#Tsar Paul I
Text


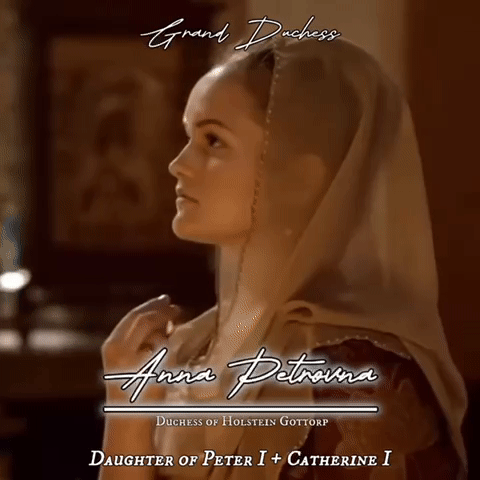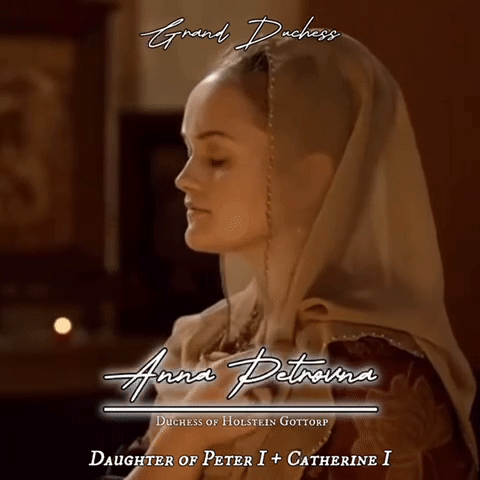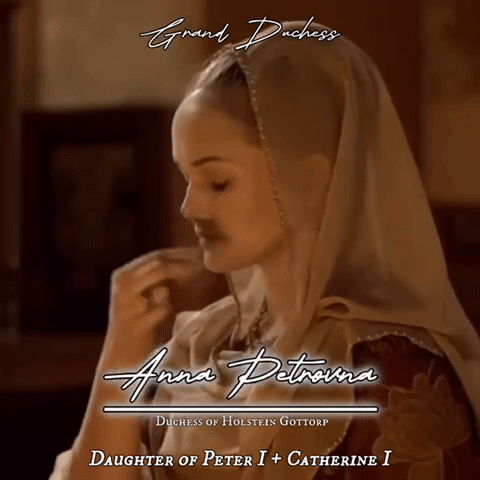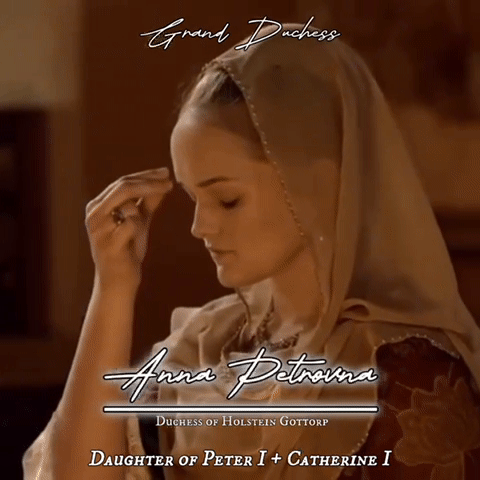






Eldest daughters of all Romanov Monarchs of Russia gifset
❦
#my first gifset!#it turned out okay but I will keep improving#Romanovs#Romanov#russian imperial family#Russian history#irina mikailovna#tsar mikhail I#evdokia alexeivna#tsar Alexei I#Catherine ivanovna#tsar Ivan v#Anna petrovna#Peter the great#Catherine I#Catherine the great#Alexandra pavlovna#tsar Paul I#maria alexandrovna#tsar Alexander i#Maria nikolaevna#tsar Nicholas I#Alexandra Alexandrovna#tsar Alexander III#xenia alexandrovna#tsar Alexander ii#olga nikolaevna#tsar nicholas ii#my edit#made by me
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

And he wasn’t even wrong
#memes#my memes#Napoleon#Tsar Paul I#Paul I of Russia#napoleon bonaparte#history memes#napoleonic era#napoleonic#Russia#France#first french empire#french empire#history#coalition wars
71 notes
·
View notes
Text


















