#dataredundancy
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

RUTC50 YOUR 5G WIRELESS MULTITOOL
The RUTC50 is a 5G router featuring dual-band Wi-Fi 6 technology with multi-user MIMO, ensuring ultra-high cellular speeds of up to 3.4 Gbps.
For more information, Visit: https://www.newtrend.ae/ Live chat: +971 507542792
#RUTC50#5GRouter#WiFi6#MultiUserMIMO#UltraHighSpeed#DataRedundancy#AutoFailover#IndustrialRouter#RemoteManagement#Teltonika
0 notes
Text
Star Schema vs Snowflake Schema: Choosing the Right Data Structure for Your Business
In the fast-paced world of data management, selecting the right schema is crucial for efficient data storage and retrieval. In this video, we explore the Star and Snowflake schemas, comparing their structures, advantages, and challenges. Whether you're managing a simple data environment or a complex system, this guide will help you choose the best schema to optimize your analytical capacity. Learn how each schema can impact performance, storage efficiency, and data integrity for your organization.
youtube
#DataManagement#StarSchema#SnowflakeSchema#DataWarehousing#DataModeling#DataStorage#BigData#Analytics#BusinessIntelligence#SQL#DatabaseDesign#TechTrends#DataScience#DataArchitecture#DataRetrieval#StorageOptimization#DatabasePerformance#BusinessAnalytics#DataRedundancy#DataIntegrity#Youtube
0 notes
Text
IBM Cloud’s DAL14 Boosts Hybrid Cloud And Data Redundancy

