#alfonso xi of castile
Text
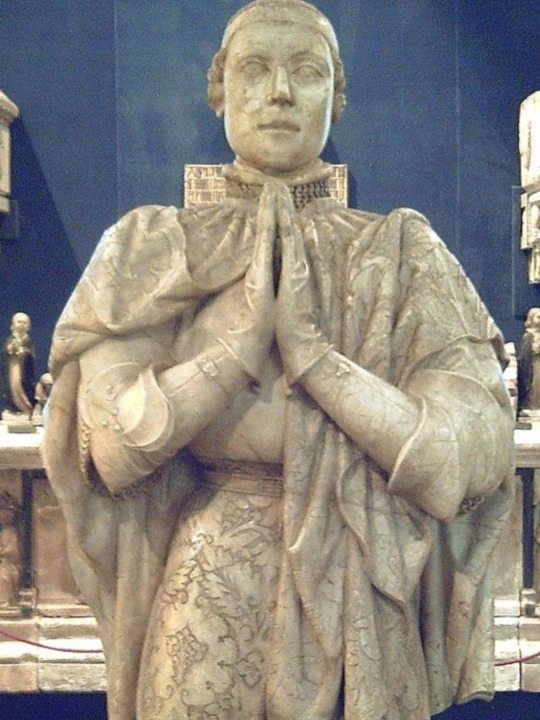
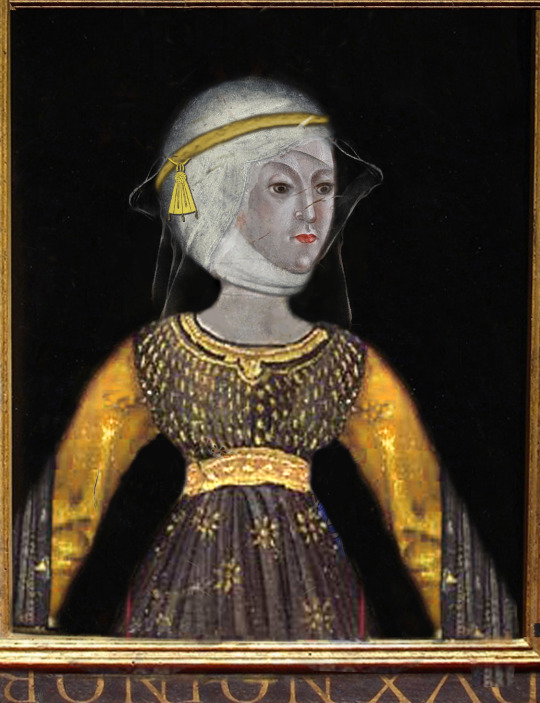










The Bastard Kings and their families
This is series of posts are complementary to this historical parallels post from the JON SNOW FORTNIGHT EVENT, and it's purpouse to discover the lives of medieval bastard kings, and the following posts are meant to collect portraits of those kings and their close relatives.
In many cases it's difficult to find contemporary art of their period, so some of the portrayals are subsequent.
1) Henry II of Castile ( 1334 – 1379), son of Alfonso XI of Castile and Leonor de Guzmán; and his son with Juana Manuel de Villena, John I of Castile (1358 – 1390)
2) His wife, Juana Manuel de Villena (1339 – 1381), daughter of Juan Manuel de Villena and his wife Blanca de la Cerda y Lara; with their daughter, Eleanor of Castile (1363 – 1415/1416)
3) His father, Alfonso XI of Castile (1311 – 1350), son of Ferdinand IV of Castile and his wife Constance of Portugal
4) His mother, Leonor de Guzmán y Ponce de León (1310–1351), daughter of Pedro Núñez de Guzmán and his wife Beatriz Ponce de León
5) His brother, Tello Alfonso of Castile (1337–1370), son of Alfonso XI of Castile and Leonor de Guzmán
6) His brother, Sancho Alfonso of Castile (1343–1375), son of Alfonso XI of Castile and Leonor de Guzmán
7) Daughters in law:
I. Eleonor of Aragon (20 February 1358 – 13 August 1382), daughter of Peter IV of Aragon and his wife Eleanor of Sicily; John I of Castile's first wife
II. Beatrice of Portugal (1373 – c. 1420) daughter of Ferdinand I of Portugal and his wife Leonor Teles de Meneses; John I of Castile's second wife
Son in law:
III. Charles III of Navarre (1361 –1425), son of Charles II of Navarre and Joan of Valois; Eleanor of Castile's huband
8) His brother, Peter I of Castile (1334 – 1369), son of Alfonso XI of Castile and Mary of Portugal
9) His niece, Isabella of Castile (1355 – 1392), daughter of Peter I of Castile and María de Padilla
10) His niece, Constance of Castile (1354 – 1394), daughter of Peter I of Castile and María de Padilla
#jonsnowfortnightevent2023#henry ii of castile#john i of castile#juana manuel de villena#eleanor of castile#alfonso xi of castile#leonor de guzmán#tello alfonso of castile#sancho alfonso of castile#peter i of castile#constance of castile#isabella of castile#asoiaf#a song of ice and fire#day 10#echoes of the past#historical parallels#medieval bastard kings#bastard kings and their families#eleanor of aragon#beatrice of portugal#charles iii of navarre#canonjonsnow
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alfonso XI, El Justiciero (The Avenger) - Siege of Priego 1341
by Rocío Espín Piñar
#alfonso xi#king#castile#léon#siege#art#reconquista#spain#iberia#spanish#history#europe#european#castle#priego de córdoba#castillo de priego de cordoba#medieval#middle ages#knights#andalucía#andalucia#fortress#rocío espín piñar#illustration#reconquest#crusades#crusade#crusaders#crusader#castilian
91 notes
·
View notes
Photo
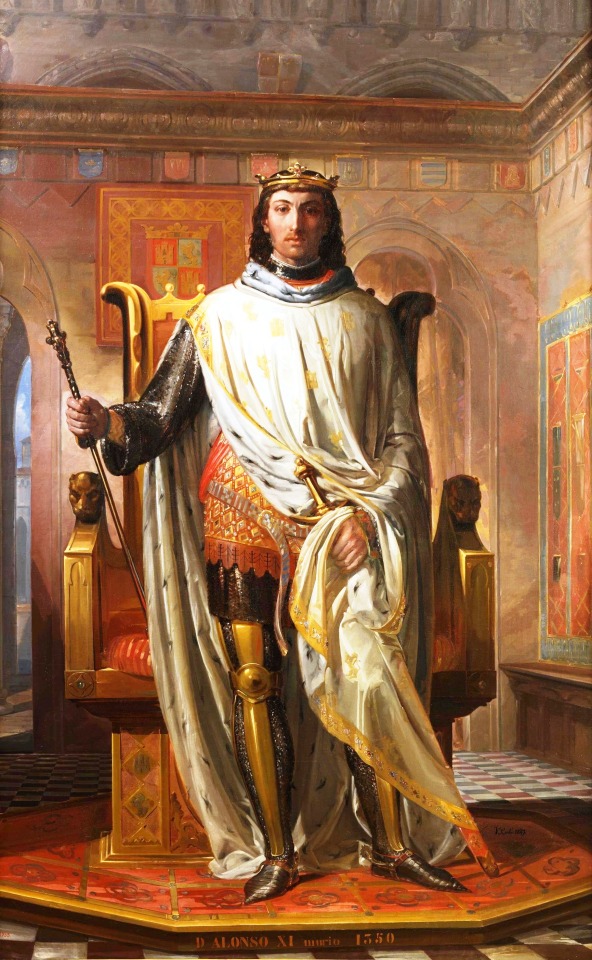

King Alfonso XI of Castile (1311-1350). By Francisco Cerdá de Villarestan.
