#alligator snapping turtle
Text
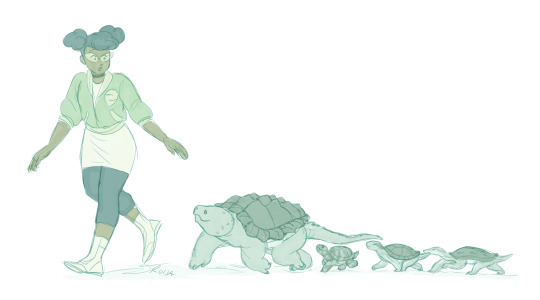


April encounters some strange turtles.
Everyday I think about how cute irl turtles are and yearn to hug them. I'm coping by drawing April doing it instead.
#tmnt#rottmnt#april o'neil#leonardo#raphael#michelangelo#donatello#turtles#alligator snapping turtle#red eared slider#spiny softshell turtle#eastern box turtle
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
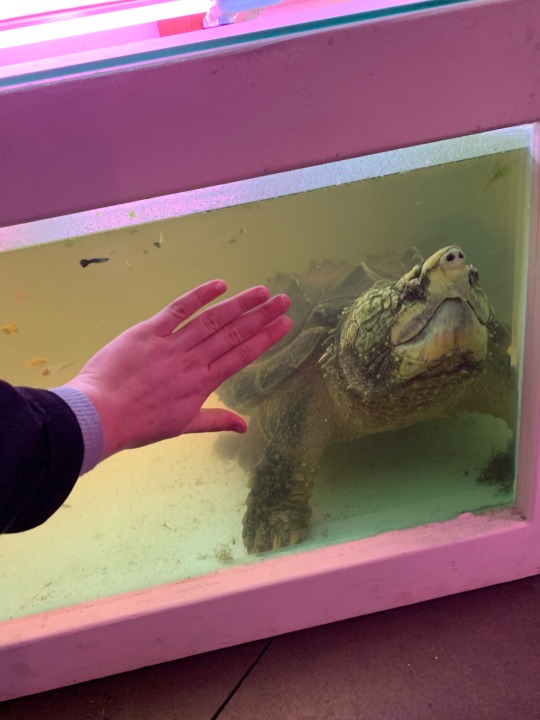


The hugest boy in the world. The biggest boy I’ve ever seen
1K notes
·
View notes
Text




The Stupendous Alligator Snapping Turtle
Alligator snapping turtles (Macrochelys temminkii) are one of three recognised species of snapping turtle, all of which are found in North America. This particular species is found in the southeastern United States and the Mississippi Basin in particular. Macrochelys temminkii prefers deep freshwater, and is especially common in deep rivers, wetlands, and lakes.
The alligator snapping turtle is the largest freshwater turtle in North America, and is one of the heaviest in the world. Most individuals weigh between 70-80 kg (154-176 lbs), and are about 79-101 cm (31-39 in) long. However, the largest verified indiviual weighed over 113 kg (249 lb), and many others have been recorded in excess of 100 kg. The species is easily identifiable by its large, boxy head and thick shell with three rows of raised spikes. Typical alligator snapping urtles are solid black, brown, or olive green, though the shells of many older individuals can be covered in green algae.
M. temminkii is famous for its strong bite, which is most often utilised when feeding. The turtle's tongue resembles a worm, and at night individuals lie on the bottom of the river or lake bed with their mouths open. Fish are enticed by the bait-tongue, and when they get close enough the alligator snapping turtle's mouth clamps down around them. In addition to fish, this species may also feed on amphibians, invertebrates, small mammals, water birds, other turtles, and even juvenile alligators where their territories overlap. The alligator snapping turtle's relies on ambush techniques, and so hunters can remain submerged for up to 40 minutes. In some cases, individuals can also 'taste' the water to detect neaby mud and musk turtles. Because of this species' thick shell and ferocious bite, adults have few predators, but eggs and hatchlings may fall prey to raccoons, predatory fish, and large birds.
This species spends most of its time in the water, only emerging to nest or find a new home if their current habitat becomes unsuitable. Mating occurs between Februrary and May, starting later in the northern regions of the species' range. Males and females seek each other out, but generally don't travel great distances. About two months after mating, females dig a nest near a body of water and deposit between 10-50 eggs. Incubation takes up to 140 days, and the average temperature of the nest determines the sex of the hatchings; the hotter it is, the more males are produced. In the fall, hatchings emerge and are left to fend for themselves. Sexual maturity is reached at between 11 and 13 years of age, and individuals can live as old as 45 years in the wild.
Conservation status: The alligator snapping turtle is listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN. The species is threatened by overharvesting for meat and for the pet trade, and by habitat destruction.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
Photos
Ed Godfrey
Cindy Hayes
Eva Kwiatek
Nathan Patee
#alligator snapping turtle#Testudines#Chelydridae#snapping turtles#freshwater turtles#reptiles#freshwater fauna#freshwater reptiles#lakes#lake reptiles#wetlands#wetland reptiles#rivers#river reptiles#north america#southern north america#animal facts#biology#zoology
455 notes
·
View notes
Text

