#flexible current probes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Dependable Insulation Tester for Every Project by Meco Instruments

Ensuring electrical safety is crucial for every industry and home. Our advanced insulation testers are designed to deliver accurate and reliable measurements, helping you identify faults and prevent potential hazards. These insulation tester are perfect for evaluating the integrity of electrical circuits, cables, and equipment, whether for maintenance, troubleshooting, or installations. Offering both analogue and digital insulation testers, our products provide consistent performance in harsh environments and demanding applications. With user-friendly interfaces and robust construction, they make diagnostics efficient and straightforward. Trust Meco Instruments for high-quality tools that help safeguard your systems and ensure smooth operations.
Visit Us: https://www.mecoinst.com/meco-products/Analog-Digital-Insulation-Testers.aspx
#dual input thermometer#flexible current probe#lux meters#multifunction meter#flexible current probes#power guard
0 notes
Text

My phylogeny of frog monsters as of the release of wilds
The toxin toads: The most basal of this family of monstrous amphibians, these creatures can be found in a variety of habitats and take the chemical defenses common among frogs to the next level. Of the four species known, three can spew an aerosolized concoction from their mouths in self-defense, with the fourth regurgitating an explosive chyme. These toxins are potent enough to affect creatures hundreds of times their size upon contact, making them a handy species for hunters to use. It’s currently thought that these toxins are synthesized from their diet of bugs.
These creatures are, despite their basal position, already very distinct from other frogs. The genus has two sails supported by bony extensions of the ribs, a feature unique to them, which supports a dense network of blood vessels that can be constricted. This feature can be used to thermoregulate in the wide variety of environments they can be found in, constricting and reducing blood flow in cold environments to retain heat and flushing with blood to vent heat in hot environments.
The toxin toads also have very short tails, which is a feature common amongst this family. This is actually very weird for a frog as ordinarily they re-absorb their tails when transitioning from a tadpole to an adult, and genes responsible for the particular shape of the hip bones in frogs is also intrinsically linked with the re-absorption of the tail in their tadpole stage. The re-absorption of the tail allows for the specialized muscles and unique hip structure that allows frogs to jump to be present. Because of this, you can only really have one or the other.
It could be possible that the tails of the monster frogs could be extensions of the colon like the Tailed Frog, but we don’t see them squash or stretch like a boneless appendage and instead move like they have a rigid support structure. This doesn’t necessarily mean that they have vertebrae in their tails, but this is the logical conclusion. And if they are true tails then that implies that this family either descend from very early frogs or stem-frogs, splitting off before the loss of the tail as adults became hard baked into the genome of other frogs. This would also imply that their hips, and by extension how they leap, is very different from other frogs.
Armored frogs
Thorntoad: Amphibians native to the citadel and by extension the mega-forest it once was, in self defense they vomit noxious chemicals into the faces of attackers. This isn’t all too different from the toxin toads, implying that this could be an ancestral trait to the family.
Two defining features of this species are their long flexible tongues and armor.
Despite what is seen in media, frog tongues are not long or especially flexible. They are actually short and situated at the front of the mouth folded backwards, and when a frog opens its mouth to grab something the tongue flips forward into a more normal position to slap the prey item with its stickiness. So for a frog to have a long flexible tongue like that of say an anteater is rather fascinating, and could imply a diet specializing in animals that make small burrows. Unable to dig prey up, it simply sends its tongue down to probe for it.
The osteoderms, which are common among the monster frogs, is also strange as frogs famously lack scales. But that isn’t to say that they are unfamiliar with doing strange things with their skin, as many species have hard bony skin around the face and shoulders, and Leptobrachium boringii males can grow a mustache of keratinous spines during mating season. In a land with dragons and dinosaurs, large frogs might be pressured into dermal protection.
Chatacabra: Monstrous frogs with long tongues and upright limbs native to deserts. Chatacabra are perhaps most unique for their body plan that has converged with the cursorial old world monkeys such as Blagonga and Rajang, and they seem to have near similar range of movement in their limbs and can even knuckle walk. What could have possibly caused such an adaptation in a frog is unclear. While a more upright body posture would keep the underside off the hot sand, the arms are subject to guesswork. The unique range of arm movements in primates is a result of their arboreality and brachiation movements, so it could be possible that the ancestors of Chatacabra were arboreal.
The long tongue of Chatacabra seems to be a holdover from more basal armored frogs, and while still used for prey capture, is also used to smear the forelimbs with sticky mucus. This same mucus is used to attach rocks to their forelimbs to make their attacks more damaging to anything willing to attack them.
Three features present in Chatacabra are common to the rest of the monstrous frogs and is worth bringing up here. Teeth on the mandibles, claws, and supporting the organs without a ribcage.
Frogs lack teeth on their bottom jaws as they lost the genes for them 200 million years ago, but it is not impossible for the monstrous frogs to have re-evolved them. The frog Gastrotheca guentheri managed to do it, likely because the genes that tell teeth were to grow are tied to the genes for gums. Claws are also not impossible for a frog when faced with the right pressure, as the African Clawed Frog has keratinous extensions on three of its toes it uses for prey processing.
Frogs also don’t have a rib cage, and ordinarily this limits how big they can get as past a certain size their organs might threaten to fall out of their body or get jostled around. But the monstrous frogs get around this with very well developed obliquus externus and rectus abdominis muscles with a high amount of elastin to prevent damage when getting jostled around. They also have hypertrophied procoracoids, sternums, and xiphisternums to further mimic a proper ribcage.
In the desert there is rarely large long lasting water bodies for tadpoles, so Chatacabra had to develop a work-around. Much like Rain Frogs, Chatacabra mothers will dig a hole for her to lay eggs in, and these eggs will give birth to miniature fully formed Chatas via a process called direct development.
Tetranadon: Amphibians that can be found in river systems in more eastern parts of the world, Tetras are unique for their hard turtle-like shell and beak.
The species spends most time submerged and inactive for long stretches of time, as long wisps of algae are commonly seen growing off their bodies. They occasionally experience periods of activity where they forage along the bottom of water bodies, shuffling through the muck with their fleshy bill. This bill is lined with electroreceptors like a platypus, and they use it to detect prey, particularly a species of freshwater slug called Goocumbers, which is their preferred prey. Upon detection a Tetranadon then ravenously scarfs down its meal, along with the surrounding water and dirt.
The shell of a Tetranadon is composed of many large fused osteoderms, but unlike a turtle shell it is completely separate from the ribs and vertebrae. Tetranadon are also capable of standing and moving upright, and can even pick up objects with their forelimbs.
Tetsucabra: Possibly the most famous genus within this froggy family, Tetsucabra are a common sight in habitats with rocky terrain.
The species is fossorial, and creates elaborate dens and tunnels with their large claws and massive tusks. Their skulls are notoriously robust and their tusks and brows give them an intimidating appearence. They are equipped with rather flat peg shaped teeth, and this coupled with the fact they are capable of eating grains and rice indicates an omnivorous diet. Tetsu are also smart enough to be trained and tamed individuals exist, although they are very food motivated creatures.
If their powerful legs and massive jumps are unable to carry them to safety, their tough hide and powerful bite can deter attackers. They can even manipulate boulders with their mouths and toss them as well as spit a noxious substance much like the Thorn Toad and Toxin Toads.
During the breeding season male Tetsucabra fight violently for females like African Bullfrogs. A successful male will then dig out a nursery for his offspring that he maintains diligently.
Inflatable frogs
Zamitrios: Arctic amphibians known for their striking appearance, massive maw, and rapid metamorphic lifecycle.
The primary species is found around the polar seaway and its surrounding environments, and deals with the temperatures through antifreeze compounds in the blood and gigantothermy. The species is aquatic, swimming with powerful webbed feet and a fluked tail after prey which they dispatch via shark-like jaws and teeth. But they need to be careful not to fall prey to other monsters such as the massive parave Ukanlos.
They drink seawater, and their specialized kidneys can filter out the salt. In self defense they can spray some of their water reserves along with bits of liquid nitrogen from groves along their hide. In the freezing temperatures of their habitat this instantly freezes over their body to form ice armor. If that fails they can suck in a bunch of air to inflate themselves and make themselves look bigger.
Zamtrios tadpoles are already born with forelimbs and have large jagged cranial horns. They target large animals and drill into their hides to eat them alive from the inside, and then rapidly metabolize their meals to grow into subadults. Subadults are very similar to juveniles but have proper hind limbs. This rapid growth is a defensive mechanism, as without parental care it is in a juvenile’s best interest to grow big quickly since in such harsh arctic environments any predator is willing to make a quick snack of them.
There exists a desert dwelling subspecies that, as a water retention adaptation, has lost the ability to create ice armor.
Tricktoad: A small member of the family that takes the inflatable abilities of Zamtrios to the next level. Lighter than air gases are retained from their digestive system and used to float. They then use various fins to (clumsily) propel themselves. In self defense they can secrete a substance that smells good to large predators before making a hasty getaway in hopes of eliminating a would-be predator.
Yama Tsukami: Traditionally put in the slight wastebasket taxon that is the elder dragon class, its placement here is controversial. Not much is known about the species.
Yama spend very long periods of time on the forest floor of the forests and jungles they call home, long enough that flora grows on their skin and adds a layer of camouflage. Occasionally they experience periods of activity where they then proceed to quite literally inhale plants and any animals not fast enough to escape its massive maw, which is equipped with massive human-like teeth perfect for processing woody material. Great Thunderbugs also live symbiotically within their mouths where they keep it mostly clean of debris, plaque, and cavities.
They accomplish flight via the same way as Tricktoads, but instead of using fins for propulsion they use gas and inhaled air that is vented from “gills” on their underside. So reliant are Yama on floating for movement that the muscles in their limbs have atrophied and their skeleton isn’t ossified outside of their jaws as a weight saving adaptation. If they ever find themselves grounded they are incapable of movement until able to re-inflate.
As the species is very poorly understood, their reproductive habits are a mystery. But Mezeporta hunters have reported a variation of the monster called Yama Kurai, although these are likely just very old Yamas.
Other notes
Gelidron: A recently discovered species of giant salamander native to the oilwell basin. They live their lives in the slow lane in groups, lazily foraging for various endemic crustaceans. To navigate rough terrain they are equipped with claws and gecko-like foot pads.
