#apple repairs
Text
I Custom Repairs and Retail is a family-owned cellphone and computer repair business that strives to offer the best in both customer service and quality.
#Phone repair service#Mobile Phones Repairs#Apple Repairs#Cellphone#Computer#Tablet Repairs#usa#repairs service#ipad repair#repair service
1 note
·
View note
Text
Your car spies on you and rats you out to insurance companies

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me TOMORROW (Mar 13) in SAN FRANCISCO with ROBIN SLOAN, then Toronto, NYC, Anaheim, and more!

Another characteristically brilliant Kashmir Hill story for The New York Times reveals another characteristically terrible fact about modern life: your car secretly records fine-grained telemetry about your driving and sells it to data-brokers, who sell it to insurers, who use it as a pretext to gouge you on premiums:
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/03/11/technology/carmakers-driver-tracking-insurance.html
Almost every car manufacturer does this: Hyundai, Nissan, Ford, Chrysler, etc etc:
https://www.repairerdrivennews.com/2020/09/09/ford-state-farm-ford-metromile-honda-verisk-among-insurer-oem-telematics-connections/
This is true whether you own or lease the car, and it's separate from the "black box" your insurer might have offered to you in exchange for a discount on your premiums. In other words, even if you say no to the insurer's carrot – a surveillance-based discount – they've got a stick in reserve: buying your nonconsensually harvested data on the open market.
I've always hated that saying, "If you're not paying for the product, you're the product," the reason being that it posits decent treatment as a customer reward program, like the little ramekin warm nuts first class passengers get before takeoff. Companies don't treat you well when you pay them. Companies treat you well when they fear the consequences of treating you badly.
Take Apple. The company offers Ios users a one-tap opt-out from commercial surveillance, and more than 96% of users opted out. Presumably, the other 4% were either confused or on Facebook's payroll. Apple – and its army of cultists – insist that this proves that our world's woes can be traced to cheapskate "consumers" who expected to get something for nothing by using advertising-supported products.
But here's the kicker: right after Apple blocked all its rivals from spying on its customers, it began secretly spying on those customers! Apple has a rival surveillance ad network, and even if you opt out of commercial surveillance on your Iphone, Apple still secretly spies on you and uses the data to target you for ads:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/14/luxury-surveillance/#liar-liar
Even if you're paying for the product, you're still the product – provided the company can get away with treating you as the product. Apple can absolutely get away with treating you as the product, because it lacks the historical constraints that prevented Apple – and other companies – from treating you as the product.
As I described in my McLuhan lecture on enshittification, tech firms can be constrained by four forces:
I. Competition
II. Regulation
III. Self-help
IV. Labor
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/30/go-nuts-meine-kerle/#ich-bin-ein-bratapfel
When companies have real competitors – when a sector is composed of dozens or hundreds of roughly evenly matched firms – they have to worry that a maltreated customer might move to a rival. 40 years of antitrust neglect means that corporations were able to buy their way to dominance with predatory mergers and pricing, producing today's inbred, Habsburg capitalism. Apple and Google are a mobile duopoly, Google is a search monopoly, etc. It's not just tech! Every sector looks like this:
https://www.openmarketsinstitute.org/learn/monopoly-by-the-numbers
Eliminating competition doesn't just deprive customers of alternatives, it also empowers corporations. Liberated from "wasteful competition," companies in concentrated industries can extract massive profits. Think of how both Apple and Google have "competitively" arrived at the same 30% app tax on app sales and transactions, a rate that's more than 1,000% higher than the transaction fees extracted by the (bloated, price-gouging) credit-card sector:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/07/curatorial-vig/#app-tax
But cartels' power goes beyond the size of their warchest. The real source of a cartel's power is the ease with which a small number of companies can arrive at – and stick to – a common lobbying position. That's where "regulatory capture" comes in: the mobile duopoly has an easier time of capturing its regulators because two companies have an easy time agreeing on how to spend their app-tax billions:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/05/regulatory-capture/
Apple – and Google, and Facebook, and your car company – can violate your privacy because they aren't constrained regulation, just as Uber can violate its drivers' labor rights and Amazon can violate your consumer rights. The tech cartels have captured their regulators and convinced them that the law doesn't apply if it's being broken via an app:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/18/cursed-are-the-sausagemakers/#how-the-parties-get-to-yes
In other words, Apple can spy on you because it's allowed to spy on you. America's last consumer privacy law was passed in 1988, and it bans video-store clerks from leaking your VHS rental history. Congress has taken no action on consumer privacy since the Reagan years:
https://www.eff.org/tags/video-privacy-protection-act
But tech has some special enshittification-resistant characteristics. The most important of these is interoperability: the fact that computers are universal digital machines that can run any program. HP can design a printer that rejects third-party ink and charge $10,000/gallon for its own colored water, but someone else can write a program that lets you jailbreak your printer so that it accepts any ink cartridge:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2020/11/ink-stained-wretches-battle-soul-digital-freedom-taking-place-inside-your-printer
Tech companies that contemplated enshittifying their products always had to watch over their shoulders for a rival that might offer a disenshittification tool and use that as a wedge between the company and its customers. If you make your website's ads 20% more obnoxious in anticipation of a 2% increase in gross margins, you have to consider the possibility that 40% of your users will google "how do I block ads?" Because the revenue from a user who blocks ads doesn't stay at 100% of the current levels – it drops to zero, forever (no user ever googles "how do I stop blocking ads?").
The majority of web users are running an ad-blocker:
https://doc.searls.com/2023/11/11/how-is-the-worlds-biggest-boycott-doing/
Web operators made them an offer ("free website in exchange for unlimited surveillance and unfettered intrusions") and they made a counteroffer ("how about 'nah'?"):
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/07/adblocking-how-about-nah
Here's the thing: reverse-engineering an app – or any other IP-encumbered technology – is a legal minefield. Just decompiling an app exposes you to felony prosecution: a five year sentence and a $500k fine for violating Section 1201 of the DMCA. But it's not just the DMCA – modern products are surrounded with high-tech tripwires that allow companies to invoke IP law to prevent competitors from augmenting, recongifuring or adapting their products. When a business says it has "IP," it means that it has arranged its legal affairs to allow it to invoke the power of the state to control its customers, critics and competitors:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
An "app" is just a web-page skinned in enough IP to make it a crime to add an ad-blocker to it. This is what Jay Freeman calls "felony contempt of business model" and it's everywhere. When companies don't have to worry about users deploying self-help measures to disenshittify their products, they are freed from the constraint that prevents them indulging the impulse to shift value from their customers to themselves.
Apple owes its existence to interoperability – its ability to clone Microsoft Office's file formats for Pages, Numbers and Keynote, which saved the company in the early 2000s – and ever since, it has devoted its existence to making sure no one ever does to Apple what Apple did to Microsoft:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/adversarial-interoperability-reviving-elegant-weapon-more-civilized-age-slay
Regulatory capture cuts both ways: it's not just about powerful corporations being free to flout the law, it's also about their ability to enlist the law to punish competitors that might constrain their plans for exploiting their workers, customers, suppliers or other stakeholders.