#monarquia española#museo del prado#francisco Cerda de villarestan#reyes de españa#reyes de castilla#alfonso xi#rey de castilla#viva el rey#spain in the middle ages#kingdom of spain#full length portrait#house of ivrea#house of ivrea in spain#crown of castile#full-length portrait
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Making this a separate post so I don’t go off on a tangent in that love stories post...
Pedro and Inês’ love story was set against a very chaotic historical backdrop (but I guess that’s the norm...) The below is an extremely summarised version:
- Pedro’s wife Constança was the daughter of a very powerful Castilian nobleman, and King Afonso IV of Portugal worried that her father could turn against him due to how his daughter was being treated. Afonso IV himself had actually invaded Castile some years earlier because King Alfonso XI of Castile had mistreated his wife Maria, who was Afonso IV’s daughter.
- Inês’ brothers' political influence over Pedro was met with discontent and worry by the Portuguese nobility, especially the possibility that Pedro was being encouraged by them to get involved in Castilian affairs.
- Afonso IV was also worried about the possibility of an attempt on the life of his only legitimate grandson, the frail prince Fernando, in favour of Inês’ healthier children. Afonso IV himself had had to go to war against his father to secure his succession rights, as his father had favoured an illegitimate son. That civil war had lasted 5 years.
- And that illegitimate son was Afonso Sanches, who was declared a traitor by Afonso IV and who fled to Castile and had a son called João Afonso de Albuquerque.
- And that João Afonso de Albuquerque was the leader of a rebellion against king Pedro I of Castile, and offered prince Pedro of Portugal the crown of Castile in exchange for his support. This meeting was facilitated by Inês.
- King Afonso IV was absolutely determined not to have Portugal dragged into a foreign civil war, and this is what sealed Inês’ fate; her beheading was a gruesome warning to Pedro.
In the end it seems like Afonso IV only managed to delay the inevitable. His grandson king Fernando I of Portugal took after Pedro not only in matters of the heart, but he actually meddled in Castilian affairs, which led to the unsuccessful Fernandine wars and the ultimate end of the first dynasty and the interregnum. And then one of Pedro's illegitimate sons was crowned king anyway, just not any of those he had with Inês.
#lunie blabbers#this is absolutely irrelevant but did you know that Constança was first married to Alfonso XI of Castile?#who then got their marriage annulled (they'd been super young) so he could marry Maria#who was Pedro's older sister....the Pedro who Constança would later marry.....#history is wild. you can't make this up.#pedro and constança and inês were also all each other's cousins. which isn't as wild but i never knew that#i do respect invading castile cos your son-in-law is being an absolute dick to your daughter though i can't fault afonso iv for that
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
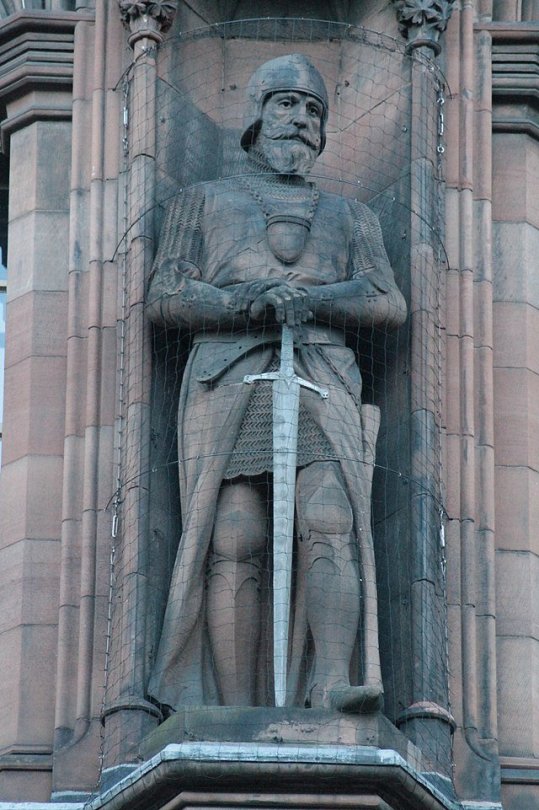
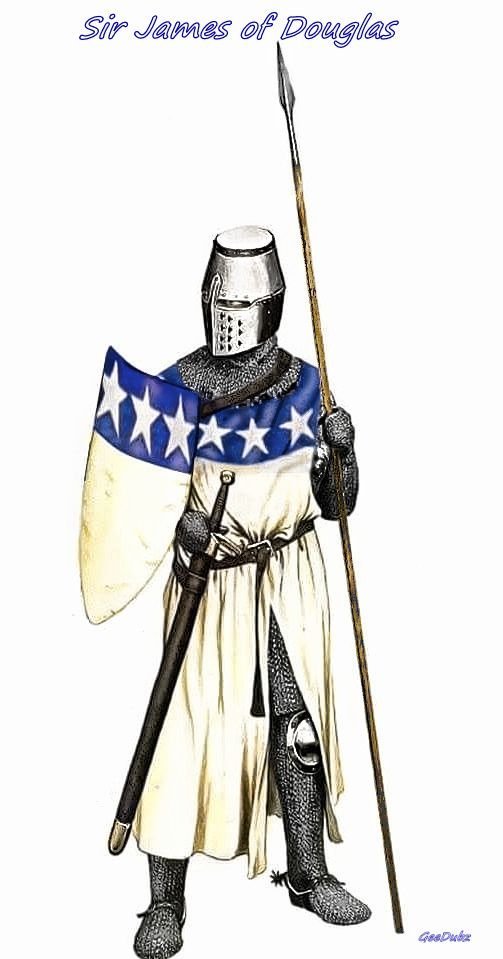





On February 1st 1329, Sir James Douglas bestowed land and money to Newbattle Abbey before he left for with The Bruce’s heart for the Holy Land.
The Good Sir must have known it was a dangerous journey he was going to undertake, he gave the land so that each year a mass would be sung for St Bride and 13 poor people would be fed so the saint would intercede with God for his immortal soul.
