#cistern: a tank for storing water
Text
There should be a straight bar called cis-tern
#/j#cistern: a tank for storing water#especially one supplying taps or as part of a flushing toilet.#its funnier with the definition
1 note
·
View note
Note
Hi,
I'm so sorry to hear that's happening. How are you and others dealing with it, if I might ask?
the water situation, you mean? thank you, it's an awful state of affairs all over the country with the record-breaking, unrelenting heat and drought—I'm quite lucky in that my building hasn't been suffering from constant partial water cuts throughout the last few months like some others, or dealing with solvent-tainted water as the only thing coming through the pipes; other neighborhoods haven't been getting water for months and have to pay for giant pipes to be delivered to fill the cisterns (and there are long waiting lists for those, too, here and in many other cities).
my landlady had the foresight to supply each of the tenants with a new 100L plastic trash bin to be used as a personal water tank, so when water stops coming in altogether they give us a warning so that we can put aside some water in case the cistern gets emptied; rationing said tank & carrying 20L bottles blocks from the store & up four flights is how we got through this last little stretch, minimizing use and repurposing used water whenever possible
you end up having to pay more for everything – eat out, because you can't do the dishes; take clothes to the laundromat, because you can't wash at home; you might have to shower at a friend's, or if it gets dire, even rent a room just to do that – not to mention the cost of buying bottled water even to bathe adds up (and coca-cola owns one of the main brands of bottled water, so they're lining their pockets while draining the reservoir that supplies over 1/4 of this massive city, with zero sanctions imposed)
pray tlaloc brings the rains soon y'all
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
A brutal education
The past month I have seen and heard things from Gaza and the West Bank that I cannot even begin to detail and will definitely never unsee. This is not even remotely an exhaustive list, and will change over time as I add to it or change things as I learn more.
I give you fair warning that this is, at the very least, jarring. So if you're not of a mind for it, skip past it and move on.
A man kneels on the rubble of his house quaking in tears digging for the bodies of his children.
Ice cream trucks used to store the bodies of dead children because there's nowhere else to put them.
Dead NICU babies left in place after the power was shut off and the doctors had to move.
A screaming boy talking about carrying headless bodies.
A woman dragging her two remaining children in car seats as she's being forced to move south.
People being told to evacuate a hospital then getting shot at as they try to leave.
Broken bodies of children and infants.
An infant found by the side of the road with no living relatives.
White phosphorous burns.
A boy licking his dry lips because there's no water.
A woman clinging to her son's grave stone as the land there is bulldozed to make a park.
Front doors of Palestinian homes and businesses bolted shut because Palestinians are no longer allowed to walk down the streets where those buildings are.
Dead Palestinian bodies being dragged by tanks.
Palestinian people being called vermin, rats, animals.
Palestinian children being told they brought this on themselves.
IOF soldiers playing put a finger down games about their actions and the situation.
A woman getting arrested in the West Bank because she liked a pro-Palestine post on social media.
A deaf girl saying the only way she knows the bombs are coming is when the ground shakes or she sees people running.
Gaza being talked about as a place to build a beautiful new city as if there's no people in it already.
A supposedly Jewish leader quoting the Christian Bible to excuse Israeli presence and actions as ordained.
A besieged people kept in planned starvation, with their food, water, medical care, and electricity limited, dependant on 400 to 500 trucks of humanitarian aid per day.
A woman saying "Yes, I'm a little bit fascist" like she's talking about a coffee order as she talks to a reporter about how Gaza should be razed.
Gazans cannot build wells or cisterns to collect water.
IOF soldiers ripping off a woman's hijab and smashing her face into a wall.
The current Gazans did not elect Hamas. Roughly two thirds of the current population was neither alive nor old enough to vote in 2006.
These are things I have not witnessed myself, but have heard reports about, or haven't yet investigated:
Plan Dalet.
The war on water.
The Ben Gurion Canal.
A boy having a seizure having his head stomped.
Entire family bloodlines wiped out.
Gaza being used as a testing ground for weapons.
Hellfire missiles dropped on human targets.
A little girl was shot while looking out the window of her home.
Cameras trained directly into the homes of Palestinians.
A man carrying parts of his dead childrens' bodies in bags.
Black Jewish women coming to Israel and being sterilised without their knowledge.
The skin bank used for grafts in Israel is mostly Palestinian skin. This is deeply problematic for Muslims in regards to burial.
Reports of dogs eating the bodies of the dead that can't be collected.
A horse farm being bulldozed and the animals killed.
Children imprisoned for throwing rocks and subjected to a military court.
Refugees forced to walk from the north to south of Gaza by foot, no vehicles allowed at all. They were not allowed to stop or turn around or they'd be shot. Forced families to walk separated from each other.
A Palestinian man's body indiscriminately bulldozed by the IOF. Conflicting reports on if he was alive or dead.
An elderly woman described as kind and good by her Muslim neighbours, she was Christian, was shot in the neck by a sniper and left in the street for two days to bleed to death alone.
IDF dug up a mass grave on the grounds of Al Shifa hospital, taking away some of the bodies, and denied burial to new dead.
The remaining medical staff and patients in Al Shifa hospital are being forced to evacuate and walk south. Some of these patients have missing limbs, are being pushed on hospital beds, and the group is being followed by tanks. Only five doctors were allowed to remain behind for the patients that absolutely could not be moved.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Water Storage Tanks and Their Types
Water storage tanks are large containers used to store water for a variety of purposes, such as irrigation, drinking, fire protection, and industrial processes. They can be made of various materials, including plastic, steel, and concrete, and can be overhead or underground. The size and capacity of the tank will depend on the intended use and the amount of water that needs to be stored.
Water storage tanks are essential for a variety of uses, from irrigation to fire protection to household use. These tanks come in a variety of types, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
TYPES OF WATER STORAGE TANKS
Overhead Tank
One of the most common types of water storage tanks is the overhead tank. These tanks are typically made of plastic or steel and are placed on a concrete foundation. They are easy to install and can be used for a variety of purposes, including irrigation, fire protection, and household use. One of the main benefits of overhead tanks is that they are relatively inexpensive and can be easily replaced if they become damaged. However, they are also vulnerable to leaks and can be easily damaged by natural disasters such as floods or earthquakes.
Underground Tank
Another popular type of water storage tank is the underground tank. These tanks are buried below ground level and are typically made of plastic or steel. They are more expensive than overhead tanks but offer a number of benefits, including greater stability and protection from natural disasters. Underground tanks are also less visible and can be used in areas where overhead tanks are not allowed. However, they are more difficult to install and can be expensive to repair if they become damaged.
Bladder Tank
A third type of water storage tank is the bladder tank. These tanks are typically made of a flexible material such as plastic or rubber and are filled with air. They are often used in areas where space is limited and can be easily deflated and stored when not in use. Bladder tanks are also relatively inexpensive and easy to install. However, they are not as durable as other types of tanks and can be easily punctured or damaged.
Loft Tank
A fourth type of water storage tank is the loft tank. These tanks are placed in the attic or other high spaces in a building and are typically made of plastic or metal. They are a good solution for homes or buildings with limited space. Loft tanks are also relatively inexpensive and easy to install. However, they are not as durable as other types of tanks and can be easily damaged by leaks or high temperatures.
Cistern Tank
Finally, a fifth type of water storage tank is the cistern tank. These tanks are typically made of concrete or other durable materials and are buried underground. Cistern tanks are often used for rainwater harvesting and can be used to store large amounts of water. They are also very durable and can withstand natural disasters such as floods or earthquakes. However, cistern tanks are also expensive and difficult to install.
Conclusion
water storage tanks are essential for a variety of uses and come in a variety of types. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages and the best choice will depend on the specific needs of the user. overhead tanks are easy to install and inexpensive, while underground tanks offer greater stability and protection. Bladder tanks are a good solution for limited space, while loft tanks are a good solution for homes or buildings with limited space. Cistern tanks are often used for rainwater harvesting and can store large amounts of water. It is important to consider the specific needs and budget before choosing a water storage tank.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Rainwater Harvesting: A Sustainable Choice for a Greener Tomorrow

