#csma
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Diretór CSMA Ameasa Lori Governu bá Tribunál, Ministru Samuél Marçal Dehan Ne’e Direitu
Hatutan.com, (06 Fevereiru 2024), Díli—Ministru Obras Publika (MOP), Samuél Marçal hateten Diretór Koléjiu São Miguel Arcanjo (CSMA, sigla portugés), Armindo Krisna Caeteno, iha direitu tomak atu lori Governu bá Ministériu Públiku ka Tribunál. Continue reading Diretór CSMA Ameasa Lori Governu bá Tribunál, Ministru Samuél Marçal Dehan Ne’e Direitu

View On WordPress
#Diretór CSMA Ameasa Lori Governu bá Tribunál#Koléjiu São Miguel Arcanjo#Ministru Samuél Marçal Dehan Ne’e Direitu
0 notes
Text

Theoretical Foundations to Nobel Glory: John Hopfield’s AI Impact
The story of John Hopfield’s contributions to artificial intelligence is a remarkable journey from theoretical insights to practical applications, culminating in the prestigious Nobel Prize in Physics. His work laid the groundwork for the modern AI revolution, and today’s advanced capabilities are a testament to the power of his foundational ideas.
In the early 1980s, Hopfield’s theoretical research introduced the concept of neural networks with associative memory, a paradigm-shifting idea. His 1982 paper presented the Hopfield network, a novel neural network architecture, which could store and recall patterns, mimicking the brain’s memory and pattern recognition abilities. This energy-based model was a significant departure from existing theories, providing a new direction for AI research.A year later, at the 1983 Meeting of the American Institute of Physics, Hopfield shared his vision. This talk played a pivotal role in disseminating his ideas, explaining how neural networks could revolutionize computing. He described the Hopfield network’s unique capabilities, igniting interest and inspiring future research.
Over the subsequent decades, Hopfield’s theoretical framework blossomed into a full-fledged AI revolution. Researchers built upon his concepts, leading to remarkable advancements. Deep learning architectures, such as Convolutional Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks, emerged, enabling breakthroughs in image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and more.
The evolution of Hopfield’s ideas has resulted in today’s AI capabilities, which are nothing short of extraordinary. Computer vision systems can interpret complex visual data, natural language models generate human-like text, and AI-powered robots perform intricate tasks. Pattern recognition, a core concept from Hopfield’s work, is now applied in facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, and data analysis.
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2024 honored Hopfield’s pioneering contributions, recognizing the transformative impact of his ideas on society. This award celebrated the journey from theoretical neural networks to the practical applications that have revolutionized industries and daily life. It underscored the importance of foundational research in driving technological advancements.
Today, AI continues to evolve, with ongoing research pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Explainable AI, quantum machine learning, and brain-computer interfaces are just a few areas of exploration. These advancements build upon the strong foundation laid by pioneers like Hopfield, leading to more sophisticated and beneficial AI technologies.
John J. Hopfield: Collective Properties of Neuronal Networks (Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, 1983)
youtube
Hopfield Networks (Artem Kirsanov, July 2024)
youtube
Boltzman machine (Artem Kirsanov, August 2024)
youtube
Dimitry Krotov: Modern Hopfield Networks for Novel Transformer Architectures (Harvard CSMA, New Technologies in Mathematics Seminar, May 2023)
youtube
Dr. Thomas Dietterich: The Future of Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Computer Vision (Craig Smith, Eye on A.I., October 2024)
youtube
Friday, October 11, 2024
#neural networks#hopfield networks#nobel prize#ai evolution#talk#ai assisted writing#machine art#Youtube#presentation#interview
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A primer on MESH networks and MESH cyber security - CyberTalk
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/a-primer-on-mesh-networks-and-mesh-cyber-security-cybertalk/
A primer on MESH networks and MESH cyber security - CyberTalk


Gergana Kungalova is a Security Engineer for Check Point in Bulgaria. She started her journey in the Cyber Security field as Network Security Support Engineer, working with customers across the globe. In her current role, she is connecting people and processes with technology by matching the clients’ business needs with security solutions and services.
