#carnegie collection
Photo

A more simple drawing for once - Allosaurus with colors based on the old Carnegie Collection model, one of my favorite toys back then
#my art#paleoart#allosaurus#theropod#dinosaur#carnivore#morrison formation#extinct#animal#jurassic#carnegie collection#paleontology#carnosaur#prehistoric
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dinosaur figure of the day: Safari LTD Carnegie Collection Giganotosaurus (2007)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

#carnegie museum of natural history#carnivora#canidae#mesocyon#from annals of the carnegie 1903-1904#bones#skull#illustration#paleontology#collection
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Peter von Arx – Max Mathys (photograph), Sidney und Harriet Janis Collection. Werke amerikanischer und europäischer Künstler des 20. Jahrh / Theo Eble. Werke 1960 bis 1970, Kunsthalle Basel, February 28 – March 30, 1970 [Museum für Gestaltung Zürich. Carnegie Mellon University Libraries, Pittsburgh, PA]
#graphic design#typography#art#exhibition#poster#peter von arx#max mathys#sidney and harriet janis collection#theo eble#museum für gestaltung zürich#carnegie mellon university libraries#1970s
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

Marc Bohan for Christian Dior Spring/Summer 1962 Haute Couture Collection. Buxy Gancia and Joan wear the evening sets, "Carnegie Hall" and "Comédie Française". Photo by William Souhami.
Marc Bohan pour Christian Dior Collection Haute Couture Printemps/Été 1962. Buxy Gancia et Joan portent les ensembles du soir, "Carnegie Hall" et "Comédie Française". Photo William Souhami.
#marc bohan#christian dior#collection haute couture#french designer#french style#fashion 60s#1962#spring/summer#printemps/été#william souhami#buxy gancia#joan#carnegie hall#comédie française#evening set#ensemble du soir
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
#hattie carnegie#designer#vintage jewelry#vintage style#statement#statement piece#statement jewelry#collectibles
0 notes
Text
The committee concluded that the thousands of records, along with the elaborate indexing system, concerning family heredity were "unsatisfactory for the study of human genetics."
"In the Name of Eugenics: Genetics and the Uses of Human Heredity" - Daniel J. Kevles
#book quote#in the name of eugenics#daniel j kevles#nonfiction#blue ribbon committee#committee#carnegie#indexing#data collection#bad data#unsatisfactory#genetics
0 notes
Text
Carnegie Museum of Natural History
Discovering the Carnegie Museum of Natural History
Located in Pittsburgh’s Oakland neighborhood lies an iconic museum that has been capturing the curiosity and imaginations of its visitors for over a century. The Carnegie Museum of Natural History (CMNH) is a remarkable institution dedicated to the exploration and preservation of our planet’s rich natural history.
A Journey Through Time and…

View On WordPress
#Carnegie Museum of Natural History#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History About#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History Admission#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History Collections#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History Contact#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History Exhibits#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History In Pittsburgh#Carnegie Museum Of Natural History T Rex#The Carnegie Museum Of Natural History
1 note
·
View note
Text
Pauline Trigère - Trigère
Pauline Trigère - Trigère
#PaulineTrigère #Trigère #maisontrigère #creatoredistile #perfettamentechic
Pauline Trigère, è stata una couturière franco-americana fondatrice del brand Trigère.
Gli stili pluripremiata Pauline Trigère raggiunsero l’apice della popolarità negli Stati Uniti negli anni ’50 e ’60. Riconosciuta all’inizio della sua carriera come innovatrice del taglio e della costruzione, Trigère ha portato alle donne di tutte le età di tutto il mondo novità come la tuta, il cappotto senza…

View On WordPress
#Accessori moda#Adele Simpson#Alta moda#Alta moda in Italia#Alta Moda Italiana#Atelier di Alta Moda#Ben Gershal#Brandeis University Archives & Special Collections#Colazione da Tiffany#Cotton Award#Coty Awards#Coty Fashion Hall of Fame#Fashion Critics Award#Fashion Institute of Technology#Franklin Benjamin Elman#Hattie Carnegie#Kent State University Museum Designer Archives#Lazar Radley#Lifetime Achievement Award#Martial et Armand#McCall#Memphis#Neiman-Marcus Award#Patricia Neal#Pauline#Pauline Trigère#PT Concepts#Return Award#Seventh Avenue#tartaruga
0 notes
Text