The final historical constraint on tech companies was their own workers. Tech has very low union-density, but that's in part because individual tech workers enjoyed so much bargaining power due to their scarcity. This is why their bosses pampered them with whimsical campuses filled with gourmet cafeterias, fancy gyms and free massages: it allowed tech companies to convince tech workers to work like government mules by flattering them that they were partners on a mission to bring the world to its digital future:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/10/the-proletarianization-of-tech-workers/
For tech bosses, this gambit worked well, but failed badly. On the one hand, they were able to get otherwise powerful workers to consent to being "extremely hardcore" by invoking Fobazi Ettarh's spirit of "vocational awe":
https://www.inthelibrarywiththeleadpipe.org/2018/vocational-awe/
On the other hand, when you motivate your workers by appealing to their sense of mission, the downside is that they feel a sense of mission. That means that when you demand that a tech worker enshittifies something they missed their mother's funeral to deliver, they will experience a profound sense of moral injury and refuse, and that worker's bargaining power means that they can make it stick.
Or at least, it did. In this era of mass tech layoffs, when Google can fire 12,000 workers after a $80b stock buyback that would have paid their wages for the next 27 years, tech workers are learning that the answer to "I won't do this and you can't make me" is "don't let the door hit you in the ass on the way out" (AKA "sharpen your blades boys"):
https://techcrunch.com/2022/09/29/elon-musk-texts-discovery-twitter/
With competition, regulation, self-help and labor cleared away, tech firms – and firms that have wrapped their products around the pluripotently malleable core of digital tech, including automotive makers – are no longer constrained from enshittifying their products.
And that's why your car manufacturer has chosen to spy on you and sell your private information to data-brokers and anyone else who wants it. Not because you didn't pay for the product, so you're the product. It's because they can get away with it.
Cars are enshittified. The dozens of chips that auto makers have shoveled into their car design are only incidentally related to delivering a better product. The primary use for those chips is autoenshittification – access to legal strictures ("IP") that allows them to block modifications and repairs that would interfere with the unfettered abuse of their own customers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/24/rent-to-pwn/#kitt-is-a-demon
The fact that it's a felony to reverse-engineer and modify a car's software opens the floodgates to all kinds of shitty scams. Remember when Bay Staters were voting on a ballot measure to impose right-to-repair obligations on automakers in Massachusetts? The only reason they needed to have the law intervene to make right-to-repair viable is that Big Car has figured out that if it encrypts its diagnostic messages, it can felonize third-party diagnosis of a car, because decrypting the messages violates the DMCA:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2013/11/drm-cars-will-drive-consumers-crazy
Big Car figured out that VIN locking – DRM for engine components and subassemblies – can felonize the production and the installation of third-party spare parts:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/08/about-those-kill-switched-ukrainian-tractors/
The fact that you can't legally modify your car means that automakers can go back to their pre-2008 ways, when they transformed themselves into unregulated banks that incidentally manufactured the cars they sold subprime loans for. Subprime auto loans – over $1t worth! – absolutely relies on the fact that borrowers' cars can be remotely controlled by lenders. Miss a payment and your car's stereo turns itself on and blares threatening messages at top volume, which you can't turn off. Break the lease agreement that says you won't drive your car over the county line and it will immobilize itself. Try to change any of this software and you'll commit a felony under Section 1201 of the DMCA:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/04/02/innovation-unlocks-markets/#digital-arm-breakers
Tesla, naturally, has the most advanced anti-features. Long before BMW tried to rent you your seat-heater and Mercedes tried to sell you a monthly subscription to your accelerator pedal, Teslas were demon-haunted nightmare cars. Miss a Tesla payment and the car will immobilize itself and lock you out until the repo man arrives, then it will blare its horn and back itself out of its parking spot. If you "buy" the right to fully charge your car's battery or use the features it came with, you don't own them – they're repossessed when your car changes hands, meaning you get less money on the used market because your car's next owner has to buy these features all over again:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/28/edison-not-tesla/#demon-haunted-world
And all this DRM allows your car maker to install spyware that you're not allowed to remove. They really tipped their hand on this when the R2R ballot measure was steaming towards an 80% victory, with wall-to-wall scare ads that revealed that your car collects so much information about you that allowing third parties to access it could lead to your murder (no, really!):
https://pluralistic.net/2020/09/03/rip-david-graeber/#rolling-surveillance-platforms
That's why your car spies on you. Because it can. Because the company that made it lacks constraint, be it market-based, legal, technological or its own workforce's ethics.
One common critique of my enshittification hypothesis is that this is "kind of sensible and normal" because "there’s something off in the consumer mindset that we’ve come to believe that the internet should provide us with amazing products, which bring us joy and happiness and we spend hours of the day on, and should ask nothing back in return":
https://freakonomics.com/podcast/how-to-have-great-conversations/
What this criticism misses is that this isn't the companies bargaining to shift some value from us to them. Enshittification happens when a company can seize all that value, without having to bargain, exploiting law and technology and market power over buyers and sellers to unilaterally alter the way the products and services we rely on work.
A company that doesn't have to fear competitors, regulators, jailbreaking or workers' refusal to enshittify its products doesn't have to bargain, it can take. It's the first lesson they teach you in the Darth Vader MBA: "I am altering the deal. Pray I don't alter it any further":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/26/hit-with-a-brick/#graceful-failure
Your car spying on you isn't down to your belief that your carmaker "should provide you with amazing products, which brings your joy and happiness you spend hours of the day on, and should ask nothing back in return." It's not because you didn't pay for the product, so now you're the product. It's because they can get away with it.
The consequences of this spying go much further than mere insurance premium hikes, too. Car telemetry sits at the top of the funnel that the unbelievably sleazy data broker industry uses to collect and sell our data. These are the same companies that sell the fact that you visited an abortion clinic to marketers, bounty hunters, advertisers, or vengeful family members pretending to be one of those:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/07/safegraph-spies-and-lies/#theres-no-i-in-uterus
Decades of pro-monopoly policy led to widespread regulatory capture. Corporate cartels use the monopoly profits they extract from us to pay for regulatory inaction, allowing them to extract more profits.
But when it comes to privacy, that period of unchecked corporate power might be coming to an end. The lack of privacy regulation is at the root of so many problems that a pro-privacy movement has an unstoppable constituency working in its favor.
At EFF, we call this "privacy first." Whether you're worried about grifters targeting vulnerable people with conspiracy theories, or teens being targeted with media that harms their mental health, or Americans being spied on by foreign governments, or cops using commercial surveillance data to round up protesters, or your car selling your data to insurance companies, passing that long-overdue privacy legislation would turn off the taps for the data powering all these harms:
https://www.eff.org/wp/privacy-first-better-way-address-online-harms
Traditional economics fails because it thinks about markets without thinking about power. Monopolies lead to more than market power: they produce regulatory capture, power over workers, and state capture, which felonizes competition through IP law. The story that our problems stem from the fact that we just don't spend enough money, or buy the wrong products, only makes sense if you willfully ignore the power that corporations exert over our lives. It's nice to think that you can shop your way out of a monopoly, because that's a lot easier than voting your way out of a monopoly, but no matter how many times you vote with your wallet, the cartels that control the market will always win:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/05/the-map-is-not-the-territory/#apor-locksmith