"Over the centuries, the Empire has grown in size and in the number of conquered peoples. It once possessed an area equivalent to one-sixth of the globe, stretching from the Pacific to the German border, on which the sun never set and which was ruled by an autocrat Tsar who owed satisfaction only to God."
The last tsars - a brief untold history about the Romanovs | Paulo Rezzutti.
(Loose translation)
#tsar#tsarina#facts#romanovs#russian history#the romanovs 2013#tsar michael i#tsar alexei i#tsar nicholas ii#catherine the great#tsar paul i#tsar peter ii#tsar peter iii#peter the great#tsarina elizabeth#tsarina catherine i#tsar alexander ii#tsar alexander iii#tsar alexander i#tsar nicholas i#tsar ivan v#tsar ivan vi#tsarina anna#tsarina anna i#tsarina elizabeth i#nicholas and alexandra 1971#zvezda imperii 2008#poor poor paul#roman imperatora 1994#delo dekabristov
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
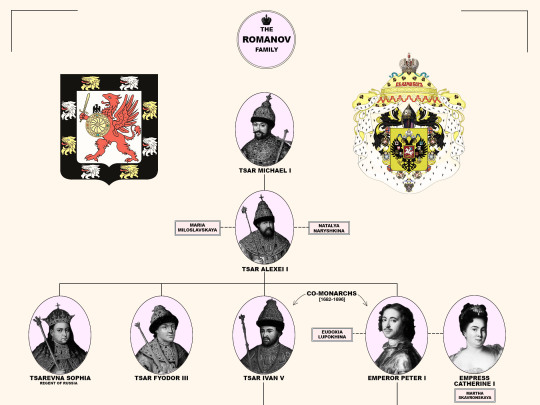
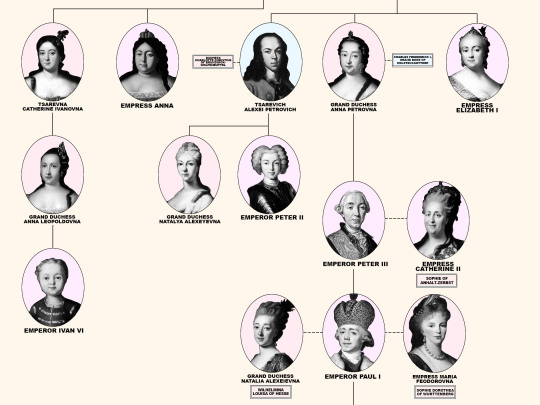
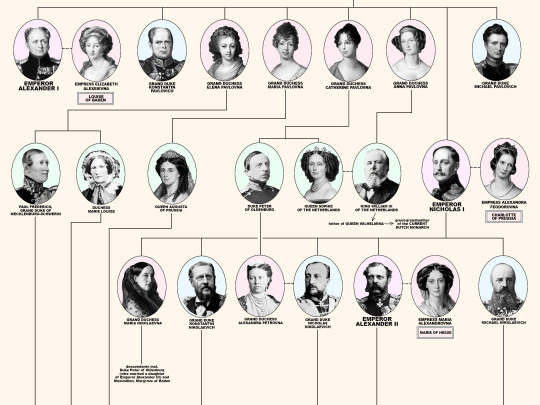
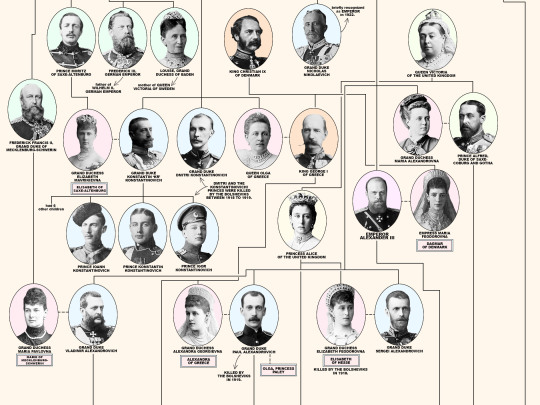
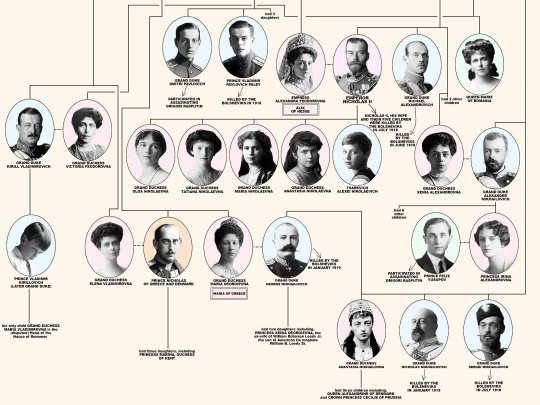
Members of the House of Romanov, the last reigning Dynasty of Russia.
From the first Romanov Russian Tsar Michael I (reigned 1613-1645) until the last Emperor Nicholas II (reigned 1894-1917). Including the 18 members of the house executed from 1918 until 1919; Grand Duke Michael Alexandrovich (13 June 1918). Nicholas II, Empress Alexandra Feodorovna, Grand Duchesses Olga Nikolaevna, Tatiana Nikolaevna, Maria Nikolaevna, Anastasia Nikolaevna, and Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich (17 July 1918). Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna, Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovich, Prince Ioann Konstantinovich, Prince Konstantin Konstantinovich, Prince Igor Konstantinovich, and Prince Vladimir Paley (18 July 1918). Grand Duke Paul Alexandrovich, Grand Duke Dmitri Konstantinovich, Grand Duke Nicholas Mikhailovich, and Grand Duke George Mikhailovich (28 January 1919).
#romanovs#history#nicholas ii#alexandra feodorovna#olga nikolaevna#tatiana nikolaevna#maria nikolaevna#anastasia nikolaevna#alexei nikolaevich#myedits#peter i#peter ii#Peter iii#peter iii#Catherine the great#tsar alexei i#tsar michael#tsar paul i#alexander i#alexander ii#alexander iii#nicholas i#ancestry
390 notes
·
View notes
Text
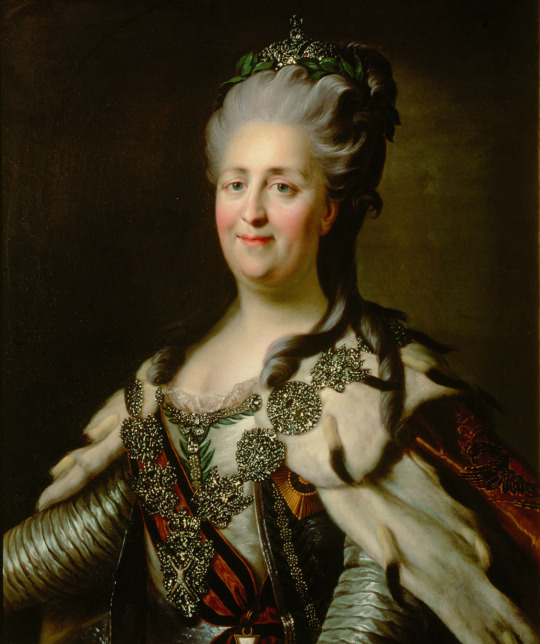
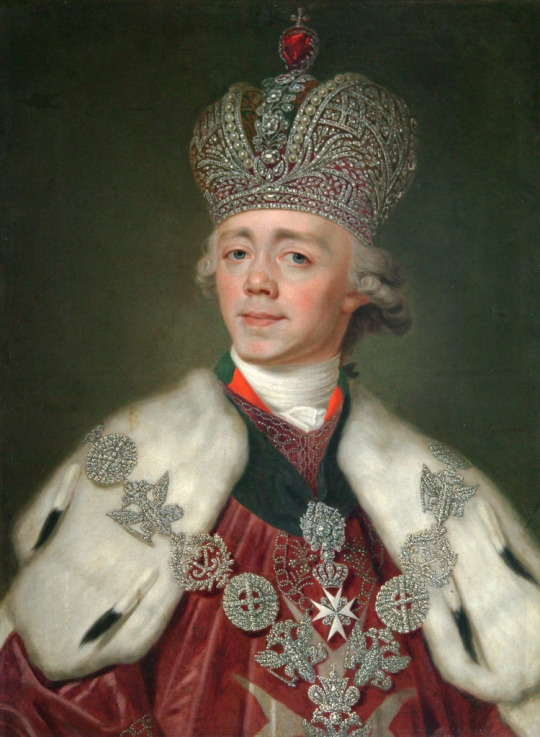
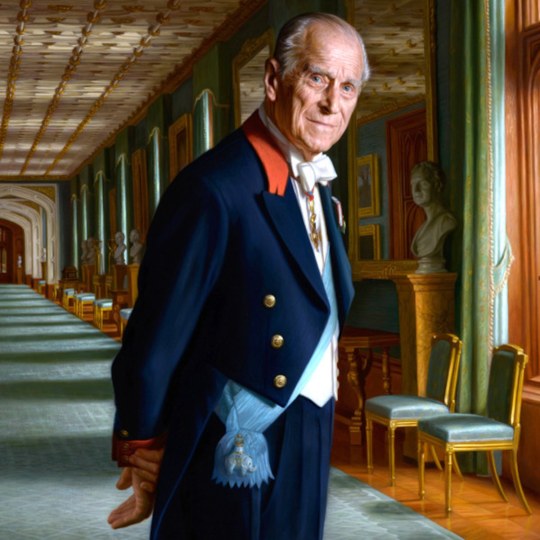
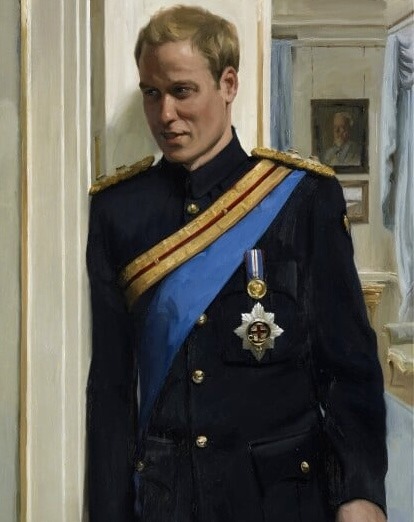









