#South African Memorial
Text




just made mysefl a lovely Damascus rose drinc folowing the low quality recipe I found on da internet. well its not that bad but I think I’m losin consciousness y’all 😄🤣🤣 bruh that was too flavored 4 me lol gotta post it before I forget my own ass name 😂🤣🤣🤣
#amnesia the dark descent#it’s a very old recipe on some abandoned blog#i lowkey wanted to try it for about 4months and got the chance today#well for you to know guys and girls#the rose flavor is strong as hell and literally makes you dizzy#to this day I though amnesia lore with those roses was just a romantic trope but today I know the real reason.#rose’s smell and flavor is just like a goddamn gasoline#so yeah that’s definetely NOT for everyone’s taste#yet I tried it and I think I’m going to fall asleep now it made my head really heavy and not even with the alcohol.#in case I’ll find this post tomorrow with my memory wiped clean:#hi your name is Shandy Yay you’re 21yo animation student you’re russian and you’re CRINGE#and your husbands name is Leon de Vries he’s South African tho if he’s not home go to Algiers and find him he’s somewhere there#that’s it byeeee <3
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

THE REAL HISTORY ABOUT MEMORIAL DAY. KNOW YOUR HISTORY:
It was not originally called Memorial Day. It was changed from Decoration Day to Memorial Day and made into a Federal Holiday by Congress some 100 years after the Civil War.
The importance of teaching African History as it is American History
Memorial Day was started by former slaves on May, 1, 1865 in Charleston, SC to honor 257 dead Union Soldiers who had been buried in a mass grave in a Confederate prison camp. They dug up the bodies and worked for 2 weeks to give them a proper burial as gratitude for fighting for their freedom. They then held a parade of 10,000 people led by 2,800 African children where they marched, sang and celebrated.
"Resolved that the Congress of the United States, in recognition of the patriotic tradition set in motion one hundred years ago in the Village of Waterloo, NY, does hereby officially recognize Waterloo, New York as the birthplace of Memorial Day..."
On May 26, 1966, President Lyndon B. Johnson, signed a Presidential Proclamation recognizing Waterloo as the Birthplace of Memorial Day.
Nonetheless, as the New York Times noted in 2012, dozens of other places still lay claim, based on a variety of criteria, to being the true birthplace of the modern Memorial Day:
According to the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, roughly two dozen places claim to be the primary source of the holiday, an assertion found on plaques, on Web sites and in the dogged avowals of local historians across the country.

#memorial day#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#afrakans#brown skin#african culture#south carolina#charleston sc
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Memorial Day 2022, we take a look at the African American origins of the federal holiday established to remember America’s fallen soldiers.
Although May 30, 1868 is cited as the first national commemoration of Memorial Day at Arlington National Cemetery, events lead by African Americans in Charleston, South Carolina to decorate the graves of fallen Civil War soldiers occurred on May 1, 1865, less than a month after the Confederacy surrendered.
Reports of this early version of Memorial Day or “Decoration Day” as it was called, were rediscovered in the Harvard University archives in the late 1990s by historian David Blight, author of the 2018 biography Frederick Douglass: Prophet of Freedom.
To quote from history.com:
When Charleston fell and Confederate troops evacuated the badly damaged city, those freed from enslavement remained. One of the first things those emancipated men and women did was to give the fallen Union prisoners a proper burial. They exhumed the mass grave and reinterred the bodies in a new cemetery with a tall, whitewashed fence inscribed with the words: “Martyrs of the Race Course.”
And then on May 1, 1865, something even more extraordinary happened. According to two reports that Blight found in The New York Tribune and The Charleston Courier, a crowd of 10,000 people, mostly freed slaves with some white missionaries, staged a parade around the race track.
Three thousand Black schoolchildren carried bouquets of flowers and sang “John Brown’s Body.” Members of the famed 54th Massachusetts and other Black Union regiments were in attendance and performed double-time marches. Black ministers recited verses from the Bible.
Despite the size of the gathering and newspaper coverage, the memory of this event was “suppressed by white Charlestonians in favor of their own version of the day,” Blight stated in the New York Times in 2011.
On May 31, 2010, near a reflecting pool at Hampton Park, the city of Charleston reclaimed this history by installing a plaque commemorating the site as the place where Blacks held the first Memorial Day on May 1, 1865.

During the dedication of the plaque, the city’s mayor at the time, Joe Riley, was present to celebrate the historic occasion which included a brass band and a reenactment of the Massachusetts 54th Regiment.
In 2017, the City of Charleston erected yet another sign reclaiming the history and commemorating the event:
“On May 1, 1865 a parade to honor the Union war dead took place here. The event marked the earliest celebration of what became known as “Memorial Day.” The crowd numbered in the thousands, with African American school children from newly formed Freedmen’s Schools leading the parade. They were followed by church leaders, Freedpeople, Unionists, and members of the 54th Massachusetts 34th and 104th U.S. Colored Infantries. The dead were later reinterred in Beaufort.”
To learn more about African Americans’ role in the creation of Memorial Day, check out the links to sources provided in today’s show notes and in the episode’s full transcript posted on goodblacknews.org.
This has been a daily drop of Good Black News, written, produced and hosted by me, Lori Lakin Hutcherson.
For more Good Black News, check out goodblacknews.org or search and follow @goodblacknews anywhere on social.
Sources:
https://www.history.com/news/memorial-day-civil-war-slavery-charleston
https://www.lx.com/black-legacy/dont-overlook-memorial-days-black-southern-roots/53453/
https://www.live5news.com/2020/02/18/charleston-claims-first-memorial-day-celebration-with-african-americans-playing-significant-role/
https://amsterdamnews.com/news/2022/05/28/freed-slaves-started-first-memorial-day-in-the-us/
https://aaregistry.org/story/the-first-american-memorial-day-is-commemorated/
https://www.harlemworldmagazine.com/memorial-day-african-americans-memorial-day-charleston-south-carolina-1865/
#How “Decoration Day” in May 1865#Held by African Americans in South Carolina Led to Memorial Day#freedmen#Black Families#reconstruction#Beaufort S.C.memorial day#memorial day
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
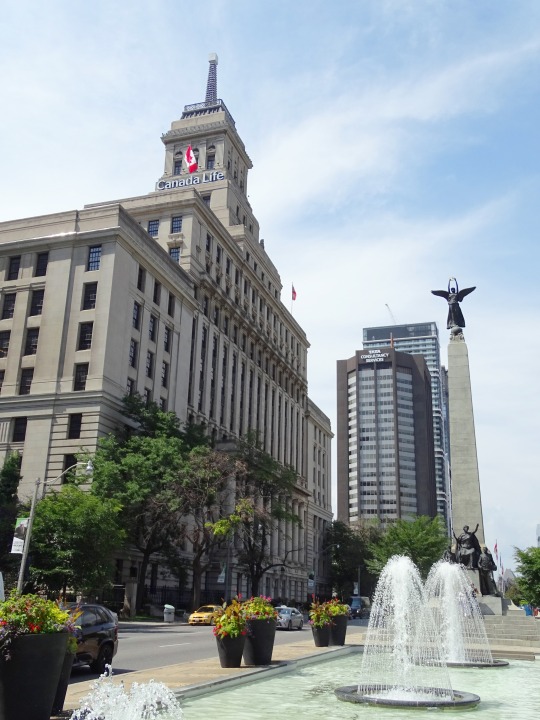
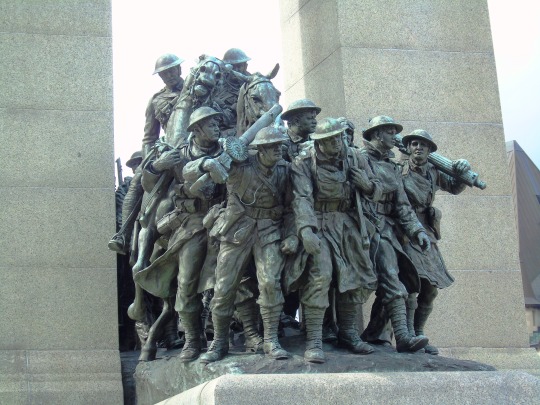
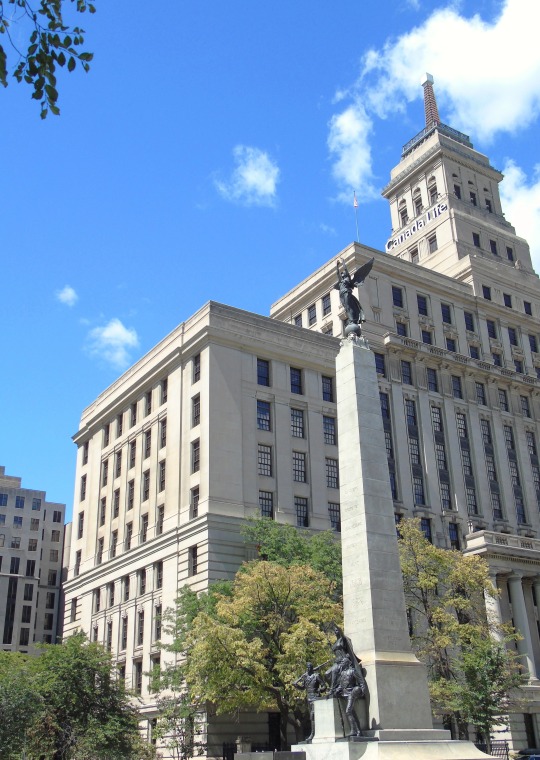
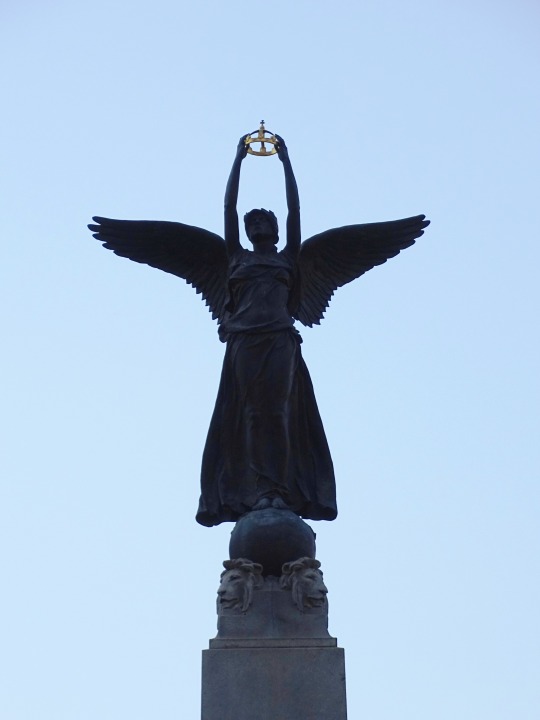
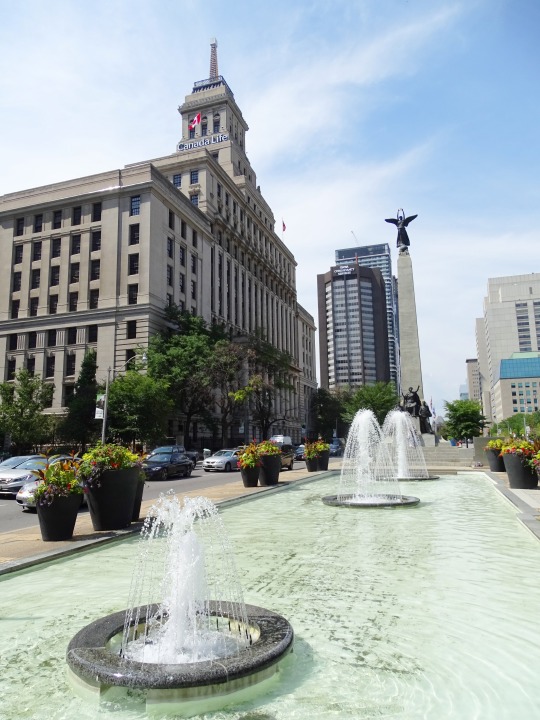