My little vinyl collection of Nina Simone 🙃
#nina simone#vinyl records#vinyl collection#vinyls#records#newport jazz festival#carnegie hall#philips records#nina simone sings the blues#nina simone at new port#strange fruit#forbidden fruit#piano#piano music#classical piano#the high priestess of soul#the high priestess#village gate#town hall#strings#i put a spell on you#sunday morning classics#Ellington#Simone#Lisa Simone#Pastel Blues
1 note
·
View note
Photo






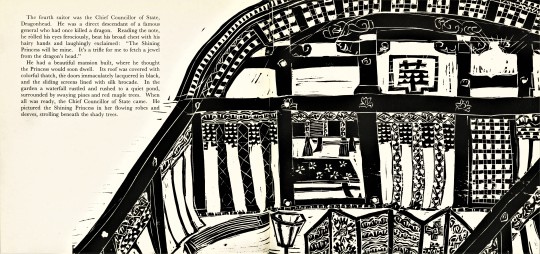



Staff Pick of the Week
My staff pick this week is the trade edition of The Tale of the Shining Princess by Japanese-born writer Hisako Matsubara (b.1935) and Japanese-Canadian artist-printmaker Naoko Matsubara (b.1937), published by Kodansha International LTD. Tokyo, Japan in 1966.
As a artist-printmaker and bookmaker who makes woodcuts, I am greatly inspired by Naoko’s prints. Naoko Matsubara’s work carries on traditions of Japanese printmaking while having its own contemporary flavor. Her woodcuts are ecstatic, they are vibrating with movement. Her use of bold shapes and the white line of the the carving tool makes the most of what woodcut has to offer. In the book form, the active images carry the reader’s eyes through the book space. Her use of negative space activates the page. Additionally, her woodcuts have translated beautifully to commercial printing.
The Matsubara sisters are daughters of a senior Shinto priest, and were raised in Kyoto. Both studied, lived, and worked in the United States. Hisako received her Master of Arts degree from Pennsylvania State College, moving to Germany where she continued her studies and became a prominent writer, publishing her work in Japanese, English, and German. In the 1980s she moved back to the United States, this time to California where she worked at Stanford University.
Naoko received her Master of Fine Arts from Carnegie Institute of Technology in Pittsburgh, now Carnegie Mellon University. After her studies she traveled across Europe and Asia. She returned to the United States and became the personal assistant to the artist and wood engraver Fritz Eichenberg, an artist who has been featured many times on our blog. Naoko taught at Pratt University in New York and at the University of Rohde Island. She also lived in Cambridge, Massachusetts for a time. Naoko is currently living and working in Canada in Oakville, Ontario, where she continues to work and exhibit nationally.
The work of both Hisako and Naoko have had great influence inside the United States and around the world. So lets celebrate their accomplishments!
This book has end sheets of mulberry paper with inclusions of Bamboo leaves, the cover is a red textured paper with a gold stamped design by Naoko.



View some of our other AAPI selections for this month.
View our other Staff Picks.
- Teddy, Special Collections Graduate Intern
#staff pick of the week#The Tale of The Shining Princess#hisako matsubara#naoko matsubara#Japanese artists#Japanese writers#Japan#AAPI Hertitage Month#Asian American and Pacific Islander Heritage Month#AAPI#canadian artists#trade edition#Matsubara#woodcuts#printmaking#color printmaking#fiction#stories#teddy
421 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Book illustration, portrait of Galileo Galilei [photograph made from an unidentified book] [The Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science Collection at the Huntington Library, San Marino, CA] / [Giuseppe Zocchi del: Franc:o Allegrini inc: 1760. Bibl.: Serie di ritratti d'uomini illustri toscani con gli elogj istorici dei medesimi... Volume secondo, Firenze, appresso Giuseppe Allegrini, 1768, ritratto XLII (source)]
#astronomy#mathematics#physics#philosophy#book#galileo galilei#carnegie institution for science collection#the huntington library#no date#1760s
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the subject of Dinosaur Documentaries...
So Life On Our Planet dropped a few days ago, another installment of this seeming boom of these kind of shows since Prehistoric Planet last year, and it got me thinking about this whole little niche genre.