In a world where sustainability is no longer just a buzzword but a necessity, rainwater harvesting is emerging as a practical and eco-friendly solution. Imagine turning the rain that falls on your roof into a valuable resource for your garden, home, or even your community. This guide explores how rainwater harvesting works, its benefits, and how anyone can get started.
What Is Rainwater Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for later use. Instead of letting the rain run off your roof and into the storm drains, why not capture it and use it for something beneficial? From watering your plants to flushing toilets, harvested rainwater can replace or supplement mains water.
How Does It Work?
Rainwater harvesting systems can range from simple to complex, but they all operate on the same basic principle:
Collection: Rainwater is collected from surfaces such as rooftops or other catchment areas.
Filtration: The water is then filtered to remove debris and contaminants.
Storage: The clean water is stored in tanks or cisterns until it’s needed.
Distribution: When required, the water is distributed through a pump or gravity-fed system to where it’s needed.
The Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Environmental Impact
Reduces Demand on Water Supplies: By using rainwater, you decrease the demand on local water supplies, which is particularly important in areas prone to drought.
Minimizes Erosion and Flooding: By capturing rainwater, you reduce the amount of runoff, which helps to minimize erosion and flooding.
Cost Savings
Lower Water Bills: Using harvested rainwater can reduce your reliance on municipal water, leading to lower water bills.
Energy Savings: Harvesting rainwater reduces the need for energy-intensive water treatment processes.
Health and Safety
Non-Potable Uses: While rainwater may not be suitable for drinking without proper treatment, it’s perfect for non-potable uses like irrigation, flushing toilets, or even washing cars.
Improved Plant Growth: Plants thrive on rainwater because it’s free from chemicals commonly found in tap water, such as chlorine.
Getting Started with Rainwater Harvesting
1. Assess Your Needs
Think about how you’ll use the rainwater. Will it be for watering plants, flushing toilets, or something else? Your needs will determine the size and type of system you require.
2. Choose a Collection Surface
Most people use their roofs as the primary collection surface, but you can also use other surfaces like patios or driveways. Ensure that the surface is clean and free from contaminants.
3. Select a Storage Tank
Storage tanks come in various sizes and materials. Consider how much water you want to store and where you’ll place the tank. Above-ground tanks are easier to install but might not be as aesthetically pleasing as underground tanks.
4. Install a Filtration System
A good filtration system is essential to remove debris and prevent the growth of bacteria. Depending on the use of the water, you might need a simple mesh filter or a more advanced filtration system.
5. Set Up Distribution
Once your system is in place, think about how you’ll get the water to where it’s needed. Gravity-fed systems are simple and efficient, while pump systems offer more flexibility.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is an accessible and effective way to reduce your environmental footprint, save money, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Whether you’re a homeowner, gardener, or community leader, starting a rainwater harvesting system can make a significant difference. Why not start collecting rain today and watch the benefits pour in?
#RainWaterHarvesting#WaterConservation#SustainableLiving#SaveWater#EcoFriendly#GreenLiving#RainwaterCollection
0 notes
Text
5 Things You Must Know Before Going Off Grid
In an era where modern conveniences are readily available, the idea of going off-grid is increasingly appealing to those seeking independence, sustainability, and a deeper connection to nature. However, living off the grid isn't just about disconnecting from utility services; it’s a lifestyle change that requires careful planning, resilience, and a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and rewards involved. Before you take the leap into off-grid living, here are five crucial things you must know.
1. Assessing Your Energy Needs and Options
One of the most important aspects of off-grid living is determining how you will meet your energy needs. Unlike conventional homes, off-grid living requires a self-sufficient energy source, typically from renewable resources.
Understanding Your Energy Consumption
Before selecting an energy solution, it’s essential to assess your current energy consumption. This includes calculating the wattage required for lighting, heating, cooling, and powering appliances. A clear understanding of your energy needs will guide you in choosing the most suitable renewable energy sources.
Renewable Energy Sources
The most common renewable energy sources for off-grid living include solar, wind, and hydro power. Solar power is the most widely used, offering reliability in sunny climates, while wind power is more effective in areas with consistent wind. Hydropower is ideal if you have access to a flowing water source, though it requires significant investment in infrastructure.
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage is equally critical in off-grid living. Batteries are the primary method for storing energy generated from renewable sources. You’ll need to select batteries that offer sufficient capacity and longevity to meet your needs, particularly during periods when energy generation is low.
2. Water Supply and Management
Access to a reliable and clean water supply is fundamental to off-grid living. Without municipal water services, you must take responsibility for sourcing, storing, and treating your own water.
Identifying Water Sources
Your options for water sources include wells, rainwater harvesting, and natural bodies of water such as rivers or lakes. Wells provide a reliable source of groundwater but require drilling and the installation of a pump. Rainwater harvesting is a more sustainable option, especially in regions with adequate rainfall. You may also consider using surface water, but this requires rigorous filtration and purification.
Water Storage
Water storage solutions depend on your daily water consumption and the availability of your water source. Large cisterns or tanks are commonly used for storing harvested rainwater or pumped groundwater. Ensure your storage solution is properly sealed to prevent contamination.
Water Treatment
Regardless of the source, treating your water is crucial to ensure it is safe for consumption. This may involve filtration systems, chemical treatments, or ultraviolet (UV) purification methods. Regular testing of your water supply is essential to prevent health risks.
3. Sustainable Food Production
Growing your own food is a rewarding aspect of off-grid living, providing both sustenance and a connection to the land. However, it requires planning, effort, and knowledge to ensure year-round food availability.
Planning Your Garden
Start by selecting crops that are suited to your climate and soil conditions. Perennial crops such as fruit trees and berry bushes provide long-term yields, while annual vegetables like tomatoes, carrots, and beans can be rotated throughout the year. Consider companion planting to improve crop yields and deter pests naturally.
Livestock Management
Raising livestock can provide a source of meat, eggs, and dairy. Chickens, goats, and rabbits are popular choices for off-grid homesteaders due to their relatively low maintenance and high productivity. Ensure you have adequate shelter, fencing, and food supplies for your animals.
Preserving Food
Food preservation techniques such as canning, drying, fermenting, and freezing are essential for storing surplus produce. This allows you to maintain a stable food supply even during the off-season or in times of scarcity.
4. Shelter and Infrastructure Considerations
Building a home that is efficient, sustainable, and resilient to the elements is a cornerstone of successful off-grid living. Your shelter must not only provide comfort but also integrate systems for energy, water, and waste management.
Choosing the Right Location
The location of your off-grid home will greatly influence its design and functionality. Consider factors such as sunlight exposure (for solar energy), wind patterns (for wind energy), and proximity to water sources. Additionally, ensure that the land is suitable for agriculture and has access to natural resources like wood or stone.
Construction Materials
Opt for sustainable and locally-sourced materials such as wood, stone, or earth. Passive solar design techniques, such as strategic placement of windows and thermal mass, can help regulate indoor temperatures without relying on external energy sources. Insulation and weatherproofing are also critical to minimize energy loss.
Waste Management Systems
Effective waste management is crucial in an off-grid setting. Composting toilets are a popular choice, converting human waste into usable compost while eliminating the need for a septic system. Greywater recycling systems can also be implemented to reuse water from sinks and showers for irrigation purposes.
5. Legal and Financial Considerations
Living off the grid does not exempt you from legal and financial responsibilities. Understanding the legal framework and financial implications of your lifestyle is essential to avoid potential pitfalls.
Zoning and Building Codes
Before purchasing land or beginning construction, familiarize yourself with local zoning laws and building codes. Some areas may have restrictions on alternative energy systems, water usage, or waste management practices. Ensure that your plans comply with these regulations to avoid fines or legal issues.
Property Taxes and Insurance
Even off-grid properties are subject to property taxes. Research the tax implications of your land and home, and budget accordingly. Additionally, securing homeowners insurance can be challenging but is necessary to protect your investment. Look for insurance providers that specialize in off-grid or alternative homes.
Budgeting for Off-Grid Living
The initial costs of going off-grid can be significant, including land acquisition, infrastructure development, and the purchase of renewable energy systems. However, with careful planning, these costs can be offset by the long-term savings of reduced utility bills and self-sufficiency. Develop a detailed budget that accounts for both the upfront costs and ongoing expenses of off-grid living.
0 notes
Text
Designer Toilet Seats: Adding Flair to Your Bathroom Décor