The Second Boer War erupted in South Africa between the British-ruled Cape Colony, and the Boer-ruled Transvaal and Orange Free State on October 11, 1899.
#South African (Boer War) Memorial by Walter Allwards#Second Boer War#travel#11 October 1899#anniversary#Canadian history#Toronto#Ontario#Ottawa#Canada#summer 2018#original photography#cityscape#architecture#fountain#public art#sculpture#2015#The Response#Canadian National War Memorial#National War Memorial by Vernon March
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
When South Africa dismantled apartheid, it did not end with the expulsion of all white South Africans. They became part of the new South Africa, just without the criminal discriminatory oligarchic powers the apartheid goverment had. When Bolivia recognized its indigenous heritage and became a plurinational state, it did not mean that people of European descent were expelled in masse. It meant the recognition of the previously discriminated indigenous and mestizo people of Bolivia and the beginning of a path of integration and revalidation.
What I mean is that it's ridiculous to think that decolonization inherently means mass suffering and relocation, that's what colonization does. Decolonization is recognizing the crimes of colonization, but more importantly, material, political and social steps to give power and self-determination to the exploited native people who were victims of colonialism and imperialism.
In multicultural societies, you don't go like in that Peter Griffin meme with a skin tone chart and saying 'well, you go back to Europe, you go back to Africa, you stay here'. You build a new society on the paradigm of dignity for exploited people and equality under the law. People are acting like this is some sort of fantastic utopia instead of real initiatives that were done in living memory, with successes and failures, as all such initiatives have. One must ask why are some so insistent that multicultural societies can't thrive, especially when for most of history, societies were indeed like that. Consider why you think like that.
39K notes
·
View notes
Text
This article is from 2022, but it came up in the context of Palestine:
Here are some striking passages, relevant to all colonial aftermaths but certainly also to the forms we see Zionist reaction taking at the moment:
Over the decade I lived in South Africa, I became fascinated by this white minority [i.e. the whole white population post-apartheid as a minority in the country], particularly its members who considered themselves progressive. They reminded me of my liberal peers in America, who had an apparently self-assured enthusiasm about the coming of a so-called majority-minority nation. As with white South Africans who had celebrated the end of apartheid, their enthusiasm often belied, just beneath the surface, a striking degree of fear, bewilderment, disillusionment, and dread.
[...]
Yet these progressives’ response to the end of apartheid was ambivalent. Contemplating South Africa after apartheid, an Economist correspondent observed that “the lives of many whites exude sadness.” The phenomenon perplexed him. In so many ways, white life remained more or less untouched, or had even improved. Despite apartheid’s horrors—and the regime’s violence against those who worked to dismantle it—the ANC encouraged an attitude of forgiveness. It left statues of Afrikaner heroes standing and helped institute the Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which granted amnesty to some perpetrators of apartheid-era political crimes.
But as time wore on, even wealthy white South Africans began to radiate a degree of fear and frustration that did not match any simple economic analysis of their situation. A startling number of formerly anti-apartheid white people began to voice bitter criticisms of post-apartheid society. An Afrikaner poet who did prison time under apartheid for aiding the Black-liberation cause wrote an essay denouncing the new Black-led country as “a sewer of betrayed expectations and thievery, fear and unbridled greed.”
What accounted for this disillusionment? Many white South Africans told me that Black forgiveness felt like a slap on the face. By not acting toward you as you acted toward us, we’re showing you up, white South Africans seemed to hear. You’ll owe us a debt of gratitude forever.
The article goes on to discuss:
"Mau Mau anxiety," or the fear among whites of violent repercussions, and how this shows up in reported vs confirmed crime stats - possibly to the point of false memories of home invasion
A sense of irrelevance and alienation among this white population, leading to another anxiety: "do we still belong here?"
The sublimation of this anxiety into self-identification as a marginalized minority group, featuring such incredible statements as "I wanted to fight for Afrikaners, but I came to think of myself as a ‘liberal internationalist,’ not a white racist...I found such inspiration from the struggles of the Catalonians and the Basques. Even Tibet" and "[Martin Luther] King [Jr.] also fought for a people without much political representation … That’s why I consider him one of my most important forebears and heroes,” from a self-declared liberal environmentalist who also thinks Afrikaaners should take back government control because they are "naturally good" at governance
Some discussion of the dynamics underlying these reactions, particularly the fact that "admitting past sins seem[ed] to become harder even as they receded into history," and US parallels
And finally, in closing:
The Afrikaner journalist Rian Malan, who opposed apartheid, has written that, by most measures, its aftermath went better than almost any white person could have imagined. But, as with most white progressives, his experience of post-1994 South Africa has been complicated. [...]
He just couldn’t forgive Black people for forgiving him. Paradoxically, being left undisturbed served as an ever-present reminder of his guilt, of how wrongly he had treated his maid and other Black people under apartheid. “The Bible was right about a thing or two,” he wrote. “It is infinitely worse to receive than to give, especially if … the gift is mercy.”
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
Pearl and Gem glance at each other. Then, as one, they glance back at Tango, who is, evidently, not Tango.
“Do we have an amnesiacold on our hands?” Gem asks.
“Maybe,” says Pearl, glancing back at Tango again. “Tango, buddy, you feeling alright?”
“I—” Tango opens his mouth. Closes it again. “I mean, I’m a little under the weather, to tell you the truth—I ate a South African sausage and it disagreed with me.”
Pearl hums. “And it’s messed with your memory a bit, right?”
“Yes! I mean, no—I mean, how did you—?”
“Would you say that you have a bit of an amnesiacold, Tango?” asks Gem.
“Amnesiacold?”
“You know. Amnesiacold!” Gem says. “When you get sick and forget everything and feel like somebody else?”
“Ah.” Tango pulls himself to shore. Frowns. “It’s more of an amnesia-food-poisoning, if I’m honest.”
Pearl winces. “Your poor digestive system.”
“It’s not very nice Pearl, I’ll tell you that much,” Tango says, voice low, one hand pressed against his stomach as he pulls a face.
“Okay, that’s enough, I don’t need to hear about your gut issues,” Gem interrupts. “But—you have an amnesiacold! You know, I was an amnesiacold last season.”
“You mean, you had an amnesiacold?”
“No, I was one.” Gem winks. “Like—Tango has an amnesiacold. But you? You’re the amnesiacold. You know?”
Tango’s shoulders hike up with discomfort. “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I’m Tango. And I think you guys should—should skadoodle somewhere else. Should bother-someone-else-ificate. Begone.”
“I had an amnesiacold last season, you know,” Pearl says. “Gem was one. You can tell us, buddy, we’re not gonna tell anyone.”
“Promise,” Gem says with a nod. “This is a safe space! You don’t have to pretend to be someone you’re not with us.”
Tango stares at them for a long, long moment, then sags, face falling. He looks exhausted, suddenly, and Pearl feels a rush of sympathy. It can’t be easy, being thrown into the game halfway through, with no context for anything.
“It’s been rough, dudes,” Tango says, voice cracking. “It’s been really really rough. I forgot how hard it was to get anything done on this server! There’s so much chaos, and—”
Wait.
“Ren?”
Not-Tango grins. “In the flesh,” he says with a bow of his head. “Or… not my flesh, exactly.”
“Ren?” Gem asks, tilting her head in confusion.
“Oh, that’s right, you’ve never met…”
Gem and Ren peer at each other for a moment. “You do look familiar,” Ren says eventually.
“Yeah,” Gem agrees. “I mean, obviously you look familiar—you look like Tango!—but… yeah.”
They stare at each other for a moment more.
“Maybe we met in a dream?” Ren says at last.
Gem nods. “Sure. Makes as much sense as anything else.”
Pearl glances between them, rocking awkwardly back on her heels. She clears her throat, drawing their attentions back to her. “Welcome back, buddy,” she says to Ren. “Good to see you again.”
“I wish that I could say the same,” Ren says morosely. “I thought I was—I was done, Pearl.” Now that she knows it's Ren, she can hear his cadence in Tango’s voice, voice dropping rough and low with drama as he bows his head. “I was done. No more games, not for the ol’ diggity dog. And now… Here I am!” He laughs a little, stretching out his arms to indicate the server at large. “In a body that’s not mine, in a world I’ve never seen, in a game I do not understand.”
“Oh, Ren…” Pearl frowns. She doesn’t know what to say.
Gem jumps in. “Hey, it’s okay! It’s just one session, you know? You can do one session!”
“I suppose I must.” Ren looks up at them, jaw tightening. “If I am here—I suppose I must.”
“I’d never been in any of these games before I was Cleo for a bit last season,” Gem says. “So you have an advantage there! And, hey—maybe you can come back next season, and we can meet for real?”
Ren shifts uncomfortably. There’s something heavy hanging about him, something Pearl can’t quite understand. She remembers the last time she’d seen him, skull caved in from the dripstone spike dropped on his head. She remembers her own amnesiacold, the exhaustion that had dragged at her before it had settled in, the memories that had plagued her and just wouldn’t go away. And she wonders—
Just how exhausted would you have to be that your body would have to leave as well as the rest of your self?
Just how sick would you have to be before you didn’t want to come back?
Still, Ren steadies himself. Quirks Tango’s mouth into a smile. “Maybe,” he says, meeting Gem’s gaze. “That would be nice, to meet for real.”
#secret life#spoilers#fanfiction#obligatory post-session ficlet time!#there was so much going on this session i could have gone with almost anything for this#but amnesiacolds is where we landed#this one is very much playing with martyn's lore which i think is very fun#also. i miss rendog when will he come back from the war ;-;#magpie feather quill
722 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily update post:
Another independent Palestinian terrorist attack happened today, it was another stabbing, much like yesterday's, and I feel nauseous that we're at the point where, when I'm looking for an online source in English, I'm struggling to find the latest one out of all the terrorist attacks reported recently. I heard an eyewitness say the terrorist entered a cafe, stood in line, then started stabbing those standing in front of him. The terrorist is a 22 years old Israeli Arab, originally a Gazan. From what I understand, his dad is a Gazan who married an Israeli Arab woman, both men got Israeli citizenship, and the terrorist has lived in Israel for the last 4 years, during which he married an Israeli woman, like his dad. On his mother's side of the family, he has two relatives who are Israeli heroes: one is a soldier, who died not that long ago fighting in Gaza, another is a cop, who saved several people from the Hamas massacre at the Nova music festival. I've heard now 2 Israeli Arab citizens from the community where he lived denouncing him. The terrorist was neutralized. At least 2 people are reported injured, one man in his 60's is lightly wounded, another is in his 50's. One man (in a white shirt with stripes in the vid below) at the cafe saw the terrorist and jumped him with bare hands. Stripes Man kept trying to detain the terrorist until he saw one of the wounded managed to pull out a gun, Stripes Man moved out of the way, the injured one shot more than once and stopped the terrorist, but outside he collapsed, and was hospitalized in a mortal state.
The global rise in antisemitic incidents under the guise of anti-Zionism continues, this time we get insane news from Australia. I'm just gonna quote the report directly: "Two pro-Palestinian activists in Australia were charged on Tuesday with kidnapping and assaulting a victim for the perceived crime of being employed by a Jew."

