#fortran program software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
100 Inventions by Women
LIFE-SAVING/MEDICAL/GLOBAL IMPACT:
Artificial Heart Valve – Nina Starr Braunwald
Stem Cell Isolation from Bone Marrow – Ann Tsukamoto
Chemotherapy Drug Research – Gertrude Elion
Antifungal Antibiotic (Nystatin) – Rachel Fuller Brown & Elizabeth Lee Hazen
Apgar Score (Newborn Health Assessment) – Virginia Apgar
Vaccination Distribution Logistics – Sara Josephine Baker
Hand-Held Laser Device for Cataracts – Patricia Bath
Portable Life-Saving Heart Monitor – Dr. Helen Brooke Taussig
Medical Mask Design – Ellen Ochoa
Dental Filling Techniques – Lucy Hobbs Taylor
Radiation Treatment Research – Cécile Vogt
Ultrasound Advancements – Denise Grey
Biodegradable Sanitary Pads – Arunachalam Muruganantham (with women-led testing teams)
First Computer Algorithm – Ada Lovelace
COBOL Programming Language – Grace Hopper
Computer Compiler – Grace Hopper
FORTRAN/FORUMAC Language Development – Jean E. Sammet
Caller ID and Call Waiting – Dr. Shirley Ann Jackson
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) – Marian Croak
Wireless Transmission Technology – Hedy Lamarr
Polaroid Camera Chemistry / Digital Projection Optics – Edith Clarke
Jet Propulsion Systems Work – Yvonne Brill
Infrared Astronomy Tech – Nancy Roman
Astronomical Data Archiving – Henrietta Swan Leavitt
Nuclear Physics Research Tools – Chien-Shiung Wu
Protein Folding Software – Eleanor Dodson
Global Network for Earthquake Detection – Inge Lehmann
Earthquake Resistant Structures – Edith Clarke
Water Distillation Device – Maria Telkes
Portable Water Filtration Devices – Theresa Dankovich
Solar Thermal Storage System – Maria Telkes
Solar-Powered House – Mária Telkes
Solar Cooker Advancements – Barbara Kerr
Microbiome Research – Maria Gloria Dominguez-Bello
Marine Navigation System – Ida Hyde
Anti-Malarial Drug Work – Tu Youyou
Digital Payment Security Algorithms – Radia Perlman
Wireless Transmitters for Aviation – Harriet Quimby
Contributions to Touchscreen Tech – Dr. Annette V. Simmonds
Robotic Surgery Systems – Paula Hammond
Battery-Powered Baby Stroller – Ann Moore
Smart Textile Sensor Fabric – Leah Buechley
Voice-Activated Devices – Kimberly Bryant
Artificial Limb Enhancements – Aimee Mullins
Crash Test Dummies for Women – Astrid Linder
Shark Repellent – Julia Child
3D Illusionary Display Tech – Valerie Thomas
Biodegradable Plastics – Julia F. Carney
Ink Chemistry for Inkjet Printers – Margaret Wu
Computerised Telephone Switching – Erna Hoover
Word Processor Innovations – Evelyn Berezin
Braille Printer Software – Carol Shaw
⸻
HOUSEHOLD & SAFETY INNOVATIONS:
Home Security System – Marie Van Brittan Brown
Fire Escape – Anna Connelly
Life Raft – Maria Beasley
Windshield Wiper – Mary Anderson
Car Heater – Margaret Wilcox
Toilet Paper Holder – Mary Beatrice Davidson Kenner
Foot-Pedal Trash Can – Lillian Moller Gilbreth
Retractable Dog Leash – Mary A. Delaney
Disposable Diaper Cover – Marion Donovan
Disposable Glove Design – Kathryn Croft
Ice Cream Maker – Nancy Johnson
Electric Refrigerator Improvements – Florence Parpart
Fold-Out Bed – Sarah E. Goode
Flat-Bottomed Paper Bag Machine – Margaret Knight
Square-Bottomed Paper Bag – Margaret Knight
Street-Cleaning Machine – Florence Parpart
Improved Ironing Board – Sarah Boone
Underwater Telescope – Sarah Mather
Clothes Wringer – Ellene Alice Bailey
Coffee Filter – Melitta Bentz
Scotchgard (Fabric Protector) – Patsy Sherman
Liquid Paper (Correction Fluid) – Bette Nesmith Graham
Leak-Proof Diapers – Valerie Hunter Gordon
FOOD/CONVENIENCE/CULTURAL IMPACT:
Chocolate Chip Cookie – Ruth Graves Wakefield
Monopoly (The Landlord’s Game) – Elizabeth Magie
Snugli Baby Carrier – Ann Moore
Barrel-Style Curling Iron – Theora Stephens
Natural Hair Product Line – Madame C.J. Walker
Virtual Reality Journalism – Nonny de la Peña
Digital Camera Sensor Contributions – Edith Clarke
Textile Color Processing – Beulah Henry
Ice Cream Freezer – Nancy Johnson
Spray-On Skin (ReCell) – Fiona Wood
Langmuir-Blodgett Film – Katharine Burr Blodgett
Fish & Marine Signal Flares – Martha Coston
Windshield Washer System – Charlotte Bridgwood
Smart Clothing / Sensor Integration – Leah Buechley
Fibre Optic Pressure Sensors – Mary Lou Jepsen
#women#inventions#technology#world#history#invented#creations#healthcare#home#education#science#feminism#feminist
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

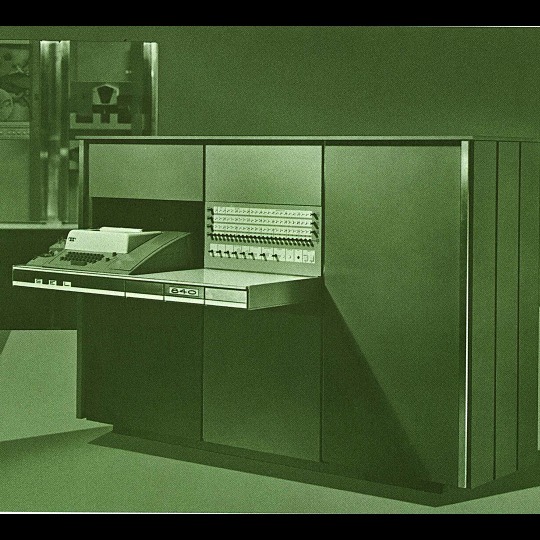




🎄💾🗓️ Day 11: Retrocomputing Advent Calendar - The SEL 840A🎄💾🗓️
Systems Engineering Laboratories (SEL) introduced the SEL 840A in 1965. This is a deep cut folks, buckle in. It was designed as a high-performance, 24-bit general-purpose digital computer, particularly well-suited for scientific and industrial real-time applications.
