#childhood diabetes type 2 symptoms
Text

Obese Kids, Future Diabetics
The WHO describes childhood obesity as one of the 21st Century’s most serious public health challenges. If nothing else, just the knowledge of how difficult it is to treat obesity makes prevention of childhood obesity vital. Here are some simple yet effective ways to prevent childhood obesity.
Click here to read more: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/obese-kids-future-diabetics/2718
#childhood obesity and diabetes#childhood obesity and type 2 diabetes#type 2 diabetes in children#child diabetes symptoms#childhood diabetes type 2#childhood obesity#causes of childhood obesity#childhood obesity symptoms
0 notes
Note
hi beeee!! i hope you're doing okay 💖💖💖
ooohohohoho okay for the kiss thingy: god knows why cuz it sounds potentially very painful but i feel so compelled to request 28 🙏
sweet deanna! i'm hanging in, thanks love! 💖 so you & @lingy910y both requested #28 & i want to fill both of your prompts. but because you were (rightfully) afraid of pain, i gave you one that's a bit strange, but has a promisingly happy ending? you can be the judge! xx
- - - - -
send me a number & i'll write you a smoocheroo 😚
- - - - -
#28: ...as a lie
ps. this is inspired by this post about dealer!mickey & insomniac!ian, who have now rotted my brain.
Ian hasn’t slept in days.
It’s happened before—endless energy is one of his tried-and-true symptoms of mania—but this isn’t that. He’s taking his meds, his skin isn’t crawling and his mind is fairly quiet. Quiet enough to frustrate him as he tosses and turns and wonders what the fuck’s going on.
His schedule has been all over the place lately; his normal routine lost to the endless cycles of employment and Gallagher family responsibilities. He’d been hoping to add school to the mix this semester so that he could have other, less hectic options than a rig-riding EMT, but he’d pushed it off. A pity, now that all-nighters are apparently his thing.
Night two, he googles a few things, which is a huge mistake. Who can fall asleep after reading about how even just twenty-four hours without sleep can begin to derail your bodily systems? Sleep deprivation can cause or worsen conditions like Type 2 diabetes, High blood pressure, Stroke, Heart attack—his pulse leaps as his phone clatters to the ground.
Night three, he takes to the streets, running around the Southside until his lungs burn and his knees wobble. As he passes the clinic that gave his seventeen-year-old self a lifetime prescription for antipsychotics, he knows that if this lasts much longer, he should call his doctor. Tell them his nighttime meds aren’t putting him to sleep anymore. Nip this insomnia thing in the bud before it can overthrow the delicate balance he’s worked so hard to maintain.
Night four, desperate and a bit delusion, he pulls up a number he hasn’t used in years, saved under a contact labeled, DO NOT TEXT.
He breaks his own rule: Hey. Still making house calls?
The response is almost immediate: the fuck u care for?
Ian rolls his bloodshot eyes, typing: It’s an emergency.
Three little dots herald a response that makes him laugh: a weed emergency?
He stays strong: Wouldn’t ask if I didn’t need it.
The next text makes his chest clench: u ok?
He decides to keep it vague—I can’t sleep, but it’s not what you think.—and hopes he doesn’t have to explain further and is relieved to read: u want ur usual?
Another clench: Indica
Two texts arrive in rapid succession: what else do u want? can i give u head while u smoke or no?
There it is: the reason Ian doesn’t use this number anymore.
Maybe in another life it would be a blessing to have a weed dealer to lovers arc with your childhood crush, but in this one, it was a curse. A curse that lasted almost a whole year, bringing with it an endless bouquet of blissful fucks and free weed, and a million moments of tenderness Ian knew nobody else was getting out of the guy. A curse that eventually came to collect payment in the form of bloodied knuckles, broken hearts and ego wounds. A curse that still clings to Ian’s psyche, filling his dreams with gentle, tattooed fingers and bright blue eyes and a sweet and savory scent that can only be described as Mickey.
Mickey, now DO NOT TEXT.
On second thought, maybe he should never sleep again.
The knock at the door makes him hard—a Pavlovian response that irks him more than the three sleepless nights he’s suffered so far. Three raps, one right after the other. The last one no more than a brush of his hand.
Ian adjusts himself and answers the door.
Fuck, one look at that smug asshole and he’s immediately right back in it. Lust and like and maybe even a little bit of reckless fucking love fill his body, rising to the surface like sweet cream. A layer of fat on the roof of one’s mouth; a treat to lick later, a reminder that they didn’t end things because they weren’t insanely hot for one another and potentially soulmates. They were just idiots. Stubborn, petty dicks.
Oh Pride, the great slayer of men.
Jesus, he needs to sleep.
“First one’s on the house,” Mickey says as he crosses the threshold, a joint held tightly between C and K.
Hours slip by. They laugh, they smoke. It feels like old times. Ian’s body is loose in a way it hasn’t been in years. It feels good. Like maybe-he-could-sleep-tonight good. And as he melts further into the couch, he starts to get a little horny too. Because Mickey’s yapping on and on about some asshole that frequents the bar he works at, and Ian’s listening, he swears he’s listening, but he’s also staring at Mickey’s mouth like he wants to take Mickey up on that text message and shut him the fuck up with his dick.
Like he wants to taste the stale smoke of his tongue.
Wants him to stay the night.
Forever, maybe.
Mickey finishes his story. His eyes go soft and he drums his fingers against his knee. “Should get outta your hair, Gallagher,” he says. “Letcha sleep.”
That’s the last thing Ian wants.
“Not tired,” he fibs.
Mickey cocks an eyebrow. “You’re not? ’S been days, man. This shit’s gotta be hittin’ ya by now.”
It’s true. It has been days and this shit is hitting him. Or maybe he’s having a sleep-deprivation-induced stroke. He just knows Mickey can’t go.
“Can’t go to sleep without a goodnight kiss.”
Mickey’s already leaning in when he asks, “Then you promise you’ll hit the hay?”
Ian nods as Mickey presses a kiss to his lying lips.
#welp - throws whatever this is at you#alskfjalkj#i realized that both of my kisses are at the very end of the ficlet & aren't actually described#lolol#maybe my next attempt should be 1K words of just describing the kiss#no actual context needed#just tongues#anyway THANKS DEANNA I LOVE YOU DEANNA#shameless#shameless fanfiction#prompt fill#ian x mickey
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
Experts Call Long COVID in Kids a Public Health Crisis. Why Is It Being Ignored? - Published Aug 26, 2024
For years, public health experts have said that COVID-19 infections in children are “mild.” According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most common symptoms of COVID in kids are a fever and cough. While some children with the coronavirus are admitted to the ICU and there are pediatric deaths, studies have found that underlying medical conditions including obesity, diabetes, cardiac and lung disorders, increase the risk of severe outcomes.
This research has contributed to how COVID is managed in schools. However, a new study in the Journal of the American Medical Association sheds light on the effect a coronavirus infection can have on children over a longer period. While many people recover quickly from COVID, some don’t, experiencing symptoms that can last for months or years. This condition, known as long COVID, not only affects adults but also children. The new research helps us understand the extent kids experience these debilitating conditions — and how we can treat it.
“This is one of the first large-scale national studies to do research related to long COVID across the entire lifespan, with a particular focus on children and understanding the differences in long COVID in different aged children,” Dr. Rachel Gross, an associate professor in the Departments of Pediatrics and Population Health at NYU Langone and the study’s principal investigator, told Salon.
In the study, led by the National Institutes of Health’s RECOVER Initiative, researchers asked caregivers to tell them about the symptoms that their children or teenagers had been experiencing more than four weeks after a coronavirus infection. For some children in the study, that meant their symptoms went on for three months after their COVID infection. For others, it was up to two years. Researchers looked at the symptoms in those children with persisting symptoms and compared them to children who had never been infected with the coronavirus in the past. They then identified similarities in the prolonged symptoms and found they were distinguishable based on age.
“In school-aged children, we heard commonly that children were experiencing trouble with their memory, focusing, headaches, having trouble sleeping, and stomach pain,” Gross told Salon. “And in the teenagers, we were hearing about symptoms related to fatigue and pain, having body or muscle or joint pain, being very tired or sleepy, having low energy, as well as having trouble with memory and focusing.”
A unique symptom the researchers saw in the teenage group was changes in or a loss of smell or taste. Additionally, researchers found clusters of symptoms that are unique to school-aged children and teenagers. The first were symptoms that affect every organ system in the body.
“These are the children with the highest burden of symptoms,” Gross said, adding that caregivers described these children as having a “lower quality of life and more impact on their overall health.” “The second type of long COVID we also saw across both the ages was predominantly characterized by fatigue and pain.”
Studies estimating its prevalence in pediatric populations are limited and conflicting, estimating up to 25% of children infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus could go on to develop long COVID. A study published in 2024 estimated that up to 5.8 million young people have long COVID.
“This is a public health crisis for children,” Gross said. “We know that child health is so critically important for how children grow and even as they become adults, that chronic illness during childhood and adverse experiences during childhood greatly affects the adults that they can become.”
Gross said the U.S. will see the “long-term impacts of experiencing long covid In childhood for decades to come.”
Dr. Dean Blumberg, chief of pediatric infectious diseases and associate professor in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of California, Davis, told Salon he agreed long COVID is a “public health crisis” for children.
“Some of these kids with long COVID, they are severely affected, they can’t do their normal activities, they fall behind school, they can’t go to school,” Blumberg said. “And then in this study, they highlighted a lot have had some neurocognitive effects, and that really interferes with with learning.”
For Blumberg, the takeaway from this study, he told Salon, is a “call to arms to increase vaccination rates,” which among children, he said are “abysmal.”
According to a recent KFF survey, while both flu and COVID vaccines are recommended for school-aged children, flu vaccination rates were over three times higher than COVID vaccination rates. While COVID-19 vaccines are recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in the pediatric immunization schedule, they aren’t required for school attendance. According to one study published in the journal Pediatrics, vaccination reduced the risk of an acute infection, but it is less clear whether it protects against long COVID. The latest COVID vaccines were approved by the Food and Drug Administration last week, which the CDC recommends for anyone six months or older.
Now, researchers will be tasked with figuring out why long COVID affects children differently based on their age. When it comes to adults, some studies have shown that subsequent COVID infections increase a person’s risk of getting long COVID. The CDC estimates that one in 13 adults in the United States currently have long COVID symptoms.
Gross told Salon she hopes this research raises awareness for both healthcare providers, as well as schools and educators, that “long COVID in children is not rare.”