In Texas, everything is larger, even the footprint of the IBM Cloud Network. The tenth data center for IBM Cloud, which supports its virtual private cloud (VPC) operations, opened its doors today in Dallas, Texas. The fourth availability zone in the Dallas, Texas, IBM Cloud area is DAL14, the most recent addition. It is an addition to the current configuration, which consists of one federal data center, two network points of presence (PoPs), and one single-zone region (SZR).
DAL14
DAL14, the fourth availability zone (AZ) in the Dallas, Texas, region, is the newest addition to IBM Cloud.
The new availability zone in IBM Cloud’s Dallas area, DAL14, provides companies with a number of important advantages:
Enhanced Resilience: By dispersing applications and services over several zones, users can create highly resilient architectures using the four availability zones (including DAL14). In the event that a failure occurs in any one zone, this lowers the chance of downtime.
Scalability: In order to accommodate traffic spikes and demand surges without sacrificing performance, IBM Cloud users can scale workloads across several availability zones, including DAL14.
Data Redundancy: By offering a second geographic location inside the same region, DAL14 improves the choices for data redundancy. Ensuring that data is replicated and kept in a safe, remote location is essential for applications that need disaster recovery.
Low Latency: Dallas-area users can now execute and store data closer to their consumers by integrating DAL14. This improves response times and lowers latency, particularly for applications that need to process data quickly and in real-time.
Support for Hybrid Clouds: DAL14 facilitates the use of IBM Cloud’s security and flexibility to enable businesses to integrate cloud resources with on-premises data centers.
Strict regulatory and compliance criteria are followed by IBM Cloud, and the new zone will continue to provide strong security standards with firewall protections, encryption, and other security measures.
With this expansion, IBM Cloud’s overall capabilities in North America are strengthened, offering organizations more alternatives and flexibility when developing and implementing their cloud infrastructures.
The facility is built to support the utilization of enterprise-grade cloud computing workloads, including generative AI, secret computing, large-scale in-memory databases, and high-volume online applications with fluctuating traffic peaks.
According to Jay Jubran, Director of IBM Cloud Product Management Infrastructure Services, “the new state-of-the-art DAL14 expansion zone is a testament to our VPC growth providing additional capacity for our clients in the Dallas region and a commitment to our delivery of advanced networking solutions.” “Our customers can expand their workloads in IBM Cloud with peace of mind when they invest in our data centers.”
Refresher on terminology: zones, regions, and IBM Cloud VPC
Built on an extremely secure and robust software-defined network (SDN), IBM Cloud VPC allows you to create separate private clouds for your business needs while still enjoying the adaptable advantages of a public cloud. You select the processing, storage, and networking resources you need, and IBM Cloud offers hyperscalability and optimal availability.
Let’s take a brief look at the fundamental ideas behind zones and regions as they relate to IBM Cloud VPC setups.
Region: An abstraction associated with the geographical area where a virtual private cloud (VPC) is installed is called a region. There are several zones, or separate fault domains, within each area. A VPC can cover more than one zone in the designated area.
Zones: A zone is a physical representation of a data center that houses network, compute, and storage resources as well as the associated power and cooling systems. It also offers services and applications. To reduce latency, enhance fault tolerance, and remove shared single points of failure, zones are segregated from one another. Applications and databases are intended to be highly available, fault tolerant, and scalable through the use of availability zones.Image credit to IBM
Dallas’s cloud industry has a bright future
The Texas data center market has been expanding, and it doesn’t seem like it will slow down any time soon, much like the number of businesses relocating to the state. The Dallas data center market is estimated by Moder Intelligence to be worth 419.64 MW this year, and over the next five years, it is expected to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.7% to 941.92 MW.
The report’s market trends list COVID-19, the need for hyperscalability, the demand for hybrid clouds, and the growing acceptance of AI as some of the causes driving up cloud computing demand in Dallas.
As the amount of data generated in Dallas increases in sectors including government, financial services, telecom, and healthcare, IBM Cloud hopes to increase its networking presence in the region in response to customer and business partner requests.
DAL14’s solutions for IBM Cloud VPC
Additionally, the complete IBM Cloud VPC line will reside in DAL14. Every affordable choice is designed to meet specific needs for platform as a service (PaaS), infrastructure as a service (IaaS), and hybrid cloud, including x86 with 4th Gen Intel Xeon processing capability, VMware, SAP, and IBM Z.
For example, IBM Cloud Virtual Servers, a portfolio that includes recent news on using Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerators, will be housed at the new multizone region (MZR) site. IBM Cloud Direct Link, IBM Cloud Block and File Storage, IBM Cloud Bare Metal Servers for VPC, and other features will also be supported. With seven MZRs in all and eighteen availability zones constructed to specification for fast access, low latency, low cost migration, and certified security, the complete range is global in scope.
Resiliency, performance, security, and compliance are at the heart of IBM Cloud’s commitment to supporting clients and enterprises who are expanding their operations to Dallas and other metro areas in the greater southwest region.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#IBMCloud#DAL14Boost#HybridCloud#DAL14#DataRedundancy#IBMCloudNetwork#generativeAI#publiccloud#IBMCloudVPC#x86#intel#news#technology#technews#IBMCloudVirtualServers#Gaudi3AIaccelerators#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
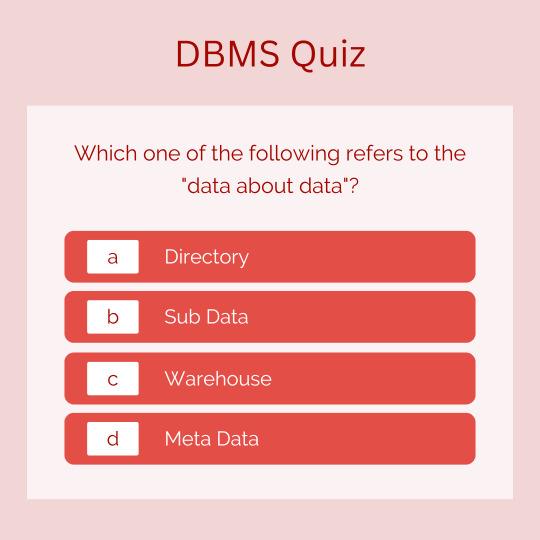
Test Your Knowledge: DBMS Quiz Challenge!!! 📝🧠
Which one of the following refers to the "data about data"?🤔
For more interesting quizzes, check the link below! 📚
https://bit.ly/3Y3UAsC
For the explanation of the right answer, you can check Q.No. 17 of the above link. 📖
#dbms#datamanipulationlanguage#dml#datadefinitionlanguage#ddl#database#datamanagement#datamining#dataredundancy#metadata
0 notes
Text
LACIE HDD EXTERNAL 32TB 2BIG DOCK THUNDERBOLT3
Stay connected with CFexpress B, CFast 2.0, and SD card slots, aUSB 3.2 Type A hub port, and a DisplayPort 1.4 Dual Thunderbolt 3 ports daisy chain up to 5 devices Easily configure RAID 0/1 optimal system performance and dataredundancy Works with Windows, iPad USB-C and Mac Backed by industry-leading 5-year limited warranty with RescueData Recovery Services plan1

