#css border
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

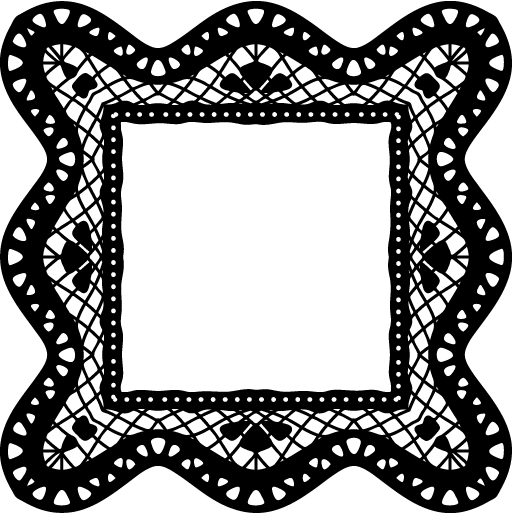
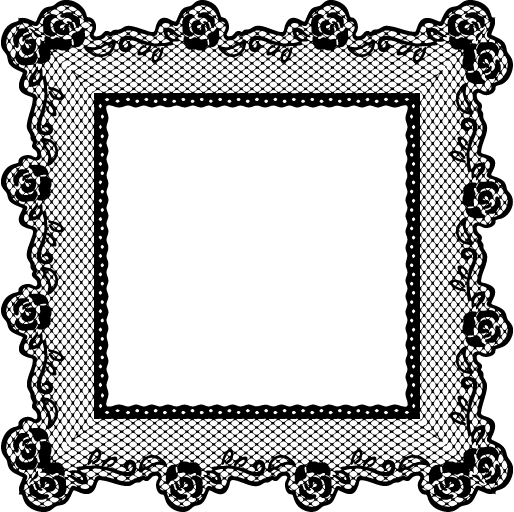
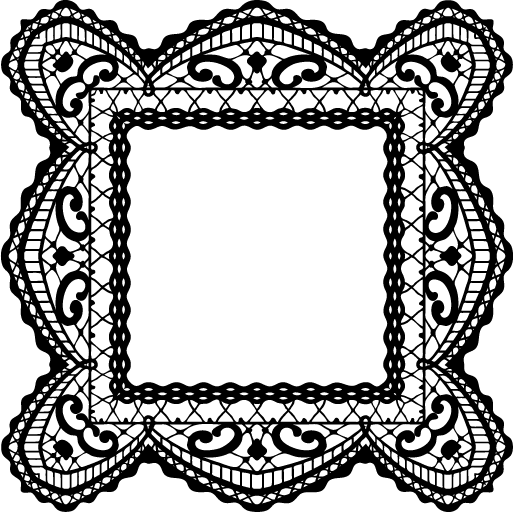
☆ resources to make your own rentry/bundlrs border!
sources from da-lace.com f2u, like + reblog appreciated!
i forgot da-lace existed and then i remembered.. anyway have fun with these! no need to credit since i didn't make them
#☆ ◟ my resources !#rentry#rentry resources#rentry inspo#rentry metadata#rentry border#bundlrs border#bundlrs#rentry decor#bundlrs resources#html css#rentry stuff#editblr
2K notes
·
View notes
Text







Here’s all the borders I’ve made! Feel free to use them, credit is appreciated!
#art#f2u#stamps#f2u graphics#pixel art#artists on tumblr#graphics#stamp#artist#2010s#pixels#web graphics#nostalgia#template#stamp template#borders#html css#neocities#rentry decor#web decor
439 notes
·
View notes
Text





borders I made. 1st & 4th are hand drawn and the others are edited.
375 notes
·
View notes
Text
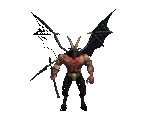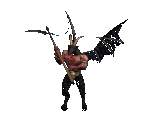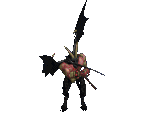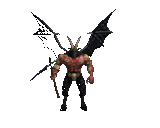


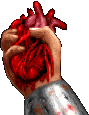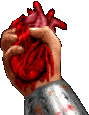

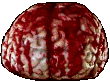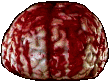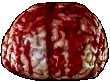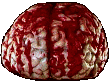