The very first "Paleodoc" was released in 1922, made by the Carnegie Museum of Natural History to educate museum goers on how the fossils they saw were collected and prepared. This began the format I like to call the "Talking Heads" Paleodoc which is mainly in the form of interviews or narration over actual footage of Paleontologists at work with the occasional "Live" Dinosaur for visual aid. These are by far the most common form of dinosaur documentary you'll find, even today, mainly because they're cheap to produce and fit in the general style of most science documentaries.
For many decades throughout the 20th century, Paleodocs were pretty rare. They would pop up time to time, and with the sudden influx of attention they got after Jurassic Park, we got some really good ones. Yet they were all the same Talking Head types. What really changed the game was the good ol Magnum Opus of the field: Walking With Dinosaurs.

WWD pioneered the second type of Paleodoc I believe to exist, which are the "In Their World" Paleodocs. These are different in the fact they focus almost entirely on the live visual aids, with the human presence being limited to narration or brief pauses for context. They're meant to simulate the modern nature documentary, like Planet Earth, that focus more on showcasing animal behavior with state of the art filming techniques than being a source of in-depth science.
The success of WWD cannot be overstated, and I have to say I do find the In Their World format a lot more engaging and easier to connect with. They portray the wonder of prehistory spectacularly, letting audiences get emotionally connected in the animal characters the story creates, even if this has lead to criticisms of anthropomorphism. These programs also almost always use real footage of modern day earth for their prehistoric creatures to roam on, which I'm sure is very sad for the people who want to see their favorite dead plants on screen.
The Walking With... series would expand into sequels and spin-offs and Nigel Marven, and other companies like Discovery would jump on the bandwagon and release their own takes on the concept, but by the mid 2010s the format had basically died out. We'd get one or In Their World style doc every few years until we just didn't get anything. Outside of the occasional TV special that reused When Dinosaurs Roamed America footage, it was empty.
It took until Disney's Live Action remake of The Lion King of all things for that pendulum to start swinging again. Seeing those expressionless CGI cats got Jon Favreau thinking about how he could use this technology and the talented people behind it to make something really cool, and we got Prehistoric Planet.

And, in a repeat of Walking With Dinosaurs, we're seeing more of these In Their World type shows. The original guys behind WWD are even making a comeback with their own series, Surviving Earth. Plus even more little hints and rumors of massive incoming projects from overexcited paleontologists trying not to break their embargo.
It looks like the 2020s will be another resurgence in these types of spectacle Paleodocs, and while a good ol Talking Head will always be there, I can't help but get excited for these animated spectacles and all the weird and wonderful ways they flash those visual aids across our TV screens.
164 notes
·
View notes
Text

