#adducent
Text
Straight teen ankle socks fuck gay first time Before he blows his
Indian wife fuck with friend absence of her husband in shower
Gold digger Mom licks Daghters pussy as punishment
Lesbian toying teens ass
movies of latino boy gangster teens having gay sex xxx There are so
Summertime Saga Part 62: Getting Maria AND Jenny Pregnant!
Izzy Bell and Silvia Saige share big thick cock stud
bangladeshi pissing ctg
Ebony teen spermed in pov
vintage twinks threesome
#oxgang#porto#Calycanthaceae#adducent#unpatched#overweighting#colloids#meconiums#grandiosity#Gypsy#extraterritorial#Wolffia#Roselia#caballos#phoenicopterous#rugged#encodings#yeasayer#hydrofluate#unstalled
0 notes
Text
Horny Queen of spades wife
Enticing Ashlyn Rae actively fucked
veterana se masturba
Big ass Latina slut Kesha Ortega
Bitches Abroad - Sex Addict Tenant With Big Tits Fucks Landlord
MOST EXOTIC SLOW MOTION HUGE CUM LOAD
Fucking Machine with Estim and Stockings
Fellation La pipe des pipes, par Sharon Lee
Hot mom gets plowed with biggest cock and cream on her leg
Airplane Sex
#Chrysler#residuation#bugeyed#polly-parrot#masto-#unconventionalized#conceptualising#nontraceableness#locutorium#schrank#nonintrospectiveness#tappets#oxgang#porto#Calycanthaceae#adducent#unpatched#overweighting#colloids#meconiums
0 notes
Text
ok y’all are boring I’m going to my character AI
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me when I see people espouse comedically inaccurate or shallow readings of a text that in all actuality just belie an even more profound trend regarding a refusal to seriously engage with a text's themes


#'haha Walter White is such a dumb man why would he let his pride allow him to turn down financial support so he could start a drug empire'#oh wow it's almost like the show is deeply invested in the American context of manhood and capitalism in ways that inform the tragedy#which is in and of itself still a simplification! but it's less of deferral of engagement#online media discussions are so bad#walt's feelings of emasculation and his relationship to violence/power are fairly par for the course in terms of analyzing patriarchy under#capitalism in the sense that 'the faustian bargain' poor men make is that they can go to work and be humiliated by their boss because#patriarchy at least gives them the seductive 'release valve' of being the Boss of the nuclear family#thus when you look at how patriarchal violence manifests in the USA -- rather than patriarchal violence in non-/pre-capitalist systems --#that is something that informs the shape that the neuroses and peculiarity of the collective psyche of The Oppressor tm that then informs#the kinds of violence (systemic or interpersonal) you see play out#similar to how impoverished whiteness still allows the opium of a sense of superiority to exist that then is adduced as to why those white#people should fight to uphold white supremacy and all its economic facets#again it's the core idea that one is groomed into playing a role to uphold a system of oppression by the way the system is so unquestionabl#unquestionably built into the fabric of your reality -- as opposed to any idea of inherent and inescapable ontological Badness
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
ADDUCE #adduce #synonym #ingles #allege #apply #cite #advance #offer #antonym #retract #except #withdraw #duct #portugues #aduzir #alegar #aplicar #citar #avançar #oferecer #introduzir
ADDUCE #adduce #synonym #ingles #allege #apply #cite #advance #offer #antonym #retract #except #withdraw #duct #portugues #aduzir #alegar #aplicar #citar #avançar #oferecer #introduzir
Inglês: Adduce
Synonyms
Allege, apply, cite, advance, offer, introduce, produce, add, import, name, mention, quote.
Antonyms
Retract, except, withdraw, duct, deduce, suppress.
Português: Aduzir
Alegar, aplicar, citar, avançar, oferecer, introduzir, produzir, adicionar, importar, nomear, mencionar, citar
Thank you for visiting us! Obrigado pela visita!

View On WordPress
#Add#Adduce#Advance#allege#antonym#apply#cite#Deduce#duct#Except#Import#Introduce#mention#name#Offer#Produce#quote#retract#suppress#synonym#withdraw
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pier Adduce | Dove vola la cicogna
Etichetta: La Chute Dischi
Tracce: 9 – Durata: 34:22
Genere: Pop Rock, Cantautori
Sito: Facebook, Instagram
Voto: 7/10
Bizzarro tema quello affrontato da Pier Adduce (Guignol) per il suo secondo album solista. Dove arriva la cicogna è una sorta di concept sulla fertilità, un omaggio alla gioventù, con tutte le contraddizioni che essa porta, con le paure della crescita che fano a botte…
youtube
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Mature handjob at the beach
My hot wife
tattoo girl anal sex final
Amber Rayne and Aurora Snow Have Their Face Fucked
Cum on Pussy
Lesbian fitness coach rimming blonde Milf
Blonde milf threesome dp One more messy crook is taken off the
AfroCandy and the Big Dick Mandingo
That thick Korean ass looks amazing in doggy.