They’re able to gradually shift their color to be darker when in oilslits and their iridescent mucus further aids in this camouflage. If threatened they open their mouths as a threat display, but are otherwise easy and nutritious meals. They primarily rely on their explosive reproduction for defense.
Yes I know I wouldn’t have needed to make various workarounds for these guys if I just made them Temnospondyls instead of frogs but shhhh let me have some fun and talk about weird frogs and frog anatomy.
#monster hunter#monhun#monster hunter biology#monsterhunter#speculative biology#speculative evolution#speculative zoology#taxonomy#phylogenetics#phylogeny#cladistics#tetsucabra#amphibians#zamtrios#chatacabra#yama tsukami#paratoad
64 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’m so glad I stepped back a little. It’s so fun to have her angst a little.
Ping patrol: @soup-for-ghosts @lesbian-empress-nero @stars-and-loops @meme-boys-blog
Cws: Death, Persona 3 spoilers.
———————————————-
"Hey! I called the left seat!"
"Well I didn't hear you."
"You had it on the way here!"
"Did not."
"Did too!"
“Did not!”
“Did too!!”
(Sighs) "Makoto's right. Kotone, let him sit there."
"But mooom... the view is really pretty! I wanna see it!"
"You saw it last time, Kotone. Next time we go on a trip like this, it'll be your turn, alright?"
"Okay…"
—————————————
The ocean is a place of endless movement. With waves rippling across its surface; moving along the currents in twisting ways. The moon perhaps, would be its partner, controlling the cosmic push and the pull of the tides. With grace it dances with the sea, in a slow waltz across the land and sky.
Life and death move in a similar way.
There is a shadow upon the spire of a bridge tonight. A dark blotch on the meger canvas of stars. She waits for events that were remembered from times long past. But it is not a silent vigil. She has been quietly singing to herself, leaving her words echoing across the sea and towards the full moon.
A harp accompanies her. It rings with cascading notes that soothe alongside the crashing waves.
Theres a still tension in the swell;
Of dreamt debris afloat amidst the waves and then dispel.
The harp continues to play while the singer is left in thought. It is almost time, but that won’t stop her from finishing this set. A few key notes are highlighted, but the cascade still persists.
Aimless thoughts and papers blown around;
A million moments meant remembered rest in deep dark sound.
Game the mess.
I’d like to know why you,
Are all alone while I’m,
Lost at sea.
Maybe we’ll be there when you want.
A violin unexpectedly joins in. From where, it is unknown. It dips in and out, with long pulls and short pushes. The harp continues despite it all, acknowledging the violin at some points, but still following its own path.
Anchorless and unmoored set amiss.
Awake would only probe the fantasy made lucid sense;
Sail on, sail on.
I’d like to know why you,
Are all alone while I’m,
Lost at sea.
Maybe we’ll be there when you want.
She hums, letting the harp and violin heighten in tone. All three of them lay in harmony now, leaving only the ocean to perform as the percussion.
The moon stares on, impassive as ever. Perhaps it is charmed by the shadow’s song.
A single car races down the bridge.
There's a still tension in the swell,
So give into the vast receiving emptiness of ti-
The world turns a sickly shade of green.
Once dark waters of the ocean are now a deep shade of red. Gentle ripples move more ferociously, whitecaps tinted with ivory plasma. Stars are swallowed whole, coffins line the streets of the surrounding city.
Tires screech on the road beneath; a boy and a girl scream before being abruptly silenced by a loud crash.
The song is interrupted. A shame, but it’s not the first time Kurokami had to be flexible.
She drops down from its vantage point. From a distance, she appears to be a particularly large raindrop. The shadow reforms, and glides over to the smoking remains of the vehicle.
She wanted to see him again. To thank him, even though he didn’t know what he did to deserve it. She wanted to cherish him as she was now, even when he felt unwanted. She wanted to comfort him in this time of crisis, when he didn’t even know her name. He was the reason she had for being. Why she existed. He was the catalyst, the beginning of the end for Her. And Kurokami couldn’t wait any longer.
Her eyes widened in horror.
He can’t be. No. It’s not possible. He is destined-
But here he is.
A young Makoto Yuki's head is pressed against the spiderwebbed glass. Blood slowly seeps from his temple, turning once dark blue hair a shade of dark dark red. He looks peaceful, almost. Like the day She lost him. There was no blood that day. No pain, just letting go knowing that everything would end up fine.
She could hardly believe it. Was she too late? What could she do now, now that there was no one to fulfill the fates’ design? All of her efforts, the connections, the time.
Was it all wasted on this?
He could be on the edge of life, yes? She just needed to get a hand in there.
She reached through the cracks, and felt for a pulse.
There was none.
“No…”
He was gone.
Someone, anyone should have survived. Someone had to. She would have known if this damned world was to be consumed already, so this place would be fine.
She looked frantically around the wreckage, desperate to find any form of life, circling around the two coffins in the front seats. The parents, no doubt. A sad sight, but she did not linger. They were going to die anyway.
A lock of red hair caught her eye. She lay there, passed out upon a deflating airbag. Unlike Makoto, she truly looked like she was sleeping.
As soon as she felt her weak pulse, she looked.
It was muted with unconsciousness, but she could still feel the warmth. She is a bright soul, charming and kind. She was… beautiful. Kurokami had never seen a soul so unmarred.
Who was this?
Kotone Shiomi. Sibling.
She blinked.
A sister. Nobody had mentioned that Makoto was an only child. They had only said he was an orphan. Kurokami could hardly believe it, but the resemblance was right there. Silver and gold, moon and sun, Artemis and Apollo, Hades and Persephone, Orpheus and-
...Eurydice.
Was her Persona already-
A distant explosion.
Kurokami knew what it signified. She cannot linger for long. Already, she feels the sheer power of what is to come. And if she were to be caught in the crossfire…
She departs, leaving only a single lotus petal on Her Martyr’s chest.
It is the least she can do.
Death arrives, with a weapon soon behind.
They fight in spectacular fashion, a brutal display of power from both sides.
A girl keens in the night, the weapon takes advantage of the opening it grants.
Two bodies collapse in the middle of the road. They are seperated. Neither will remember this incident until it is too late.
The One Who Stares Back looks forlornly, and follows one.
There is a saying amongst many, that curiosity oft killed the cat.
But many do not know of its second part: speaking of the satisfaction that brought it back.
………
Alone…
At the edge of a universe humming a tune.
For merely dreaming we were snow.
Mmm mmm mmmmm mm…
A siren sounds,
Like the goddess who promises endless apologies of paradise.
And only she can make it right.
So things are different tonight.

do they know?
gotta say wasn’t expecting ‘makoto also dies in the car crash’ to be the kotone wildcard justification but this is the world we live in now I suppose
very nice song choices again as usual tho! yippee
#asks#vinegar-on-main#inbox fic#also is the bolded ‘her’s and kurokami the. same person?#like are they in reference to them
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Essential Predictive Analytics Techniques
With the growing usage of big data analytics, predictive analytics uses a broad and highly diverse array of approaches to assist enterprises in forecasting outcomes. Examples of predictive analytics include deep learning, neural networks, machine learning, text analysis, and artificial intelligence.
Predictive analytics trends of today reflect existing Big Data trends. There needs to be more distinction between the software tools utilized in predictive analytics and big data analytics solutions. In summary, big data and predictive analytics technologies are closely linked, if not identical.
Predictive analytics approaches are used to evaluate a person's creditworthiness, rework marketing strategies, predict the contents of text documents, forecast weather, and create safe self-driving cars with varying degrees of success.
Predictive Analytics- Meaning
By evaluating collected data, predictive analytics is the discipline of forecasting future trends. Organizations can modify their marketing and operational strategies to serve better by gaining knowledge of historical trends. In addition to the functional enhancements, businesses benefit in crucial areas like inventory control and fraud detection.
Machine learning and predictive analytics are closely related. Regardless of the precise method, a company may use, the overall procedure starts with an algorithm that learns through access to a known result (such as a customer purchase).
The training algorithms use the data to learn how to forecast outcomes, eventually creating a model that is ready for use and can take additional input variables, like the day and the weather.
Employing predictive analytics significantly increases an organization's productivity, profitability, and flexibility. Let us look at the techniques used in predictive analytics.
Techniques of Predictive Analytics
Making predictions based on existing and past data patterns requires using several statistical approaches, data mining, modeling, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Machine learning techniques, including classification models, regression models, and neural networks, are used to make these predictions.
Data Mining
To find anomalies, trends, and correlations in massive datasets, data mining is a technique that combines statistics with machine learning. Businesses can use this method to transform raw data into business intelligence, including current data insights and forecasts that help decision-making.
Data mining is sifting through redundant, noisy, unstructured data to find patterns that reveal insightful information. A form of data mining methodology called exploratory data analysis (EDA) includes examining datasets to identify and summarize their fundamental properties, frequently using visual techniques.
EDA focuses on objectively probing the facts without any expectations; it does not entail hypothesis testing or the deliberate search for a solution. On the other hand, traditional data mining focuses on extracting insights from the data or addressing a specific business problem.
Data Warehousing
Most extensive data mining projects start with data warehousing. An example of a data management system is a data warehouse created to facilitate and assist business intelligence initiatives. This is accomplished by centralizing and combining several data sources, including transactional data from POS (point of sale) systems and application log files.
A data warehouse typically includes a relational database for storing and retrieving data, an ETL (Extract, Transfer, Load) pipeline for preparing the data for analysis, statistical analysis tools, and client analysis tools for presenting the data to clients.
Clustering
One of the most often used data mining techniques is clustering, which divides a massive dataset into smaller subsets by categorizing objects based on their similarity into groups.
When consumers are grouped together based on shared purchasing patterns or lifetime value, customer segments are created, allowing the company to scale up targeted marketing campaigns.
Hard clustering entails the categorization of data points directly. Instead of assigning a data point to a cluster, soft clustering gives it a likelihood that it belongs in one or more clusters.
Classification
A prediction approach called classification involves estimating the likelihood that a given item falls into a particular category. A multiclass classification problem has more than two classes, unlike a binary classification problem, which only has two types.
