#cloud and data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Master Cloud Computing with Expert Training

Enhance your skills with Cloud Computing Training at African eDevelopment Resource Centre. Gain hands-on experience in cloud architecture, security, and deployment. Learn from industry experts and stay ahead in the digital era. Enroll now and boost your career with cutting-edge cloud technology. Visit us at African eDevelopment Resource Centre. Learn More: https://africanedevelopment.hashnode.dev/empowering-africas-future-the-need-for-data-training-and-certification-for-sustainable-development
#cloud and data#cloud computing training#data protection and security training#data protection and security courses#data training and certification
0 notes
Text

406 notes
·
View notes
Text


elle n vlad 2025
#thought i lost these 2 forever#3 months ago i lost not only my mods folder but my tray files as well...nearly killed me tbh#but then I got these two back n im not so sad abt it anymore :)#my build folder rip 2019-2024 will haunt me for a while#im also getting this wierd bug where my game will CTD as soon as I add ANY new cc with “game data is corrupt or missing”#so i go back n delete random pieces of cc and it will load fine again but the thing is the cc i deleted isn't the cause of the crash#like I added some remussiron eye cc and it crashes I take it out and it runs put it back in it crashes#but if i add remussirion eye cc back AND delete a random hair it will run fine#so my mod folder is an orobors eating itself atm#maybe its bc windows 11 for some god forsaken reason puts the document folder in your one drive which is uploaded to a cloud service u#need to pay for n well one day i will kill whoever was responsible for that#my sims#vladislaus straud#elle de vampiro
392 notes
·
View notes
Text
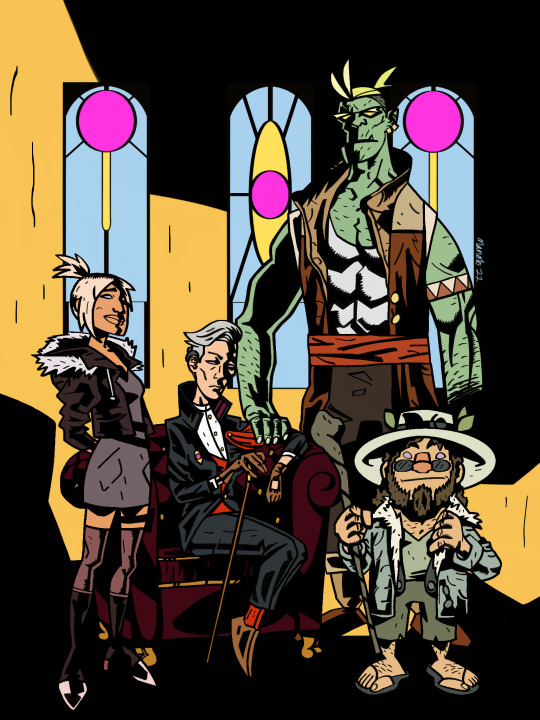
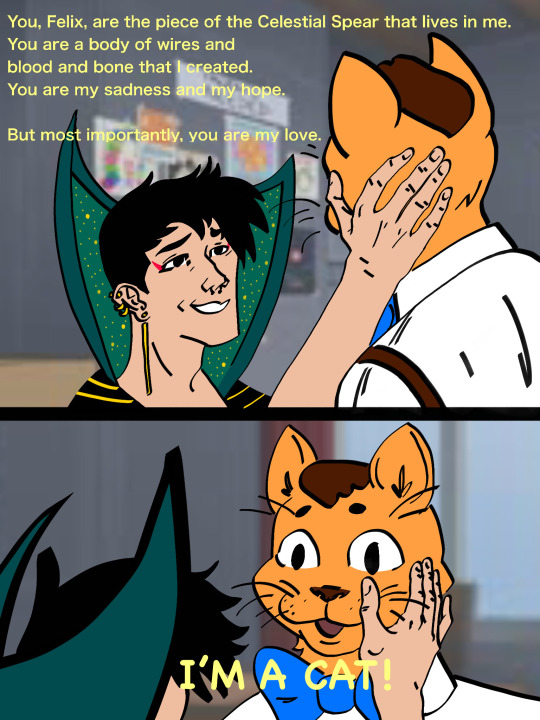




Reuploading some Drawtectives fanart for season 3 HYPE
Edit: the most important one