Meanwhile, the Holocaust memorial at the transit camp of Drancy, through which the Jews of France were deported to their extermination in the east, was vandalized. I'll say it again, the timing is not a coincidence, as we see more and more antisemitic incidents, it's clear each one will get less attention, and less resources allocated to correcting the wrong, since it's all being spread so thin.

I wrote yesterday about a pilot program, which is one of many attempts by Israel to allow humanitarian aid into Gaza without about 60% of it being hijacked by Hamas. I'm sad to say that the pilot has failed, and the aid has been looted. Interestingly, it's not clear by whom. Which is many a good moment to add this: in addition to Hamas taking over the aid, so do existing Gazan mob families (presumably, the criminals are taking over the aid in order to sell it back to regular Gazans at exploitative prices).

A South African minister has announced that her country will be arresting all citizens of South Africa returning from fighting for Israel in Gaza. I do not recall any such announcement regarding South Africans returning from fighting for either side in any other area in the world, such as Ukraine or Syria. I think there's a chance we're watching South Africa ethnically cleansing itself of Jews.

These are Israeli-American mother Judith Raanan and her teenage daughter Natalie.
About a month after the start of the war, they were the first 2 Israeli hostages to be released by Hamas. Here is a short vid where Judith talks about their experiences, including how the nurses at the Gazan hospital Hamas took them to after they were kidnapped CHEERED at the sight of (in her words) "Israeli Jewish prey":
youtube
(for all of my updates and ask replies regarding Israel, click here)
#israel#antisemitism#israeli#israel news#israel under attack#israel under fire#terrorism#anti terrorism#hamas#antisemitic#antisemites#jews#jew#judaism#jumblr#frumblr#jewish#israelunderattack#Youtube
161 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reading list for Afro-Herbalism:
A Healing Grove: African Tree Remedies and Rituals for the Body and Spirit by Stephanie Rose Bird
Affrilachia: Poems by Frank X Walker
African American Medicine in Washington, D.C.: Healing the Capital During the Civil War Era by Heather Butts
African American Midwifery in the South: Dialogues of Birth, Race, and Memory by Gertrude Jacinta Fraser
African American Slave Medicine: Herbal and Non-Herbal Treatments by Herbert Covey
African Ethnobotany in the Americas edited by Robert Voeks and John Rashford
Africanisms in the Gullah Dialect by Lorenzo Dow Turner
Africans and Native Americans: The Language of Race and the Evolution of Red-Black Peoples by Jack Forbes
African Medicine: A Complete Guide to Yoruba Healing Science and African Herbal Remedies by Dr. Tariq M. Sawandi, PhD
Afro-Vegan: Farm-Fresh, African, Caribbean, and Southern Flavors Remixed by Bryant Terry
Barracoon: The Story of the Last “Black Cargo” by Zora Neale Hurston
Big Mama’s Back in the Kitchen by Charlene Johnson
Big Mama’s Old Black Pot by Ethel Dixon
Black Belief: Folk Beliefs of Blacks in America and West Africa by Henry H. Mitchell
Black Diamonds, Vol. 1 No. 1 and Vol. 1 Nos. 2–3 edited by Edward J. Cabbell
Black Faces, White Spaces: Reimagining the Relationship of African Americans to the Great Outdoors by Carolyn Finney
Black Food Geographies: Race, Self-Reliance, and Food Access in Washington, D.C. by Ashanté M. Reese
Black Indian Slave Narratives edited by Patrick Minges
Black Magic: Religion and the African American Conjuring Tradition by Yvonne P. Chireau
Black Nature: Four Centuries of African American Nature Poetry edited by Camille T. Dungy
Blacks in Appalachia edited by William Turner and Edward J. Cabbell
Caribbean Vegan: Meat-Free, Egg-Free, Dairy-Free Authentic Island Cuisine for Every Occasion by Taymer Mason
Dreams of Africa in Alabama: The Slave Ship Clotilda and the Story of the Last Africans Brought to America by Sylviane Diouf
Faith, Health, and Healing in African American Life by Emilie Townes and Stephanie Y. Mitchem
Farming While Black: Soul Fire Farm’s Practical Guide to Liberation on the Land by Leah Penniman
Folk Wisdom and Mother Wit: John Lee – An African American Herbal Healer by John Lee and Arvilla Payne-Jackson
Four Seasons of Mojo: An Herbal Guide to Natural Living by Stephanie Rose Bird
Freedom Farmers: Agricultural Resistance and the Black Freedom Movement by Monica White
Fruits of the Harvest: Recipes to Celebrate Kwanzaa and Other Holidays by Eric Copage
George Washington Carver by Tonya Bolden
George Washington Carver: In His Own Words edited by Gary Kremer
God, Dr. Buzzard, and the Bolito Man: A Saltwater Geechee Talks About Life on Sapelo Island, Georgia by Cornelia Bailey
Gone Home: Race and Roots through Appalachia by Karida Brown
Ethno-Botany of the Black Americans by William Ed Grime
Gullah Cuisine: By Land and by Sea by Charlotte Jenkins and William Baldwin
Gullah Culture in America by Emory Shaw Campbell and Wilbur Cross
Gullah/Geechee: Africa’s Seeds in the Winds of the Diaspora-St. Helena’s Serenity by Queen Quet Marquetta Goodwine
High on the Hog: A Culinary Journey from Africa to America by Jessica Harris and Maya Angelou
Homecoming: The Story of African-American Farmers by Charlene Gilbert
Hoodoo Medicine: Gullah Herbal Remedies by Faith Mitchell
Jambalaya: The Natural Woman’s Book of Personal Charms and Practical Rituals by Luisah Teish
Just Medicine: A Cure for Racial Inequality in American Health Care by Dayna Bowen Matthew
Leaves of Green: A Handbook of Herbal Remedies by Maude E. Scott
Like a Weaving: References and Resources on Black Appalachians by Edward J. Cabbell
Listen to Me Good: The Story of an Alabama Midwife by Margaret Charles Smith and Linda Janet Holmes
Making Gullah: A History of Sapelo Islanders, Race, and the American Imagination by Melissa Cooper
Mandy’s Favorite Louisiana Recipes by Natalie V. Scott
Medical Apartheid: The Dark History of Medical Experimentation on Black Americans from Colonial Times to the Present by Harriet Washington
Mojo Workin’: The Old African American Hoodoo System by Katrina Hazzard-Donald
Motherwit: An Alabama Midwife’s Story by Onnie Lee Logan as told to Katherine Clark
My Bag Was Always Packed: The Life and Times of a Virginia Midwife by Claudine Curry Smith and Mildred Hopkins Baker Roberson
My Face Is Black Is True: Callie House and the Struggle for Ex-Slave Reparations by Mary Frances Berry
My Grandmother's Hands: Racialized Trauma and the Pathway to Mending Our Hearts and Bodies by Resmaa Menakem
On Her Own Ground: The Life and Times of Madam C.J. Walker by A'Lelia Bundles
Papa Jim’s Herbal Magic Workbook by Papa Jim
Places for the Spirit: Traditional African American Gardens by Vaughn Sills (Photographer), Hilton Als (Foreword), Lowry Pei (Introduction)
Post Traumatic Slave Syndrome by Dr. Joy DeGruy
Rooted in the Earth: Reclaiming the African American Environmental Heritage by Diane Glave
Rufus Estes’ Good Things to Eat: The First Cookbook by an African-American Chef by Rufus Estes
Secret Doctors: Ethnomedicine of African Americans by Wonda Fontenot
Sex, Sickness, and Slavery: Illness in the Antebellum South by Marli Weiner with Mayzie Hough
Slavery’s Exiles: The Story of the American Maroons by Sylviane Diouf
Soul Food: The Surprising Story of an American Cuisine, One Plate at a Time by Adrian Miller
Spirituality and the Black Helping Tradition in Social Work by Elmer P. Martin Jr. and Joanne Mitchell Martin
Sticks, Stones, Roots & Bones: Hoodoo, Mojo & Conjuring with Herbs by Stephanie Rose Bird
The African-American Heritage Cookbook: Traditional Recipes and Fond Remembrances from Alabama’s Renowned Tuskegee Institute by Carolyn Quick Tillery
The Black Family Reunion Cookbook (Recipes and Food Memories from the National Council of Negro Women) edited by Libby Clark
The Conjure Woman and Other Conjure Tales by Charles Chesnutt
The Home Place: Memoirs of a Colored Man’s Love Affair with Nature by J. Drew Lanham
The Jemima Code: Two Centuries of African American Cookbooks by Toni Tipton-Martin
The President’s Kitchen Cabinet: The Story of the African Americans Who Have Fed Our First Families, from the Washingtons to the Obamas by Adrian Miller
The Taste of Country Cooking: The 30th Anniversary Edition of a Great Classic Southern Cookbook by Edna Lewis
The Tuskegee Syphilis Study: An Insiders’ Account of the Shocking Medical Experiment Conducted by Government Doctors Against African American Men by Fred D. Gray
Trace: Memory, History, Race, and the American Landscape by Lauret E. Savoy
Vegan Soul Kitchen: Fresh, Healthy, and Creative African-American Cuisine by Bryant Terry
Vibration Cooking: Or, The Travel Notes of a Geechee Girl by Vertamae Smart-Grosvenor
Voodoo and Hoodoo: The Craft as Revealed by Traditional Practitioners by Jim Haskins
When Roots Die: Endangered Traditions on the Sea Islands by Patricia Jones-Jackson
Working Conjure: A Guide to Hoodoo Folk Magic by Hoodoo Sen Moise
Working the Roots: Over 400 Years of Traditional African American Healing by Michelle Lee
Wurkn Dem Rootz: Ancestral Hoodoo by Medicine Man
Zora Neale Hurston: Folklore, Memoirs, and Other Writings: Mules and Men, Tell My Horse, Dust Tracks on a Road, Selected Articles by Zora Neale Hurston
The Ways of Herbalism in the African World with Olatokunboh Obasi MSc, RH (webinar via The American Herbalists Guild)
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hoodoo, Rootwork and Conjure sources by Black Authors
Because you should only ever be learning your ancestral ways from kinfolk. Here's a compilation of some books, videos and podcast episodes I recommend reading and listening to, on customs, traditions, folk tales, songs, spirits and history. As always, use your own critical thinking and spiritual discernment when approaching these sources as with any others.