“That they are likely to have children experiencing these prolonged symptoms within their healthcare systems and their schools,” Gross said. “And that many of the symptoms that I’ve described, trouble with memory and focusing, headache, trouble sleeping, these are symptoms that you know can impact a child and their schooling.”
#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#sars cov 2#wear a mask#coronavirus#public health#still coviding#wear a respirator#long covid
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Credit: Dana Smith
Understanding The Sudden Rise of Type 2 Diabetes In Children
The Metabolic Disorder Was Long Known as a Disease of Adulthood. Now, It’s Spiking in Kids and Teens, With Worrisome Consequences.
— By Charlotte Huff | July 31, 2024
The appearance of type 2 diabetes in children and teens puzzled physicians from the start. Fida Bacha recalls working as a pediatric endocrinology fellow in Pittsburgh shortly after 2000 when young, overweight and obese patients began to arrive at the clinic, some describing increased thirst, more frequent trips to the bathroom and other symptoms of what was then called adult-onset diabetes.
“It was a new realization that we are dealing with a disease that used to be only an adult disease that is now becoming a disease of childhood,” says Bacha, who practices at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston.
More than two decades later, physicians and researchers are still trying to unravel what’s driving the emergence and proliferation of youth-onset disease, particularly among marginalized communities including Hispanics/Latinos. The increasing prevalence of obesity among young people is clearly one contributor, but researchers are also scrutinizing the potential influence of other lifestyle and environmental factors — everything from exposure to chronic stress and air pollution to sugar-rich diets. Along with physiological factors, such as where they carry excess fat, youths from lower socioeconomic levels may be vulnerable due to aspects of daily life beyond their control, such as more limited access to healthy food and opportunities to safely exercise in less-polluted neighborhoods.
As researchers try to sort out the interplay among genetics, metabolic factors and environmental influences in Hispanic and other populations, their goal is to answer this key question: Why do some seemingly at-risk adolescents progress to diabetes while others do not?
Long-term, the challenges and health stakes are significant. When type 2 diabetes first emerged in youths, clinicians initially thought its progression would mirror that in adults and thus could be treated accordingly. That hasn’t panned out, says Barbara Linder, a pediatric endocrinologist and senior advisor for childhood diabetes research at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). For instance, researchers have determined that metformin, a commonly prescribed oral antidiabetic medication in adults, doesn’t work as well in young people.
“We know that the disease is very aggressive in youth and very difficult to treat,” Linder says. “So it’s really imperative that we develop effective approaches to prevention. And to do this we obviously need to be able to effectively identify which youth are at the highest risk.”
Even with treatment, young people develop other medical problems related to diabetes faster than adults, according to a study that followed 500 youths, more than one-third of them Hispanic. Sixty percent developed at least one complication within about 15 years after diagnosis, when just in their 20s.
“It’s really alarming,” says Luisa Rodriguez, a pediatric endocrinologist who studies type 2 diabetes and obesity in children at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. For every 10 adolescents with youth-onset diabetes, she points out, “six of them, within a decade span, are going to develop a significant comorbidity that will highly impact their lifespan and quality of life.”

Complications of diabetes appear more quickly in young people than in older adults. Researchers studied 500 overweight adolescents, aged 10 to 17, who had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Within 15 years of their diagnosis, 60 percent of the participants had developed at least one medical complication of diabetes, and 28 percent had developed two or more.
Insulin Resistance
In type 2 diabetes, the body struggles to use insulin effectively. This vital hormone, made by beta cells in the pancreas, helps glucose in the bloodstream enter cells in muscle, fat and the liver, where it’s used for energy. But sometimes those cells gradually lose their ability to respond to insulin, forcing the beta cells to pump out more and more of it. If the beta cells can’t keep up, blood glucose levels will begin to rise, leading to a diagnosis of prediabetes and, eventually, diabetes.
In the past, type 2 diabetes typically didn’t arise until well into adulthood. But now, cases in US youths ages 10 to 19 are rising fast. Since 2002-2003, overall diagnoses have doubled from 9 per 100,000 youths to 17.9 per 100,000 in 2017-2018, particularly among Asians, Pacific Islanders, Blacks and Hispanics. If those rising rates persist, the number of type 2 diabetes cases in young people is projected to skyrocket from 28,000 in 2017 to 220,000 by 2060.
Various factors have been linked to insulin resistance in childhood or adolescence, including obesity, inactivity and genetics, according to a review of the causes of type 2 diabetes in youths published in the 2022 Annual Review of Medicine. The disease tends to run in families regardless of race or ethnicity, which suggests that genes matter. Among US Hispanics, adults of Mexican or Puerto Rican heritage are most likely to be diagnosed, followed by Central and South Americans and Cubans.
Obesity is also a contributing factor: Slightly more than one-fourth of Hispanic youths are obese, a higher percentage than for any other major racial or ethnic group. Children also are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if their mother has the disease or developed gestational diabetes during pregnancy. One theory is that fetal exposure to maternal diabetes while in the womb can spur metabolic changes following birth.
Puberty is also highly influential — most cases are diagnosed after its onset. During puberty, youths temporarily experience insulin resistance, due in large part to an increase in hormones, Linder says. Most youths offset that transient resistance by secreting more insulin, she says. But for reasons that are still unclear, a subpopulation of adolescents does not. “When they’re faced with this stress test of puberty, they can’t increase their insulin secretion enough to compensate,” Linder says. “And that’s probably why they develop type 2 diabetes.”
One analysis, which looked at type 2 diabetes trends from 2002 to 2018, identified the peak age for diagnosis as 16 years in boys and girls. The sole exception involved Black youths, in whom diagnoses peaked at 13 years, and possibly earlier among Black girls, which may be linked to an earlier start of menstruation.
American Diabetes Association guidelines recommend that clinicians screen overweight or obese youths for the disease starting at age 10 or once puberty starts, whichever is earlier, if they have one or more risk factors. These include a family history of the disease, signs of insulin resistance or affiliation with certain racial/ethnic groups, including Hispanic/Latino.
During checkups, clinicians can look for a visible sign of insulin resistance, an associated skin condition called acanthosis nigricans, says Paulina Cruz Bravo, a physician and diabetes researcher at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The skin changes tend to appear in the neck area or along folds in the skin, including in the armpits and on the elbows and knees, she says. “The top layer of the skin gets thickened. It’s described as a velvety appearance of the skin — it’s darker compared to the skin in other places.”

The thickened, darker, velvety skin shown here, known as acanthosis nigricans, is a potential warning sign of developing type 2 diabetes. The condition is likely to appear on the neck, elbows, knees and other areas where the skin folds. People who notice acanthosis nigricans on themselves or their children should bring it to a doctor’s attention. Credit: S. Dulebohn/Statpearls 2024
Where an adolescent carries any excess pounds also matters, as insulin resistance has been associated with a type of fat called visceral fat, says Alaina Vidmar, a pediatric endocrinologist at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles. Unlike the more common type of fat, called subcutaneous and felt by pinching around the waistline, visceral fat surrounds the liver and other vital organs, increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease and other conditions.
“You really need the liver to process glucose to be able to utilize your insulin well,” Vidmar says. “And if it is full of fat, you are unable to do that.” Fatty liver disease, which has been associated both with obesity and type 2 diabetes, is most common in Hispanic adults, followed by white adults and Black adults, according to a meta-analysis looking at 34 studies.
Imaging scans would be the ideal way to identify the extent and location of visceral fat in adolescents, Vidmar says. But given that routine scanning would be costly, clinicians can instead measure an adolescent’s waist circumference, “a great surrogate marker,” she says.

Diabetes risk depends not just on how much fat you carry, but where you carry it. People with an “apple” body shape, with much of their fat in the abdomen, are at higher risk of diabetes than those with a “pear” body shape, who carry their fat under the skin, especially on the hips.
Still, obesity accounts for only a portion of the type 2 risk profile, reflecting the complexities involved in understanding the pathophysiology of youth-onset disease. Roughly one-fourth of youths with type 2 diabetes are not obese, according to a meta-analysis published in 2022 in JAMA Network Open. Asian youths are least likely to be obese; roughly one-third don’t meet the criteria for obesity.
Moreover, while obesity and insulin resistance boost the risk of developing diabetes, those factors alone don’t predict whether an adolescent is eventually diagnosed with the disease, according to the authors of the Annual Review of Medicine overview. Instead, they point to the role of impaired beta cell function.
In one study involving 699 youths with type 2 diabetes, the standard antidiabetic drug metformin controlled blood glucose levels in only about half the participants. (The medication was least effective among Black youths, for reasons that are unclear, according to the researchers.) Another analysis of the same study population identified a 20 percent to 35 percent decline in beta function each year in diabetic youths, compared with prior studies showing about a 7 percent to 11 percent annual decline in diabetic adults.
“What we see in the youth is that beta cell function fails very rapidly,” Linder says, adding that the beta cell decline tends to correlate with the lack of response to metformin.
It’s unknown whether specific racial or ethnic groups are more vulnerable to loss of beta cell function, says Linder, who hopes that a new large-scale NIDDK study launching this summer will identify any such physiological and other differences among populations. The study, called Discovery of Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes in Youth Consortium, aims to enroll 3,600 overweight or obese adolescent boys and girls, 36 percent of them Hispanic. Bacha and other investigators on the project plan to follow the youths through puberty, looking at genetic and physiological markers such as insulin resistance and beta cell function. Their goal is to track who develops type 2 diabetes and what factors precipitate the disease.
In addition, researchers will learn about the participants’ mental health, lifestyles and social determinants of health, Linder says. To that end, families will be asked to share details about nutrition, physical activity and sleep, as well as food insecurity, exposure to racism and other stressors.
“Stress induces certain hormones that antagonize insulin, so they create more insulin resistance,” Linder says. “Stress also is associated with chronic inflammation in the body, which affects the ability of the body to respond normally.”

Young people experience many of the risk factors that predispose people to type 2 diabetes, such as prenatal exposures, junk food, sedentary lifestyles and high levels of stress.
Zooming in on Risk Factors in Hispanic Kids
Already, researchers who have studied at-risk Hispanic youths and their families have begun to flesh out environmental and other influences rooted in daily life that can boost the likelihood of obesity or diabetes. Michael Goran, a child obesity researcher at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, has led a research project called the Study of Latino Adolescents at Risk (SOLAR), which tracked 328 Hispanic/Latino youths considered at highest risk of youth-onset diabetes based on their body mass index and family history of the disease. The participants, recruited in two waves between 2000 and 2015, completed health questionnaires and underwent annual exams, including imaging scans and other measurements.