In this amazing expert interview, Gergana Kungalova explains why MESH networks can be more advantageous than traditional networks, she addresses common misperceptions around MESH, and then highlights MESH-specific cyber security measures. Don’t miss this!
What is the core idea behind MESH networks?
The MESH network provides ultimate connectivity between nodes like users, servers/applications, and network components. The main driver for this architecture is to provide reliable access that is not dependent on a single device or route.
Why might an organization choose to have a MESH network over traditional network architecture?
The traditional network architecture was suitable for organizations when they had well-defined perimeters and point-to-point connections. All services were hosted within the data centers and users were working strictly from the office. Nowadays, the demand for mobility and scalability has completely changed the picture. We have services that are hosted in the cloud and/or in the data center. At the same time, our users are roaming and should access these services from everywhere. The new connectivity requirements have increased the complexity of managing networks and security to an extreme degree. Many organizations are choosing the MESH networks as an enabler for flexible and scalable infrastructure. It allows them to reduce the management overhead and cut costs.
What are some common misperceptions about MESH that we should debunk for readers, if any?
The most common misperception is that the MESH networks are more secure. They are more agile and resilient, but they introduce new dynamics in the monitoring and the maintenance which may pose risk of security breach. The nature of MESH networks may increase the amount of time required for identifying breaches, determining which nodes have been affected and what the business impact looks like. Also, the root cause analysis is more complex and time consuming.
It is critical to implement cyber security measures at every point of the infrastructure, in the early stages. The security must be multi-layered and part of the planning phase. A cyber security platform that is consolidated and focused on prevention is the best approach to ensure business continuity within organizations with MESH networks.
Examples of typical cyber security threats seen on MESH networks?
The cyber security threats seen on MESH networks are the same as the threats seen on the traditional networks – vulnerability exploits, phishing attacks, account takeover…etc. The only difference is how they are executed.
How does the decentralized nature of MESH networks impact the design and implementation of robust cyber security measures?
The dynamic nature of MESH networks requires multi-layered enforcement of cyber security. The best-of-breed method is bringing more complexity then benefits – multiple management consoles, no full visibility on security posture, lack of expertise…etc. To address these challenges, we should talk about the concept of Cyber Security Mesh Architecture (CSMA)*.
The CSMA approach focuses on platform security that is collaborative across all components in the customer’s environment and it’s built on the following pillars: Security Analytics and Intelligence, Distributed Identity Fabric, Consolidated Privacy and Posture Management, and Consolidated Dashboards. It means that all security components talk with each other, share intelligence and have one single pane of glass for management. The efficient implementation of CSMA has to be enforced based on user identity and zero trust principals, not on network-based access.
*“CSMA is a concept developed by Gartner to help companies move past siloed security to a more collaborative and flexible approach to security. CSMA is designed to make security more composable and scalable by modularizing security functions and enabling them to interoperate through a set of supportive layers. By making security more cohesive and collaborative, CSMA enables an organization to achieve better security with fewer resources.” — Quoted from Check Point’s What is Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA)?
Given the potential for node compromise in MESH networks, what strategies can be employed to enhance the security posture of individual nodes, as to prevent cascading security issues across the network?
In case of compromise, the time spent for identification and mitigation is what really matters, as does determining how big the impact on the business will be. The prevention first methodology has to be incorporated into the cyber security strategy. From my experience, it does not matter as to how many security measures are in place – they have to be configured in prevention mode in order to block the attack. Of course, to cover all possible threat vectors, we should have in place strong encryption, zero-day prevention, anti-phishing, anti-ransomware, vulnerability, and patch management.
What other kinds of tools or technologies can cyber leaders use to monitor for suspicious activities within a MESH network?
Cyber leaders can benefit from integrated AI engines:
AI integrated within the prevention engines can reduce the time for mitigation, improve catch rate and discover attacks chains in next to no time.
AI integrated in the monitoring can improve behavior analysis and discover anomalies, provide sophisticated reports, and reduce the time for root cause analysis.
An example of a technology that combines both is MDR/MPR (Managed Detection/Prevention and Respond). It can provide a deeper overview of what is going on in the environment and help to further decrease the reaction time. Basically, it’s providing automation and optimization for how the SOC teams are working with data and dangerous threats.