japanese rare flim strangling
#barque#entreasured#tail-tied#shaloms#unwithstood#hypnotistic#unriotously#leeways#Nydia#overshadowment#lievrite#Agana#Reblochon#drv3#semistriate#adduced#wardrobe#sclerocorneal#trochleas#incurves
0 notes
Text
Hooters Cuckquean Natasha nice Hot spring Sleepover Rent Chinese hooker Hotkinkyjo Wax Japanese amateur leak遇見激似細川百合子鈴木里美三田杏的網紅本土絲襪中學生初中全讓我給嫩模美魔女多人影片日本劇情中文字幕偷拍視訊妹破處無修正台灣射顏大嫂正妹強上偷拍偷拍極品自拍
Gozando muito ela
nude beach house sasha storm
Jayden James Crashes Avys Set
Yummy angel gets her pussy stimulated well and makes pissing
Jaycee Star sucks LP Officers big cock
Brooklyn thot giving handjob
ManRoyale Celebration Gay Pride Fuck
Black teenager with small tits masturbates
Bbw girl wants to cheat on her bf for a BBC
#rapiers#Dunmore#hingeflower#blunt-nosed#intercentral#unapportioned#inculcation#sucupira#reconvict#Budworth#maths#passport#triptycas#adducing#whimsy#dendrography#Wahhabi#Jake#axman#costae
0 notes
Text
A few months ago, an article by Just Like Us about a survey of young UK adults regarding LGBT topics (and other articles on The Pink News and Gay Times UK that reported on that article) did the rounds on here.
The headline of the Gay Times article, written by Amy Ashenden (a cisgender butch lesbian and the interim CEO of Just Like Us, who hired the consultancy that conducted the survey) was "Lesbians being anti-trans is a lesbophobic trope"; of the results of the survey, she writes "I’m so glad that we finally have the research to demonstrate what most lesbians already knew: this narrative is completely false."
A lot of this initial reporting focused on the claims that "most anti-trans adults don’t know a trans person in real life" and "lesbians are the most supportive of trans people of any identity group, and it's a lesbophobic trope that they are anti-trans." These articles were written before the full report of the survey's data had been released.
The full report that these claims are based on is now out, for anyone who wants to take a closer look at the results for themselves. The pdf appears to be OCR readable but not image-described. The survey deals with many topics including being "out" and "feeling supported" at school and at work, but I'll just try to break down the evidence for the above-mentioned two claims.
How respondents were selected:
Just Like Us's report says that "Participants were drawn in partnership between Just Like Us and from Cibyl’s independent database of UK students and young adults" (p. 69). Cibyl offers "bespoke studies and focus groups," and says that "Using our Cibyl-ings student panel, we can source specific students to look at themes and topics important to you and ask the unique questions you want the answers to." This is rather vague.
Sample group and size:
3,695 young adults aged between 18 and 25. 86% cisgender and 12% transgender; 47% LGBT and 53% non-LGBT (used as a control group to compare LGBT responses to); 72% white; 79% students; 54% "female" (self-declared), 36% "male", 8% non-binary (pp. 69-70).
Support for the articles' central claims:
There is no full breakdown of the data resulting from the survey that would allow anyone else to do their own statistical analysis. Here's (what Just Like Us gives of) the data that the "most anti-trans people don't know a trans person in real life" claim is based on:
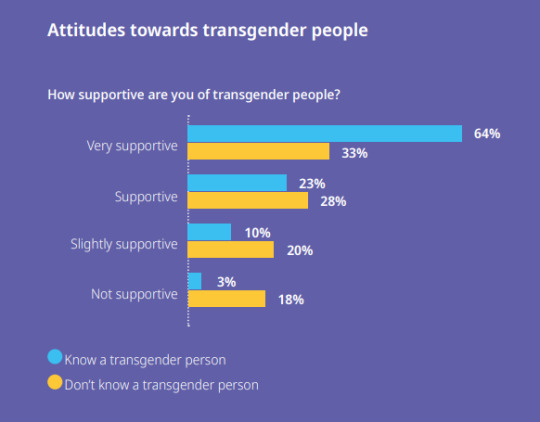
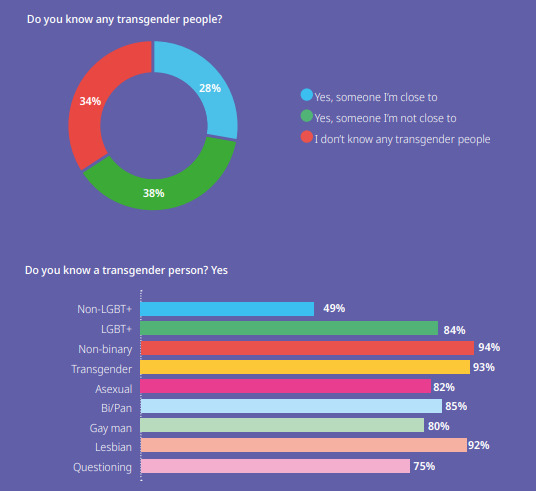
[ID: Headline reading "Attitudes towards transgender people. Question reading "How supportive are you of transgender people? Of people who "know a transgender person," 64% said "very supportive"; "supportive" 23%; "slightly supportive" 10%; "not supportive" 3%. Of those who "don't know a transgender person," 33% said "very supportive"; "supportive" 28%; "slightly supportive" 20%; "not supportive" 18%. Second question "Do you know any transgender people?" Result: 28% "Yes, someone I'm close to"; 38% "Yes, someone I'm not close to"; 34% "I don't know any transgender people." Further breakdown of the question "Do you know a transgender person?": 49% of "non-LGBT+" people said "yes"; 84% of LGBT+ people; 94% of non-binary people; 93% of transgender people; 82% of asexual people; 85% of bi/pan people; 80% of gay men; 92% of lesbians; 75% of questioning people. End ID]
The "do you know any transgender people" question is worded slightly differently each time—plus, the Just Like Us article and the report (p. 8) adduce the phrase "in real life" to "know a trans person," but this page doesn't—so I don't think we're getting the exact wording for that question that the survey respondents saw. The data for "how supportive are you of transgender people" isn't broken down according to whether the respondent said they were "close" or "not close" to the transgender person or people they knew; it also doesn't seem to be broken down into trans or nonbinary versus cisgender respondents.