In the 1849 book Registrum S. Marie de Neubotle the story is told as such:
On St. Bride’s day, or the 1st of February, in the end of the year 1329, at the park of Douglas, the “good Sir James of Douglas,” being then about to depart for the Holy Land with the heart of his royal master, bestowed on the monastery of Newbattle his half of the land of Kilmad, the other half of which it already possessed by gift of Roger de Quinci; while the monks, on their part, became bound to sing a mass at St. Bridget’s altar within their abbey church on the feast of St. Bridget, yearly for evermore, and to feed thirteen poor folk, that the saint might make special intercession with God for the weal of the good knight.
If you are wondering why it says “in the end of the year 1329” it is because we were still using the Julian calendar back then, the New Year began on March 25th.
Of course most of you will know that Douglas only made it to Spain, landing at Santander where a stone, now lost, recalled the hero ‘El Duglas’. Douglas and the Scots joined King Alfonso XI of Castile in his war against the Sultan of Granada, Muhammed IV.
In Castile an English knight marvelled at Douglas’s unscarred face - he expected the famed warrior to be covered in battle scars, as he himself was. Douglas replied, ‘God be praised, I always had my hands to defend my head.’
On August 30th 1330 Douglas alongside several Scots, including Simon Lockhart of Lee, William Keith, Robert Logan of Restalrig and Walter Logan, William Borthwick, Kenneth Moir, William St Clair of Rosslyn and John St Clair, charged into battle against The Moors at The Battle of Teba, Douglas and the Scots knights died at Teba.
James’s body was found by the silver casket. Muhammed IV had the bodies of the Scots sent with guard of honour to King Alfonso. The surviving Scots, Sir William Keith and Sir Simon Lockhart, cut out their friends’ hearts and boiled their bodies down in a cauldron. They took the knights’ bones and hearts back to Scotland. You may have seen artwork of James throwing the heart ahead of him, this is just artistic licence, he would not be expecting to die, and the casket would most definitely have remained around his neck, as seen in the statue in the second pic, which is on The National Portrait gallery wall in Edinburgh.
It was after Teba that the Douglas Arms were changed, the heart being added to show his devotion to The Bruce.
31 notes
·
View notes
Note
DIVINE RIGHT IS MADE UP AND THE RULES DON’T MATTER. Edward IV was a hugely suspected bastard. Mary I, England's first queen regnant, was legally a bastard. Same for Elizabeth I, who was also considered a bastard by Catholic Europe and a large part of her population. Paul I of Russia was also reportedly a bastard. William the Conqueror was a bastard (literally every Plantaganet claims, the longest running dynasty in English, came from William). Isabella the Catholic's great-great-grandfather and founder of the Trastámara dynasty was King Henry II of Castile, illegitimate son of Alfonso XI and his mistress, Eleanor de Guzmán. John I of Portugal, a bastard as well.
Not to be all 'it's a social construct' but it really is. Bastardy, male primogeniture and divine right are social constructs.
Yep, pretty much. Every time a Green stan screams about 'bastard can't inherit' I am like... How about you look a little at history? There are even bastards that inherit in Westeros and Rhaenyra's sons are not bastards by the legal term of the word. So their pearl clutching about it is ridiculous.
Anyway, going back to my novel where my 'bastard' protagonist is declared the heir by her father over her oh so legitimate brother. 🤷
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo
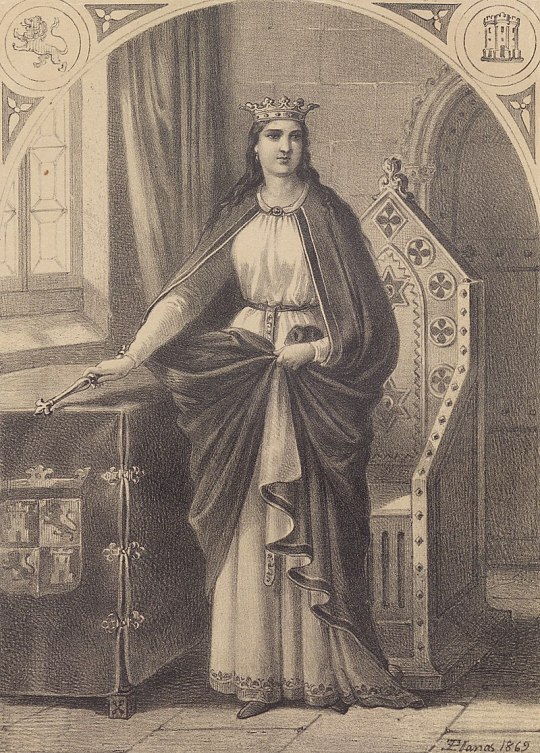

María Alfonso Téllez de Meneses (c. 1265 – 1321), known as María de Molina, was queen consort of Castile and León from 1284 to 1295 by marriage to Sancho IV of Castile, and served as regent for her minor son Ferdinand IV (1295 - c.1301) and later her grandson Alfonso XI of Castile (1312-1321).
#María Alfonso Téllez de Meneses#María de Molina#House Ivrea#XIII century#XIV century#Illustration#art#arte
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
i recently read and confirmed elsewhere (on tudorhistory q/a ... of all things) that there was actually a (single, afaik) precedent for a royal marriage wherein the widow married her husband’s brother, it was however very different in circumstance to the marriage of catherine and arthur and subsequently henry which is maybe why it was never brought up precedentially by either side....
On 18 October 1319 the wedding ceremony between James of Aragon and Eleanor of Castile took place. James, according to the chronicles of the time, refused to give the kiss of peace during the ceremony, and James II had to do it.[2] After the ceremony, officiated by the Archbishop of Tarragona, the bridegroom again transmitted to his father his desire to renounce his rights to the throne and enter a convent. After the wedding ceremony, and after a discussion with his father, he fled on horseback, leaving his wife abandoned, and in December 1319, renounced his rights to the throne of Aragon in the Convent of San Francisco of Tarragona. Immediately, he took the habit of the Knights Hospitaller in the Convent of Santo Domingo of the same city.[2]
Alfonso, King James II's younger son, was proclaimed heir apparent. The rejection of Eleanor could have caused serious diplomatic incidents between the Castilian and Aragonese courts. James II informed Eleanor's grandmother, Queen Maria, about his regret for the actions of his eldest son, incomprehensible to him. During the spring of 1320 Eleanor remained lodged in the city of Tortosa; during her stay there, James II and Alfonso became aware that the younger James planned to recover his wife and his rights to the throne, and the conspiracy was thwarted by his father.[3]
After her stay in Tortosa, Eleanor lived in the cities of Zaragoza, Calatayud and Ateca, from where some Castilian ricohombres returned her to the Kingdom of Castile and León.[4] Once in her homeland, Eleanor retired to the Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas, although she never took the veil.[5] In early 1325, King Edward II of England proposed the marriage of his eldest son, Edward, with Eleanor, and sent his proxies to negotiate the terms of the wedding by charter dated 6 February 1325. The union never took place due to Edward's deposition.