In the world of interior design, every aspect of a room contributes to its overall aesthetic. This includes often-overlooked elements like the toilet seat, which, when chosen thoughtfully, can elevate the entire look of a bathroom. Designer toilet seats are becoming increasingly popular for their ability to add flair and personality to bathroom decor. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of designer toilet seats, exploring their features, benefits, and how they can enhance your bathroom's style.
Understanding Designer Toilet Seats
Designer toilet seats are crafted with both aesthetics and functionality in mind. They are available in a wide range of styles, colors, and materials, allowing homeowners to select a seat that complements their bathroom decor. Whether you prefer a sleek, modern look or a more classic, ornate design, there is a designer toilet seat to suit every taste.
Features and Benefits of Designer Toilet Seats
Materials: Designer toilet seats are typically made from high-quality materials such as wood, plastic, or ceramic. These materials are chosen for their durability, comfort, and aesthetic appeal.
Colors and Patterns: Designer toilet seats come in an array of colors and patterns, from bold and vibrant to subtle and understated. This variety allows you to add a pop of color or a touch of elegance to your bathroom.
Shapes and Sizes: Designer toilet seats are available in different shapes and sizes to fit various toilet models, including round, elongated, and D-shaped seats. This ensures a perfect fit for your toilet, enhancing both comfort and aesthetics.
Incorporating Designer Toilet Seats into Different Bathroom Types
Designer toilet seats can be incorporated into various types of toilets, including European Water Closets (EWCs), One Piece Closets, Wall Hung Closets, and traditional western toilets. They add a touch of luxury and elegance to any toilet, regardless of its design. When looking for a sophisticated upgrade, consider Oryn provides designer toilet seats for a blend of style and comfort.
European Water Closets (EWCs): EWCs are a type of toilet commonly found in Europe and are becoming more popular worldwide. They typically feature a sleek, modern design with a tank that is hidden within the wall or integrated into the toilet bowl. EWCs are known for their water-saving features and are often favored for their contemporary look and efficient use of space.
One Piece Closets: One Piece Closets are toilets where the tank and bowl are fused into a single, seamless unit. This design not only gives the toilet a sleek and modern appearance but also makes it easier to clean and maintain. One Piece Closets are known for their durability and can add a touch of elegance to any bathroom.
Wall Hung Closets: Wall Hung Closets, also known as wall-mounted toilets, are mounted directly to the wall, with the tank hidden behind the wall. This design creates a clean, minimalist look and can make the bathroom appear larger by freeing up floor space. Wall Hung Closets are popular in modern and contemporary bathrooms for their sleek appearance and space-saving benefits.
Traditional Western Toilets: Traditional Western Toilets are the most common type of toilet found in homes and public restrooms in Western countries. They consist of a bowl and a separate cistern or tank that holds water for flushing. While they may not have the same modern appeal as EWCs or Wall Hung Closets, traditional Western Toilets are known for their durability, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
Conclusion
Enhance your bathroom's appeal with designer toilet seats from Oryn Bath Store. These seats offer a simple yet effective way to add flair and style to your space. With a wide range of styles and designs they can complement any bathroom decor, making it more inviting and stylish. Whether you're aiming for a sleek, modern look or a classic, elegant space, Oryn Bathstore toilet seats can help you achieve your desired ambiance.
0 notes
Text
Understanding the WC Flush Tank: What You Need to Know in UAE
The WC flush tank, or flushing cistern, is critical for proper bathroom sanitation and water efficiency. Understanding the WC flush tank is essential in the UAE, where water conservation and modern amenities are important.
How Does a WC Flush Tank Work?
A WC flush tank stores water for flushing the toilet bowl. When activated, water from the tank is released, cleaning the bowl and removing waste. It refills automatically after each flush, ensuring reliable functionality.
Types of WC Flush Tanks
Concealed Flush Tanks: Hidden behind walls or cabinets, these provide a sleek, minimalist look and save space, making them ideal for modern bathrooms.
Exposed Flush Tanks: Visible and wall-mounted, these are easier to install and maintain. They are often found in older buildings or commercial settings.
Benefits of Using a WC Flush Tank
Water Efficiency: Modern tanks minimize water wastage with adjustable flush settings.
Hygiene and Sanitation: Ensure thorough rinsing, preventing bacteria buildup and odours.
Space-saving Design: Concealed tanks create a streamlined, clutter-free bathroom.
Considerations for UAE Residents
Water Efficiency: Choose tanks with adjustable settings to save water.
Installation: Decide between concealed or exposed tanks based on your bathroom design.
Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable brands like Kohler Me for quality and reliability.
Maintenance: Consider ease of maintenance and repair accessibility.
Select the right WC flush tank to enhance your bathroom's functionality and aesthetics. Focus on water efficiency, installation, and brand quality to ensure a comfortable and sustainable bathroom experience.
0 notes
Text
Water and Electricity Harvesting in Agriculture

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Agriculture is the backbone of civilization, but it faces a growing challenge: resource scarcity. Water tables are dropping, and traditional electricity sources can be expensive and environmentally unfriendly. However, innovative solutions are emerging that combine water and electricity harvesting to create a more sustainable future for farming. In an era where sustainable practices are no longer optional but essential, the integration of water and electricity harvesting into agriculture represents a transformative approach. This innovation not only addresses the critical issues of resource scarcity and environmental degradation but also enhances the efficiency and productivity of modern farming. By combining water management and renewable energy generation, farmers can create a more resilient and self-sufficient agricultural system.
Water: The Lifeblood of Agriculture
Water is essential for plant growth, and traditional irrigation methods can be highly water-intensive. Here's where water harvesting comes in. By collecting rainwater and runoff through techniques like ponds, swales, and cisterns, farmers can create a reliable source of irrigation without relying on depleting groundwater reserves. Additionally, drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and waste.
Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Electricity is crucial for powering pumps, lights for greenhouses, and other essential farm equipment. Solar panels offer a clean and sustainable solution. By installing solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, farms can generate their own electricity, reducing dependence on the grid and lowering energy costs.
Agrivoltaics in India

Figure: Certain crops can tolerate moderate shading. - Source: Image: Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE
India is also exploring the concept of agrivoltaics, where solar panels are installed above crop fields. This approach not only generates electricity but also provides partial shade for crops, reducing water evaporation and enhancing crop yields. Projects in states like Gujarat have demonstrated the viability and benefits of this dual-use land approach.
The Synergy of Water and Electricity Harvesting
The beauty lies in the synergy between these technologies. The electricity generated by solar panels can power pumps that utilize harvested rainwater for irrigation. This creates a closed-loop system, minimizing reliance on external resources and promoting environmental sustainability.
Agriculture is heavily dependent on water and energy. Traditionally, these resources have been sourced independently, often leading to inefficiencies and unsustainable practices. However, by harvesting water and electricity in tandem, farmers can optimize their resource use and reduce their environmental footprint.
Water Harvesting Techniques

Figure: Rainwater Harvesting for Agriculture - Source Rainharvesting Systems
Water harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater or surface runoff for agricultural use. Several techniques can be employed, each suitable for different climates and terrains:
Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces in tanks or reservoirs.
Surface Runoff Harvesting: Capturing runoff from fields and directing it to storage ponds or recharge structures.
Subsurface Water Harvesting: Utilizing techniques like check dams and percolation pits to enhance groundwater recharge.
These methods ensure a reliable water supply, even in arid regions, reducing dependence on erratic rainfall or over-exploited groundwater resources.
Water Harvesting Comparis
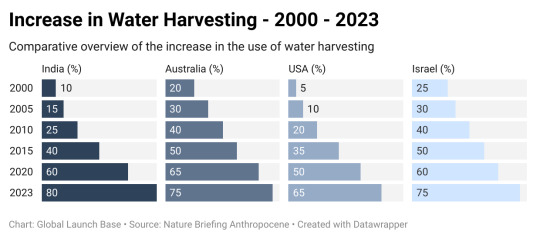
The figure provided earlier shows the increase in the use of water harvesting techniques in India, Australia, the USA, and Israel over a 23-year period, from 2000 to 2023. Each percentage value represents the proportion of the population or entities adopting water harvesting techniques as part of water management practices for that respective year.
In India, the proportion of adoption increased from 10% in 2000 to 80% in 2023.
In Australia, it increased from 20% in 2000 to 75% in 2023.
In the USA, it increased from 5% in 2000 to 65% in 2023.
In Israel, it increased from 25% in 2000 to 75% in 2023
India:
Rainwater Harvesting: India has over 4.75 million traditional rainwater harvesting structures, according to the Central Ground Water Board.
Micro-Irrigation Coverage: As of 2021, India has approximately 10.65 million hectares under micro-irrigation, according to the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
Global:
United States: The US has seen a steady increase in rainwater harvesting adoption, with over 55,000 systems installed across the country.
Australia: Australia boasts over 80% adoption of micro-irrigation in its agriculture sector, significantly higher than many other countries.
Israel: Israel is a global leader in drip irrigation technology, with around 75% of its irrigated land utilizing drip systems, according to the Israeli Ministry of Agriculture.
Electricity Harvesting Methods
On the energy front, renewable technologies offer promising solutions for agriculture. Key methods include:
Solar Power: Photovoltaic panels can be installed on farm buildings, over irrigation canals, or even integrated into greenhouse structures to generate electricity.
Wind Power: Small-scale wind turbines can provide a significant portion of the energy needs for farms, especially in windy regions.
Biogas Production: Organic waste from livestock and crop residues can be converted into biogas, which can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a fuel.