Classification models produce a serial number, usually called confidence, that reflects the likelihood that an observation belongs to a specific class. The class with the highest probability can represent a predicted probability as a class label.
Spam filters, which categorize incoming emails as "spam" or "not spam" based on predetermined criteria, and fraud detection algorithms, which highlight suspicious transactions, are the most prevalent examples of categorization in a business use case.
Regression Model
When a company needs to forecast a numerical number, such as how long a potential customer will wait to cancel an airline reservation or how much money they will spend on auto payments over time, they can use a regression method.
For instance, linear regression is a popular regression technique that searches for a correlation between two variables. Regression algorithms of this type look for patterns that foretell correlations between variables, such as the association between consumer spending and the amount of time spent browsing an online store.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are data processing methods with biological influences that use historical and present data to forecast future values. They can uncover intricate relationships buried in the data because of their design, which mimics the brain's mechanisms for pattern recognition.
They have several layers that take input (input layer), calculate predictions (hidden layer), and provide output (output layer) in the form of a single prediction. They are frequently used for applications like image recognition and patient diagnostics.
Decision Trees
A decision tree is a graphic diagram that looks like an upside-down tree. Starting at the "roots," one walks through a continuously narrowing range of alternatives, each illustrating a possible decision conclusion. Decision trees may handle various categorization issues, but they can resolve many more complicated issues when used with predictive analytics.
An airline, for instance, would be interested in learning the optimal time to travel to a new location it intends to serve weekly. Along with knowing what pricing to charge for such a flight, it might also want to know which client groups to cater to. The airline can utilize a decision tree to acquire insight into the effects of selling tickets to destination x at price point y while focusing on audience z, given these criteria.
Logistics Regression
It is used when determining the likelihood of success in terms of Yes or No, Success or Failure. We can utilize this model when the dependent variable has a binary (Yes/No) nature.
Since it uses a non-linear log to predict the odds ratio, it may handle multiple relationships without requiring a linear link between the variables, unlike a linear model. Large sample sizes are also necessary to predict future results.
Ordinal logistic regression is used when the dependent variable's value is ordinal, and multinomial logistic regression is used when the dependent variable's value is multiclass.
Time Series Model
Based on past data, time series are used to forecast the future behavior of variables. Typically, a stochastic process called Y(t), which denotes a series of random variables, are used to model these models.
A time series might have the frequency of annual (annual budgets), quarterly (sales), monthly (expenses), or daily (daily expenses) (Stock Prices). It is referred to as univariate time series forecasting if you utilize the time series' past values to predict future discounts. It is also referred to as multivariate time series forecasting if you include exogenous variables.
The most popular time series model that can be created in Python is called ARIMA, or Auto Regressive Integrated Moving Average, to anticipate future results. It's a forecasting technique based on the straightforward notion that data from time series' initial values provides valuable information.
In Conclusion-
Although predictive analytics techniques have had their fair share of critiques, including the claim that computers or algorithms cannot foretell the future, predictive analytics is now extensively employed in virtually every industry. As we gather more and more data, we can anticipate future outcomes with a certain level of accuracy. This makes it possible for institutions and enterprises to make wise judgments.
Implementing Predictive Analytics is essential for anybody searching for company growth with data analytics services since it has several use cases in every conceivable industry. Contact us at SG Analytics if you want to take full advantage of predictive analytics for your business growth.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sensing and controlling microscopic spin density in materials
By fine-tuning the spin density in some materials, researchers may be able to develop new quantum sensors or quantum simulations.
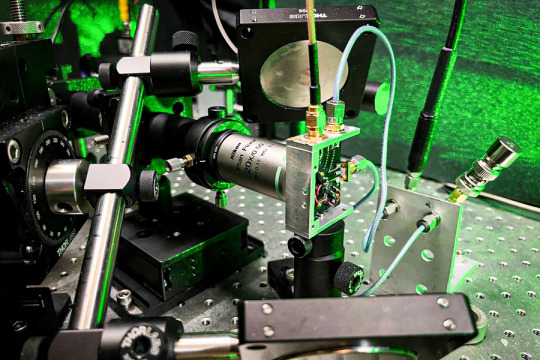
David L. Chandler | MIT News
Electronic devices typically use the charge of electrons, but spin — their other degree of freedom — is starting to be exploited. Spin defects make crystalline materials highly useful for quantum-based devices such as ultrasensitive quantum sensors, quantum memory devices, or systems for simulating the physics of quantum effects. Varying the spin density in semiconductors can lead to new properties in a material — something researchers have long wanted to explore — but this density is usually fleeting and elusive, thus hard to measure and control locally.
Now, a team of researchers at MIT and elsewhere has found a way to tune the spin density in diamond, changing it by a factor of two, by applying an external laser or microwave beam. The finding, reported this week in the journal PNAS, could open up many new possibilities for advanced quantum devices, the authors say. The paper is a collaboration between current and former students of professors Paola Cappellaro and Ju Li at MIT, and collaborators at Politecnico of Milano. The first author of the paper, Guoqing Wang PhD ’23, worked on his PhD thesis in Cappellaro’s lab and is now a postdoc at MIT.
A specific type of spin defect known as a nitrogen vacancy (NV) center in diamond is one of the most widely studied systems for its potential use in a wide variety of quantum applications. The spin of NV centers is sensitive to any physical, electrical, or optical disturbance, making them potentially highly sensitive detectors. “Solid-state spin defects are one of the most promising quantum platforms,” Wang says, partly because they can work under ambient, room-temperature conditions. Many other quantum systems require ultracold or other specialized environments.
“The nanoscale sensing capabilities of NV centers makes them promising for probing the dynamics in their spin environment, manifesting rich quantum many body physics yet to be understood”, Wang adds. “A major spin defect in the environment, called P1 center, can usually be 10 to 100 times more populous than the NV center and thus can have stronger interactions, making them ideal for studying many-body physics.”
But to tune their interactions, scientists need to be able to change the spin density, something that had previously seldom been achieved. With this new approach, Wang says, “We can tune the spin density so it provides a potential knob to actually tune such a system. That’s the key novelty of our work.”
Such a tunable system could provide more flexible ways of studying the quantum hydrodynamics, Wang says. More immediately, the new process can be applied to some existing nanoscale quantum-sensing devices as a way to improve their sensitivity.
Li, who holds a joint appointment in MIT’s departments of Nuclear Science and Engineering and Materials Science and Engineering, explains that today’s computers and information processing systems are all based on the control and detection of electrical charges, but some innovative devices are beginning to make use of the property called spin. The semiconductor company Intel, for example, has been experimenting with new kinds of transistors that couple spin and charge, potentially opening a path to devices based on spintronics.
“Traditional CMOS transistors use a lot of energy,” Li says, “but if you use spin, as in this Intel design, then you can reduce the energy consumption by a lot.” The company has also developed solid-state spin qubit devices for quantum computing, and “spin is something people want to control in solids because it’s more energy efficient, and it’s also a carrier of quantum information.”
In the study by Li and his colleagues, the newly achieved level of control over spin density allows each NV center to act like a kind of atomic-scale “radar” that can both sense and control the nearby spins. “We basically use a particular NV defect to sense the surrounding electronic and nuclear spins. This quantum sensor reveals the nearby spin environment and how that’s affected dynamically by the charge flow, which in this case is pumped up by the laser,” Li says.
This system makes it possible to dynamically change the spin concentration by a factor of two, he says. This could ultimately lead to devices where a single point defect or a single atom could be the basic computational unit. “In the long run, a single point defect, and the localized spin and the localized charge on that single point defect, can be a computing logic. It can be a qubit, it can be a memory, it can be a sensor,” he says.
He adds that much work remains to develop this newly found phenomenon. “We’re not exactly there yet,” he says, but what they have demonstrated so far shows that they have “really pushed down the measurement and control of the spin and charge state of point defects to an unprecedented level. So, in the long run, I think this would support using individual defect, or a small number of defects, to become the information processing and sensing devices.”
In this work so far, Wang says, “we find this phenomenon and we demonstrate it,” but further work is needed to fully understand the physical mechanism of what is taking place in these systems. “Our next step is to dig more deeply into the physics, so we would like to know better what’s the underlying physical mechanism” behind the effects they see. In the long term, “with better understanding of these systems, we hope to explore more quantum simulation and sensing ideas, such as simulating interesting quantum hydrodynamics, and even transporting quantum information between different spin defects.”
The findings were made possible, in part, by the team’s development of a new wide-field imaging setup that allows them to measure many different spatial locations within the crystalline material simultaneously, using a fast single-photon detector array, combined with a microscope. “We are able to spatially image the density distribution over different spin species like a fingerprint, and the charge transport dynamics,” although that work is still preliminary, Wang says.
Although their work was done using lab-grown diamond, the principles could be applied to other crystalline solid-state defects, he says. NV centers in diamond have been attractive for research because they can be used at room temperature and they have already been well-studied. But silicon vacancy centers, donors in silicon, rare-earth ions in solids, and other crystal materials may have different properties that could turn out to be useful for particular kinds of applications.
“As information science progresses, eventually people will be able to control the positions and the charge of individual atoms and defects. That’s the long-term vision,” Li says. “If you can have every atom storing different information, it’s a much larger information storage and processing capability” compared to existing systems where even a single bit is stored by a magnetic domain of many atoms. “You can say it’s the ultimate limit of Moore’s Law: eventually going down to one defect or one atom.”
While some applications may require much more research to develop to a practical level, for some kinds of quantum sensing systems, the new insights can be quickly translated into real-world uses, Wang says. “We can immediately improve the quantum sensors’ performance based on our results,” he says.
“Overall, this result is very exciting for the field of solid-state spin defects,” says Chong Zu, an assistant professor of physics at Washington University in St. Louis, who specializes in quantum information but was not involved in this work. “In particular, it introduces a powerful approach of using charge ionization dynamics to continuously tune the local spin defect density, which is important in the context of applications of NV centers for quantum simulation and sensing.”