so...never lived together, never so much as even shared the same bed the night of the wedding, not to mention he takes orders before he can do any of these things, and abdicates (although apparently he gets cold feet/buyers’ remorse later...). very different case, but, funnily enough, eleanor does have sons by her previous husband’s brother after their marriage:
In Ágreda in January 1329 the betrothal between Eleanor and King Alfonso IV of Aragon was signed, and the wedding ceremony took place one month later, on 5 February in the Church of San Miguel de Tarazona. The ceremony was attended by King Alfonso XI of Castile and King James II's children, Maria, John, Peter and Ramón Berenguer. Alfonso IV gave his new wife the city of Huesca and other villages and castles belonging to the Aragonese crown.[4] This marriage improved relations between Castile and Aragon in a renewed alliance formed with the aim of reconquering Granada. The Kingdom of Aragon had breached several marriage agreements, returning to Castile several princesses after breaking off engagements, and this union put an end to the practice.
Eleanor became a disruptive influence in Aragon, plotting to advance the interests of her own sons over those of her stepson, Peter, born from Alfonso IV's first marriage with Teresa d'Entença, Countess of Urgell, who died in 1327. She convinced her husband to consent to make significant territorial donations to the children born to them, Ferdinand and John. Alfonso IV was generous and on 28 December 1329, he granted Ferdinand the Marquisate of Tortosa and the cities of Albarracín, Orihuela, Callosa, Guardamar, Alicante, Monforte, Elda, La Mola, Novelda and Aspe.[7] Eleanor's younger son John also received several lordships: Elche, Biel and Bolsa.
These donations made by Alfonso IV diminished the territorial patrimony of the crown and mainly affected Peter, producing a climate of resentment in the Aragonese court. Because of this the nobility was divided into two camps. One of the two sides was in favor of Queen Eleanor and her sons, and the other defended the prerogatives of Peter and his full siblings. When the King granted his son Ferdinand the cities of Xàtiva, Alzira, Sagunto, Morella, Borriana and Castellón de la Plana, all located in the Kingdom of Valencia, the local subjects protested, and for this reason the King decided to revoke these last donations
although...
Her youngest son, John of Aragon, was assassinated in Bilbao on 12 June 1358 by order of his cousin the Castilian sovereign,[10] and one year later (March/April 1359), she was murdered in the castle of Castrojeriz by order of her nephew.[5]Four years later, in 1363, her oldest son, Ferdinand of Aragon, was assassinated in Burriana by order of his half-brother, King Peter IV.[11]
#i believe catherine argued that the short life of henry nyp proved otherwise but anyway i do wonder if either were aware of this precedent#because clearly to henry the death via illness counted as 'without [sons]' you wonder if 'unnatural' death would have counted#in his mind/faith as well#it was very messy to speak of curses of god but particularly so when it becomes further tangled with the idea of free will#bcus god could not force someone else to murder#'abandonment' was also grounds for annulment#as im reminded from this#which adds some texture to catherine refusing to visit her daughter alone#although unless it was prolonged i don't think henry could have credibly claimed abandonment/desertion... i think she#was becoming somewhat paranoid. understandably . that any laxity was going to be used against her#probably not helped by chapuys telling her they were going to shove a man in her closet and allege adultery#or an assassin. i believe he claimed both to charles in 1533
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo










Old Town Viveiro, Spain (No. 1)
The oldest historical documentation that is preserved is from the twelfth century, from the year 1112, when Queen Doña Urraca I of León (to whom her father King Alfonso VI granted the county of Galicia), granted the lordship of the then borough to the bishop of Mondoñedo Don Nuño Alfonso.
The son of Doña Urraca, King Alfonso VII of León, would delimit for the first time the territory belonging to the lordship of Vivero, by means of a letter published in Palencia on July 10, 1128. This manor was also part of the municipality of Vivero, which would later become those of Vicedo, Orol, Jove, Cervo and Burela.
The inhabitants of Vivero showed their rejection of the lordship, engaging in a struggle with the bishopric that lasted almost two centuries. Faced with the continuous struggles, King Alfonso IX of León had to mediate in the dispute between the inhabitants of Vivero and the bishop, forcing them to protect and help each other. However, the monarch stipulated that the rights and slanders be divided between the House of Burgundy, the bishop of Mondoñedo and the mayor of Vivaria, while the requests for maravedis, portazgos and other profits were distributed equally between the monarch and the bishop. This dictate was also maintained by his successor, Ferdinand III the Saint, who confirmed it in February 1252.
After a brief period in calm, the inhabitants of Vivero again rebelled against the bishop of Mondoñedo. Bishop Don Álvaro Gómez reported this to the justice, which issued in 1287 a sentence against the Vivarienses. Finally, in 1346 King Alfonso XI of Castile granted him the status of royalty, keeping only the bishops an annual tribute of eighteen reales for the loading and unloading of goods from ships in the port of Vivero.
Source: Wikipedia
#Carlos V Gate#Puente Mayor o de la Misericordia#street scene#architecture#travel#vacation#cityscape#tourist attraction#landmark#summer 2021#original photography#Porta Maior#Galicia#Viveiro#province of Lugo#Spain#A Mariña Occidental#España#Northern Spain#Northern Europe
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
What's something you love?
Tell me about it. I'd love to know. <3
Odd History like this
The Bubonic Plague.
A little background:
Infectious Disease caused by a bacteria called Yersinia Pestis. The Plague was by Fleas on the back of Rats who came over on 12 ships in October of 1347, dubbed "Death Ships" from the Black Sea dock in the Sician port of Messina. The Rats and Fleas got the Plague from other rats and Fleas involved in the "Great Pestilence" on the Trade routes of the Near and Far East. In the early 1340's Black Death had struck China, India, Persia, Syria, and Egypt. In the East, Kipchak khan Janibeg was leading a campaign against the trading post of Kaffa (the modern?? City?? of Feodosiya) in Crimea. When his army was struck by the black death. So, with his army disintegrating, he started catapulting the bodies of deceased plague victims over the walls of the town in the hopes of infecting his enemies.
Cause:
The cause of this disease is an infection caused by the Yersinia Pestis (Y. Pestis) bacterium. Spread most often by Fleas on Rats or other animals. Humans who are bitten by the fleas come down with the plague. Making this a Zoonotic Disease as it is trans-species.
Note: Cats are Particularly vulnerable to the plague, getting infected by the fleas or by the rodents that they eat. Then passing it on to their owners or the vets who treat them through droplets.
Person to Person transmission is Rare, unless the person has Pneamonic, spreading the droplets through the air.