Is there anything else that you would like to share with the Cyber Talk CxO audience?
Cyber security requires a continuous process of risk management and effectiveness optimization. Building robust architecture requires approach that is collaborative, redistributed within all parts of the environment and focused on prevention.
Stay (cyber) safe 🙂
#account takeover#agile#ai#AI engines#amazing#Analysis#Analytics#applications#approach#architecture#automation#Behavior#breach#Building#Bulgaria#Business#business continuity#Check Point#Cloud#collaborative#Companies#complexity#connectivity#consolidated#continuous#course#csma#CXO#cyber#cyber security
1 note
·
View note
Text
ESIC Strengthens Healthcare Access for Pensioners Through Hospital Tie-ups
📅 Notification Date: 11th June 2025 📌 Issued By: Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC)
The Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) has taken a significant step to enhance the quality and reach of medical care for its pensioner community. In a notification dated 11th June 2025, ESIC has directed all Regional Directors to facilitate tie-up arrangements with premier healthcare institutions including AIIMS, CGHS, CSMA, and other State Government-approved private hospitals.

This initiative is aligned with the broader goal of providing cashless, accessible, and comprehensive healthcare to beneficiaries under the ESIC Pensioners’ Medical Scheme (ESIC-PMS), particularly ensuring availability of tertiary care.
🩺 Key Highlights of the Circular:
Tie-Up with Recognized Hospitals: Regional Directors are required to establish partnerships with AIIMS, CGHS, CSMA-affiliated hospitals, and approved private medical institutions within their jurisdiction.
Comprehensive & Cashless Treatment: Eligible pensioners will receive cashless treatment based on their entitlement, ensuring seamless access to primary, secondary, and tertiary medical services.
Standardized Terms: The terms and conditions for these tie-ups will follow the existing CGHS (Central Government Health Scheme) model, ensuring uniformity and quality in service delivery.
🧓 What This Means for ESIC Pensioners:
The directive aims to remove healthcare access barriers faced by retired ESIC employees. With dedicated tie-ups, pensioners can now expect:
Shorter wait times for treatment
Access to multi-specialty care without financial stress
Standardized quality of healthcare, irrespective of geography
Reduction in paperwork through integrated claim systems
This move by ESIC not only improves healthcare outcomes but also reflects a growing recognition of the need for dignified and equitable post-retirement medical support.
💬 Expert Insight from Sankhla Corporate Services Pvt. Ltd.
At Sankhla Corporate Services Pvt. Ltd., we recognize the importance of such progressive steps by statutory bodies. As specialists in ESIC compliance and advisory services, we assist employers and employees — including retirees — in accessing the full spectrum of ESIC benefits with ease.
Whether it’s registration, contribution management, claim support, or ESIC-PMS facilitation, our experts are here to guide you every step of the way.
📞 Need Help Navigating ESIC Services?
Reach out to Sankhla Corporate Services Pvt. Ltd. for ESIC compliance, employee benefits management, and hassle-free support under the latest ESIC-PMS updates.
📧 Email: [email protected] 🌐 Website: www.sankhlaco.com 📍 Serving clients across India
ESIC-PMS hospital tie-up 2025
ESIC pensioner medical scheme
Cashless healthcare for ESIC retirees
ESIC compliance consultants
AIIMS ESIC tie-up
CGHS hospital ESIC partnership
ESIC tertiary care hospital list
Sankhla Corporate Services ESIC support
Let me know if you’d like this content as a newsletter, carousel post, or client advisory note.
0 notes
Text
ECE/CS 438: Communication Networks Machine Problem 4
This machine problem tests your understanding of the random backoff and medium access in a wired network. 1 The Scenario In this assignment, you will develop a toy simulator that evaluates the performance of simplified CSMA protocols in a wired network. In this toy simulator, start with two nodes only – nodes A and B – and assume each node always has packets to transmit to its counterpart (later…
0 notes
Text
Ve489 Computer Networks Homework Set 4
Answer following questions about random access protocols: What is the vulnerable period for Aloha? How about slotted Aloha? Explain it. What is vulnerable period of CSMA? How can we make sure the performance of CSMA is better than Aloha? Why collision detection (CD) can improve performance of CSMA? Considering the CSMA/CA based DCF in IEEE 802.11, answer the following questions: What is…
0 notes
Text
Great trends in information technology (2024)
Trends in information technology (IT) are continually evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology, changing user needs, and global innovations. As organizations and individuals become increasingly reliant on digital solutions, certain trends are shaping the future of IT. Below are some of the most significant trends currently influencing the industry.