One analysis found that Hispanic youths who lived in neighborhoods with higher levels of air pollution were more likely to experience a breakdown in beta cell function. “Which we weren’t necessarily expecting — we don’t know the mechanism of that,” says Goran, who coauthored a close look at pediatric insulin resistance in the 2005 Annual Review of Nutrition.
In more recent years, he’s turned his attention to studying nutrition shortly after birth, with a focus on infant formulas that contain corn syrup. Those formulas are more likely to spike blood sugar than are lactose-based formulas, he says. “If you’re spiking blood glucose with corn syrup in babies,” he says, “you can see how that would be problematic for long-term control of blood sugars.”
In one study, Goran and colleagues looked at obesity trends in 15,246 children who received formula through the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC). Babies who consumed any formula with corn syrup were 10 percent more likely to be obese by age 2 than babies who didn’t. Nearly 90 percent of the study’s participants were Hispanic.
In other research, epidemiologist Carmen Isasi of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York helped lead the Study of Latinos (SOL) Youth study, which delved into the extent to which a child’s family circumstances contribute to obesity and metabolic changes that may boost risk of youth-onset diabetes. Isasi and colleagues found chronic stress to be pervasive. Three-quarters of parents and caregivers reported stress and 29 percent detailed three or more stressors related to health, work or relationships. The higher the number of parental stressors, the more likely the child was to be obese.
Isasi also has looked at the relationship between food insecurity and metabolic health. Hispanic youths raised in households with the highest levels of food insecurity had significantly worse metabolic results, including elevated blood glucose and triglycerides, a type of cholesterol. Families dealing with food insecurity, Isasi says, probably have a lower-quality diet and skimp on costlier protein and fresh produce.
Preventing diabetes has proved challenging. A review paper looking at diet-related and other lifestyle initiatives targeting Hispanic youths found few studies to date that have shown improvements in body mass index or blood glucose levels.
Adolescents of lower socioeconomic status may also shoulder responsibilities that can undercut efforts to stay healthy, says Erica Soltero, a behavioral scientist at Houston’s Baylor College of Medicine, who works with Hispanic youths. For instance, older teens may struggle to attend an exercise class if they have an after-school job or must pick up younger siblings or start dinner. Technology, Soltero says, may be a better way to reach busy Hispanic teens; she’s piloting a study that will provide text-based lifestyle guidance to Hispanic teens with obesity.
Approved medication options remain limited for children and teens. If metformin doesn’t work, the alternative is insulin, and parents may resist giving injections because of the difficulties involved, Rodriguez says. She’s involved with an ongoing study in youths with type 2 diabetes to study the effectiveness of oral semaglutide, one of the newer diabetes drugs that also has achieved notable weight loss. Rodriguez estimates the results will be available by 2026.
The new NIDDK study won’t assess medication treatments, as it’s an observational study. But researchers involved are bullish that study-related insights could lead to better prevention and treatment approaches. “If someone is predisposed to beta cell dysfunction, should we be much more aggressive in treating their overweight/obesity,” Bacha says, “so that this beta cell function is preserved for a longer period of time?” Doctors could, for example, decide to start treatment earlier, she says.
Neither are researchers like Soltero deterred by the long-standing difficulties involved with revamping lifestyle habits. Soltero, who has worked with overweight and obese Hispanic adolescents to improve exercise and make dietary changes, describes them as often highly motivated given the damage they’ve seen the disease inflict on their own families.
“A lot of times they’ll have a touch point with a relative who’s on dialysis and maybe had a digit amputated,” Soltero says. Or “they’ll say, ‘I don’t want to prick myself every day like my Uncle So-and-So.’ Or ‘I don’t want to be on medicine for the rest of my life like my grandma.’ ”
#Knowable Magazine#Diabetes#Type-2 Diabetes#Charlotte Huff#Children#Metabolic Disorder#Disease of Adulthood#Spikining Diabetes | Kids | Teens#Epedemiology#Food | Environment#Health & Disease#Nutrition#Public Health#Society
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diabetes
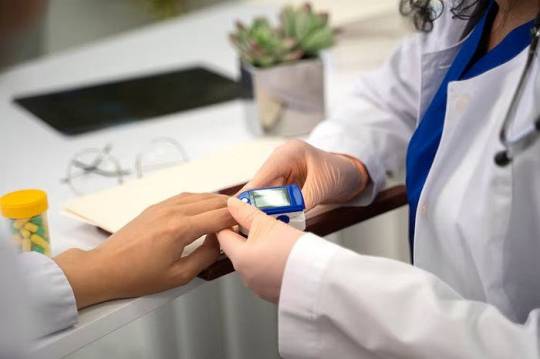
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, arises from abnormalities in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The condition’s prevalence has reached epidemic proportions globally, with significant health, economic, and social implications.
Types of Diabetes
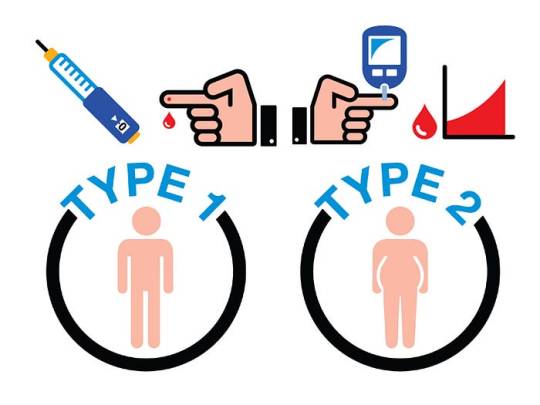
Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune disease results from the destruction of pancreatic beta cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Genetics and environmental triggers play pivotal roles in its pathogenesis. Despite being less common than Type 2 diabetes, its onset during childhood or adolescence significantly impacts individuals’ lives.
Type 2 Diabetes: Predominantly a disorder of insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes accounts for the majority of diabetes cases worldwide. Lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and obesity contribute to its development. Its insidious onset often leads to delayed diagnosis and increased risk of complications.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurring during pregnancy, gestational diabetes poses risks to both maternal and fetal health. Hormonal changes and insulin resistance characterize its pathophysiology. Effective screening and management are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes.
Other Types of Diabetes: Variants like MODY, LADA, and secondary diabetes present unique challenges in diagnosis and management, requiring tailored approaches to care.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Diabetes prevalence varies across demographics, with disparities observed in age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. The escalating burden of diabetes underscores the urgent need for targeted prevention and management strategies.
Symptoms and Causes
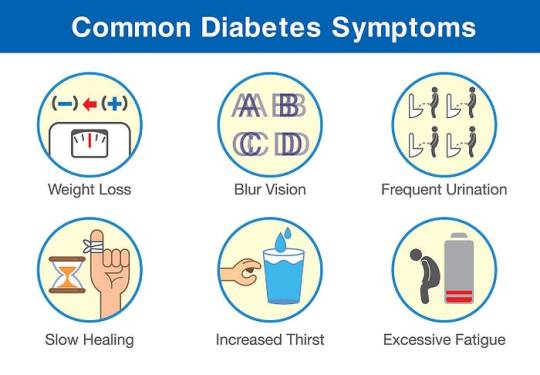
Hyperglycemia-induced symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, and unexplained weight loss serve as clinical indicators for diabetes diagnosis. Understanding the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors elucidates the condition’s etiology.
Complications
Diabetes complications encompass a spectrum of microvascular and macrovascular disorders, significantly impacting quality of life and life expectancy. From diabetic retinopathy to cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and diabetic foot complications, the ripple effects of uncontrolled diabetes are profound.
Diagnosis and Tests
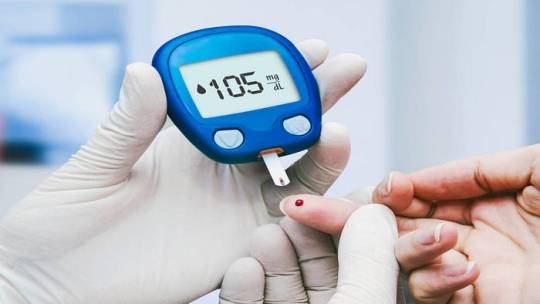
Accurate diagnosis relies on comprehensive evaluation, including fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance tests, and hemoglobin A1c measurements. Screening recommendations aim to identify at-risk individuals early, facilitating timely intervention and risk reduction.
Management and Treatment
Diabetes management strategies encompass pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, patient education, and multidisciplinary care. Individualized treatment plans address glycemic control, blood pressure management, lipid optimization, and prevention of complications.
Prevention
Prevention initiatives target modifiable risk factors through health promotion, public health interventions, and community engagement. Emphasizing the role of nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral changes empowers individuals to mitigate their diabetes risk.
Outlook and Prognosis
Prognostic factors such as glycemic control, adherence to therapy, comorbidity burden, and psychosocial support influence long-term outcomes. Enhanced collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential to improve diabetes prognosis globally.
Living With Diabetes

Coping with diabetes requires resilience, self-management skills, and social support networks. Empowering individuals through education, self-monitoring tools, and peer support enhances their capacity to navigate the challenges of daily diabetes management.
Impact on Individuals and Society
Diabetes exerts a profound socioeconomic burden, encompassing healthcare costs, productivity losses, and reduced quality of life. Addressing the psychosocial dimensions of diabetes care is integral to fostering holistic well-being and societal resilience.
Future Directions and Research

Advancements in diabetes research, including precision medicine, digital health technologies, and novel therapeutics, offer promising avenues for disease management and prevention. Collaborative research endeavors aim to translate scientific discoveries into tangible clinical benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes represents public health challenge necessitating a comprehensive, patient-centered approach. By fostering awareness, promoting early detection, and advancing evidence-based interventions, we can mitigate the impact of diabetes on individuals, families, and communities worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at [email protected] for assistance.
#assignment help#healthcare#medical students#nursing student#nursing school#medical school#medical student#medicine#health tips#health and wellness#health#health & fitness#diabetes#diabetic#medical help#medical assistance#pharmacy student#pharmacy technician#homework help#academic assignments#expert assignment writers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How will ayurvedic medicine heal Arthritis?

