#What are the differences between FTP and HTTP?
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
These scams fall in line with a lot of the:
'There was an error delivering your package' <insert fake UPS/Fedex' link here>. And it's usually all from the same branch of scammers!
Several ways you can tell that these are scams are:
Noting the area code that the text comes from.
+63, if you didn't know, is the area code for the Philippines, so that right there is a big red flag that this is 100% a scam.
Pay attention to how the URL is structured in the link.
Even though it has .gov in it, it is not a .gov website.
To give you a visual of how a URL is structured, here is an image from intezer.com from their article URL Analysis 101!
This graphic is used only for educational purposes only I do not take credit for it.

As they describe in their article:
Let’s quickly describe the different parts of the URL (see fig 1):
The protocol: describes the way a browser should retrieve information from a certain web source. What matters for us here is the distinction between HTTPS and HTTP which basically differ by being secure (or encrypted) and not secure. Another protocol to transfer files is FTP. The hostname: is made of the domain name and the subdomain name. The domain name consists of the second-level domain which is the name of your website and the top-level domain which specifies the type of website it is going to be, for example, .com is intended for commercial, .edu for educational and so on. The combination of the top-level and second-level domain is the only part that is unique in the URL and we can’t stress enough how important that is. The subdomain is like a specific “zone” inside your website. For example, you might have a URL like this: “your-organization.salesforce.com” which basically says salesforce has a sub-website for your organization. The path is basically like a path on your personal computer to a specific file. It indicates what resource you want to get from the website.
If you look at the scam link, rather than the .gov being at the end, it's inside the link, so it's part of the 2nd level domain rather than the actual top-level domain.
If a url isn't fedex.com or usps.com when you get a text about your package, and if you never got an email that said there was an issue with your order?
If you never went through a toll, had issues with your bank, your twitter account, cable/TV account, or anything of the like and got a text telling you to click a link?
Ignore the text, check your email, or call the bank/company.
But never, ever, reply to the text or click the links.
----
You also see this a lot in fake emails from scammers of all kinds, especially the paypal scammers where they will send you emails from accounts like:
paypal-service###@gmail.com or paypal-admin##@gmail.com.
The biggest giveaway? It's not from a @paypal.com domain.
It's from gmail.com, meaning it's from a person, not a company.
Remember to stay safe and don't get scammed. :)
-Bee
THIS IS A SCAM


This is specifically for Ohio, but applies elsewhere (I had a customer show me one they got allegedly from the Michigan DMV.):
THIS IS A SCAM.
Do not click on any links in the text or reply to it. Select “Report Junk” or whatever your phone’s equivalent is and move on.
Several ways you can tell:

1. The return phone number starts with a country code (in this case 63). Any phone number from a US source is likely to just start with the area code.

2. They mix up the use of BMV & DMV. Ohio has a BMV - Bureau of Motor Vehicles. They get the initials right at first, but call it the Department of Motor Vehicles immediately before. Then, later in the message, they call it the DMV again. (Above)

3. They try to hide the fake web address by using one that looks like it belongs to the .gov domain. [gov-tollbillr{….} .cyou.] Legitimate .gov links will end with .gov or .gov/ (examples: ohiobmv.gov or irs.gov/forms). This web address actually ends with .cyou.
4. Their own bullet point #4 makes no sense. What are they going to transfer to a toll booth? Are they going to magically send you there? And then charge you 35% to send you back? If they had that capability, they would be so rich they wouldn’t need to scam you out of your money! {They would probably be scamming you some other way.}

74 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discover the key differences between HTTP and FTP protocols in this comprehensive guide. Learn how they differ in function, and usage to get complete clarity.
#what is the difference between http and ftp#differentiate between http and ftp#What are the differences between FTP and HTTP?
0 notes
Text
Moon Missions
What’s going on with the moon?
The United States recently had a solar eclipse on April 8th, 2024, and some might be surprised to learn that the moon is, in fact, affected by solar radiation. The charged particles emitted by the sun, called the solar wind, reach the moon with no interruption from its atmosphere, as it has none. It also has no global magnetic field, another layer of protection that Earth does have, in comparison.
The moon does, however, have small areas of magnetic fields. We can see this because these areas remain lighter in photos whereas chemical reactions from radiation darken the unprotected areas.
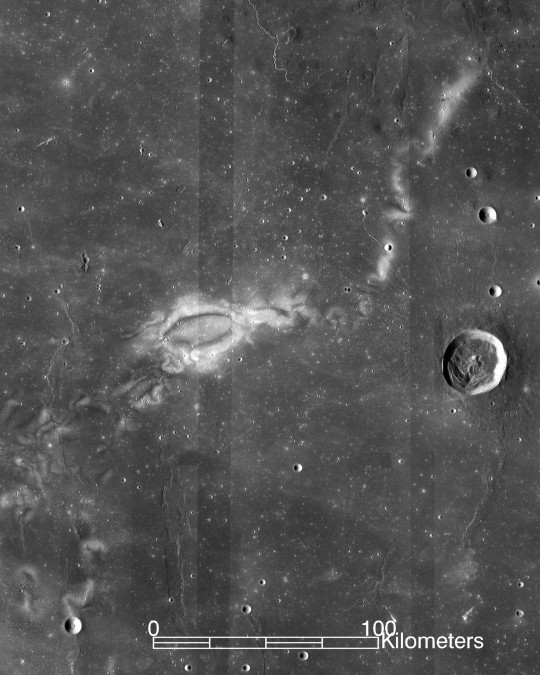
Fortunately, most of these charged particles cannot pass through the hulls of space stations, so astronauts are safe in orbit. Cosmic rays, made of stronger and faster-moving particles, are more dangerous. Even on Earth, under the atmosphere and magnetosphere, cosmic radiation reaches humans, though not enough to be considered damaging to our health.
A lander and rover launched in 2018 delivered the first measurements of radiation levels on the moon 4. Based on those data, astronauts on the moon can be exposed to up to 150 times higher radiation levels than on Earth.
Radiation is a leading reason for the pause in lunar landing missions. It raises risks of cataracts, heart diseases, radiation illness, cancer, and other ailments. Longer missions, of course, would heavily exacerbate these radiation doses.
Other Health Concerns
Cosmic rays contain High-Energy (HZE) ions. In different exposure such as from nuclear accidents or irradiation therapy, HZE ions have been found to cause dysregulation in the mitochondria and damage to DNA. Because of this, prolonged exposure is linked to health effects often associated with aging, such as hippocampus synapse loss and metabolic disruption caused by damage to mitochondrial DNA.
Long-duration space flights have also been linked to cardiovascular disorders. For astronauts on the Apollo missions, heart attack was “the second leading cause of death” 8. For additional space flights outside of Earth’s magnetosphere, astronauts also had a higher mortality rate due to cardiovascular diseases.
In a previous article, we discussed the relationship between circadian rhythms and health. These rhythms are another thing that space travel can impact, causing sleep and mental health disturbances in astronauts 9.
While various studies are investigating the conditions of these health risks, a current NASA mission is specifically investigating radiation protection.
Long-term Mission
NASA plans on eventually returning to human-manned missions to the moon.
First, they have to address the issues discussed above.
In November of 2022, Artemis I launched with two manikins bearing radiation detectors. From this mission, NASA was able to confirm the success of the intended trajectory, launch of ground systems, and the Orion spacecraft. The radiation results from this mission are still being analyzed.
The Artemis missions are intended to explore more of the moon than ever before, and lay groundwork for eventual missions to Mars.