Little libraries -
Free little Libraries are a great passive mutual aid project. Originally inspired by DIY projects they are easy to build, are generally low maintenance once established, creative and fun artworks within themselves, and its a great way to introduce a gift economy into your neighborhood!
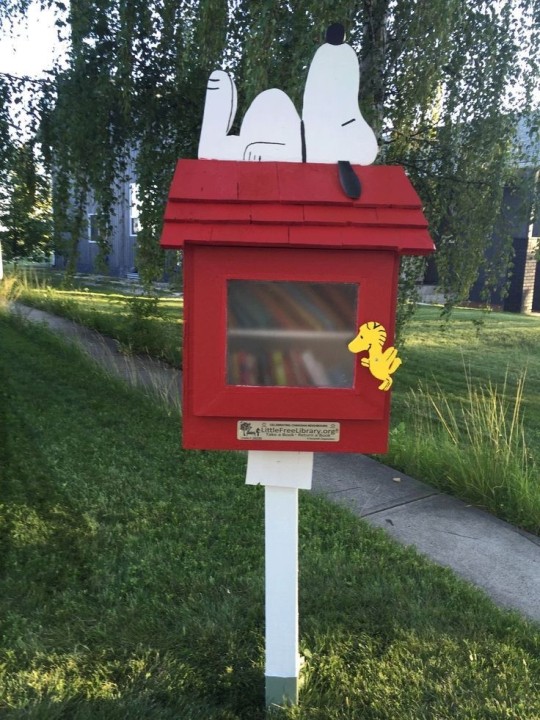
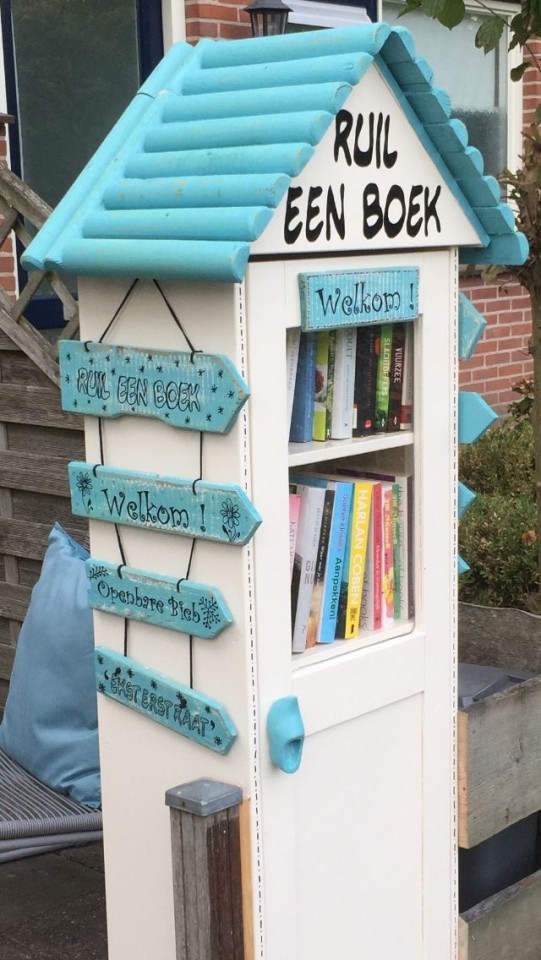