Another edit: This one was traced from a Mike Mignola strip
#old posts hastily deleted with third party AI data mining announcement🙃#munohlow art#drawfee#drawfee fanart#drawtectives#drawtectives fanart#celestial spear#murder on crescent hill#jancy drawtectives#jancy true#york rogdul#drawtectives york#drawtectives rosé#grenda highforge#grendan highforge#drawtectives grendan#drawtectives grandma#eugene finch#drawtectives eugene#felix drawtectives#lotta justice#Harper justice#my art#digital art#digital painting#butt cloud
573 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bump 'n' Jump (NES) (1988)
#nintendo#nes#famicom#data east#video games#gaming#games#retro gaming#retro games#arcade#aesthetic#backgrounds#game backgrounds#clouds#sky#sunset#pixelart#pixelaesthetic
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
The flotsam and jetsam of our digital queries and transactions, the flurry of electrons flitting about, warm the medium of air. Heat is the waste product of computation, and if left unchecked, it becomes a foil to the workings of digital civilization. Heat must therefore be relentlessly abated to keep the engine of the digital thrumming in a constant state, 24 hours a day, every day. To quell this thermodynamic threat, data centers overwhelmingly rely on air conditioning, a mechanical process that refrigerates the gaseous medium of air, so that it can displace or lift perilous heat away from computers. Today, power-hungry computer room air conditioners (CRACs) or computer room air handlers (CRAHs) are staples of even the most advanced data centers. In North America, most data centers draw power from “dirty” electricity grids, especially in Virginia’s “data center alley,” the site of 70 percent of the world’s internet traffic in 2019. To cool, the Cloud burns carbon, what Jeffrey Moro calls an “elemental irony.” In most data centers today, cooling accounts for greater than 40 percent of electricity usage.
[...]
The Cloud now has a greater carbon footprint than the airline industry. A single data center can consume the equivalent electricity of 50,000 homes. At 200 terawatt hours (TWh) annually, data centers collectively devour more energy than some nation-states. Today, the electricity utilized by data centers accounts for 0.3 percent of overall carbon emissions, and if we extend our accounting to include networked devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets, the total shifts to 2 percent of global carbon emissions. Why so much energy? Beyond cooling, the energy requirements of data centers are vast. To meet the pledge to customers that their data and cloud services will be available anytime, anywhere, data centers are designed to be hyper-redundant: If one system fails, another is ready to take its place at a moment’s notice, to prevent a disruption in user experiences. Like Tom’s air conditioners idling in a low-power state, ready to rev up when things get too hot, the data center is a Russian doll of redundancies: redundant power systems like diesel generators, redundant servers ready to take over computational processes should others become unexpectedly unavailable, and so forth. In some cases, only 6 to 12 percent of energy consumed is devoted to active computational processes. The remainder is allocated to cooling and maintaining chains upon chains of redundant fail-safes to prevent costly downtime.
520 notes
·
View notes
Text
webfishing with my 2 worst enemies

#im so mad all my progress and save data got NUKED#BECAUSE WEBFISHING DOESNT DO CLOUD SAVE#whatever. starting from square 1 i guess
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cloudburst