#halloween gifs#horror aesthetic#tw blood#myspace#neocities#dividers#web design#borders#horror pixels#html css#rentry graphics#carrd graphics#png#y2k aesthetic#vampire aesthetic#2000s nostalgia
255 notes
·
View notes
Text
hate to have to post like this but i am #goingthruit at the moment. i guess im asking if anyone could maybe send me some money for some groceries/food on apple pay today it would be a blessing fr fr
apple pay is 8282668648
thanks for reading, things will be better soon, i am sure :)
#cybercore#ok to rb#visa cashapp rb#money#pay me money#send help#please help#pls help#groceries#food#food money#mutual aid#mutual funds#trans day of visibility#online visibility#donations#like really#hungrry#neocities#css#web graphics#funny#furry art#html border#f2u graphics#dragcave#editing resources#old web graphics#youtube#html css
50 notes
·
View notes
Text

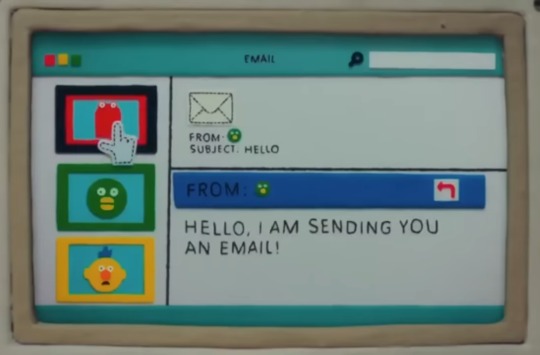
Customizing the theme and made a handful of images :^) going to make the curs downloadable someday for anyone who wants to invite red guy to live in their blog .
#i talk#dhmis#i live making images#these are largely temporary as im just using the current theme as a placeholder and experiment to test the waters of css#cant give out the post borders </3 its bound by the windows xp theme . i have no idea if itll will work on other themes#permanent theme i wanna make is for the recolours. love them too much and id like to do some fun website stuff with them#art
399 notes
·
View notes
Text