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The Rise of Web3 and Its Impact on High-Storage Applications
Web3, the third generation of the internet, is a revolutionary concept that brings decentralization to the forefront. Powered by blockchain technology and other decentralized technologies, Web3 aims to redefine how we interact with digital services, shifting from traditional centralized models to decentralized peer-to-peer networks. This article explores the potential of Web3 in revolutionizing high-storage applications, enabling greater user control, privacy, and data ownership.
1. Decentralization: Empowering Users and Enhancing Data Integrity
At its core, Web3 is built on blockchain technology, leveraging its distributed ledger to maintain a cryptographically-secured and continuously growing list of records called blocks. This decentralized nature enables direct peer-to-peer interactions, ensuring that no single entity has complete control or ownership over data. Unlike traditional centralized systems, Web3 safeguards data from censorship, manipulation, and single-point-of-failure risks, enhancing data integrity and availability.
2. Interoperability: Connecting Blockchain Networks for Enhanced Accessibility
Web3 introduces interoperability as a significant aspect, allowing different blockchain networks to connect seamlessly. Interoperability protocols, such as cross-chain bridges, enable users to transfer assets from one blockchain to another. Leveraging interoperability, high-storage applications can be developed to make them accessible on multiple blockchain networks, expanding their reach and usability.
3. Distributed File Systems: Secure and Scalable Storage Solutions
Web3 incorporates distributed file systems like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and Swarm, which provide secure and scalable storage solutions for high-storage applications. These file systems break down files into smaller chunks, distribute them across multiple nodes, and utilize content-based addressing. By ensuring data redundancy and efficient retrieval, distributed file systems enhance the reliability and performance of storage systems, making them ideal for high-storage applications.
4. Smart Contracts and Tokenization: Enforcing Rules and Incentivizing Participation
Web3 enables the use of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions encoded within the blockchain. Smart contracts facilitate trustless and automated interactions, allowing high-storage applications to enforce rules, handle transactions, and manage access control for data storage and retrieval. Moreover, Web3 introduces tokenization, where digital assets or tokens represent ownership or access rights. Tokenization incentivizes participants to contribute their storage resources, creating a cost-effective and scalable decentralized network.
5. Overcoming Challenges: Scalability, Storage Optimization, and Data Availability
While blockchain technology holds immense potential for high-storage applications, it faces scalability challenges when handling large amounts of data. To support such applications, blockchain networks need to enhance their scalability through solutions like sharding, layer-2 protocols, or sidechains, enabling parallel processing and increased capacity. Efficient utilization of storage resources is another crucial factor. Blockchain networks must optimize data storage by employing techniques such as data compression, deduplication, and data partitioning to minimize storage requirements while maintaining data integrity and availability. Ensuring data availability is essential for high-storage applications. Blockchain networks need to incentivize storage nodes to maintain high availability and integrate distributed file systems like IPFS or Swarm to replicate data across multiple nodes, enhancing data availability and reliability.
6. Privacy and Security: Safeguarding Sensitive Data
High-storage applications often deal with sensitive data, making data privacy and security paramount. Blockchain networks must incorporate robust encryption techniques and access control mechanisms to protect stored data. Privacy-focused technologies like zero-knowledge proofs or secure multiparty computation can be integrated to enable secure and private data storage and retrieval.
7. Governance, Consensus, and User Experience
Efficient governance and consensus mechanisms are crucial for blockchain networks handling large volumes of data. Transparent and decentralized governance models, such as on-chain or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), can facilitate collective decisions regarding storage-related policies and upgrades. Adopting efficient consensus algorithms like proof-of-stake (PoS) or delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) can ensure faster and more energy-efficient consensus for data storage transactions. Improving the user experience is also vital, as blockchain technology in high-storage applications should provide a user-friendly interface and seamless integration with existing applications. Tools, libraries, and frameworks simplifying the development and deployment of high-storage blockchain applications should be readily available.
8. Regulatory Compliance: Meeting Specific Requirements
High-storage applications may need to adhere to specific regulatory requirements, such as data protection regulations or industry-specific compliance standards. Blockchain networks must provide features and mechanisms that allow compliance with such regulations. Built-in privacy controls, auditability features, or integration with identity management systems can ensure regulatory compliance while utilizing blockchain-based storage.
Conclusion
Web3 has the potential to revolutionize high-storage applications, offering a decentralized and secure infrastructure that empowers users and ensures data integrity. By harnessing the capabilities of decentralization, interoperability, distributed file systems, smart contracts, and tokenization, Web3 provides a scalable, incentivized, and resilient environment for storing and retrieving large volumes of data. Overcoming challenges related to scalability, storage optimization, data availability, privacy, security, governance, consensus, and user experience will pave the way for blockchain technology to unleash its full potential in high-storage applications. Embrace the era of Web3 and unlock the future of data storage and ownership. For more articles visit: Cryptotechnews24 Source: cointelegraph.com
Latest Posts
Read the full article
#blockchainnetworks#blockchaintechnology#CryptoNews#dataavailability#dataintegrity#dataownership#dataredundancy#decentralizedpeer-to-peernetworks#decentralizedweb#distributedfilesystems#high-storageapplications#InterPlanetaryFileSystem(IPFS)#layer-2protocols#privacy#scalabilitychallenges#sidechains#smartcontracts#storageoptimization#Swarm#tokenization#Web3
0 notes
Text
Do I need a hardware RAID controller?