Enshittification isn’t inevitable: under different conditions and constraints, the old, good internet could have given way to a new, good internet. Enshittification is the result of specific policy choices: encouraging monopolies; enabling high-speed, digital shell games; and blocking interoperability.
First we allowed companies to buy up their competitors. Google is the shining example here: having made one good product (search), they then fielded an essentially unbroken string of in-house flops, but it didn’t matter, because they were able to buy their way to glory: video, mobile, ad-tech, server management, docs, navigation…They’re not Willy Wonka’s idea factory, they’re Rich Uncle Pennybags, making up for their lack of invention by buying out everyone else:
https://locusmag.com/2022/03/cory-doctorow-vertically-challenged/
But this acquisition-fueled growth isn’t unique to tech. Every administration since Reagan (but not Biden! more on this later) has chipped away at antitrust enforcement, so that every sector has undergone an orgy of mergers, from athletic shoes to sea freight, eyeglasses to pro wrestling:
https://www.whitehouse.gov/cea/written-materials/2021/07/09/the-importance-of-competition-for-the-american-economy/
But tech is different, because digital is flexible in a way that analog can never be. Tech companies can “twiddle” the back-ends of their clouds to change the rules of the business from moment to moment, in a high-speed shell-game that can make it impossible to know what kind of deal you’re getting:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/27/knob-jockeys/#bros-be-twiddlin
To make things worse, users are banned from twiddling. The thicket of rules we call IP ensure that twiddling is only done against users, never for them. Reverse-engineering, scraping, bots — these can all be blocked with legal threats and suits and even criminal sanctions, even if they’re being done for legitimate purposes:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Enhittification isn’t inevitable but if we let companies buy all their competitors, if we let them twiddle us with every hour that God sends, if we make it illegal to twiddle back in self-defense, we will get twiddled to death. When a company can operate without the discipline of competition, nor of privacy law, nor of labor law, nor of fair trading law, with the US government standing by to punish any rival who alters the logic of their service, then enshittification is the utterly foreseeable outcome.
To understand how our technology gets distorted by these policy choices, consider “The Cloud.” Once, “the cloud” was just a white-board glyph, a way to show that some part of a software’s logic would touch some commodified, fungible, interchangeable appendage of the internet. Today, “The Cloud�� is a flashing warning sign, the harbinger of enshittification.
When your image-editing tools live on your computer, your files are yours. But once Adobe moves your software to The Cloud, your critical, labor-intensive, unrecreatable images are purely contingent. At at time, without notice, Adobe can twiddle the back end and literally steal the colors out of your own files:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/28/fade-to-black/#trust-the-process
The finance sector loves The Cloud. Add “The Cloud” to a product and profits (money you get for selling something) can turn into rents (money you get for owning something). Profits can be eroded by competition, but rents are evergreen:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/24/rent-to-pwn/#kitt-is-a-demon
No wonder The Cloud has seeped into every corner of our lives. Remember your first iPod? Adding music to it was trivial: double click any music file to import it into iTunes, then plug in your iPod and presto, synched! Today, even sophisticated technology users struggle to “side load” files onto their mobile devices. Instead, the mobile duopoly — Apple and Google, who bought their way to mobile glory and have converged on the same rent-seeking business practices, down to the percentages they charge — want you to get your files from The Cloud, via their apps. This isn’t for technological reasons, it’s a business imperative: 30% of every transaction that involves an app gets creamed off by either Apple or Google in pure rents:
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/doctorow/red-team-blues-another-audiobook-that-amazon-wont-sell/posts/3788112
And yet, The Cloud is undeniably useful. Having your files synch across multiple devices, including your collaborators’ devices, with built-in tools for resolving conflicting changes, is amazing. Indeed, this feat is the holy grail of networked tools, because it’s how programmers write all the software we use, including software in The Cloud.
If you want to know how good a tool can be, just look at the tools that toolsmiths use. With “source control” — the software programmers use to collaboratively write software — we get a very different vision of how The Cloud could operate. Indeed, modern source control doesn’t use The Cloud at all. Programmers’ workflow doesn’t break if they can’t access the internet, and if the company that provides their source control servers goes away, it’s simplicity itself to move onto another server provider.
This isn’t The Cloud, it’s just “the cloud” — that whiteboard glyph from the days of the old, good internet — freely interchangeable, eminently fungible, disposable and replaceable. For a tool like git, Github is just one possible synchronization point among many, all of which have a workflow whereby programmers’ computers automatically make local copies of all relevant data and periodically lob it back up to one or more servers, resolving conflicting edits through a process that is also largely automated.
There’s a name for this model: it’s called “Local First” computing, which is computing that starts from the presumption that the user and their device is the most important element of the system. Networked servers are dumb pipes and dumb storage, a nice-to-have that fails gracefully when it’s not available.