Trends in information technology
AI and ML are trends in information technology that have moved beyond experimental stages to become integral in various applications across industries. Businesses are effectively leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) for tasks such as predictive analytics, natural language processing, image recognition, and autonomous systems.
Chatbots powered by AI are improving customer interactions, while machine learning algorithms are transforming industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing by enabling smarter decision-making processes. Cloud computing continues to dominate the information technology landscape.
Organizations are increasingly adopting trends in information technology such as cloud services to reduce infrastructure costs, enhance scalability, and improve data accessibility. Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies are particularly popular, allowing businesses to use a combination of private and public cloud services.
Platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud remain central to this transformation, while edge computing, processing data closer to the source, gains traction for its efficiency and low latency. With the rise of remote work, digital transformation, and sophisticated cyber threats, cybersecurity is a top priority.
Trends in information technology such as zero-trust architecture, advanced threat detection, and AI-driven security solutions are becoming essential. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA) is yet another emerging effective approach to ensure flexible, scalable, and reliable security systems.
Companies are also focusing on training employees to recognize and mitigate security risks. On the other hand, IoT is expanding rapidly, connecting billions of devices worldwide. Smart homes, industrial IoT (IIoT), and wearable technologies are just a few examples of how this field is changing the way we interact with technology.
Businesses are leveraging trends in information technology such as IoT for real-time data collection and analysis, improving operational efficiency, and developing innovative customer experiences. Challenges like interoperability and security, however, remain critical focus areas. The rollout of 5G networks is set to revolutionize connectivity with faster speeds, lower latency, and enhanced capacity.
This technology enables advancements in areas like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and immersive AR/VR experiences. For businesses, 5G will facilitate better communication and data transfer, supporting technologies like IoT and edge computing. Data is at the core of IT innovation. Companies are investing in big data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, optimize operations, and drive business strategies.
Trends in information technology like data lakes, warehouses, and real-time analytics are helping organizations process and analyze vast volumes of data. The rise of data visualization tools has made it easier to interpret complex sets, empowering non-technical stakeholders to make data-driven decisions.
The shift to remote and hybrid work models has transformed workplace IT requirements. Video conferencing platforms, collaboration tools, and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) are essential for maintaining productivity. Innovations like virtual reality (VR) workspaces and AI-powered collaboration tools are reshaping how teams interact and collaborate in a distributed environment.
While initially associated with cryptocurrency, blockchain technology has found applications in supply chain management, identity verification, and secure transactions. Smart contracts and decentralized finance (DeFi) are other trends in information technology where blockchain is making a significant impact. As businesses look for more transparent and tamper-proof systems, blockchain adoption is expected to grow.
Sustainability is becoming a key consideration in IT development. Companies are investing in energy-efficient technologies, green data centers, and circular IT practices to reduce their environmental footprint. Innovations like AI-driven energy management and eco-friendly hardware design reflect the growing importance of sustainability in the industry.
Although still in its early stages, quantum computing is another one among trends in information technology, holding tremendous promise for solving complex problems that are beyond the capabilities of traditional computers. Fields such as cryptography, materials science, and financial modeling are likely to benefit from breakthroughs in quantum computing.
Tech giants like IBM, Google, and Microsoft are leading the charge in this area. AR and VR technologies are evolving rapidly, finding applications beyond gaming in industries like education, healthcare, and retail. From immersive training programs to virtual property tours, these technologies are enhancing user experiences and providing innovative solutions to real-world challenges.
In an increasingly digital world, personalization is key to engaging users. Trends in information technology are leveraging AI, big data, and real-time analytics to tailor experiences to individual preferences. E-commerce platforms, for example, use recommendation engines to offer personalized shopping experiences, while financial institutions create custom financial advice based on user data.