Symptoms and Types:
-Sudden High Fever
- Pain in abdomen, arms and legs
-Headaches
- Large swollen lumps on lymph nodes (Buboes) that form and leak pus
Septicemic:
When infection goes throughout the body
May include: Blackened tissue from Gangrene (Medical Condition where lack of blood supply to body tissue causes said tissue to die. Though Gangrene can happen throughout the body, it starts in Digits, hands, and feet) involving digits, toes or unusual bleeding.
Pneumonic:
When the infection goes to the lungs
May have additional: trouble breathing and might cough up blood. May also feel nausea or vomit.
Modern Treatment:
Antibiotics:
Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Mosiflocacion, Gentamicin, Doxycycline
Death Toll:
Europe (14th century): over 25 million people, about 2/3 of Europe at the time.
Including:
Eleanor, Queen of Peter IV of Aragon
King Alfonso XI of Castile
Joan, the daughter of King Edward III, who died on her way to be wed to King Alfonso's son.
Archbishop John de Stratford
Archbishop Thomas Bradwardine
Poet Petrarch's Muse Laura and his patron, Giovanni Cardinal Colonna
1/4 of the Papel Court in Avignon
as well as many villages and families.
Still Killing??
Yes! The Black death still occurs around the world. About 7 cases happen in the US every year. Half of the cases are made up by people from ages 12 to 45. In the US the cases are in Northern: New Mexico and Arizona, Southern Colorado and Oregon, Western Nevada, and sometimes in California.
Interesting Facts:
Black Death gets its name as most people who contracted the disease died (death) and often had blackened tissue (Black) due to Gangrene.
Many Historians believe that the Nursery Rhyme "Ring around the Rosy" is about the symptoms of the Black Plague.
Anti-Semitism greatly incressed as Jews were blamed for the plauge.
Unlike Neopalten or Hitler, the black plague succeeded in defeating Russia.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 2: Beatrice of Castile
Beatrice of Castile (also spelled Beatriz)
Born: 1293
Died: 25 October 1359
Parents: Sancho IV and María de Molina
Infanta of Castile
Queen of Portugal as the wife of Afonso IV ( 7 January 1325 – 28 May 1357)
Children: Maria (1313 – 18 January 1357) - the wife of Alfonso XI of Castile and mother of the future king Peter I of Castile.
Alfonso (1315– 1317)
Denis (born 12 February 1317) - died a few months after his birth
Peter (8 April 1320 – 18 January 1367) - King of Portugal
Isabel (21 December 1324 – 11 July 1326)
John (23 September 1326 – 21 June 1327)
Eleanor (1328 – 1348) - the wife of Peter IV of Aragon
She was born in Toro, Kingdom of Castile.
On 13 September 1297, the Treaty of Alcañices was signed by her mother, regent at the time, and the King of Portugal. The treaty included marriage clauses to reinforce the peace.
The four year old Beatrice abandoned Castile the same year to move to the Portuguese court where she was raised alongside her future spouse , Infante Afonso, who was 2 years her senior. She was raised in a refined environment, courtesy of her future father-in-law King Denis of Portugal.
Upon her arrival, she was given multiple wedding tokens including properties by the king. After marriage the number of estates increased, her husband gifting her a great number before even ascending the throne. She received even more properties after her son became king.
Before the marriage could take place a papal dispensation was required.
The papal bull was issued in 1301 but the marriage was postponed until Beatrice and Alfonso were of age.
In 1309 the two were married, aged 16 and 18. The marriage was celebrated in Lisbon on 12 September 1309. The marriage was happy and successful, Alfonso did not have a single child out of wedlock. The couple had 7 children, 3 living past infancy.
She played an important role in the affairs of the kingdom, mediated numerous conflicts, founded a hospital and left numerous properties and sums to religious establishments.
She had 7 children, only 3 reaching adulthood.
Beatrice died aged 66 in Lisbon. She is buried in Lisbon Cathedral next to her husband.
#portuguese history#spanish history#women history#history#medieval history#14th century#1300s#13th century
0 notes
Text







A guide through the monarchs of Aragon in La Catedral del mar & Los Herederos de la tierra
@asongofstarkandtargaryen
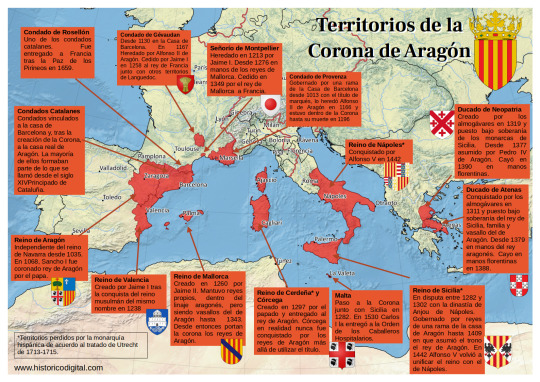
During the series the role of the members of the monarchy is secondary, but they are used to help to establish a concrete historical context and they're very determinant in the situation of the Puig and Entanyol families involving political estrategies of supporting this or that king, that gave them benefits or dacay (Arnau's rise with Pedro IV, Genís & Roger rise with Juan I and Martín I and Bernat with Fernando I). So, I wanted to make a recopilation of the monarchs shown during these series and their families.
House of Aragon/ House of Barcelona (descendants of the Jimena dinasty)
The Jimena dinasty is called like that because its origin was Jimeno "the Strong", grandfather of Eneko Arizta, and one of its branches was the Arista-Iñiga dinasty started by Eneko.
Eneko, his son García Iñiguez and his grandson Fortún Garcés were Lords of Pamplona, Fortún Garcés married Awriya bint Lubb ibn Musa (great-grandaughter of Musa the Great), and one of their daughters was Oneka Fortúnez, who married Abd Allah I of Cordoba (their son was Muhammad, who fathered the calipha Abd al-Rahman III with a basque woman called Muzna) and then Oneka married Aznar Sánchez de Larraún, and had a daughter with him, Toda Aznárez. Toda married Sancho Garcés I, the truly first king of Pamplona, was Sancho Garcés I (the first king of the Jimena dinasty).
Sancho Garcés III (992-1036) was king of Pamplona, Count of Aragon and king consort of Castile, whose bastard son with Sancha de Aibar, Ramiro I, inherited the counties of Aragon, Sobarbe and Ribagorza, and united them to form the kingdom of Aragon.
Then Petronila I (1136-1173), Ramiro I's great-grandaughter, married Ramón Berenguer IV count of Barcelona. Their son Alfonso II of Aragon was the first king of the Crown of Aragon and Pedro IV's great-great- great-grandfather.