CSS Button Animation
#css button border animation#css buttons#codenewbies#html css#html5 css3#frontenddevelopment#css#css animation examples#pure css animation#css animation tutorial#code#css tricks#css snippets#html5#frontend
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Create Multi-Step Forms With Vanilla JavaScript and CSS
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/how-to-create-multi-step-forms-with-vanilla-javascript-and-css/
How to Create Multi-Step Forms With Vanilla JavaScript and CSS
Multi-step forms are a good choice when your form is large and has many controls. No one wants to scroll through a super-long form on a mobile device. By grouping controls on a screen-by-screen basis, we can improve the experience of filling out long, complex forms.
But when was the last time you developed a multi-step form? Does that even sound fun to you? There’s so much to think about and so many moving pieces that need to be managed that I wouldn’t blame you for resorting to a form library or even some type of form widget that handles it all for you.
But doing it by hand can be a good exercise and a great way to polish the basics. I’ll show you how I built my first multi-step form, and I hope you’ll not only see how approachable it can be but maybe even spot areas to make my work even better.
We’ll walk through the structure together. We’ll build a job application, which I think many of us can relate to these recent days. I’ll scaffold the baseline HTML, CSS, and JavaScript first, and then we’ll look at considerations for accessibility and validation.
I’ve created a GitHub repo for the final code if you want to refer to it along the way.
The structure of a multi-step form
Our job application form has four sections, the last of which is a summary view, where we show the user all their answers before they submit them. To achieve this, we divide the HTML into four sections, each identified with an ID, and add navigation at the bottom of the page. I’ll give you that baseline HTML in the next section.
Navigating the user to move through sections means we’ll also include a visual indicator for what step they are at and how many steps are left. This indicator can be a simple dynamic text that updates according to the active step or a fancier progress bar type of indicator. We’ll do the former to keep things simple and focused on the multi-step nature of the form.,
The structure and basic styles
We’ll focus more on the logic, but I will provide the code snippets and a link to the complete code at the end.
Let’s start by creating a folder to hold our pages. Then, create an index.html file and paste the following into it:
Open HTML
<form id="myForm"> <section class="group-one" id="one"> <div class="form-group"> <div class="form-control"> <label for="name">Name <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> <input type="text" id="name" name="name" placeholder="Enter your name"> </div> <div class="form-control"> <label for="idNum">ID number <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> <input type="number" id="idNum" name="idNum" placeholder="Enter your ID number"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="form-control"> <label for="email">Email <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> <input type="email" id="email" name="email" placeholder="Enter your email"> </div> <div class="form-control"> <label for="birthdate">Date of Birth <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> <input type="date" id="birthdate" name="birthdate" max="2006-10-01" min="1924-01-01"> </div> </div> </section> <section class="group-two" id="two"> <div class="form-control"> <label for="document">Upload CV <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> <input type="file" name="document" id="document"> </div> <div class="form-control"> <label for="department">Department <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> <select id="department" name="department"> <option value="">Select a department</option> <option value="hr">Human Resources</option> <option value="it">Information Technology</option> <option value="finance">Finance</option> </select> </div> </section> <section class="group-three" id="three"> <div class="form-control"> <label for="skills">Skills (Optional)</label> <textarea id="skills" name="skills" rows="4" placeholder="Enter your skills"></textarea> </div> <div class="form-control"> <input type="checkbox" name="terms" id="terms"> <label for="terms">I agree to the terms and conditions <span style="color: red;">*</span></label> </div> <button id="btn" type="submit">Confirm and Submit</button> </section> <div class="arrows"> <button type="button" id="navLeft">Previous</button> <span id="stepInfo"></span> <button type="button" id="navRight">Next</button> </div> </form> <script src="script.js"></script>
Looking at the code, you can see three sections and the navigation group. The sections contain form inputs and no native form validation. This is to give us better control of displaying the error messages because native form validation is only triggered when you click the submit button.
Next, create a styles.css file and paste this into it:
Open base styles
:root --primary-color: #8c852a; --secondary-color: #858034; body font-family: sans-serif; line-height: 1.4; margin: 0 auto; padding: 20px; background-color: #f4f4f4; max-width: 600px; h1 text-align: center; form background: #fff; padding: 40px; border-radius: 5px; box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); display: flex; flex-direction: column; .form-group display: flex; gap: 7%; .form-group > div width: 100%; input:not([type="checkbox"]), select, textarea width: 100%; padding: 8px; border: 1px solid #ddd; border-radius: 4px; .form-control margin-bottom: 15px; button display: block; width: 100%; padding: 10px; color: white; background-color: var(--primary-color); border: none; border-radius: 4px; cursor: pointer; font-size: 16px; button:hover background-color: var(--secondary-color); .group-two, .group-three display: none; .arrows display: flex; justify-content: space-between align-items: center; margin-top: 10px; #navLeft, #navRight width: fit-content; @media screen and (max-width: 600px) .form-group flex-direction: column;
Open up the HTML file in the browser, and you should get something like the two-column layout in the following screenshot, complete with the current page indicator and navigation.
Adding functionality with vanilla JavaScript
Now, create a script.js file in the same directory as the HTML and CSS files and paste the following JavaScript into it:
Open base scripts
const stepInfo = document.getElementById("stepInfo"); const navLeft = document.getElementById("navLeft"); const navRight = document.getElementById("navRight"); const form = document.getElementById("myForm"); const formSteps = ["one", "two", "three"]; let currentStep = 0; function updateStepVisibility() formSteps.forEach((step) => document.getElementById(step).style.display = "none"; ); document.getElementById(formSteps[currentStep]).style.display = "block"; stepInfo.textContent = `Step $currentStep + 1 of $formSteps.length`; navLeft.style.display = currentStep === 0 ? "none" : "block"; navRight.style.display = currentStep === formSteps.length - 1 ? "none" : "block"; document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", () => navLeft.style.display = "none"; updateStepVisibility(); navRight.addEventListener("click", () => if (currentStep < formSteps.length - 1) currentStep++; updateStepVisibility(); ); navLeft.addEventListener("click", () => if (currentStep > 0) currentStep--; updateStepVisibility(); ); );