Catherine II the Great, Empress of Russia: 6th great-grandmother of The Prince of Wales.
Catherine II of Russia -> Paul I of Russia -> Nicholas I of Russia -> Grand Duke Konstantin Nikolayevich of Russia -> Olga Constantinovna, Queen consort of Greece -> Prince Andrew of Greece and Denmark -> Prince Philip, The Duke of Edinburgh -> King Charles III of GB -> The Prince of Wales.
#ktd#british royal family#prince william#brf#throwback#king charles lll#prince philip#catherine the great#the great#empress of russia#russian imperial family#tsar Paul I#Paul I#greek royal family#art#art history#history#european royalty
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

Yayayya Paul and Alexander
I do not know much besides Alexander agreeing to overthrow paul(but he didn’t know his father would get killed), Paul getting strangled, stabbed and trampled to death so mistakes will definitely be there…(in case I get jumped for getting something wrong)
Also I gave up on drawing Alexander’s hair
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Paul I after sighning the new Law of Succession: Finally, no more women on the Russian throne! A reign of logic and reason will begin for the XIX century!
Alexander I:

#I love you Paul but you eldest son is a petty vengeful bitch#ok I’m struggling through reading about thr last years of his reign abd his stupid Holy Union#tsar alexander i#paul I of russia#paul i
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
March is very fruitful for death of tyrants
(5 March - Stalin; 15 March - Caesar)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Lost Grand Duchesses part 2: Alexandra Pavlovna
When she was born at 7:40 in the morning in 1783, the baby Grand Duchess Alexandra Pavlovna was instantly viewed as second class. Her grandmother, Catherine II ‘the Great’, wrote “I infinitely more like boys than girls”, and told her staff that she found the newborn to be very ugly. She called the baby “a very ugly creature.” This dislike of Alexandra continued into her toddler years, when Catherine continuously compared the young Alexandra to her baby sister, insisting that little Elena was much more charming and intelligent than Alexandra.
Despite this, Alexandra adored her grandmother, who wrote that the little girl would do “anything just to please me.” Alexandra and Elena were painted together as a gift to Catherine, and the two little girls lovingly hold up and caress a diamond encrusted miniature portrait of their grandmother.