Artemis II will not launch any earlier than September of 2025. It is planned to last ten days, consist of a 4-person crew, and be a lunar flyby to ensure the proper functioning of the spacecraft’s systems.
It has seemed for years that lunar exploration has halted. Manned missions have indeed been paused, for good reasons. Ensuring the safety of astronauts is a priority, and they face serious health risks even when missions go as expected. But NASA intends to continue exploring space, the moon, and Mars. The current Artemis missions are discovering improved, new ways to ensure the safety of astronauts while making scientific progress.
Additional Resources
1. https://science.nasa.gov/moon/solar-wind/
2. https://phys.org/news/2012-01-solar-flares-astronauts.html
3. https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1211/1211.3962.pdf
4. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11214-020-00725-3
5.https://www.nasa.gov/missions/artemis/orion/orion-passengers-on-artemis-i-to-test-radiation-vest-for-deep-space-missions/
6.https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/how-space-radiation-threatens-lunar-exploration-180981415/
7.https://www.nasa.gov/humans-in-space/analysis-confirms-successful-artemis-i-moon-mission-reviews-continue-2/
8.https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/physiology/articles/10.3389/fphys.2020.00955/full
9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9818606/
#radiation#moon#moon mission#nasa#nasa photos#article#research#solar wind#solar radiation#cosmic rays#cosmic radiation#space exploration#science#space#Work has been horribly busy so the next article might not be out on the usual schedule
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Different organizations and books have different views on what defines web services. Some of these are as follows. A web service is simply an XML-based information exchange system that employs the use of the Internet for direct communication. The systems used may be in the form of programs, messages, objects, or documents. A web service is a modular, self-contained, dynamic, and distributed software which can be described, located, published, or initiated over the network to create processes, products as well as supply chains. This software can be local, web-based or distributed. A web service is usually built with the help of unfastened standards like HTTP, HTML, TCP/IP, XML, and Java. What Is A Web Service? A web service is any service which: Is accessible on the Internet Employs the use of XML encoding for transferring information Are independent of programming languages Makes use of a common language Can be discovered through a simple mechanism The topic of web services require a lot more details that are covered in dedicated tutorials on this playlist we have compiled on Youtube. How Web Services Work Web services make communication possible through many applications by employing the use of open standards like XML, SOAP, HTML, and WSDL. They make use of: SOAP to send and receive messages. Learn more about SOAP Web Services on This YouTube tutorials Series about SOAP web services. WSDL to notify if the service is available. XML to mark the data This makes it possible for you to build Java-enabled web services on a Mac, which will be easily reached from the visual- basic program that runs on your windows. What Are the Benefits of Web Services? Making Use of Existing Functions on Networks Web services are managed codes that can be accessed and activated by making use of HTTP requests. A web service allows you to use the functionality of your code that already exists over the network. Once the function is exposed on the network, then there is a possibility of other programs making use of its functionality. Interoperability A web service makes it possible for different applications to communicate with each other and share services and data. Various software suites can also use web services. For instance, .NET or Java can communicate with a VB web services and the other way around. Web services ensure the independence of technology and application platforms. Reduced Communication Cost A web service makes use of SOAP rather than the HTTP protocol; therefore, you can employ the Internet to implement web services. This makes it much less costly when compared to other solutions such as EDI/B2B. Apart from the preference of SOAP over HTTP, it is possible to implement web services through other reliable transport mechanism such as FTP. Characteristics of Web Services Today, Web Services are independent applications that can be distributed, found, and fabricated on the Internet. Web Services offer a standard method for interoperability between various programming applications. eXtensible Markup Language (XML) gives the extensibility and dialect nonpartisanship that is the key for the interoperability of Web Services. They perform functions that can incorporate anything from basic inquiry results to complex business forms. Once a Web Service is sent, different applications can find and invoke it. At present, Web Services require human communication for recognizable proof and execution. Based on XML A web service employs the use of XML during data transportation as well as data representation. The use of XML removes the need for any operating system, networking or platform binding. This makes web services extremely interoperable applications at their core level. Loosely Tied A consumer using a web service is not tied directly to the web service. The interface of the web service can change with time without affecting the ability of the client to make use of the service. If the system were to be tightly coupled,
it means that the server logic and the client are both tied together, and a change in one requires a corresponding update on the other for smooth functioning. Using a loose system makes it easier to manage and gives room for simpler integration among various systems. Coarse-Grained Using object-oriented technologies such as C# release their services by making use of individual methods. Producing a C# program means that you have to create many fine-grained methods that are then integrated into a coarse-grained service used by a client or another service. The interfaces and the businesses that are released should be coarse-grained. Web services technology gives a natural way for coarse-grained services to apply the right amount of business logic. Supports Document Exchange Two major advantages of XML is representing data generically and also representing complex documents. These documents can be as simple as a current address and can also have the complexity of an entire book. The transparent exchange of documents is possible on web services that facilitate business integration. Technology for Web Services Service Discovery A program should first have the capacity to naturally discover, or find, a suitable Web service. Neither one of the Web Service Description Language (WSDL) nor Universal Discovery and Description dialect (UDDI) takes into account programming to figure out what a Web service offers to the customer. Execution Software must have the capacity to consequently decide how to summon or execute the service. For instance, if executing the task is a multi-step technique, the product has to know how to collaborate to finish the vital arrangement Composition Software must have the capacity to choose and consolidate various Web services to complete a specific goal. The services need to interoperate with each other flawlessly so that the consolidated outcomes are legitimate. Monitoring Agent programming should have the capacity to confirm and screen the services’ properties while in operation. Resources https://www.w3.org/TR/soap/ https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms996486.aspx http://www.xmlfiles.com/xml/
0 notes
Text
Understanding SOCKS5 Proxies
Understanding SOCKS5 Proxies: A Comprehensive Guide In the realm of internet security and privacy, SOCKS5 proxies stand out as a versatile and powerful tool. But what exactly is a SOCKS5 proxy, and how does it work? This article will delve into the intricacies of SOCKS5 proxies, their benefits, and their applications.To get more news about socks5, you can visit pyproxy.com official website.
What is a SOCKS5 Proxy? SOCKS5, short for Socket Secure version 5, is a protocol that routes network packets between a client and a server through a proxy server. Unlike its predecessors, SOCKS5 offers enhanced security and performance, making it a popular choice for various applications.
How Does a SOCKS5 Proxy Work? A SOCKS5 proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you send a request to access a website, the request is first sent to the SOCKS5 proxy server. The proxy server then forwards the request to the web server. The web server processes the request and sends the data back to the proxy server, which then forwards it to your device. This process helps to mask your IP address, providing an additional layer of privacy and security.