History-
2009- Todd Bol of Hudson, Wisconsin, built a model of a one room schoolhouse. It was a tribute to his mother; she was a teacher who loved to read. He filled it with books and put it on a post in his front yard. His neighbors and friends loved it, so he built several more and gave them away.
UW-Madison’s Rick Brooks saw Bol’s do-it-yourself project while they were discussing potential mutual aid projects. They were inspired by community gift-sharing networks, “take a book, leave a book” collections in coffee shops and public spaces, and most especially by the philanthropist Andrew Carnegie.
2010 the name Little Free Library was established and the purpose of these Little Free Library book exchanges became clear: to share good books and bring communities together.As Bol and Brooks continued to give away Little Free Libraries with wooden charter signs, engraved with official charter numbers, curiosity and demand for more Libraries grew. The acceleration centered on the enthusiasm of early adopters and stewards, who were crucial advocates. Some small grants and informal partnerships began to have an impact on Little Free Library’s ability to keep up with demand.
2011 brought national media attention, and by the end of the year there were nearly 400 Little Free Libraries in existence. That number would skyrocket to over 4,000 Libraries within a year.
2012 Little Free Library became a registered 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization in the states!
Little Free Libraries have continued to grow by leaps and bounds every year. In 2022 we surpassed 150,000 registered Libraries in more than 120 countries worldwide. Even establishing an online map and app to help people locate the libraries!
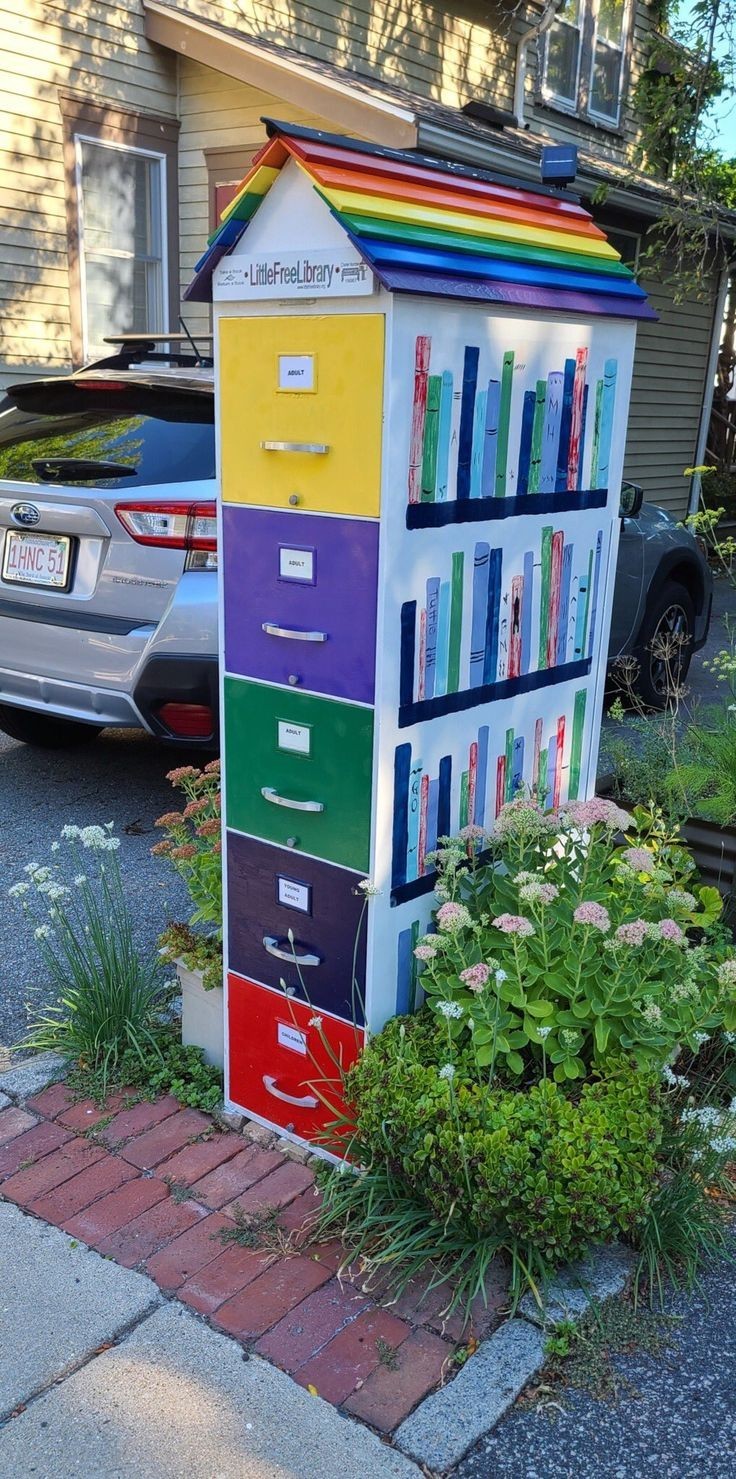
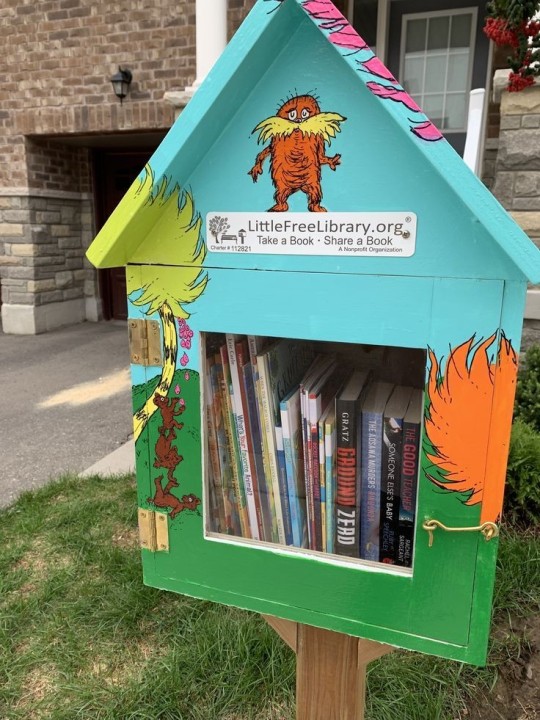