In summary all the Aragonese monarchs are descedants of Eneko Arizta (and that's the way we can link Irati with LCDM/LHDLT)
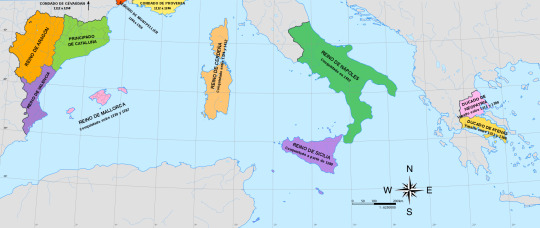
Pedro IV
Pedro IV of Aragon, II of Valencia and I of Mallorca (Balaguer, Lleida, Catalonia, September 5, 1319 - Barcelona, Catalonia, January 5, 1387), called "the Ceremonious" or the Punyalet ('the one with the dagger', due to a dagger he used to carry), son of Alfonso IV of Aragon and Teresa de Entenza.
King of Aragon, Valencia and Mallorca (1344-1387); Duke of Athens (1380-1387) and Neopatria (1377-1387); count of Barcelona (1336-1387) and of Ampurias (1386-1387).
In 1338 he married María de Navarra (1326-1347), daughter of Felipe III and Juana II of Navarra. Offspring:
Constanza (1343-1363), married in 1361 to Federico III of Sicily, and Juana (1344-1385), married in 1373 with Juan I de Ampurias.
In 1347 he married Leonor of Portugal (1328-1348), daughter of Alfonso IV of Portugal. She died the following year of the Black Death.
In 1349 he married Eleanor of Sicily (1325-1375), daughter of Pedro II of Sicily. Offspring:
Juan I (1350-1396), Martin I (1356-1410) and Leonor (1358-1382), married to Juan I of Castile. Leonor was the mother of Fernando I of Aragon.
In 1377 he married Sibila de Fortiá, daughter of the Empordà nobleman Berenguer de Fortiá. Offspring:
Isabel (1380–1424), who married Jaime II of Urgel, future suitor for the aragonese crown.
During his reign the Aragonese expansionism in the Mediterranean continued, focused on southern Italy and Greece.
Although he was ally of Alfonso XI, Pedro IV had a great rivalry with his son Pedro I of Castile and fought against him in some conflicts, like the War of the two Pedros (1356-1369) and the first Castilian Civil War (1351-1369), in which Pedro I was supported by Pedro I of Portugal (one of his bastard sons, Juan I of Portugal, was the founder and first king of the Avis dinasty) and Muhammad V of Granada, and Pedro IV supported the bastard children of Alfonso XI with his lover Leonor de Guzmán (Pedro de Aguilar, Sancho Alfonso, Fadrique Alfonso, Enrique II of Castile, Fernando Alfonso, Tello, Juan Alfonso, Juana Alfonso, Sancho and Pedro Alfonso), who started several revolts against Pedro I of Castile. The wars ended when Enrique killed Pedro I, and he became the first king of Castile of the Trastamara dinasty.
Sibila de Fortiá
Sibila de Fortiá (Fortiá, Girona, Catalonia, 1350 - Barcelona, Catalonia, 1406), queen consort of the Crown of Aragon (1377-1387). She was the daughter of Berenguer de Fortiá and his wife Francesca de Vilamarí. In 1371 she married for the first time Artal de Foces, an Aragonese nobleman, whom she widowed in 1374, and then she the lover of Pedro IV and had a daughter with him, Isabel.Pedro and Sibila married in 1377. After the wedding, Pedro surrounded himself with Empordà nobles as well as Sibila's relatives.
Pedro IV was very ill at the end of the year 1386, and Sibila, fearful of the wrath of the future King Juan, fled to the castle of San Martín de Sarroca (Barcelona), which belonged to her brother Bernat de Fortiá. There she was imprisoned by Juan I, who treated her harshly, accusing her of abandoning the king on his deathbed and of several robberies in the palace. She was confined in the castle of Moncada (Barcelona) until she renounced his property granted by the king. Finally, Sibila retired to the convent of San Francisco in Barcelona, where she died in 1406.
Juan I
Juan I of Aragon, called the Hunter or the Lover of All Kindness (Perpignan, Occitania, France, 1350 - Torroella de Montgrí, Girona, Catalonia, 1396), King of Aragon, Valencia, Mallorca, Sardinia and Corsica, and Count of Barcelona, Roussillon and Cerdanya ( 1387-1396). Son of Pedro IV and Leonor of Sicily.
His first marriage was with Marta de Armagnac (1347-1378), daughter of Count Juan I de Armagnac. With whom he had: Jaime (1374), Juana, (1375-1407) who married Mateo, Count of Foix. After the death of her father, she claimed the throne with her husband, but they were defeated; Juan (1376), Alfonso (1377) and Leonor (1378).
Widowed, Juan married Violante de Bar (1365-1431), daughter of Robert I, Duke of Bar. Offspring:
Jaime Duke of Girona (1382-1388), Yolanda, who married Louis II of Anjou, titular king of Naples. Their son, Luis III, claimed the throne after the death of Martín I, in the engagement of Caspe; Fernando Duke of Girona (1389), Antonia (1391-1392), Juan Duke of Girona (1392-1396), Eleanor (1393), Pedro Duke of Girona (1394) and Juan (1396)
Martin I
Martin I of Aragon, also called the Human or the Old (Girona, July 29, 1356-Barcelona, May 31, 1410), was king of Aragon, of Valencia, of Majorca, of Sardinia and count of Barcelona (1396-1420) and king of Sicily (1409-1410). Second son of Pedro IV of Aragon and his third wife Leonor of Sicily.
Martín was called "the Human" because of his great passion for the Humanities and books. The library of Martín I is the first that could be considered from Renaissance, if at that time in the history of the Iberian peninsula the term can already be used.
Martin married in 1372 with Maria de Luna, daughter of Lope, the first count of Luna, in 1374. From this union they were born:
Jaime (1378), Juan (1380) and Margarita (1388) and Martin I of Sicily "the Younger" (1376-1409), first husband of Blanca I of Navarra.
When Martin the Younger died, Martin married Margarita de Frades, although they left no issue.
His entire reign was marked by the Western Schism that divided Christianity since 1378. He was a supporter of the popes of Avignon (where he went the year of his coronation to swear allegiance to Benedict XIII "the Pope Luna", Pedro Martínez de Luna y Pérez de Gotor, with whom it seems that he came to establish a friendly relationship ), from whom he obtained support in his claims over the kingdom of Sicily against the Anjou, supporters of the popes of Rome. In 1400, he would marry his niece Yolanda to Louis II of Anjou in order to defuse tensions. He met in Avignon with the antipope Benedict XIII, Aragonese and a relative of the queen, with the intention of reaching a solution to the schism and, later, in 1403 he intervened militarily against the siege that Benedict suffered in his papal seat, rescuing him and welcoming him in Peñíscola .