Hoodoo in America by Zora Neale Hurston (1931)
Mules and Men by Zora Neale Hurston (1936)
Tell my horse by Zora Neale Hurston (1938)
Let Nobody Turn Us Around: An African American Anthology by Manning Marable and Leith Mullings, editors (2003)
Black Magic: Religion and the African American Conjuring Tradition by Yvonne P. Chireau (2006)
African American Folk Healing by Stephanie Mitchem (2007)
Hoodoo Medicine: Gullah Herbal Remedies by Faith Mitchell (2011)
Mojo Workin': The Old African American Hoodoo System by Katrina Hazzard-Donald (2012)
Rootwork: Using the Folk Magick of Black America for Love, Money and Success by Tayannah Lee McQuillar (2012)
Talking to the Dead: Religion, Music, and Lived Memory among Gullah/Geechee Women by LeRhonda S. Manigault-Bryant (2014)
Working the Roots: Over 400 Years Of Traditional African American Healing by Michele Elizabeth Lee (2017)
Barracoon: The Story of the Last "Black Cargo" by Zora Neale Hurston (2018)
Jambalaya: The Natural Woman's Book of Personal Charms and Practical Rituals by Luisa Teish (2021)
African American Herbalism: A Practical Guide to Healing Plants and Folk Traditions by Lucretia VanDyke (2022)
youtube
youtube
youtube
youtube
These are just some suggestions but there's many many more!! This is by no means a complete list.
I recommend to avoid authors who downplay the importance of black history or straight out deny how blackness is central to hoodoo. The magic, power and ashé is in the culture and bloodline. You can't separate it from the people. I also recommend avoiding or at the very least taking with a huge grain of salt authors with ties to known appropriators and marketeers, and anyone who propagates revisionist history or rather denies historical facts and spreads harmful conspiracy theories. Sadly, that includes some black authors, particularly those who learnt from, and even praise, white appropriators undermining hoodoo and other african and african diasporic traditions. Be careful who you get your information from. Keeping things traditional means honoring real history and truth.
Let me also give you a last but very important reminder: the best teachings you'll ever get are going to come from the mouths of your own blood. Not a book or anything on the internet. They may choose to put certain people and things in your path to help you or point you in the right direction, but each lineage is different and you have to honor your own. Talk to your family members, to the Elders in your community, learn your genealogy, divine before moving forwards, talk to your dead, acknowledge your people and they'll acknowledge you and guide you to where you need to be.
May this be of service and may your ancestors and spirits bless you and yours 🕯️💀
#hoodoo#conjure#rootwork#black hoodoo authors#Youtube#hoodoo books#african american conjure#african american history#black history#black folklore#african american folklore#black magic#african american magic#witches of color#ATRs#Spotify
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
Howdy, i’m curious if you’ve looked into or have an opinion on the use of apartheid in israel vs south africa? No doubt israel is genocidal but i’ve seen some south african’s get caught up on the use of the word due to the fact it was created to specifically describe south africa and doesn’t match the racial bias (though ethnic and religious, yes) as sa apartheid did
the concept of apartheid is not unique to South Africa although it's named after the South African policy. according to international law this is a totally settled question: apartheid can happen anywhere. many many South Africans have talked about how similar apartheid in Palestine is to what they were subjected to, idk who you're talking to but they're probably right wing and just interested in shutting down criticism of Israel. sorry this response is a little aggro, I just feel like we're way past this discussion, and I've only ever seen this question asked in bad faith
youtube
186 notes
·
View notes
Text
Black People Invented Memorial Day
Memorial Day, formally known as Decoration Day, was originally started by a group of African Americans. The History Channel and many credible historians have confirmed that the popular holiday was, in fact, initially an event held by newly liberated Blacks in Charleston, South Carolina. It happened on May 1, 1865 right after the Civil War ended.
Thousands of newly freed slaves and regiments of the U.S. Colored Troops gathered to march around a Confederate Army prison camp in honor of the unnamed fallen Union soldiers who fought for their freedom.
Also in attendance were thousands of Black women and children who reportedly sang hymns and carried flowers, wreaths, and crosses.
And then the holiday was whitewashed
Historian and author, David W. Blight, said in his book Race and Reunion: The Civil War in American Memory that years later African Americans were suddenly erased from the story by white Democrats after regaining control of state politics at the end of Reconstruction.
Yes, that's right. A day that originally celebrated Black liberation was now being utilized for white supremacy, and it apparently all started from an 1865 article that was published in the Charleston Daily Courier that tried to discredit the facts.
After discovering that news article, many historians have agreed that after being freed, one of the first things this group of African Americans did was gather to pay tribute to those who died while fighting for freedom. Sadly, you usually don't hear that part of the story.
According to LiberationSchool.org, "the spirit of the first Decoration Day - the struggle for Black liberation and the fight against racism - has unfortunately been whitewashed from the modern Memorial Day."
#Black People Invented Memorial Day#memorial day#decoration day#Freedmen#reconstruction#African Americans#south carolina
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
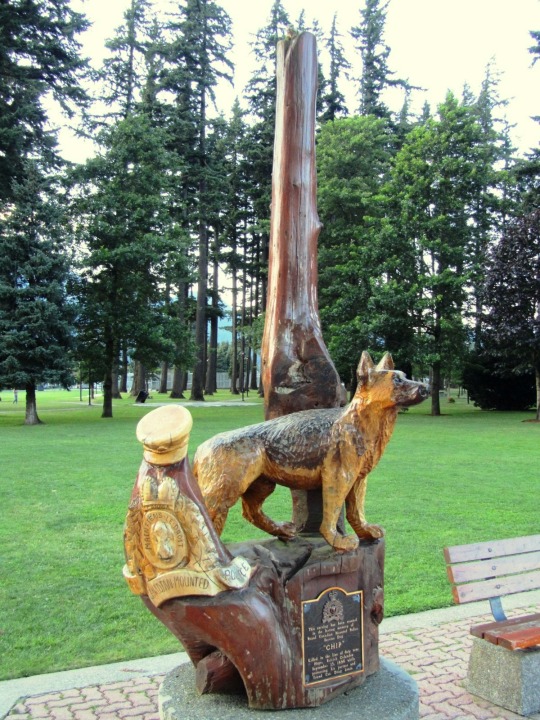
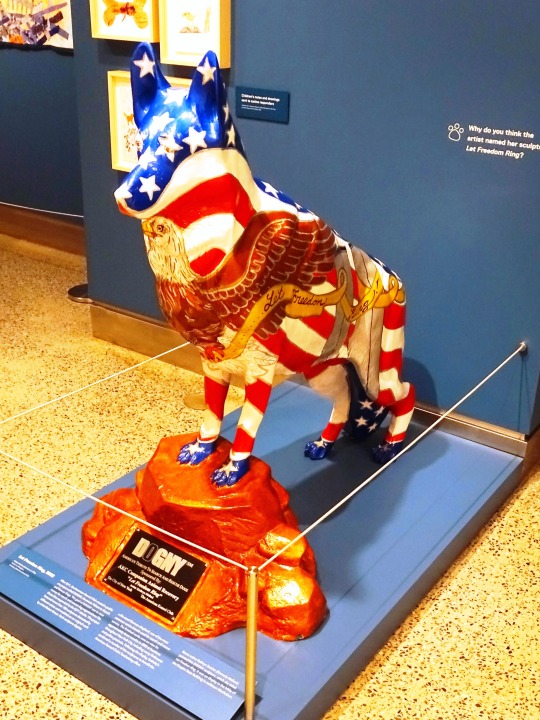
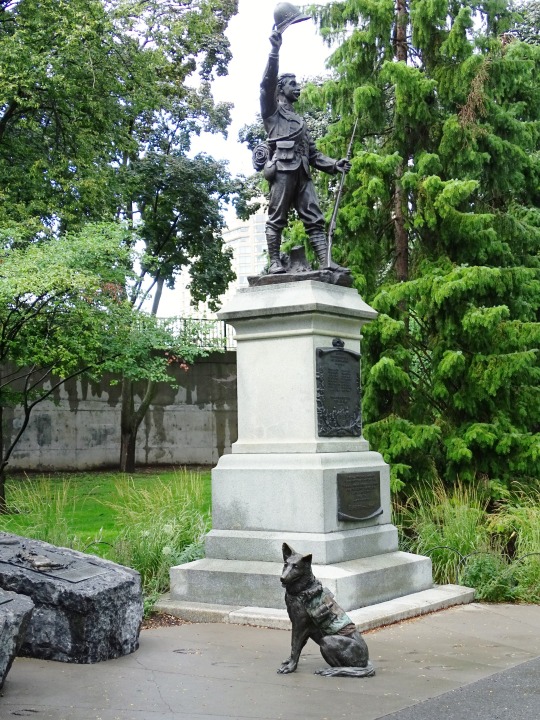
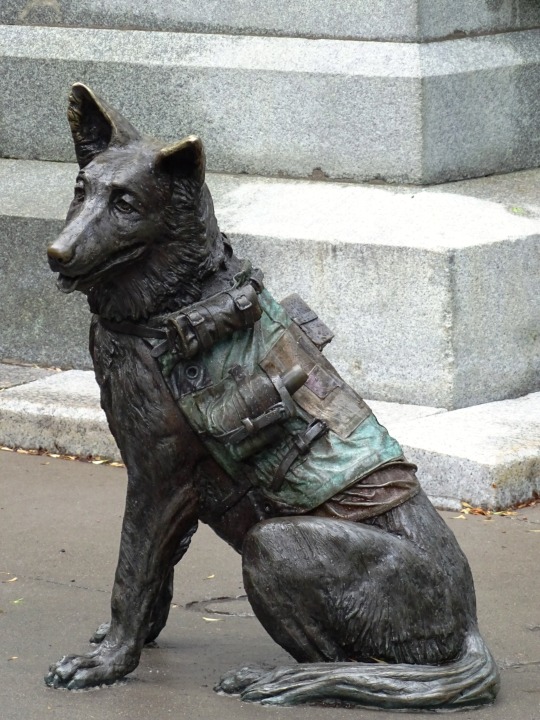