The research team included Changhao Li, Hao Tang, Boning Li, Francesca Madonini, Faisal Alsallom, and Won Kyu Calvin Sun, all at MIT; Pai Peng at Princeton University; and Federica Villa at the Politecnico de Milano, in Italy. The work was partly supported by the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How AI Is Reshaping M&A Strategy Amid Trade Tensions and Global Volatility
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/how-ai-is-reshaping-ma-strategy-amid-trade-tensions-and-global-volatility/
How AI Is Reshaping M&A Strategy Amid Trade Tensions and Global Volatility


As we head into summer 2025, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) stands at a crossroads. Geopolitical tensions, economic headwinds, and rapid advances in technology are forcing dealmakers to rethink how they source, structure, and close transactions. Trade policy is emerging as a major variable. Unpredictable tariffs, shifting alliances, and growing regulatory scrutiny have pushed global deal activity into more cautious territory. Yet amid the uncertainty, artificial intelligence is coming into focus.
AI is no longer a futuristic add-on. It’s becoming central to the way companies approach M&A. In a climate where speed, precision, and risk management matter more than ever, AI is giving dealmakers a critical edge. It helps surface opportunities faster, pressure-test assumptions, and spot risks early, before they derail a transaction. AI isn’t just making M&A faster. It’s making it smarter.
Trade Uncertainty Is Reshaping M&A Strategy
Changing US trade policies are stalling cross-border deals and making future revenue streams harder to predict. As a result, dealmakers face a two-sided challenge: how to keep deal momentum alive while insulating portfolios from geopolitical shocks.
Some of the effects are already evident on Datasite, which handles over 19,000 new deals a year. New deal kickoffs, especially asset sales and mergers, are up 4% globally in the first four months of this year compared to the same time a year ago. Since these are deals at inception before they are announced, it can provide a good sense of what’s to come and some of the momentum that has already occurred.
Yet there’s caution, too. Deal completion rates on Datasite sank to 44% after the first major US tariff announcement on April 2, down from 49% year-over-year (YoY). This means buyers are slowing down. They want more time to evaluate risks. They’re asking more questions. They’re probing the fine print, and if necessary, they are walking away.
A key reason is tariffs. When tariffs are imposed on imported goods or raw materials, they can directly impact the cost structures and profit margins of target companies, especially those with global supply chains. This creates volatility in financial projections, which complicates valuation models and discourages dealmaking. Buyers face added risk as they try to assess whether a target’s current revenue performance can be sustained under changing trade conditions. In many cases, tariffs prompt companies to reconsider expansion into or acquisition within certain countries, shifting M&A activity toward regions with more stable trade relationships.
Additionally, ongoing trade tensions, such as those between the US and China, have led to increased regulatory scrutiny, which further delays or derails deals. These combined factors force dealmakers to spend more time conducting due diligence, modeling various tariff scenarios, and adding protective clauses to deal structures. This then makes the M&A process more complex and costly.
Tariffs are not just increasing operational expenses, they are also reshaping strategic planning by making it more difficult to forecast long-term growth, return on investment, and integration outcomes in cross-border transactions.
Risk models now routinely factor in tariff exposure. Buyers are looking not just at what a target company earns today, but how future trade policy could affect that cash flow. Some deals, particularly cross-border ones, are being paused or restructured entirely as the investment math shifts.
To stay competitive, dealmakers must adapt. That means embracing better tools, faster workflows, and more rigorous diligence. It also means building flexibility into the deal process to account for economic swings.
AI Streamlines Diligence and Strengthens Risk Controls
This is where AI is stepping in. It’s helping deal teams process more information in less time and with greater accuracy. Due diligence is a critical but resource-intensive process that traditionally involves manually reviewing large volumes of documents and information. This approach can be time-consuming and laborious, often placing significant strain on professionals, especially when working under tight deadlines. As a result, the quality and thoroughness of the review may be compromised. AI offers a solution to this challenge by enabling faster and more efficient analysis. AI tools can quickly sort, summarize, and highlight key clauses and relevant obligations within documents, allowing dealmakers to focus on the most important information. This not only improves accuracy but also significantly reduces the time required to complete the due diligence process. For example, AI can organize, categorize and flag key data and risks across thousands of documents in a virtual data room in real time, helping to reduce human error and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
It’s no surprise that one in five dealmakers now use generative AI in the M&A process, while many more say AI adoption is their top operational priority this year. Why? Because the M&A playbook is changing. Reviews are more intense. Regulators ask more questions. Investors demand deeper insight. AI helps answer the call.
Virtual data rooms are also evolving. It’s now common for deal teams to use AI-powered Q&A tools to interrogate information before making a move. In fact, the use of Q&A tools on Datasite has climbed since the start of the year, reflecting an increased need for sellers to be ready to respond quickly and thoroughly to buyers who want to see clean, complete data.
Additionally, AI is increasingly playing a valuable role in identifying potential acquisition targets. By analyzing various market signals, such as company descriptions, geographic compatibility, and size-related criteria, AI can help buyers pinpoint suitable candidates more efficiently. These insights are often derived from a combination of public, private, and proprietary data sources. As a result, some AI-powered platforms are already enabling dealmakers to discover potential targets more quickly and accurately. This proactive approach can improve strategic alignment, making it easier for companies to integrate new capabilities post-acquisition and achieve the growth objectives intended by the deal.
AI can also contribute to the valuation process by offering data-driven analyses based on historical trends and current market conditions. It can also automate routine and labor-intensive tasks, such as redacting sensitive information in documents. By streamlining these operational steps, AI allows professionals to focus more on high-level strategy and innovative thinking, ultimately improving the quality and effectiveness of decision-making throughout the M&A lifecycle.
Dealmakers Must Shift from Reactive to Proactive
In today’s environment, waiting for the perfect moment to launch a deal isn’t a strategy, it’s a liability. Timing matters, but preparation matters more. Those who succeed in this market will be the ones who invest early in deal readiness. That can include cleaning up financials, mapping supply chain dependencies, reviewing IP portfolios, and aligning management on deal terms.
Of course, AI alone isn’t the answer. The best strategies combine human insight with machine intelligence. Use AI to surface options. Use your team to make the calls. Technology should guide the process, not replace judgment.
The Future of M&A Is Here
M&A will always carry risk. But how to manage that risk is changing. AI is raising the bar. It’s giving dealmakers the tools to work faster, smarter, and with more foresight.
In a world where tariffs will likely continue to evolve, and regulators can shift course mid-review, speed and insight matter. The future belongs to dealmakers that are data-driven, tech-forward, and strategically agile.
#000#2025#acquisition#acquisitions#ADD#add-on#adoption#agile#ai#AI adoption#ai tools#AI-powered#amp#analyses#Analysis#approach#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#border#Building#challenge#China#climate#Companies#compliance#course#data#data sources#data-driven#datasite
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Manual Fixture for Your Testing Needs: A Step-by-Step Guide
In the world of electronics testing and precision manufacturing, the right tools can make the difference between flawless performance and costly rework. Among those tools, the manual fixture plays a pivotal yet often underrated role in ensuring quality, consistency, and efficiency. Whether you're testing PCBs, wiring harnesses, or microelectronic components, selecting the ideal manual fixture is crucial for optimizing test results and minimizing downtime.
But with countless configurations, materials, and functions available, how do you determine which fixture is best suited for your testing environment?
In this guide, we’ll break down the key steps and considerations to help you choose the perfect manual fixture for your specific needs—whether you’re a test engineer, production manager, or quality control specialist.
Step 1: Define Your Testing Objectives Clearly
Before exploring fixture options, clarify what you want the fixture to accomplish. Are you focused on functional testing, continuity testing, or high-voltage isolation? Will it be used in a high-volume production environment or for prototype verification?
Understanding your goals will help narrow down the required features, such as:
Contact type (spring-loaded pins, pogo pins, etc.)
Force requirements
Number of test points
Load/unload speed
At Equip-Test, manual fixture solutions are available for everything from standard bed-of-nails setups to fully customized designs tailored to specific PCB layouts and test flows.
Step 2: Assess the Component or Board Geometry
Next, evaluate the physical characteristics of the unit under test (UUT):
What are the dimensions of the board or component?
Are there connectors or edge contacts?
Does the test require double-sided probing?
These factors will influence the fixture’s platform size, the arrangement of test probes, and whether a top-side pressure plate or vacuum hold-down is necessary.
Equip-Test offers both standard and modular manual fixture systems, making it easier to accommodate complex board geometries without reinventing the wheel every time.
Step 3: Choose the Right Probing Technology
One of the most critical aspects of a manual fixture is the selection of test probes. Depending on the signal integrity, current rating, and pitch requirements, you might need:
Standard spring-loaded probes for through-hole or SMT pads
High-frequency probes for RF circuits
Kelvin probes for low-resistance measurements
Special probes for surface wear or sensitive contacts
Don’t overlook the importance of probe life cycle and accessibility, especially in high-throughput environments.
Equip-Test's vast test probe catalog is engineered to support virtually every test scenario imaginable, ensuring precision and durability.
Step 4: Factor in Ergonomics and Operator Safety
Manual fixtures should not only be functional but also comfortable and safe to use. Consider:
Lever mechanisms or pneumatic assist for high-contact-count boards
Clear visibility and easy access to the DUT
Built-in ESD protection
Shielding for high-voltage applications
A poorly designed manual fixture can increase operator fatigue and error rates. Ergonomic enhancements also reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries during continuous operation.
Step 5: Plan for Scalability and Maintenance
If your test needs might change in the near future, it’s wise to invest in a modular or upgradable fixture. Look for designs that allow:
Easy probe replacement
Interchangeable probe plates
Quick fixture swaps for different board versions
This is where modular fixture platforms from Equip-Test really shine. These fixtures can be easily reconfigured or upgraded, providing flexibility without excessive downtime or new tooling costs.
Step 6: Work with a Trusted Fixture Manufacturer
Even with a clear checklist, designing the perfect fixture isn’t always DIY-friendly. Partnering with a company that specializes in test fixture development ensures:
Optimal layout and mechanical design
High-quality materials and build
Fast turnaround and support for modifications
Integration with test equipment (ICT, functional testers, etc.)
Equip-Test has been at the forefront of manual fixture solutions for years, supporting global electronics manufacturers with robust, reliable test platforms. Whether you're outfitting a new production line or upgrading legacy systems, their engineering team brings unmatched expertise to every custom fixture build.