Benefits of Using a SOCKS5 Proxy Using a SOCKS5 proxy offers several advantages:
Enhanced Security: SOCKS5 proxies provide a higher level of security by masking your IP address and encrypting your data. This makes it difficult for hackers to intercept your online activities. Improved Performance: SOCKS5 proxies are known for their speed and reliability. They can handle a wide range of traffic types, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and even torrent traffic. Bypass Geo-Restrictions: SOCKS5 proxies can help you access content that is restricted in your region. By routing your traffic through a proxy server located in a different country, you can bypass geo-blocks and access the content you want. Anonymity: By masking your IP address, SOCKS5 proxies help to keep your online activities anonymous. This is particularly useful if you are concerned about privacy and want to avoid being tracked by websites and advertisers. Applications of SOCKS5 Proxies SOCKS5 proxies are used in various scenarios, including:
Online Privacy: Many users employ SOCKS5 proxies to maintain their anonymity online. By routing their traffic through a proxy server, they can hide their original IP address and avoid being tracked. Bypassing Network Restrictions: In some cases, schools, workplaces, or public networks may block access to certain websites. A SOCKS5 proxy can help you bypass these restrictions and access the content you need. Secure File Transfers: In corporate environments, SOCKS5 proxies are often used for secure file transfers. They can handle different protocols and provide a secure, authenticated connection, making them ideal for transferring sensitive data. Streaming and Gaming: SOCKS5 proxies are also popular among streamers and gamers. They can handle high-speed connections and reduce latency, providing a smoother streaming and gaming experience. How to Set Up a SOCKS5 Proxy Setting up a SOCKS5 proxy is relatively straightforward. Here are the steps to follow:
Choose a Reliable Proxy Service: There are many SOCKS5 proxy services available, both free and paid. Some popular options include ProxySite, HideMyAss, and Hide.me1. When choosing a proxy service, consider factors such as speed, reliability, and privacy features. Configure Your Device: Once you have chosen a proxy service, you will need to configure your device to use the proxy. This typically involves entering the proxy server’s IP address and port number in your device’s network settings. Detailed instructions can usually be found on the proxy service’s website. Start Browsing: After configuring your device, you can start using the SOCKS5 proxy to browse the internet. Simply open your web browser and navigate to the websites you want to access. The proxy server will route your requests, providing enhanced security and privacy. Conclusion SOCKS5 proxies are a powerful tool for enhancing online security, privacy, and performance. By acting as intermediaries between your device and the internet, they help to mask your IP address, protect your data, and provide access to restricted content. Whether you are an individual looking to safeguard your online activities or a business aiming to improve network performance, SOCKS5 proxies offer a valuable solution.
0 notes
Text
What types of network security Questions asked in Interview?
With the ever-growing dependence on computerized data, network security experts are in high demand. But before you get your dream job in your dream company, you will have to be a pro to face the interview round. This web journal post will help you understand a vital aspect of network security interview questions for freshers: The questions you might be asked. We'll find distinctive categories of network security interview questions, centring particularly on those asked from freshers ( candidates with little to no experience).
By understanding these interview questions and brushing up on your core concepts, you will be well on your way to impressing your interviewer and securing the perfect network security job opportunity.

Network Security Basics ( Fresher Level)
Let's begin with the building blocks. These network security interview questions are for freshers to assess their skills and abilities on the basics of network security:
what could be a network? A network may be a collection of interconnected gadgets that can share assets and communicate with each other. It can be small connections of devices at your home (LAN) or a larger network just like the web (WAN).
What is the distinction between a LAN, WAN and MAN? LAN (Local Area Network) covers a small geographical range like a domestic or office. WAN (Wide Area Network) ranges a bigger range, interfacing geologically removed areas. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) Covers a particular metropolitan range, regularly interfacing numerous LANs within a city.
What may be a convention? A convention could be a set of rules that oversees communication between gadgets on a network. Common conventions incorporate TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Convention), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and FTP (File Transfer Protocol).
What is the CIA triad in Network Security? CIA stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These are the three central standards of network security:
Confidentiality: Guaranteeing as it was authorized clients can get to sensitive data.
Integrity: Ensuring information remains precise and unaltered amid transmission and capacity.
Availability: Ensuring authorized clients can access information and assets when required.
Network Security Danger and Vulnerabilities (Fresher Level)
Now, let's dig more profound into the challenges you'll confront. These questions gage your awareness of common dangers and vulnerabilities that comprise network security:
What could be a security risk? A security risk is a potential risk of misusing a vulnerable in an arrangement, causing harm.
What is the distinction between risk and vulnerabilities? A risk may be a pernicious on-screen character or occasion that can exploit a vulnerability. A vulnerability may be a weakness in a framework that can be misused by a danger.
Can you title a few common network security dangers? Cases incorporate malware (viruses, worms, and Trojan horses), phishing assaults, denial-of-service (DOS) attacks, and man-in-the-middle (MitM) assaults.
What could be a firewall? A firewall could be a security framework that can screen approaching and actively organize activity, permitting authorized activity and blocking suspicious action.
Network Security Apparatuses and Innovations (Freshers Level)
The battle against cyber dangers requires solid abilities. These questions test your recognition with basic network security tools:
What is the purpose of the antivirus computer program? They look for and prevent infections created by malware viruses and any other malicious software.
What is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)? This is a secure network communication channel established on the basis of someone's internet connections, to keep off intruders.
How is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) different from an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)? This detail highlights that, whereas one is able to identify doubtful actions within certain networks, the other is capable of externally preventing any such moves as well.
Scenario-Based Network Security Questions (Fresher Level)
The interviewer may show speculative scenarios to check your problem-solving skills and approach to network security challenges:
You suspect a malware infection on a company computer. What steps would you take? Your answer should showcase a systematic approach, including isolating the infectious computer, running antivirus checks, reporting the incident, and potentially seeking proficient offer assistance.
A client reported website looked suspicious when attempting to get a company's assets. How would you handle this situation? To show that you know about phishing attacks, you could say something like making sure that it is legitimate before you visit or informing him of possible tricks for him not to share any important details.
Showcasing Your Interest:
Plan quick questions: Do not just reply to network security interview questions, inquire thoughtful ones approximately the company's security posture, current challenges, or future ventures. This shows veritable intrigued and initiative.
Highlight your Learning Potential: Express your eagerness to learn advanced technologies and stay updated on advancing dangers.
showcase your passion: Talk about any projects or certifications that you have dome personally in relation to network security.
0 notes
Text
What's the difference between TCP and UDP? Take you to understand network protocols in seconds!
TCP and UDP are two very important transport layer protocols in network communication. Although they are both used to transfer data in the network, their working methods and application scenarios are very different. The following is a detailed analysis of the differences between TCP and UDP, as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages.

1. Transmission
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, which means that before sending data, the two sides need to establish a reliable connection. tcp will segment the data during transmission, and each packet arrives at the target location in order. If a packet is lost during transmission, TCP automatically retransmits the packet until it is received by the target device.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
UDP is a connectionless protocol that does not establish a connection or perform packet acknowledgments. Data is sent in separate datagrams, which may not be received in the same order as sent by the receiver, and packets are not automatically retransmitted after they are lost. This makes UDP transmission more efficient but less reliable.
2. Reliability
TCP: High Reliability
TCP establishes a connection through three handshakes and uses an acknowledgement mechanism and flow control during data transmission to ensure reliable data transmission. If data is lost or an error occurs, TCP will retransmit it. This reliability makes TCP widely used in scenarios that require high-precision data transfer, such as file transfer, email services, web browsing, etc.
UDP: Less Reliable
UDP does not provide packet acknowledgement and retransmission mechanism, so the data transmission is faster but less reliable. If the network quality is not good, UDP may suffer from data loss, duplication or disorder. Therefore, UDP is mostly used in applications that require high real-time performance but lower data integrity, such as live video streaming, online games, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), etc.
3. Speed and efficiency
TCP: Slower but stable
Since TCP requires connection establishment and packet acknowledgement, the transmission speed is relatively slow. However, this slowness is exchanged for a stable and reliable transmission, which is especially suitable for applications that require complete data transmission.
UDP: Fast, but unstable
UDP has no connection establishment and confirmation mechanism, so the data transmission speed is very fast. However, because of this, it is less stable and less reliable, and is suitable for scenarios that do not require 100% accuracy of data, but require a quick response.