K-9 Veterans Day
Joseph White, a retired military working dog trainer, came up with the idea for K-9 Veterans Day. By his efforts, his home state of Florida recognized the day in 2009. Other states have since recognized it as well, although it has not been recognized on the national level. The day is dedicated not only to K-9 veterans of the military, but also to customs dogs, search and rescue dogs, police dogs, border patrol dogs, and secret service dogs. March 13 is the date of the holiday because the K-9 Corps was created on March 13, 1942. The Quartermaster Corps of the Army began training dogs on that date, making it the moment when dogs officially became part of the U.S. Armed Forces.
Three months before Pearl Harbor, U.S. Army Sgt. Robert H. Pearce started a small K-9 command program at Fort MacArthur in San Pedro, Los Angeles. He brought Hollywood dog trainer Carl Spitz on board. (Spitz was known for owning and training a Cairn Terrier named Terry, who was best known for playing the role of Toto in The Wizard of Oz.) In January of 1942, they began asking people in Los Angeles to bring their dogs to Pershing Square to be used in the war effort. Over 1,000 dogs were brought, including Rudy Vallee’s Doberman Pinscher, King, and Mary Pickford’s German Shepherd, Silver. The program was known as Dogs for Defense. These dogs would go on to be used by the K-9 Corps.
Originally, thirty breeds of dogs were accepted by the K-9 Corps, but this was narrowed down to seven: German Shepherds, Siberian Huskies, collies, Belgian Sheepdogs, Doberman Pinschers, Eskimo dogs, and Malamutes. New dogs were first given obedience training. They were then given additional training to be a scout or patrol, messenger, sentry, or mine detector. Within eight to twelve weeks they completed their training. The original idea was to have 200 dogs in the K-9 Corps, but by the end of World War II, the number had ballooned to more than 10,400. Most of the dogs were family pets.
Although dogs were first formally trained for military service during World War II, they have been used in war since antiquity. More recently, some were used informally during the Civil War. During World War I, the German, British, and Belgian armies used them to pull carriages and wagons loaded with guns and supplies, to pull telephone lines, to carry messages, and to comfort those who had been injured. About 7,000 dogs were used in World War I, but not only a few of these were from the United States.
As of the late 2010s, over 2,500 dogs actively serve in the military, and about 700 are deployed overseas. Military dogs sniff out bombs and weapons, search and patrol, perform guard duty, and serve as companions to those who suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury. Military dogs are usually German Shepherds, Belgian Malinois, or Labrador Retrievers. Dogs in the military now can receive medals and awards, and they often have retirement and memorial services held for them. In law enforcement, dogs began being used more in the 1970s. These dogs patrol, perform search and rescue missions, and detect drugs, explosives, cadavers, and arson accelerants. Dogs in both military and law enforcement roles, as well as dogs in other similar official roles, are all honored today.
How to Observe
Here are some ideas on how to celebrate the day:
If you have, work with, or train a military dog, law enforcement dog, or dog in a similar role, make the day extra special for them.
Contact your representatives and encourage them to support a K-9 Veterans Day on the state or national level.
Support K-9 Courage, a group that provides healthcare assistance to retired police and military dogs, and gives support to service dogs who assist veterans with post-traumatic stress and traumatic brain injury. You could help raise funds or have your own dog participate in “Dogs Salute Dogs.”
Learn about notable dogs who have served in the military, such as Sgt. Stubby, Chips, Lex, and Cairo.
Visit a memorial dedicated to dogs, such as the War Dog Memorial at the March Field Air Museum in Riverside, California; the War Dog Memorial in Hartsdale Pet Cemetery in Hartsdale, New York; the National War Dog Cemetery and War Dog Memorial at Naval Base Guam; The Pennsylvania War Dog Memorial; or the Military Working Dog Teams National Monument in San Antonio, Texas.
Visit Sgt. Stubby, who is stuffed and on display, and covered with a blanket that holds his medals, in an exhibit titled “The Price of Freedom: Americans at War” at the National Museum of American History.
Watch a movie or documentary about military or police dogs such as Max, Sgt. Stubby: An American Hero, War Dog: A Soldier’s Best Friend, Megan Leavey, or War Dogs: America’s Forgotten Heroes.
Source
#Animals in War Memorial by David Clendining#K-9 Veterans Day#Hope#BC#Ottawa#Ontario#British Columbia#sculpture#travel#vacation#USA#New York City#Lower Manhattan#K9VeteransDay#RCMP dog Chip#Let Freedom Ring by Kathryn Mellusi#Sirius by Ron Burns#National September 11 Memorial & Museum#South African War Memorial by Hamilton MacCarthy#13 March
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lynching victim Rubin Stacy’s story being told by his family in film screening at NSU

Anne Naves knew something bad had happened to her uncle when her male relatives came home from fishing, each wearing a pall of silence. Dad wasn’t cracking jokes like usual. Grandfather looked grave. And her uncle, Rubin Stacy, hadn’t come back. The next day, someone from the funeral home said a body had been dropped off.
Naves, 8 years old at the time, only discovered the full gruesome truth about her uncle years later. On July 19, 1935, acting on an unproven accusation from a white woman, a masked lynch mob strung up Stacy under a Fort Lauderdale tree, hanged him and shot him 17 times as spectators gawked and children laughed.
The brutality and silence of Stacy’s lynching is revisited in the new documentary, “Rubin,” which will screen on Tuesday, Oct. 3, at Nova Southeastern University. In the hourlong film, the farmhand’s death is recounted through the eyes of his surviving descendants, but mainly through Naves, who was the last living eyewitness to the trauma — and to the secrecy — that followed.
The film, the first to be made by relatives of Stacy’s family, also chronicles the history of lynchings in America, used as a tool of punishment and to foster silence.
“I think (my family) knew that, without telling us (kids) what really happened, they would save us a lot of trauma,” Naves says in the documentary. “The neighbors and our church members respected our silence, too, because they knew that if it could happen to our family, it could happen to theirs.”
For “Rubin” director Tenille Brown, who is a cousin of Rubin Stacy, the film has in recent weeks also morphed into something else: a posthumous tribute to Naves. After filming her interviews for the documentary, she died on Sept. 18 at age 96, leaving behind a strong legacy: She was a Broward County educator for 25 years, teaching at Pines Middle and other schools.
“The biggest piece of the film was Anne,” Brown says in an interview with the South Florida Sun Sentinel. “Without her, there’s no story. She’s the driving force. She was ready to talk. She told me to record her. She really pushed me when I didn’t feel confident and said, ‘Record me anyway. Just go.’ ”
The rest of America witnessed the cruelty of Stacy’s lynching long before Naves did. A series of photos immortalize the moment when a white crowd gathered around Stacy’s body hanging from a tree. These images ran in newspapers nationwide, were published by the NAACP, Life magazine and National Geographic, and are now archived in the Library of Congress.
It was a tale of Jim Crow-era racism that Fort Lauderdale would’ve rather forgotten — the brother of a corrupt Broward County sheriff participated in the lynching — but city officials have made strides in recent years to acknowledge the tragedy by placing memorial markers around Fort Lauderdale. One is on Davie Boulevard and Southwest 31st Avenue, also known as Martin Luther King Jr. Avenue, near where Stacy took his last breath. There’s another on the 800 block of Northwest Second Street, where he lived, and a third at Woodlawn Cemetery, his final resting place. In February 2022, a section of Davie Boulevard was renamed Rubin Stacy Memorial Boulevard.
“I’m glad they acknowledged it,” says Brown, of Pompano Beach. “These stories make some people in the state uncomfortable, but if they are based on fact, we need to tell the truth. You can’t turn your head. These are things you can’t ignore.”
For Brown, it was these memorials — and Naves’ willingness to break her silence — that motivated her to reconstruct Stacy’s story. To do so, she also interviewed Ken Cutler, Parkland commissioner and historian, and Tameka Bradley Hobbs, library regional manager of Fort Lauderdale’s African American Research Library and Cultural Center.
“My family didn’t want to talk about it out of fear for years,” Brown says. “There was shame. There’s an element of hurt, and you can hear that emotion in Anne’s voice. Now it feels freeing. This is a story that was suppressed for years and by sharing it, this is how we overcome.”
Michael Anderson, a producer for “Rubin,” says the film also tackles what too many school textbooks don’t stress enough: the history of Black lynchings.
“For Black youth to know their stories, they have to know the history of lynchings,” Anderson says. “They still don’t know how lynchings were used as a weapon to keep a community quiet. That’s exactly what it did to Rubin Stacy’s family.”
IF YOU GO
WHAT: “Rubin”
WHEN: 7 p.m. Tuesday, Oct. 3
WHERE: NSU’s Rose & Alfred Miniaci Performing Arts Center, 3100 Ray Ferrero Jr. Blvd., Davie
COST: Free, but tickets must be presented for entry
INFORMATION: 954-462-0222; MiniaciPAC.com
#https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/other/lynching-victim-rubin-stacy-s-story-being-told-by-his-family-in-film-screening-at-nsu/ar-AA1huFAr#Lynching in america#Black People#Black American Lynchings#Lynching victim Rubin Stacy’s story being told by his family in film screening at NSU
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
Denazification, truth and reconciliation, and the story of Germany's story