"How supportive are you of transgender people?" was the only question dealing with this issue, and the responses "very supportive," "supportive," "slightly supportive," and "not supportive" were the only options available; there's nothing breaking down what "support" means in terms of policy (e.g. support versus non-support for consent-based clinics, national funding for transition care, non-discrimination laws, bathroom laws, &c. &c.). There is also no distinction made between "support" for trans women and trans men.
The claim "UK adults between the ages of 18 and 25 who answer 'not supportive' to the question 'How supportive are you of transgender people?' are several times more likely to also answer 'no' to the question 'do you know a transgender person' (or maybe 'do you know a transgender person in real life')" is supported, in my opinion. The sample size is large enough for that 3% to not be random noise.
The analysis in the Just Like Us article groups together "very supportive" and "supportive" when providing percentages of respondents of given identities who support trans people:
Of all LGBT+ identities, other than trans and non-binary people themselves, lesbian young adults were most likely to say they know a trans person (92%), and most likely to say they are “supportive” or “very supportive” of trans people (96%).
In comparison, 89% of LGBT+ people overall said they were “supportive” or “very supportive” of trans people, and just 69% of non-LGBT+ people said the same.
There is no full breakdown of how many people are "very supportive," "supportive," "slightly supportive" or "not supportive" of trans people by identity label. The relevant data is on p. 63 of the report:
"Looking at who was the most supportive of transgender people:
non-binary respondents were 97% supportive or very supportive with 1% of respondents indicating they were not supportive;
lesbian respondents were 95% supportive or very supportive [everywhere else in the report and in the reporting says 96%, so perhaps this is a typo] (3% were not supportive);
bi/pansexual respondents were 92% supportive or very supportive
(2% were not supportive).
Of respondents who were gay men, 82% were supportive or very supportive of transgender people, with 7% indicating they were not supportive.
Among non-LGBT+ respondents 69% were supportive of transgender people, with 12% indicating they were not supportive."
It's not clear to me how they dealt with e.g. lesbians who were also transgender. Pages 69-70 of the report go into the questions that people were asked to identify their identity label for the purposes of statistical analysis ("Is your gender identity the same as the one you were originally assigned at birth?"; and "What is your sexual orientation?"). The fact that these are separate questions (as they should be) tells me that there's overlap between groups throughout the study; any data that says e.g. "83% of lesbian respondents" is combining cis and trans lesbians, and any result that says "67% of trans people" is combining heterosexual and LGB trans people.
So, while narrowing the respondents down to just cisgender LGB people to compare their support for trans people would have been one way to analyse the data, I'm guessing they didn't do that (plus, there's the article's wording of "LGBT+ people overall"; it wouldn't make statistics-analytical sense to compare cis lesbians with all LGBT+ people, plus it would presumably make the higher support % of lesbians less stark, which seems like the opposite of what Ashenden wanted to do).
When the article says "other than trans and non-binary people themselves," they don't mean that they excluded trans and non-binary people from the percentages given; they mean "other than the number you get if you measure support for transgender people just from trans and non-binary people." We're not given the number that would result from doing this. The number we're given in the report for non-binary people is 97% supportive (this number is not included in the article); we are not given a number for just trans people, but we can probably assume it also approaches 100%.
This means that the 96% support presumably measures support from cis and trans lesbians; the 82% of "supportive" and "very supportive" gay men includes cis and trans men; &c.
There is a major statistics-analytical problem with acknowledging that trans and non-binary respondents have the highest rates of support for trans people, but then not controlling the results of this question for whether the respondent was cis or trans. If a higher percentage of lesbian respondents were trans than the percentage of gay men respondents that were trans, this would itself skew the numbers for lesbian support higher. There's no reason to suppose that this did happen, but there is not enough information given about the data that Just Like Us collected to rule it out. Again, at no point are we given information about overlap between LGB and trans groups or a breakdown of what that overlap looked like (how many trans respondents were heterosexual versus LGB, &c.).
As I mentioned above, some of the survey focused on whether respondents "felt supported" at home and at school. Some snippets on the results of these questions can be found on pages 45-49 of the report. "[M]ore than 1 in 4" LGBT+ respondents "felt unsupported" in school compared to "1 in 10" non-LGBT+ respondents; 37% of transgender respondents and 39% of nonbinary respondents said they felt unsupported in school. Despite the survey's focus on the outcomes of felt support, and despite all respondents being asked if they were "supportive" of transgender people, no question asked transgender respondents if they "felt supported" by cisgender LGB people.
Generalisability of claims:
The sampling of the data (which is drawn entirely from people in the UK aged 18-25, mostly students) also means that the claims are not generalisable to the entire UK population; you can't say the "majority of anti-trans adults don’t know a trans person in real life" (the headline of the Just Like Us article) or "Most anti-trans adults don’t actually know a trans person in real life" (the headline of the Pink News article), since the survey did not take a representative sample of all adults. You can't say "lesbians are not anti-trans" (the url of the Gay Times article), since the survey is not representative of all lesbians.