House of Trastamara (the Aragonese branch)
Fernando I
Ferdinand I of Aragon (Medina del Campo, Valladolid, Castile and Leon, November 27, 1380-Igualada, April 2, 1416), also called Fernando de Trastámara and Fernando de Antequera, the Just and the Honest, was an infant of Castile, king of Aragon, Valencia, Mallorca, Sardinia, Count of Barcelona (1412-1416), and regent of Castile (1406-1415), during the minority of Juan II of Castile. Son of Juan I of Castile and Leonor of Aragon.
He was the first Aragonese monarch of the Castilian dynasty of the Trastámara, although he was of Aragonese origin on his mother's side.
He married Leonor de Alburquerque
Alfonso the Magnanimous (Medina del Campo, 1394-1458), king of Aragon, with the name of Alfonso V, and of Naples and Sicily, with the name of Alfonso I.
María de Aragón (Medina del Campo, 1396-1445), first wife of Juan II of Castile and mother of Enrique V of Castile
Juan II (Medina del Campo, 1397-1479), King of Aragon and King consort of Navarre.
Enrique (1400-Calatayud, 1445), II Duke of Villena, III Count of Alburquerque, Count of Ampurias, Grand Master of the Order of Santiago.
Leonor (1402-1445), who married Eduardo I of Portugal. Mother of Alfonso V of Portugal, Juana of Portugal (Enrique IV's second wife) and Leonor of Portugal, who married Frederick III of Habsburg (they were parents of emperor Maximilian I of Austria)
Pedro (1406-1438), IV Count of Alburquerque, Duke of Noto.
Sancho (1400-1416)
Alfonso V
Alfonso V of Aragon (Medina del Campo, 1396 – Naples, June 27, 1458), also called the Wise or the Magnanimous, king of Aragon, of Valencia, of Majorca, of Sicily, of Sardinia and Count of Barcelona (1426-1458); and King of Naples (1446-1458).
Alfonso V can be considered as a genuine prince of the Renaissance, since he developed an important cultural and literary patronage that earned him the nickname of the Wise and that would make Naples the main focus of the entry of Renaissance humanism in the sphere of the Crown of Aragon.
From his relationship with his lover Giraldona de Carlino, a napolitan noblewoman, he had three children:
Fernando (1423-1494), his successor in the kingdom of Naples under the name Fernando I.
Maria (1425-1449), married to Lionel, Marquis of Este and Duke of Ferrara.
Leonor, or Diana Eleonora (?-1450), married the nobleman Marino Marzano, Prince of Rossano.
Maria of Castile
María of Castile (Segovia, Castile and Leon, November 14, 1401-Valencia, October 4, 1458). Infanta of Castile, Princess of Asturias (1402-1405) and Queen of Aragon (1416-1458) for her marriage to Alfonso the Magnanimous. First daughter of Enrique III "the Mourner" and Catherine of Lancaster. Sister of Juan II of Castile, untie of Enrique IV and Isabel I.
The marriage between María and Alfonso is celebrated in the Cathedral of Valencia on October 12, 1415. The ceremony was officiated by the antipope Benedict XIII, who also granted the matrimonial dispensation for the wedding.
In 1420, when the king left for Naples for the first time, he left the government of his kingdoms in the hands of Maria as lieutenant general. The absence of the Magnanimous would last three years, during which María had to face the rapid deterioration of the economic situation in Catalonia, the territorial struggle with the Castilian Crown, as well as the conflicts of a social nature that shook her in different kingdoms. On his return to Aragon in 1423, Alfonso V began the war with Castile, along with his brother King Juan of Navarra. But her financial resources were exhausted and in 1429 Queen María had to act as a mediator between her husband and her brother, King Juan II of Castile, to put an end to the dispute. However, Alfonso's situation did not improve, due to the recession suffered by the Catalan economy and the social conflicts caused by it. The Courts of Barcelona in 1431 demanded from the king a series of measures to correct the enormous deficit of the Catalan treasury and trade. But Alfonso, fed up with these matters, returned to Italy and gave full powers to the queen as ruler of Aragon; he left the Iberian Peninsula forever on May 29, 1432. This marked Alfonso V's final break with the Crown of Aragon, which, however, he never renounced.
+ Bonus track (although he doesn't appear in this series)
Juan II
Juan II of Aragon and Navarra, the Great, or the Faithless according to the Catalan rebels who rose up against him (Medina del Campo, June 29, 1398-Barcelona, January 20, 1479) was Duke of Peñafiel, King of Navarre (1425-1479), King of Sicily (1458-1468) and King of Aragon, Mallorca, Valencia, Sardinia (1458-1479) and Count of Barcelona, son of Ferdinand I of Aragon and Leonor de Albuquerque.
From his first marriage to Blanca I of Navarra (daughter of Leonor of Castile and Carlos III of Navarra):
Carlos (1421-1461), Prince of Viana and Girona, Duke of Gandia and Montblanch, titular King of Navarra as Carlos IV (1441–1461), married Agnes of Cleves. He wrote the 'Chronicles of the Monarchs of Navarra', about the history of his antecessors, from Eneko Arizta in the 8th century up to the 15th century.
Juan (1423-1425)
Blanca of Navarra (1424-1464), first wife of Enrique IV of Castile
Leonor (1425-1479), married to Gastón IV de Foix, Queen of Navarre under the name of Leonor I.
From his second marriage to Juana Enríquez:
Leonor of Aragon (1448)
Fernando II (1452-1516), king iure uxoris of Castile (1474-1504) and then regent between 1507 and 1516, under the name of Fernando V due to his marriage to Isabel I, king of Sicily (as Fernando II, 1468-1516), Aragon and Sardinia (as Fernando II, 1479-1516), Naples (as Fernando III, 1504-1516), and from Navarra (as Fernando I, 1512-1516)
Juana (1455-1517), second wife of Fernando I of Naples. Her daughter Juana married Fernando II of Naples (Fernando I of Naples' grandson)
During his youth, Juan fought in the Castilian-Aragonese war (1429-30) and the Castilian Civil War (1437-1445) in the Aragonese team against Juan II of Castile, his son Enrique and the Constable Álvaro de Luna (favourite of Juan II), due to the Aragonese political influences in Castile and the full control that Álvaro de Luna had over Juan II of Castile that allowed him to become very powerful, so some members of the Castilian nobility wanted to remove Álvaro out of Juan II side because of that, and the Aragonese reacted to the anti-aragonese convictons of Álvaro.
Álvaro de Luna arranged a new marriage between Juan II of Castile and Isabel of Portugal (mother of Isabel I) in 1447. The constable intended with this dynastic alliance to strengthen the political ties that united Castile and Portugal against the common enemy: the Catalan-Aragonese Crown, but from 1449, Isabella of Portugal indirectly supported the maneuvers of the Great League of Nobles (allies of the Aragonese) formed against the constable. But it would not be until 1453 when Juan II of Castile, possibly tired of the continuous pressure from the aristocracy, left Álvaro on his own. It has often been said that it was the queen herself who demanded that her husband signed the prison order against Álvaro, through Juan Pacheco, Marquis of Villena.