Germany is the “world champion in remembrance,” celebrated for its post-Holocaust policies of ensuring that every German never forgot what had been done in their names, and in holding themselves and future generations accountable for the Nazis’ crimes.
All my life, the Germans have been a counterexample to other nations, where the order of the day was to officially forget the sins that stained the land. “Least said, soonest mended,” was the Canadian and American approach to the genocide of First Nations people and the theft of their land. It was, famously, how America, especially the American south, dealt with the legacy of slavery and Jim Crow.
Silence begets forgetting, which begets revisionism. The founding crimes of our nations receded into the mists of time and acquired a gauzy, romantic veneer. Plantations — slave labor camps where work was obtained through torture, maiming and murder — were recast as the tragiromantic settings of Gone With the Wind. The deliberate extinction of indigenous peoples was revised as the “taming of the New World.” The American Civil War was retold as “The Lost Cause,” fought over states’ rights, not over the right of the ultra-wealthy to terrorize kidnapped Africans and their descendants into working to death.
This wasn’t how they did it in Germany. Nazi symbols and historical revisionism were banned (even the Berlin production of “The Producers” had to be performed without swastikas). The criminals were tried and executed. Every student learned what had been done. Cash reparations were paid — to Jews, and to the people whom the Nazis had conquered and brutalized. Having given in to ghastly barbarism on an terrifyingly industrial scale, the Germans had remade themselves with characteristic efficiency, rooting out the fascist rot and ensuring that it never took hold again.
But Germany’s storied reformation was always oversold. As neo-Nazi movements sprang up and organized political parties — like the far-right Alternative für Deutschland — fielded fascist candidates, they also took to the streets in violent mobs. Worse, top German security officials turned out to be allied with AfD:
https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2018/08/04/germ-a04.html
Neofascists in Germany had fat bankrolls, thanks to generous, secret donations from some of the country’s wealthiest billionaires:
https://www.spiegel.de/international/germany/billionaire-backing-may-have-helped-launch-afd-a-1241029.html
And they broadened their reach by marrying their existing conspiratorial beliefs with Qanon, which made their numbers surge:
https://www.thedailybeast.com/how-fringe-groups-are-using-qanon-to-amplify-their-wild-messages
Today, the far right is surging around Europe, with the rot spreading from Hungary and Poland to Italy and France. In an interview with Jacobin’s David Broder, Tommaso Speccher a researcher based in Berlin, explores the failure of Germany’s storied memory:
https://jacobin.com/2023/07/germany-nazism-holocaust-federal-republic-memory-culture/
Speccher is at pains to remind us that Germany’s truth and reconciliation proceeded in fits and starts, and involved compromises that were seldom discussed, even though they left some of the Reich’s most vicious criminals untouched by any accountability for their crimes, and denied some victims any justice — or even an apology.
You may know that many queer people who were sent to Nazi concentration camps were immediately re-imprisoned after the camps were liberated. Both Nazi Germany and post-Nazi Germany made homosexuality a crime:
https://time.com/5953047/lgbtq-holocaust-stories/
But while there’s been some recent historical grappling with this jaw-dropping injustice, there’s been far less attention given to the plight of the communists, labor organizers, social democrats and other leftists whom the Nazis imprisoned and murdered. These political prisoners (and their survivors) struggled mightily to get the reparations they were due.
Not only was the process punitively complex, but it was administered by bureaucrats who had served in the Reich — the people who had sent them to the camps were in charge of deciding whether they were due compensation.
This is part of a wider pattern. The business-leaders who abetted the Reich through their firms — Siemens, BMW, Hugo Boss, IG Farben, Volkswagon — were largely spared any punishment for their role in the the Holocaust. Many got to keep the riches they acquired through their part on an act of genocide.
Meanwhile, historians grappling with the war through the “Historikerstreit” drew invidious comparisons between communism and fascism, equating the two ideologies and tacitly excusing the torture and killing of political prisoners (this tale is still told today — in America! My kid’s AP history course made this exact point last year).
The refusal to consider that extreme wealth, inequality, and the lust for profits — not blood — provided the Nazis with the budget, materiel and backing they needed to seize control in Germany is of a piece with the decision not to hold Germany’s Nazi-enabling plutocrats to account.
The impunity for business leaders who collaborated with the Nazis on exploiting slave labor is hard to believe. Take IG Farben, a company still doing a merry business today. Farben ran a rubber factory on Auschwitz slave labor, but its executives were frustrated by the delays occasioned by the daily 4.5m forced march from the death-camp to its factory:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/02/plunderers/#farben
So Farben built Monowitz, its own, private-sector concentration camp. IG Farben purchased 25,000 slaves from the Reich, among them as many children as possible (the Reich charged less for child slaves).
Even by the standards of Nazi death camps, Monowitz was a charnel house. Monowitz’s inmates were worked to death in just three months. The conditions were so brutal that the SS guards sent official complaints to Berlin. Among their complaints: Farben refused to fund extra hospital beds for the slaves who were beaten so badly they required immediate medical attention.
Farben broke the historical orthodoxy about slavery: until Monowitz, historians widely believed that enslavers would — at the very least — seek to maintain the health of their slaves, simply as a matter of economic efficiency. But the Reich’s rock-bottom rates for fresh slaves liberated Farben from the need to preserve their slaves’ ability to work. Instead, the slaves of Monowitz became disposable, and the bloodless logic of profit maximization dictated that more work could be attained at lower prices by working them to death over twelve short weeks.
Few of us know about Monowitz today, but in the last years of the war, it shocked the world. Joseph Borkin — a US antitrust lawyer who was sent to Germany after the war as part of the legal team overseeing the denazification program — wrote a seminal history of IG Farben, “The Crime and Punishment of I.G. Farben”:
https://www.scribd.com/document/517797736/The-Crime-and-Punishment-of-I-G-Farben
Borkin’s book was a bestseller, which enraged America’s business lobby. The book made the connection between Farben’s commercial strategies and the rise of the Reich (Farben helped manipulate global commodity prices in the runup to the war, which let the Reich fund its war preparations). He argued that big business constituted a danger to democracy and human rights, because its leaders would always sideline both in service to profits.