Final Thoughts: Precision Starts at the Fixture
Your test equipment is only as good as the connection it makes with the unit under test—and that connection starts with a well-chosen manual fixture. By carefully considering your application requirements, board design, probe technology, ergonomics, and future needs, you can ensure accurate, repeatable test results while keeping costs under control.
Ready to explore your options or need expert advice? Visit Equip-Test to discover high-performance manual fixtures designed to elevate your testing process from the ground up.
0 notes
Text
fluke dealers in bangalore
393 FC CAT III 1500 V True-RMS Clamp Meter with iFlex®
The Fluke 393 FC is engineered specifically for technicians working in high-voltage DC environments such as solar arrays, wind power systems, electric railways, and data center battery banks supporting uninterruptible power supplies.
This robust clamp meter measures:
Up to 1500 V DC
Up to 1000 V AC
Up to 999.9 A AC/DC through the clamp jaw
With the included iFlex® flexible current probe, you can extend AC current measurements up to 2500 A, enabling greater flexibility in tight or crowded spaces.
Designed for convenience and accuracy in demanding settings, the clamp features a slim jaw profile, making it easy to access conductors in congested combiner boxes. The test leads are also built for high-voltage environments and rated to CAT III 1500 V DC, ensuring safe and reliable performance on the job.
0 notes
Text
Diathermy: Uses, Benefits, And Risks As one of the oldest treatment modalites, the therapeutic effects of heat have been experienced for several hundred years. In order to use heat in the treatment of deep muscle injury, diathermy treatment is the therapy of choice. Diathermy uses high-frequency electrical currents to heat deep muscular tissues. This heating results in pain relief, increased blood flow, and increased flexibility. Research has demonstrated evidence both for and against the effectiveness of diathermy treatment. Attention must be given, however, to risk factors predisposing some patients to serious adverse effects due to diathermy treatment. Diathermy: Uses, benefits, and risks Diathermy refers to the use of high-frequency electrical currents to heat deep muscular tissues. This heat increases the flow of blood to the area, which in turn, speeds up recovery. The term diathermy is a derivative of the Greek words therma, meaning heat, and dia, meaning through. Therefore, the term diathermy literally means heating through. The therapeutic effects of heat have been recognized for thousands of years, and the practice of diathermy has its roots in therapies utilized in ancient Rome. More than 2000 years ago, Romans built hot-spring bathhouses in order to take advantage of the healing effects of heat. Various methods of heat related therapy have evolved since then. A French physiologist by the name of Arsene d'Arsonval began studying the medical application of high frequency currents in the early 1890s. German physician Carl Franz Nagelschmidt coined the term diathermy and developed a prototype apparatus in 1906. American doctor J.W. Schereschewsky commenced the study of the physiological effects of high-frequency electrical currents in animals in 1925. However, this was only a start, and it took several years for the fundamentals of diathermy to be understood and put into practice. As one of the oldest modalities of pain relief, heat decreases muscle spasm and improves function. Superficial heat can be provided through the use of hot packs, hot water bottles, hot-moist compresses, electrical heating pads, or chemical/gel packs. Heat can also be provided through immersion in water. All these modalities for the provision of heat convey heat by convection or conduction. These types of superficial heat elevate the temperature of tissues provides the greatest therapeutic effect at 0.5 cm or less from the surface of the skin. On the other hand, the deep heating provided by diathermy is achieved by converting electrical energy to heat. Diathermy increases temperature to depths of 3 to 5 cm. The physiological effects produced by heat include analgesia or relief from pain, increased flexibility of collagenous tissues, reduction of muscle spasm, increase in blood flow, and mental relaxation. Diathermy is used to treat conditions involving stiff, painful joints, such as arthritis and bursitis. It is also used to treat some pelvic infections and sinusitis. Diathermy is also sometimes used in surgical procedures, where electrically heated probes are used to seal blood vessels in order to prevent excessive bleeding. Physicians can also use diathermy to destroy abnormal growths, like tumors, warts, and infected tissues. A benefit of diathermy is that is a painless procedure that can be quickly administered in a clinic setting. Another benefit of diathermy is that the treatment relieves pain, which may allow some patients to discontinue pain killers, thus avoiding high costs and adverse side effects. Diathermy works to alleviate pain and discomfort by heating deep muscular tissue. When heat is applied to the area of concern, blood flow increases and cellular metabolism speeds up. This in turn accelerates tissue repair. The heat created by diathermy also reduces nerve fiber sensitivity, which increases the patient's pain threshold. There are three general methods of diathermy: shortwave diathermy, ultrasound diathermy, and microwave diathermy. In each method, energy is delivered to the deep tissues, where it is converted to heat. In shortwave diathermy, the body part to be treated is placed between two capacitor plates. High-frequency waves travel through the body tissues between the plates, heat is consequently generated, and inflammation is reduced. This type of diathermy is most often used to treat areas covered with a dense tissue mass, like the hip, and it is also used to treat sinusitis and pelvic infections. The frequency allowed for shortwave diathermy treatment is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission, and most machines function at 27.33 megahertz. In ultrasound diathermy, heat is generated in deep tissues through the use of high-frequency acoustic vibrations. Microwave diathermy uses radar waves to heat the tissue to be treated. This form of diathermy is the easiest to use, but the microwaves cannot penetrate deep muscle tissue. There are two general categories of diathermy: monopolar and bipolar. In Monopolar diathermy, an electrical plate is placed on the patient and acts as an indifferent electrode. The electrical current passes between the instrument and the indifferent electrode, and localized heating is produced at the tip of the instrument, while minimal heat is produced at the indifferent electrode. Bipolar diathermy involves the use of two electrodes that are combined in the instrument, such as forceps. The current passes between the two electrodes, and not through the patient. In preparation for treatment, patients are asked to remove clothing from the body part being treated, to prevent sweating. If sweating occurs, electrical currents may pool in the moist area, which causes burns. Any clothing or jewellery containing metal must also be removed. In addition, watches and hearing aids must also be removed because the electrical waves may interrupt their functions. Certain precautionary measures must be taken into account before diathermy is used on a patient. Patients with metal implants should not undergo diathermy treatment because the metal can act as a heat conductor, and this can result in severe internal burns. Moreover, females with metallic uterine implants, like an IUD, should avoid diathermy treatment in the pelvic area. Furthermore, diathermy should not be used in joints that have been replaced with prosthesis or in patients with sensory impairment who may not be able to sense if they are burning. Diathermy should also not be used during pregnancy, as it can result in abnormal fetal development. In addition, patients with hemophilia should avoid diathermy treatment because the increased blood flow caused by the treatment could result in haemorrhaging. Also, channelling effects can occur if diathermy is used on appendages, such as on a finger during surgery. There are some side effects related to the use of diathermy treatment. Some patients may experience superficial burns at the treatment site. Therefore, extra care must b taken to avoid burns, especially in patients who have sustained injuries that have caused decreased sensitivity to heat. Diathermy has also been found to affect pacemaker function. Also, female patients who receive diathermy treatment in the lower back or pelvic area may experience increased menstrual flow. Research has proven the beneficial therapeutic effects of diathermy. Peres et al. (2002) conducted a study to compare the effects of three treatments on ankle dorsiflexion range of motion. The three treatments under study were prolonged long-duration stretching, pulsed shortwave diathermy followed by stretching, and pulsed shortwave diathermy, stretching, and ice combined. The dependent variable in the study was the range of motion change triceps and flexibility. Results indicated that after 14 days of treatment, the range-of-motion increase was greater after heat and stretching than after stretching alone. After 6 additional days of rest, the heat and stretching range-of-motion increase was greater than that of stretching alone. The researchers concluded that pulsed shortwave diathermy application before prolonged static stretching was more effective than stretching alone in increasing flexibility throughout a 3-week period. Furthermore, after 14 treatments, prolonged long-duration stretching combined with pulsed shortwave diathermy followed by ice application resulted in greater immediate and total range-of motion increases than prolonged long-duration stretching alone. Goats (1989) explained how continuous shortwave diathermy is the best available technique when uniform elevation of temperature is required in deep tissues. This type of diathermy permits superficial structures to be heated selectively. Sub-acute and chronic conditions have been found to respond best to continuous shortwave diathermy, which works as effectively as ultrasound. Continuous shortwave diathermy can help to relieve muscle spasm and pain, resolve inflammatory states and reduce swelling, increase the compliance of connective tissue, promote vasodilation, and increase joint range and decrease stiffness of joints. On the other hand, some research has demonstrated that diathermy does not result in significantly improved results. A study by Draper et al. (2002) compared the effects of low-load, short duration stretching with and without high-intensity, pulsed shortwave diathermy on hamstring flexibility. The three independent variables in the study were treatment mode, pretest and posttest measurements, and day. The treatment mode of the study had 3 levels: diathermy and stretching, stretching alone, and control. The dependent variable in the study was range-of-motion. Hamstring flexibility was tested using a sit-and-reach box before and after each treatment. The results indicated that the average increases in hamstring flexibility over the 5 treatment days for the diathermy and stretching group was 6.06 cm (19.6%), the stretching-only group was 5.27 cm. (19.7%), and the control group was 3.38 cm (10.4%). Three days later after no treatment, the values for the three groups were 8.27 cm (26.7%), 6.83 cm (25.3%), and 4.15 cm (14.2%), respectively. These results demonstrated no significant differences in hamstring flexibility among the groups. The researchers therefore concluded that diathermy and short-duration stretching were no more effective than short-duration stretching alone at increasing hamstring flexibility. However, the researchers do note that the effects of diathermy with longer stretching times need to be investigated. There has been a recent risk of serious injury or death associated with the use of diathermy treatment on patients with implanted electrical leads (Feigal, 2002). The FDA received reports in which patients with implanted deep brain stimulators (DBS) died after receiving diathermy treatment. One patient had diathermy treatment after oral surgery, while the other patient had the treatment for chronic scoliosis. In both cases, severe brain damage occurred due to the interaction of the diathermy with the implanted device. Shortwave and microwave diathermy, but not ultrasound diathermy, can result in serious injury or death to patients with implanted devices with leads. Patients with any implanted metallic lead are at risk of these serious effects. These effects occur even if the implanted device is not turned on and even if the lead is no longer connected to an implanted system. The interaction between the diathermy energy and the implanted lead causes excessive heating of the tissue surrounding the lead electrodes. It is unknown, at this point, if there is a safe distance between the implant system and the diathermy instrument. In order to prevent serious injury or death, practitioners using diathermy treatment must be sure to ask patients about possible implants, and to not administer shortwave or microwave diathermy to patients who have had implants in the past unless absolute certainty can be guaranteed as to whether the implant and all leads have been removed in their entirety. As a treatment modality, diathermy is effective in the relief of pain and muscle spasm. It also aids in increasing flexibility and blood flow, which accelerate healing. However, diathermy treatment is not ideal for every therapy situation. Physicians must demonstrate care in screening patients for possible risk factors, such as metallic implants or pregnancy, which can possibly result in serious injury, and in some instances, death. References Frick, L. (2001). Diathermy. Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine. http://www.findarticles.com/g2603/0003/2603000326/p1/article.jhtml. Peres, S., Draper, D., Knight, K., Ricard, M. (2002). Pulsed shortwave diathermy and prolonged long-duration stretching increase dorsiflexion range of motion more than identical stretching without diathermy. Journal of Athletic Training, 37(1), 43-50. Draper, D., Miner, L., Knight, K., Ricard, M. (2002). The carry-over effects of diathermy and stretching in developing hamstring flexibility. Journal of Athletic Training, 37(1), 37-42. Diathermy. http://www.orthoteers.co.uk/Nrujp~ij331m/Orthdiathermy.htm Feigal, D. (2002). FDA public health notification: Diathermy interactions with implanted leads and implanted systems with leads. U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Center For Devices and Radiological Health. http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/safety/121902.html. Goats, C. (1989). Continuous short-wave (radio-frequency) diathermy. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 23(2), 123-127. Vasudevan, S. (1997). Physical rehabilitation in managing pain. Pain: Clinical Updates, 5(3). http://www.iasp-pain.org/PCU97c.html. Moyer, P. (2002). AAO-HNSF: Bipolar diathermy and disposable instruments safe, despite worrisome anecdotal reports. Doctor's Guide. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Introducing Meco Instruments, your go-to for reliable electrical testing gear! Meco Instruments offers a wide range of tools to make your job easier. Whether you're a professional electrician or a DIY enthusiast, Meco has you covered. Their products are known for their durability and accuracy. Plus, with their flexible current probes, you can easily measure currents in tight spaces.