How do I do this?
The little library website hosts a bunch of plans and blueprints to make a library or get ideas for locations. Even having ready to order kits if you want!
You will need either land or public approval to establish one however, this can be by the city, neighbours, or other public spaces but they are technically put on private land. You wont find anyone ho would object to their installation but I would not recommend just installing one unless your okay with it being taken down.
Pick a location that has a lot of foot traffic and be highly visible to anyone nearby and is accessible as possible.
Register your library! You can get an official charter sign by doing this step!!
Fill it up with books!!
#solarpunk#ref#sprout guide#reaping week#anticapitalism#mutual aid#little libraries#cottage core#reading#books
183 notes
·
View notes
Text
Everything advertised on social media is overpriced junk

In “Behavioral Advertising and Consumer Welfare: An Empirical Investigation,” a trio of business researchers from Carnegie Mellon and Pamplin College investigate the difference between the goods purchased through highly targeted online ads and just plain web-searches, and conclude social media ads push overpriced junk:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4398428
If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this thread to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/08/late-stage-sea-monkeys/#jeremys-razors
Specifically, stuff that’s pushed to you via targeted ads costs an average of 10 percent more, and it significantly more likely to come from a vendor with a poor rating from the Better Business Bureau. This may seem trivial and obvious, but it’s got profound implications for media, commercial surveillance, and the future of the internet.
Writing in the New York Times, Julia Angwin — a legendary, muckraking data journalist — breaks down those implications. Angwin builds a case study around Jeremy’s Razors, a business that advertises itself as a “woke-free” shaving solution for manly men:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/04/06/opinion/online-advertising-privacy-data-surveillance-consumer-quality.html
Jeremy’s Razors spends a fucking fortune on ads. According to Facebook’s Ad Library, the company spent $800,000 on FB ads in March, targeting fathers of school-age kids who like Hershey’s, ultimate fighting, hunting or Johnny Cash:
https://pluralistic.net/jeremys-targeting
Anti-woke razors are an objectively, hilariously stupid idea, but that’s not the point here. The point is that Jeremy’s has to spend $800K/month to reach its customers, which means that it either has to accept $800K less in profits, or make it up by charging more and/or skimping on quality.
Targeted advertising is incredibly expensive, and incredibly lucrative — for the ad-tech platforms that sit between creative workers and media companies on one side, and audiences on the other. In order to target ads, ad-tech companies have to collect deep, nonconsensual dossiers on every internet user, full of personal, sensitive and potentially compromising information.
The switch to targeted ads was part of the enshittification cycle, whereby companies like Facebook and Google lured in end-users by offering high-quality services — Facebook showed you the things the people you asked to hear from posted, and Google returned the best search results it could find.
Eventually, those users became locked in. Once all our friends were on Facebook, we held each other hostage, each unable to leave because the others were there. Google used its access to the capital markets to snuff out any rival search companies, spending tens of billions every year to be the default on Apple devices, for example.
Once we were locked in, the tech giants made life worse for us in order to make life better for media companies and advertisers. Facebook violated its promise to be the privacy-centric alternative to Myspace, where our data would never be harvested; it switched on mass surveillance and created cheap, accurate ad-targeting:
https://lawcat.berkeley.edu/record/1128876?ln=en
Google fulfilled the prophecy in its founding technical document, the Pagerank paper: “advertising funded search engines will be inherently biased towards the advertisers and away from the needs of the consumers.” They, too, offered cheap, highly targeted ads:
http://infolab.stanford.edu/~backrub/google.html
Facebook and Google weren’t just kind to advertisers — they also gave media companies and creative workers a great deal, funneling vast quantities of traffic to both. Facebook did this by cramming media content into the feeds of people who hadn’t asked to see it, displacing the friends’ posts they had asked to see. Google did it by upranking media posts in search results.
Then we came to the final stage of the enshittification cycle: having hooked both end-users and business customers, Facebook and Google withdrew the surpluses from both groups and handed them to their own shareholders. Advertising costs went up. The share of ad income paid to media companies went down. Users got more ads in their feeds and search results.