US companies like Standard Oil and Dow Chemicals poured resources into discrediting the book and smearing Borkin, forcing him into retirement and obscurity in 1945, the same year his publisher withdrew his book from stores.
When we speak of Germany’s denazification effort, it’s as a German program, but of course that’s not right. Denazification was initiated, designed and overseen by the war’s winners — in West Germany, that was the USA.
Those US prosecutors and bureaucrats wanted justice, but not too much of it. For them, denazification had to be balanced against anticommunism, and the imperatives of American business. Nazi war criminals must go on trial — but not if they were rocket scientists, especially not if the USSR might make use of them:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wernher_von_Braun
Recall that in the USA, the bizarre epithet “premature antifascist” was used to condemn Americans who opposed Nazism (and fascism elsewhere in Europe) too soon, because these antifascists opposed the authoritarian politics of big business in America, too:
https://www.thenation.com/article/archive/premature-antifascist-and-proudly-so/
When 24 Farben executives were tried at Nuremberg for the slaughter at Monowitz, then argued that they had no choice but to pursue slave labor — it was their duty to their shareholders. The judges agreed: 19 of those executives walked.
Anticommunism hamstrung denazification. There was no question that German elites and its largest businesses were complicit in Nazi crimes — not mere suppliers, but active collaborators. Antifacism wasn’t formally integrated into the denazification framework until the 1980s with “constitutional patriotism,” which took until the 1990s to take firm root.
The requirement for a denazification program that didn’t condemn capitalism meant that there would always be holes in Germany’s truth and reconciliation process. The newly formed Federal Republic set aside Article 10 of the Nuremberg Charter, which would hold all members of the Nazi Party and SS responsible for their crimes. But Article 10 didn’t survive contact with the Federal Republic: immediately upon taking office, Konrad Adenauer suspended Article 10, sparing 10 million war criminals.
While those spared included many rank-and-file order-followers, it also included many of the Reich’s most notorious criminals. The Nazi judge who sent Erika von Brockdorff to her death for her leftist politics was given a judge’s pension after the war, and lived out his days in a luxurious mansion.
Not every Nazi was pensioned off — many continued to serve in the post-war West German government. Even as Willy Brandt was demonstrating historic remorse for Germany’s crimes, his foreign ministry was riddled with ex-Nazi bureaucrats who’d served in Hitler’s foreign ministry. We still remember Brandt’s brilliant 1973 UN speech on the Holocaust:
https://www.willy-brandt-biography.com/historical-sources/videos/speech-uno-new-york-1973/
But recollections of Brandt’s speech are seldom accompanied by historian Götz Aly’s observation that Brandt couldn’t have given that speech in Germany without serious blowback from the country’s still numerous and emboldened antisemites (Brandt donated his Nobel prize money to restore Venice’s Scuola Grande Tedesca synagogue, but ensured that this was kept secret until after his death).
All this to say that Germany’s reputation as “world champions of memory” is based on acts undertaken decades after the war. Some of Germany’s best-known Holocaust memorials are very recent, like the Wannsee Conference House (1992), the Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe (2005), and the Topography of Terror Museum in (2010).
Germany’s remembering includes an explicit act of forgetting — forgetting the role Germany’s business leaders and elites played in Hitler’s rise to power and the Nazi crimes that followed. For Speccher, the rise of neofacist movements in Germany can’t be separated from this selective memory, weighed down by anticommunist fervor.
And in East Germany, there was a different kind of incomplete rememberance. While the DDR’s historians and teachings emphasized the role of business in the rise of fascism, they excluded all the elements of Nazism rooted in bigotry: antisemitism, homophobia, sectarianism, and racism. For East German historians, Nazism wasn’t about these, it was solely “the ultimate end point of the history of capitalism.”
Neither is sufficient to prevent authoritarianism and repression, obviously. But the DDR is dust, and the anticommunism-tainted version of denazification is triumphant. Today, Europe’s wealthiest families and largest businesses are funneling vast sums into far-right “populist” parties that trade in antisemitic “Great Replacement” tropes and Holocaust denial:
https://corporateeurope.org/sites/default/files/2019-05/Europe%E2%80%99s%20two-faced%20authoritarian%20right%20FINAL_1.pdf
And Germany’s coddled aristocratic families and their wealthy benefactors — whose Nazi ties were quietly forgiven after the war — conspire to overthrow the government and install a far-right autocracy:
https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/25-suspected-members-german-far-right-group-arrested-raids-prosecutors-office-2022-12-07/
In recent years, I’ve spent a lot of time thinking about denazification. For all the flaws in Germany’s remembrance, it stands apart as one of the brightest lights in national reckonings with unforgivable crimes. Compare this with, say, Spain, where the remains of fascist dictator Francisco Franco were housed in a hero’s monument, amidst his victims’ bones, until 2019:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pedro_S%C3%A1nchez#Domestic_policy
What do you do with the losers of a just war? “Least said soonest mended” was never a plausible answer, and has been a historical failure — as the fields of fluttering Confederate flags across the American south can attest (to say nothing of the failure of American de-ba’athification in Iraq):
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De-Ba%27athification
But on the other hand, people who lose the war aren’t going to dig a hole, climb in and pull the dirt down on top of themselves. Just because I think Germany’s denazification was hobbled by the decision to lets its architects and perpetrators walk free, I don’t know that I would have supported prison for all ten million people captured by Article 10.
And it’s not clear that an explicit antifascism from the start would have patched the holes in German denazification. As Speccher points out, Italy’s postwar constitution was explicitly antifascist, the nation “steeped in institutional anti-fascism.” Postwar Italian governments included prominent resistance fighters who’d fought Mussolini and his brownshirts.
But in the 1990s, “the end of the First Republic” saw constitutional reforms that removed antifascism — reforms that preceded the rise of the corrupt authoritarian Silvio Berlusconi — and there’s a line from him to the neofascists in today’s ruling Italian coalition.
Is there any hope for creating a durable, democratic, anti-authoritarian state out of a world run by the descendants of plunderers and killers? Can any revolution — political, military or technological — hope to reckon with (let alone make peace with!) the people who have brought us to this terrifying juncture?