Name your price for 18 of my DRM-free ebooks and support the Electronic Frontier Foundation with the Humble Cory Doctorow Bundle.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/12/market-failure/#car-wars

Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#if you're not paying for the product you're the product#if you're paying for the product you're the product#cars#automotive#enshittification#technofeudalism#autoenshittification#antifeatures#felony contempt of business model#twiddling#right to repair#privacywashing#apple#lexisnexis#insuretech#surveillance#commercial surveillance#privacy first#data brokers#subprime#kash hill#kashmir hill
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
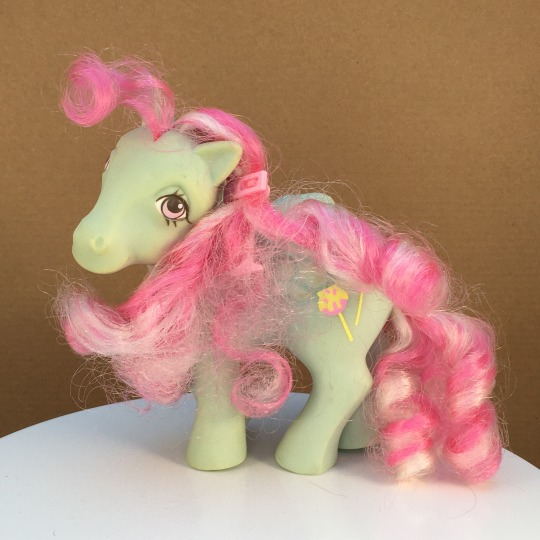
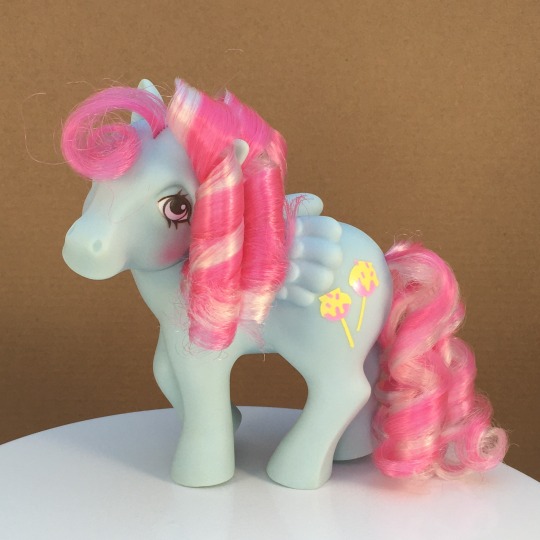
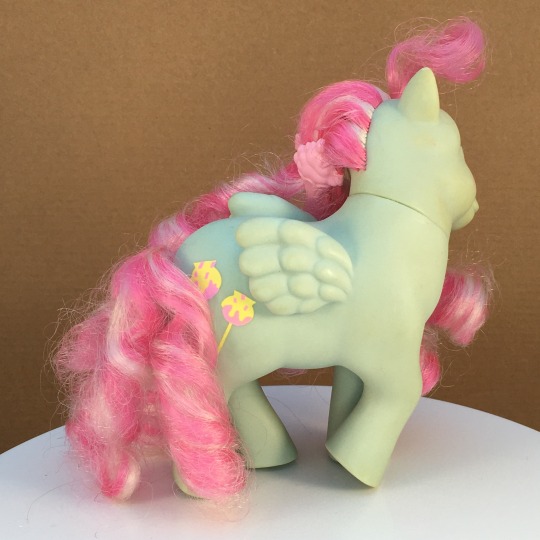