Whether you need hardware RAID depends on your usage needs and data importance. If you want to save money (who doesn't?), then you can use a single operating system to access the RAID array, or you are using RAID 0 or RAID 1, then using software RAID can have the same RAID protection and experience instead of higher-cost similar products.
The hardware RAID solution has more features, higher performance and data security, which is especially suitable for video editing professionals. If you can handle the initial investment, then hardware RAID is definitely the way to go. It can make you get rid of the limitation of software RAID, and give you greater flexibility in usage and configuration types. Learn More: sourl.cn/BKbuAu
#terramaster#hardwareRAID#softwareRAID#databackup#dataprotection#dataredundancy#RAIDstorage#networkattachedstorage#datarecovery
0 notes
Text
RUTX50
INDUSTRIAL 5G ROUTER
RUTX50 is a dual-SIM multi-network router offering 5G mobile communication for high-speed and data-heavy applications. Together with 5x Gigabit Ethernet ports and dual-band Wi-Fi, it provides data connection redundancy with auto-failover.
For more information,
Visit: https://www.newtrend.ae/
Live chat: +971 507542792
#RUTX50#IndustrialRouter#5GRouter#DualSIMRouter#HighSpeedConnectivity#DataRedundancy#GigabitEthernet#WiFiRouter#AutoFailover#TechSolutions#MobileCommunication#NetworkReliability#5GTechnology#IoTConnectivity#BusinessConnectivity#NetworkRouter#TechInnovation#NewTrend
0 notes
Text

Test Your Knowledge: DBMS Quiz Challenge!!! 📝🧠
Which one of the following refers to the copies of the same data (or information) occupying the memory space at multiple places ?🤔
For more interesting quizzes, check the link below! 📚
https://bit.ly/3Y3UAsC
For the explanation of the right answer, you can check Q.No. 16 of the above link. 📖
#dbms#datamanipulationlanguage#dml#datadefinitionlanguage#ddl#database#datamanagement#datamining#dataredundancy#metadata
0 notes
Text

est Your Knowledge: DBMS Quiz Challenge!!! 📝🧠
Which of the following can be used to extract or filter the data & information from the data warehouse?🤔
For more interesting quizzes, check the link below! 📚
https://bit.ly/3Y3UAsC
For the explanation of the right answer, you can check Q.No. 15 of the above link. 📖
#dbms#datamanipulationlanguage#dml#datadefinitionlanguage#ddl#database#datamanagement#datamining#dataredundancy#metadata
0 notes
Text