The trends in information technology are reshaping industries and redefining how we live and work. From AI and cloud computing to IoT and 5G, these advancements offer unparalleled opportunities for innovation and growth. However, they also bring challenges such as cybersecurity threats, ethical considerations, and environmental impact.
Link Article Here
0 notes
Text
Great trends in information technology (2024)
Trends in information technology (IT) are continually evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology, changing user needs, and global innovations. As organizations and individuals become increasingly reliant on digital solutions, certain trends are shaping the future of IT. Below are some of the most significant trends currently influencing the industry.
Trends in information technology
AI and ML are trends in information technology that have moved beyond experimental stages to become integral in various applications across industries. Businesses are effectively leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) for tasks such as predictive analytics, natural language processing, image recognition, and autonomous systems.
Chatbots powered by AI are improving customer interactions, while machine learning algorithms are transforming industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing by enabling smarter decision-making processes. Cloud computing continues to dominate the information technology landscape.
Organizations are increasingly adopting trends in information technology such as cloud services to reduce infrastructure costs, enhance scalability, and improve data accessibility. Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies are particularly popular, allowing businesses to use a combination of private and public cloud services.
Platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud remain central to this transformation, while edge computing, processing data closer to the source, gains traction for its efficiency and low latency. With the rise of remote work, digital transformation, and sophisticated cyber threats, cybersecurity is a top priority.
Trends in information technology such as zero-trust architecture, advanced threat detection, and AI-driven security solutions are becoming essential. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA) is yet another emerging effective approach to ensure flexible, scalable, and reliable security systems.
0 notes
Text
Telecommunication protocols application interaction
Let's look at the basics of transferring information between two application processes in the OSI model.
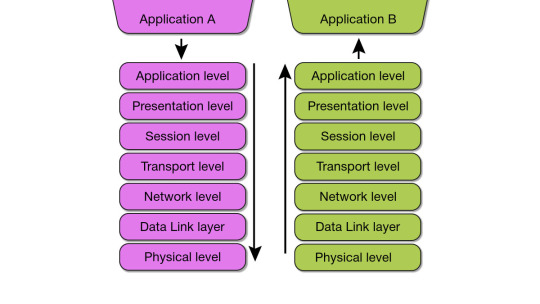
Say an application (in the picture above) needs to access a file service on another computer. It sends a request to the application layer. Based on it, the software generates a standard format message consisting of a data field and a service header. The latter contains a description of actions for the application layer of the other machine to perform, as well as instructions for the adjacent lower layer. The presentation layer, in turn, formats the data according to the instructions received and adds its own header (some protocol implementations also include service data at the end of the message), after which the information is sent to the session layer. This procedure, called encapsulation, is repeated further as data and service information move to the physical layer.
When arriving at the physical layer, i.e., the network, data passes through many other devices (network adapters, hubs, routers, bridges, etc.) and, upon reaching the destination (for example, a SIP phone), undergoes a reverse encapsulation process (right side of the picture).
Data networks can be of two types: local (local area network, LAN) and global (wide area network, WAN). The latter connects any two networks within the globe with dedicated or switched communication channels. Local networks differ in transmission medium, topology, and access control. Depending on the transmission medium, they are divided into wired (using coaxial, twisted pair, or fiber-optic cable) and wireless (WLAN), and according to the type of topology, into networks with 'bus', 'ring', or 'star' topologies.
Each computer on the local network is connected to the transmission medium through a special adapter that "sees" what any other adapter on the same network is transmitting; such systems are called broadcasts.
The MAC protocol regulates the sequence of nodes' access to the transmission medium. It is implemented using two types of schemes: polling or contention-based MAC schemes.
MAC polling networks can be centralized or distributed. Centralized ones have a star topology with a hub as the control node. In contrast, distributed ones have a ring or bus topology with token passing. Contention-based MACs are often implemented as carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) or carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA). The first is used in all types of Ethernet LANs, and the second is used in most wireless WLANs.
The unrivaled leader among local networks is the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet network, where coaxial, twisted pair (designated by the letter T for 'twisted') and fiber-optic cables are used as transmission media. The transition to twisted-pair cable made it possible to implement full-duplex transmission over two twisted pairs, leaving the concept of collision meaningless since transmission and reception became independent operations. Ethernet has transmission speeds of 10, 100 ('Fast Ethernet'), 1000 Mbit/s (1 Gbit/s, 'Gigabit Ethernet'), and up to 400 Gigabit Ethernet.