The data structures of source-code are among the most complicated formats we have; if we can do this for code, we can do it for spreadsheets, word-processing files, slide-decks, even edit-decision-lists for video and audio projects. If local-first computing can work for programmers writing code, it can work for the programs those programmers write.
Local-first computing is experiencing a renaissance. Writing for Wired, Gregory Barber traces the history of the movement, starting with the French computer scientist Marc Shapiro, who helped develop the theory of “Conflict-Free Replicated Data” — a way to synchronize data after multiple people edit it — two decades ago:
https://www.wired.com/story/the-cloud-is-a-prison-can-the-local-first-software-movement-set-us-free/
Shapiro and his co-author Nuno Preguiça envisioned CFRD as the building block of a new generation of P2P collaboration tools that weren’t exactly serverless, but which also didn’t rely on servers as the lynchpin of their operation. They published a technical paper that, while exiting, was largely drowned out by the release of GoogleDocs (based on technology built by a company that Google bought, not something Google made in-house).
Shapiro and Preguiça’s work got fresh interest with the 2019 publication of “Local-First Software: You Own Your Data, in spite of the Cloud,” a viral whitepaper-cum-manifesto from a quartet of computer scientists associated with Cambridge University and Ink and Switch, a self-described “industrial research lab”:
https://www.inkandswitch.com/local-first/static/local-first.pdf
The paper describes how its authors — Martin Kleppmann, Adam Wiggins, Peter van Hardenberg and Mark McGranaghan — prototyped and tested a bunch of simple local-first collaboration tools built on CFRD algorithms, with the goal of “network optional…seamless collaboration.” The results are impressive, if nascent. Conflicting edits were simpler to resolve than the authors anticipated, and users found URLs to be a good, intuitive way of sharing documents. The biggest hurdles are relatively minor, like managing large amounts of change-data associated with shared files.
Just as importantly, the paper makes the case for why you’d want to switch to local-first computing. The Cloud is not reliable. Companies like Evernote don’t last forever — they can disappear in an eyeblink, and take your data with them:
https://www.theverge.com/2023/7/9/23789012/evernote-layoff-us-staff-bending-spoons-note-taking-app
Google isn’t likely to disappear any time soon, but Google is a graduate of the Darth Vader MBA program (“I have altered the deal, pray I don’t alter it any further”) and notorious for shuttering its products, even beloved ones like Google Reader:
https://www.theverge.com/23778253/google-reader-death-2013-rss-social
And while the authors don’t mention it, Google is also prone to simply kicking people off all its services, costing them their phone numbers, email addresses, photos, document archives and more:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/22/allopathic-risk/#snitches-get-stitches
There is enormous enthusiasm among developers for local-first application design, which is only natural. After all, companies that use The Cloud go to great lengths to make it just “the cloud,” using containerization to simplify hopping from one cloud provider to another in a bid to stave off lock-in from their cloud providers and the enshittification that inevitably follows.
The nimbleness of containerization acts as a disciplining force on cloud providers when they deal with their business customers: disciplined by the threat of losing money, cloud companies are incentivized to treat those customers better. The companies we deal with as end-users know exactly how bad it gets when a tech company can impose high switching costs on you and then turn the screws until things are almost-but-not-quite so bad that you bolt for the doors. They devote fantastic effort to making sure that never happens to them — and that they can always do that to you.
Interoperability — the ability to leave one service for another — is technology’s secret weapon, the thing that ensures that users can turn The Cloud into “the cloud,” a humble whiteboard glyph that you can erase and redraw whenever it suits you. It’s the greatest hedge we have against enshittification, so small wonder that Big Tech has spent decades using interop to clobber their competitors, and lobbying to make it illegal to use interop against them:
https://locusmag.com/2019/01/cory-doctorow-disruption-for-thee-but-not-for-me/
Getting interop back is a hard slog, but it’s also our best shot at creating a new, good internet that lives up the promise of the old, good internet. In my next book, The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of Computation (Verso Books, Sept 5), I set out a program fro disenshittifying the internet:
https://www.versobooks.com/products/3035-the-internet-con
The book is up for pre-order on Kickstarter now, along with an independent, DRM-free audiobooks (DRM-free media is the content-layer equivalent of containerized services — you can move them into or out of any app you want):
http://seizethemeansofcomputation.org
Meanwhile, Lina Khan, the FTC and the DoJ Antitrust Division are taking steps to halt the economic side of enshittification, publishing new merger guidelines that will ban the kind of anticompetitive merger that let Big Tech buy its way to glory:
https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2023/07/biden-administration-corporate-merger-antitrust-guidelines/674779/
The internet doesn’t have to be enshittified, and it’s not too late to disenshittify it. Indeed — the same forces that enshittified the internet — monopoly mergers, a privacy and labor free-for-all, prohibitions on user-side twiddling — have enshittified everything from cars to powered wheelchairs. Not only should we fight enshittification — we must.