I have gotten to work on a few Candy Cane Pony Sugar Apples, though.
#candy cane pony#sugar apple#candy cane pony sugar apple#my little pony#mlp g1#mlp#doll hair#doll repair#before and after
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This is also the reason older generations say younger generations don’t know how to fix things!
#Youtube#some more news#cody johnston#right to repair#big tech#fast fashion#planned obsolescence#fuck apple#john deere#elon musk#Tesla#leftist#leftism#socialism#agriculture#U.S.A#recycling#reduce reuse recycle#plastic waste#tech waste#please recycle#capitalism#late stage capitalism
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 1, Group 6
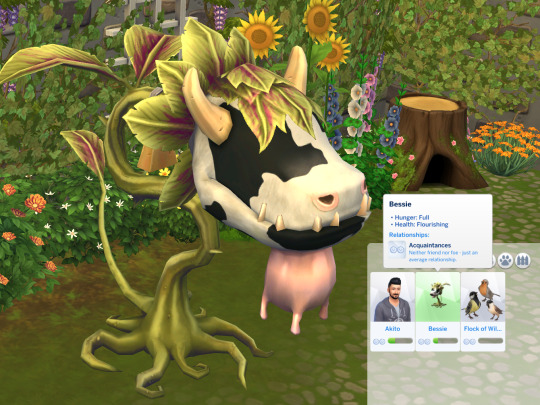

Propaganda and spoilers under cut
Cowplant: Extends the life of a sim. Mod Note: I love when fictional plants have scientific names and the cowplant DOES: Laganaphyllis simnovorii. Lagana - pancake, flat cake; phyllis - foliage; simnovorii - sim eater
Ebony Queen's Apple: First off, it’s based off of the Evil Queen from Snow White. It can communicate telepathically and the first thing it says in-game is “Bring Snow White.” Which is even more interesting when you take into account that in Limbus Company’s prequel, Lobotomy Corporation, there’s a being known as Snow White’s Apple. Also it can function without its head which is pretty cool.
#round 1#sims 4#limbus company#*sees 'flock of wild birds'* maybe i WILL play the sims 4..........#last time i had sims installed my laptop died. badly. and had to go for repairs :'3#but......... flock of wild birds#ALSO when i realised the Ebony Queens Apple's arms were VINES and NOT bones???? omg omg omg thats so GOOD
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
They Literally Don't Make Things Like They Used To | SOME MORE NEWS
#cody johnston#planned obsolescence#capitalism#consumer engineering#fast fashion#apple#tesla#john deere#right to repair#e-waste
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
getting a new laptop tomorrow/monday. my current one's really started to break down (programs freeze constantly and it starts overheating at the slightest of strain), so it'll be nice to have a fresh one. i'm gonna try to resume making six edits once i get it.
#redlady speaks#my brother was gifted a mac for his high school graduation years ago by my dad's old boss#but he never used it because the one he had/has was working fine#i convinced him to give it to me last week but the battery was messed up from having sit unused for so long#so i had to send it off to apple to get repaired#it was supposed to arrive today but my dad and i were out and no one was there to sign for it
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I have this printer ...

Not that one specifically, that one is beautiful and in great condition, but one like it — Apple ImageWriter II. Specifically mine is the ImageWriter II/L variant, the last revision of the ImageWriter II line, but it looks like this one.
Or at least it did once upon a time.
My family acquired this printer second-hand in the late 90s along with a Mac Classic. It got used regularly for school reports and letters and business documents and tax forms for a few years until we finally were able to get a new computer with a color inkjet printer.
Long story short, like the computer that went with it, ultimately this poor printer ended up sitting in storage without air conditioning in East Texas heat and humidity for nearly twenty years. It's a sad story of slow decay.
My ImageWriter is now yellowed and scuffed and scraped and rusted and missing a piece or two; just a dim reminder of its former beauty. Given the state of it, what hope do we have of ever again hearing it sing the song of its people?
Well, I'm not going to let it go without a fight. Time to dig in and see what we can ...
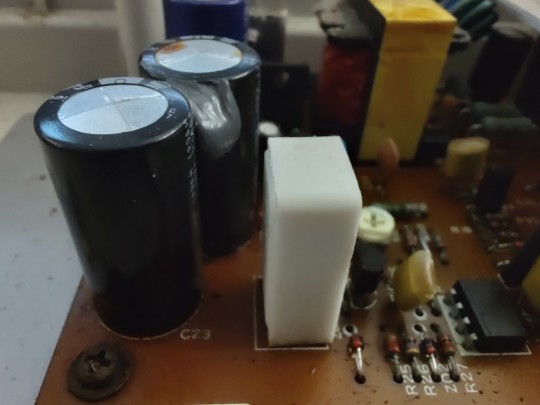