Wireless local networks (wireless LAN, WLAN) have also become widespread. Their parameters are stated in the IEEE 802.11 specifications, known as Wi-Fi.
Today, the most common Wi-Fi 5 or 802.11ac defines the operation of wireless local area networks in the 2.4/5 GHz ranges with a data transfer rate of 1.3 Gbit/s. Shortly, speeds will reach 9.6 Gbit/s over 6 GHz frequency bands.
The range of most WLAN systems is 120 m, depending on the number and type of obstacles encountered. Additional access points will help expand the coverage area. Using two or three carrier frequencies instead of one can increase the number of users and network capacity.
Obviously, with Wi-Fi, network security becomes an important issue. A priori, wireless networks must be equipped with additional means of ensuring reliability compared to wired ones. WLAN uses direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technology, which is highly resistant to data corruption and interference, including intentional ones. The problem of user authentication can be solved by introducing system identifiers. The wired equivalent privacy (WEP) mode is provided to transmit necessary information. In this case, the signal is encrypted with an additional algorithm, and the data is controlled using an electronic key.
Like all IEEE 802.3 standards, 802.11 refers to the lower two layers of the OSI model: physical and link. Any network application, operating system, or protocol (such as TCP/IP) will function equally well on an 802.11 network or Ethernet one.
The original 802.11 standard defines the basic architecture - the features of 802.11 services. The 802.11x specification only addresses the physical layer, introducing higher access speeds.
In conclusion, we should note that thanks to the close ties between Ethernet and the IP protocol, the scope of Ethernet applications is expanding, particularly in broadband subscriber access (BSA) networks.
0 notes
Text
Sobu Edifísiu CSMA Obrigatóriu, Armindo Ameasa Lori IX Governu bá Ministériu Públiku
Hatutan.com, (05 Fevereiru 2024), Díli—Fundadór eskola Koléjiu São Miguel Arcanjo (CSMA-Sigla Português) Armindo Crisna Caetano ameasa lori IX Governu Konstitusionál liu liu Sekretáriu Estadu bá Toponímia no Organizasaun Urbana (SEATOU), Germano Santa Brites Dias, bá Ministériu Públiku (MP) tanba konsidera sobu obrigatóriu edifísiu CSMA nian hanesan sobu fahi-luhan. Continue reading Sobu Edifísiu…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Un día como hoy (11 de noviembre) en la computación


El 11 de noviembre de 1973 se instala la primera red Ethernet. Constaba de mil metros de cable coaxial usando el protocolo CSMA/CD. Todo viene de un memo que escribiera Robert Metcalfe llamado Alto Ethernet, escrito en mayo 22 de ese año. Ethernet se ha convertido de facto en el estándar de redes locales para negocios y hogar #retrocomputingmx #ethernet
0 notes
Text
Ethernet TSN vs. Traditional Ethernet: Key Differences and Advantages
Ethernet Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and traditional Ethernet represent two distinct approaches to network communication, each tailored to specific requirements and applications. This article compares Ethernet TSN with traditional Ethernet, highlighting their key differences, advantages, and the implications for various industries, including automotive, industrial automation, and telecommunications.
Understanding Traditional Ethernet
Traditional Ethernet, based on IEEE 802.3 standards, has been the cornerstone of local area networks (LANs) for decades. It operates using Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD), where devices contend for network access and manage collisions to ensure data integrity.
Key Features of Traditional Ethernet
Best-Effort Communication: Traditional Ethernet uses a best-effort approach to data transmission, where data packets are sent without guarantees regarding latency or timing. This non-deterministic behavior makes it suitable for applications with less stringent timing requirements.
Limited Quality of Service (QoS): QoS mechanisms in traditional Ethernet prioritize traffic based on predefined rules but do not guarantee timely delivery or latency control. As a result, it may not meet the requirements of real-time applications or safety-critical systems.