Feeding the local turtle
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: alligator snapping turtle
This will be a shorter WBW than usual, as I forgot to prep a post in advance and am writing this on short notice. Today's topic is the alligator snapping turtle, a beast from the bayou almost looks like a dinosaur. Macrochelys temminckii is the only member of its genus and, along with the three members of the genus Chelydra, is one of the four living snapping turtle species. Some scientists suggest splitting it into three species, but this is still a matter of debate. Snapping turtles are large, predatory turtles known for their very sharp beaks, extreme bite forces, and alleged aggressiveness.

(Image ID: an alligator snapping turtle sitting on gravel. It is a large, brown turtle. Its shall has three spiked ridged running down it. The head is large and angular, with a very sharp beak. It has small, brown eyes. Its mouth is open in a threat display. End ID)
The alligator snapping turtle is one of the largest freshwater turtles in the world, surpassed only by a few species of rare Asian softshells. The alligator snapping turtle can be distinguished from the common snapping turtle, whose range overlaps with that of the alligator snapping turtle, by the three spiky ridges going down its shell. These ridges, along with its powerful jaws, are often compared to those of an alligator, hence the common name. The turtles grow through their entire lives and can reach truly huge sizes. In the wild, adult males (who are larger than females) range between 35 and 80.8 cm (13.8 to 31.8 in) in caprapace (top shell) length and weigh between 8.4 and 80 kg (19 to 176 lbs). Sometimes, a true giant will be found, usually an old male. Reported weights of giant males include 113, 107, and 135 kg (249, 236, 298 lbs). The tail is longer and thicker than in most turtles. The head is large and thick and can deliver bites with a force averaging 159 newtons. This is less than the bite force of the common snapping turtle, but still enough to bite someone's finger off. The inside of the mouth is brownish and the tongue has an appendage that looks like a worm on it. Unlike most turtles, the alligator snapping turtle cannot withdraw into its shell. The plastron (lower shell) covers less of the body than in most species and cannot cover retracted limbs, heads, or tails.

(Image ID: a close-up of the head of an alligator snapping turtle with its mouth open. The tongue is visible, which has a pink, fleshy appendage that looks like a worm. End ID)
Alligator snapping turtles live in the southeast USA in rovers, streams, and lakes, preferably with deep water. They spend most of their lives in the water, only leaving if in search of a new home or when laying eggs. They are nocturnal, but may still hunt during the day. The turtles are passive ambush predators who sit perfectly still with their mouths open and tongues exposed. The worm-like appendage on the tongue is used to attract prey, which the turtle will bite down on quickly and with extreme force. This is a form of aggressive mimicry. You may be wondering what they eat and the answer is just about anything. Fish, amphibians, and snails appear to be the most common prey, but they will also feed on crayfish, insects, snakes, worms, birds, small mammals, other turtles, and even small alligators. Basically if it can fit in the turtle's mouth, it will be eaten. While not active predators, they will dig up burrows in search of food. They also feed on carrion and will sometimes eat aquatic plants. A turtle can go 50 minutes between breaths and they sit still so much that most individuals will have a thick layer of algae growing on their shells. The algae helps them camouflage as rocks when not moving. Fishermen tales often say that alligator snapping turtles can depopulate all of the fish in a body of water, but this does not appear to be true. Adult alligator snapping turtles have no natural predators while juveniles are eaten by fish, birds, raccoons, and other snapping turtles.