Facebook and Google illegally colluded to rig the ad-market with a program called Jedi Blue that let the companies steal from both advertisers and media companies:
https://techcrunch.com/2022/03/11/google-meta-jedi-blue-eu-uk-antitrust-probes/
Apple blocked Facebook’s surveillance on its mobile devices, but increased its own surveillance of Iphone and Ipad users in order to target ads to them, even when those users explicitly opted out of spying:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/14/luxury-surveillance/#liar-liar
Today, we live in the enshittification end-times, red of tooth and claw, where media companies’ revenues are dwindling and advertisers’ costs are soaring, and the tech giants are raking in hundreds of billions, firing hundreds of thousands of workers, and pissing away tens of billions on stock buybacks:
https://doctorow.medium.com/mass-tech-worker-layoffs-and-the-soft-landing-1ddbb442e608
As Angwin points out, in the era before behavioral advertising, Jeremy’s might have bought an ad in Deer & Deer Hunting or another magazine that caters to he-man types who don’t want woke razors; the same is true for all products and publications. Before mass, non-consensual surveillance, ads were based on content and context, not on the reader’s prior behavior.
There’s no reason that ads today couldn’t return to that regime. Contextual ads operate without surveillance, using the same “real-time bidding” mechanism to place ads based on the content of the article and some basic parameters about the user (rough location based on IP address, time of day, device type):
https://pluralistic.net/2020/08/05/behavioral-v-contextual/#contextual-ads
Context ads perform about as well as behavioral ads — but they have a radically different power-structure. No media company will ever know as much about a given user as an ad-tech giant practicing dragnet surveillance and buying purchase, location and finance data from data-brokers. But no ad-tech giant knows as much about the context and content of an article as the media company that published it.
Context ads are, by definition, centered on the media company or creative worker whose work they appear alongside of. They are much harder for tech giants to enshittify, because enshittification requires lock-in and it’s hard to lock in a publication who knows better than anyone what they’re publishing and what it means.
We should ban surveillance advertising. Period. Companies should not be allowed to collect our data without our meaningful opt-in consent, and if that was the standard, there would be no data-collection:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/03/22/myob/#adtech-considered-harmful
Remember when Apple created an opt out button for tracking, more than 94 percent of users clicked it (the people who clicked “yes” to “can Facebook spy on you?” were either Facebook employees, or confused):
https://www.cnbc.com/2022/02/02/facebook-says-apple-ios-privacy-change-will-cost-10-billion-this-year.html
Ad-targeting enables a host of evils, like paid political disinformation. It also leads to more expensive, lower-quality goods. “A Raw Deal For Consumers,” Sumit Sharma’s new Consumer Reports paper, catalogs the many other costs imposed on Americans due to the lack of tech regulation:
https://advocacy.consumerreports.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/A-Raw-Deal-for-US-Consumers_March-2023.pdf
Sharma describes the benefits that Europeans will shortly enjoy thanks to the EU’s Digital Markets Act and Digital Services Act, from lower prices to more privacy to more choice, from cloud gaming on mobile devices to competing app stores.
However, both the EU and the US — as well as Canada and Australia — have focused their news industry legislating on misguided “link taxes,” where tech giants are required to pay license fees to link to and excerpt the news. This is an approach grounded in the mistaken idea that tech giants are stealing media companies’ content — when really, tech giants are stealing their money:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/04/18/news-isnt-secret/#bid-shading
Creating a new pseudocopyright to control who can discuss the news is a terrible idea, one that will make the media companies beholden to the tech giants at a time when we desperately need deep, critical reporting on the tech sector. In Canada, where Bill C-18 is the latest link tax proposal in the running to become law, we’re already seeing that conflict of interest come into play.
As Jesse Brown and Paula Simons — a veteran reporter turned senator — discuss on the latest Canadaland podcast, the Toronto Star’s sharp and well-reported critical series on the tech giants died a swift and unexplained death immediately after the Star began receiving license fees for tech users’ links and excerpts from its reporting:
https://www.canadaland.com/paula-simons-bill-c-18/