4. Application Scenarios
TCP: Suitable for scenarios that require reliable data transmission, such as file transfer (FTP), mail transfer (SMTP), web browsing (HTTP/HTTPS), etc.
UDP: Suitable for scenarios that require high speed and allow partial data loss, such as video streaming (live), online games, VoIP, etc.
TCP and UDP have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different application scenarios. If you are building a network application, choose the appropriate transport protocol according to the actual needs.711Proxy can provide you with high-quality proxy IP services in multiple nodes around the world, ensuring you a smooth flow in any network environment.
0 notes
Text
Bridge Creative Multi-Purpose WordPress Theme v30.6.1
https://themesfores.com/product/bridge-creative-multi-purpose-wordpress-theme/ Bridge Creative Multi-Purpose WordPress Theme v30.6.1 BRIDGE is a responsive retina multipurpose WordPress theme perfect for just about anyone. Whether you are a creative, a corporate team, a lawyer, a medical doctor, or a freelancer looking for a modern portfolio website or a personal blog, Bridge is your best option. Bridge Feature 500+ Unique Demos – You’ll find what you need in one of our fully equipped demos, whether you’re in search of a blog, a business website, or even something as specific as an online store for your pet shop. Easy to import and highly customizable, we created the Bridge Demos to make your life easier. 24 Layout Concepts – Explore all Bridge possibilities with 24 new layout concepts – ranging from standard site layouts to authentic and innovative designs. You’re certain to find the perfect solution for your perfect website within our collection of creative concepts. Qode Video Tutorials – Get started with Bridge even faster! Visit the official Qode Interactive YouTube channel to check out our comrehensive step-by-step video tutorials. NEW Full Listing Functionality – Bridge now comes with a fully functional listing plugin that lets you create listing and directory websites. The plugin includes a new Listing post type, a variety of shortcodes for displaying your listings, and much more. NEW Full News Functionality – Create your News website with Bridge. Thanks to the awesome News plugin, Bridge now comes with a variety of shortcodes specifically designed for displaying posts in beautiful news and magazine style layouts. NEW Full Restaurant Functionality – The Bridge Restaurant plugin lets you create a beautiful and fully functional presentation for your restaurant or cafe. Create a reastaurant menu, display your working hours, let clients book tables by connecting your website with your OpenTable account, and much more. NEW Front-End Login Functionality – Let your website users create their own accounts or login via their social network profiles with the all-new Membership plugin for Bridge. Qode Slider – Amazing responsive full-screen image & video slider with parallax and the option to choose between full responsiveness and a fixed / responsive height. With fade in/out elements animations, and slide/fade transitions. Also, for each slide you can choose if the header should be dark or light, set different positions for the graphic and text, choose different animation for the graphic (flip or fade), fully control the titles and texts (size, color, fonts, line-height, weight, shadow), set custom color for the navigation, set an overlay pattern image for video… Easy-To-Use Powerful Admin Interface – BRIDGE comes with an extremely intuitive, easy-to-use admin interface. Add unlimited sliders and slides while you are editing pages/posts/portfolios, add unlimited portfolio images or videos while editing your portfolio items, add unlimited parallax sections to any page, customize typography styles, upload multiple logo versions, and much more. Take complete control over your website. Auto Update – Sick of manually updating your WordPress theme via FTP? We’ve made sure you won’t have to ever again. Update BRIDGE with the click of a button using the Envato Toolkit. YITH WooCommerce Quick View & YITH WooCommerce Wishlist plugin compatibility – Thanks to the YITH WooCommerce Quick View the website visitors can easily check out the offered items and view product details with just a single mouse click. YITH WooCommerce Wishlist, on the other hand, enables them to check the product availability and to add items to their wishlist. New Quick Links Custom Post Type – Make all your latest news and essential updates easily accessible at all times with the Quick Links functionality. Fully Customizable Headers – Choose between top and side positions for your header. The collection of 10 separate header types, each with its own set of options, is sure to satisfy your every need. Each page can have it’s own custom header with a dark or light skin, and a different color and transparency. Define styles for your menus, and turn on a Side Area, Search functionality, Header Top, and Fullscreen Menu with the click of a button. Fully Customizable Title Area – Choose between a responsive title image, parallax title image, zoom in/out title image and no image. Show or hide each title area. Choose the position of the title text. Choose different types of animations: animate the text, animate the whole title area or no animation. Choose colors, separators & much more. Apply those settings on a global or page specific level. Fully Customizable Mega Menu – Customize both the standard and mobile menu, create wide or normal sub-menus at the same time, choose wide menu layout with or without icons. Add widgets to one of the columns of the wide menu and create any layout you want. Create awesome one-page web sites using anchors in the menu. Left Menu – Choose a left menu instead of the top header and create beautiful portfolio websites. View an example of a left menu website by clicking on Live Preview. You can make it transparent (text will have dark/light skin variations on each slide change). You can choose a background image to fit the whole Left Menu area. All of that on a global or per page level. Fullscreen Menu – Easily enable the beautiful Fullscreen Menu which opens when you click on the 3-bar (hamburger) icon in the header (if enabled). You can also upload a separate logo version to appear in the full screen menu. Section Video Background – Add full width video backgrounds to sections and set different pattern images for each section. Fixed Header – You can set header to be fixed, and set it to shrink on page scroll. Sticky Header – You can set header to be sticky and control the scroll amount (relative to the top of the page) at which the sticky header will appear. If there is a slider on the page, then the height of the slider is the default “scroll amount” for the appearance of the sticky header. Sticky Header With Menu On Bottom – Same as the sticky header, the only difference is that the menu is on the bottom of the header with a different layout https://themesfores.com/product/bridge-creative-multi-purpose-wordpress-theme/ #Multi-PurposeThemes #WordpressTheme
0 notes
Text
Dell Boomi Basic Interview Questions

Title: Ace Your Dell Boomi Interview: A Guide to Basic Questions
Introduction
Dell Boomi is a market-leading iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) solution known for its flexibility, scalability, and ease of use in cloud-based integration. As its popularity grows, so does the demand for skilled Boomi developers. If interviewing for a Dell Boomi role, you must be prepared for questions designed to assess your foundational knowledge. Let’s dive into some common basic questions.
Key Concepts
What is Dell Boomi?
Be ready to define concisely: “Dell Boomi is a cloud-based integration platform that enables businesses to connect various applications, data sources, and systems seamlessly within both cloud-based and on-premises environments.”
Components of a Boomi Process
Understand the core building blocks of integration flows in Boomi:
Start Shape: Initiates the process.
Connectors: Facilitate communication with specific applications or systems.
Maps: Define how data is transformed between systems.
Shapes: Represent actions like data manipulation, decision-making, routing, and error handling.
What is an Atom?
Explain its role: “An Atom is the lightweight runtime engine of Dell Boomi. It’s responsible for executing integration processes. Atoms can be installed on-premises or in a private cloud.”
Differences between Atom, Molecule, and Atom Cloud
Atom: A single runtime engine suitable for more minor integrations.
Molecule: A Atoms cluster designed for higher data volumes and scalability.
Atom Cloud: A collection of atoms or molecules with high availability and fault tolerance.
What are Connectors?
Describe their purpose: “Connectors are pre-built components in Boomi that simplify connections to popular applications and technologies (e.g., Salesforce, SAP, NetSuite, databases, FTP, HTTP). They streamline integration by handling the complexities of communication protocols and authentication.”
Technical Questions
Error Handling in Boomi
Demonstrate your understanding of error management by Discussing approaches like try/catch blocks, exception shapes, process reporting, and notifications.