(Image ID: an alligator snapping turtle underwater in an aquarium. Picture from the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute. End ID)
Mating takes place in spring, earlier in the season in more southern climates. Laying takes place around two months later. The females will leave the water and travel around 50 meters inland. The distance is to prevent the eggs from being flooded, which would kill them. She will build a nest in sandy soil and bury the eggs. No further care is provided. Clutches consist of between 8 and 60 eggs at a time. After 100-140 days, the eggs hatch. The hatchlings are fully independent and must make their own way in life. The sex of the hatchlings is determined by the temperature of the soil they are incubated in. Soil of 29-30 degrees C (84.2 to 86 F) results in primarily females, 25 to 27 C (77 to 80.6 F), results in primarily males, and anything in between results in a mix. Individuals become sexually mature after about 11-12 years. The maximum lifespan of wild turtles is unknown, but individuals in captivity can live over a century.
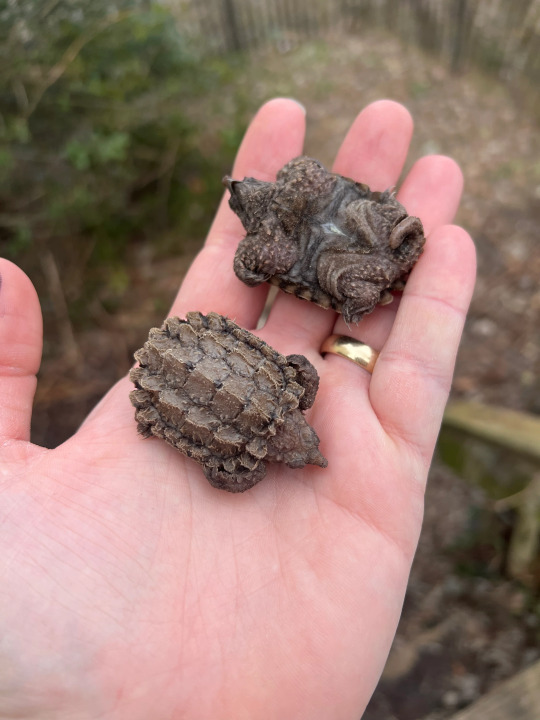

(Image ID: two baby alligator snapping turtles held in a person's hand. They are smaller than the person's palm, but otherwise look no different than the adults. One is on its back, displaying the small plastron. End ID)

(Image ID: alligator snapping turtles hatching in captivity. The eggs are small white spheres that look like ping-pong balls. The number 19 has been written on them in what appears to be sharpie. Several of the eggs have already hatched. In the middle of the picture, a turtle is pertially emerged from its egg. End ID
Alligator snapping turtles are classified as vulnerable by the IUCN. Their primary threat is habitat loss as wetlands are drained and dammed. They are also hunted and used as food by humans. This is common enough that some states have had to pass laws protecting the turtles. Despite being characterized as aggressive, alligator snapping turtles rarely attack humans and only in self-defense. Because they cannot retract into their shells, the turtles defend themselves by facing a potential threat with their mouths open as a warning. This has furthered its reputation as an aggressive animal. Because the turtles take so long to reproduce, restoring populations is a very slow process. Alligator snapping turtles are sometimes used as pets, though they need expert care due to their sheer size and the potential danger of handling them. Use in the pet trade has resulted in the turtles being introduced outside of their native range. They have become an invasive species on some places, notably in southern Africa.

(Image ID: an alligator snapping turtle next to a human man. The human is holding it up by the front of the shell to show its size. End ID)
#wet beast wednesday#alligator snapping turtle#snapping turtle#turtle#freshwater biology#biology#ecology#zoology#reptile#animal facts
210 notes
·
View notes
Text
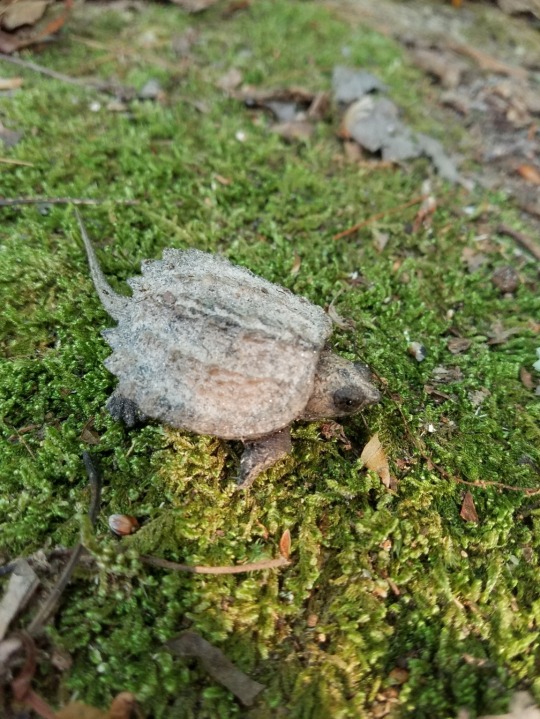