Ortho Veda oil has shown excellent results in recovering from arthritis problem whose major symptoms are:
1) Inflammation
2) Pain
3) Swelling
4) Aching
5) Stiffness
The word” arthritis “ itself indicates joint inflammation. It is the loss of cartilage that gives rise to inflammation, intense pain and mobility issues to the person and that can spread across other connecting issues which are ligaments and tendons.
Researchers point out 100 types of arthritis that can happen at any age , pertaining to nutritional deficiency , sedentary habits, and alcoholism.
Types of Arthritis
-----------------------------------
Let’s understand the selected major types of arthritis damaging the physical mobility and mental health are:
1) Inflammatory arthritis
For unexplained reasons, several people have been diagnosed with inflammatory arthritis. It gives rise to swelling, pain and stiffness. Without experiencing injuries or cuts, one can get affected with inflammatory arthritis in several joints. Damage is done to the surface and also to the bones. Examples are rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondilytis
2) Degenerative
Degenerative arthritis is characterized by loss of cartilage from the surface of the bones which actually holds the bones together, causing lubrication and smooth movement.
3) Connective tissue disorder
In this type of arthritis, one experiences destruction in the tendons and ligaments apart from cartilage. It can further damage the connecting tissues of skin, lungs and kidney. The examples of connective tissue disorder are:
1) Scleroderma
2) Lupus or SLE
3) Dermatomyosytis.
4) Sjogren’s
4) Metabolic
This type of arthritis occurs in the form of deposits of uric acid crystals in the area of joints due to disorder in the urinary system. And it leads to development of gout arthritis. It is one of the major signs noted in diabetic persons in the form of sudden pain and swelling.
5) Septic
It is the result of bacterial or fungal infection that can affect the knee and hip area of the body. Infection from the external sources like injury or surgery, reaching the joints and bones through the blood
6) Childhood
It is a juvenile rheumatoid arthritis which can do permanent damage to the bones.
For any of the above mentioned types of arthritis , Ortho Veda oil will be highly effective.
Lakhs of people have realized the value of Ortho Veda oil within a few days of use.

Key factors that determine the positive impact of this veda oil are:
1) Composition : Cow milk, Black sesame oil, Wild asparagus, camphor and eucalyptus are the major ingredients. No chemicals added. The composition is 100% natural and ayurvedic
2) Ortho Veda oil price: Ortho Veda oil price in India is cost effective. You can buy it easily from SKinRange online store at a moderate price. You can also get from Amazon at a discount right now.
3) Recovery effects: a) It will boost blood circulation and warmth in the affected area.
b) It will reduce swelling and inflammation.
c) It will produce relief from pain.
d) It will prevent cartilage loss.
e) It will boost lubrication and flexibility in joints.
4) Certification : Ayush Certified vata massage oil.
5) Side effects if any:No side effects found.
Direction of using this ayurvedic oil
Apply and massage the oil on the affected area as many times a day.
In order to boost immunity, strength, flexibility and longevity of bones and joints, you must eat vitamin D, C and calcium enriched foods along with Omega 3 fatty acids and zinc. Further, you must keep the habit of practicing exercise or yoga for keeping your joints and bones active.
#health#ayurvedicoil#arthritis#joint pain#joint pain relief#skinrange#ayurvedictreatment#essential oils
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes back in January. With the support of my wonderful & amazing doctor, my family & friends, and the help of a dietician who specializes in diabetes I drastically changed my eating habits and learned how to manage my blood sugar. Just with those changes alone I've been slowly losing weight all year.
Last night I had a moment in a dressing room that I thought would never happen - I zipped up a pair of size 22 jeans and they fit perfectly fine.
I was wearing a 26 in January.
I started wearing a 24 in August.
I haven't worn a 22 since high school.
I sat down on the little bench in the dressing room in total shock and almost burst into tears. Both in joy at this accomplishment and in sadness & frustration at myself, wondering how much sooner I could have reached this milestone if I had started this journey 10 years earlier.
I've been plus-size my entire life and (with the best of intentions of my mother & grandmother) have been on almost every fad diet since 5th grade. It wasn't until my mid 20s that I learned that both the weight gain and difficulty in losing weight were due to an underlying health reason - polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS.
[the rest of my story is under the cut because this post ended up way longer than I had anticipated]
TL;DR - I'm 35 and I've been working on my health this past year and while I'm so happy to celebrate my successes, I wish I had started this journey sooner. Please don't do what I did and ignore symptoms for years. And if you have a young girl in your life that has irregular periods, get her checked for PCOS. Because if I had been given that diagnosis & started treatment decades earlier (and no, being given birth control is NOT a treatment for PCOS - it's lazy medical treatment at best and malpractice at worst) I know my life would be different right now because the majority of my life has been dictated by my size.
I'd had irregular periods my entire life but for some reason, none of my childhood doctors or even my mother ever thought to check for it. I was checked for thyroid issues and vitamin deficiencies but for some reason, PCOS was never brought up (not that I would have known to ask about it as a child). But one day I was having a physical done by a new doctor (not my current doctor) and when I mentioned my irregular periods she started asking me more questions about them and after looking at the rest of my medical history decided to have me checked for PCOS. And low and behold I had it.
I can't tell you the relief I felt finding out there was an actual medical reason for why I had struggled with my weight my entire life. Because up until that moment I'd always been made to feel like it was all my fault that I was fat. If I just ate better or stuck to a strict diet or exercised more (I can't even begin to describe the embarrassment and humiliation of being forced to go to exercise classes with your mother when you're 12yr old and you're the only kid in a class full of adults). It was never ever directly said to me, but it was obvious in the way things were said and the way people acted around me.
The doctor also explained to me that I was pre-diabetic as PCOS can cause diabetes if left untreated (this will be important to remember in just a minute). So we started working on getting my hormones back on track and I was told to try to cut back on my sugar intake. Unfortunately not too long afterward, the job I had at the time decided to switch our health insurance provider. Suddenly my doctor was out of network and continuing to see her was becoming very expensive for me as I wasn't making a whole lot at the time (I was working at a childcare center). Add in the fact that she was on the opposite side of town from me and that it was almost impossible to get time off work for appointments, I just kind of stopped seeing her.
The next part of my story is where I wish I could go back in time and shake some sense into my younger self. Because did I try to find a new doctor that my insurance would pay for? Nope. Did I at least try to cut back on my sugar and eat a little better? Also, no. For the next almost ten years, despite knowing I had PCOS and knowing I was pre-diabetic, I didn't change my eating habits at all. Every once in a while I'd get on a "health" kick and go for walks at the park and try to eat more whole wheat bread than white bread, but those never lasted long. I wasn't in the best space mentally either so there was also a lot of emotional eating as well. I figured as long as I never had to go up another pant size I was doing all right just "maintaining". If I got sick and needed to see a doctor, I just went to one of those minute clinic things at Walgreens. Yeah, mid & late 20s me was an idiot.
Fast forward to a few years ago when it started being pretty obvious that I had crossed the line from pre-diabetic to actually diabetic. I had all the classic signs and symptoms yet I was still being an idiot and ignoring my health. Unfortunately, I've always had a horrible bad habit of thinking if I just ignore whatever issues or problems I'm currently having that they'll just go away. Yeah, I know. I finally get to the point where I know I can't ignore my health anymore and January of 2020 I make it my New Year's goal to start getting myself back on track. By the time I worked up the courage to call and set up an appointment with my old doctor (I had a new job by then with better insurance that included her again) two things happened: March of 2020 and the building her practice was in was destroyed in a fire.
So I told myself I'd just "wait until this whole covid thing was over" before trying to set up an appointment again. And we all know how the rest of 2020 went. Now it's December of 2021 and I still haven't made an appointment with my old doctor. But I was at an eye doctor appointment that I'd also been putting off for years despite knowing it was time for a new prescription. After checking my eyes, the eye doctor tells me that I need to see my doctor as soon as possible because he saw signs of diabetic retinopathy in my eyes. And as someone who's always had poor eyesight and one of their greatest fears is going blind, THAT was the kick in the pants I needed to finally see a doctor.
I ended up having a heart-to-heart with my mom about my health (something I would always avoid talking about with her) and admitting that I really didn't want to go back to my old doctor because I never really felt a good connection with her but I was willing to deal with that issue since she was also a practicing Catholic and it's hard to find not only a good doctor but a Catholic one as well (I know there are plenty of good doctors out there who aren't Catholic, but as a practicing Catholic, it does make things so much easier when your doctor also follows Church teachings when it comes to health & medical issues). My mom then suggested I set up an appointment with her new doctor who is not only a general MD, but also specialized in treating PCOS and also just happened to be Catholic as well.
So I set up an appointment with Dr. Holly for after the New Year and the rest, as they say, is history. She's just a few years older than me and I have never in my life been so at ease with a doctor. She and I hit it off right away and when I explained everything to her she didn't make me feel bad for waiting for so long to do anything like I was afraid she would. Instead, she listened to all of my concerns, validated them, and then right there came up with a plan of attack listing out all of the health issues we needed to tackle right away (getting the diabetes under control & start treating the PCOS) and what health issues weren't immediately pressing (some small patches of eczema & trying out meds for my ADHD again).
It also helps that she's diabetic as well so she knows exactly what I'm going through and have to deal with on a day to day basis. With her help and support (plus the advice from the dietician she recommend to me), I brought down my A1C from a staggering 12.7% to a much better 7.2% at my last appointment with her and, of course, have been slowly and steadily losing weight.
I decided early on that I wasn't going to obsess over the numbers on the scale, instead mostly tracking my progress by how my clothes are fitting. Since January I'm down not only two pant sizes but also a shirt size! I'm able to comfortably wear again all of the 2XL shirts I own and I've gone to a few events where I was able to buy a shirt as a souvenir because I didn't have to worry if they had a 3XL because I knew would be able to fit in a 2XL.
I still have a lot of work to do (I really do need to start actually exercising) but I am so happy with what progress I've made so far already. If you had told me last year that I'd be wearing a size 22 pair of jeans, I would have laughed in your face. I still can't believe it sometimes, but then I look at pictures of myself from last year compared to this year and the differences are kind of shocking. And that's been another little victory for me - actually not hating how I look in photos. I've taken more photos of myself/allowed myself to be in more photos this year than in at least the last five years if not more.
I never know how to end posts like this, so if you've actually read this far down, thanks. 💙
#personal#about me#this really got away from me#but it ended up being kind of cathartic to write it all out#health journey
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Healing Childhood Trauma
Many people face unfortunate, scarring events in their childhood. Most often, the consequences of these can lead to prolonged childhood trauma, which people are left to deal with during their adulthood. If left unaddressed, childhood trauma can have long-term ill effects on the quality of someone's life.