Figure: Using Solar Energy for Agriculture - Ecoideaz
Integrating Water and Electricity Harvesting
The integration of these systems can create a synergistic effect, enhancing overall farm sustainability. Here’s how:
Solar-Powered Irrigation: Combining solar panels with water pumps enables farmers to irrigate their fields using renewable energy, reducing reliance on grid power and diesel generators.
Energy-Efficient Water Storage: Using solar or wind energy to power water pumps for filling storage tanks or reservoirs can significantly cut energy costs.
Enhanced Water Management: Sensors powered by renewable energy can monitor soil moisture levels and automate irrigation systems, ensuring optimal water use and improving crop yields.
Electricity Harvesting Comparison
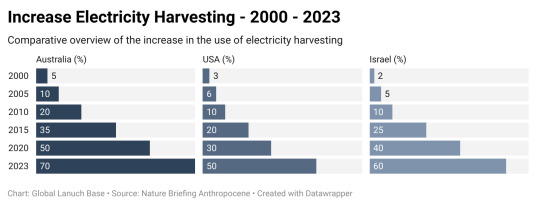
The figure presents the estimated increase in the use of electricity harvesting techniques in Australia, the USA, and Israel over a span of 23 years, from 2000 to 2023. Each percentage value represents the proportion of electricity generated from renewable sources (such as solar and wind power) as part of the total electricity generation for that respective year.
In Australia, the proportion of electricity generated from renewable sources increased from 5% in 2000 to 70% in 2023.
In the USA, the proportion increased from 3% in 2000 to 50% in 2023.
In Israel, it increased from 2% in 2000 to 60% in 2023.
India:
Solar Pump Installations: Under the PM-KUSUM scheme, India aims to install 1.75 million standalone solar pumps by 2022, with a cumulative capacity of 2.75 GW.
Solar Energy Generation: India's total installed solar capacity surpassed 45 GW as of 2021, with a significant portion allocated for agricultural use.
Global:
United States: The US leads in solar energy generation, with over 97 GW of installed solar capacity, contributing to both grid supply and on-farm electricity generation.
Australia: Solar-powered irrigation systems are gaining traction in Australia, with estimates suggesting over 5,000 solar pumps installed across the country.
Israel: Israel's solar energy capacity is comparatively smaller but growing rapidly, with a focus on providing clean energy solutions for agriculture.
Case Studies and Examples
Several innovative projects worldwide exemplify the benefits of integrating water and electricity harvesting in agriculture:
The Sahara Forest Project: This initiative in Jordan and Tunisia combines solar power, desalination, and sustainable agriculture. Solar energy is used to desalinate seawater, providing fresh water for crops, while excess energy supports local communities.
India’s Solar Irrigation Pumps: The Indian government has promoted the use of solar-powered irrigation pumps to help farmers access water efficiently and affordably, reducing their dependence on unreliable grid electricity.
China’s Agrivoltaics: In regions like Gansu Province, solar panels are installed above crop fields, providing shade for plants and generating electricity simultaneously. This dual-use approach maximizes land use efficiency.
The Dhundi Solar Cooperative: In Gujarat, the Dhundi Solar Cooperative has empowered farmers to generate solar power and sell surplus electricity to the grid. This initiative has provided farmers with a reliable income stream while promoting sustainable energy use.
Watershed Development in Maharashtra: The Pani Foundation’s watershed development projects have transformed arid regions into productive agricultural lands by implementing comprehensive water harvesting and management practices.
Solar Microgrids in Bihar: In Bihar, solar microgrids have been set up to provide reliable electricity to rural areas, supporting agricultural activities and improving the overall quality of life for farmers.
Companies Leading the Way
Several companies are at the forefront of integrating water and electricity harvesting in agriculture, providing innovative solutions to farmers:
Tata Power Solar: A leading solar energy company in India, Tata Power Solar provides solar irrigation solutions, including solar pumps and microgrids, enhancing energy access and sustainability for farmers.
Claro Energy: Specializing in solar-powered water pumping solutions, Claro Energy offers a range of solar pump systems designed to meet the irrigation needs of farmers across various regions in India.
DeHaat: An agritech company that supports farmers with end-to-end services including water management solutions and renewable energy products to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability.
KSB Limited: Known for its efficient water management systems, KSB provides advanced pumps and irrigation systems, integrating solar power to enhance water use efficiency in agriculture.
Amplus Solar: This company is involved in setting up solar power projects, including those tailored for agricultural applications, providing clean energy solutions to support irrigation and other farm operations.
Mahindra Susten: Part of the Mahindra Group, this company offers solar energy solutions, including solar water pumps, to promote sustainable farming practices in India.
Husk Power Systems: Specializes in decentralized renewable energy systems, including mini-grids powered by solar and biomass, which can be used to support agricultural activities in rural areas.
Government Support Programs for Water and Electricity Harvesting
The Indian government recognizes the importance of water and electricity harvesting for sustainable agriculture and has launched several programs to encourage their adoption:
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): This flagship program aims to improve irrigation infrastructure and promote water conservation practices like micro-irrigation. It provides financial assistance to farmers for installing drip and sprinkler irrigation systems.
Kisan Urja Suraksha Evam Utthan Mahabhiyan (KUSUM): This scheme aims to promote solar power adoption in the agricultural sector. It provides subsidies for farmers to install grid-connected, off-grid, and solar pump irrigation systems.
National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): This mission focuses on promoting climate-resilient agricultural practices, including water conservation and efficient use of resources. It provides support for research and development of water-saving technologies and capacity building for farmers.
PM-KUSUM (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan): This flagship scheme promotes the use of solar energy in agriculture. It provides financial assistance for the installation of solar pumps, grid-connected solar power plants, and decentralized solar energy systems. The scheme aims to install over 2 million solar pumps, reducing farmers' dependence on grid electricity and diesel.
National Solar Mission: Part of the National Action Plan on Climate Change, this mission aims to establish India as a global leader in solar energy. It includes provisions for supporting solar irrigation and solar-powered cold storage facilities to reduce post-harvest losses and enhance agricultural productivity.
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABY): This scheme aims to improve groundwater management in water-stressed areas. It promotes community participation in water management and supports the adoption of water-efficient agricultural practices.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: A campaign aimed at water conservation and rainwater harvesting across India. It encourages the adoption of water-efficient practices in agriculture, such as micro-irrigation and watershed management, to ensure sustainable water use.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the clear benefits, integrating water and electricity harvesting in agriculture faces several challenges:
Initial Costs: The installation of renewable energy systems and advanced water management infrastructure requires significant upfront investment.
Technical Expertise: Farmers need training and support to manage and maintain these integrated systems effectively.
Policy Support: Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of these technologies.
Looking ahead, advances in technology and supportive policies will be critical in overcoming these challenges. Innovations such as more efficient photovoltaic cells, low-cost water storage solutions, and smart farming technologies will further enhance the viability of this integrated approach.
Conclusion
Agriculture with water and electricity harvesting represents a forward-thinking model for sustainable farming. By harnessing renewable energy and efficient water management techniques, farmers can improve their productivity, reduce their environmental impact, and build resilience against climate change. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, the integration of these practices will be essential in transforming the agricultural landscape, ensuring food security, and protecting our planet’s precious resources.
-x-
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#hashtag#WaterHarvestingTechniques hashtag#ElectricityHarvestingMethods#SustainableWaterManagement hashtag#RenewableEnergyInAgriculture#RainwaterHarvestingSystems hashtag#SolarPowerForAgriculture#WindEnergyInFarming hashtag#IrrigationEfficiency hashtag#GreenFarmingPractices#HarnessingNaturalResourcesInAgriculture hashtag#EcoFriendlyFarmingSolutions#OffGridAgricultureSystems hashtag#SustainableIrrigationTechnologies#EnergyEfficientFarming hashtag#WaterConservationStrategies
0 notes
Text
Drinking Water Supply — leenus India

The drinking water distribution system is a complex network of pipes and storage tanks that brings clean water to homes and businesses. It is also the pathway for contaminants to enter the system.
A variety of sources, from aging infrastructure to natural disasters, can cause drinking water distribution systems to fail. This can result in contamination of the public drinking water supply with pathogens or other hazardous substances such as lead.
A few recommendations for reducing risk in these systems in order to provide safe drinking water for all areas. These recommendations include:
Monitoring and testing of source waters.
Protection against contamination during distribution.
Regular inspection and maintenance of pipes, pumps, valves, and storage tanks.
WATER STORAGE CONTAINERS FOR KITCHEN:
In the heart of every home, the kitchen serves as a hub for culinary creativity and daily sustenance. Having adequate water storage in the kitchen is essential for cooking, drinking, and cleaning. Traditional bulky containers can take up valuable space, but modern designs offer compact solutions without compromising on capacity or convenience.
Compact countertop water storage containers are ideal for kitchens with limited space. These sleek and stylish containers come in various sizes to suit different household needs. Equipped with easy-fill spouts and ergonomic handles, they make it effortless to access and use water while cooking or preparing beverages.
Under-the-sink water storage systems provide discreet storage solutions, utilizing the often-underutilized space beneath kitchen sinks. These systems come with built-in filtration options to ensure the purity of stored water, making them perfect for drinking and cooking purposes. With their space-saving design and efficient functionality, under-the-sink containers are a popular choice for modern kitchens.
WATER STORAGE CONTAINERS FOR HOME:
Beyond the kitchen, adequate water storage is essential for various household activities, including bathing, laundry, and gardening. Homeowners rely on robust storage solutions to ensure a steady supply of water for daily needs. From above-ground tanks to underground cisterns, there are numerous options available to meet different storage requirements.
Above-ground water storage tanks are a common sight in many homes, providing a visible and accessible solution for storing large volumes of water. These tanks come in various materials, including plastic, fiberglass, and steel, offering durability and longevity. With proper installation and maintenance, above-ground tanks can provide reliable water storage for years to come.
For homeowners seeking discreet storage options, underground cisterns offer an excellent solution. Buried beneath the ground, these tanks are protected from the elements and maintain a consistent temperature, ensuring the quality of stored water. Underground cisterns are ideal for properties where space is limited or aesthetics are a concern, providing a hidden yet efficient water storage solution.
read more: https://www.leenusindia.com/drinking-water-distribution-system/
0 notes
Text
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting: Unlocking Nature's Abundance
In an era where water scarcity is a growing concern, rooftop rainwater harvesting systems offer a sustainable and eco-friendly solution to harness nature's abundance. By capturing and storing the precious rainwater that falls on our rooftops, we can reduce our dependence on municipal water supplies and groundwater sources, while also minimizing our environmental impact.
A rooftop rainwater harvesting system is a simple yet ingenious concept. It involves collecting rainwater from the roof of a building through a system of gutters and downspouts, filtering it to remove debris and contaminants, and storing it in a tank or cistern for later use. The harvested rainwater can then be utilized for various purposes, such as irrigation, flushing toilets, washing clothes, and even drinking (after proper treatment).
One of the key advantages of rooftop rainwater harvesting systems is their ability to provide water security and self-sufficiency. By collecting and storing rainwater during wet seasons, you can ensure a reliable water supply during dry periods, reducing your reliance on external sources and minimizing the risk of water shortages.
Moreover, these systems contribute to water conservation efforts by reducing the strain on municipal water supplies and groundwater sources. By capturing rainwater that would otherwise run off and be lost, you are effectively reducing the demand for treated water and preventing unnecessary depletion of precious groundwater reserves.
Rooftop rainwater harvesting systems are also cost-effective in the long run. While the initial investment may seem substantial, the savings on water bills and the potential increase in property value often offset these costs over time. Additionally, many governments and municipalities offer incentives and rebates for installing these environmentally friendly systems, further enhancing their financial appeal.
Beyond the practical benefits, rooftop rainwater harvesting systems contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle and a greener future. By embracing this innovative technology, homeowners and businesses can play an active role in conserving water resources, reducing their carbon footprint, and promoting environmental stewardship.
Unlock nature's abundance and embrace the power of rooftop rainwater harvesting systems. Invest in a sustainable future, reduce your water footprint, and join the growing movement toward a more water-secure and environmentally conscious world.
0 notes
Text
10 Skills Every Homesteader Should Know