Meanwhile, in Australia, the proposed “news bargaining code” stampeded the tech giants into agreeing to enter into “voluntary” negotiations with the media companies, allowing Rupert Murdoch’s Newscorp to claim the lion’s share of the money, and then conduct layoffs across its newsrooms.
While in France, the link tax depends on publishers integrating with Google Showcase, a product that makes Google more money from news content and makes news publishers more dependent on Google:
https://www.politico.eu/article/french-competition-authority-greenlights-google-pledges-over-paying-news-publishers/
A link tax only pays for so long as the tech giants remain dominant and continue to extract the massive profits that make them capable of paying the tax. But legislative action to fix the ad-tech markets, like Senator Mike Lee’s ad-tech breakup bill (cosponsored by both Ted Cruz and Elizabeth Warren!) would shift power to publishers, and with it, money:
https://www.lee.senate.gov/2023/3/the-america-act
With ad-tech intermediaries scooping up 50% or more of every advertising dollar, there is plenty of potential to save news without the need for a link tax. If unrigging the ad-tech market drops the platforms’ share of advertising dollars to a more reasonable 10%, then the advertisers and publishers could split the remainder, with advertisers spending 20% less and publishers netting 20% more.
Passing a federal privacy law would end surveillance advertising at the stroke of a pen, shifting the market to context ads that let publishers, not platforms, call the shots. As an added bonus, the law would stop Tiktok from spying on Americans, and also end Google, Facebook, Apple and Microsoft’s spying to boot:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/30/tik-tok-tow/#good-politics-for-electoral-victories
Mandating competition in app stores — as the Europeans are poised to do — would kill Google and Apple’s 30% “app store tax” — the percentage they rake off of every transaction from every app on Android and Ios. Drop that down to the 2–5% that the credit cards charge, and every media outlet’s revenue-per-subscriber would jump by 25%.
Add to that an end-to-end rule for tech giants requiring them to deliver updates from willing receivers to willing senders, so every newsletter you subscribed to would stay out of your spam folder and every post by every media company or creator you followed would show up in your feed:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
That would make it impossible for tech giants to use the sleazy enshittification gambit of forcing creative workers and media companies to pay to “boost” their content (or pay $8/month for a blue tick) just to get it in front of the people who asked to see it:
https://doctorow.medium.com/twiddler-1b5c9690cce6
The point of enshittification is that it’s bad for everyone except the shareholders of tech monopolists. Jeremy’s Razors are bad, winning a 2.7 star rating out of five:
https://www.facebook.com/JeremysRazors/reviews
The company charges more for these substandard razors, and you are more likely to find out about them, because of targeted, behavioral ads. These ads starve media companies and creative workers and make social media and search results terrible.
A link tax is predicated on the idea that we need Big Tech to stay big, and to dribble a few crumbs for media companies, compromising their ability to report on their deep-pocketed beneficiaries, in a way that advantages the biggest media companies and leaves small, local and independent press in the cold.
By contrast, a privacy law, ad-tech breakups, app-store competition and end-to-end delivery would shatter the power of Big Tech and shift power to users, creative workers and media companies. These are solutions that don’t just keep working if Big Tech goes away — they actually hasten that demise! What’s more, they work just as well for big companies as they do for independents.
Whether you’re the New York Times or you’re an ex-Times reporter who’s quit your job and now crowdfunds to cover your local school board and town council meetings, shifting control and the share of income is will benefit you, whether or not Big Tech is still in the picture.
Have you ever wanted to say thank you for these posts? Here’s how you can: I’m kickstarting the audiobook for my next novel, a post-cyberpunk anti-finance finance thriller about Silicon Valley scams called Red Team Blues. Amazon’s Audible refuses to carry my audiobooks because they’re DRM free, but crowdfunding makes them possible.
Image:
freeimageslive.co.uk (modified)
http://www.freeimageslive.co.uk/free_stock_image/using-mobile-phone-jpg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
[Image ID: A man's hand holds a mobile phone. Its screen displays an Instagram ad. The ad has been replaced with a slice of a vintage comic book 'small ads' page.]
#pluralistic#ad-tech#ads#surveillance ads#commercial surveillance#behavioral ads#contextual ads#link taxes#platform economics#enshittification#instagram#julia angwin#end to end
473 notes
·
View notes