... oh. Oh dear that won't do at all.
A good rule to follow when working with these 30+ year old systems, is to (carefully!) open and inspect before applying any power. In this case I'm very glad I did. Three large filter capacitors on the power supply have very obviously swollen and burst, spreading their corrosive bile all over the neighborhood.

The back side of the power supply circuit board was a wasteland of rotting solder mask, corroded traces, and displaced silkscreen. The electrolyte has eaten its way down the leads, through the solder, and left carnage in its wake all across the bottom of the board.


First order of business is getting those old capacitors removed from the board so cleanup can begin. If you've never worked with hardware of this vintage, a fair warning — make sure you're working in a well-ventilated area. Sure the solder has lead and the flux ain't great for the lungs, but the big concern here is the unholy stench of heated capacitor electrolyte hitting the nostrils like the revenge of Poseidon's refuse bin. The local fish market has nothing on these things.
The old solder, especially when mixed with the electrolyte, tends to behave in a very un-solder-like fashion. It will refuse to melt and when it does it will slump around like wet sand rather than flow like liquid metal should. While it may seem counter-intuitive, the best way to get rid of it is to add more fresh solder to it. On these single-sided boards with large components like this, a spring-action solder pump works well for getting the old parts removed, and then some solder braid will clean up the pads well.
Once the old parts are out, I like to thoroughly clean the area with isopropyl alcohol to remove the electrolyte and years of grease and dirt and pet hair that may have cemented itself to the board. In this case I also needed to use a mild abrasive to remove that damaged solder mask where it had bubbled up off the corroding copper traces. I was lucky here that none of the traces were actually broken or corroded through completely. Clear nail polish works well for protecting the now bare copper (just make sure it's not the UV-cure gel stuff).
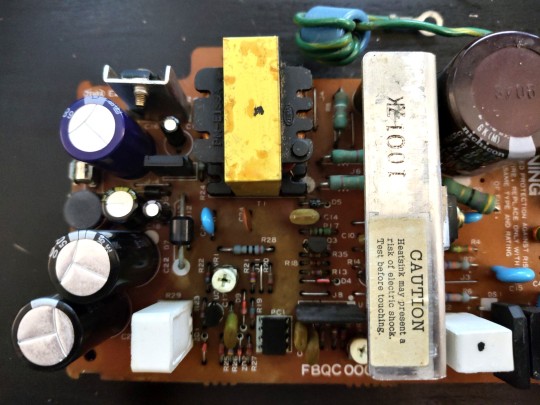

From here I turned my attention to the case, because the power supply is the last item removed and first installed when conducting a complete tear down of this printer, and it didn't make sense to put my newly cleaned power supply into a dirty old case.


I'm not really a fan of retrobrite, and these large case pieces would be a real challenge anyway. So all I want is to clean up the dirt and rust and as many scuff marks as I can. As far as I'm concerned, the rest is just part of the history of the item. Each mark tells a story of how this item was used, not just put up on a shelf to be looked at. And if I didn't have any interest in using the machine until it completely falls to pieces, I wouldn't be bothering with going fishing replacing old capacitors.
This is a good point to do some testing. There may still be more wrong with that power supply. Output voltages could have drifted out of spec from other components aging, or maybe I installed capacitors that don't quite match the originals. The ImageWriter II/L power supply has three outputs — +5VDC, -5VDC, & +26VDC. With no load on the power supply, I measured the outputs at around ±7V and 30V. That seems high, but it's not outside of what I would expect for a power supply that's not actually driving anything. This would be a good point to use an adjustable test load, but since I don't have one of those, I'll just have to move forward with my "well it seems fine'
Spoiler: it was not fine.
As part of its startup sequence, the ImageWriter exercises all of its stepper motors to get everything to a known state. This high current draw immediately after power on was more than its old power supply could give. There's clearly more than bad capacitors on the supply, but identifying what exactly is still beyond my current skill level.
So in the interest of getting the machine working (because I have plans for it), I opted to try replacing the power supply with something more modern. The catch here is the odd assortment of voltages the original supply provided. It's easy to find a ±5VDC supply, but 26V is virtually unheard-of.
Apple's documentation for the printer mentions the +26V supply is for driving the motors. I suspected that the 26V supply was less carefully regulated and probably targeting something more like 24V. Sure enough, the stepper with the highest voltage rating on its label was 24V. With a little extra current capacity available, I figured the printer would function just fine with a 24V supply.
The catch is, 24V & ±5V is not a common configuration. There are plenty of 12V & ±5V supplies, but that won't do here. I settled on a Mean Well 24V & 5V supply with a -5V inverter ... And promptly ordered the wrong part. I had a nice new 12V & 5V supply. That's ok, once I got it in hand it was a bit too large to fit in the space I had anyway.
So I got a different Mean Well 24V supply and a separate 24V-5V DC-DC converter. It's a bit of a mess all crammed into the bottom of the case, but it should give all the right voltages (or near enough).