Funding sources:
The report was sponsored by Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, a firm offering professional services (accounting, auditing, consulting, financial advisory, litigation consulting, and other services offered to businesses).
Cibyl, an independent research firm in the UK, "led on research design and delivery, then worked in partnership with Just Like Us to produce the report." They include the report ("Positive Futures") as an example of their work on their website. Their summary of the study focuses on the claim that "support in LGBT+ young adults’ teenage years" is necessary to the future development of their careers, and on what "employers and careers professionals can do to help LGBT+ young people feel safe and supported." This is the same kind of thing that Deloitte talks about when it comes to LGBT+ issues (namely, inclusion versus exclusion and support versus non-support in the workplace).
A video that Asheden produced with Mags Scott (partner at Deloitte) also focuses on how "support" for LGBT+ people "at home, in school, and in the workplace" leads to confidence in "career prospects" and ability to be onself "at work," and is necessary for LGBT+ people's mental wellbeing.
Just Like Us has an interest in promoting research that suggests that support for LGBT+ people in school will benefit them in their careers, since they sell training resources on forming LGBT+ groups, and talks with LGBT+ speakers, to schools. Just Like Us is a non-profit organisation.
Declaration of conflicts of interest and peer review:
This is an industry-sponsored study and not an academic one. There is no declaration of conflicts of interest required, and the study was not peer-reviewed.
Tl;dr:
Some breakdown of data was revealed in the report. The exact questions that respondents saw were not given. The data is not given with enough granularity to allow for anyone else to conduct statistical analysis based on it.
There is not enough evidence to say whether the study supports the claim that (cis?) lesbians are more supportive of trans people than any other identity group, since the survey was not clear what "support" means (someone may claim to support trans people as individuals while not supporting transition care, for example, due to some kind of "love the sinner, hate the sin" logic).
There is also a statistical problem with the support for this claim, since overlap between "transgender" and "cisgender" respondents is not controlled for. There is not enough data given in the report to allow anyone else to control for this factor. The results would hold if we assumed that similar percentages of e.g. lesbian, bisexual, and gay male respondents were transgender.
The results apply only to people in the UK aged 18-25 and cannot be generalised to all adults in the UK.
Summaries of this report given by the firms that funded and conducted it centre on the idea that "support" of LGBT+ people at home, at school, and in the workplace is necessary to allow them to thrive in the workplace. Just Like Us, who put out the report, sell LGBT+ talks and training to schools.
523 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some new conclusions regarding the Hand of Irulegi

The stippled text can be read as follows:
sorioneku ⋅
kunekebeekiŕateŕe/ /n
oTiŕtan ⋅ eseakaŕi
eŕaukon ⋅
The script used for the text on the Irulegi hand clearly belongs to the family of the Palaeohispanic semi-syllabaries. 18 different signs can be discerned. The presence of the T sign in a non-numismatic text is highly significant, because it demonstrates that this sign was used in multiple epigraphic contexts and because it confirms the existence of a graphic subsystem that, considering its geographical distribution and the increasingly solid linguistic evidence associated with it, must be described as a ‘Vasconic script’. Where and how such an adaptation occurred are aspects about which we currently know very little.
None of the words identified can be directly related to Vasconic or Iberian anthroponyms. The remarkable similarity between the first word in the text, sorioneku, and the Basque word zorioneko—‘of good fortune’, a flection-derivation of the sequence zori ‘fortune’ + (h)on ‘good’—could be taken to be a coincidence, were it not for the evident symbolism of the artefact and its findspot at the heart of Vasconic territory. Both words are of early date within the Basque vocabulary; even the union of both elements is recorded in the oldest Basque documents (e.g. zorionean ‘fortunately’ used by both Joan Perez Lazarraga and Bernat Dechepare in the 16th century).
The sgraffito version, however, offers sorioneke. The reason for this difference is obscure; the final -(e)ke may be the ending of some Basque-Aquitaine divinities recorded in Latin inscriptions on altars, such as the theonyms Larrahe and Herauscorritsehe. This word could mention the divinity, be it Good Fortune or another deity, to which the inscription would have been dedicated.
In line 3 it is possible to isolate oTiŕtan. This could be interpreted as a toponym given the possible presence of a formative suffix ta [da] in its lexical structure, (which is identical to that of the well-known toponym iltiŕta = Ilerda) as well as the Vasconic locative -n desinence. Depending on the value given, it would be the toponym Osserda or Ol(l)erda in its Latin transcription.
Among the rest of the words identified, eŕaukon is the most likely to be a verbal form, both because of its form and its final position. Its form recalls the Basque form of the past tense of the auxiliary verb zeraukon, used in eastern dialects; it is a form of *eradun—causative of *edun—‘to make have’ > ‘to give’, marginally used as an autonomous verb still in the sixteenth century, prior to its use as an auxiliary. The meaning of this verb would make sense in the case of a votive dedication, although several aspects are debatable.

The rest of the inscription on the Irulegi hand remains quite obscure. While here are problems in relation to the Basque words adduced as parallels, the inscription can be interpreted as a dedication to a divinity named at the beginning (sorioneke /-ku), with a dedication verb at the end (eŕaukon) whose object would go immediately before (ese-agaŕi). A place (oTiŕtan) may likewise be indicated, leaving the expression of the individual making the dedication and some other specification in the obscure line 2.
The inscription provides support for a growing awareness that the ancient Vascones knew and made use of writing, at least to a degree.