0 notes
Text
A flexible robot can help emergency responders search through rubble
New Post has been published on https://sunalei.org/news/a-flexible-robot-can-help-emergency-responders-search-through-rubble/
A flexible robot can help emergency responders search through rubble
When major disasters hit and structures collapse, people can become trapped under rubble. Extricating victims from these hazardous environments can be dangerous and physically exhausting. To help rescue teams navigate these structures, MIT Lincoln Laboratory, in collaboration with researchers at the University of Notre Dame, developed the Soft Pathfinding Robotic Observation Unit (SPROUT). SPROUT is a vine robot — a soft robot that can grow and maneuver around obstacles and through small spaces. First responders can deploy SPROUT under collapsed structures to explore, map, and find optimum ingress routes through debris.
“The urban search-and-rescue environment can be brutal and unforgiving, where even the most hardened technology struggles to operate. The fundamental way a vine robot works mitigates a lot of the challenges that other platforms face,” says Chad Council, a member of the SPROUT team, which is led by Nathaniel Hanson. The program is conducted out of the laboratory’s Human Resilience Technology Group.
First responders regularly integrate technology, such as cameras and sensors, into their workflows to understand complex operating environments. However, many of these technologies have limitations. For example, cameras specially built for search-and-rescue operations can only probe on a straight path inside of a collapsed structure. If a team wants to search further into a pile, they need to cut an access hole to get to the next area of the space. Robots are good for exploring on top of rubble piles, but are ill-suited for searching in tight, unstable structures and costly to repair if damaged. The challenge that SPROUT addresses is how to get under collapsed structures using a low-cost, easy-to-operate robot that can carry cameras and sensors and traverse winding paths.
Play video
How a Flexible Robot Helps Find Survivors Inside Collapsed Buildings Video: MIT Lincoln Laboratory
SPROUT is composed of an inflatable tube made of airtight fabric that unfurls from a fixed base. The tube inflates with air, and a motor controls its deployment. As the tube extends into rubble, it can flex around corners and squeeze through narrow passages. A camera and other sensors mounted to the tip of the tube image and map the environment the robot is navigating. An operator steers SPROUT with joysticks, watching a screen that displays the robot’s camera feed. Currently, SPROUT can deploy up to 10 feet, and the team is working on expanding it to 25 feet.
When building SPROUT, the team overcame a number of challenges related to the robot’s flexibility. Because the robot is made of a deformable material that bends at many points, determining and controlling the robot’s shape as it unfurls through the environment is difficult — think of trying to control an expanding wiggly sprinkler toy. Pinpointing how to apply air pressure within the robot so that steering is as simple as pointing the joystick forward to make the robot move forward was essential for system adoption by emergency responders. In addition, the team had to design the tube to minimize friction while the robot grows and engineer the controls for steering.
While a teleoperated system is a good starting point for assessing the hazards of void spaces, the team is also finding new ways to apply robot technologies to the domain, such as using data captured by the robot to build maps of the subsurface voids. “Collapse events are rare but devastating events. In robotics, we would typically want ground truth measurements to validate our approaches, but those simply don’t exist for collapsed structures,” Hanson says. To solve this problem, Hanson and his team made a simulator that allows them to create realistic depictions of collapsed structures and develop algorithms that map void spaces.
SPROUT was developed in collaboration with Margaret Coad, a professor at the University of Notre Dame and an MIT graduate. When looking for collaborators, Hanson — a graduate of Notre Dame — was already aware of Coad’s work on vine robots for industrial inspection. Coad’s expertise, together with the laboratory’s experience in engineering, strong partnership with urban search-and-rescue teams, and ability to develop fundamental technologies and prepare them for transition to industry, “made this a really natural pairing to join forces and work on research for a traditionally underserved community,” Hanson says. “As one of the primary inventors of vine robots, Professor Coad brings invaluable expertise on the fabrication and modeling of these robots.”
Lincoln Laboratory tested SPROUT with first responders at the ��Massachusetts Task Force 1 training site in Beverly, Massachusetts. The tests allowed the researchers to improve the durability and portability of the robot and learn how to grow and steer the robot more efficiently. The team is planning a larger field study this spring.
“Urban search-and-rescue teams and first responders serve critical roles in their communities but typically have little-to-no research and development budgets,” Hanson says. “This program has enabled us to push the technology readiness level of vine robots to a point where responders can engage with a hands-on demonstration of the system.”
Sensing in constrained spaces is not a problem unique to disaster response communities, Hanson adds. The team envisions the technology being used in the maintenance of military systems or critical infrastructure with difficult-to-access locations.
The initial program focused on mapping void spaces, but future work aims to localize hazards and assess the viability and safety of operations through rubble. “The mechanical performance of the robots has an immediate effect, but the real goal is to rethink the way sensors are used to enhance situational awareness for rescue teams,” says Hanson. “Ultimately, we want SPROUT to provide a complete operating picture to teams before anyone enters a rubble pile.”
0 notes
Text
Advanced Charge and Discharge Testing System for Lithium Battery Packs: Semco SI-Y BCDS 50V (5A/10A) 35CH
The Semco SI-Y BCDS 50V (5A/10A) 35CH is a high-performance charge and discharge testing system engineered for lithium battery packs used in electric tools, solar energy storage systems, electric bicycles, scooters, and similar applications. This versatile system provides a complete solution for cycle testing, functional verification, and performance evaluation of battery packs, ensuring they meet strict safety and quality standards.

This advanced system is capable of testing battery packs with voltages up to 50V, making it ideal for a wide range of lithium battery configurations. It comes in two current range options—5A and 10A—offering flexibility depending on the specific testing requirements. Both versions deliver the same advanced features and functions, differing only in their current capacity. Each variant is equipped with 35 independent channels, allowing simultaneous testing of up to 35 different battery packs at a time. This high channel count greatly enhances testing efficiency and throughput, particularly in production and quality control environments.

Designed for rigorous and repetitive testing, the system offers stable and accurate charge and discharge operations. It supports constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) charging modes, along with constant current discharging. These functions are crucial for monitoring battery pack performance, capacity, and durability over repeated cycles. By accurately simulating real-world operating conditions, the system helps identify any charging or discharging irregularities and ensures the battery’s built-in protection mechanisms are functioning properly.
The Semco SI-Y BCDS 50V (5A/10A) 35CH operates reliably in varying environmental conditions, with an operational temperature range of -10°C to 45°C. It is designed for use in clean, vibration-free environments, free from corrosive, flammable, or explosive gases, making it ideal for precision testing labs or production facilities.

Safety is a top priority in the system’s design. It incorporates anti-reverse connection protection, voltage upper and lower limit safeguards, safe discharge current settings, and power failure data protection. These features ensure both the battery packs and the equipment are protected during testing, even in the event of unexpected power interruptions.
The system offers flexible connectivity options to support different scales of operation. For smaller setups, up to five instruments can be connected to a PC via a serial port. For larger installations, network communication enables centralized control of up to 30 instruments from a single PC terminal. This scalable design allows seamless integration into both small R&D environments and large-scale production lines.
The Semco SI-Y BCDS 50V (5A/10A) 35CH features a user-friendly software platform compatible with Windows-based operating systems. It leverages an SQL database to manage test data efficiently, providing real-time monitoring and visual display of charge and discharge curves. Users can easily filter data by battery barcode, time, or equipment number and export reports in formats such as Excel and TXT for further analysis.
Physically, the system is compact and efficiently organized, with 35 channels arranged in a 7-row by 5-column structure. It is supplied with essential accessories like test probe lines, user manuals, and upper computer software, ensuring easy setup and operation from day one.