Back my anti-enshittification Kickstarter here!

If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad- free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/03/there-is-no-cloud/#only-other-peoples-computers

Image: Drahtlos (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Motherboard_Intel_386.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
—
cdsessums (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Monsoon_Season_Flagstaff_AZ_clouds_storm.jpg
CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#web3#darth vader mba#conflict-free replicated data#CRDT#computer science#saas#Mark McGranaghan#Adam Wiggins#evernote#git#local-first computing#the cloud#cloud computing#enshittification#technological self-determination#Martin Kleppmann#Peter van Hardenberg
889 notes
·
View notes
Text
Geneva-based Infomaniak has been recovering 100 per cent of the electricity it uses since November 2024.
The recycled power will be able to fuel the centralised heating network in the Canton of Geneva and benefit around 6,000 households.
The centre is currently operating at 25 per cent of its potential capacity. It aims to reach full capacity by 2028.
Swiss data centre leads the way for a greener cloud industry
The data centre hopes to point to a greener way of operating in the electricity-heavy cloud industry.
"In the real world, data centres convert electricity into heat. With the exponential growth of the cloud, this energy is currently being released into the atmosphere and wasted,” Boris Siegenthaler, Infomaniak's Founder and Chief Strategy Officer, told news site FinanzNachrichten.
“There is an urgent need to upgrade this way of doing things, to connect these infrastructures to heating networks and adapt building standards."
Infomaniak has received several awards for the energy efficiency of its complexes, which operate without air conditioning - a rarity for hot data centres.
The company also builds infrastructure underground so that it doesn’t have an impact on the environment.
Swiss data centre recycles heat for homes
At Infomaniak, all the electricity that powers equipment like servers, inverters and ventilation is converted into heat at a temperature of 40 to 45C.
This is then channelled to an air/water exchanger which filters it into a hot water circuit. Heat pumps are used to increase its temperature to 67C in summer and 85C in winter.
How many homes will be heated by the data centre?
When the centre is operating at full capacity, it will supply Geneva’s heating network with 1.7 megawatts, the amount needed for 6,000 households per year or for 20,000 people to take a 5-minute shower every day.
This means the Canton of Geneva can save 3,600 tonnes of CO2 equivalent (tCO2eq) of natural gas every year, or 5,500 tCO2eq of pellets annually.
The system in place at Infomaniak’s data centre is free to be reproduced by other companies. There is a technical guide available explaining how to replicate the model and a summary for policymakers that advises how to improve design regulations and the sustainability of data centres.
#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#climate change#climate crisis#switzerland#geneva#Infomaniak#cloud storage#cloud data#carbon emissions#heat pumps
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
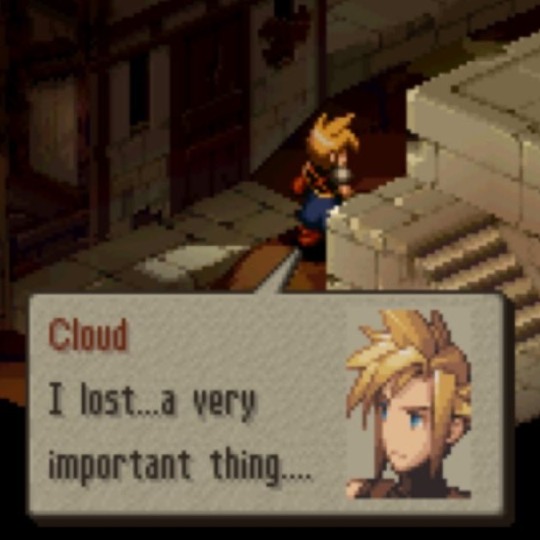
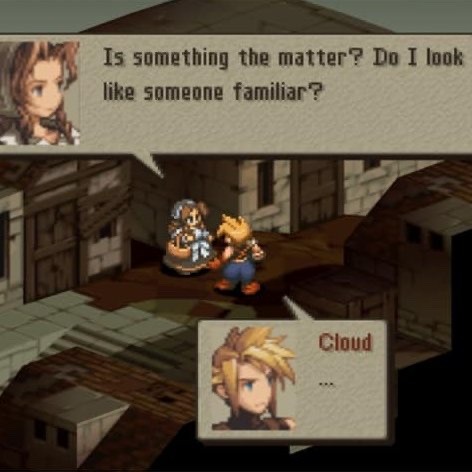
soriku kh4 reunion angst thoughts
#ff#clerith#kh4#soriku#last reblog prompted me to bring this here#cloud losing his taisetsu na hito 🤝 riku losing his taisetsu na hito#both continuing to look for them and hopefully both getting them back in future games#both of them connecting in dreamlike states#and Cloud and Sora having sky themed names while Aerith and Riku have earth themed names#hearing Aerith be described as Cloud’s taisetsu no hito made me scream in soriku#also I love how in the Riku episode in remind Aerith is beside him during all the cutscenes#cause I was getting screenshots of Sora and Cloud and Riku and Aerith together to make a post and I noticed they were always close#earth themed second protagonist solidarity + them being friends is neat I think#and regarding Sora and Cloud my fave scene with them is in coded when Cloud and Herc praise data Sora and he blushes and panics ndjsjs#its got nothing to do with this parallel but it’s iconic to me djjsjs#Sora’s type is strong men
106 notes
·
View notes
Text