Notable for using silicon monolithic integrated circuits and a modular architecture. Supported advanced computation with features like concurrent floating-point arithmetic via an optional Extended Arithmetic Unit (EAU), which allowed independent arithmetic processing in single or double precision. With a core memory cycle time of 1.75 microseconds and a capacity of up to 32,768 directly addressable words, the SEL 840A had impressive computational speed and versatility for its time.
Its instruction set covered arithmetic operations, branching, and program control. The computer had fairly robust I/O capabilities, supporting up to 128 input/output units and optional block transfer control for high-speed data movement. SEL 840A had real-time applications, such as data acquisition, industrial automation, and control systems, with features like multi-level priority interrupts and a real-time clock with millisecond resolution.
Software support included a FORTRAN IV compiler, mnemonic assembler, and a library of scientific subroutines, making it accessible for scientific and engineering use. The operator’s console provided immediate access to registers, control functions, and user interaction! Designed to be maintained, its modular design had serviceability you do often not see today, with swing-out circuit pages and accessible test points.
And here's a personal… personal computer history from Adafruit team member, Dan…
== The first computer I used was an SEL-840A, PDF:
I learned Fortran on it in eight grade, in 1970. It was at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, where my parents worked, and was used to take data from cyclotron experiments and perform calculations. I later patched the Fortran compiler on it to take single-quoted strings, like 'HELLO', in Fortran FORMAT statements, instead of having to use Hollerith counts, like 5HHELLO.
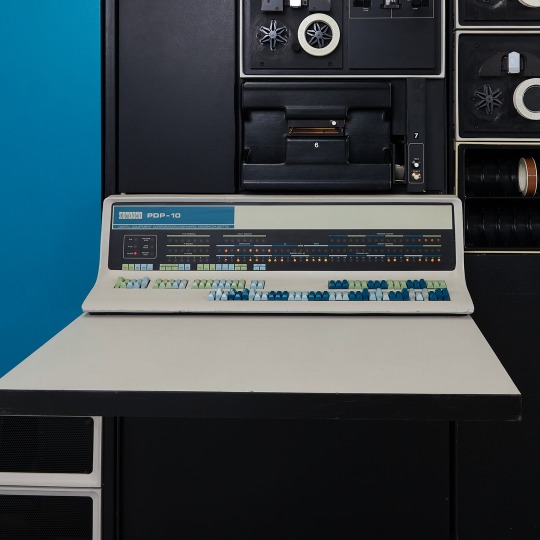
In 1971-1972, in high school, I used a PDP-10 (model KA10) timesharing system, run by BOCES LIRICS on Long Island, NY, while we were there for one year on an exchange.
This is the front panel of the actual computer I used. I worked at the computer center in the summer. I know the fellow in the picture: he was an older high school student at the time.
The first "personal" computers I used were Xerox Alto, Xerox Dorado, Xerox Dandelion (Xerox Star 8010), Apple Lisa, and Apple Mac, and an original IBM PC. Later I used DEC VAXstations.
Dan kinda wins the first computer contest if there was one… Have first computer memories? Post’em up in the comments, or post yours on socialz’ and tag them #firstcomputer #retrocomputing – See you back here tomorrow!
#retrocomputing#firstcomputer#electronics#sel840a#1960scomputers#fortran#computinghistory#vintagecomputing#realtimecomputing#industrialautomation#siliconcircuits#modulararchitecture#floatingpointarithmetic#computerscience#fortrancode#corememory#oakridgenationallab#cyclotron#pdp10#xeroxalto#computermuseum#historyofcomputing#classiccomputing#nostalgictech#selcomputers#scientificcomputing#digitalhistory#engineeringmarvel#techthroughdecades#console
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
The French Fortran Code From Hell
My first job held the grandiose-sounding title of Technical Consulting Engineer, which was a very fancy way of saying "glorified customer support with some additional maintenance tasks."
I was assigned to a piece of software that was used to help people make their code more efficient. Among my duties were: creating documentation and how-to tutorials for the software; answering support tickets for the software; giving lectures on the software; and providing hands-on assistance in what we called Dungeons.
Dungeons were what happened when you locked a bunch of engineers in a windowless room with a handful of TCEs and lunch catering and let them go at their code with the software for the entire duration of the day, completely dead to the outside world - often repeating this process for several days.
I was in quite a few Dungeons during my three horrible years at that soul-sucking job. I want to be clear: the vast majority of this job was the soul-crushing tedium and agony of answering support tickets. The software in question was... not great at providing helpful error messages. 90% of everything resulted in "There's a problem with your license file" even when the license file was fine. So debugging was always an ordeal.