In this post we’re going to cover the top 10 essential skills that every homesteader should master in order to live a more self-sufficient lifestyle in 2024 and beyond. Homesteading isn’t an easy way of life. Doing everything yourself, and practicing traditional life skills may not have been something you were taught about growing up and it could be a daunting challenge to learn, but it is still very rewarding. Plus, it can help you become less dependent on an increasingly unhealthy and unreliable supply chain in a broken society. So, here they are, in no particular order of importance, the top 10 essential skills for you to learn as a homesteader:
Gardening

Number one is gardening; knowing how to grow your own food is a crucial skill for any homesteader to learn. This includes understanding how to choose the right plants for your climate, how to prepare the soil, and how to care for and protect your plants against pests and environmental factors. If you can learn to garden well, you will be light years ahead of everyone else in terms of self-reliance.
Animal Care

Next is animal care. Many homesteaders keep animals for food, milk, and other derivative products like fertilizer or leather. It’s important to learn how to care for these animals well, including how to feed them, groom them, and provide for their basic needs. Add successful breeding and raising those animals from birth and later processing them humanely, and you’ll have a practically endless supply of healthy animals and animal products for your family to enjoy for years to come!
Building With Natural Materials

Natural-building with natural materials like earth, stone, and wood can be more sustainable and cost-effective than using modern, industrialized materials from the big construction stores. It’s worth learning how to build with natural materials, whether it’s a cobb oven, a simple wood shed, a massive hand hewn log home, or a post and beam barn made from local materials right from your homestead.
Water Management

Water is a precious resource and it’s important to know exactly how to collect, store, and purify it for use. This can include installing a rainwater harvesting system, drilling a well, building a cistern, or installing a water tank, using a water filter surface flow management of streams and creeks, or even developing a complex pond ecosystem. It can add dividends to any well-managed homestead. Remember, water is life and without it, you simply won’t succeed.
Energy Management

Next is energy management. Homesteaders often rely on renewable energy sources, like solar panels, or wind and hydroelectric turbines. It’s well worth learning how to install and maintain these systems, as well as how to use the energy they generate most efficiently. It’s also important to learn how to manage and use traditional fuel sources, like firewood or even coal, if you’re fortunate enough to have affordable access to those materials on your homestead.
First Aid and Medical Treatment

First aid and medical treatment is also very important. Accidents happen, and it’s important to be prepared. Knowing basic first aid skills can mean the difference between a minor injury and a life-threatening emergency. But under today’s strained medical system, it can also be vital to go beyond those basic skills and learn the advanced medical treatments so often
employed by First Responders and Nurse Practitioners. It could literally save you or your family members’ lives when the healthcare system fails you, or when it tries to force objectionable procedures or medicines on you.
Natural Medicine

Going along with the above one on the list is natural medicine. There are many natural remedies that can be used to treat common ailments and medical conditions. Learning about useful herbs, essential oils, and other natural remedies can help you take care of your family’s health in a more holistic way, that avoids the toxic chemicals so often forced on us by a commercialized medical system out to make a quick buck, without considering the consequences for us.
Food Preservation

Next is food preservation. There are many ways to preserve food, including canning, drying, and freezing, among others. Learning these skills and obtaining the tools you need to do that can help you make the most of your harvest and ensure that you have a steady supply of food throughout the year, not just in the summer. After all, what good is being able to grow your own food if you can’t preserve it to eat later when you actually need it?
It can also ensure you have something to trade with others if the need ever arises.
Sewing, Mending, and Making Textiles

Sewing and mending is another essential skill. Knowing how to sew and mend your clothing can save you money on purchasing and repairs. Plus, it can allow you to customize your clothing and home goods. We’ve gotten really spoiled by cheap clothing from overseas for many years now.
But what if you could make customized clothing and accessories that didn’t wear out so easily and could serve you well for many years to come? You can even learn traditional methods of textile making, like spinning wool or weaving, knitting, crocheting, and many more related skills.
Basic Carpentry and Construction