Data Mapping
Explain how you would structure a map to transform data from one format to another. Be prepared to discuss essential transformation functions.
Boomi Process Deployment
Outline the steps in deploying a process from a development to a production environment.
General Cloud Concepts
Benefits of Cloud Integration
Highlight advantages like cost-effectiveness, scalability, reduced IT overhead, accessibility, and faster updates.
Cloud Security
Address potential concerns and discuss measures cloud providers and Boomi employ to ensure data protection during integration.
Tips
Showcase Practical Knowledge: Cite examples from your past projects to solidify your answers.
Project Enthusiasm: Demonstrate your passion for integration and problem-solving with Boomi.
Be Prepared for Non-Technical Questions: These assess your communication, teamwork, and adaptability skills.
Conclusion
Mastering these basic concepts lays a solid foundation for your Dell Boomi interview. While companies may have specific technical questions, understanding these fundamentals will boost your confidence and position you for success.
youtube
You can find more information about Dell Boomi in this Dell Boomi Link
Conclusion:
Unogeeks is the No.1 IT Training Institute for Dell Boomi Training. Anyone Disagree? Please drop in a comment
You can check out our other latest blogs on Dell Boomi here – Dell Boomi Blogs
You can check out our Best In Class Dell Boomi Details here – Dell Boomi Training
Follow & Connect with us:
———————————-
For Training inquiries:
Call/Whatsapp: +91 73960 33555
Mail us at: [email protected]
Our Website ➜ https://unogeeks.com
Follow us:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/unogeeks
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/UnogeeksSoftwareTrainingInstitute
Twitter: https://twitter.com/unogeek
0 notes
Text
does vpn require port forwarding
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does vpn require port forwarding
VPN basics
Understanding the Basics of VPN
In an age where online privacy and security are paramount, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as indispensable tools for internet users worldwide. But what exactly is a VPN, and how does it work?
At its core, a VPN is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, typically the internet. This encrypted connection is established by routing your internet traffic through a server operated by the VPN provider. As a result, your data becomes virtually unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept it, whether it's hackers, government agencies, or even your internet service provider (ISP).
One of the primary purposes of using a VPN is to protect your online privacy. By encrypting your internet traffic and masking your IP address, a VPN shields your online activities from prying eyes. This means that your browsing history, online communications, and sensitive information remain confidential and inaccessible to third parties.
Moreover, VPNs enable users to bypass geo-restrictions and censorship. By connecting to a server in a different location, you can access content and websites that may be blocked or restricted in your current location. This is particularly useful for accessing streaming services, social media platforms, and websites that are otherwise unavailable in certain regions.
Additionally, VPNs enhance security when using public Wi-Fi networks. These networks are notorious for their vulnerability to cyber attacks and data breaches. However, by encrypting your connection, a VPN ensures that your data remains secure, even when connected to unsecured Wi-Fi hotspots.
In summary, VPNs offer a myriad of benefits, including enhanced privacy, security, and accessibility. Whether you're concerned about safeguarding your personal information or accessing restricted content, using a VPN can provide peace of mind and empower you to navigate the internet safely and freely.
Port forwarding explanation
Port forwarding is a crucial concept in networking that allows devices on a local network to communicate with services running on a remote network or the internet. Essentially, it enables incoming connections to reach a specific port or service on a device within a private local network.
Here’s how it works: When a device on the internet initiates a connection to a specific port on your router's public IP address, the router receives the connection request. However, without port forwarding configured, the router doesn't know which device on the local network should handle the incoming connection. Port forwarding solves this issue by instructing the router to forward incoming traffic on a specific port to a designated device on the local network.
For instance, if you have a web server running on a computer within your home network, you can set up port forwarding to route incoming HTTP (port 80) or HTTPS (port 443) traffic to that server. This allows users from outside your network to access your website.
Port forwarding is commonly used for online gaming, remote desktop connections, file sharing, and hosting services such as websites, FTP, and email servers.
It's essential to configure port forwarding properly to ensure security and efficient network communication. Incorrectly configured port forwarding can expose your devices to security risks, such as unauthorized access or attacks.
In conclusion, port forwarding plays a vital role in enabling external access to services hosted on devices within a private network. By directing incoming traffic to the appropriate devices, it facilitates seamless communication between devices on different networks. However, it's crucial to implement port forwarding with caution to mitigate security risks.
VPN without port forwarding
A VPN without port forwarding is a solution that prioritizes privacy and security over the ability to host services or access certain applications that require port forwarding.
Port forwarding is a technique used to allow external devices to connect to specific services or applications within a private network. It's commonly used for activities like online gaming, file sharing, or running server applications. However, port forwarding can also pose security risks by exposing specific ports to potential vulnerabilities or attacks from malicious actors.
By opting for a VPN without port forwarding capabilities, users can enjoy enhanced security and anonymity while browsing the internet or accessing online services. Without port forwarding, the VPN server acts as a middleman between the user and the internet, encrypting all data traffic and hiding the user's IP address. This ensures that online activities remain private and protected from prying eyes, such as ISPs, government surveillance, or hackers.
While some users may miss the convenience of port forwarding for specific applications, the trade-off for increased privacy and security is often worth it. Additionally, there are alternative methods available for accessing certain services without port forwarding, such as utilizing VPN-compatible applications or services that don't require direct inbound connections.
Ultimately, the decision to use a VPN without port forwarding depends on individual preferences and priorities. For those who prioritize privacy and security above all else, a VPN without port forwarding can provide peace of mind knowing that their online activities are shielded from potential threats.
VPN with port forwarding
Title: Unlocking the Potential of VPN with Port Forwarding
In the world of cybersecurity and online privacy, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become essential tools for safeguarding our digital footprints. However, while traditional VPNs offer anonymity and encryption, they often lack the ability to support certain applications and services that require port forwarding. This is where VPNs with port forwarding capabilities come into play, offering a solution that combines security with versatility.
Port forwarding is a networking technique that allows devices within a private network to access resources outside the network, such as servers or applications, by opening specific ports and forwarding incoming traffic to designated destinations. Typically, this feature is not available in standard VPN configurations due to security concerns. However, VPNs with port forwarding functionality address this limitation by providing users with the ability to selectively open ports and redirect traffic through the VPN server.
The benefits of using a VPN with port forwarding are manifold. Firstly, it enables users to access services that are typically blocked or restricted when using a standard VPN connection. This includes online gaming, peer-to-peer file sharing, and accessing home security cameras or NAS devices remotely. Additionally, port forwarding can improve connection speeds and reduce latency for certain applications by optimizing the routing of data packets.
From a security standpoint, VPNs with port forwarding maintain the same level of encryption and anonymity as traditional VPNs, ensuring that user data remains protected from prying eyes and potential cyber threats. However, it's essential for users to exercise caution when configuring port forwarding rules, as opening unnecessary ports can expose their devices to vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, VPNs with port forwarding offer a powerful combination of security and flexibility, allowing users to enjoy the benefits of a VPN while still being able to access a wide range of online services and applications. By understanding how to leverage port forwarding effectively, individuals can maximize the utility of their VPN and enhance their online experience.
Benefits of port forwarding
Port forwarding is a crucial networking technique that offers several benefits for both individuals and businesses. By enabling port forwarding on a router or firewall, users can direct incoming traffic from specific ports to designated devices or services within a private network. Here are some key advantages of port forwarding:
Improved Remote Access: Port forwarding allows users to access devices or services within their network from remote locations. For example, it enables employees to connect to their office computers or servers securely from outside the office network, facilitating remote work and increasing productivity.