I did have to remove the power switch from the old supply though. That particular part has long since been discontinued, and compatible replacements proved difficult to find.
Now that it's all assembled, it's time to test. This is the part that always makes me nervous, especially when dealing with mains voltages. There's so much that can go so very horribly wrong.
I started out with a smoke test — switching on power briefly to make sure there were no direct shorts that might cause an explosive failure. No smoke is a good sign, so check the voltages. With no load, the new supply rails read 23.99V, 5.00V, and -5.55V. That's about as good as I could ever ask for. So now there's only one thing left to test … does it actually print?

Success!
It's not perfect. Every once in a while it will stutter while printing and get stuck with the carriage on one side or the other. It really needs a complete disassembly, thorough cleaning, and relubrication. That kind of mechanical teardown is a bit beyond what I'm comfortable with at the moment, but I'll happily settle for mostly working over not working at all.
#vintage computing#macintosh#imagewriter#imagewriter ii/l#computer repair#apple#apple computers#dot matrix printer#mean well#it's always the power supply#power supply
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
sorry not sorry, but Raven Queen from EAH sounds and behaves hella aro to me. i wish i had that story to watch back in the end of 90's. ahem.
#k's wave#ever after high#raven queen#angry aromantic#grey or demi maybe but still#the way she interacts with Apple. ouch. ouch.#a queer person in their mid thirties has no better idea#than to watch EAH#it all started with WTW Kitty doll which is waiting for repair#she truly caused chaos lol
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
with all the shit going on in my life rn especially considering my financial issues the last thing i needed was my fucking tablet screen to crack
#it’d be one thing if it was just a crack but it’s across the whole screen and pressing on it causes the backlight to warp#? is that the right word? warp#idk but i can’t see what i’m drawing or writing and it’s very distracting#and apple is charging $420 for repairs because they’re worthless greedy fucking savages#taking it to a computer shop later and hopefully they can do something about it#fml#anyway if someone wants to help me not go broke ig you can DM me or send an ask @cozybees for a commission
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
#free congo#congo genocide#save congo#congo#boycott tesla#boycott apple#ways you can help#ONE - spread awareness#TWO - stop buying electronics just because it’s advertised as the newest thing#if your current or “old” phone is still functional then you have no need to get a new a new fucking phone#if your current or old phone has become damaged and you ABSOLUTELY NEED IT then get the phones repaired#THREE - do the same with any other products developed by these companies#FOUR - find any organisations working to aid the congo or shut this slavery down#FOUR POINT FIVE - if you do find anything of the sorts but don’t have the means to put money into it then spread awareness/links#on social media platforms#Instagram
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Apple fucked us on right to repair (again)

Today (September 22), I'm (virtually) presenting at the DIG Festival in Modena, Italy. Tonight, I'll be in person at LA's Book Soup for the launch of Justin C Key's "The World Wasn’t Ready for You." On September 27, I'll be at Chevalier's Books in Los Angeles with Brian Merchant for a joint launch for my new book The Internet Con and his new book, Blood in the Machine.