This script defines a method that shows and hides the section depending on the formStep values that correspond to the IDs of the form sections. It updates stepInfo with the current active section of the form. This dynamic text acts as a progress indicator to the user.
It then adds logic that waits for the page to load and click events to the navigation buttons to enable cycling through the different form sections. If you refresh your page, you will see that the multi-step form works as expected.
Multi-step form navigation
Let’s dive deeper into what the Javascript code above is doing. In the updateStepVisibility() function, we first hide all the sections to have a clean slate:
formSteps.forEach((step) => document.getElementById(step).style.display = "none"; );
Then, we show the currently active section:
document.getElementById(formSteps[currentStep]).style.display = "block";`
Next, we update the text that indicators progress through the form:
stepInfo.textContent = `Step $currentStep + 1 of $formSteps.length`;
Finally, we hide the Previous button if we are at the first step and hide the Next button if we are at the last section:
navLeft.style.display = currentStep === 0 ? "none" : "block"; navRight.style.display = currentStep === formSteps.length - 1 ? "none" : "block";
Let’s look at what happens when the page loads. We first hide the Previous button as the form loads on the first section:
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", () => navLeft.style.display = "none"; updateStepVisibility();
Then we grab the Next button and add a click event that conditionally increments the current step count and then calls the updateStepVisibility() function, which then updates the new section to be displayed:
navRight.addEventListener("click", () => if (currentStep < formSteps.length - 1) currentStep++; updateStepVisibility(); );
Finally, we grab the Previous button and do the same thing but in reverse. Here, we are conditionally decrementing the step count and calling the updateStepVisibility():
navLeft.addEventListener("click", () => if (currentStep > 0) currentStep--; updateStepVisibility(); );
Handling errors
Have you ever spent a good 10+ minutes filling out a form only to submit it and get vague errors telling you to correct this and that? I prefer it when a form tells me right away that something’s amiss so that I can correct it before I ever get to the Submit button. That’s what we’ll do in our form.
Our principle is to clearly indicate which controls have errors and give meaningful error messages. Clear errors as the user takes necessary actions. Let’s add some validation to our form. First, let’s grab the necessary input elements and add this to the existing ones:
const nameInput = document.getElementById("name"); const idNumInput = document.getElementById("idNum"); const emailInput = document.getElementById("email"); const birthdateInput = document.getElementById("birthdate") const documentInput = document.getElementById("document"); const departmentInput = document.getElementById("department"); const termsCheckbox = document.getElementById("terms"); const skillsInput = document.getElementById("skills");
Then, add a function to validate the steps:
Open validation script
function validateStep(step)
Here, we check if each required input has some value and if the email input has a valid input. Then, we set the isValid boolean accordingly. We also call a showError() function, which we haven’t defined yet.
Paste this code above the validateStep() function:
function showError(input, message) const formControl = input.parentElement; const errorSpan = formControl.querySelector(".error-message"); input.classList.add("error"); errorSpan.textContent = message;
Now, add the following styles to the stylesheet:
Open validation styles
input:focus, select:focus, textarea:focus outline: .5px solid var(--primary-color); input.error, select.error, textarea.error outline: .5px solid red; .error-message font-size: x-small; color: red; display: block; margin-top: 2px; .arrows color: var(--primary-color); font-size: 18px; font-weight: 900; #navLeft, #navRight display: flex; align-items: center; gap: 10px; #stepInfo color: var(--primary-color);
If you refresh the form, you will see that the buttons do not take you to the next section till the inputs are considered valid:
Finally, we want to add real-time error handling so that the errors go away when the user starts inputting the correct information. Add this function below the validateStep() function:
Open real-time validation script
function setupRealtimeValidation() nameInput.addEventListener("input", () => if (nameInput.value.trim() !== "") clearError(nameInput); ); idNumInput.addEventListener("input", () => if (idNumInput.value.trim() !== "") clearError(idNumInput); ); emailInput.addEventListener("input", () => if (emailInput.validity.valid) clearError(emailInput); ); birthdateInput.addEventListener("change", () => if (birthdateInput.value !== "") clearError(birthdateInput); ); documentInput.addEventListener("change", () => if (documentInput.files[0]) clearError(documentInput); ); departmentInput.addEventListener("change", () => if (departmentInput.value !== "") clearError(departmentInput); ); termsCheckbox.addEventListener("change", () => if (termsCheckbox.checked) clearError(termsCheckbox); );
This function clears the errors if the input is no longer invalid by listening to input and change events then calling a function to clear the errors. Paste the clearError() function below the showError() one:
function clearError(input) const formControl = input.parentElement; const errorSpan = formControl.querySelector(".error-message"); input.classList.remove("error"); errorSpan.textContent = "";
And now the errors clear when the user types in the correct value:
The multi-step form now handles errors gracefully. If you do decide to keep the errors till the end of the form, then at the very least, jump the user back to the erroring form control and show some indication of how many errors they need to fix.
Handling form submission
In a multi-step form, it is valuable to show the user a summary of all their answers at the end before they submit and to offer them an option to edit their answers if necessary. The person can’t see the previous steps without navigating backward, so showing a summary at the last step gives assurance and a chance to correct any mistakes.
Let’s add a fourth section to the markup to hold this summary view and move the submit button within it. Paste this just below the third section in index.html:
Open HTML
<section class="group-four" id="four"> <div class="summary-section"> <p>Name: </p> <p id="name-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="name-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <div class="summary-section"> <p>ID Number: </p> <p id="id-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="id-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <div class="summary-section"> <p>Email: </p> <p id="email-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="email-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <div class="summary-section"> <p>Date of Birth: </p> <p id="bd-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="bd-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <div class="summary-section"> <p>CV/Resume: </p> <p id="cv-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="cv-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <div class="summary-section"> <p>Department: </p> <p id="dept-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="dept-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <div class="summary-section"> <p>Skills: </p> <p id="skills-val"></p> <button type="button" class="edit-btn" id="skills-edit"> <span>✎</span> <span>Edit</span> </button> </div> <button id="btn" type="submit">Confirm and Submit</button> </section>