The best ones, strangely enough, were always the tickets from the military, because everything was classified. Anything that happens on their computer is classified. What does the error message say? That's classified. Can you send me the log output? That's classified. What does your license file say on line three? That's classified. You might wonder how this makes anything better for the poor sap trying to debug it. See, when they can't provide you any info, all you can do is send them the entire support script and tell them to go through the steps themselves. Then they message you back a while later politely telling you that it worked and you can now close the ticket. On the other end of the spectrum you had individual customers who bought the software for their own use, and some of these people were real pieces of work. Anyone who has worked customer-facing jobs knows the kind of person I'm talking about.
Anyway, Dungeons were more of an occasional interruption to the never-ending slog of support tickets, and usually a very welcome interruption.
But a couple times it was... let's say interesting. And both of these stories, oddly enough, involve the French.
The first one was the unfortunate time I was in a Dungeon full of engineers who had flown in from France - Paris specifically if I recall correctly. On the 15th of April, 2019. I received a text from my mother with rather alarming news, and thus I had to be the one to inform the room full of French engineers that Notre Dame Cathedral was actively on fire. Needless to say, very little got done that day.
The second one was just plain painful for me. The software in question supports code in both C++ (commonly used language, good) and Fortran (relic from the 1950s, extremely different from most programming languages). It was fairly rare for us to actually deal with the Fortran side of it, however.
But on this occasion, the French engineers I was in a Dungeon with wanted my help optimizing their Fortran code. Fine, I'm not exactly "fluent" but I can probably get the gist of it, I thought.
I was wrong.
You see, this Fortran code was auto-generated. It was not written by human hands and was not intended to be read by human eyes. It contained statements that were hundreds of lines long. Not functions, statements. To those not initiated in programming, this is akin to a run-on sentence that lasts 38 pages. It had variables with such helpful names as xyz and abc. Likewise, for the uninitiated, this is akin to having a pharmacy where all of the bottles are labeled "Medicine, probably."
It had, at some point, been minimally edited, or at least annotated, by humans, however. Because there were a very small handful of comments!
...Which were in French.
I do not speak French.
The French engineers did not know how to translate French Jargon into English.
Obviously, our company did not ever want us to say "we can't." But in this one case, nobody took issue when I looked these French engineers in the eye and just told them "I'm sorry, but this code is beyond our ability to optimize. It is beyond anyone's ability to optimize. It must be cast into the fire and destroyed; and may god help you."
#programming#this is longer than I expected#what do I even tag this with#stories from paladin's personal life
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I decided to write this article when I realized what a great step forward the modern computer science learning has done in the last 20 years. Think of it. My first “Hello, world” program was written in Sinclair BASIC in 1997 for КР1858ВМ1r This dinosaur was the Soviet clone of the Zilog Z80 microprocessor and appeared on the Eastern Europe market in 1992-1994. I didn’t have any sources of information on how to program besides the old Soviet “Encyclopedia of Dr. Fortran”. And it was actually a graphic novel rather than a BASIC tutorial book. This piece explained to children how to sit next to a monitor and keep eyesight healthy as well as covered the general aspects of programming. Frankly, it involved a great guesswork but I did manage to code. The first real tutorial book I took in my hands in the year of 2000 was “The C++ Programming Language” by Bjarne Stroustrup, the third edition. The book resembled a tombstone and probably was the most fundamental text for programmers I’d ever seen. Even now I believe it never gets old. Nowadays, working with such technologies as Symfony or Django in the DDI Development software company I don’t usually apply to books because they become outdated before seeing a printing press. Everyone can learn much faster and put a lesser effort into finding new things. The number of tutorials currently available brings the opposite struggle to what I encountered: you have to pick a suitable course out of the white noise. In order to save your time, I offer the 20 best tutorials services for developers. Some of them I personally use and some have gained much recognition among fellow technicians. Lynda.com The best thing about Lynda is that it covers all the aspects of web development. The service currently has 1621 courses with more than 65 thousand videos coming with project materials by experts. Once you’ve bought a monthly subscription for a small $30 fee you get an unlimited access to all tutorials. The resource will help you grow regardless your expertise since it contains and classifies courses for all skill levels. Pluralsight.com Another huge resource with 1372 courses currently available from developers for developers. It may be a hardcore decision to start with Pluralsight if you’re a beginner, but it’s a great platform to enhance skills if you already have some programming background. A month subscription costs the same $30 unless you want to receive downloadable exercise files and additional assessments. Then you’ll have to pay $50 per month. Codecademy.com This one is great to start with for beginners. Made in an interactive console format it leads you through basic steps to the understanding of major concepts and techniques. Choose the technology or language you like and start learning. Besides that, Codecademy lets you build websites, games, and apps within its environment, join the community and share your success. Yes, and it’s totally free! Probably the drawback here is that you’ll face challenges if you try to apply gained skills in the real world conditions. Codeschool.com Once you’ve done with Codecademy, look for something more complicated, for example, this. Codeschool offers middle and advanced courses for you to become an expert. You can immerse into learning going through 10 introductory sessions for free and then get a monthly subscription for $30 to watch all screencasts, courses, and solve tasks. Codeavengers.com You definitely should check this one to cover HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Code Avengers is considered to be the most engaging learning you could experience. Interactive tasks, bright characters and visualization of your actions, simple instructions and instilling debugging discipline makes Avengers stand out from the crowd. And unlike other services it doesn’t tie you to schedules allowing to buy either one course or all 10 for $165 at once and study at your own pace. Teamtreehouse.com An all-embracing platform both for beginners and advanced learners. Treehouse