What is Childhood Trauma?
Childhood trauma can be explained as an emotionally painful or distressing event resulting in physical, mental, and emotional consequences. The traumatic experience can range from losing a parent suddenly to physical abuse or a natural disaster. It can even be something as seemingly innocuous as overhearing a conversation with triggering content.
Learning to understand and cope with difficulties, trauma, and tragedies is a natural part of growing up. But in more serious cases, a lack of exposure to proper mental healthcare can result in childhood trauma in adults.
Effects of Childhood Trauma on the Psyche
Childhood trauma can affect neurological development, hormonal regulation, and cognitive and emotional competencies. It also increases impulsive and risky behaviour, such as substance abuse. This claim is substantiated by a 2021 study by Auckland Univerisity on the themes of child abuse and neglect.
What can Cause Childhood Trauma?
Neglect
Familial issues such as divorce
Death of someone close to them
Psychological, physical, emotional, and sexual abuse
Natural disasters
Substance abuse
Community or school violence
Life-threatening illness

Trauma Signs in Children
In preschool and elementary age, childhood trauma symptoms include separation anxiety, difficulty sleeping, frequent nightmares, feelings of anxiety, crying for no reason, decreased appetite, moodiness, and increased aggression.
In teens, the signs of childhood trauma are irritability, academic problems, sudden withdrawal from social activities, self-blame, difficulty concentrating, feelings of depression, and increased behaviors like sexual activity and alcohol and substance abuse.
What Happens if Trauma Remains Unresolved?
Effects of childhood trauma and early childhood trauma are distorted self-perception, feelings of shame and guilt, chronic physical pain, and anxiety.
Repressed childhood trauma can also cause depression, panic attacks, fatigue, impulsiveness, insomnia, self-harm, eating disorders, and suicidal ideation. Childhood trauma in adults also increases the risk of mental health disorders. Depressive, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive bipolar, and substance use are some disorders caused by childhood trauma.
Adults with childhood trauma are more common than you imagine. ‘Childhood trauma therapist near me' is among the more common internet searches. In 2020, the World Health Organization estimated that globally, around 1 billion children aged between 2–17 years have experienced physical, sexual, or emotional violence or neglect.
Therapy for childhood trauma is needed to prevent problems in adulthood.
Effect of Childhood Trauma on Health
There are several childhood trauma signs in adults. Toxic stressors in childhood can take a lifelong toll and can manifest in adulthood. So, when adults show signs of trauma, it can be a result of the trauma they experienced in childhood.
Studies have found that the chances of getting a heart disease increased in adults who had experienced abuse, witnessed interpersonal violence, or lived in a household where there was substance abuse. The odds of asthma and diabetes also rose for adults who experienced childhood trauma, such as mental illness, substance abuse, and divorce.
The study found that those who experienced even one type of childhood trauma, such as a family member in jail, were associated with an increased risk of poor mental health. Since types of childhood trauma often involve a trusted loved one, a caregiver, or even a family member, in adulthood, this can lead to trust issues and deeply rooted feelings of insecurity.
Here are some of the signs of childhood trauma that adults might exhibit:
Adults who experience childhood trauma are more prone to depression, mood disorders, and suicidal thoughts.
They are also likely to engage in substance abuse.
Adults affected by childhood trauma may exhibit unexplained and irrational anger or irritability.
Adults with childhood trauma could find maintaining old or establishing new, healthy relationships challenging.
How to Heal Childhood Trauma
Several forms of therapy can help heal childhood trauma, some of which are:
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT): CPT aims to help a person change how they think about the event(s) that led to the trauma, thereby relieving the adverse effects.
Prolonged exposure therapy (PE): This involves confronting the source of fear to reduce anxiety and support healing from childhood trauma.
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT): Therapists use CBT to help people identify and correct unhealthy behaviour patterns and develop new ways to cope in case of mental illness caused by childhood trauma.
Hypnotherapy: This is a popular alternative childhood trauma therapy for adults, especially those who have struggled with other therapy types. Here, the therapist works to help reduce the emotion attached to the event by working with the subconscious mind.
While there are several coping mechanisms to deal with childhood trauma, the key is to try different methods and find one that works for you. Since healing is a long process, the sooner you identify the method that suits you best, the better.
Summing up
Recovering from childhood trauma is a long and gradual process. Along the healing journey, chances are that you will experience helplessness and isolation. However, the first step in healing from childhood trauma is to acknowledge the trauma. Do not try to push your feelings under the carpet or minimize them. Acknowledge your emotions, and you are ready for the next step to reclaiming control - seeking support.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Where can I get tested for diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce or effectively use insulin, a hormone essential for glucose regulation. There are several types of diabetes, with Type 1 and Type 2 being the most common. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas fails to produce insulin, often diagnosed in childhood, while Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for the majority of cases, typically develops in adults and is often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. Symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Globally, diabetes affects approximately 537 million adults, a number projected to rise significantly in the coming years, highlighting the need for effective management strategies, including lifestyle modifications and medication.

Conducting timely tests for diabetes is crucial for several reasons, primarily related to early diagnosis, management, and prevention of complications.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Asymptomatic Nature of Diabetes: Many individuals with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, may not exhibit noticeable symptoms initially. This lack of symptoms can lead to undiagnosed diabetes, which increases the risk of severe health complications over time, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
2. Timely Intervention: Regular testing allows for the early detection of prediabetes or diabetes. Early diagnosis enables healthcare providers to recommend lifestyle changes or medications that can prevent the progression of the disease. For instance, identifying elevated blood sugar levels early can lead to interventions that may reverse prediabetes and prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes[2][4].
Monitoring and Management
1. Regular Monitoring: For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, ongoing monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. This helps in assessing how well the current treatment plan is working and allows for timely adjustments to medications, dietary changes, or physical activity levels. Regular blood sugar checks can prevent both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), which can have immediate health risks.
2. Understanding Long-term Trends: Tests like the HbA1c provide insights into average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This long-term perspective is vital for evaluating the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies and making necessary adjustments.
Prevention of Complications
1. Reducing Long-term Risks: Timely testing and management of diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels. These complications can include cardiovascular diseases, retinopathy (eye damage), neuropathy (nerve damage), and nephropathy (kidney damage).
2. Informed Decision-Making: Regular testing provides individuals with critical information about their health status, empowering them to make informed decisions regarding their lifestyle and treatment options. This proactive approach can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Tests for diabetes
Before we delve into testing locations, let's briefly understand the common diabetes tests:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Involves drinking a sugary liquid and measuring blood sugar levels over time.
A1C Test: Reflects average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Places to Get Tested for Diabetes
Primary Care Physician:
Your primary care physician is often the first point of contact for diabetes screening.
They can assess your risk factors, order appropriate tests, and provide guidance on diabetes management.
Clinics and Health Centers:
Many communities offer clinics and health centres that provide diabetes screening and testing services.
These facilities are often more affordable and accessible than private practices.
Hospitals:
Hospitals have dedicated diabetes clinics and laboratories for comprehensive testing and evaluation.
They are equipped to handle complex cases and provide specialised care.
Diagnostic Laboratories:
These labs offer a wide range of diabetes tests and can provide quick results.
You may need a referral from your doctor to get tested at a diagnostic laboratory.
Pharmacies:
Some pharmacies offer over-the-counter diabetes screening tests.
These tests are convenient but may not provide a complete picture of your diabetes status. It's essential to follow up with a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Community Health Fairs and Events:
Many community health fairs and events offer free or low-cost diabetes screenings.
This is a great opportunity to learn about diabetes prevention and management while getting tested.

New Scientific Breakthrough Offers Hope For Better Diabetes Control
Online Resources and At-Home Tests:
Several online platforms and retailers offer at-home diabetes testing kits.
While convenient, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider to interpret results and discuss next steps.
0 notes
Text
Best Sugar Specialist Doctor Near Me | 8010931122

It is important to understand the causes, types, long-term effects of diabetes to control a disease like diabetes. If you are looking for the Best Doctor for Diabetes in Delhi who can give you relief from such a disease, Dr. Monga Clinic for Diabetics offers expert care and guidance.
What Causes Diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when the body cannot effectively regulate blood sugar levels. This condition can be due to various factors:
Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
Lifestyle: Unhealthy eating habits, lack of exercise, and obesity are significant contributors.
Autoimmune Reactions: In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Insulin Resistance: In Type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to insulin, causing elevated blood sugar levels.
Types of Diabetes You Should Understand
Understanding the different types of diabetes is essential for proper management:
Type 1 Diabetes: Often diagnosed in childhood, this type is an autoimmune condition where the body does not produce insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common type, usually developing in adulthood. It occurs when the body does not use insulin properly.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and can increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Prediabetes: A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. It indicates a high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Long-Term Effects of Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications:
Cardiovascular Disease: Increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and hypertension.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Can cause pain, tingling, or loss of sensation in the limbs.
Kidney Damage (Nephropathy): High blood sugar can damage the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease.
Eye Damage (Retinopathy): May cause vision problems or blindness.
Foot Complications: Poor circulation and nerve damage increase the risk of foot infections and ulcers, potentially leading to amputations.
Signs You Should Not Ignore That Can Lead You to Diabetes
Recognizing early signs of diabetes can prevent complications:
Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels cause excess sugar to be filtered out by the kidneys, increasing urination.
Excessive Thirst: Frequent urination can lead to dehydration, causing persistent thirst.
Extreme Fatigue: The body's inability to use sugar efficiently for energy can cause tiredness.
Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can pull fluid from your eye lenses, affecting your vision.
Slow Healing Wounds: High glucose levels can impair blood circulation and slow down the healing process.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. At Dr. Monga Clinic, we provide comprehensive diabetes care to help you manage your condition optimally. Our team is considered the Best Doctors for Diabetes in Delhi, providing personalized treatment tailored to your needs.
If you need expert advice or treatment for diabetes, visit Dr. Monga Clinic today and consult the Best Sugar Specialist Doctor Near Me.