Introducing Ethernet TSN
Ethernet TSN enhances traditional Ethernet by incorporating time-sensitive capabilities necessary for real-time communication and deterministic behavior. It builds upon IEEE 802.1 standards and includes mechanisms for time synchronization, traffic shaping, and low-latency transmission.
Key Features of Ethernet TSN
Deterministic Communication: Ethernet TSN ensures deterministic behavior by synchronizing network clocks, prioritizing critical traffic, and minimizing network latency and jitter. This capability is essential for applications that require precise timing, such as industrial automation, automotive systems, and multimedia streaming.
Enhanced Quality of Service: TSN provides advanced QoS features, including time-aware scheduling and traffic shaping, to prioritize critical data streams. It guarantees timely delivery of time-sensitive data while optimizing bandwidth usage and network efficiency.
Advantages of Ethernet TSN
Real-Time Capabilities: TSN supports real-time communication with predictable latency, making it suitable for applications like industrial control systems, autonomous vehicles, and multimedia streaming where timing is critical.
Scalability and Flexibility: TSN accommodates scalable network architectures and diverse application requirements without compromising performance. It integrates seamlessly with existing Ethernet infrastructure, facilitating gradual adoption and interoperability.
Applications and Industry Implications
Automotive Industry: Ethernet TSN enhances vehicle connectivity, supports autonomous driving functionalities, and improves safety through precise control and synchronization of vehicle systems.
Industrial Automation: TSN optimizes production processes by enabling synchronized control and monitoring of manufacturing equipment, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Future Directions and Adoption
Standardization and Interoperability: Industry efforts focus on standardizing Ethernet TSN to ensure compatibility and interoperability across diverse applications and network environments.
Integration with Emerging Technologies: TSN integrates with 5G networks, edge computing platforms, and IoT devices to support advanced applications in smart cities, healthcare, and transportation.
Conclusion
Ethernet TSN represents a significant evolution from traditional Ethernet, offering deterministic communication, enhanced QoS, and real-time capabilities crucial for modern applications. As industries embrace TSN to meet stringent timing requirements and support innovative technologies, the technology drives advancements in connectivity, efficiency, and reliability across diverse sectors.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Tipos de estándares
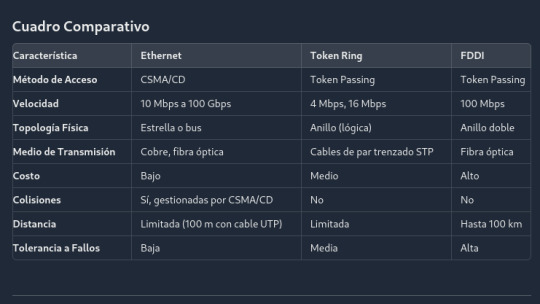
1. Ethernet
Descripción
Ethernet es el estándar de red más popular y ampliamente utilizado en redes LAN. Fue desarrollado en los años 70 y se basa en el protocolo CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection). Ethernet permite que múltiples dispositivos compartan el mismo medio de comunicación y manejen colisiones de datos para garantizar una transmisión eficiente.
Usos
Ethernet se utiliza en la mayoría de las redes domésticas y empresariales, conectando computadoras, impresoras, servidores y otros dispositivos en una red LAN.
Ventajas
Costo: Económico y fácil de implementar.
Velocidad: Desde 10 Mbps hasta 100 Gbps en sus versiones más avanzadas.
Compatibilidad: Amplia gama de dispositivos compatibles.
Desventajas
Colisiones: En redes muy congestionadas, pueden ocurrir colisiones de datos.
Distancia limitada: La longitud de los cables es limitada en comparación con otros estándares.
2. Token Ring
Descripción
Token Ring, desarrollado por IBM, utiliza una topología de anillo donde un "token" especial circula alrededor de la red. Solo el dispositivo que posee el token puede transmitir datos, lo que elimina las colisiones.
Usos
Se utilizó en entornos corporativos que requerían una alta confiabilidad y una gestión eficiente del tráfico de red.
Ventajas
Sin colisiones: El método de acceso evita colisiones, mejorando la eficiencia en redes ocupadas.
Determinismo: Garantiza tiempos de acceso predecibles a la red.