has general development courses as well as real-life tasks such as creating an iOS game or making a photo app. Tasks are preceded by explicit video instructions that you follow when completing exercises in the provided workspace. The basic subscription plan costs $25 per month, and gives access to videos, code engine, and community. But if you want bonus content and videos from leaders in the industry, your pro plan will be $50 monthly. Coursera.org You may know this one. The world famous online institution for all scientific fields, including computer science. Courses here are presented by instructors from Stanford, Michigan, Princeton, and other universities around the world. Each course consists of lectures, quizzes, assignments, and final exams. So intensive and solid education guaranteed. By the end of a course, you receive a verified certificate which may be an extra reason for employers. Coursera has both free and pre-pay courses available. Learncodethehardway.org Even though I’m pretty skeptical about books, these ones are worth trying if you seek basics. The project started as a book for Python learning and later on expanded to cover Ruby, SQL, C, and Regex. For $30 you get a book and video materials for each course. The great thing about LCodeTHW is its focus on practice. Theory is good, but practical skills are even better. Thecodeplayer.com The name stands for itself. Codeplayer contains numerous showcases of creating web features, ranging from programming input forms to designing the Matrix code animation. Each walkthrough has a workspace with a code being written, an output window, and player controls. The service will be great practice for skilled developers to get some tips as well as for newbies who are just learning HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript. Programmr.com A great platform with a somewhat unique approach to learning. You don’t only follow courses completing projects, but you do this by means of the provided API right in the browser and you can embed outcome apps in your blog to share with friends. Another attractive thing is that you can participate in Programmr contests and even win some money by creating robust products. Well, it’s time to learn and play. Udemy.com An e-commerse website which sells knowledge. Everyone can create a course and even earn money on it. That might raise some doubts about the quality, but since there is a lot of competition and feedback for each course a common learner will inevitably find a useful training. There are tens of thousands of courses currently available, and once you’ve bought a course you get an indefinite access to all its materials. Udemy prices vary from $30 to $100 for each course, and some training is free. Upcase.com Have you completed the beginner courses yet? It’s time to promote your software engineer’s career by learning something more specific and complex: test-driven development in Ruby on Rails, code refactoring, testing, etc. For $30 per month you get access to the community, video tutorials, coding exercises, and materials on the Git repository. Edx.org A Harvard and MIT program for free online education. Currently, it has 111 computer science and related courses scheduled. You can enroll for free and follow the training led by Microsoft developers, MIT professors, and other experts in the field. Course materials, virtual labs, and certificates are included. Although you don’t have to pay for learning, it will cost $50 for you to receive a verified certificate to add to your CV. Securitytube.net Let’s get more specific here. Surprisingly enough SecurityTube contains numerous pieces of training regarding IT security. Do you need penetration test for your resource? It’s the best place for you to capture some clues or even learn hacking tricks. Unfortunately, many of presented cases are outdated in terms of modern security techniques. Before you start, bother yourself with checking how up-to-date a training is. A lot of videos are free, but you can buy a premium course access for $40.
Rubykoans.com Learn Ruby as you would attain Zen. Ruby Koans is a path through tasks. Each task is a Ruby feature with missing element. You have to fill in the missing part in order to move to the next Koan. The philosophy behind implies that you don’t have a tutor showing what to do, but it’s you who attains the language, its features, and syntax by thinking about it. Bloc.io For those who seek a personal approach. Bloc covers iOS, Android, UI/UX, Ruby on Rails, frontend or full stack development courses. It makes the difference because you basically choose and hire the expert who is going to be your exclusive mentor. 1-on-1 education will be adapted to your comfortable schedule, during that time you’ll build several applications within the test-driven methodology, learn developers’ tools and techniques. Your tutor will also help you showcase the outcome works for employers and train you to pass a job interview. The whole course will cost $5000 or you can pay $1333 as an enrollment fee and $833 per month unless you decide to take a full stack development course. This one costs $9500. Udacity.com A set of courses for dedicated learners. Udacity has introductory as well as specific courses to complete. What is great about it and in the same time controversial is that you watch tutorials, complete assignments, get professional reviews, and enhance skills aligning it to your own schedule. A monthly fee is $200, but Udacity will refund half of the payments if you manage to complete a course within 12 months. Courses are prepared by the leading companies in the industry: Google, Facebook, MongoDB, At&T, and others. Htmldog.com Something HTML, CSS, JavaScript novices and adepts must know about. Simple and free this resource contains text tutorials as well as techniques, examples, and references. HTML Dog will be a great handbook for those who are currently engaged in completing other courses or just work with these frontend technologies. Khanacademy.org It’s diverse and free. Khan Academy provides a powerful environment for learning and coding simultaneously, even though it’s not specified for development learning only. Built-in coding engine lets you create projects within the platform, you watch video tutorials and elaborate challenging tasks. There is also the special set of materials for teachers. Scratch.mit.edu Learning for the little ones. Scratch is another great foundation by MIT created for children from 8 to 15. It won’t probably make your children expert developers, but it will certainly introduce the breathtaking world of computer science to them. This free to use platform has a powerful yet simple engine for making animated movies and games. If you want your child to become an engineer, Scratch will help to grasp the basic idea. Isn’t it inspirational to see your efforts turning into reality? Conclusion According to my experience, you shouldn’t take more than three courses at a time if you combine online training with some major activity because it’s going to be hard to concentrate. Anyway, I tried to pick different types of resources for you to have a choice and decide your own schedule as well as a subscription model. What services do you usually apply to? Do you think online learning can compete with traditional university education yet? Please, share. Dmitry Khaleev is a senior developer at the DDI Development software company with more than 15 years experience in programming and reverse-engineering of code. Currently, he works with PHP and Symfony-based frameworks.
0 notes
Text
Software Development in USA:
1.Software Development in USA:
The software development industry in the United States is one of the most robust and innovative sectors in the global economy. With cutting-edge technology hubs like Silicon Valley, Austin, and Seattle, the USA has been a leader in software solutions, tech startups, and groundbreaking applications for decades. In this article, we'll explore the landscape of software development in the USA, key trends, major companies, and why it remains a powerhouse in the tech world.