The use of sorioneku or sorioneke at the beginning of the text, isolated from what follows as an introduction admits comparison with Basque zori (h)on (‘good fortune’), and other elements, such as the verbal form eŕaukon or the locative in -n of a place-name, suggest that the inscription is in the Vasconic language, the longest and earliest known to date.
The implications of the discovery of the Irulegi hand for the epigraphic and historical understanding of the Vasconic territory, as well as the possible linguistic connections between the Vasconic, Iberian and modern Basque languages, require further in-depth analysis. Given the scarcity of other firm evidence, the Irulegi hand and its inscription will henceforth constitute an indispensable starting point for the establishment of a linguistic map of the region and any debate on the origin and development of the Vasconic language and script.
Full article
Eskerrik asko @glendathegoodone for sharing this!
#euskal herria#pays basque#basque country#pais vasco#euskadi#culture#hand of irulegi#irulegiko eskua#irulegi#nafarroa#history#linguistics#archaeology#news#vascones
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the age of Hindu identity politics (Hindutva) inaugurated in the 1990s by the ascendancy of the Indian People's Party (Bharatiya Janata Party) and its ideological auxiliary, the World Hindu Council (Vishwa Hindu Parishad), Indian cultural and religious nationalism has been promulgating ever more distorted images of India's past.
Few things are as central to this revisionism as Sanskrit, the dominant culture language of precolonial southern Asia outside the Persianate order. Hindutva propagandists have sought to show, for example, that Sanskrit was indigenous to India, and they purport to decipher Indus Valley seals to prove its presence two millennia before it actually came into existence. In a farcical repetition of Romanic myths of primevality, Sanskrit is considered—according to the characteristic hyperbole of the VHP—the source and sole preserver of world culture.
This anxiety has a longer and rather melancholy history in independent India, far antedating the rise of the BJP. [...] Some might argue that as a learned language of intellectual discourse and belles lettres, Sanskrit had never been exactly alive in the first place [...] the assumption that Sanskrit was never alive has discouraged the attempt to grasp its later history; after all, what is born dead has no later history. As a result, there exist no good accounts or theorizations of the end of the cultural order that for two millennia exerted a transregional influence across Asia-South, Southeast, Inner, and even East Asia that was unparalleled until the rise of Americanism and global English. We have no clear understanding of whether, and if so, when, Sanskrit culture ceased to make history; whether, and if so, why, it proved incapable of preserving into the present the creative vitality it displayed in earlier epochs, and what this loss of effectivity might reveal about those factors within the wider world of society and polity that had kept it vital.
[...] What follows here is a first attempt to understand something of the death of Sanskrit literary culture as a historical process. Four cases are especially instructive: The disappearance of Sanskrit literature in Kashmir, a premier center of literary creativity, after the thirteenth century; its diminished power in sixteenth century Vijayanagara, the last great imperial formation of southern India; its short-lived moment of modernity at the Mughal court in mid-seventeenth century Delhi; and its ghostly existence in Bengal on the eve of colonialism. Each case raises a different question: first, about the kind of political institutions and civic ethos required to sustain Sanskrit literary culture; second, whether and to what degree competition with vernacular cultures eventually affected it; third, what factors besides newness of style or even subjectivity would have been necessary for consolidating a Sanskrit modernity, and last, whether the social and spiritual nutrients that once gave life to this literary culture could have mutated into the toxins that killed it. [...]
One causal account, however, for all the currency it enjoys in the contemporary climate, can be dismissed at once: that which traces the decline of Sanskrit culture to the coming of Muslim power. The evidence adduced here shows this to be historically untenable. It was not "alien rule un sympathetic to kavya" and a "desperate struggle with barbarous invaders" that sapped the strength of Sanskrit literature. In fact, it was often the barbarous invader who sought to revive Sanskrit. [...]
One of these was the internal debilitation of the political institutions that had previously underwritten Sanskrit, pre-eminently the court. Another was heightened competition among a new range of languages seeking literary-cultural dignity. These factors did not work everywhere with the same force. A precipitous decline in Sanskrit creativity occurred in Kashmir, where vernacular literary production in Kashmiri-the popularity of mystical poets like Lalladevi (fl. 1400) notwithstanding-never produced the intense competition with the literary vernacular that Sanskrit encountered elsewhere (in Kannada country, for instance, and later, in the Hindi heartland). Instead, what had eroded dramatically was what I called the civic ethos embodied in the court. This ethos, while periodically assaulted in earlier periods (with concomitant interruptions in literary production), had more or less fully succumbed by the thirteenth century, long before the consolidation of Turkish power in the Valley. In Vijayanagara, by contrast, while the courtly structure of Sanskrit literary culture remained fully intact, its content became increasingly subservient to imperial projects, and so predictable and hollow. Those at court who had anything literarily important to say said it in Telugu or (outside the court) in Kannada or Tamil; those who did not, continued to write in Sanskrit, and remain unread. In the north, too, where political change had been most pronounced, competence in Sanskrit remained undiminished during the late-medieval/early modern period. There, scholarly families reproduced themselves without discontinuity-until, that is, writers made the decision to abandon Sanskrit in favor of the increasingly attractive vernacular. Among the latter were writers such as Kesavdas, who, unlike his father and brother, self-consciously chose to become a vernacular poet. And it is Kesavdas, Biharilal, and others like them whom we recall from this place and time, and not a single Sanskrit writer. [...]