The Semco SI-Y BCDS 50V (5A/10A) 35CH is an indispensable tool for lithium battery development, production, and quality control professionals. Its precise testing capabilities, robust safety features, and scalable design make it a reliable and efficient solution for ensuring battery pack quality and performance, whether in small labs or high-volume manufacturing environments.
The Semco SI-Y BCDS 50V (5A/10A) 35CH delivers exceptional performance, safety, and flexibility for those seeking a comprehensive, high-efficiency battery testing system. Additionally, it is compatible with Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Battery Pack Charging and Discharging Machine, Prismatic Battery Pack Charging and Discharging Cabinets, and various battery making machines, battery making equipment, and battery cell making machines, making it a versatile solution for battery testing and manufacturing.
#Cylindrical Lithium Ion Battery Pack Charging and Discharging Machine#lithium ion batteries#lithium ion battery packs#charging and discharging cabinets#charging and discharging machines#cylindrical lithium ion battery pack#prismatic lithium ion battery packs#prismatic lithium ion battery pack charging and discharging cabinets
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right SMT Testing Equipment for Your PCB Assembly Line

In today’s fast-paced electronics manufacturing environment, SMT testing is critical to ensuring the quality, reliability, and functionality of printed circuit boards (PCBs). With shrinking component sizes, denser board layouts, and increasing complexity, selecting the right SMT testing equipment is more important than ever. The right tools not only detect defects but also enhance productivity, reduce rework costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
If you're setting up or upgrading a PCB assembly line, here's a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right SMT testing equipment for your needs.
1. Understand Your Testing Objectives
Before selecting any testing equipment, define your goals clearly. Are you primarily testing for manufacturing defects, functional issues, or both? Different types of SMT testing equipment serve different purposes:
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection): For detecting surface-level defects like solder bridges, misaligned components, or missing parts.
ICT (In-Circuit Testing): For verifying electrical performance and component values.
Functional Testing (FCT): For simulating real-world operating conditions and checking overall board functionality.
Flying Probe Testing: Ideal for low-volume or prototype production where fixture-based testing is cost-prohibitive.
Understanding what you need to test will guide the selection process and help you prioritize features.
2. Consider Production Volume and Board Complexity
Your production volume and the complexity of your PCBs will significantly impact the type of SMT testing equipment you require.
High-Volume Production: For large-scale manufacturing, speed and automation are critical. High-speed AOI and ICT machines with multi-board support and automated defect classification systems are ideal.
Low-Volume or Prototype Production: Flying probe testers and manual visual inspection systems can offer greater flexibility without the upfront cost of fixtures.
Complex Boards: If your designs include high-density interconnects (HDI), BGA components, or multi-layer boards, advanced AOI with 3D inspection and X-ray systems may be necessary.
3. Evaluate Automation and Integration Capabilities
Modern SMT testing equipment should easily integrate with your existing production line and MES (Manufacturing Execution System). Look for features such as:
Real-time defect reporting
Barcode/QR code traceability
Automated board handling systems
Remote diagnostics and data logging
Automation not only speeds up testing but also improves consistency and traceability, which is essential for quality control and compliance.
4. Prioritize Test Coverage and Accuracy
The effectiveness of your SMT testing process depends on the test coverage and accuracy. For example:
AOI should offer both 2D and 3D inspection for more accurate solder joint analysis.
ICT machines should be able to test a wide range of components including resistors, capacitors, diodes, and ICs.
Functional testers should simulate real operating conditions and measure parameters like voltage, current, and signal integrity.
A higher test coverage means fewer defects slip through to the final product — saving time and reducing costly rework.
5. Think About Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While initial purchase price is important, don’t overlook the total cost of ownership. This includes:
Maintenance and calibration
Fixture costs (especially for ICT)
Software updates and licensing fees
Training and support services
Choose a supplier known for reliability, customer service, and long-term support to maximize your return on investment.
6. Scalability and Future-Proofing
As your production grows or technology evolves, your SMT testing needs may change. Select equipment that is modular or upgradable. Some AOI and ICT platforms offer software-based upgrades or allow for additional camera modules, faster processors, or enhanced analytics features — enabling your system to evolve without total replacement.
Conclusion
Choosing the right SMT testing equipment for your PCB assembly line is not just about buying a machine — it's about investing in your product quality and manufacturing efficiency. By considering your production needs, board complexity, automation goals, and long-term scalability, you can make informed decisions that lead to fewer defects, smoother operations, and satisfied customers.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Fishing Rod Combos for Beginners | Tested & Rated
Fishing in the great outdoors—whether casting into the stillness of a dawn lake, battling currents along a riverbank, or pursuing a trophy catch over a weekend—marries patience with the visceral excitement of the chase. As angling surges in popularity through 2025, blending honed technique with reliable equipment transforms a casual outing into a rewarding pursuit. The 2.1m Lure Fishing Rod Combo with Reel, Line, and Tackle Bag, available in striking blue (RC1000) or red (PC1000) configurations, delivers a comprehensive solution for anglers seeking performance and adaptability. This article explores the core principles of outdoor fishing—rod functionality, lure strategies, and aquatic behavior—while evaluating how this combo enhances the experience. From the physics of casting to the subtleties of fish habitats, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to excel on the water.
The Pivotal Role of Fishing Gear
Success in fishing hinges on preparation, where equipment serves as the critical link between angler and quarry. A 2023 survey of recreational fishermen revealed that 70% of unsuccessful trips stemmed from inadequate gear—rods lacking flexibility, reels prone to jamming, or lures mismatched to conditions. A well-rounded lure fishing rod setup, like this 2.1m combo, bridges that gap, offering a 6.9-foot rod for balanced reach, a robust water drop reel for smooth operation, and a curated selection of baits for diverse scenarios. Paired with a tackle bag for organization, it ensures readiness—whether targeting bass in tangled cover or trout in swift streams—elevating each cast from guesswork to precision.
Understanding Rod Mechanics
A fishing rod functions as an extension of the angler’s intent, its design dictating cast distance, control, and fish-fighting capability. At 2.1 meters, this rod strikes an optimal compromise—long enough to achieve casts of 50-70 feet, yet manageable for accurate flicks into tight spaces like overhanging branches or rocky outcrops. Constructed from durable materials—likely a carbon or fiberglass composite—it flexes under load without snapping, absorbing the thrashing of a 5-pound bass or the sudden sprint of a trout. The collapsible handle, interchangeable for right- or left-handed use, enhances ergonomic comfort over extended sessions, though caution is advised against excessive force to prevent jamming, as noted in the product guidance.
In practice, this rod excels across lure weights—light 1/8-ounce baits sail for distance, while 1/2-ounce options sink to probe deeper waters. Complemented by the metal water drop reel’s precise gearing, it delivers line with consistency, making it a dependable tool for both novice and seasoned anglers.
Decoding Water Dynamics
Fish are creatures of their environment, and understanding water’s rhythms is fundamental to locating them. In rivers, current shapes behavior—trout seek refuge in eddies with 1-2 mph flows, while bass favor calmer pools adjacent to faster runs. Lakes respond to wind; a 10 mph gust concentrates baitfish along downwind shores, drawing predators in tow. Depth varies seasonally—bass linger at 5-15 feet in spring spawning grounds, dropping to 20 feet or more during summer heat, per fishery data. Structure is a magnet—submerged logs, weed beds, or steep drop-offs shelter fish in 80% of documented catches, according to a 2022 ecological study.
Strategically, casting upstream with a slow retrieve mimics natural prey movement, increasing strike probability. This 2.1m fishing set adapts seamlessly, its pre-loaded line and assortment of soft and hard baits aligning with shifting conditions—blue for subtlety, red for visibility—ensuring versatility across aquatic landscapes.
Lure Strategies for Success
Lures are the angler’s baitfish proxies, each type engineered to provoke a response. Soft baits—think worms or grubs—undulate gently, ideal for enticing bass in murky shallows where visibility is low. Hard baits—crankbaits or spoons—generate flash and vibration, luring trout from deeper, clearer runs. Color influences outcomes: bright hues (mirroring the red combo) stand out in turbid water, while muted tones (like the blue variant) blend into pristine flows. Size dictates prey simulation—1-3-inch lures target panfish, while 4-6-inch options tempt larger pike or walleye. Research from 2024 indicates 60% of strikes occur at retrieve speeds of 1-3 feet per second—too rapid deters, too sluggish disinterests.
This combo’s tackle bag supplies both soft and hard options, enabling experimentation—soft plastics for finesse presentations, hard baits for aggressive retrieves. The reel’s adjustable drag ensures control during the fight, preserving line integrity and securing the catch.
Reel Dynamics—Precision in Action
The reel is the mechanical heart of the setup, translating rod movement into line management. Water drop reels, as featured in the RC1000 (blue) and PC1000 (red) variants, optimize casting efficiency—thumb-controlled spools launch lures 50 feet with a 1/4-ounce weight, minimizing tangles common to novice casters. Metal construction enhances durability over plastic counterparts, providing the torque to reel in a 3-pound fish without hesitation. Drag settings, ideally tuned to 25% of line strength (e.g., 3 pounds on 12-pound test), allow fish to run while fatiguing them, reducing break-offs.
Testing reveals this reel’s strength—smooth operation paired with the rod’s flex handles sudden pulls with finesse. Its design supports beginners mastering short 10-foot casts before scaling up, making it a reliable partner for any skill level.
Positioning for the Catch
Location drives results—fish congregate where conditions align. Shorelines rich with cover—rocks, fallen timber—host 70% of catches, per a 2023 angling report. Windy conditions concentrate bait at lake points, prime for casting. Seasonal depth shifts matter—shallow spawning zones (2-5 feet) in spring give way to deeper haunts (15-25 feet) in summer. Overhead activity, like diving birds, signals baitfish schools—and predators below. This 2.1m rod’s collapsible design stows compactly, unfolding quickly with its fishing combo kit—reel, line, and baits at the ready.
In practice, wading a shoreline and casting parallel to weed lines—20-30-foot retrieves—mimics fleeing prey, boosting hookups. The tackle bag keeps essentials organized, ensuring rapid redeployment to the next hotspot.