Test Your Knowledge: DBMS Quiz Challenge!!! 📝🧠
Which one of the following refers to the copies of the same data (or information) occupying the memory space at multiple places ?🤔
For more interesting quizzes, check the link below! 📚
For the explanation of the right answer, you can check Q.No. 16 of the above link. 📖
#dbms#datamanipulationlanguage#dml#datadefinitionlanguage#ddl#database#datamanagement#datamining#datawarehouse#dataredundancy
0 notes
Text

Test Your Knowledge: DBMS Quiz Challenge!!! 📝🧠
Which of the following can be used to extract or filter the data & information from the data warehouse? 🤔
For more interesting quizzes, check the link below! 📚
For the explanation of the right answer, you can check Q.No. 15 of the above link. 📖
#dbms#datamanipulationlanguage#dml#datadefinitionlanguage#ddl#database#datamanagement#datamining#datawarehouse#dataredundancy
0 notes
Text

Test Your Knowledge: DBMS Quiz Challenge!!! 📝🧠
A huge collection of the information or data accumulated form several different sources is known as ________:🤔
For more interesting quizzes, check the link below! 📚
For the explanation of the right answer, you can check Q.No. 14 of the above link. 📖
#dbms#datamanipulationlanguage#dml#datadefinitionlanguage#ddl#database#datamanagement#datamining#datawarehouse#dataredundancy
0 notes
Text
Why is hardware RAID better than software RAID?

If uptime and stability are important to you or your business, hardware RAID is very useful. Backup will help you to avoid catastrophic data loss. However, restoring large amounts of data (for example, in the event of a drive failure) may take several hours to perform. Hardware RAID allows you to withstand the failure of one or more drives without losing data and in many cases without causing any downtime. Hardware RAID is also useful if you are experiencing speed issues in multitasks, when applications are waiting to perform tasks on disk. By using hardware RAID, you can ensure that the high-speed array reads and writes data at a high speed, thereby providing you with additional throughput. In addition, if you use hardware RAID, the hardware RAID controller will include additional memory as a cache, which reduces the burden on the physical hardware and improves overall performance.
Learn More: https://sourl.cn/BKbuAu
#terramaster#hardwareRAID#softwareRAID#databackup#dataprotection#dataredundancy#RAIDstorage#networkattachedstorage#datarecovery
0 notes
Text
What is hardware RAID?

For hardware RAID, all drives are connected to a hardware RAID controller, which can be located on a separate RAID card, on a different server or built into the motherboard. The hardware RAID controller manages the RAID array, configures and supports multiple RAID levels. It contains a microprocessor (often called an I/O processor, or ROC ‘RAID on Chip’). In some cases, RAID controllers with their own processors can act as mini-computers because they have the ability to perform tasks independently. During the hardware RAID installation process, the drive is connected to the RAID controller board. This applies not only to large servers, but also to desktop computers. Processing hardware RAID refers to discrete controllers at the disk storage system level (such as ATA RAID, SATA, DELTA PLC, etc.).
PROS: Will not occupy or affect the performance of the computer or server; Compatible with different operating systems; Prevent data damage due to power outage during the backup process; It is easy to replace a failed disk.
CONS: The cost is higher than software RAID; If your RAID controller fails, you must find a compatible RAID controller to be replaced.
Learn More: https://sourl.cn/BKbuAu
#terramaster#hardwareRAID#databackup#dataprotection#dataredundancy#RAIDstorage#networkattachedstorage#datarecovery#RIADcontroller
0 notes
Text
What is software RAID?

A simple way to describe software RAID is that the RAID task runs on the CPU of the computer system. It is a built-in function on many operating systems that can convert the disks connected to the server into a RAID array. All you need to do is to connect the drives and configure the desired RAID level.
What are the PROS and CONS of software RAID? PROS: Low cost; Easy to install; Same RAID driver can be implemented to the same operating system; If the processor performance is strong, it can easily handle RAID 0 and RAID 1.
CONS: Increasing the burden of the computer operating system; Replace a failed disk is relatively complicated; Limited to the RAID levels supported by a specific operating system; Performance will significantly decrease with complex RAID configuration, etc.
Learn More: https://sourl.cn/BKbuAu
#terramaster#hardwareRAID#softwarRAID#databackup#dataprotection#dataredundancy#RAIDstorage#networkattachedstorage#datarecovery#RI
0 notes