Then update the formStep in your Javascript to read:
const formSteps = ["one", "two", "three", "four"];
Finally, add the following classes to styles.css:
.summary-section display: flex; align-items: center; gap: 10px; .summary-section p:first-child width: 30%; flex-shrink: 0; border-right: 1px solid var(--secondary-color); .summary-section p:nth-child(2) width: 45%; flex-shrink: 0; padding-left: 10px; .edit-btn width: 25%; margin-left: auto; background-color: transparent; color: var(--primary-color); border: .7px solid var(--primary-color); border-radius: 5px; padding: 5px; .edit-btn:hover border: 2px solid var(--primary-color); font-weight: bolder; background-color: transparent;
Now, add the following to the top of the script.js file where the other consts are:
const nameVal = document.getElementById("name-val"); const idVal = document.getElementById("id-val"); const emailVal = document.getElementById("email-val"); const bdVal = document.getElementById("bd-val") const cvVal = document.getElementById("cv-val"); const deptVal = document.getElementById("dept-val"); const skillsVal = document.getElementById("skills-val"); const editButtons = "name-edit": 0, "id-edit": 0, "email-edit": 0, "bd-edit": 0, "cv-edit": 1, "dept-edit": 1, "skills-edit": 2 ;
Then add this function in scripts.js:
function updateSummaryValues() nameVal.textContent = nameInput.value; idVal.textContent = idNumInput.value; emailVal.textContent = emailInput.value; bdVal.textContent = birthdateInput.value; const fileName = documentInput.files[0]?.name; if (fileName) const extension = fileName.split(".").pop(); const baseName = fileName.split(".")[0]; const truncatedName = baseName.length > 10 ? baseName.substring(0, 10) + "..." : baseName; cvVal.textContent = `$truncatedName.$extension`; else cvVal.textContent = "No file selected"; deptVal.textContent = departmentInput.value; skillsVal.textContent = skillsInput.value || "No skills submitted"; }
This dynamically inserts the input values into the summary section of the form, truncates the file names, and offers a fallback text for the input that was not required.
Then update the updateStepVisibility() function to call the new function:
function updateStepVisibility() formSteps.forEach((step) => document.getElementById(step).style.display = "none"; ); document.getElementById(formSteps[currentStep]).style.display = "block"; stepInfo.textContent = `Step $currentStep + 1 of $formSteps.length`; if (currentStep === 3) updateSummaryValues(); navLeft.style.display = currentStep === 0 ? "none" : "block"; navRight.style.display = currentStep === formSteps.length - 1 ? "none" : "block";
Finally, add this to the DOMContentLoaded event listener:
Object.keys(editButtons).forEach((buttonId) => const button = document.getElementById(buttonId); button.addEventListener("click", (e) => currentStep = editButtons[buttonId]; updateStepVisibility(); ); );
Running the form, you should see that the summary section shows all the inputted values and allows the user to edit any before submitting the information:
And now, we can submit our form:
form.addEventListener("submit", (e) => e.preventDefault(); if (validateStep(2)) alert("Form submitted successfully!"); form.reset(); currentFormStep = 0; updateStepVisibility(); );
Our multi-step form now allows the user to edit and see all the information they provide before submitting it.
Accessibility tips
Making multi-step forms accessible starts with the basics: using semantic HTML. This is half the battle. It is closely followed by using appropriate form labels.
Other ways to make forms more accessible include giving enough room to elements that must be clicked on small screens and giving meaningful descriptions to the form navigation and progress indicators.
Offering feedback to the user is an important part of it; it’s not great to auto-dismiss user feedback after a certain amount of time but to allow the user to dismiss it themselves. Paying attention to contrast and font choice is important, too, as they both affect how readable your form is.
Let’s make the following adjustments to the markup for more technical accessibility:
Add aria-required="true" to all inputs except the skills one. This lets screen readers know the fields are required without relying on native validation.
Add role="alert" to the error spans. This helps screen readers know to give it importance when the input is in an error state.
Add role="status" aria-live="polite" to the .stepInfo. This will help screen readers understand that the step info keeps tabs on a state, and the aria-live being set to polite indicates that should the value change, it does not need to immediately announce it.
In the script file, replace the showError() and clearError() functions with the following:
function showError(input, message) const formControl = input.parentElement; const errorSpan = formControl.querySelector(".error-message"); input.classList.add("error"); input.setAttribute("aria-invalid", "true"); input.setAttribute("aria-describedby", errorSpan.id); errorSpan.textContent = message; function clearError(input) const formControl = input.parentElement; const errorSpan = formControl.querySelector(".error-message"); input.classList.remove("error"); input.removeAttribute("aria-invalid"); input.removeAttribute("aria-describedby"); errorSpan.textContent = "";
Here, we programmatically add and remove attributes that explicitly tie the input with its error span and show that it is in an invalid state.
Finally, let’s add focus on the first input of every section; add the following code to the end of the updateStepVisibility() function:
const currentStepElement = document.getElementById(formSteps[currentStep]); const firstInput = currentStepElement.querySelector( "input, select, textarea" ); if (firstInput) firstInput.focus();
And with that, the multi-step form is much more accessible.
Conclusion
There we go, a four-part multi-step form for a job application! As I said at the top of this article, there’s a lot to juggle — so much so that I wouldn’t fault you for looking for an out-of-the-box solution.
But if you have to hand-roll a multi-step form, hopefully now you see it’s not a death sentence. There’s a happy path that gets you there, complete with navigation and validation, without turning away from good, accessible practices.
And this is just how I approached it! Again, I took this on as a personal challenge to see how far I could get, and I’m pretty happy with it. But I’d love to know if you see additional opportunities to make this even more mindful of the user experience and considerate of accessibility.
References
Here are some relevant links I referred to when writing this article:
How to Structure a Web Form (MDN)
Multi-page Forms (W3C.org)
Create accessible forms (A11y Project)
#:not#Accessibility#ADD#aria#Article#Articles#attention#attributes#background#border-radius#box#box-shadow#browser#buttons#challenge#change#classes#code#Color#content#CSS#CV#dept#direction#display#email#error handling#event#Events#Exercise
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gradient Border Animation
#css border animation#css gradient background animation#codingflicks#html css#frontend#html#css#frontenddevelopment#css3#webdesign#html css animation#css animation examples#border animation css#neduzone
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
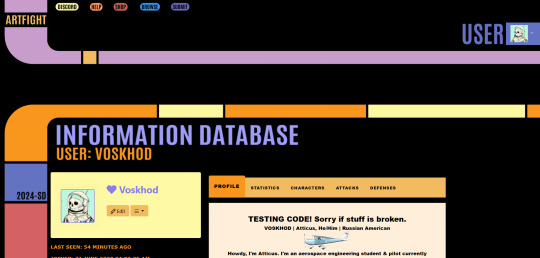
Fuck you *LCARSs your Art Fight*
#not art#artfight#star trek#I don't want to talk about how much time I've spent on this#Art Fight please give me border radius perms so I can make better stupid CSS themes
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