Enhanced Gaming Experience: Gamers often utilize port forwarding to optimize their gaming experience. By opening specific ports required by online gaming services, players can reduce latency, minimize connection issues, and enjoy smoother gameplay.
Efficient File Sharing: Port forwarding facilitates efficient file sharing within a network. Users can set up file servers or peer-to-peer file sharing applications and configure port forwarding to allow external users to access shared files securely.
Seamless Hosting of Services: Businesses can host various services such as websites, email servers, or video conferencing platforms internally while still making them accessible to external users. Port forwarding enables organizations to run these services securely without exposing the entire network to external threats.
Optimized IoT Device Connectivity: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, port forwarding becomes essential for managing and accessing smart devices remotely. Whether it's controlling home automation systems or monitoring security cameras, port forwarding ensures seamless connectivity and control.
Customized Network Configuration: Port forwarding provides users with greater control over their network traffic. By selectively forwarding ports, users can prioritize specific applications or services, optimize bandwidth usage, and enhance network security by restricting access to sensitive resources.
In conclusion, port forwarding offers a wide range of benefits, including improved remote access, enhanced gaming experiences, efficient file sharing, seamless hosting of services, optimized IoT device connectivity, and customized network configuration. By implementing port forwarding effectively, users can maximize the utility and security of their networks.
0 notes
Text
does a vpn help port forwarding
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does a vpn help port forwarding
VPN and Port Forwarding
VPN and Port Forwarding are two essential tools that serve different purposes when it comes to internet security and network management. Let's delve into each of these technologies and understand their significance.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a service that allows users to create a secure connection to another network over the internet. By using encryption and other security features, VPNs ensure that all data transmitted between the user's device and the VPN server is protected from prying eyes. This is especially crucial when accessing public Wi-Fi networks or when looking to maintain privacy and anonymity online. VPNs are commonly used by individuals, businesses, and organizations to safeguard sensitive information and shield their online activities from surveillance and hacking attempts.
On the other hand, Port Forwarding is a technique used to direct internet traffic from a specific port or range of ports to a particular device or service within a private network. This enables external users to access services hosted on devices behind a router or firewall. Port Forwarding is commonly used for online gaming, remote access applications, and hosting websites or servers from home. While Port Forwarding can enhance connectivity and accessibility, it also poses security risks if not configured correctly. Opening ports indiscriminately can expose devices to potential cyber threats and attacks.
In conclusion, VPNs and Port Forwarding play distinct yet vital roles in ensuring online security and network efficiency. By leveraging these technologies effectively and understanding their strengths and limitations, users can navigate the digital landscape with confidence and peace of mind.
VPN Tunneling and Port Forwarding
VPN tunneling and port forwarding are two essential concepts in the world of online privacy and security. Let's delve deeper into what they are and how they work to protect your data and enhance your browsing experience.
VPN tunneling is a technique used to create a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. When you connect to a VPN server, your data is encapsulated and encrypted before being transmitted through the tunnel. This ensures that your online activities, such as browsing history, online transactions, and personal information, are protected from prying eyes and potential cyber threats.
Port forwarding, on the other hand, is a method that allows you to direct incoming internet traffic to a specific device or service within a private network. By forwarding specific ports through your router, you can access devices remotely, host online gaming sessions, or set up secure connections for services like FTP and HTTP servers.
Combining VPN tunneling and port forwarding can further enhance your online security and accessibility. By using a VPN with port forwarding capabilities, you can encrypt your data while also accessing specific services or devices within your network from anywhere in the world. This combination is particularly useful for remote workers, online gamers, and individuals who prioritize privacy and security in their online activities.
In conclusion, VPN tunneling and port forwarding play crucial roles in safeguarding your online privacy and improving your internet experience. Whether you're looking to protect your data from cyber threats or access devices remotely, understanding these concepts can help you make informed decisions about your online security practices. Stay safe, stay secure, and enjoy the benefits of a more private and unrestricted internet experience with VPN tunneling and port forwarding.
Benefits of Using VPN for Port Forwarding
Using a VPN for port forwarding can significantly enhance your online experience and provide various benefits. Port forwarding allows internet traffic to bypass a router and access specific devices or services within a private network. When combined with a VPN (Virtual Private Network), it adds an extra layer of security and functionality. Here are some key advantages of utilizing a VPN for port forwarding:
Enhanced Security: By using a VPN, all your internet traffic is encrypted, making it extremely difficult for hackers or malicious entities to intercept your data. When port forwarding is implemented through a VPN, it ensures that the forwarded ports remain secure, protecting your devices and network from potential threats.
Access to Restricted Content: Some services or applications may be restricted based on your geographical location or network settings. By port forwarding through a VPN server located in a different region, you can bypass these restrictions and access content that may otherwise be unavailable in your area.
Improved Privacy: VPNs mask your IP address and provide anonymity online. When port forwarding is utilized within a VPN environment, it adds an extra layer of privacy by concealing the origin of the forwarded traffic. This helps in preserving your online identity and activities from being tracked by third parties.
Remote Access: Port forwarding through a VPN enables you to access devices or services within your home network remotely. Whether you need to access files on your home computer or manage IoT devices, utilizing port forwarding over a VPN connection allows for secure and convenient remote access from anywhere in the world.
Secure File Sharing: With port forwarding via VPN, you can securely share files or host services such as FTP servers without exposing them to the open internet. The encrypted connection provided by the VPN ensures that your data remains protected during transmission, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
In conclusion, using a VPN for port forwarding offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security, access to restricted content, improved privacy, remote access capabilities, and secure file sharing. Whether for personal or business use, implementing port forwarding through a VPN adds an extra layer of functionality and protection to your online activities.
VPN and Network Configuration for Port Forwarding
VPN (Virtual Private Network) services offer a secure way to protect your online privacy and security by encrypting your internet connection. While VPNs are commonly used to bypass geo-restrictions and ensure anonymity, they can also be utilized for network configuration, particularly for port forwarding.
Port forwarding is a technique used to direct internet traffic coming into a specific port of a device to another port on a different device. This is often necessary for online gaming, setting up a home server, or accessing devices remotely. However, configuring port forwarding can be tricky due to security concerns and potential vulnerabilities.
Using a VPN for port forwarding can enhance security and privacy by encrypting the data traffic before it reaches the forwarded ports. This adds an extra layer of protection against potential cyber threats and unauthorized access to your network. Additionally, a VPN can help you bypass any restrictions set by your internet service provider (ISP) that may block certain ports.
When setting up port forwarding with a VPN, ensure that the VPN provider supports this feature and offers dedicated servers for port forwarding. It is essential to follow the VPN provider's guidelines and recommendations to configure port forwarding correctly without compromising security.
In conclusion, combining VPN services with network configuration for port forwarding can provide an added layer of security and privacy for your online activities. By following best practices and choosing a reliable VPN provider, you can enjoy the benefits of port forwarding while keeping your network safe from potential threats.
VPN vs
VPN vs. Proxy: Understanding the Difference
In the realm of online privacy and security, both VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and proxies play crucial roles. However, they serve distinct purposes and offer varying levels of protection. Understanding the differences between the two is essential for choosing the right solution for your needs.
A VPN establishes a secure and encrypted connection between your device and the internet through a remote server operated by the VPN provider. This encryption ensures that your online activities remain private and protected from prying eyes, such as hackers, government surveillance, or even your internet service provider (ISP). Additionally, VPNs can mask your IP address, making it appear as though you're accessing the internet from a different location, thus bypassing geo-restrictions on content.