Little tiny baby alligator snapper 🐢❤️
#alligator snapping turtle#turtle#turtles#baby turtle#turtles of tumblr#teenage mutant ninja turtles#cute#baby#nature#photography#colorful#green#travel#animals#babies#pets
80 notes
·
View notes
Text

Skulltober day 13: alligator snapping turtle
Ink, 7 x 5 inches
JoJo Seames, 2023
#skull#skeleton#drawtober#skulltober#turtle#snapping turtle#alligator snapping turtle#art#illustration#ink#drawing#ink drawing#jojo seames
78 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alligator snapping turtle !
[ID: an illustration of an alligator snapping turtle. It is facing to the right with its mouth open. It is on a purple background with simple wave shapes. End.]
689 notes
·
View notes
Text


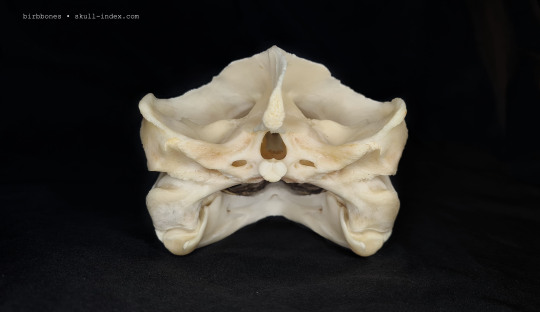
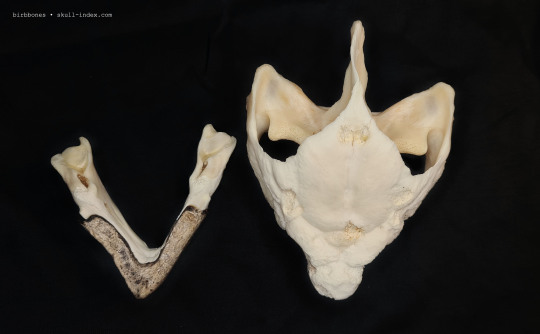
Alligator Snapping Turtle - Macrochelys temminckii
#my collection#the skull index#vultureculture#alligator snapping turtle#skulls#animal skulls#turtle skull
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
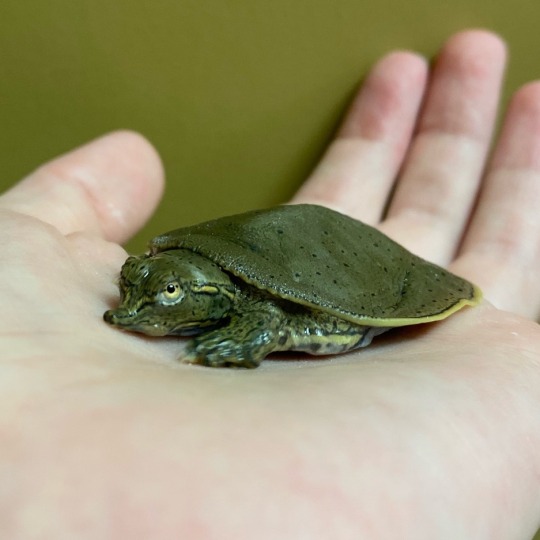
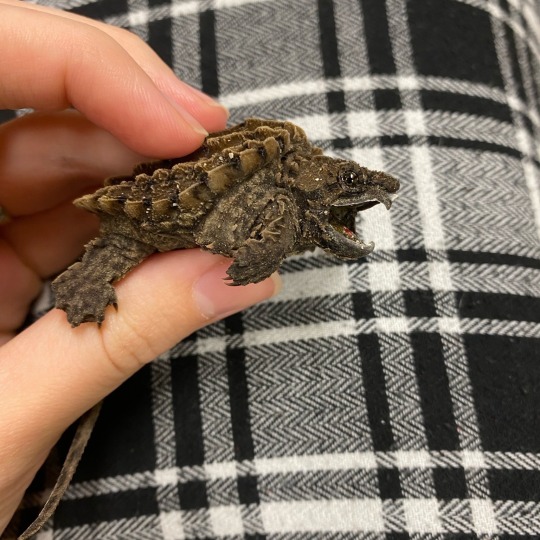