my friends!!! which arrows for the scroll bars do you prefer? i think both are fine but do u like the solid or non solid ones...please do tell me :3
#i had to make them myself bc the font used for windows 95 windows is a font only licensed to microsoft so i cant use it </3#also im Nearly done this layout??? i think??? i gotta change around some borders & stuff and try to make it draggable#bc u can do that with css so :3c but i also think itll fuck the scaling up so =_= many decisions...#anyways!!! please give me an opinion <3#oh i could also do a ver. of the arrows that are 1px wide while not being solid inside if that would be better...idk#🎆.txt
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
am currently working on a neocities site (which i cannot give you the url for yet because im working on the css still and there's no content also it looks ugly still) and oh man does it take me back to ye olde days of custom theme editing on here. i still use a custom theme obvs but back in like 2014/2015ish when i was really into indie rp custom themes were all the rage and you would spend hours editing some character specific image for your bg and then another several hours trying to make the css line up with your image (never at any point did i attempt to actually like. learn html or css. i just read other people's theme codes and edited the parts i could understand and solved problems as they arose. i distinctly remember one time i was using a base that had two sidebars and i only wanted one and deleting the section broke the theme in disastrous ways [bc i had no idea what i was doing] so i literally just made all the elements in the sidebar transparent and moved them off the screen LMAO. the best i ever got was moving from fully built custom themes that i edited to base themes that i built off of)
anyway while im slightly better now (im even reading tutorials! am i following them? sorry i have to go i think someones calling me) i am using a layout builder to build the homepage so it is even more reminding me of mid-2010s tumblr. much like building off a base theme, and definitely easier to understand than tumblr theme building (this time i at least know what all the different pieces of code are doing, even when im not sure how or why, or how to duplicate the effect under slightly different circumstances. but progress is progress!).
a good but annoying thing about the layout that im using is that i havent actually edited the site wide stylesheet, just used internal css on that one page, so when i go to make literally any other page i'll have to start from scratch. this is good because i am learning a lot and i think without doing it this way i would end up with a bunch of useless stuff in the stylesheet that really should be page-specific that i would have to correct with internal or inline css later. annoying because what do you mean i have to make decisions about the sizing and positions of the content? i literally just did that
also im kind of nervous to touch the general stylesheet because im pretty sure what i'll actually want to do is have a couple of stylesheets for different 'sections' of the website, to maintain cohesion between pages of the 'same' type but still allow a lot of fun customization on a per-page basis, but that requires deciding what 'sections' i want on the website and that is a whole other can of worms. but also you can't start without starting so i should probably just try to build a really simple layout and go from there (after all, if it sucks, it's not like i can't just create a new stylesheet, or do the css for each page independently until i hit a groove that's actually worth moving to the stylesheet). but also first i have to finish this goddamn homepage. which means i gotta find a header image that doesn't look ugly as shit
#good idea generator#i dont need a header but im scared of deleting the image in case i break the code and if i go back to the layout maker#i'll have to redo all the code i already did. and im not doing that it was so annoyinggggggg#im having so much fun though. enrichment in my enclosure or whatever#also i found a bunch of my old theme editing stuff while looking for resources and i was like woww i even look like i know what im doing#but ultimately the trick was 90% of my background image should have been css elements instead#like i had a nice box around my content. i should have used a container with a border in the css#but what i did was make a bg img with a box in it already. then try to fit the content to that box#and if youre wondering no i never tested shit all on different screens and i def did not understand positioning#so definitely the boxes did not line up on anyone elses screen. well you live and you learn!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Got my PC back today and the random compulsive project of the night was to try and recreate UTDR dialogue boxes on my website!!