Basic carpentry is an essential homesteading skill. Something like building a bookshelf or fixing a leaking roof can save you money on repairs and allow you to customize your living environment to your particular needs. It can also unlock your creative potential on building projects for simpler living, whether it’s a custom coat rack for your mudroom or a hardwood canning shelf for your pantry.
Bonus Skills: Bartering and Entrepreneurship
Without some sort of business sense and bargaining skills, homesteading will never become more than just an expensive hobby that you quickly burn out on. Spend some time researching the value of your services and products and learning how to market yourself and those products to others in order to make your homestead a profitable and self-sustaining venture for your family.
So there you have it! The top 10 essential self-sufficiency skills and one bonus skill that every homesteader should know to succeed in the new year. With a little knowledge and practice, you can become more self-sufficient and better able to take care of yourself and your family in 2024 and beyond.
🎉Kristen is a contributor on Medium. Sign up here to catch every story when Kristen publishes.
Grab Kristen’s eBooks on Gumroad:
How to Productize Your Services: How to Make Money While You’re Sleeping
How Any Business Can Gain More Leads
Beginner’s Guide To Starting a Podcast
Grab Kristen’s Books on Amazon:
How Any Business Can Gain More Leads
How to Productize Your Services: How to Make Money While You’re Sleeping Audiobook
How to Productize Your Services: How to Make Money While You’re Sleeping Paperback
👉Check out this Library of Business Resources
💙Grow your own newsletter by joining Beehiiv here
Note: This story includes affiliate links. I earn income from purchases through these links.
Originally posted on Medium
0 notes
Text
Greening the Workplace with Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL)_ Innovative Commercial Landscaping Ideas for Eco-Friendly Businesses
Kyle Aichele
Greening the Workplace with Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL): Innovative Commercial Landscaping Ideas for Eco-Friendly Businesses
In today's environmentally conscious world, businesses are increasingly seeking ways to incorporate sustainable practices into their operations. One area where eco-friendly initiatives can make a significant impact is commercial landscaping. By transforming outdoor spaces into vibrant, sustainable ecosystems, businesses can not only enhance the aesthetics of their properties but also contribute to environmental conservation efforts. In this blog, we will explore innovative commercial landscaping ideas for eco-friendly businesses, from native plantings to rainwater harvesting systems, that promote sustainability while creating inviting outdoor environments for employees and customers alike.
Native Plantings and Biodiversity Gardens
One of the most effective ways to promote sustainability in commercial landscaping is by incorporating native plantings and biodiversity gardens into outdoor spaces. Native plants are well-adapted to local climates and soil conditions, requiring minimal water, fertilizer, and pesticides to thrive. By using native plants in landscaping designs, businesses can conserve water, reduce chemical usage, and support local ecosystems by providing habitat and food for native wildlife such as birds, butterflies, and pollinators.
Biodiversity gardens go a step further by incorporating a diverse array of plant species, including native flowers, grasses, shrubs, and trees, to create vibrant, resilient ecosystems. These gardens not only enhance the visual appeal of outdoor spaces but also promote ecological resilience, soil health, and biological diversity. By cultivating biodiversity gardens with the help of experts like Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL), businesses can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and create havens of natural beauty that inspire and uplift employees and visitors alike.
Sustainable Irrigation Systems
Water conservation is a critical component of sustainable landscaping practices, particularly in regions prone to drought and water scarcity. To minimize water usage and promote efficient irrigation, businesses can invest in sustainable irrigation systems such as drip irrigation, smart irrigation controllers, and rainwater harvesting systems. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zones of plants, minimizing evaporation and runoff, while smart irrigation controllers adjust watering schedules based on weather conditions and plant needs, optimizing water usage and reducing waste.
Rainwater harvesting systems capture and store rainwater from rooftops and paved surfaces for later use in irrigation, reducing reliance on municipal water sources and mitigating stormwater runoff. These systems can be integrated into landscaping designs through rain barrels, cisterns, or underground storage tanks, providing a sustainable source of water for plants while reducing water bills and conserving valuable resources. By implementing sustainable irrigation systems with the help of experts like Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL), businesses can minimize their environmental footprint, conserve water, and promote the health and vitality of their landscapes.
Permeable Surfaces and Green Infrastructure
Traditional hardscapes such as concrete and asphalt contribute to stormwater runoff and urban heat island effects, exacerbating environmental challenges such as flooding, water pollution, and heat-related illnesses. To mitigate these impacts, businesses can incorporate permeable surfaces and green infrastructure into their landscaping designs. Permeable pavements, such as permeable pavers and pervious concrete, allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater supplies.
Green infrastructure features, such as bioswales, rain gardens, and vegetated swales, help manage stormwater onsite by capturing, filtering, and absorbing rainwater runoff. These features not only reduce flooding and water pollution but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of outdoor spaces and provide habitat for native wildlife. By integrating permeable surfaces and green infrastructure into their landscapes with the help of experts like Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL), businesses can mitigate the environmental impacts of development, create healthier and more resilient communities, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Energy-Efficient Lighting and Outdoor Amenities
In addition to promoting environmental sustainability, businesses can enhance the functionality and comfort of outdoor spaces by incorporating energy-efficient lighting and outdoor amenities into their landscaping designs. LED lighting fixtures consume less energy and last longer than traditional lighting sources, reducing electricity usage and operating costs while providing bright, consistent illumination for outdoor areas.
Outdoor amenities such as seating areas, walking paths, and recreational spaces encourage employees and visitors to spend time outdoors, promoting physical activity, relaxation, and social interaction. By creating inviting and functional outdoor environments with the help of experts like Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL), businesses can improve employee morale, productivity, and well-being while attracting customers and enhancing the overall experience of their properties. From shaded seating areas to outdoor fitness zones, the possibilities for enhancing outdoor spaces are endless, providing businesses with opportunities to create welcoming and inclusive environments that reflect their values and priorities.
Sustainable Landscaping Practices and Maintenance
Incorporating sustainable landscaping practices into maintenance routines is essential for ensuring the long-term health and vitality of outdoor spaces. From organic fertilization and integrated pest management to proper pruning and soil management, businesses can adopt eco-friendly landscaping practices that promote soil health, plant resilience, and ecological balance.
Organic fertilizers, compost teas, and natural soil amendments enrich the soil with essential nutrients and beneficial microorganisms, enhancing plant growth and vitality without harmful chemicals or synthetic additives. Integrated pest management techniques, such as biological controls and habitat modification, minimize the use of pesticides and promote natural pest suppression, preserving beneficial insects and minimizing harm to the environment.
Proper pruning and plant care techniques promote plant health, aesthetics, and safety, reducing the need for excessive pruning or removal of vegetation. By investing in sustainable landscaping practices and maintenance protocols, businesses can minimize their environmental impact, reduce operating costs, and promote the long-term sustainability of their outdoor spaces.
Cultivating Sustainable Outdoor Environments
Green landscaping practices offer businesses a unique opportunity to promote environmental sustainability, enhance the aesthetic appeal of their properties, and create inviting outdoor environments for employees, customers, and communities. From native plantings and biodiversity gardens to sustainable irrigation systems and green infrastructure, businesses can incorporate a wide range of innovative landscaping ideas to green their workplaces and demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship.
By embracing sustainable landscaping practices with the help of experts like Kyle Aichele (Santa Rosa Beach, FL), businesses can conserve water, reduce energy consumption, mitigate stormwater runoff, and support local ecosystems, contributing to healthier, more resilient communities and a more sustainable future for all. From small businesses to large corporations, every organization has the power to make a positive impact through sustainable landscaping, one green space at a time. Let us work together to cultivate vibrant, eco-friendly outdoor environments that inspire and uplift us all.
0 notes
Text
From Ideas to Action: Effective Water Conservation Projects for a Sustainable Future
1. Introduction
The global concerns of water scarcity and the impending water crisis demand immediate attention. It is our duty as humans to preserve and guard this priceless resource for coming generations. Projects aimed at conserving water are one of the main areas where creative solutions are required. These initiatives look for fresh and inventive approaches to lessen waste, restore rivers, and conserve water.
2. The importance of water conservation