By the age of four, Alexandra’s education had begun, and her intelligence in languages (being fluent in four) and writing made Catherine finally pay more attention to her, but for entirely different reasons.
As soon as the little girl turned eleven, Catherine wrote that the little girl who loved to dance, draw, and play music, was now to be “considered an adult”, and be made to marry. “It is time for the older one to get married” she concluded, not even mentioning Alexandra’s name.
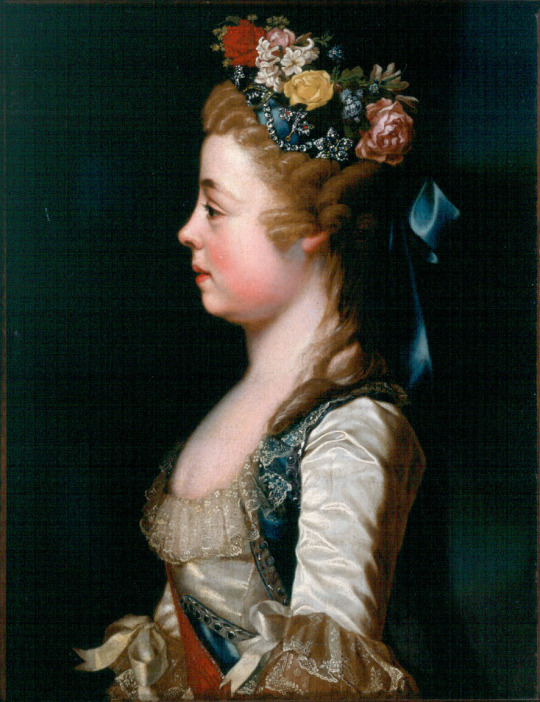
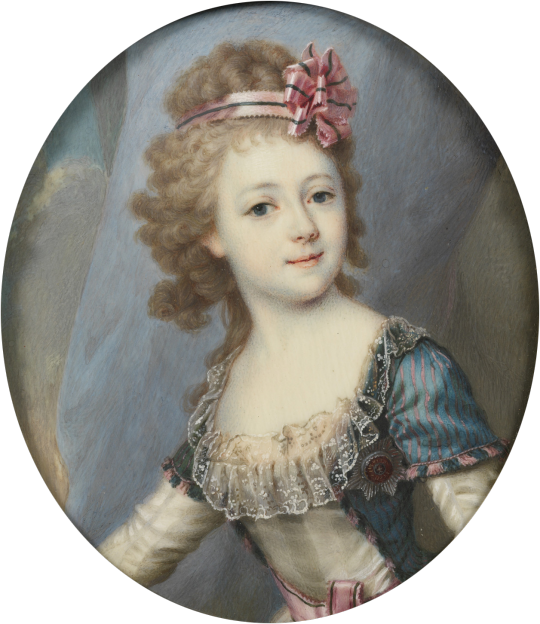


A long and embarassing debacle followed, in which the child was left at the alter. Catherine admitted that the young girl, not yet a teenager, often adopted a “confused look” when having to meet with potential husbands, and did not want to speak to them.
Catherine died in 1797, temporarily putting Alexandra’s fate in limbo. She returned to her daily life as an unmarried girl, and even published anonymous articles that she had translated in French under the pseudonym ‘A’. However, in 1799, the prospect of an Austrian-Russian alliance was apparently too attractive to pass on, and the thirty-year-old Archduke Joseph of Austria, the Palatine of Hungary, travelled to Russia to meet the thirteen-year-old Alexandra.
The marriage was finalised, and Alexandra was forced to leave Russia - and her family - in order to move to Hungary with her new husband. Joseph wrote a letter to his brother in which he stated he was “convinced that with this marriage my domestic bliss is assured for the entirety of my life.”
Alexandra, on the other hand, was miserable. Countess Varvara Golovina, a lady at court and potential lover of the Tsarina Elizaveta Alexeievna, wrote in her memoirs that Alexandra was sad, and did not want to be forced to leave Russia. Her father, Pavel I, constantly said that he would “not see her again” and that she was “being sacrificed.” Despite this, Pavel could have prevented the marriage at any time. A single lock of golden hair fashioned into a flower was all that she left behind.


Although Alexandra was popular in Hungary among all classes, she was deeply depressed. Her friendly and charming personality had been replaced by a new temperament which was “always serious and sad”. Alexandra especially did not get on well with her mother in law, the Empress Maria Theresa of Hungary, who was intensely jealous of the young girl’s popularity. Maria Theresa intentionally antagonised the teenager, and sought to treat her badly.
In 1800, Alexandra fell pregnant, and was struck with health problems. Her mother-in-law ordered the hiring incompetent doctors (known to her to be incompetent) and insisted that the doctors obey her orders, rather than present their own educated solutions. Orders from Maria Theresa included cooking meals which Alexandra would not be able to eat, making her weak and frail.
In March 1801, Alexandra gave birth to a little girl, named Alexandrine of Austria. The pregnancy and labour had been incredibly difficult, and the baby sadly passed away within a few hours of birth. Alexandra, depressed at having been forcibly taken from her home and after having to endure cruel treatment by her mother-in-law, said: “Thank God that my daughter was now with the angels, without experiencing the miser that we are exposed to.”
Alexandra contracted puerperal fever. The doctors misdiagnosed her poor health after the birth several times, treating her for gastric diseases and typhoid rather than ‘childbed’ fever. She succumbed to the disease aged just seventeen years old.
Alexandra was not buried until two years after her death due to disagreements in the Catholic Austrian court over where to bury a Russian Orthodox. In 1981, thieves broke into Alexandra’s Mausoleum, looting her coffin and taking jewellery and clothing from her remains. Due to the vandalism, she was reburied with the deceased wives and children of her husband in the crypt of Buda Castle, which went against her wishes to be buried in an Orthodox Church. In 2004, she was reburied at the Üröm Mausoleum, in a small park surrounded by a moat. Inside the tomb, Orthodox icons line the walls, a reflection of Alexandra’s beloved faith, and her deep connection with Russia, which endured even after being “sacrificed”.