Original Source
1 note
·
View note
Text
In a 2020 survey from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 47.1 million American adults (19.1%) reported current use of a tobacco product. Current smoking of cigarettes declined from 20.9% of adults in 2005 to 12.5% in 2020. E-cigarettes were used by 3.7% of American adults in 2020, cigars by 3.5%, smokeless tobacco by 2.3%, and pipes by 1.1%. Two or more types of tobacco products were used by 17.3% of American adults. Current commercial tobacco use was more common in the following subgroups5:
Men
Adults aged <65 years
Non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native adults and non-Hispanic adults categorized as of “other” or multiple races
Adults in rural (nonmetropolitan) areas
Those whose highest level of educational attainment was a general educational development certificate (GED)
Those with an annual household income of less than $35,000
Lesbian, gay, or bisexual adults
Uninsured adults or those with Medicaid
Adults living with a disability
Those who regularly had feelings of anxiety or depression
PHARMACOLOGIC EFFECTS OF NICOTINE AND BEHAVIORAL PATTERNS IN NICOTINE USE
Nicotine is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream through traditional cigarettes, e-cigarettes, snuffs, and other tobacco and nicotine products. It immediately stimulates the adrenal glands to secrete adrenalin (epinephrine). Epinephrine increases blood pressure and heart and respiratory rates. It also stimulates the release of the pleasure hormone dopamine and activates pleasure centers in the central nervous system.11
People develop habits in their daily routines centered around nicotine use and enjoy the hand-mouth stimulation that accompanies smoking. Social connections are made with other users, and the risk of additional substance use disorders increases. Once addicted to nicotine, attempts at cessation quickly produce various withdrawal symptoms that contribute to generally low cessation rates and high relapse rates among those able to quit. When cessation is successful, the fact that the person’s friends and/or work companions smoke can contribute to relapse.11
The adverse effects of nicotine as an individual drug are difficult to sort out from multiple effects on the body of nicotine-delivery systems (e.g., smoke and heated vapors). Rapidly released nicotine stresses the heart and cardiovascular system and sets the user up for addiction to other substances by priming the pleasure and reward pathways. The risk increases for major adverse cardiovascular events such as stroke and myocardial infarction.11 In contrast, nicotine-replacement systems such as gums and transdermal products release nicotine more slowly and have lower risks for producing chest pain and palpitations.12
The adverse consequences of tobacco smoking are well documented: lung and other cancers, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, heart disease (myocardial infarction, heart failure, and stroke), leukemia, cataracts, type 2 diabetes, and pneumonia. Exposure to secondhand smoke carries many of these risks, including increased cardiovascular and cancer risks, and evidence shows that secondhand exposure to vapors carries some of these risks. Smoking by pregnant persons is associated with increased risk for miscarriage, stillbirth, fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, placental abruption, and complications in the offspring, including sudden infant death syndrome and impaired lung function in childhood.11,13-16
The good news for smokers, former smokers, and those around them is that the risk of these events occurring can be minimized over time following cessation and continued abstinence. As many as 10 years can be added to a smoker’s life when they stop. The American Cancer Society has a graphic that explains to smokers the following timeline for benefits from cessation11,13,14:
Within 20 minutes, your heart rate and blood pressure drop.
A few days after quitting, the carbon monoxide in your blood drops to normal.
At 2 weeks to 3 months after quitting, your circulation improves and your lung function increases.
At 1 to 12 months after quitting, coughing and shortness of breath decrease as cilia regain their normal functions of moving mucus out of the lungs and the risk of infection is lowered.
At 1 to 2 years after quitting, your risk of heart attack drops dramatically.
At 5 to 10 years after quitting, your risk of cancers of the mouth, throat, and voice box (larynx) is cut in half and your stroke risk decreases.
At 10 years after quitting, your risk of lung cancer is about half that of a person who is still smoking, and your risk of cancer of the bladder, esophagus, and kidney decreases.
At 15 years after quitting, your risk of coronary heart disease is close to that of a nonsmoker.
BEHAVIORAL INTERVENTIONS IN NICOTINE CESSATION
Behavioral interventions are important in smoking and nicotine cessation. These increase the effectiveness of prescription and nonprescription medication options, minimize relapses through changes in habits and lifestyle, and provide a nondrug option for monotherapy in people who are pregnant. An important point to remember is that health professionals — including pharmacists and pharmacy technicians — should make strong recommendations to patients about control of their dependence on nicotine. While some acronyms such as “assist” or “refer” may sound passive, health professionals should be proactive in their assistance and direct in their advice to seek help.
Before making a behavioral intervention, health professionals must first identify those in need and assess their readiness for change. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPTSF) recommends that clinicians ask all pregnant persons about tobacco use, advise them to stop, and provide behavioral interventions for cessation. For nonpregnant adults, clinicians should ask about tobacco use and provide behavioral and pharmacotherapy to help in stopping use of those using tobacco products (see Figure 2).15
To determine a user’s readiness for cessation, the CDC’s 5 A’s are useful for pharmacy personnel and other clinicians:
Ask about smoking, vaping, and the use of other nicotine products
Advise the person to quit through clear individualized messages
Assess the patient’s willingness to quit
Assist in quitting
Arrange follow-up and support
“Ask, Advise, Refer” is another approach for identifying, counseling, and helping patients obtain the medications and behavioral interventions needed to achieve cessation. The American Lung Association has adapted this approach in its Ask, Advise, Refer to Quit Don’t Switch training program. It offers a free, online, 1-hour course that covers behavioral changes, interventions, and treatments.
Because tobacco product use often starts before adulthood, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) states the problem directly: “Tobacco use is a pediatric disease.” Prevention is critical to avoid the challenges of a lifelong battle to control nicotine addiction. Counseling patients in middle childhood and adolescence about the dangers of smoking and the addictive properties of nicotine is very important, AAP says. Since tobacco use is more common among children whose parents smoke — and those kids are exposed to secondhand smoke — AAP has established the INSPIRE program to help parents of hospitalized children reduce tobacco smoke exposure. An acronym for “Interventions to Help Smoking Parents of Inpatients Reduce Exposure,” INSPIRE uses in-hospital motivational interviewing sessions with trained tobacco coaches to develop personalized plans to control nicotine dependence. Nicotine replacement products are provided to caregivers before the child is discharged, and the tobacco coach follows up after the family returns home to conduct brief motivational interviewing sessions.
In a 2021 evidence report and systematic review, the USPSTF reported that behavioral interventions significantly but modestly increase cessation rates at 6 months. In-person advice and support from clinicians; individual-, group-, telephone-, and mobile phone–based support; interactive and tailored internet-based interventions; and the use of financial or other incentives are among the many effective behavioral options available for people looking to control their nicotine dependence. Their use has increased relative cessation rates by 15% to 88% in studies. Other interventions have not been shown effective but are also not as well studied. These include motivational interviewing, decision aids, print-based, nontailored self-help materials, real-time video counseling, biofeedback (feedback on smoking exposure, smoking-related disease, or smoking-related harms), exercise, acupuncture, hypnotherapy, and system change interventions. None of the behavioral interventions has produced serious adverse events in clinical trials. In addition, behavioral interventions are preferred in adults who are pregnant (given the unknown effects of medications on the developing offspring) and in children and adolescents (for whom no drug products have been approved by FDA or shown to be safe during the final stages of brain development).15 (Patnode et al., 2021)
Despite limited evidence on its effectiveness for controlling nicotine dependence, motivational interviewing is a tool that pharmacists know well and can apply in the pharmacy setting. By asking patient-focused questions, listening attentively, and remaining nonconfrontational, pharmacists and pharmacy technicians trained in this technique can identify and point out discrepancies between the patient’s goals and their current behaviors.17 (Lindson-Hawley et al., 2015)
NIDA's website suggests adjusting patients’ resistance to change and supporting self-efficacy and optimism. NIDA also suggests cognitive behavioral therapy for helping patients identify triggers for tobacco product use and teaching them relapse-prevention skills. CBT can be an important adjunct to pharmacotherapy in cessation programs by partnering with counselors trained in this technique.
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC TOOLS IN NICOTINE CESSATION
People with uncontrolled compulsions in their use of tobacco and nicotine products frequently visit pharmacies for help with quitting. For them, pharmacotherapeutic options include oral medications and various nicotine-replacement products. These can be thought of along the lines of treatments for asthma or diabetes: controllers that provide sustained basal actions and relievers that address acute cravings for nicotine.
All drug therapies work best when combined with behavioral interventions. As described above, these can begin with counseling, strong recommendations, and motivational interviews by pharmacy personnel who can provide appropriate services and refer patients for other types of interventions by the treatment team. Some pharmacies have established smoking cessation programs that include services of other health professionals as needed for behavioral interventions. Patients hospitalized for related conditions such as myocardial infarction and lung cancer are often motivated to quit, which allows health-system pharmacists to become involved in cessation efforts.
Mounting evidence shows that cessation efforts are more successful when a multipronged intervention is used, including behavioral plus drug therapy or using 1 or more drug products (oral medications plus NRT). When patients are not participating in individual or group counseling sessions or other types of behavioral support for nicotine cessation, brief interventions by the pharmacist can be effective in increasing quit rates.18,19
The question of which of these pharmacotherapeutic interventions to try first depends on whether the patient is an adult, whether the person is pregnant, what behavioral services are available and affordable to the patient, cost considerations for the medication, and if needed, medical visits for prescriptions, and what products the patient prefers based on the information and recommendation gathered by the pharmacy team or provided by other health professionals. The American Thoracic Society recommends varenicline as the drug of choice for beginning pharmacologic therapy. Still, it emphasizes that combination therapy is needed to achieve a baseline control of urges (“controllers” that provide sustained basal actions) as well as products that can help patients during periods of craving or withdrawal symptoms (“relievers” for acute challenges). With behavioral interventions, monotherapy or combination therapy with FDA-approved agents gives the patient their best chance of controlling their nicotine dependence.1,20,21
Nicotine does not affect the hepatic metabolism of other drugs, but tobacco smoke induces certain isoenzymes, increasing their rate of metabolism. When the patient stops smoking, doses of drugs metabolized by CYP1A2, CYP2E1, and some uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyl-transferases may need to be reduced.
0 notes
Text
Diabetes Treatment: A Simple Guide
Diabetes is a common health problem that affects many people around the world. It happens when your blood sugar levels are too high. If not managed properly, diabetes can lead to serious health issues. But don’t worry, with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, diabetes can be managed effectively.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where the body either does not make enough insulin or cannot use the insulin it produces effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps move sugar from the blood into the cells to be used for energy. When there is not enough insulin, sugar stays in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Types of Diabetes
There are mainly two types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: This type is when the body does not produce insulin at all. It usually starts in childhood or young adulthood.