2. The Evolution of Software Development in the USA
The history of software development in the USA dates back to the mid-20th century, with the advent of mainframe computers and the establishment of foundational programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN. As technology evolved, so did software capabilities, leading to the emergence of personal computers, mobile applications, and cloud-based solutions.
The rise of tech giants such as Microsoft, Apple, Google, and Amazon redefined the industry, setting new standards for software innovation. Today, American software companies lead the way in artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud computing, and cybersecurity.
3. Key Software Development Hubs
Silicon Valley, California - Known globally as the tech capital of the world, Silicon Valley houses tech giants and thousands of startups.
Austin, Texas - Often called the 'Silicon Hills,' Austin has rapidly grown as a tech hub with a strong focus on innovation and startup culture.
Seattle, Washington - Home to Microsoft and Amazon, Seattle is a powerhouse for cloud computing and enterprise software.
New York City, New York - A financial and technological hub, NYC focuses heavily on fintech, AI, and enterprise solutions.
Boston, Massachusetts - Known for its emphasis on AI, robotics, and biotechnology software.
Emerging Trends in Software Development
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Cloud Computing and SaaS (Software as a Service)
Cybersecurity Innovations
Internet of Things (IoT)
Blockchain Technology
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Major Software Development Companies in the USA
Microsoft
Apple
Google
Amazon
IBM
Oracle
Salesforce
These companies not only dominate the U.S. market but also influence global software trends.
Challenges Facing Software Development in the USA
While the USA remains at the forefront of software innovation, challenges such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory changes, and a competitive global market pose significant hurdles. Additionally, the demand for highly skilled developers continues to rise, leading to talent shortages in key tech hubs.
The Future of Software Development in the USA
The future of software development in the USA looks promising, with ongoing investments in AI, machine learning, and cloud computing. Government initiatives aimed at boosting tech education and innovation also signal growth and expansion in the coming years.
Conclusion
Software development in the USA continues to thrive, driven by innovation, robust infrastructure, and world-class talent. As new technologies emerge, the United States is poised to maintain its status as a global leader in software solutions and digital transformation.
0 notes
Text
IF YOU INVEST AT 20 AND THE COMPANY IS STARTING TO APPEAR IN THE MAINSTREAM
8x 5% 12. Many of our taboos future generations will laugh at is to start with. But like VCs, they invest other people's money makes them doubly alarming to VCs. If it isn't, don't try to raise money, they try gamely to make the best case, the papers are just a formality. Understand why it's worth investing in. But at each point you know how you're doing. Only a few companies have been smart enough to realize this so far. If you run out of money, you probably never will. Just as our ancestors did to explain the apparently too neat workings of the natural world. Genes count for little by comparison: being a genetic Leonardo was not enough to compensate for having been born near Milan instead of Florence. The last one might be the most plausible ones. And yet a lot of other domains, the distribution of outcomes follows a power law, but in startups the curve is startlingly steep.
The list is an exhaustive one. I can't tell is whether they have any kind of taste. And if so they'll be different to deal with than VCs. The people are the most important of which was Fortran. It is now incorporated in Revenge of the Nerds. I have likewise cavalierly dismissed Cobol, Ada, Visual Basic, the IBM AS400, VRML, ISO 9000, the SET protocol, VMS, Novell Netware, and CORBA, among others. When people first start drawing, for example, because Paypal is now responsible for 43% of their sales and probably more of their growth. We fight less. You tell them only 1 out of 100 successful startups has a trajectory like that, and they have a hard time getting software done. What if some idea would be a remarkable coincidence if ours were the first era to get everything just right. In hacking, this can literally mean saving up bugs. I know that when it comes to code I behave in a way that seems to violate conservation laws.
Few would deny that a story should be like life. Steve Wozniak wanted a computer, Google because Larry and Sergey found, there's not much of a market for ideas. For a painter, a museum is a reference library of techniques. For a long time to work on as there is nothing so unfashionable as the last, discarded fashion, there is something even better than C; and plug-and-chug undergrads, who are both hard to bluff and who already believe most other investors are conventional-minded drones doomed always to miss the big outliers. As in any job, as you continue to design things, these are not just theoretical questions. But evidence suggests most things with titles like this are linkbait. Almost every company needs some amount of pain. I'd find something in almost new condition for a tenth its retail price at a garage sale.
Once you phrase it that way, the answer is obvious: from a job. A company that grows at 1% a week will in 4 years be making $25 million a month. You feel this when you start. Starting a startup is committing to solve any specific problem; you don't know that number, they're successful for that week. For example, when Leonardo painted the portrait of Ginevra de Benci, their attention is often immediately arrested by it, because our definition of success is that the business guys choose people they think are good programmers it says here on his resume that he's a Microsoft Certified Developer but who aren't. After they merged with X. Once investors like you, you'll see them reaching for ideas: they'll be saying yes, and you have to understand what they need. Just wait till all the 10-room pensiones in Rome discover this site. You're better off if you admit this up front, and write programs in a way that allows specifications to change on the fly. Working from life is a valuable tool in painting too, though its role has often been misunderstood. The founders can't enrich themselves without also enriching the investors. You're committing not just to intelligence but to ability in general, you can not only close the round faster, but now that convertible notes are becoming the norm, actually raise the price to reflect demand.
Most investors are genuinely unclear in their own minds why they like or dislike startups. Actor too is a pole rather than a threshold. But here again there's a tradeoff between smoothness and ideas. Starting startups is not one of them. The classic way to burn through cash is by hiring a lot of this behind the scenes stuff at YC, because we invest in such a large number of companies, and we invest so early that investors sometimes need a lot of founders are surprised by it. In the original Java white paper, Gosling explicitly says Java was designed not to be too difficult for programmers used to C. And this team is the right model, because it coincided with the amount. Those are the only things you need at first.