Gear Specifications: 2.1m Lure Fishing Rod Combo
Key details:FeatureDetails Name 2.1m Lure Fishing Rod Combo Rod Length 2.1m (6.9 ft), collapsible handle Reel Water drop metal (RC1000 blue/PC1000 red) Colors Blue or red Includes Rod, reel, line, soft/hard baits, tackle bag Note Avoid over-pulling to prevent jams Use Cases Bass, trout, lake/river fishing
FAQs—Fishing Gear Insights
Q: What’s the casting range of the 2.1m rod? A: With practice, 50-70 feet—light lures extend reach, heavier ones target depth.
Q: Can the reel handle larger fish? A: Yes—metal drag manages 3-5-pound catches; adjust light, wear them down.
Q: Are soft or hard baits more effective? A: Soft excels in slow, murky bites; hard draws fast strikes—both included for flexibility.
Q: Is the collapsible handle reliable? A: Durable with care—avoid excessive force, and it holds for years.
Q: Does the tackle bag fit extra gear? A: Yes—houses the set plus small additions, keeping it tight and accessible.
Fishing in 2025 demands a fusion of wilderness expertise and dependable equipment. The 2.1m Lure Fishing Rod Combo in blue or red—complete with rod, reel, line, and tackle bag set—stands tested and rated as a cornerstone for anglers. From mastering water currents to deploying the perfect lure, this kit empowers every cast, ensuring your next catch is within reach.
0 notes
Text
Telecom Service Assurance Market Overview: Key Innovations and Future Trends 2032
Telecom Service Assurance Market size was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 22.6 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 9.8 % over the forecast period of 2024-2032
The Telecom Service Assurance Market is experiencing rapid growth as telecom operators seek to enhance network performance, ensure seamless service delivery, and improve customer experience. The rising adoption of 5G, IoT, and cloud-based solutions is driving demand for advanced assurance tools. With increasing network complexities, telecom providers are investing in AI-driven analytics and automation to optimize operations.
The Telecom Service Assurance Market continues to expand as service providers focus on minimizing downtime, reducing operational costs, and enhancing service quality. The growing reliance on digital communication, coupled with increasing customer expectations, is pushing telecom companies to adopt real-time monitoring and predictive analytics solutions. As networks become more software-driven, assurance solutions are evolving to ensure reliability, security, and efficiency.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3679
Market Keyplayers:
Nokia (Nokia AVA, Nokia NetGuard)
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. (Huawei SmartCare, Huawei U2020)
Ericsson (Ericsson Expert Analytics, Ericsson Network IQ)
NEC Corporation (NetCracker Service Assurance, NEC iPASOLINK)
Amdocs (Amdocs SmartOps, Amdocs CES)
IBM Corporation (IBM Netcool, IBM SevOne)
Comarch S.A. (Comarch Service Assurance, Comarch OSS Suite)
Accenture (Accenture Intelligent Operations, Accenture Network Assurance)
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) (TCS Digital Service Assurance, TCS HOBS)
EXFO Inc. (EXFO Nova, EXFO Active Testing)
Market Trends Driving Growth
1. AI and Automation in Service Assurance
Telecom operators are leveraging AI and automation to enhance network monitoring, detect issues proactively, and optimize service delivery. Predictive analytics and self-healing networks are improving operational efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
2. Cloud-Based and Virtualized Networks
With the shift towards cloud-native architectures and virtualized networks, service assurance solutions are evolving to support Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). These technologies enable scalability, flexibility, and faster deployment of network services.
3. The Impact of 5G Deployment
The global rollout of 5G networks is significantly driving demand for advanced service assurance solutions. High-speed connectivity, low latency, and increased network complexity require telecom operators to adopt real-time performance monitoring tools.
4. Customer Experience Enhancement
Service assurance is no longer just about network performance; it plays a crucial role in customer experience management. Telecom providers are using analytics-driven insights to improve service quality, reduce complaints, and enhance overall user satisfaction.
5. Growing Demand for Security and Compliance
As cyber threats and regulatory requirements increase, telecom companies are integrating security-focused assurance solutions. These tools help monitor vulnerabilities, detect fraud, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Enquiry of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/enquiry/3679
Market Segmentation:
By Component
Solution
Probe System
Network Management
Workforce Management
Fault Management
Quality Monitoring
Others
Services
Professional Services
Managed Services
By Operator
Mobile Operator
Fixed Operator
By Deployment
On-premise
Cloud
By Enterprise Size
Large Enterprises
Small & Medium Enterprises
Market Analysis and Current Landscape
Key factors driving this growth include:
Rising Network Complexity: The integration of IoT, cloud computing, and 5G technology is increasing the need for real-time assurance solutions.
Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: Automation is enabling predictive maintenance, reducing service disruptions, and improving operational efficiency.
Growing Investments in Digital Transformation: Telecom providers are modernizing their infrastructure with cloud-based and software-defined solutions to enhance agility.
Competitive Landscape: Leading players such as Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, and Cisco are investing in AI-driven assurance solutions to maintain their market leadership.
Despite strong growth prospects, challenges such as high implementation costs, integration complexities, and data security concerns remain. However, ongoing innovations in AI, cloud computing, and automation are helping address these issues effectively.
Regional Analysis: Key Growth Markets
North America: Leading the market with significant investments in 5G infrastructure and AI-powered assurance solutions. The presence of major telecom companies and increasing demand for high-speed connectivity are driving growth.
Europe: Witnessing steady growth with regulatory compliance requirements and digital transformation initiatives shaping the market. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are key contributors.
Asia-Pacific: Expected to see the highest growth rate due to rapid urbanization, expanding 5G networks, and increasing smartphone penetration. Major markets include China, India, and Japan.
Middle East & Africa: Emerging as a growth hub with rising telecom investments and government-led digital transformation initiatives.
Latin America: Experiencing moderate growth with telecom providers focusing on expanding network infrastructure and improving service quality.
Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead?
1. AI-Driven Predictive Assurance
AI-powered assurance solutions will continue to evolve, enabling telecom operators to anticipate and resolve network issues before they impact customers.
2. Expansion of 5G and Edge Computing
The proliferation of 5G and edge computing will require enhanced assurance capabilities to manage ultra-low latency applications and mission-critical services.
3. Shift Towards Open and Interoperable Solutions
As telecom networks become more open and software-driven, service assurance solutions will need to be interoperable, supporting multi-vendor environments.
4. Integration with IoT and Smart Cities
The increasing adoption of IoT in industries and smart city initiatives will create new demand for real-time assurance solutions to monitor and manage connected devices.
5. Enhanced Security and Compliance Solutions
Cybersecurity and regulatory compliance will become integral to service assurance, with telecom providers adopting AI-based security monitoring and fraud detection tools.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/telecom-service-assurance-market-3679
Conclusion
The Telecom Service Assurance Market is poised for significant growth as telecom operators prioritize network optimization, service quality, and customer experience. With the expansion of 5G, AI-driven automation, and cloud-based networks, service assurance solutions will play a crucial role in ensuring seamless connectivity and operational efficiency. As the industry continues to evolve, investment in innovative assurance technologies will be key to maintaining competitive advantage and meeting the growing demands of digital connectivity.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Telecom Service Assurance Market#Telecom Service Assurance Market Analysis#Telecom Service Assurance Market Scope#Telecom Service Assurance Market Trends
0 notes
Text
Understanding the OPI Exam: A Comprehensive Guide to Oral Proficiency Testing

Language proficiency is a crucial skill in today’s globalized world. Whether for academic, professional, or immigration purposes, demonstrating one’s speaking abilities can open doors to new opportunities. The OPI Exam, or Oral Proficiency Interview, is a widely recognized test that assesses spoken language skills through a structured yet flexible conversation format.
What is the OPI Exam?
The OPI Exam is an internationally recognized test designed to evaluate an individual's oral proficiency in a given language. It is administered by the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) and is commonly used by educational institutions, government agencies, and private organizations to measure language skills.
Unlike traditional multiple-choice language exams, the OPI Exam is a live, one-on-one interview conducted by a certified examiner. The test adapts to the examinee’s responses, making it a dynamic and accurate assessment of their speaking ability.
Structure of the OPI Exam
The OPI Exam typically lasts between 20 to 30 minutes and follows a structured format:
Warm-up: The examiner begins with a casual conversation to put the candidate at ease.
Level Checks: The examiner presents progressively complex topics to gauge the candidate’s proficiency level.
Probes: More challenging questions push the candidate beyond their comfort zone to determine their true speaking ability.
Wind-down: The test concludes with a return to familiar topics, ensuring a smooth finish.
OPI Exam Proficiency Levels
The OPI Exam rates candidates on the ACTFL proficiency scale, which includes:
Novice (Low, Mid, High) – Basic communication with limited vocabulary.
Intermediate (Low, Mid, High) – Ability to hold simple conversations.
Advanced (Low, Mid, High) – More structured and detailed discussions.
Superior – High-level fluency with professional and academic discussion capabilities.
Distinguished – Near-native fluency with cultural and idiomatic understanding.
Benefits of Taking the OPI Exam
Recognized Worldwide: The OPI Exam is accepted by universities, employers, and government bodies globally.
Accurate and Flexible: As a conversational test, it provides a precise evaluation of real-world language use.
Career Advancement: Many organizations require language proficiency for international roles.
Academic Requirements: Some schools and universities use OPI scores for language placement and graduation requirements.
Immigration and Visa Applications: Demonstrating oral proficiency can be a requirement for visa and residency applications in certain countries.
How to Prepare for the OPI Exam
Success in the OPI Exam requires practice and familiarity with conversational language skills. Here are some preparation tips:
Engage in Regular Conversations: Speak the target language daily with native speakers or language partners.
Expand Vocabulary: Learn new words and phrases relevant to various topics, such as work, travel, and current events.
Practice with Mock Interviews: Simulate the test experience by practicing structured conversations.
Listen and Respond: Improve listening skills by engaging with native speakers through podcasts, news, and movies.
Seek Professional Guidance: Consider language coaching or preparatory courses to enhance proficiency.
Conclusion
The OPI Exam is an essential tool for evaluating spoken language skills in a real-world setting. Its adaptability and accuracy make it a preferred choice for individuals seeking to prove their oral proficiency. Whether you’re a student, professional, or traveler, taking the OPI Exam can be a valuable step toward achieving your language goals.
0 notes