things are Like This is because there was a war and things got bad. It's not necessarily a bleak town, but there's definitely a listlessness to it, a "what's the point".
So you're a farmer, but no one is really a farmer anymore. Maybe there are a few books, but you don't learn farming from books, you learn it from practical experience; that's a lot of what this game is about. When you start, there's no one to buy seeds from, there's just a bunch of wilderness where farms once stood, now all long overgrown.
So you go out and forage, for a start, and you clear the land, and you pay attention to the plants and how they can be used, and you start in on making recipes with them, maybe with the help of your grandfather's old, partially incomplete books. You find some wild corn that's a descendant of the old times. You find some tomato seeds in an urn. You discover potatoes because you see them dug up by a wild boar, which itself was once a domesticated animal.
In my ideal game, you need to pay attention to the soil quality, to how far apart things are planted, to what crops work well together. Farming is a matter of companion planting and polycultures. You get some chickens by giving them consistent feed, and you keep them around because they're natural pest control. Your climbing beans climb the stalks of your maize. You're attracting pollinators. (From a gameplay perspective, yeah, we probably put this all into a grid, and you have crop bonuses from adjacencies, and emergent gameplay that comes from all that, some plants providing shade, others providing nitrogen fixing.) You're a scientist making observations about the plants, maybe with your incomplete book giving you confirmation on the nature of all your crops once you hit certain production goals or a perfect specimen or whatever.
Cooking is the same. There has got to be a system that I like better than just "combine tomato with bread to get tomato bread". I'm pretty sure that it's some variant of the actual process I use when cooking, which is making sure that things are properly cooked, balancing flavors against each other, adding in a little salt or acidity or umami or whatever. Time in the kitchen, in this game, is often about making meals, ensuring that if you have a fatty piece of meat you have some asparagus that's coated with lemon to go with it. (From a gameplay perspective, I think building the dish once is probably sufficient and it can be automated after that, and building the meal is the same. I don't want to play this minigame every time I'm cooking a dish, I just want to play it a single time until I have good knowledge of the best way to grill a BBQ chicken breast with a homemade sauce.)
But if we're having a little minigame here where we pay attention to how long we're cooking the kale to make sure that it's the right texture, and we're paying attention to abstractified mouthfeel and palette, then we can get something else for free: variation. See, you're not just cooking to get an S grade, you're cooking for people with different tastes. The cobbler has a sweet tooth, the librarian loves fruity things, the mayor cannot stand fish, that sort of thing. From a gameplay perspective, maybe we represent this with a radar graph with some specific favorite and least favorite individual flavors, and maybe it's visible to the player, but the important thing is that player gets feedback and have a reason to strive for both "good" and "perfection" and some of this is going to depend on the quality of the ingredients.
And this is, gradually, how the town is brought back into the fullness of life. You're not just cooking for these people, you're also selling them food, and they're making their own recipes, and all the stuff that's not food is making their businesses not suck anymore. After the first test keg of ale goes swimmingly, the tavernkeeper wants more, a lot more, and puts in an order for hops, wheat, grapes, anything he can use to make things that will improve nights at the tavern. The clothier will skeptically take in wool and spin her own yarn, and then eagerly want more, because how awesome is it to have a new textile? There's a chemist who is extremely interested in dyes and paints, and wants you to bring him all kinds of things to see what might be viable for going beyond the ~3 colors that the doodads can provide.
So by year two, if you're doing things right, you're the lynchpin of the revivalist movement. People are now moving to the town, for the first time in decades, because they hear that you're there and doing interesting things with the wilderness. Maybe there are other farmers following in your wake, but maybe it's just new characters who are specifically coming because a crate of wine was shipped to the capital city. Maybe some of them bring new techniques for you, or a handful of plants from a botanical garden, and there are new elements for the minigames, or maybe some automation for the stuff that's old hat.
I think something that's important to me is that there's a reason for the crops you plant and the things you do. I always like these games best when it feels like I'm doing something for someone, when I can look at a plot of cabbages and think "ah, those are the cabbages I owe to Leon". Where these games are at their worst, everything is entirely fungible and I've planted eight million blueberries because they have the highest ROI.
And yeah, in most of these games, there are other minigames like fishing and mining and logging and crafting, and since this is just a blog post and not a game, I definitely could massively expand an already sizeable scope.
I think for mining the player would use doodads of their own, and maybe you could make a mining minigame out of that, using the same planting tile system to instead create an automated ore harvesting machine that plumbs the depths of the earth (possibly dealing with rocks of different hardness, the water table, and other challenges along the way).
Fishing is a question of understanding the different fish species, what they eat, where they congregate, and then setting nets or lines, since I have never met a fishing minigame I really enjoyed. Again, there's some idea that the player is gaining information over time, building up a profile of these fish, noticing that some of them go nuts when it rains, understanding the spawning season, that they go to deeper water when it's cold, etc.
Crafting really depends on what you're crafting, but if you're reintroducing traditional artisan processes to this town, then people are going to need tools and machines and things. I'm not sure I know what a proper crafting game looks like. The only experience I have to draw on is wood shop, where I made wooden boxes, cutting boards, and picture frames. Since this is an engineering-lite puzzle-lite game, you could maybe do something in that vein, e.g. defining a number of steps that get you the correct thing you're trying to make, but ... eh. I love the idea of designing a chicken coop, for example, or building a trellis if I want my climbing beans to not need maize, or whatever, but I don't know how you actually implement that. There are definitely voxel-based and snap-to-grid games where you build bases, and I tend to find that fun ... but it's mostly cosmetic, for the obvious reason that doing it any other way than cosmetic requires programmatic evaluation, which is difficult and maybe unintuitive. The closest I think I've seen is ... maybe Tears of the Kingdom? Contraption building? But I don't know how you translate that to a farming game. Maybe I should ask my wife about this, because she's always doing little projects around the house (an outdoor enclosure for our cats, a 3D-printed holder for our living room keyboard, a mounting for our TV).
Making an interesting crafting system is difficult, which is why pretty much no one has done it.
And if I'm talking pie in the sky, without concern for budget or scope, I want the villagers to all have a mammoth amount of writing for them. I want petty little dramas and weird obsessions, lives that evolve with or without my input, rudimentary dialog trees that let me nudge things in different directions. This is just an unbelievable amount of work on its own, it would be crazy, but I would love having a tiny little town game where sometimes other people would fall in love. I would like to be invited to a wedding, maybe one that happened because I encouraged the chemist to hang out with the clothier, and in the course of working together on dyes, they fell in love. With twenty people in town and another ten that come in over the course of the game if you hit the right triggers, I do think this is just a matter of having a ton of time/budget. You write tons and tons of dialogue so there's not much that's repeated, you have some lines of conversation between characters that are progressed through, you have others that trigger off of events, and then you have personal relationships between NPCs that can be progressed through time or with player intervention. Give single characters a pool of love interests, have their affections depend on their routine which depends on what's changed in town ... very difficult to do without spending loads and loads of time on it though.
Anyway, that's one of my dream games. No one is ever going to make it, it would be a niche of a niche, and as scoped here, is too much for a small team to ever actually finish, let alone polish. But it's the sort of thing I'm imagining in my head when I think about playing Stardew Valley and its successors.
189 notes
·
View notes