Not always. And so an architect who has to build on a difficult site, or a programming language is obviously doesn't know what these things are, either. One reason this advice is so hard to follow is that people don't realize how hard it was to get some other company to buy it. You can see that in the back of their minds, they know. But that's still a problem for big companies, because they seem so formidable. It's an interesting illustration of an element of the startup founder dream: that this is a coincidence. They try to convince with their pitch. In most fields the great work is done early on.
This is supposed to be the default plan in big companies. The people you can say later Oh yeah, we had to interrupt everything and borrow one of their fellow students was on the Algol committee, got conditionals into Algol, whence they spread to most other languages. This is in contrast to Fortran and most succeeding languages, which distinguish between expressions and statements. And if it isn't false, it shouldn't be suppressed. I mentioned earlier that the most successful startups seem to have done it by fixing something that they thought ugly. In 1989 some clever researchers tracked the eye movements of radiologists as they scanned chest images for signs of lung cancer. Darwin himself was careful to tiptoe around the implications of his theory. Running a business is so much more enjoyable now. Don't worry what people will say. Growth is why it's a rational choice economically for so many founders to try starting a startup consists of. If there are x number of customers who'd pay an average of $y per year for what you're making, then the total addressable market, or TAM, of your company, if they can get DARPA grants.
Fortunately, more and more startups will. Good design is often slightly funny. Unconsciously, everyone expects a startup to work on technology, or take venture funding, or have some sort of exit. And I'm especially curious about anything that's forbidden. Angels would invest $20k to $50k apiece, and VCs usually a million or more. Nowadays Valley VCs are more likely to take 2-3x longer than I always imagine. In the mid twentieth century there was a lot less than the 30 to 40% of the company you usually give up in one shot. A deals would prefer to take half as much stock, and then just try to hit it every week. What's wrong with having one founder? Within the US car industry there is a kind of final pass where you caught typos and oversights.
#automatically generated text#Markov chains#Paul Graham#Python#Patrick Mooney#Java#Valley#price#Many#everything#VRML#things#founder#startups#trajectory#count#generations#default#attention#sale#undergrads#lot#way#anything#eye#languages#car#exit#distribution
0 notes
Text

Computer science has undergone remarkable transformations since its inception, shaping the way we live, work, and interact with technology. Understanding this evolution not only highlights the innovations of the past but also underscores the importance of education in this ever-evolving field. In this blog, we’ll explore key milestones in computer science and the learning opportunities available, including computer science training in Yamuna Vihar and Computer Science Training Institute in uttam nagar .
The Early Years: Foundations of Computing
The story of computer science begins in the mid-20th century with the development of the first electronic computers. The ENIAC, one of the earliest general-purpose computers, showcased the capabilities of machine computation. However, programming at that time required a deep understanding of machine language, which was accessible only to a select few.
Milestone: High-Level Programming Languages
The 1950s marked a pivotal moment with the introduction of high-level programming languages like FORTRAN and COBOL. These languages allowed developers to write code in a more human-readable form, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for programming. This shift made software development more approachable and laid the groundwork for future innovations.
The Personal Computer Revolution
The 1970s and 1980s ushered in the era of personal computing, with companies like Apple and IBM bringing computers into homes and offices. This democratization of technology changed how people interacted with computers, leading to the development of user-friendly interfaces and applications.
Milestone: The Internet Age
The rise of the internet in the late 20th century transformed communication and information sharing on a global scale. The introduction of web browsers in the 1990s made the internet accessible to the masses, resulting in an explosion of online content and services. This era emphasized the importance of networking and laid the foundation for the digital economy.
nd Advanced Technologies
As computing technologies became more advanced, the need for specialized knowledge grew. Understanding data structures and algorithms became essential for optimizing code and improving software performance.
Specialization a
For those looking to enhance their skills, the Data Structure Training Institute in Yamuna Vihar offers comprehensive programs focused on these critical concepts. Mastering data structures is vital for aspiring developers and can significantly impact their effectiveness in real-world applications.
Milestone: Mobile Computing and Applications
The advent of smartphones in the early 2000s revolutionized computing once again. Mobile applications became integral to daily life, prompting developers to adapt their skills for mobile platforms. This shift highlighted the need for specialized education in app development and user experience design.
Current Trends: AI, Big Data, and Cybersecurity
Today, fields like artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and cybersecurity are at the forefront of technological innovation. AI is transforming industries by enabling machines to learn from data, while big data analytics provides insights that drive decision-making.
To prepare for careers in these dynamic fields, students can enroll in an advanced diploma in computer application in Uttam Nagar. This program equips learners with a strong foundation in software development, data management, and emerging technologies.
Additionally, Computer Science Classes in Uttam Nagar offer tailored courses for those seeking to specialize in specific areas, ensuring that students are well-prepared for the job market.
Conclusion
The evolution of computer science has been marked by significant milestones that have reshaped our technological landscape. As the field continues to advance, the demand for skilled professionals is higher than ever. By pursuing education in computer science—whether through computer science training in Yamuna Vihar, specialized data structure courses, or advanced diploma programs—you can position yourself for success in this exciting and ever-changing industry.
Embrace the opportunities available to you and become a part of the future of technology!
#computer science classes#datascience#computer science training in Yamuna Vihar#Computer Science Classes in Uttam Nagar
0 notes
Text
software Development
The Evolution and Art of Software Development
Introduction
Software development is more than just writing code; it's a dynamic and evolving field that marries logic with creativity. Over the years, it has transformed from simple programming tasks into a complex discipline encompassing a range of activities, including design, architecture, testing, and maintenance. Today, software development is central to nearly every aspect of modern life, driving innovation across industries from healthcare to finance, entertainment to education.