#the lost grand duchesses#alexandra pavlovna#what happened to her was so preventable#they just didn't love daughters enough to care#1700s#1800s#womens history#romanov#romanov family#russian history#hungarian history#pavel i#paul i#tsar paul#get the tissues out#justice for alexandra#the alexandra curse
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Through her visits to her mother's family, Alexandra was no stranger to Russia or for that matter to the Orthodox religion, in which she too had been brought up. Settling into a palace of their own behind the Church of the Annunciation on the Neva embankment in St Petersburg, Paul and Alexandra's closest friends and companions were Ella and Serge. In fact, the two young grand duchesses, Elisabeth Feodorovna and Alexandra Georgievna, not only became great friends but were like sisters, as close to one another as their husbands had always been. 'I do love her so dearly', Ella wrote on one occasion to Alexandra's brother Prince Nicholas of Greece and in a further letter referred to herself as 'your own sisters sister'. (...)
After doing the rounds of the family sick beds [after a typhus epidemic in 1889], which she likened to visiting a 'real family hospital', Ella, whose own evidently robust state of health saw her safely through the epidemic, went to sit with Alexandra Georgiyevna, who was now four months pregnant with her first child. Seeing Paul ill, Ella wrote, 'makes her very nervous and she will think it worse than it really is'. To help distract her, Ella took Alexandra to the opera (...).
A month later, the epidemic had started to pass and the sick were restored to health. Despite a very high wind which whipped up the waters of the Neva and the city's canals, Serge and Paul both ventured out of doors, albeit by carriage. Their destination was the Winter Palace where, during the first week of December, they took part in a reading of a forthcoming production of Tolstoy's Tsar Boris, in which they were both to appear. With the Emperor's permission, the play was staged in the Hermitage theatre at the end of January.
"Ella: Princess, Saint And Martyr" - Christopher Warwick

#paul alexandrovich#alexandra georgievna#elizabeth feodorovna#sergei alexandrovich#romanov#romanov family#19th century#greek royal family#imperial russia
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of my other special interests beside dragon age used to be napoleonic wars and especially tsar of russia alexander i, grandson of catherine the great (who is said to have arranged murder of her son paul i, which gave alexander - a child she raised herself - the throne) who, according to a legend, faked his own death and lived rest of his life as a monk. and i mention it to you, my fair dragon age followers, bcos i'm calling it, that caterina dellamorte, the matriarch of the antivan crows, arranged the murder of her child/children so she could raise lucanis and illario herself - and then after lucanis was thought to be dead the position of the heir shifted to illario, just as after the obvious favorite alexander's death the throne went to his brother nicholas i.
#dragon age#dragon age the veilguard#lucanis dellamorte#illario dellamorte#caterina dellamorte#i mean this has to be the inspiration right??#idk canadian education system bcos here we talk a lot of catherine the great on the basis of her fuckin invading my country#but even abroad surely the autocratic despot named caterina who raised her grandsons to her liking is the obvious reference
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
In Tsarist Russia, you can keep your job after killing the head of state, but then lose your job for moving a Christian icon.

*Palen was one of the conspirators of the assassination of Tsar Paul I, which Tsar Alexander was aware of.
#also sometimes spelled as Pahlen#Peter Ludwig von der Pahlen#Palen#tsar Paul I#tsar Alexander I#napoleonic era#napoleonic#history#1800s#quote#book pic#alexander kornilov#19th century Russia#dowager empress Marie#Alexander’s mother
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
do you know where the first few of the romanovs resided before all of the palaces were built and if so, are any of them remaining? do we know what they look like?
I'm afraid very little from the earliest days of the Romanov dynasty had survived the ravages of time. By the time of Nicholas II, many early residences had already been either destroyed or replaced by the modern and elegant palaces we see today. Here's a few that survived.
The Cabin of Peter the Great
May 1703
Built during the founding of the city of Saint Petersburg, the log cabin was the first St. Petersburg "palace" of Tsar Peter the Great. The small wooden house was constructed in just three days, by soldiers of the Semyonovskiy Regiment.
At that time, the new St. Petersburg was described as "a heap of villages linked together, like some plantation in the West Indies".
The Cabin was boarded up and camouflaged during the Second World War. It was the first St. Petersburg museum to reopen in September 1944, after the end of the Siege of Leningrad.
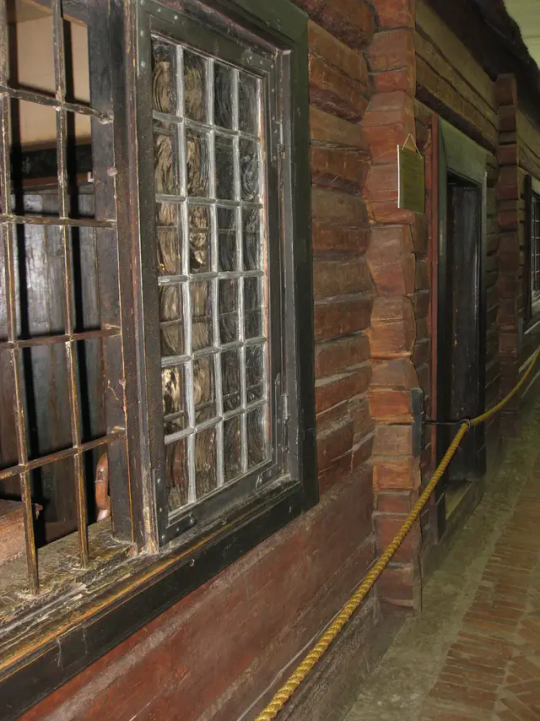