The project and significance of the self-described "new intellectuals" in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries [...] what these scholars produced was a newness of style without a newness of substance. The former is not meaningless and needs careful assessment and appreciation. But, remarkably, the new and widespread sense of discontinuity never stimulated its own self-analysis. No idiom was developed in which to articulate a new relationship to the past, let alone a critique; no new forms of knowledge-no new theory of religious identity, for example, let alone of the political-were produced in which the changed conditions of political and religious life could be conceptualized. And with very few exceptions (which suggest what was in fact possible), there was no sustained creation of new literature-no Sanskrit novels, personal poetry, essays-giving voice to the new subjectivity. Instead, what the data from early nineteenth-century Bengal-which are paralleled every where-demonstrate is that the mental and social spheres of Sanskrit literary production grew ever more constricted, and the personal and this-worldly, and eventually even the presentist-political, evaporated, until only the dry sediment of religious hymnology remained. [...]
In terms of both the subjects considered acceptable and the audience it was prepared to address, Sanskrit had chosen to make itself irrelevant to the new world. This was true even in the extra-literary domain. The struggles against Christian missionizing, for example, that preoccupied pamphleteers in early nineteenth-century Calcutta, took place almost exclusively in Bengali. Sanskrit intellectuals seemed able to respond, or were interested in responding, only to a challenge made on their own terrain-that is, in Sanskrit. The case of the professor of Sanskrit at the recently-founded Calcutta Sanskrit College (1825), Ishwarachandra Vidyasagar, is emblematic: When he had something satirical, con temporary, critical to say, as in his anti-colonial pamphlets, he said it, not in Sanskrit, but in Bengali. [...]
No doubt, additional factors conditioned this profound transformation, something more difficult to characterize having to do with the peculiar status of Sanskrit intellectuals in a world growing increasingly unfamiliar to them. As I have argued elsewhere, they may have been led to reaffirm the old cosmopolitanism, by way of ever more sophisticated refinements in ever smaller domains of knowledge, in a much-changed cultural order where no other option made sense: neither that of the vernacular intellectual, which was a possible choice (as Kabir and others had earlier shown), nor that of the national intellectual, which as of yet was not. At all events, the fact remains that well before the consolidation of colonialism, before even the establishment of the Islamicate political order, the mastery of tradition had become an end in itself for Sanskrit literary culture, and reproduction, rather than revitalization, the overriding concern. As the realm of the literary narrowed to the smallest compass of life-concerns, so Sanskrit literature seemed to seek the smallest possible audience. However complex the social processes at work may have been, the field of Sanskrit literary production increasingly seemed to belong to those who had an "interest in disinterestedness," as Bourdieu might put it; the moves they made seem the familiar moves in the game of elite distinction that inverts the normal principles of cultural economies and social orders: the game where to lose is to win. In the field of power of the time, the production of Sanskrit literature had become a paradoxical form of life where prestige and exclusivity were both vital and terminal.
The Death of Sanskrit, Sheldon Pollock, Comparative Studies in Society and History, Vol. 43, No. 2 (Apr., 2001), pp. 392-426 (35 pages)
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
Geological and Historical Evidence for Jesus’ Crucifixion Account

At Jesus’ crucifixion, Matthew (27:45-54) reported “From noon until three in the afternoon darkness came over all the land. About three in the afternoon Jesus cried out in a loud voice ‘My God, my God, why have you forsaken me?’ (cf., Psalm 22)…And when Jesus had cried out again in a loud voice, he gave up his spirit. At that moment, the curtain of the temple was torn in two from top to bottom. The earth shook, the rocks split and the tombs broke open. The bodies of many holy people who had died were raised to life. They came out of the tombs after Jesus’ resurrection and went into the holy city and appeared to many people. When the centurion and those with him who were guarding Jesus saw the earthquake and all that happened, they were terrified, and exclaimed, ‘Surely he was the son of God!’”
Matthew’s passage includes two events that can be historically and geologically confirmed: (1) Darkness covered the land for three hours (c.f., Matthew 27:45; Mark 15:33; Luke 23:44-45) and (2) An earthquake occurred.
“At that same moment about noontide, the day was withdrawn; and they, who knew not that this was foretold concerning Christ, thought it was an eclipse. But this you have in your archives; you can read it there. Yet nailed upon the cross, Christ exhibited many notable signs, by which his death was distinguished from all others. At his own free-will, he with a word dismissed from him his spirit, anticipating the executioners’ work. In the same hour, too, the light of day was withdrawn, when the sun at the very time was in his meridian blaze. Those who were not aware that this had been predicted about Christ, no doubt thought it was an eclipse.”
- Tertullian (197 AD), Jewish Consul
“In the 4th year of the 202nd Olympiad, there was a great eclipse of the sun, greater than had ever been known before, for at the 6th hour the day was changed into night and the stars were seen in the heavens. An earthquake occurred in Bythinia and overthrew a great part of the city of Nicaea.”
- Phlegon (2nd century AD) Greek historian, “Olympiads”
“With regard to the eclipse in the time of Tiberius Caesar, in whose reign Jesus appears to have been crucified, and the great earthquakes which then took place, Phlegon too I think has written in the 13th or 14th book of his Chronicles…Celsus imagines also that both the earthquake and darkness were an invention, but regarding these, we have in the preceding pages made our defense, according to our ability, adducing the testimony of Phlegon, who relates that these events took place at the time when our Savior suffered.”