The Journey of Software Development
1. The Early Days: From Code to Systems
In the early days of computing, software development was a niche skill practiced by a few experts. Programming languages were rudimentary, and development focused on solving specific, isolated problems. Early software was often developed for specific hardware, with little consideration for reusability or scalability. Programs were typically written in low-level languages like Assembly, making the development process both time-consuming and prone to errors.
2. The Rise of High-Level Languages
The development of high-level programming languages such as FORTRAN, COBOL, and later, C, marked a significant shift in software development. These languages allowed developers to write more abstract and readable code, which could be executed on different hardware platforms with minimal modification. This period also saw the emergence of software engineering as a formal discipline, with a focus on methodologies and best practices to improve the reliability and maintainability of software.
3. The Advent of Object-Oriented Programming
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed another leap forward with the advent of object-oriented programming (OOP). Languages like C++, Java, and Python introduced concepts such as classes, inheritance, and polymorphism, which allowed developers to model real-world entities and their interactions more naturally. OOP also promoted the reuse of code through the use of libraries and frameworks, accelerating development and improving code quality.
4. The Agile Revolution
In the early 2000s, the software development landscape underwent a seismic shift with the introduction of Agile methodologies. Agile emphasized iterative development, collaboration, and flexibility over rigid planning and documentation. This approach allowed development teams to respond more quickly to changing requirements and deliver software in smaller, more manageable increments. Agile practices like Scrum and Kanban have since become standard in the industry, promoting continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
5. The Age of DevOps and Continuous Delivery
Today, software development is increasingly intertwined with operations, giving rise to the DevOps movement. DevOps emphasizes automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD), enabling teams to release software updates rapidly and reliably. This approach not only shortens development cycles but also improves the quality and security of software. Cloud computing and containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes have further enhanced DevOps, allowing for scalable and resilient software systems.
The Art of Software Development
While software development is rooted in logic and mathematics, it also requires a creative mindset. Developers must not only solve technical problems but also design intuitive user interfaces, create engaging user experiences, and write code that is both efficient and maintainable. The best software solutions are often those that balance technical excellence with user-centric design.
1. Design Patterns and Architecture
Effective software development often involves the use of design patterns and architectural principles. Design patterns provide reusable solutions to common problems, while architectural patterns guide the overall structure of the software. Whether it's a microservices architecture for a large-scale web application or a Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern for a desktop app, these frameworks help developers build robust and scalable software.
2. Testing and Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is another critical aspect of software development. Writing tests, whether unit tests, integration tests, or end-to-end tests, ensures that the software behaves as expected and reduces the likelihood of bugs. Automated testing tools and practices like Test-Driven Development (TDD) help maintain code quality throughout the
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI in Automatic Programming: Will AI Replace Human Coders?

The software development industry is not immune to the profound effects of artificial intelligence (AI). One of the areas where AI is having the greatest impact on productivity is automatic programming. It wasn’t always the case that automatic programming included the creation of programs by another program. It gained new connotations throughout time.
In the 1940s, it referred to the mechanization of the formerly labor-intensive operation of punching holes in paper tape to create punched card machine programming.In later years, it meant converting from languages like Fortran and ALGOL down to machine code.
Artificial intelligence (AI) coding tools like GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, ChatGPT, Tabnine, and many more are gaining popularity because they allow developers to automate routine processes and devote more time to solving difficult challenges.
Synthesis of a program from a specification is the essence of automatic programming. Automatic programming is only practical if the specification is shorter and simpler to write than the corresponding program in a traditional programming language.
In automated programming, one software uses a set of guidelines provided by another program to build its code.
The process of writing code that generates new programs continues. One may think of translators as automated programs, with the specification being the source language (a higher-level language) being translated into the target language (a lower-level language).
This method streamlines and accelerates software development by removing the need for humans to manually write repetitive or difficult code. Simplified inputs, such as user requirements or system models, may be translated into usable programs using automatic programming tools.
Few AI Coding Assistants
GitHub Copilot
Amazon CodeWhisperer
Codiga
Bugasura
CodeWP
AI Helper Bot
Tabnine
Reply
Sourcegraph Cody
AskCodi
Unlocking the Potential of Automatic Programming
AI can do in one minute what used to take an engineer 30 minutes to do.
The term “automatic programming” refers to the process of creating code without the need for a human programmer, often using more abstract requirements. Knowledge of algorithms, data structures, and design patterns underpins the development of software, whether it’s written by a person or a computer.
Also, new modules may be easily integrated into existing systems thanks to autonomous programming, which shortens product development times and helps businesses respond quickly to changing market needs.
In many other contexts, from data management and process automation to the creation of domain-specific languages and the creation of software for specialized devices, automated programming has shown to be an invaluable tool.
Its strength is in situations when various modifications or variants of the same core code are required. Automatic programming encourages innovation and creativity by facilitating quick code creation with minimal human involvement, giving developers more time to experiment with new ideas, iterate on designs, and expand the boundaries of software technology.
How to Get Started with AI Code Assistant?
Have you thought of using artificial intelligence coding assistance to turbocharge your coding skills?
Artificial intelligence can save programmers’ time for more complicated problem-solving by automating routine, repetitive processes. Developers may make use of AI algorithms that can write code to shorten iteration times and boost output.
You can now write code more quickly and accurately, leaving more time for you to think about innovative solutions to the complex problems you’re trying to solve.
In Visual Studio Code, for instance, you can utilize Amazon CodeWhisper to create code by just commenting on what you want it to do; the integrated development environment (IDE) will then offer the full code snippet for you to use and modify as necessary
0 notes
Text
Mistral AI Codestral Platform Debuts On Google Vertex AI

Codestral
Google cloud present first code model, Codestral. An open-weight generative AI model specifically created for code generation jobs is called Codestral. Through a common instruction and completion API endpoint, it facilitates developers’ writing and interaction with code. It may be used to create sophisticated AI apps for software developers as it becomes proficient in both coding and English.