This cabin must have appeared as a huge downgrade after the wooden palace of Tsar Alexei!
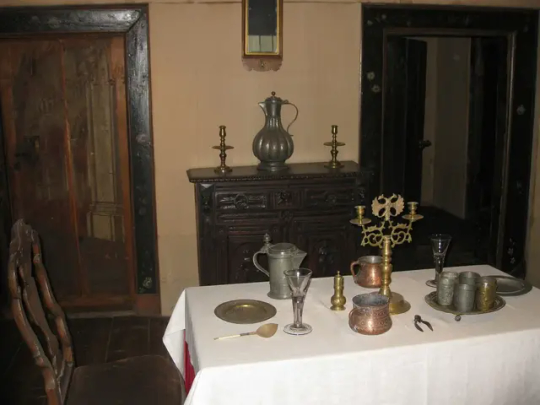
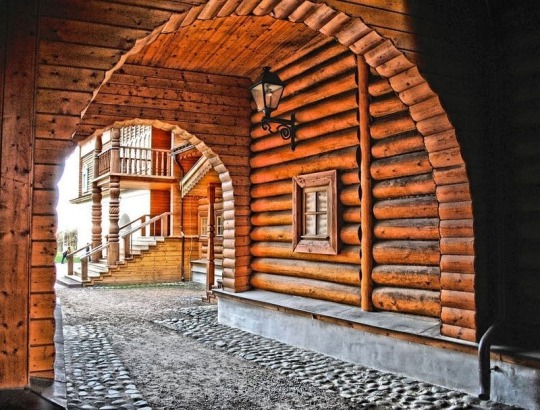
The Wooden Palace of Tsar Alexei Romanov
1667
The recreation of an authentic mid-17th century Romanov residence was built recently in 2010. The Palace of Tsar Alexei Mikhailovich, also known as the Wooden Palace of Tsar Alexei, is a large wooden palace in Kolomenskoye, near Moscow, Russia.
The original was built in 1667 without using any fasten materials, nails or hooks. The wooden palace, famed for its fanciful, fairytale roofs, was a summer residence for Russian tsars before St. Petersburg was constructed.
The palace was divided into male and female halves, with the Tsar and Tsarevitches towers and chambers in the male half and the Tsarina's towers in the female half.
The palace's interior featured rich decorations, including carving, painting, gilding, and ceramic tiles, as well as rectangular and round stoves, weathercocks, and windows and porches.
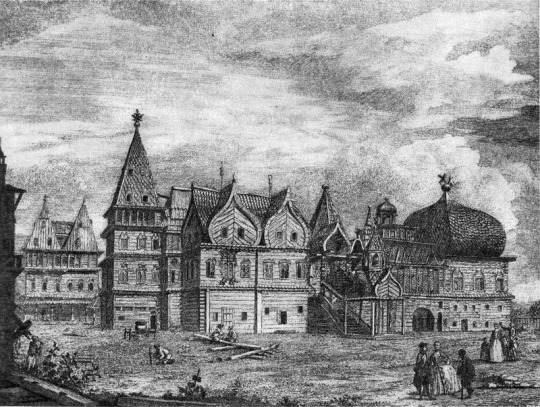



Foreigners referred to this huge maze of intricate corridors and 250 rooms, as 'an Eighth Wonder of the World'. Although basically only a summer palace, it was the favorite residence of Tsar Alexei I.
The future Empress Elizabeth Petrovna was born in the palace in 1709, and Tsar Peter the Great spent part of his youth here.
Upon the departure of the court for the swamps of St. Petersburg, the palace fell into disrepair, so that Catherine the Great refused to make it her Moscow residence. On her orders the wooden palace was demolished in 1768, but thankfully, the detailed plans of the palace had survived.
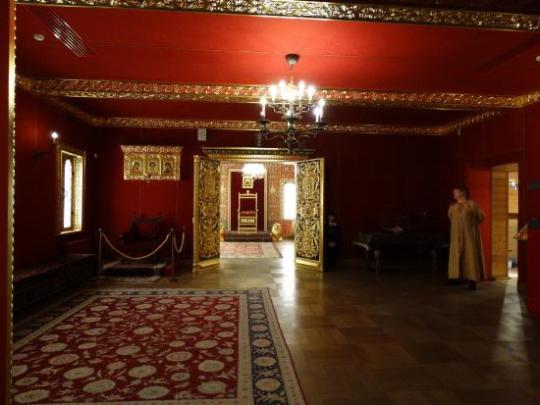