Did You Know: Scientists will analyze data from the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope in the cloud? (For most missions, research often happens on astronomers’ personal computers.) Claire Murray, a scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute, and her colleague Manuel Sanchez, a cloud engineer, share how this space, known as the Roman Research Nexus, builds on previous missions’ online platforms:
Claire Murray: Roman has an extremely wide field of view and a fast survey speed. Those two facts mean the data volume is going to be orders of magnitude larger than what we're used to. We will enable users to interact with this gigantic dataset in the cloud. They will be able to log in to the platform and perform the same types of analysis they would normally do on their local machines.
Manuel Sanchez: The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission’s science platform, known as the Timeseries Integrated Knowledge Engine (TIKE), was our first try at introducing users to this type of workflow on the cloud. With TIKE, we have been learning researchers’ usage patterns. We can track the performance and metrics, which is helping us design the appropriate environment and capabilities for Roman. Our experience with other science platforms also helps us save time from a coding perspective. The code is basically the same for our platforms, but we can customize it as needed.
Read the full interview: https://www.stsci.edu/contents/annual-reports/2024/where-data-and-people-meet
#space#astronomy#science#stsci#universe#nasa#nasaroman#roman science#roman space telescope#data#cloud engineering#big data
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Act-Fancer: Cybernetick Hyper Weapon (arcade) (1989)
#act fancer#data east#80s games#videogames#gaming#games#retrogaming#retrogames#arcade#aesthetic#backgrounds#gamebackgrounds#clouds#skyline#pixelart#pixelaesthetic#VGArt
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

135 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm gonna buy a new Iphone soon, but I don't know which color to pick ;-;

#like i really don't know#mind you i am upgrading from a 11 pro to a 16 pro#with 1TB i am sick of getting short on storage and i refuse to pay monthly for cloud data#mistress blabbling#like white is really nice and clean#but i am afraid it will get dirty quick
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Midnight Resistance (Genesis) (1989)
#midnight resistance#data east#genesis#sega genesis#sega mega drive#mega drive#videogames#gaming#games#retrogaming#retrogames#arcade#aesthetic#backgrounds#gamebackgrounds#clouds#sky#pixelart#pixelaesthetic#VGArt#sunset
31 notes
·
View notes
Note
⏮️ - Flashback for Dreamy Cloud?
✨ Outfit Prompts!
⏮️ - Flashback
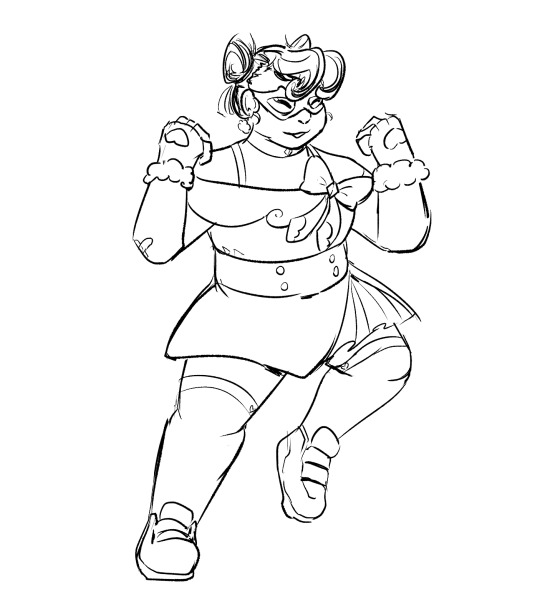

baby's first magical girl outfit that she put together all by herself (this was before her aunt found out and she got help from her to put together her current outfit)
13 notes
·
View notes