Right to repair has no cannier, more dedicated adversary than Apple, a company whose most innovative work is dreaming up new ways to sneakily sabotage electronics repair while claiming to be a caring environmental steward, a lie that covers up the mountains of e-waste that Apple dooms our descendants to wade through.
Why does Apple hate repair so much? It's not that they want to poison our water and bodies with microplastics; it's not that they want to hasten the day our coastal cities drown; it's not that they relish the human misery that accompanies every gram of conflict mineral. They aren't sadists. They're merely sociopathically greedy.
Tim Cook laid it out for his investors: when people can repair their devices, they don't buy new ones. When people don't buy new devices, Apple doesn't sell them new devices. It's that's simple:
https://www.inverse.com/article/52189-tim-cook-says-apple-faces-2-key-problems-in-surprising-shareholder-letter
So Apple does everything it can to monopolize repair. Not just because this lets the company gouge you on routine service, but because it lets them decide when your phone is beyond repair, so they can offer you a trade-in, ensuring both that you buy a new device and that the device you buy is another Apple.
There are so many tactics Apple gets to use to sabotage repair. For example, Apple engraves microscopic Apple logos on the subassemblies in its devices. This allows the company to enlist US Customs to seize and destroy refurbished parts that are harvested from dead phones by workers in the Pacific Rim:
https://repair.eu/news/apple-uses-trademark-law-to-strengthen-its-monopoly-on-repair/
Of course, the easiest way to prevent harvested components from entering the parts stream is to destroy as many old devices as possible. That's why Apple's so-called "recycling" program shreds any devices you turn over to them. When you trade in your old iPhone at an Apple Store, it is converted into immortal e-waste (no other major recycling program does this). The logic is straightforward: no parts, no repairs:
https://www.vice.com/en/article/yp73jw/apple-recycling-iphones-macbooks
Shredding parts and cooking up bogus trademark claims is just for starters, though. For Apple, the true anti-repair innovation comes from the most pernicious US tech law: Section 1201 of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA).
DMCA 1201 is an "anti-circumvention" law. It bans the distribution of any tool that bypasses "an effective means of access control." That's all very abstract, but here's what it means: if a manufacturer sticks some Digital Rights Management (DRM) in its device, then anything you want to do that involves removing that DRM is now illegal – even if the thing itself is perfectly legal.
When Congress passed this stupid law in 1998, it had a very limited blast radius. Computers were still pretty expensive and DRM use was limited to a few narrow categories. In 1998, DMCA 1201 was mostly used to prevent you from de-regionalizing your DVD player to watch discs that had been released overseas but not in your own country.
But as we warned back then, computers were only going to get smaller and cheaper, and eventually, it would only cost manufacturers pennies to wrap their products – or even subassemblies in their products – in DRM. Congress was putting a gun on the mantelpiece in Act I, and it was bound to go off in Act III.
Welcome to Act III.
Today, it costs about a quarter to add a system-on-a-chip to even the tiniest parts. These SOCs can run DRM. Here's how that DRM works: when you put a new part in a device, the SOC and the device's main controller communicate with one another. They perform a cryptographic protocol: the part says, "Here's my serial number," and then the main controller prompts the user to enter a manufacturer-supplied secret code, and the master controller sends a signed version of this to the part, and the part and the system then recognize each other.
This process has many names, but because it was first used in the automotive sector, it's widely known as VIN-Locking (VIN stands for "vehicle identification number," the unique number given to every car by its manufacturer). VIN-locking is used by automakers to block independent mechanics from repairing your car; even if they use the manufacturer's own parts, the parts and the engine will refuse to work together until the manufacturer's rep keys in the unlock code:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/24/rent-to-pwn/#kitt-is-a-demon
VIN locking is everywhere. It's how John Deere stops farmers from fixing their own tractors – something farmers have done literally since tractors were invented:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/08/about-those-kill-switched-ukrainian-tractors/
It's in ventilators. Like mobile phones, ventilators are a grotesquely monopolized sector, controlled by a single company Medtronic, whose biggest claim to fame is effecting the world's largest tax inversion in order to manufacture the appearance that it is an Irish company and therefore largely untaxable. Medtronic used the resulting windfall to gobble up most of its competitors.
During lockdown, as hospitals scrambled to keep their desperately needed supply of ventilators running, Medtronic's VIN-locking became a lethal impediment. Med-techs who used donor parts from one ventilator to keep another running – say, transplanting a screen – couldn't get the device to recognize the part because all the world's civilian aircraft were grounded, meaning Medtronic's technicians couldn't swan into their hospitals to type in the unlock code and charge them hundreds of dollars.
The saving grace was an anonymous, former Medtronic repair tech, who built pirate boxes to generate unlock codes, using any housing they could lay hands on to use as a case: guitar pedals, clock radios, etc. This tech shipped these gadgets around the world, observing strict anonymity, because Article 6 of the EUCD also bans circumvention:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/07/10/flintstone-delano-roosevelt/#medtronic-again
Of course, Apple is a huge fan of VIN-locking. In phones, VIN-locking is usually called "serializing" or "parts-pairing," but it's the same thing: a tiny subassembly gets its own microcontroller whose sole purpose is to prevent independent repair technicians from fixing your gadget. Parts-pairing lets Apple block repairs even when the technician uses new, Apple parts – but it also lets Apple block refurb parts and third party parts.
For many years, Apple was the senior partner and leading voice in blocking state Right to Repair bills, which it killed by the dozen, leading a coalition of monopolists, from Wahl (who boobytrap their hair-clippers with springs that cause their heads irreversibly decompose if you try to sharpen them at home) to John Deere (who reinvented tenant farming by making farmers tenants of their tractors, rather than their land).
But Apple's opposition to repair eventually became a problem for the company. It's bad optics, and both Apple customers and Apple employees are volubly displeased with the company's ecocidal conduct. But of course, Apple's management and shareholders hate repair and want to block it as much as possible.
But Apple knows how to Think Differently. It came up with a way to eat its cake and have it, too. The company embarked on a program of visibly support right to repair, while working behind the scenes to sabotage it.
Last year, Apple announced a repair program. It was hilarious. If you wanted to swap your phone's battery, all you had to do was let Apple put a $1200 hold on your credit card, and then wait while the company shipped you 80 pounds' worth of specialized tools, packed in two special Pelican cases:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/22/apples-cement-overshoes/
Then, you swapped your battery, but you weren't done! After your battery was installed, you had to conference in an authorized Apple tech who would tell you what code to type into a laptop you tethered to the phone in order to pair it with your phone. Then all you had to do was lug those two 40-pound Pelican cases to a shipping depot and wait for Apple to take the hold off your card (less the $120 in parts and fees).
By contrast, independent repair outfits like iFixit will sell you all the tools you need to do your own battery swap – including the battery! for $32. The whole kit fits in a padded envelope:
https://www.ifixit.com/products/iphone-x-replacement-battery
But while Apple was able to make a showy announcement of its repair program and then hide the malicious compliance inside those giant Pelican cases, sabotaging right to repair legislation is a lot harder.
Not that they didn't try. When New York State passed the first general electronics right-to-repair bill in the country, someone convinced New York Governor Kathy Hochul to neuter it with last-minute modifications:
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2022/12/weakened-right-to-repair-bill-is-signed-into-law-by-new-yorks-governor/
But that kind of trick only works once. When California's right to repair bill was introduced, it was clear that it was gonna pass. Rather than get run over by that train, Apple got on board, supporting the legislation, which passed unanimously:
https://www.ifixit.com/News/79902/apples-u-turn-tech-giant-finally-backs-repair-in-california
But Apple got the last laugh. Because while California's bill contains many useful clauses for the independent repair shops that keep your gadgets out of a landfill, it's a state law, and DMCA 1201 is federal. A state law can't simply legalize the conduct federal law prohibits. California's right to repair bill is a banger, but it has a weak spot: parts-pairing, the scourge of repair techs:
https://www.ifixit.com/News/69320/how-parts-pairing-kills-independent-repair