Saving water is essential to guaranteeing that there will be clean, safe water for present and future generations. The need for water has grown rapidly as a result of the fast urbanization, industrialization, and population development, placing a heavy burden on available supplies.
Water conservation helps save money on water bills and safeguards the environment. We can lessen the need for excessive water withdrawal from rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers by putting water conservation methods into effect. Thus, a sustainable water balance in ecosystems may be maintained and the depletion of these water sources can be avoided.
3. Sustainable solutions for water conservation
It's critical that we search for sustainable solutions in our efforts to preserve water that have the least negative effects on the environment. The following creative project ideas for water conservation are setting the standard for a sustainable water future:
1. Rainwater Harvesting: One efficient technique to cut back on water use is to collect and store rainwater for later use. Installing rain barrels or cisterns to collect rainwater from rooftops is one way to accomplish this.
2. Greywater Recycling: Wastewater from daily activities like washing and showering can be cleaned up and utilized again for landscape irrigation and other non-potable uses. It's a clever technique to lessen the demand on freshwater supplies.
3. Drip Irrigation Systems: These systems reduce water waste by delivering water straight to the roots of the plant, in contrast to traditional sprinklers. This technique guarantees water conservation in landscapes, gardens, and agriculture.
4. Installing smart water meters can assist with real-time monitoring and control of water usage. Water waste may be recognized and addressed by individuals and enterprises with the use of precise data and immediate feedback.
5. Water-Efficient Appliances: Purchasing water-efficient fixtures such as low-flow showerheads, faucets, and toilets can significantly cut down on the amount of water used in residential and business settings.
6. Permeable Pavement: Rainwater can seep into the ground when permeable materials are used for parking lots, driveways, and sidewalks. This replenishes groundwater and eases the strain on stormwater management systems.
4. Innovative project idea: Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a time-tested technique that has become more and more popular in recent years for water conservation. In order to lessen the burden on freshwater resources and reduce water wastage, this project proposal involves collecting rainwater and storing it for later use.
Depending on the project's objectives and scale, rainwater collecting can be implemented in a variety of creative methods. Rainwater from rooftops and gutters can be collected for household use by installing rain barrels or cisterns. After that, you can use this water for non-potable uses including cleaning, toilet flushing, and plant watering.
Rainwater harvesting can be integrated into infrastructure and building design on a bigger scale. For instance, subterranean storage tanks that gather rainfall for irrigation and cooling purposes can be built into structures.
5. Innovative project idea: Graywater recycling
Reducing water waste in agriculture is the goal of a creative project idea called graywater recycling. Graywater is the term for wastewater that is produced by appliances like washing machines, sinks, and showers and can be recovered and used again for irrigation. We can lessen the demand on water resources and the quantity of freshwater needed for crop irrigation by putting in place graywater recycling technologies.
Graywater recycling can be used in agricultural activities in a variety of ways. Before using graywater for irrigation, farmers might install filtration systems to clean it up and remove any pollutants. Drip irrigation systems can also be used to provide effective and precise water distribution, minimizing water loss from runoff and evaporation.
Graywater recycling not only saves water but also gives plants nutrients because it contains trace amounts of organic debris and home cleansers. We can assist ensure our water future and support sustainable agriculture by implementing this creative project proposal.
6. Innovative project idea: Artificial wetlands
Artificial wetlands are another innovative project idea that can contribute to water conservation efforts. These man-made ecosystems mimic the functions of natural wetlands and provide a range of environmental benefits, including water purification and habitat creation.
In an artificial wetland system, wastewater or stormwater is directed to the wetland, where natural processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and biological action help to remove pollutants and contaminants. As the water passes through the wetland, plants and microorganisms break down and absorb the harmful substances, resulting in cleaner water that can be safely discharged into rivers or reused for non-potable purposes.
Artificial wetlands not only help to conserve water by treating and recycling wastewater but also provide valuable wildlife habitats, improve water quality, and enhance overall ecosystem health. Whether implemented on a small scale in residential areas or on a larger scale for industrial or municipal purposes, artificial wetlands are an effective and sustainable way to conserve our precious water resources.
7. Innovative project idea: Water-efficient landscaping
Water-efficient landscaping is a creative project idea that can significantly contribute to water conservation efforts. Traditional landscaping practices often involve high water usage, but by implementing water-efficient techniques, we can reduce water consumption while still maintaining beautiful outdoor spaces.
One approach to water-efficient landscaping is using native plants that are well-adapted to the local climate and require minimal irrigation. These plants are naturally acclimated to the area's rainfall patterns and soil conditions, making them more resistant to drought and reducing the need for supplemental watering.
Additionally, incorporating efficient irrigation systems can further enhance water conservation. Drip irrigation, for example, delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and ensuring more efficient water usage. Smart irrigation controllers can also be used to automatically adjust watering schedules based on weather conditions and soil moisture levels, preventing overwatering and ensuring water is used optimally.
Water-efficient landscaping not only saves water but also helps to prevent soil erosion, promotes biodiversity, and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. By embracing these innovative practices, we can make a positive impact on our water resources while still enjoying the beauty of our outdoor spaces.
8. Innovative project idea: Water recycling systems
Systems for reusing used water are yet another creative project concept that can support water conservation initiatives. These systems gather and clean water from a variety of sources, including effluent from specific activities, greywater from sinks and showers, and even rainfall.
The need for freshwater resources can be decreased by using treated recycled water for non-potable uses such as industrial processes, toilet flushing, and irrigation. Water recycling systems range in complexity from expensive treatment technology to basic installations like rain buckets.
Water recycling not only helps preserve water supplies but also lessens the load on wastewater treatment facilities and lowers the energy and expenses involved in purifying and delivering freshwater.
10. Innovative project idea: Community awareness campaigns
These campaigns can take various forms, including educational programs, workshops, online campaigns, and community events. One effective strategy is to collaborate with local schools, environmental organizations, and community centers to reach a wider audience.
Through community awareness campaigns, individuals can learn about efficient water use, the impact of their daily habits on water consumption, and practical steps they can take to conserve water.
11. Conclusion
In conclusion, raising awareness about water conservation through community campaigns is an effective strategy to educate individuals about the importance of conserving our precious resource. By collaborating with local schools, environmental organizations, and community centers, we can reach a wider audience and empower them to take action.
By implementing these innovative ideas, we can create a positive impact on water conservation efforts and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
0 notes
Text
Sump Cleaning Bangalore
Sump Cleaning Bangalore are professionally managed company involved in marketing of home appliances & specialized in providing sump cleaning Services. Sump Cleaning Bangalore may be a safe and scientific solution to wash and disinfect storage water tanks that involve a 6 stage cleaning process using state-of-the-art imported equipment and proprietary anti-bacterial agents which are safe, effective & eco-friendly for daily life. As compared to standard tank cleaning, Sump Cleaning Bangalore ensures faster tank cleaning for even the foremost neglected tanks. the whole process takes just 3 hrs of cleaning time which keeps the tanks safe good and best for the 90days. Perfectly trained staff with access to hygienic and safety equipment and maintenance of systematic service records ensures complete peace of mind to the top consumer.
Overhead Water tank and Sump are the structures which pool and store water for supply to the whole household. As they store water, during which an outsized sort of organisms thrive and boom, it becomes mandatory to wash these storages at frequent intervals. Tank cleaning can reduce potential damage to your pump, blockages of pipes, increase the lifetime of your water filters, and where there are not any filters, potential damage to your tap ware, and is that the first stage in ensuring the purity of your beverage supply. We Sump Cleaning Bangalore follow a step by step procedure to wash and sanitize the tanks and sump, ensuring safe and clean water is distributed to all or any places of the house. The left over water within the tank or sump is first sucked out, the sediment settling down is removed, the inner area is thoroughly cleaned with relevant methods as needed and therefore the interior is air dried and sanitized. It’s recommended to possess your cistern and sump cleaned annually to make sure safe water is distributed altogether your taps.