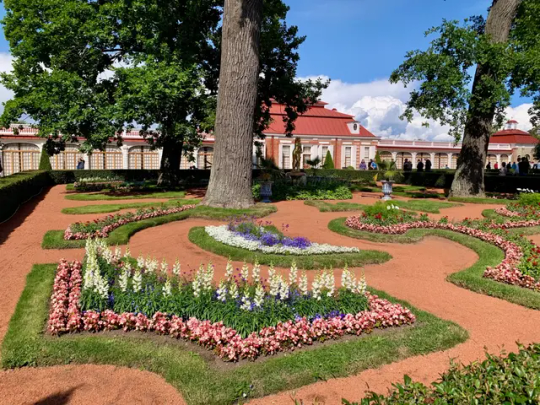
Summer Palace of Peter the Great
1714
One of the earliest imperial residences I can think of that still exists today is the modest Summer Palace of Peter the Great, which is located on an island near the Peter and Paul Fortress, the burial place of the Romanovs.
The palace was built between 1710 and 1714, a few years before the proclamation of the Russian Empire. By the time of Tsar Nicholas II's reign at the end of the 19th century, it became vacant.
During the Second World War, both the Summer Palace and Summer Gardens were badly damaged by a German bombing raid. The building was repaired, however, and the layout remains unchanged from the original.
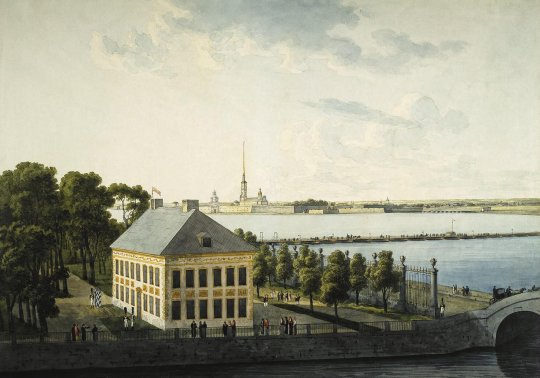
Above: The palace as depicted in 1809. Below: The residence today.



Monplaisir Palace in Peterhof
1714-1716
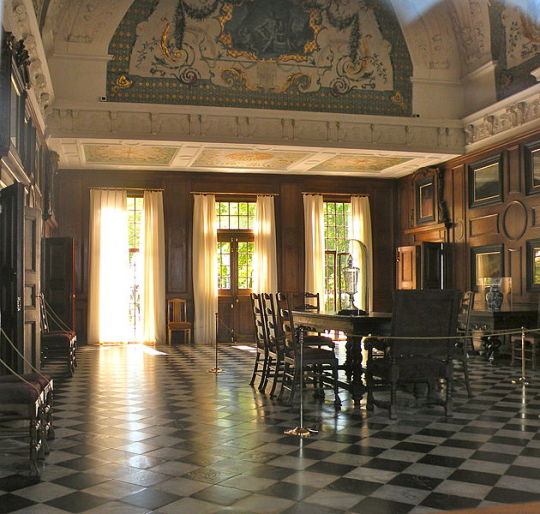
There is another residence owned by Peter the Great that is still standing today. And that is the Monplaisir Palace in Peterhof.
The following painting depicts the formidable Tsar and his son and heir Tsarevich Alexei Petrovich, who has been accused of preparing to seize power, in the interior of the Monplaisir Palace. Before pronouncing sentence, Peter I gazes into his son's eyes, still hoping to discern signs of remorse.


Above: The Parade Hall of Monplaisir Palace today.




#romanov#romanovs#palace#palaces#history#russian culture#russian history#royal history#imperial russia#moscow#saint petersburg#peterhof#russian imperial family#ask
39 notes
·
View notes
Text




Orders and Medals → ᴇᴍᴘᴇʀᴏʀ ᴘᴀᴜʟ ɪ
Emperor Paul I of Russia, was recorded to have been a recipient of thirteen awards. Five nationals: Order of Saint Andrew, Order of Saint Alexander Nevsky, Order of Saint Anna, Order of Saint Vladimir and Order of the Saint John Jerusalem. And eight foreign: Order of the White Eagle (Poland), Order of the Black Eagle (Prussia), Order of Saint Seraphim (Sweden), Order of Saint Janarius (Naples), Neapolitan Constantine Order of Saint George (Naples), Neapolitan Order of Saint Ferdinand and Merit (Naples and Sicily), Order of the Holy Spirit (France), and Order of Our Lady of Carmel and Saint Lazarus of Jerusalem (France).
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐓𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐝 𝐇𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐨𝐟 𝐂𝐡𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐟 𝐉𝐞𝐰𝐬.
I'm sick and tired of Candace Owens and her likes that are obsessed with framing Jews behind every problem that they had over the years. While we all love the Christians and while most Christians are real friends of the Jews, I think this has to be said again and again. So let's review some history and some facts.

1/ Early Christian Era:
Hostility towards Jews began as early as the 4th century when Christianity became the Roman Empire's official religion. Emperor Constantine's policies, later codified in the Theodosian Code, restricted Jewish rights. Jews were barred from public office, synagogues were destroyed, This set a precedent for future Christian rulers to marginalize Jews.

2/ First Crusade (1096):
As the Crusaders marched to the Holy Land, they massacred Jewish communities in the Rhineland (modern-day Germany). Known as the Rhineland massacres, thousands of Jews were killed in cities like Worms, Mainz, and Cologne. The violence was often enabled by Crusader preachers who framed Jews as enemies of Christianity. Many Jews chose martyrdom over forced conversion, a theme that would reappear in later persecutions.