Every generation of Apple devices does more parts-pairing than the previous one, and the current models are so infested with paired parts as to be effectively unrepairable, except by Apple. It's so bad that iFixit has dropped its repairability score for the iPhone 14 from a 7 ("recommend") to a 4 (do not recommend):
https://www.ifixit.com/News/82493/we-are-retroactively-dropping-the-iphones-repairability-score-en
Parts-pairing is bullshit, and Apple are scum for using it, but they're hardly unique. Parts-pairing is at the core of the fuckery of inkjet printer companies, who use it to fence out third-party ink, so they can charge $9,600/gallon for ink that pennies to make:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2020/11/ink-stained-wretches-battle-soul-digital-freedom-taking-place-inside-your-printer
Parts-pairing is also rampant in powered wheelchairs, a heavily monopolized sector whose predatory conduct is jaw-droppingly depraved:
https://uspirgedfund.org/reports/usp/stranded
But if turning phones into e-waste to eke out another billion-dollar stock buyback is indefensible, stranding people with disabilities for months at a time while they await repairs is so obviously wicked that the conscience recoils. That's why it was so great when Colorado passed the nation's first wheelchair right to repair bill last year:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/06/when-drm-comes-your-wheelchair
California actually just passed two right to repair bills; the other one was SB-271, which mirrors Colorado's HB22-1031:
https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billNavClient.xhtml?bill_id=202320240SB271
This is big! It's momentum! It's a start!
But it can't be the end. When Bill Clinton signed DMCA 1201 into law 25 years ago, he loaded a gun and put it on the nation's mantlepiece and now it's Act III and we're all getting sprayed with bullets. Everything from ovens to insulin pumps, thermostats to lightbulbs, has used DMCA 1201 to limit repair, modification and improvement.
Congress needs to rid us of this scourge, to let us bring back all the benefits of interoperability. I explain how this all came to be – and what we should do about it – in my new Verso Books title, The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of Computation.
https://www.versobooks.com/products/3035-the-internet-con


If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/22/vin-locking/#thought-differently

Image: Mitch Barrie (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Daytona_Skeleton_AR-15_completed_rifle_%2817551907724%29.jpg
CC BY-SA 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en
--
kambanji (modified)
https://www.flickr.com/photos/kambanji/4135216486/
CC BY 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
--
Rawpixel (modified)
https://www.rawpixel.com/image/12438797/png-white-background
#pluralistic#vin locking#apple#right to repair#california#ifixit#iphones#sb244#parts pairing#serialization#dmca 1201#felony contempt of business model#ewaste#repairwashing#fuckery
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
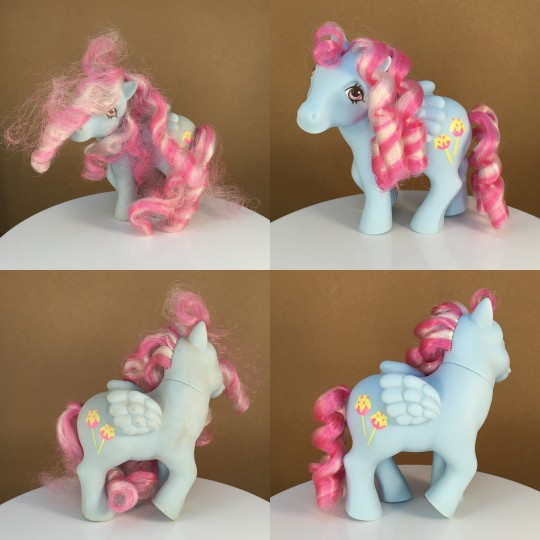


Candy Cane Pony Sugar Apple is one of those ponies I had to go and find for myself as soon as I discovered she existed.
This isn't my Sugar Apple, of course. She was part of another large batch of clean ups for someone else.
#candy cane pony#sugar apple#candy cane pony sugar apple#mlp#my little pony#mlp g1#doll hair#doll repair#before and after
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
how fast i move on from my apple pen now that something better comes along… i am making out with my new pen seemingly without a care in the world, and yet it weighs heavy on my heart
#she works better then that apple pen ever did#fuck u apple pen i thought we had something but u were always lacking#my new pen can draw from both ends and has a clip so i don’t lose her#so much better than that awful apple pen#and yet… my dear apple pen... in her lacking she was still loyal…#we had such great memories together#and i replaced her without a second thought#or did i? i tried didn’t i? i got her new tips? i looked through every youtube video and every help guide?#i suppose the effort i put in meant nothing. she wasn’t mine to repair and i suffered from my desperate attempts#our past may overwhelmingly overlap but the future is brighter without her in it#…but she’ll always hold a place in my heart
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok, y’all, I’m embarrassingly tech-illiterate, they never taught it to us in school and I never learned on my own. Does anyone know of a primer to understand such things more? I know that’s probably a big, vague question but I don’t even know exactly what I should be looking for so I’m open to suggestions lol, I just need to at least understand how to set up a wifi network and shit like that. I’m also very interested in learning more about federated/decentralized platforms and privacy-focused stuff like protonmail. Thanks for any help you offer!
#tech#technology#tech literacy#help I grew up with apple products lol#and now I don’t even know how to use a PC well let alone build one#I want to be able to do my own repairs and stuff#but rn I have no idea what I’m doing#my post#personal
14 notes
·
View notes