[Image ID: The Tor Books cover for ‘The Lost Cause,’ designed by Will Staehle, featuring the head of the snake on the Gadsen ‘Don’t Tread on Me’ flag, shedding a tear.]
Like I say, this is something I’ve spent a lot of time thinking about — not just how we might get out of this current mess, but how we’ll stay out of it. As is my wont, I’ve worked out my anxieties on the page. My next novel, The Lost Cause, comes out from Tor Books and Head of Zeus in November:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865939/the-lost-cause
Lost Cause is a post-GND utopian novel about a near-future world where the climate emergency is finally being treated with the seriousness and urgency it warrants. It’s a world wracked by fire, flood, scorching heat, mass extinctions and rolling refugee crises — but it’s also a world where we’re doing something about all this. It’s not an optimistic book, but it is a hopeful one. As Kim Stanley Robison says:
This book looks like our future and feels like our present — it’s an unforgettable vision of what could be. Even a partly good future will require wicked political battles and steadfast solidarity among those fighting for a better world, and here I lived it along with Brooks, Ana Lucía, Phuong, and their comrades in the struggle. Along with the rush of adrenaline I felt a solid surge of hope. May it go like this.
The Lost Cause is a hopeful book, but it’s also a worried one. The book is set during a counter-reformation, where an unholy alliance of seagoing anarcho-capitalist wreckers and white nationalist militias are trying to seize power, snatching defeat from the jaws of the fragile climate victory. It’s a book about the need for truth and reconciliation — and its limits.
As Bill McKibben says:
The first great YIMBY novel, this chronicle of mutual aid is politically perceptive, scientifically sound, and extraordinarily hopeful even amidst the smoke. Forget the Silicon Valley bros — these are the California techsters we need rebuilding our world, one solar panel and prefab insulated wall at a time.
We’re currently in the midst of a decidedly unjust war — the war to continue roasting the planet, a war waged in the name of continuing enrichment of the world’s already-obscenely-rich oligarchs. That war requires increasingly authoritarian measures, increasing violence and repression.
I believe we can win this war and secure a habitable planet for all of us — hell, I believe we can build a world of comfort and abundance out of its ashes, far better than this one:
https://tinyletter.com/metafoundry/letters/metafoundry-75-resilience-abundance-decentralization
But even if that world comes to being, there will be millions of people who hate it, a counter-revolution in waiting. These are our friends, our relatives, our neighbors. Figuring out how to make peace with them — and how to hold their most culpable, most powerful leaders to account — is a project that’s as important, and gigantic, and uncertain, as a just transition is.

Next weekend, I’ll be at San Diego Comic-Con:
Thu, Jul 20 16h: Signing, Tor Books booth #2802 (free advance copies of The Lost Cause— Nov 2023 — to the first 50 people!)
Fri, Jul 21 1030h: Wish They All Could be CA MCs, room 24ABC (panel)
Fri, Jul 21 12h: Signing, AA09
Sat, Jul 22 15h: The Worlds We Return To, room 23ABC (panel)

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this thread to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/19/stolpersteine/#truth-and-reconciliation

[Image ID: Three 'stumbling stones' ('stolpersteine') set into the sidewalk in the Mitte, in Berlin; they memorialize Jews who lived nearby until they were deported to Auschwitz and murdered.]
#pluralistic#stolpersteine#historians' dispute#Historikerstreit#nazis#godwin's law#mussolini#berlusconi#italy#antifa#fascism#history#truth and reconciliation#the lost cause#denazification
246 notes
·
View notes
Note
so….the robert e lee statue, thoughts ?
i ask because i recall you mentioning being both southern and a historian — so if anyone is qualified to give a nuanced analysis on the matter i figured you’d be the best candidate. i am broadly against iconoclasm of all kinds but i (a European) am not well versed in the particular history of this period or the statue itself.
mayhaps you can help.
many thanks
sure. so for people who don’t know, today, the Robert E. Lee statue formerly installed in Charlottesville, Virginia, was melted down so that a local Black public history organization can use the material to create new community art.
Luckily for you, Confederate statue removal isn’t actually a nuanced issue at all. This is unequivocally a good thing!!! it’s what the community, a substantial portion of which is Black, wanted! This was the same Robert E Lee statue whose potential removal sparked the unite the right rally in 2017, where white nationalists and nazis holding tiki torches attempted to intimidate the community into keeping the statue up. Eventually, we finally got it removed in 2021, and there was like live music and extremely loud cheering as they took that thing down.
To describe confederate memorials in the south as just iconoclasm is to me a little reductive. They are unambiguously racist. Putting up a statue of someone who fought and sometimes died to continue the mass enslavement of african-americans is racist. The history of these statues is clear: they weren’t installed during or shortly after the Civil War, when the Confederacy was still in living memory. Most of them were put up in the 1890s, during the origin of the jim crow apartheid governments, the 1920s, which saw a huge national revival of white supremacy and KKK racist terrorism, and the 1960s, with the racist backlash to the civil rights movement.
Most statues, including the Charlottesville Lee statue, were put up specifically in front of courthouses and in town squares: the goal was not to celebrate any kind of southern history, but to intimidate Black defendants going to Jim Crow court or Black residents trying to live their lives in white spaces. The message that Confederate statues were intended to send is that the community is not for African-Americans, and to remind them of the legacy of white supremacist violence inflicted against them. They are hateful and all of them need to be taken down.
Today is a great day for Charlottesville and the realization of 7 years of community activism. There are thousands of statues still left across the country to work on next.
#anyways i’m done! this is personal obvi. the years i lived in beautiful cville were a gift and i miss that place so much.#the people working on swords into plowshares are amazing
126 notes
·
View notes