On the other hand, a proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. It reroutes your internet traffic through a server, which can be located anywhere in the world. Proxies can provide some level of anonymity by hiding your IP address, but they typically lack the encryption and security features offered by VPNs. Proxies are often used for specific purposes, such as accessing region-locked content or bypassing network restrictions in workplaces or schools.
When comparing VPNs and proxies, it's crucial to consider your priorities. If your primary concern is privacy and security, a VPN is the superior choice due to its encryption capabilities. However, if you're solely looking to mask your IP address or bypass geo-blocks, a proxy may suffice.
In conclusion, while both VPNs and proxies offer ways to enhance online privacy and access restricted content, they serve different purposes and provide varying levels of security. Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs and priorities.
0 notes
Text
How to make curl request in Magento 2?

Making curl HTTP requests is typical for API integrations, data retrieval, and external service communication tasks. cURL, which stands for Client URL, is a versatile command-line tool for making HTTP requests. This guide will delve into cURL and provide a step-by-step walkthrough on creating cURL requests in Magento 2.
What is curl?
cURL is a multifaceted command-line tool and library designed to help streamline data transfer across URLs. Developers can utilize this resource for web-based projects as it handles many protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, and LDAP. Its intuitive interface makes it effortless to interact with web services, making it an indispensable tool for any developer.
Why use curl in magento 2?
API Integration:
Magento 2 provides a robust API framework for third-party services or external systems integration. cURL is frequently employed to interact with these APIs, allowing developers to send requests, retrieve data, and synchronize information between Magento and other platforms.
Data Retrieval:
Developers often use cURL to retrieve data from external sources, such as fetching product information, inventory details, or customer data from remote systems. This is particularly useful for maintaining consistent and up-to-date information across different platforms.
Web Service Communication:
Magento 2 may need to communicate with various web services, and cURL is a versatile tool for handling HTTP requests. This can include interacting with payment gateways, shipping carriers, or other external services that play a role in the eCommerce ecosystem.
Custom Module Development:
When developing custom modules or extensions in Magento 2, developers may use cURL to communicate with external APIs or services. This allows for creating feature-rich and integrated solutions that go beyond the core functionalities of Magento.
Automated Tasks:
cURL commands can be integrated into scripts and automated tasks to perform specific actions, such as data synchronization, batch processing, or any other study involving web services.
Testing and Debugging:
CURL is valuable for debugging and troubleshooting during the development and testing phases. Developers can simulate requests to APIs or services to observe responses, diagnose issues, and ensure the proper functioning of their integrations.
Headless Commerce:
In scenarios where Magento is part of a headless commerce architecture, cURL can communicate between the front end (possibly built using a different technology or framework) and the Magento 2 backend. The system enables smooth communication and coordination among other components, facilitating seamless interactions.
CRON Jobs:
Magento 2 relies on CRON jobs for scheduling and executing tasks at predefined intervals. cURL can be used within these CRON jobs to trigger specific actions, perform periodic updates, or complete tasks that require communication with external services.
How to Create a cURL Request in Magento 2?
This guide will provide clear and concise examples for performing HTTP requests. Learn how to easily retrieve data using a GET request and submit information with custom headers using the POST method, using the versatile cURL tool.
Follow the Step-by-Step Guide and Create a cURL: cURL Request
Curl is a powerful tool used for various purposes in Magento 2. For example, you can import and export data, retrieve product information, create orders, and more. With its versatility and ease of use, curl is an excellent tool for developers to interact with Magento 2’s API and streamline their development process.
Magento 2 development cURL shows up as smooth connectivity and dynamic data integration. From simple GET requests to handling complex transactions, cURL’s versatility shines through. With its capacity to support various protocols and APIs, Magento 2 development cURL provides developers with a powerful tool for secure data exchange. Its flexibility allows for the reliable handling of data transfers, making it essential to creating robust and dynamic e-commerce solutions.
The Elightwalk team is an expert in Magento 2 development and can provide customized solutions tailored to your firm’s needs. Hire the best team for your e-commerce project and make it a success.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Choose the Right Proxy Server for Your Needs

Introduction
Choosing the right proxy server is crucial for individuals and businesses seeking enhanced online privacy, access to geo-restricted content, or improved security. With a wide range of proxy options available, it can be challenging to determine which one best suits your needs. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right proxy server, considering factors such as proxy type, location, reliability, speed, and compatibility.
Understanding Proxy Servers
What are Proxy Servers? Proxy servers act as intermediaries between users and the internet, allowing users to mask their IP addresses and route their internet traffic through a different server. Proxies provide various benefits, including enhanced privacy, bypassing censorship, and accessing restricted content.
Proxy Types: There are different types of proxy servers, such as data center proxies, residential proxies, and mobile proxies. Each type has its own advantages and use cases, depending on the user’s specific requirements.
Determining Your Proxy Needs
Privacy and Anonymity: If your primary concern is privacy and anonymity, focus on proxies that offer high levels of anonymity by masking your IP address effectively and minimizing the risk of being tracked or identified.
Geo-Restricted Content Access: If accessing geo-restricted content is your goal, consider proxies that have servers located in the desired regions. Geo-targeted proxies enable you to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that is otherwise unavailable in your location.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Proxy Server
Proxy Type: Evaluate the different types of proxy servers and their characteristics. Data center proxies are cost-effective and offer faster speeds, while residential proxies provide a higher level of anonymity by using genuine residential IP addresses.
Location: Consider the geographical location of the proxy servers. Proxies in close proximity to your physical location can offer faster connection speeds, while proxies in specific regions enable access to region-restricted content.
Reliability and Uptime
Server Reliability: Opt for proxy servers that have a reputation for reliability and uptime. Unreliable proxies can lead to frequent disconnections and interruptions, impacting your browsing experience.
Redundancy and Failover: Look for proxy providers that offer redundancy and failover mechanisms. These features ensure that if one proxy server fails, your connection is automatically rerouted to another server, minimizing downtime.
Speed and Performance
Connection Speed: Assess the speed of the proxy servers. Faster connection speeds improve your browsing experience, especially when streaming media or engaging in activities that require quick data transfer.
Server Load: Consider the server load of the proxy provider. Overloaded servers can result in slower speeds due to increased traffic, so choose a provider that manages server load effectively.
Compatibility and Protocols
Application Compatibility: Determine whether the proxy server is compatible with the applications and services you intend to use. Some proxies may be optimized for web browsing, while others offer compatibility with specific protocols or applications.
Supported Protocols: Check if the proxy supports the protocols you require, such as HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS, or FTP. Different protocols serve different purposes, so ensure compatibility with your specific needs.
Security and Encryption
Encryption Capabilities: Evaluate the encryption capabilities of the proxy server. Proxies that support encryption protocols, such as SSL or TLS, provide an additional layer of security, particularly when transmitting sensitive data.
Data Logging and Privacy Policies: Review the proxy provider’s data logging and privacy policies. Choose providers that have strict privacy policies and do not log or store your browsing activities, ensuring your data remains confidential.
Customer Support and Reputation
Customer Support: Consider the quality of customer support provided by the proxy server provider. Prompt and responsive customer support can help resolve issues quickly and ensure a smooth user experience.
Provider Reputation: Research the reputation of the proxy server provider. Look for reviews, testimonials, and feedback from other users to gauge the provider’s reliability, performance, and customer satisfaction levels.
Testing and Evaluation
Free Trials and Demos: Take advantage of free trials or demos offered by proxy providers. This allows you to test the proxy servers firsthand and evaluate their performance and suitability for your specific needs.