Desventajas
Costo: Más caro que Ethernet debido a la complejidad del equipo necesario.
Velocidad: Limitado a 4 o 16 Mbps, mucho más lento que las versiones modernas de Ethernet.

3. FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)
Descripción
FDDI es un estándar que utiliza fibra óptica y topología de anillo doble, proporcionando alta velocidad y tolerancia a fallos. Fue diseñado para conectar estaciones sobre distancias más largas y soportar grandes redes corporativas.
Usos
FDDI se usa en redes backbone, donde se necesita alta velocidad y una larga distancia de transmisión, como en campus universitarios o grandes empresas.
Ventajas
Alta velocidad: Ofrece hasta 100 Mbps.
Tolerancia a fallos: La estructura de doble anillo permite continuar la operación si un anillo falla.
Desventajas
Costo: Muy caro debido al uso de fibra óptica y equipos especializados.
Complejidad: Su implementación y mantenimiento requieren más conocimientos técnicos.

0 notes
Text
Generative AI: Unleashing Telco-Centric Potential for Unmatched Customer Experience in the Digital Era

In the digital era, generative AI (Gen AI) isn't just a technological advancement; it's a strategic weapon in the telco's arsenal, unlocking its telco-centric potential. By embracing the challenges of Gen AI and its cousin, CSMA I (Customer-Centric Smart AI), telecommunication companies can unleash a wave of innovation in customer experience (CX). Imagine dynamic, AI-powered interactions and services that not only anticipate customer needs but also adapt to them in real-time. This level of customization, previously unattainable, becomes a reality. This AI revolution redefines telecommunications, transforming challenges into opportunities for unparalleled customer satisfaction and operational triumphs.
0 notes
Text
如何判断网站是CDN节点故障还是源服务器问题呢?
网卡就是计算机与局域网互连的设备。计算机主要通过网卡接入网络。网卡又称为网络适配器或网络接口卡NIC(Network interface Card),是构成计算机网络系统中最基本的、最重要的连接设备。
一、网卡主要功能
网卡在TCP/IP模型中,工作在物理层及数据链路层,用于接收和发送计算机数据。
网络中的计算机都必须拥有一个唯一的MAC地址,这个MAC地址由网卡提供,同时网卡的主要功能包括:
数据的发送(封装)和接收(解封装):发送数据时,加上首部和尾部;接收数据时,剥去首部和尾部
数据的编码和译码:物理层数据的编解码
数据链路管理:主要是CSMA/CD(冲突检测的载波监听多路访问)的实现
二、网卡的演进
现在让我们了解下网卡的这些年来的演进过程。
三、网卡的分类
网卡有哪些分类呢?现在小编就带着大家来了解一下。
服务器专用网卡VS普通网卡
相对于服务器专用网卡来说,普通网卡指应用在普通PC、工作站、消费级电子产品中的网卡对可靠性、安全性等要求不高,而服务器与普通PC工作站的不同之处是服务器一直处于工作中,且要求长时间稳定运行,这就要求服务器网卡具有以下特点:
数据传输速度快
服务器时刻处于数据计算、交换过程中,普通网10Mbps、 100Mbps的数据已不满足大数据流量网络,当前服务器常用的网卡速率为10Gbps、25Gbps等。
CPU占用率低
服务器的CPU是不停工作的,处理着大量的数据。如果一台服务器的CPU大部分时间都在为网卡提供数据响应,势必会影响到对其他任务的处理速度。服务器网卡有自带的控制芯片,可以处理一些CPU任务,从而减少CPU的计算开销。
安全性能高
如果服务器的网卡出现故障,则服务器将无法接收,发送数据,相当于宕机,所以高可靠性是是服务器网卡的必备特性。服务器网卡基本上 都具有容错功能,如Intel的AFT(网卡出错冗余),ALB(网卡负载均衡)等技术。
全球服务器 ,高防CDN加速,国内海外节点 AJCDN
云服务器,物理机,大带宽
香港 新加坡 台湾 美国
CN2,大陆优化,国际线路
防DDOS,CC攻击
免实名+可测试,满意再合作
值班客服,24小时营业
欢迎询问 ~
飞机:@ajcdn017
微信: ajcdn017
0 notes