Miniature monsters hatched in our incubators last summer
More to come soon…
#goblincore#academia#biology#herpetology#natural sciences#biology academia#reptiles#turtles#herps#stem academia#animals#alligator snapping turtle#spiny softshell turtle
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alligator snapping turtle
#alligator snapping turtle#animals#photography#animal portraits#reptiles#photographers on tumblr#artists on tumblr
24 notes
·
View notes
Text



More adventures with demutated turtles. I can't get over when basking sliders and softshells stretch out their legs, it looks so silly and cute.
Mikey's behavior is inspired by videos I've seen of box turtles climbing up their owners for... affection? Or maybe just a bite.
#tmnt#rottmnt#donatello#leonardo#michelangelo#raphael#april o'neil#rise of the tmnt#red eared slider#spiny softshell turtle#alligator snapping turtle#eastern box turtle#demutated turtles
6K notes
·
View notes
Text









Corps of Discovery
(September 22, 2021)
#2021#Afternoon#Alligator Snapping Turtle#Animals#Bear#Bird#Birds#Conservation#Day#Daytime#My Photography#My Photos#My Pics#My Pictures#My Video#Owl#Photography#Photos#Pics#Pictures#Reptile#Reptiles#Reptilian#Reptilians#September#September 2021#Snake#Turtle#Turtles#Video
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animal of the day: Alligator snapping turtle!
The alligator snapping turtle is a large species of turtle native to freshwater habitats in the United States.

The inside of the turtles mouth is camouflaged, and it has a fleshy, worm-like appendage on its tongue that it uses to lure prey!

It will eat pretty much anything it can lure in and catch, targeting abundant and easily caught prey. Handling this turtle can be extremely dangerous, as they have been known to cleanly bite off human fingers!

39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Got to see this alligator snapping turtle during fieldwork and I was able to capture one of my absolute favorite animal behaviors while this big girl was getting her physical. If you look in her mouth during this video you can see that her tongue has a pink appendage that is wiggling pretty vigorously.
This behavior is called “lingual luring” and it’s a really interesting little evolutionary trick. That wiggly appendage on the snapping turtle’s tongue very closely imitates the movement of a wriggling worm, enough that a passing fish might swim in for a closer look. Pretty clever way to hunt!
#source: Functional mechanisms and histologic composition of the lingual appendage in the alligator snapping turtle Journal of Morphology#animals#alligator snapping turtle#macrochelys
855 notes
·
View notes
Text
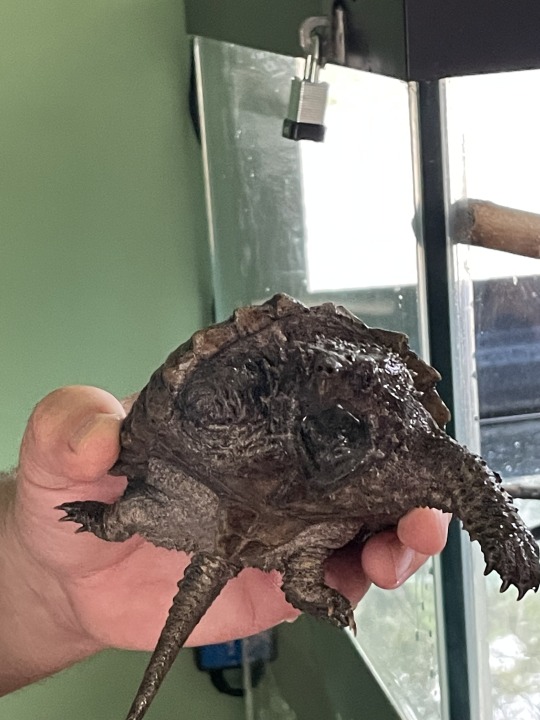
Look at the little baby alligator snapping turtle. The person holding it is a zookeeper who was giving it some medicine.


109 notes
·
View notes