Performance Testing: Conduct performance tests to measure connection speed, latency, and overall performance of the proxy servers. This helps you make an informed decision based on real-world performance metrics.
Conclusion
Choosing the right proxy server requires careful consideration of factors such as proxy type, location, reliability, speed, compatibility, security, and customer support. By understanding your specific needs and assessing these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your requirements for privacy, security, and access to online content. Remember to test and evaluate proxy servers before committing to a long-term subscription to ensure they meet your expectations.
0 notes
Text
Understanding SOCKS5 Proxies: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding SOCKS5 Proxies: A Comprehensive Guide
In the digital age, privacy and security have become paramount concerns for internet users. One of the tools that have gained popularity for enhancing online privacy is the SOCKS5 proxy. This article delves into what SOCKS5 proxies are, how they work, and their benefits.To get more news about socks5 proxies, you can visit ip2world.com official website.
What is a SOCKS5 Proxy?
A SOCKS5 proxy is a type of proxy server that routes network traffic between a client and a server through a proxy server. Unlike other proxies, SOCKS5 operates at the session layer, which means it can handle various types of traffic, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This versatility makes SOCKS5 proxies a preferred choice for many users.
How Does SOCKS5 Work?

Enhanced Privacy: By masking your IP address, SOCKS5 proxies help protect your online identity and location. Bypass Geo-Restrictions: SOCKS5 proxies can help you access content that is restricted in your region by making it appear as though you are browsing from a different location. Improved Security: SOCKS5 proxies can add an extra layer of security by filtering out malicious traffic and preventing direct connections to your device. Versatility: Unlike other proxies that only handle specific types of traffic, SOCKS5 proxies can manage various protocols, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Use Cases for SOCKS5 Proxies
Streaming Services: Access geo-restricted content on streaming platforms by routing your traffic through a SOCKS5 proxy. Online Gaming: Reduce latency and improve gaming performance by using a SOCKS5 proxy to connect to game servers. Web Scraping: Use SOCKS5 proxies to scrape data from websites without getting blocked or detected. Torrenting: Enhance your privacy while torrenting by masking your IP address with a SOCKS5 proxy. Setting Up a SOCKS5 Proxy
Setting up a SOCKS5 proxy is relatively straightforward. Here are the basic steps:
Choose a Proxy Provider: Select a reliable SOCKS5 proxy provider that offers good speed and security. Configure Your Device: Follow the provider’s instructions to configure your device to use the SOCKS5 proxy. This usually involves entering the proxy server’s IP address and port number in your device’s network settings. Test the Connection: Once configured, test your connection to ensure that your traffic is being routed through the proxy server. Conclusion
SOCKS5 proxies offer a versatile and effective solution for enhancing online privacy and security. Whether you are looking to bypass geo-restrictions, improve your online gaming experience, or protect your identity while torrenting, SOCKS5 proxies can be a valuable tool. By understanding how they work and their benefits, you can make an informed decision about whether a SOCKS5 proxy is right for you.
0 notes
Text
What is Web Protocol And its Types ?

In the ever-evolving world of technology and the internet, understanding the fundamental building blocks of how information is transmitted between devices and across the web is crucial. This is where web protocols come into play. Web protocols are the rules and conventions that govern communication on the internet. They ensure that data is transmitted reliably and consistently between different devices and across various networks. In this article, we will explore what web protocols are and delve into some of the most common types.
What is a Web Protocol?
A web protocol, short for "web protocol suite," is a set of rules and conventions that define how data is transmitted, received, and interpreted across the internet. These protocols are essential for ensuring that different devices and systems can communicate with one another effectively. Without web protocols, the internet, as we know it, would not exist.
Web protocols operate at different layers of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which is a conceptual framework used to understand how different networking technologies interact. Each layer of the OSI model corresponds to a specific aspect of network communication. Web protocols are often categorized based on the layer at which they operate.
History of Web Technology — Read Now
Types of Web Protocols
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): HTTP is one of the most well-known and widely used web protocols. It operates at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. HTTP is responsible for transmitting web pages, images, videos, and other resources from web servers to web browsers. It's the foundation of the World Wide Web and is used for browsing websites.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP. It uses encryption to protect data transmitted between a web server and a web browser, ensuring that sensitive information, such as login credentials and credit card numbers, remains confidential. HTTPS has become the standard for secure web browsing.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol): FTP operates at the application layer and is used for transferring files between computers on a network. It's commonly used by web developers to upload and download files to and from web servers.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): SMTP is responsible for sending and receiving email messages. It operates at the application layer and is crucial for the functioning of email services.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): These protocols are used for retrieving email from a mail server to a client device (e.g., email client software). POP3 downloads emails to the client device, while IMAP allows users to access emails stored on the server, making it possible to manage email from multiple devices.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): TCP/IP is not a single protocol but a suite of protocols that form the backbone of the internet. It operates at various layers of the OSI model and is responsible for routing data packets across networks, ensuring reliable and efficient communication.
DNS (Domain Name System): DNS is responsible for translating human-readable domain names (e.g., sohutech.online ) into IP addresses that computers can understand. It operates at the application layer and plays a critical role in navigating the web.
Conclusion
Web protocols are the unsung heroes of the internet, quietly working in the background to ensure that our online experiences are seamless and secure. Understanding the types and functions of web protocols is essential for anyone interested in web development, networking, or simply using the internet effectively. Whether you're browsing your favorite website, sending an email, or downloading a file, web protocols are at work, making it all possible.
What is Web Technology — Read in Breifly Tap Here
#web development#web design#website#Web protocol#computer#website design#tools#data science#tech#technology
0 notes
Text
What is the working principle of IP proxy?
The working principle of IP proxy (or proxy server) is mainly to act as an intermediary between the client and the target server to realize the purpose of hiding the real IP address of the client, improving access speed and security. The following is the basic working principle of IP proxy.
1. Client sends a request
When a user (client) wants to access a certain website or resource, the client's request will be sent to the proxy server first, instead of directly to the target server.
2. Proxy server processes the request
After the proxy server receives the client's request, it processes the request. The processing may include the following.
a. Change IP address. The proxy server replaces the client's real IP address and sends the request to the target server using its own IP address.
b.Caching content. If the proxy server has cached the target content, it can return the cached content directly to the client without sending a request to the target server, thus improving access speed.
3. Proxy Server Forwarding Requests
The proxy server forwards the processed request to the target server. At this time, the target server thinks that the request comes from the IP address of the proxy server, not the real IP address of the client.
4. Target server response
When the target server receives the request, it processes the request and returns the response to the proxy server.
5. Proxy Server Returns Response
The proxy server receives the response from the target server and forwards the response to the client. The final content received by the client is the same as that obtained by directly accessing the target server, but the target server does not know the real IP address of the client.
The main types of proxy IPs are the following.
1. HTTP proxy
HTTP proxy specializes in handling HTTP protocol requests and is suitable for applications such as web browsing and data crawling. It can cache web pages to improve access speed and can be set up with access control and content filtering, for example, 711Proxy will provide this kind of proxy.
2. HTTPS proxy
HTTPS proxy is used to handle encrypted HTTPS requests. It secures data transmission through encrypted tunnels (SSL/TLS).
3. SOCKS5 proxy
SOCKS5 proxy is a low-level proxy that can handle multiple types of traffic (e.g. HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc.). It works at the session layer and is suitable for scenarios that require high anonymity and flexibility.
By understanding how IP proxies work and their application scenarios, users and organizations can better select and use proxy services to meet different needs.

0 notes