- Origen (184 – 253 AD), Greek scholar and early Christian father who confirmed Phlegon’s writings
“Jesus Christ underwent his passion in the 18th year of Tiberius [33 AD]. Also at that time in another Greek compendium we find an event recorded in these words: ‘the sun was eclipsed, Bithynia was struck by an earthquake, and in the city of Nicaea many buildings fell.”
- Eusebius (315 AD), Historian of the Emperor Constantine.
What Caused the Three-hour Period of Darkness?
Before determining that the three-hour period of darkness is due to supernatural causes, we must rule out the natural possibilities. We have experienced natural events that have caused darkness during the daylight hours. These include when volcanoes erupt and emit dark clouds and when storms occur and cover the sky with clouds. Yet no Biblical or secular sources indicate any support for a volcanic explosion or storms, so we can rule out those two natural events.
What about an eclipse? The positioning of the sun and moon is required to answer this question. We have much support for the dating of Jesus’ crucifixion on Friday the 14th of Nissan in the year 33 (April 3, 33). This date was further predicted in the book of Daniel (9). Passovers only occurred during a full moon, so an eclipse would not have been possible due to the moon’s location on the far side of the earth away from the sun. Even if the positioning were conducive to an eclipse, eclipses only darken the earth for short moments, not for three hours, so we have another reason to rule out that natural option.
Is the Best Explanation to Explain this Event a Supernatural Explanation?
I will let readers answer that question for themselves.
Geological Support for the Earthquake

Scholars have reported that devastating earthquakes occurred in Jerusalem during Christ’s death (Mallet, 1853; Rigg, 1941). This occurred in a region that includes the Dead Sea fault, which is a plate boundary that separates the Arabian plate and the Sinai sub-plate (Garfunkel, 1981). This fault has been active since the Miocene (Kagan, Stein, Agnon, & Neuman, 2011) and the fault is still active today (De Liso & Fidani, 2014). The fault extends from the Red Sea in the south to the Taurus Mountains in the north.
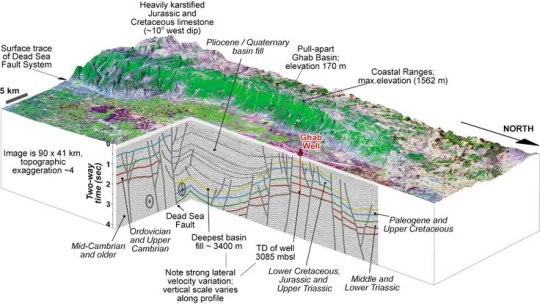
Kagan and colleagues (2011) analyzed seismites in the Holocene Dead Sea basin by constructing two age-depth chronological models based on atmospheric radiocarbon ages of short-lived organic debris with a Bayesian model. Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures, which are deformed by seismic shaking. The scholars analyzed seismites in different areas of the basin, finding that several synchronous seismites appeared in all sections during particular years, including 33 AD (+/- 2 sigma; 95% confidence interval). Other years in which earthquakes occurred as evidenced by seismites are (AD unless otherwise noted): 1927, 1293, 1202/1212, 749, 551, 419, 33, 31 BC, and mid-century B.C.
After analyzing laminated sedimentary cores recovered at the shores of the Dead Sea, Migowski, Agnon, Bookman, Negendank, and Stein (2004) also confirmed an earthquake in 33 AD with a magnitude of 5.5. They documented earthquakes around 33 AD in 31 BC and 76 AD. The scholars analyzed seismites using radiocarbon dating.
Ben-Menahem (2014) conducted a literature review of empirical studies over 4,000 years of seismicity along the Dead Sea Rift. The scholar referenced the aforementioned studies along with one by Enzel, Kadan, and Eyal (2000) before concluding that earthquakes occurred in Masada in 31 BC, Jerusalem in 33 AD, and near Nablus in 64 AD.
In summary, the literature on seismicity along the Dead Sea basin supports the assertion that an earthquake occurred either in or very close to the year 33 AD.
We can pinpoint the date even closer – to April 3, 33. A United States government federal agency, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, has documented the major earthquakes throughout history. According to their website (NOAA.gov), in 33 AD, an earthquake occurred at the crucifixion of Jesus Christ in Bithynia and Palestine and Palestine, Jerusalem.
Conclusion
In summary, we have extensive extra-biblical support for the accounts of darkness and the earthquake during Jesus’ crucifixion. Taken together, these events support the historicity of the account of Jesus’ crucifixion.
source: abbreviated from https://christian-apologist.com/2019/01/05/geological-and-historical-evidence-for-jesus-crucifixion-account/
#church history#catholic#Christian#crucifixion#good friday#geology#origen#eusebius#tertullian#phlegon
268 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi Jenn (I’m saying hi as if we don’t have an active group chat that we talk in every day 🤦🏻♀️😂)
Anyways! If you’re don’t mind my request, and if no one has asked for this yet, this shrimp asks for prompt list 1, #15 with the himbo 😉 (as if you didn’t expect this from me 😂)
Pls and thank you! 😬💛
-Shrimp 🦐

| Kiss, kiss |
Bradley Bradshaw x reader
A/N: My loooooove! I'm sorry this is so short and probably crap but here you go hahahaha. Love you lots ❤️

It all started with quick pecks behind closed doors.
Bradley didn't need anything more, actually. Just a quick peck once in a while, so he could continue with his day. He would look out for you in the hangar, and once he had seen you checking a plane that had just been repaired. Then he checks around, making sure that nobody is looking, and pulls you close by the belt loops of your jeans, crashing his lips against yours as if it was the first time in ages he’d kissed you.