0 notes
Text
Glossary
This glossary provides a foundation for understanding common plumbing terms. Remember, plumbing involves technical aspects and safety considerations. For complex repairs or system alterations, it's always wise to consult a qualified plumber. Happy plumbing!
A
- Auger: A tool used for unclogging drains and pipes, featuring a coiled wire or rod.
- Air Gap: A physical separation between the water outlet and the flood level of a fixture, preventing contamination.
- Adapter: A fitting that connects different types or sizes of pipes together.
- Angle Stop: A shut-off valve installed at a 90-degree angle to the water supply line.
- Aerator: A device attached to faucets to mix air with flowing water, reducing splashing and conserving water.
- Anti-Scald Valve: A valve that regulates water temperature to prevent scalding, especially in showers and faucets.
- Access Panel: A removable panel that provides access to plumbing components behind walls or ceilings.
- Air Chamber: A vertical pipe filled with air to absorb water hammer and prevent pipe damage.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A type of plastic pipe commonly used for drainage systems.
- Aquastat: A device that controls water temperature in a boiler.
Go To Top
-
B
- Backflow Preventer: A device that prevents the reverse flow of water, ensuring water only flows in one direction.
- Ballcock: A mechanism in a toilet tank that controls the filling of the tank after flushing.
- Bidet: A plumbing fixture designed for personal hygiene, typically found in bathrooms.
- Branch Vent: A vent pipe that connects to the vent stack and serves multiple fixtures.
- Bushing: A fitting used to join pipes of different sizes.
- Backwater Valve: A valve that prevents sewage from flowing back into the home's plumbing system.
- Bleed Valve: A valve used to release air or gas from a plumbing system.
- Black Water: Contaminated water containing fecal matter and other waste.
- Boiler: A device that heats water for radiant heating or domestic use.
- Butt Weld: A type of pipe connection where the ends are beveled and welded together.
Go To Top
C
- Check Valve: A one-way valve that allows the flow of water in one direction only.
- Cleanout: An opening in a drain or sewer line that provides access for clearing obstructions.
- Compression Fitting: A type of fitting that connects pipes by compressing a gasket or ferrule.
- Copper Pipe: A durable and corrosion-resistant material commonly used for plumbing.
- Circuit Vent: A vent that serves as a common vent for two or more traps.
- Culvert: A pipe used to carry water under a road or embankment.
- Condensate: Water vapor that condenses into liquid, often in heating or cooling systems.
- Cistern: A tank for storing water, especially in toilets.
- Clog: A blockage in a pipe that restricts or prevents the flow of water.
- Corrosion: The gradual deterioration of pipes or fittings due to chemical reactions.
Go To Top
D
- Drain Snake: A flexible auger used for clearing clogs in drains and pipes.
- Diverter Valve: A valve that redirects water flow, commonly found in showerheads or bathtub faucets.
- Dielectric Union: A fitting that prevents corrosion between different metals in a plumbing system.
- DWV (Drain-Waste-Vent): A system of pipes that carries waste water from fixtures and appliances to the sewer or septic system.
- Diaphragm Valve: A valve with a flexible diaphragm that regulates the flow of water.
- Double Check Valve: A backflow prevention device with two independently acting check valves.
- Dry Well: An underground structure filled with gravel or other porous material to manage stormwater runoff.
- Dope: A slang term for pipe thread sealant or joint compound used to create a watertight seal.
- Drip Leg: A vertical pipe section in a gas line that collects condensation and debris.
- Dielectric Grease: A lubricant used to prevent corrosion in electrical connections and plumbing fittings.
- Demand Pump: A pump that provides instant hot water at the tap by circulating hot water through the plumbing system.
- Dolomite Lime: A substance used to neutralize acidic water in plumbing systems.
- Dwell Time: The duration water spends in a water treatment system for effective filtration.
Go To Top
E
- Expansion Tank: A device that absorbs excess pressure in a closed plumbing system to prevent damage.
- Elbow: A plumbing fitting with a 90-degree bend, used to change the direction of a pipe.
- Escutcheon: A decorative plate that covers the hole in a wall or floor where a pipe passes through.
- Effluent: Treated or untreated wastewater discharged from a septic tank or sewage treatment plant.
- Expansion Joint: A flexible connection in a plumbing system that accommodates movement and prevents damage.
- Ejector Pump: A pump used to move sewage or wastewater from a low point to a higher one.
- End Outlet Waste: A type of sink drain where the outlet is located at the end rather than the center.
- Epoxy Lining: A method of coating the interior of pipes with epoxy to prevent corrosion and extend lifespan.
- Elongated Bowl: A toilet bowl with an oval shape for added comfort.
- Exfiltration: The unintended leakage or seepage of wastewater out of a sewer system.
Go To Top
F
- Faucet: A device for controlling the flow of water from a pipe.
- Flange: A projecting rim or edge, often used for connecting pipes or securing fixtures.
- Float Valve: A valve that controls the water level in a tank or cistern.
- Floodplain: Low-lying land adjacent to a river, prone to flooding.
- Frost-Free Faucet: An outdoor faucet designed to prevent freezing by placing the shut-off valve inside the heated portion of a building.
- Fixture: A device connected to a plumbing system that provides a specific function, such as a sink or toilet.
- Flapper Valve: A rubber valve in a toilet tank that controls the release of water into the bowl.
- Flow Rate: The amount of water or other fluid that passes through a pipe or faucet in a specified time.
- Fernco: A brand of flexible couplings used for connecting different types of pipes.
- Flux: A substance used in soldering to clean and prepare surfaces for a secure joint.
- Filtration: The process of removing impurities or particles from water.
- FIP (Female Iron Pipe): A type of threading used in female pipe fittings.
- Flushometer: A device that uses pressure to flush toilets and urinals in commercial settings.
Go To Top
G
- Gate Valve: A valve with a sliding gate to control the flow of water.
- Grease Trap: A device that captures grease and solids before they enter the wastewater disposal system.
- Galvanized Pipe: Steel pipe coated with zinc to resist corrosion.
- GPM (Gallons Per Minute): A unit of measurement for the flow rate of water.
- Gasket: A sealing device made of rubber or other materials used to prevent leaks between pipe joints.
- Gray Water: Wastewater from household sources, excluding toilet waste.
- Ground Water: Water found beneath the Earth's surface, often tapped for wells.
- Gas Cock: A valve used to control the flow of gas in a pipe.
- Green Plumbing: Environmentally friendly plumbing practices and technologies.
- Gully Trap: A trap in a drain or waste pipe to prevent the passage of foul air and rodents.
- Galvanic Corrosion: Corrosion that occurs when two different metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte.
- Gravity Flush Toilet: A toilet that uses gravity to move water from the tank to the bowl during flushing.
- Grounding: Connecting pipes or appliances to the ground to prevent electrical shock.
Go To Top
H
- Hose Bibb: An outdoor faucet or valve with a threaded spout for attaching a hose.
- Hydrojetting: A method of cleaning pipes using high-pressure water to remove debris and blockages.
- Heat Exchanger: A device that transfers heat between fluids in a plumbing or heating system.
- Hanger Strap: Metal straps used to support and secure pipes to a structure.
- Hard Water: Water with a high mineral content, often containing calcium and magnesium.
- Heat Tape: Electrically powered tape used to prevent pipes from freezing.
- Hub: A part of a pipe or fitting into which the end of another pipe fits.
- Horizontal Branch: A drainage pipe that runs horizontally and connects to the main soil stack.
- Hydronic Heating: A heating system that uses hot water to heat a space.
- High-Efficiency Toilet (HET): A toilet designed to use less water per flush while maintaining effective performance.
- Hydrostatic Pressure: The pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium due to the force of gravity.
- Hot Water Recirculation System: A system that circulates hot water to reduce the time it takes to get hot water at the tap.
- Hose Clamp: A device used to attach and seal a hose onto a fitting.
Go To Top
I
- Inlet Valve: A valve that controls the flow of water into a tank or appliance.
- Insulation: Material used to prevent heat loss or gain in pipes and water heaters.
- Indirect Water Heater: A water heating system that uses a heat exchanger to transfer heat from another source.
- In-Line Trap: A trap installed in a straight line rather than a traditional U or S shape.
- Iron Pipe Size (IPS): A standardized pipe sizing system used for various pipe materials.
- Inversion Layer: A layer of air in a vent or chimney that prevents the escape of gases.
- Infiltration: The unintended entry of water into a sewer system through cracks or leaks.
- Isolation Valve: A valve used to shut off the flow of water to a specific fixture or area.
- Impeller: A rotating component in a pump that moves fluid by converting rotational energy into kinetic energy.
- Inline Water Filter: A device installed in a water line to remove impurities and improve water quality.
- Inlet: The point at which water enters a plumbing system.
- Irrigation System: A system for supplying water to plants and landscapes.
- Injection Well: A well used for injecting fluids into the ground, often part of wastewater disposal systems.
Go To Top
J
- Jet Pump: A pump that moves water by creating a high-velocity stream of water or other fluid.
- Junction Box: A protective enclosure for electrical connections in a plumbing or heating system.
- Jacuzzi: A brand name often used to refer to a whirlpool bath or hot tub.
- Joint Compound: A substance used to create a watertight seal between threaded pipe connections.
- J-Hook: A device used to support and secure pipes or conduit to a wall or ceiling.
- Jetter: A high-pressure water system used for cleaning and clearing blockages in pipes.
- Junction: The point where two or more pipes or conduits meet.
- Jackhammer: A tool used for breaking or drilling through hard surfaces, often during plumbing repairs.
- Jet Flush Toilet: A toilet that uses a powerful jet of water for flushing.
- Jumper Cable: A cable used to connect two pieces of metal to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Jubilee Clip: A type of hose clamp with a worm gear mechanism for securing hoses.
- Joist: A horizontal supporting member in a structure, often used for attaching pipes.
- Jockey Pump: A small pump used to maintain pressure in a fire protection system.
Go To Top
K
- Kink: A sharp twist or bend in a pipe that restricts or blocks the flow of water.
- Knockout Plug: A removable plug used to close openings in electrical boxes or plumbing fixtures.
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): A unit of electrical energy consumption.
- Kitchen Sink Trap: A trap specifically designed for kitchen sinks to prevent foul odors and gases.
- Kitec Plumbing System: A type of plumbing system using a multilayer composite pipe.
- Key Stop Valve: A shut-off valve with a small key for turning on or off water to a specific fixture.
- Kohler: A well-known brand of plumbing fixtures and products.
- Kerf: A groove or notch made by cutting or sawing, often used in woodworking for pipe installations.
- Knee Wall: A short wall that supports a countertop or separates spaces in a room.
- Kilopascal (kPa): A unit of pressure used in plumbing systems.
- Knockout Box: An electrical box with perforated openings that can be removed for wiring.
- Kick Plate: A protective plate installed at the base of a fixture or cabinet.
- KWH Meter: An electrical meter that measures the consumption of kilowatt-hours.
Go To Top
L
- Lift Station: A pump station that raises sewage or wastewater to a higher elevation for proper disposal.
- Lavatory: Another term for a bathroom sink or basin.
- Lead-Free: Materials or products that do not contain lead, commonly used in plumbing to meet safety standards.
- Leach Field: A system of underground pipes or chambers for the disposal of liquid waste.
- Low-Flow Fixture: Plumbing fixtures designed to use less water, promoting water conservation.
- Lateral Line: The underground pipes that connect individual plumbing fixtures to the main sewer line.
- Lug Valve: A type of valve with threaded lugs on the body for easy installation.
- Leak Detector: A device or substance used to identify and locate leaks in a plumbing system.
- Lime Scale: The buildup of mineral deposits, primarily calcium carbonate, in pipes and appliances.
- Loop Vent: A vent pipe that loops back into the drain line, providing a path for air to enter and prevent siphoning.
- Locknut: A nut used to secure and tighten a plumbing fitting or connection.
- Low-Pressure System: A plumbing system with lower water pressure than the standard.
- Lateral Connection: The point where a service line connects to a main sewer line.
Go To Top
M
- Manifold: A central distribution point that connects multiple pipes or tubes.
- Mixer Tap: A faucet that blends hot and cold water to achieve a desired temperature.
- Mapp Gas: A type of fuel used in plumbing torches for soldering and brazing.
- Macerator Pump: A pump that breaks down waste into smaller particles for easier disposal.
- Municipal Water: Water supplied by a city or local government.
- Magnetic Water Conditioner: A device that uses magnets to alter the properties of water, reducing scale buildup.
- Malleable Iron: A type of iron used in plumbing fittings, known for its flexibility and strength.
- Manhole: An access point to a sewer or storm drain, typically covered with a removable lid.
- Metal Stud: A framing material used in construction that can accommodate plumbing pipes.
- Metering Faucet: A faucet that dispenses a predetermined amount of water to promote water conservation.
- Multiport Valve: A valve used in pool and water treatment systems to control the flow of water.
- Macerating Toilet: A toilet with a built-in macerator pump for waste disposal in locations with limited plumbing access.
- Molded Countertop: A countertop with a built-in sink, often made from a single molded piece.
Go To Top
N
- Nipple: A short, threaded pipe used to connect other fittings or pipes.
- NPT (National Pipe Thread): A standard thread used in the United States for pipes and fittings.
- Non-Potable Water: Water that is not suitable for drinking, often used for irrigation or industrial purposes.
- Nailing Plate: A protective plate installed over pipes to prevent damage from nails or screws during construction.
- Neutralization Tank: A tank used to neutralize acidic or alkaline wastewater before disposal.
- No-Hub Coupling: A flexible coupling used to connect pipes without using hubs or flanges.
- Non-Return Valve: A valve that allows water to flow in one direction only.
- Nipple Extractor: A tool used for removing threaded pipes or nipples.
- Nest Thermostat: A smart thermostat that can control heating and cooling systems in homes.
- Nominal Size: The approximate size of a pipe, often different from its actual dimensions.
- Non-Contact Voltage Tester: A tool used to detect the presence of electrical voltage without direct contact.
- Non-Pressurized System: A plumbing system that operates at atmospheric pressure.
- Nitrification: The biological process of converting ammonia in wastewater into nitrate.
G
Read the full article
0 notes