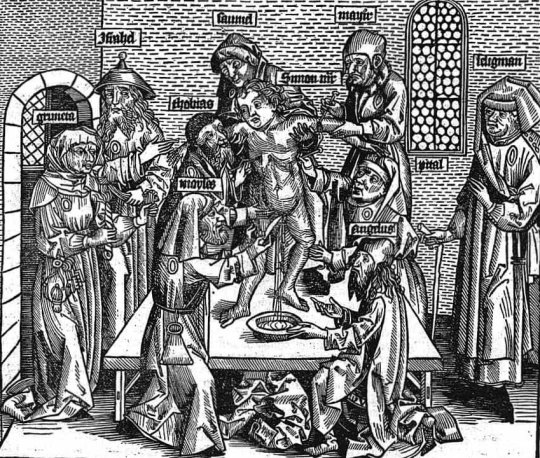
3/ Blood Libel Accusations (12th century - today):
The first known case of blood libel occurred in Norwich, England, in 1144, when Jews were falsely accused of murdering a Christian boy, William of Norwich, for ritual purposes. These accusations led to widespread violence and massacres, including notable cases in Trent (1475) and Damascus (1840). Blood libel myths fueled antisemitism, resulting in the torture, execution, and expulsion of Jews across Europe.

4/ The Black Death (1348-1351):
As the plague ravaged Europe, killing millions, Jews were scapegoated and accused of poisoning wells. Pogroms erupted across the continent, with entire Jewish communities in cities like Strasbourg being annihilated. In some areas, Jews were burned alive, while in others, they were forcibly converted or expelled. Despite papal condemnations of the violence, local authorities and priests encouraged and some even participated in the massacres.

5/ Spanish Inquisition (1478-1834):
The Inquisition targeted conversos, Jews who had converted to Christianity, suspecting them of secretly practicing Judaism. Tomas de Torquemada, the first Grand Inquisitor, led a brutal campaign of torture and execution. The Alhambra Decree of 1492, issued by Ferdinand and Isabella, expelled all Jews from Spain, forcing over 200,000 to convert or flee. This expulsion ended centuries of Jewish cultural and intellectual contributions to Spain.

6/ Expulsions in Europe:
Over centuries, Jews faced expulsion from numerous European countries. England (1290) saw the Edict of Expulsion under King Edward I, forcing Jews to leave and seizing their property. France (1306 and 1394) saw similar expulsions, as did various German states. These expulsions often followed periods of economic exploitation and violence against Jews, stripping them of property and wealth and forcing them into exile.

7/ Ghettos and Restrictions (16th-18th centuries):
In many European cities, Jews were confined to ghettos, segregated neighborhoods with curfews and restricted economic opportunities. The first ghetto was established in Venice in 1516. In Rome, Pope Paul IV established the Roman Ghetto in 1555, enforcing strict segregation. Jews in ghettos faced overcrowding, poverty, and social isolation, with limited rights and constant threat of violence.

8/ Russian Pogroms (19th-20th centuries):
The assassination of Tsar Alexander II in 1881 sparked a wave of violent pogroms against Jews across the Russian Empire. These state-sanctioned attacks involved looting, arson, and murder, with entire villages destroyed. The May Laws of 1882 further restricted Jewish rights, driving mass emigration to the United States and Israel. Pogroms continued into the early 20th century, culminating in the Kishinev Pogrom of 1903, these pogroms were influenced by various social, economic, and political factors, they occurred in a predominantly Christian society where antisemitic attitudes were pervasive and pushed by local priests, and a lot of Christians participated in the violence.

9/ Context on Christian Persecution Claims:
While millions of Christians have faced persecution over the years, those claiming they are the most persecuted group are misleading. Let’s look at some numbers:
- 1800: Approximately 22% of the world population was Christian, around 200 million out of 900 million.
- 1850: Christians made up about 28% of the world population, roughly 350 million out of 1.2 billion.
- 1900: The proportion increased to 34%, with 560 million Christians out of 1.65 billion people globally.
- 1950: Christians constituted about 35% of the global population, approximately 800 million out of 2.3 billion.
Today, around 31% of the world's population identifies as Christian, approximately 2.3 billion people out of 7.8 billion. Given these numbers, it's clear that while Christians have certainly faced persecution, the idea that they are the most persecuted group does not hold up. It's like saying the world is the most persecuted world—statistically inaccurate given the substantial and growing global Christian population.
This context does not diminish the real suffering that many Christians have endured, especially in certain regions and periods. However, the Jewish experience of persecution stands apart due to its intensity, persistence, and the often racially motivated nature of the oppression. Jews, a much smaller group historically, have faced systemic efforts aimed at their complete eradication, from medieval pogroms to the Holocaust. Their persecution involved not just religious but also racial and cultural dimensions, leading to centuries of marginalization, violence, and genocide.
10/ Conclusion:
The history of Christian persecution of Jews is a strong reminder of the consequences of intolerance and bigotry. While it's important to acknowledge and appreciate the many Christians who have stood by Jews as true friends, we cannot ignore the dark chapters where Christian societies and authorities played a significant role in the suffering of Jewish communities.
By understanding these historical contexts, we can better appreciate the resilience of the Jewish people and the importance of standing against all forms of hatred. Let's ensure that history does not repeat itself by fostering an inclusive and compassionate future. It's time to move beyond misplaced blame and work together to combat antisemitism and bigotry in all its forms...
𝐋𝐞𝐭’𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐬 𝐨𝐧 𝐰𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐥𝐲 𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐬 𝐮𝐬: 𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐬𝐡𝐚𝐫𝐞𝐝 𝐡𝐮𝐦𝐚𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐨𝐧 𝐠𝐨𝐚𝐥 𝐨𝐟 𝐡𝐚𝐩𝐩𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐮𝐥𝐟𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭.

36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shitpost
#art#napoleonic era#napoleonic wars#tsar alexander i#alexander i of russia#paul i of russia#napoleonic shitpost
47 notes
·
View notes