It was cute, and while it was risky, as not a lot of people knew about your relationship, and you wanted to keep it that way, Bradley always checked the surroundings to see if there was someone around that could notice them and spread the word.
But then, Bradley became a little shit and began to kiss you in the most inappropriate places. In the parking lot when you get out of work, and he’s waiting for you to get you home.
At the Hard Deck, when he makes you gestures from the other side of the room while you’re with your friends. He gestures you to go outside, so he can kiss you and compliment your outfit. “And I bet it looks ten times better on my bedroom floor.”
None of you enter back to the bar after he says that.
Bradley justifies his behavior adducing that he might be deployed at any moment and while most of the time you get deployed too because mechanics are always needed, it might happen that someday, somehow, he has to travel away without you.
And as soon as those words leave his mouth, it happens. He gets deployed on a mission in the Pacific for a month or so. Calls are good, when they are possible, but you usually end up texting each other, and you get texts at the most random times. It’s exasperating.
It makes you realize that you want the relationship to be public, so you don’t have to keep quiet about how much you miss him, and how much you hope he’s okay. You just have to wait and see what happens.

“Y/n, you’ve been called to the main hangar. It seems like there’s an F-18 that makes a weird noise.” Your boss says, handing you a folder with the plane number written in blue letters. You recognize that number, but it’s hard to remember as you have many planes to fix and even helicopters now.
“I’ll go right now, sir.”
You walk towards the hangar, really close from where your office is, and then start looking the said plane, the one that’s giving trouble and making ‘weird noises’. It’s surprising the amount of times you get called to check an aircraft for that reason. It’s usually an easy fix, but you always check the whole thing, just to make sure that nothing happens later when the aircraft is in the air.
Checking the number of the plane, you see the name of the pilot written on the side.
Lt. Bradley “Rooster” Bradshaw.
“When did he come back?” You ask aloud, not expecting an answer.
“Three hours ago, actually.” Bradley says, appearing from behind the plane, a bouquet of flowers in hand. He drops the flowers to the floor once he sees you running towards him, catching you mid-air. "I'm gonna guess you missed me a lot."
"It's been a whole month of not getting my kisses. I want my kisses."
He looks at you, a teasing smirk that you've missed for a whole month. "Weren't you the one who said that you didn't want to get caught by the others?"
You raise an eyebrow, carefully choosing your next words to make him suffer a bit. "Well, then. Put me down, I'm sure Hangman will be more than happy to give me a ki-"
He kisses you before you can even finish your sentence. He pulls away, a whole minute after, leaving you breathless and dizzy. "You're mine, babe. Don't forget that."
"Jealous, aren't we?"
"For you? Yes. I don't wanna lose you."
You shake your head, kissing him softly. "You're not gonna lose me, idiot. Now, what about we go get something to eat?"
"Are you on the menu?" He says, slowly leaving you on the floor.
"I can be the dessert." You smirk.
"Never have I been so excited for dessert."
#top gun maverick#top gun x reader#top gun maverick fanfic#top gun fanfiction#top gun#bradley rooster bradshaw x reader#bradley bradshaw#bradley rooster bradshaw#rooster bradshaw fic#bradley bradshaw x reader#bradley bradshaw fic#rooster x reader#rooster fanfic#rooster top gun#bradley bradshaw x y/n
259 notes
·
View notes
Text
CONVEY #convey #synonym #ingles #take #carry #transfer #relegate #bear #antonym #bring #adduce #fetch #drop #house #portugues #transmitir #tomar #transportar #transferir #relegar #suportar #transmitir
CONVEY #convey #synonym #ingles #take #carry #transfer #relegate #bear #antonym #bring #adduce #fetch #drop #house #portugues #transmitir #tomar #transportar #transferir #relegar #suportar #transmitir
Inglês: Convey
Synonyms
Take, carry, transfer, relegate, bear, transmit, consign, transport, remove.
Antonyms
Bring, adduce, fetch, drop, house, stow, deposit.
Português: Transmitir
Tomar, transportar, transferir, relegar, suportar, transmitir, consignar, transportar, remover
Thank you for visiting us! Obrigado pela visita!

View On WordPress
#Adduce#antonym#bear#bring#Carry#consign#convey#Deposit#Drop#Fetch#House#relegate#remove#stow#synonym#take#transfer#Transmit#Transport
1 note
·
View note
Text
Dracula Dictionary, August 9th
Varna: a large city in Bulgaria, on the coast of the Black Sea
ballast: heavy material that is put in the hold of a ship to make it more stable
silver sand: a fine white sand used in gardening
consign: to give over to another's care
consul: a government official sent to another country to represent the interests of his own country
charter-party: a contract between the person who owns a ship and another person who wants to use the ship
nine days' wonder: something that generates interest for a limited time and is then abandoned
S. P. C. A.: Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals
rescript: something that has been rewritten
supercargo: the person on a ship who is in charge of managing the cargo
cum grano (salis): with a grain of salt, with skepticism
adduce: offer as proof
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In Phanagoreia there is a notable temple of Aphrodite Apatouros (Deceiver). Critics derive the etymology of the epithet of the goddess by adducing a certain myth, according to which the Gigantes attacked the goddess there; but she called upon Herakles for help and hid him in a cave, and then, admitting the Gigantes one by one, gave them over to Herakles to be murdered through ‘treachery’."
- Strabo, Geography 11.2.10
14 notes
·
View notes