Type 2 Diabetes: This type is more common and usually happens in adults. In this type, the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it properly.
There is also another condition called gestational diabetes, which can occur during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
Some common symptoms of diabetes include:
Frequent urination
Feeling very thirsty
Feeling very hungry even after eating
Extreme tiredness
Blurry vision
Cuts and bruises that heal slowly
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Treatment for Diabetes
The good news is that diabetes can be managed with the right treatment. The main goals of diabetes treatment are to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range, prevent complications, and improve overall health.
1. Medications
For type 1 diabetes, insulin injections are necessary because the body cannot produce insulin. People with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed oral medications or insulin injections to help control blood sugar levels.
It’s important to take your medications as prescribed by your doctor. Never skip doses, as this can lead to high blood sugar levels.
2. Healthy Eating
A healthy diet is key to managing diabetes. Focus on eating a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It’s also important to control portion sizes and avoid foods that are high in sugar and unhealthy fats.
Some tips for healthy eating include:
Eating smaller portions more often throughout the day
Choosing whole grains instead of refined grains
Including more fruits and vegetables in your meals
Limiting sugary drinks and snacks
A dietitian can help you create a meal plan that works for you.
3. Regular Exercise
Exercise is another important part of diabetes treatment. It helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Exercise can also help with weight management, which is important for people with type 2 diabetes. Being at a healthy weight can improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
4. Regular Monitoring
Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly is a key part of diabetes treatment. This helps you understand how well your treatment plan is working and if any adjustments are needed.
You can monitor your blood sugar levels at home using a blood glucose meter. Your doctor will tell you how often to check your levels and what your target range should be.
5. Stress Management
Stress can affect your blood sugar levels, so it’s important to find ways to manage it. Activities such as deep breathing, yoga, meditation, or simply taking a walk can help reduce stress.
Complications of Diabetes
If not managed properly, diabetes can lead to complications such as:
Heart disease
Kidney disease
Eye problems
Nerve damage
The good news is that with proper diabetes treatment and lifestyle changes, these complications can often be prevented.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes may seem challenging, but with the right diabetes treatment plan and support, you can live a healthy life. Remember to take your medications as prescribed, eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, monitor your blood sugar levels, and find ways to manage stress.
If you have any concerns or questions about your diabetes treatment, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor. They can provide you with the guidance and support you need to manage your condition effectively.
0 notes
Text
Long COVID is a "public health crisis for kids," experts say - Published Aug 26, 2024
For years, public health experts have said that COVID-19 infections in children are “mild.” According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most common symptoms of COVID in kids are a fever and cough. While some children with the coronavirus are admitted to the ICU and there are pediatric deaths, studies have found that underlying medical conditions including obesity, diabetes, cardiac and lung disorders, increase the risk of severe outcomes.
This research has contributed to how COVID is managed in schools. However, a new study in the Journal of the American Medical Association sheds light on the effect a coronavirus infection can have on children over a longer period. While many people recover quickly from COVID, some don't, experiencing symptoms that can last for months or years. This condition, known as long COVID, not only affects adults but also children. The new research helps us understand the extent kids experience these debilitating conditions — and how we can treat it.
“This is one of the first large-scale national studies to do research related to long COVID across the entire lifespan, with a particular focus on children and understanding the differences in long COVID in different aged children,” Dr. Rachel Gross, an associate professor in the Departments of Pediatrics and Population Health at NYU Langone and the study's principal investigator, told Salon.
In the study, led by the National Institutes of Health’s RECOVER Initiative, researchers asked caregivers to tell them about the symptoms that their children or teenagers had been experiencing more than four weeks after a coronavirus infection. For some children in the study, that meant symptoms their symptoms went on for three months after their COVID infection. For others, it was up to two years. Researchers looked at the symptoms in those children with persisting symptoms and compared them to children who had never been infected with the coronavirus in the past. They then identified similarities in the prolonged symptoms and found they were distinguishable based on age.
“In school-aged children, we heard commonly that children were experiencing trouble with their memory, focusing, headaches, having trouble sleeping, and stomach pain,” Gross told Salon. “And in the teenagers, we were hearing about symptoms related to fatigue and pain, having body or muscle or joint pain, being very tired or sleepy, having low energy, as well as having trouble with memory and focusing.”
A unique symptom the researchers saw in the teenage group was changes in or a loss of smell or taste. Additionally, researchers found clusters of symptoms that are unique to school-aged children and teenagers. The first were symptoms that affect every organ system in the body.
“These are the children with the highest burden of symptoms,” Gross said, adding that caregivers described these children as having a “lower quality of life and more impact on their overall health.” “The second type of long COVID we also saw across both the ages was predominantly characterized by fatigue and pain.”
Studies estimating its prevalence in pediatric populations are limited and conflicting, estimating up to 25% of children infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus could go on to develop long COVID. A study published in 2024 estimated that up to 5.8 million young people have long COVID.
“This is a public health crisis for children,” Gross said. “We know that child health is so critically important for how children grow and even as they become adults, that chronic illness during childhood and adverse experiences during childhood greatly affects the adults that they can become.”
Gross said the U.S. will see the “long-term impacts of experiencing long covid In childhood for decades to come.”
Dr. Dean Blumberg, chief of pediatric infectious diseases and associate professor in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of California, Davis, told Salon he agreed long COVID is a “public health crisis” for children.
“Some of these kids with long COVID, they are severely affected, they can't do their normal activities, they fall behind school, they can't go to school,” Blumberg said. “And then in this study, they highlighted a lot have had some neurocognitive effects, and that really interferes with with learning.”
For Blumberg, the takeaway from this study, he told Salon, is a “call to arms to increase vaccination rates,” which among children, he said are “abysmal.”
According to a recent KFF survey, while both flu and COVID vaccines are recommended for school-aged children, flu vaccination rates were over three times higher than COVID vaccination rates. While COVID-19 vaccines are recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in the pediatric immunization schedule, they aren’t required for school attendance. According to one study published in the journal Pediatrics, vaccination the risk of an acute infection, but it is less clear whether it protects against long COVID. The latest COVID vaccines were approved by the Food and Drug Administration last week, which the CDC recommends for any six months or older.
Now, researchers will be tasked with figuring out why long COVID affects children differently based on their age. When it comes to adults, some studies have shown that subsequent COVID infections increase a person’s risk of getting long COVID. The CDC estimates that one in 13 adults in the United States currently have long COVID symptoms.
Gross told Salon she hopes this research raises awareness for both healthcare providers, as well as schools and educators, that “long COVID in children is not rare.”
“That they are likely to have children experiencing these prolonged symptoms within their healthcare systems and their schools,” Gross said. “And that many of the symptoms that I've described, trouble with memory and focusing, headache, trouble sleeping, these are symptoms that you know can impact a child and their schooling.”
Study: jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2822770
#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#coronavirus#sars cov 2#public health#still coviding#wear a respirator#long covid
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Difference Between Mature and Immature Cataract
Cataracts are a common eye condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly as they age. They occur when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to impaired vision. This blog will explore the differences between mature and immature cataracts, the types of cataracts, early signs and symptoms, causes, risks, and the importance of timely treatment.
Types of Cataracts
Cataracts can be classified into several types based on their location and development:
Nuclear Cataracts: Form in the center of the lens and are most commonly associated with aging.
Cortical Cataracts: Develop in the lens cortex, the outer edge of the lens, and appear as white, wedge-like opacities.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts: Form at the back of the lens and can develop more quickly than other types.
Congenital Cataracts: Present at birth or develop during childhood, often due to genetic factors or intrauterine infections.
Secondary Cataracts: Develop as a result of other medical conditions, such as diabetes, or due to medication use, particularly steroids.
Traumatic Cataracts: Result from an eye injury and can appear years after the trauma.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Cataracts develop gradually, and early signs and symptoms may include:
Blurred or cloudy vision
Difficulty seeing at night
Sensitivity to light and glare
Seeing halos around lights
Fading or yellowing of colors
Double vision in one eye
Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
What Is an Immature Cataract?
An immature cataract is an early stage of cataract development where the lens is only partially opaque. Vision impairment is present but not severe, and the lens retains some clarity.
Characteristics of Immature Cataracts:
Partial cloudiness in the lens
Moderate vision impairment
Symptoms like glare, halos, and slight blurriness
What Is a Mature Cataract?
A mature cataract is an advanced stage of cataract development where the entire lens becomes opaque. This significantly impairs vision, and the lens appears white or yellow.
Characteristics of Mature Cataracts:
Complete cloudiness of the lens
Severe vision impairment, potentially leading to blindness
Lens appears white or fully opaque
Differences Between Mature and Immature Cataracts
1. Degree of Opacity:
Immature Cataracts: Partial opacity; the lens is only partially clouded.
Mature Cataracts: Complete opacity; the entire lens is clouded.
2. Vision Impairment:
Immature Cataracts: Moderate vision impairment; patients may still have functional vision with aids.
Mature Cataracts: Severe vision impairment; vision may be significantly reduced or lost.
3. Appearance:
Immature Cataracts: The lens may appear slightly cloudy.
Mature Cataracts: The lens is visibly white or yellow and fully opaque.
4. Progression:
Immature Cataracts: Early stage; vision can still be managed with glasses or contact lenses.
Mature Cataracts: Advanced stage; surgical intervention is often necessary for vision restoration.
Differences Between Immature and Mature Cataract – Preventions
While cataracts cannot always be prevented, certain measures can help delay their progression:
For Immature Cataracts:
Regular Eye Exams: Early detection can help manage symptoms effectively.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a diet rich in antioxidants, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can slow cataract development.
UV Protection: Wearing sunglasses that block UV rays can protect the eyes from sun damage.
For Mature Cataracts:
Timely Medical Consultation: Regular check-ups can monitor the progression and determine the right time for surgery.
Managing Health Conditions: Controlling diabetes and other health conditions can prevent the rapid progression of cataracts.
Medication Review: Avoiding or carefully managing medications known to increase cataract risk, such as steroids.
Causes
Cataracts can develop due to various factors, including:
Aging: The most common cause, as the proteins in the lens break down over time.
Genetics: A family history of cataracts can increase risk.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can lead to cataract formation.
Exposure to UV Rays: Prolonged exposure to sunlight without protection.
Smoking and Alcohol Use: Both are linked to a higher risk of cataracts.
Eye Injuries: Trauma to the eye can result in cataracts.
Medications: Long-term use of steroids and certain other medications.