By 1441 Blanca I de Navarra died and Juan II married the daughter of Fadrique Enríquez (one of his Castilian allies, the admiral of Castile), Juana Enríquez y Fernández de Córdoba.
After the death of Blanca I, a dispute between Juan II and Carlos de Viana about the sucession for the Navarrese throne. Juan was king Iure uxoris of Navarre and wanted to be keep his position as king, but Carlos and his supporters claimed that the prince was the rightful king as firstborn son of the queen and in 1451 the Navarrese civil war started.
In the following years the tension between Juan and Carlos increased with the birth of Fernando, who was pushed by his mother Juana to be the heir of Aragon and Navarra, which Juan later accepted. This change in the sucession was not accepted in Catalonia, that supported Carlos de Viana birthrights, and they started a rebellion against Juan II.
Other supporter of Carlos was Enrique IV, who offered his sister Isabel to Carlos in marriage as a sign of their alliance, but the wedding never happened.
Carlos died in 1461, although the war didn't ended because the Catalan nobility proposed other suitors for the Crown of Aragon and the Principality of Catalonia, like Enrique IV, Pedro of Portugal (grandson of Jaime II of Urgell) and Renato de Anjou during the Catalan civil war, that ended in 1472.
It's interesting that the interesting that the current situation of the Estanyol family at the end of Los Herederos de la tierra is that there are two brothers from different mothers, and whose father have benefited one of them over the other, so it may lead to tensions from the part that was not benefited, Arnau Jr is the main heir in Bernat's will, so maybe in the future Marta Destorrent will try to pit her son Baltasar against his elder brother to take Arnau Jr's place. By period of time I find very likely that this happens during the reigns Maria of Castile and Juan II, and the situation of the Estanyol succession could parallel the Carlos de Viana-Fernando II problem, although in this case the younger son was the benefited one and the one who inherited his father's kingdoms and maybe the Estanyols are part of the Catalan nobility that defended Carlos' birthrights, although some other Catalan nobles supported Juan II & Fernando alongside of peasants and smallfolk, during the First Remensa War during the Catalan civil war.
The Remensa War consisted in revolts organised by peasants who wanted to end the servitude to which their feudal lords had subjected them, so I think that probably the Estanyol-Llor family would support the peasants because of their backgrounds.
#la catedral del mar#los herederos de la tierra#the cathedral of the sea#heirs to the land#history#crown of aragon#aragonese monarchs#pedro iv de aragón#juan i de aragón#martín i de aragón#sibila de fortiá#fernando i de aragón#alfonso v de aragón#maria de castilla#juan ii de aragón#gifs#period dramas#house of aragon#house of trastamara#house of barcelona#long post
21 notes
·
View notes
Photo

King Alfonso XI of Castile by José María Rodríguez de Losada.
#jose maria rodriguez de losada#monarquia española#reyes de españa#rey de castilla#alfonso xi#viva el rey#full length portrait#crown of castile#spain in the middle ages#house of ivrea#house of ivrea in spain#kingdom of spain#full-length portrait
1 note
·
View note
Text
【人物故事】Peter I of Portugal-生死不渝的愛戀,讓「死去」的愛人坐上王座?
如果大家還記得卡斯提爾的康斯坦絲(Constance of Castile)的故事(忘了歡迎回頭看),她的老爸卡斯提爾的佩德羅(Peter(Pedro)of Castile),和爺爺的私生子恩里克(Henry(Enrique) II of Castile)為搶王位而大戰,導致她和妹妹流亡海外。我曾説過要為他另寫一篇故事,但留到以後,今天我要講與其同名的舅舅的故事。
葡萄牙國王佩德羅一世(Peter I of Portugal),不僅和外甥同名,連綽號都一樣,被稱爲「殘酷者」或「正義者」,兩位不僅都是評價兩極的君主,也都為了愛,與整個宮庭為敵,只是舅舅的愛情故事比姪子的更加詭譎。
一切要從卡斯提爾的阿方索十一世(Alfonso XI of Castile)說起,阿方索繼位時尚未成年,他的叔公胡安·曼紐(Juan…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo





On February 1st 1329, Sir James Douglas bestowed land and money to Newbattle Abbey before he left for with The Bruce’s heart for the Holy Land.
The Good Sir must have known it was a dangerous journey he was going to undertake, he gave the land so that each year a mass would be sung for St Bride and 13 poor people would be fed so the saint would intercede with God for his immortal soul.
In the 1849 book Registrum S. Marie de Neubotle the story is told as such:
On St. Bride’s day, or the 1st of February, in the end of the year 1329, at the park of Douglas, the “good Sir James of Douglas,” being then about to depart for the Holy Land with the heart of his royal master, bestowed on the monastery of Newbattle his half of the land of Kilmad, the other half of which it already possessed by gift of Roger de Quinci; while the monks, on their part, became bound to sing a mass at St. Bridget’s altar within their abbey church on the feast of St. Bridget, yearly for evermore, and to feed thirteen poor folk, that the saint might make special intercession with God for the weal of the good knight.
If you are wondering why it says “in the end of the year 1329” it is because we were still using the Julian calendar back then, the New Year began on March 25th.
The pic shows a statue of Sir James Douglas on The Scottish National Portrait Gallery, not the chain and casket around his neck, which contained the heart of Robert the Bruce, King of Scots. Of course most of you will know that Douglas only made it to Spain, landing at Santander where a stone, now lost, recalled the hero ‘El Duglas’. Douglas and the Scots joined King Alfonso XI of Castile in his war against the Sultan of Granada, Muhammed IV.
In Castile an English knight marvelled at Douglas’s unscarred face - he expected the famed warrior to be covered in battle scars, as he himself was. Douglas replied, ‘God be praised, I always had my hands to defend my head.’
On August 30th 1330 Douglas alongside several Scots, including Simon Lockhart of Lee, William Keith, Robert Logan of Restalrig and Walter Logan, William Borthwick, Kenneth Moir, William St Clair of Rosslyn and John St Clair, charged into battle against The Moors at The Battle of Teba, Douglas and the Scots knights died at Teba.
James’s body was found by the silver casket. Muhammed IV had the bodies of the Scots sent with guard of honour to King Alfonso. The surviving Scots, Sir William Keith and Sir Simon Lockhart, cut out their friends’ hearts and boiled their bodies down in a cauldron. They took the knights’ bones and hearts back to Scotland.
The illustrations are from the hand of Andrew Spratt of how the Abbey may have looked back then, the interior pic is probably the oldest surviving part of the building, down in the vaults, a place I must get round to visiting, maybe this year.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
King Afonso IV quickly learned that his daughter Maria was being mistreated by her husband King Alfonso XI of Castile.
sometimes reading about historical figures fucking sucks
#personal#this is giving me a fucking headache#royals start diversifying your naming conventions please
0 notes