I have some ideas of where to use them but right now they're just here as the silly Mike broken links placeholder dialogue LOL
Below is how it looked before 😭

#Jay Talks#Neocities Tag#Mike#this all happened because I remembered border-image CSS was a thing you could do 😭#and I wanted to see how the DR frame would look :)
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
I haven't touched my website in forever since giving up on the job search for a while and going back to one of my old jobs.
Today I changed the article cards on my website. See this CSS Tricks article on how to make these borders.
Next: Week notes as my microblogging space as a catch-all life updates if Tumblr goes down.
Before → After


4 notes
·
View notes
Text
trying to make a stylus filter to fix the awful profile picture change, and I ended up making a few pixels of every image in posts disappear.
#css#the images don't even have the class I'm editing#its also a border-radius rule I'm setting#so it shouldn't even affect this.
0 notes
Text
CSS Box Model and Layouts by Abdelfattah Ragab
CSS Box Model and Layouts by Abdelfattah Ragab
Welcome to the book "CSS Box Model and Layouts". In this book, I explain the properties of CSS box model such as width, height, margin, padding and so on. By the end of this book, you will be able to position your box correctly on the page, control its size and spacing, and handle all kinds of scenarios. Let us go!
Available on https://shop.tredition.com and https://www.amazon.com

0 notes