Risks
Leaving cataracts untreated can lead to several complications:
Severe Vision Loss: Untreated cataracts can progress to the point of causing blindness.
Increased Fall Risk: Poor vision can lead to falls and injuries, particularly in older adults.
Complications in Daily Activities: Difficulty in performing routine tasks like reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
Eye Inflammation: Advanced cataracts can sometimes cause inflammation and increase the risk of glaucoma.
Importance of Timely Treatment
Timely treatment of cataracts is crucial for maintaining quality of life and preventing severe vision impairment. Early detection and monitoring can help manage symptoms and delay progression. When cataracts significantly impact vision, cataract surgery is highly effective. The procedure involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL), restoring clear vision.
Benefits of Timely Treatment:
Restored Vision: Cataract surgery can dramatically improve vision and reduce dependency on glasses.
Enhanced Quality of Life: Improved vision enables better performance of daily activities and increases independence.
Prevention of Complications: Early treatment prevents severe vision loss and associated risks.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between mature and immature cataracts is essential for effective management and treatment. While immature cataracts cause moderate vision impairment and can be managed with lifestyle changes and corrective lenses, mature cataracts lead to severe vision loss and require surgical intervention. Regular eye exams, a healthy lifestyle, and timely medical consultation are key to preventing and managing cataracts. If you notice any symptoms of cataracts, consult an eye care professional to determine the best course of action and ensure your vision health is preserved
Best eye hospital in Gurgaon
Eye hospital near me
Best eye Centre in Gurgaon
>> >>
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Reversing Diabetes: Diet, Lifestyle, and Beyond
Diabetes, a pressing health concern in India, affects millions with its two main types: type 1 and type 2. While type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, type 2 diabetes, often linked to lifestyle factors, presents an opportunity for individuals to potentially reverse its course through diet and lifestyle changes. This guide aims to shed light on effective strategies for managing and possibly reversing type 2 diabetes, offering hope and actionable steps for those affected. As we navigate the path to better health, remember, support systems like healthcare communities and resources are pivotal in managing this chronic condition effectively. Let's begin this journey towards a healthier life with informed choices and a proactive approach to diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes
In India, where the tapestry of life is rich and diverse, diabetes has woven itself into the fabric of the nation's health concerns. Understanding the nuances of type 1 and type 2 diabetes is the first step towards effective management and potential reversal of this chronic condition.
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body fails to produce insulin due to the immune system attacking pancreatic cells. It's often diagnosed in childhood and requires lifelong insulin therapy. Symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss.
Type 2 Diabetes: More prevalent in the Indian demographic, this condition is largely influenced by lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. It develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin. Symptoms overlap with type 1 but also include fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for diabetic patients to manage their condition effectively. Regular checks help in understanding how well diet, medication, and lifestyle adjustments are working to control blood sugar levels.
The distinction between these types of diabetes underscores the importance of tailored approaches to management. For those with type 2 diabetes, lifestyle modifications hold the key to potentially reversing the condition, offering a glimmer of hope for many.
In the bustling life of India, where traditional diets and modern conveniences often clash, adopting a diet for sugar diabetes patients becomes a cornerstone of diabetes management. Emphasising whole grains, fresh fruits, and vegetables over processed foods can make a significant difference in blood sugar control.
As we delve deeper into dietary and lifestyle strategies in the following sections, remember that each step taken is a stride towards better health. The journey of managing diabetes is a personal one, yet it's supported by a community ready to guide and assist at every turn.
Dietary Strategies for Managing Diabetes
In the heart of India, where culinary traditions are as diverse as its people, managing diabetes through diet becomes both a challenge and an opportunity. A diet for sugar diabetes patients doesn't mean forsaking flavour for health; rather, it's about making informed choices that embrace the richness of Indian cuisine while keeping blood sugar levels in check.
Incorporating Whole Grains: Swap refined grains with whole grains like brown rice, millets (ragi, jowar, bajra), and whole wheat. These are not only integral to the Indian diet but also help in managing blood sugar levels due to their high fibre content.
Fruits and Vegetables: Emphasise a variety of vegetables, especially leafy greens, and low-glycaemic fruits such as guava, papaya, and berries. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fibres, supporting overall health and diabetes management.
Lean Proteins: Include lean sources of protein such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, which are staples in Indian cuisine. For non-vegetarians, options like chicken, fish, and egg whites offer high-quality protein without the excess fat.
Healthy Fats: Opt for heart-healthy fats found in nuts, seeds, and oils like olive and mustard. Traditional Indian diets, rich in these nutrients, can be adapted to fit a diabetes-friendly profile without losing their essence.
Limit Sugary Sweets and Beverages: Indian sweets and sugary drinks should be consumed in moderation. Opting for natural sweeteners like stevia or enjoying fruit-based desserts can satisfy sweet cravings healthily.
Portion Control: Given the communal nature of Indian dining, practising portion control is essential. Using smaller plates and bowls can help manage portions without feeling deprived.
Adapting the traditional Indian diet to meet the needs of diabetes management doesn't require drastic changes but mindful modifications. By incorporating these dietary strategies, individuals with diabetes can enjoy the diverse flavours of Indian cuisine while maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Embrace a Healthier Tomorrow
Managing diabetes, particularly type 2, is a journey that extends beyond medication to include significant lifestyle and dietary adjustments. In India, where the diversity of food and culture presents unique challenges and opportunities, adopting a holistic approach to diabetes management is crucial. This involves adhering to a nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking support when needed. While individual efforts form the backbone of diabetes management, the journey doesn't have to be solitary. Engaging with healthcare professionals and leveraging digital health platforms can provide personalized care plans, dietary advice, and continuous monitoring, making the management process more effective and less daunting.
If you're navigating the complexities of diabetes, consider reaching out for support. Digital health platforms offer a range of services designed to assist in chronic condition management, from providing educational resources to facilitating direct communication with healthcare providers. These tools can empower you to make informed decisions about your health, track your progress, and adjust your management plan as needed. Take the first step towards a healthier lifestyle today. Embrace the changes, seek support, and remember, managing diabetes effectively can lead to a happier, healthier life.
#reverse diabetes#how to reverse diabetes#diet for sugar diabetes patients#blood sugar level for diabetic
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Diabetes: Types and Symptoms With Dr. Sanchayan Roy
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of Diabetes in the blood. It occurs when the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels and allows glucose to enter cells to be used as energy. If you are looking a Sugar Specialist Doctor Near Me so you want to contact with Dr. Sanchayan Roy.

Who is Dr. Sanchayan Roy?
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but having the right healthcare professional by your side can make all the difference. In Delhi, Dr. Sanchayan Roy stands out as one of the best Diabetes Specialist, offering expert care and personalized treatment plans to his patients. Here's why Dr. Sanchayan Roy is the top choice for individuals seeking diabetes management in Delhi.
Expertise and Experience
Dr. Sanchayan Roy is a highly experienced Sugar Specialist Doctor with years of experience in treating patients with various forms of diabetes. He holds degrees from prestigious medical institutions and has undergone extensive training in endocrinology, specializing in diabetes management.
Comprehensive Care
Dr. Sanchayan Roy provides comprehensive care for individuals with diabetes, addressing not only their medical needs but also their emotional and lifestyle concerns. He takes a holistic approach to diabetes management, considering factors such as diet, exercise, stress management, and medication adherence to develop tailored treatment plans for each patient.
Patient-Centered Approach
What sets Dr. Sanchayan Roy apart is his patient-centered approach to care. He takes the time to listen to his patients' concerns, preferences, and goals, involving them in the decision-making process every step of the way. This collaborative approach fosters trust and empowers patients to take an active role in managing their diabetes effectively.
Understanding Diabetes: Types and Causes
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: This type occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It usually develops in childhood or adolescence, and people with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. It is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet.
Gestational Diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after giving birth. However, women who develop gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Diabetes
The exact cause of diabetes varies depending on the type:
Type 1 Diabetes: The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Type 2 Diabetes: Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, age, and ethnicity.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common Symptoms
Frequent urination
Increased thirst
Extreme hunger
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Slow healing of wounds
Less Common Symptoms
Unexplained weight loss
Nausea and vomiting
Dry mouth
Itchy skin
Yeast infections
Diagnosis and Testing
Blood Glucose Tests
Diabetes is typically diagnosed through blood tests that measure glucose levels:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar levels after fasting for at least eight hours.
Random Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar levels at any time of the day, regardless of when the last meal was consumed.
A1C Test
The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months and is often used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and monitor blood sugar control in people with diabetes.
Other Diagnostic Tests
Additional tests may be conducted to assess diabetes-related complications, such as kidney function tests, lipid profile, and eye exams.
Complications Associated with Diabetes
Short-term Complications
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)
Long-term Complications
Heart disease
Stroke
Kidney disease
Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Eye damage (retinopathy)
Foot problems
Managing Diabetes Through Lifestyle Changes
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help control blood sugar levels and manage weight.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Stress Management
Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, is essential for diabetes management.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
Oral Medications
Several types of oral medications are available to help lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
Injectable Medications
Injectable medications such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors are often used in combination with oral medications to improve blood sugar control.
Insulin Therapy
People with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes require insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Self-Monitoring
Regularly checking blood sugar levels at home using a glucometer helps individuals with diabetes track their blood sugar control and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM systems provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, allowing for better diabetes management and reducing the risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Preventing Diabetes Complications
Regular medical check-ups, foot care, and eye exams are essential for detecting and managing diabetes-related complications early.
Support and Resources for Diabetics
Support Groups
Joining a diabetes support group can provide emotional support, practical tips, and motivation for managing diabetes effectively.
Educational Resources
Educational materials, workshops, and online resources provide valuable information about diabetes management, nutrition, and lifestyle changes.
Technology and Apps
Mobile apps and wearable devices help individuals with diabetes track their blood sugar levels, monitor their diet and exercise, and stay motivated to manage their condition effectively.
The Importance of a Diabetes Management Plan
Creating a personalized diabetes management plan with the help of healthcare professionals is crucial for achieving optimal blood sugar control and preventing diabetes-related complications.
More information about diabetes specialist:
Name:- Dr. Sanchayan Roy
Phone No.:- 8368021365
Address:- B - 404, Lower Ground Floor, Market No 1, Bipin Chandra Pal Marg, next to Bangiya Samaj close to, Block B,Chittaranjan Park, New Delhi – 110019
Website:- https://healthfirstcenter.in/diabetes-specialist-care/
0 notes