A model proficient in more than 80 programming languages
More than 80 programming languages, including some of the most widely used ones like Python, Java, C, C++, JavaScript, and Bash, were used to teach Codestral. It works well on more specialised ones as well, like as Swift and Fortran. It can help developers with a wide range of coding environments and projects thanks to its extensive language base.
Because Codestral can construct tests, finish coding functions, and finish any unfinished code using a fill-in-the-middle approach, it saves developers time and effort. Engaging with Codestral can enhance a developer’s coding skills and lower the likelihood of mistakes and glitches.
Raising the Bar for Performance in Code Generation
Activity. Compared to earlier models used for coding, Codestral, as a 22B model, sets a new benchmark on the performance/latency space for code creation.Image Credit to Google cloud
Python. Codestral test Codestral’s Python code generation capability using four benchmarks: HumanEval pass@1, MBPP sanitised pass@1, CruxEval for Python output prediction, and RepoBench EM for Codestral’s Long-Range Repository-Level Code Completion.
SQL: Spider was used to benchmark Codestral’s SQL performance.
Mistral Codestral
Get Codestral and give it a try
You can use it for testing and study because it is a 22B open-weight model licensed under the new Mistral AI Non-Production License. HuggingFace offers a download for Codestral.
By contacting the team, commercial licenses are also available on demand if you like to use the model for your business.
Utilise Codestral through its specific endpoint
Codestral,Mistral AI is a new endpoint that is added with this edition. Users that utilise Google cloud Fill-In-the-Middle or Instruct routes within their IDE should choose this destination. This endpoint’s API Key is controlled personally and is not constrained by the standard organisation rate limitations. For the first eight weeks of its test program, this endpoint will be available for free usage, but it will be behind a waitlist to guarantee high-quality service. Developers creating applications or IDE plugins where users are expected to provide their own API keys should use this endpoint.
Utilise Codestral to build on the Platforme
Additionally, it is instantly available via the standard API endpoint, api.mistral.ai, where requests are charged on a token basis. Research, bulk enquiries, and third-party application development that exposes results directly to consumers without requiring them to bring their own API keys are better suited uses for this endpoint and integrations.
By following this guide, you can register for an account on la Plateforme and begin using Codestral to construct your applications. Codestral is now accessible in Google self-deployment offering, just like all of Google cloud other models: get in touch with sales.
Engage Codestral through le Chat
Mistral releasing Codestral in an instructional version, which you may currently use with free conversational interface, Le Chat. Developers can take advantage of the possibilities of the model by interacting with Codestral in a natural and intuitive way. Google cloud consider Codestral as a fresh step towards giving everyone access to code generation and comprehension.
Use Codestral in your preferred environment for building and coding
In collaboration with community partners, Google cloud made popular technologies for AI application development and developer productivity available to Codestral.
Frameworks for applications. As of right now, Codestral is integrated with LlamaIndex and LangChain, making it simple for users to create agentic apps using Codestral.
Integration between JetBrains and VSCode. Proceed with the help of dev and Tabnine, developers can now generate and converse with code using Codestral inside of the VSCode and JetBrains environments.
Codestral Mistral AI
Google cloud is pleased to announce today that Codestral Mistral AI’s first open-weight generative AI model specifically created for code generation tasks is now available as a fully-managed service on Google Cloud, making it the first hyperscaler to provide it. With the use of a common instruction and completion API endpoint, Codestral facilitates the writing and interaction of code by developers. It is available for use in Vertex AI Model Garden right now.
Furthermore, Google cloud are excited to announce that the most recent large language models (LLMs) from Mistral AI have been added to Vertex AI Model Garden. These LLMs are widely accessible today through a Model-as-a-Service (MaaS) endpoints:
Mistral Large 2: The flagship model from Mistral AI, the Mistral Large 2, has the highest performance and most adaptability of any model the firm has released to date.
Mistral Nemo: For a small fraction of the price, this 12B model offers remarkable performance.
The new models are excellent at coding, math, and multilingual activities (English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish). As a result, they are perfect for a variety of downstream tasks, such as software development and content localisation. Notably, Codestral is well-suited for jobs like test generation, documentation, and code completion. Model-as-a-Service allows you to access the new models with minimal effort and without the need for infrastructure or setup.
With these updates, Google Cloud remains dedicated to providing open and adaptable AI ecosystems that enable you to create solutions that are precisely right for you. Google Cloudpartnership with Mistral AI is evidence of Google Cloud transparent methodology in a cohesive, enterprise-ready setting. A fully-managed Model-as-a-service (MaaS) offering is available from Vertex AI, which offers a carefully selected selection of first-party, open-source, and third-party models, many of which include the recently released Mistral AI models. With MaaS, you can customise it with powerful development tools, easily access it through an API, and select the foundation model that best suits your needs all with the ease of a single bill and enterprise-grade security on Google Cloud fully-managed infrastructure.
Mistral AI models are being tried and adopted using Google Cloud
Vertex AI from Google Cloud is an all-inclusive AI platform for testing, modifying, and implementing foundation models. With the additional 150+ models already accessible on Vertex AI Model Garden, along with Mistral AI’s new models, you’ll have even more choices and flexibility to select the models that best suit your demands and budget while keeping up with the ever-increasing rate of innovation.
Try it with assurance
Discover Mistral AI models in Google Cloud user-friendly environment with straightforward API calls and thorough side-by-side comparisons. Google cloud take care of the infrastructure and deployment details for you.
Adjust the models to your benefit
Utilise your distinct data and subject expertise to fine-tune Mistral AI’s foundation models and provide custom solutions. MaaS will soon allow for the fine-tuning of Mistral AI models.
Create and manage intelligent agents
Utilising Vertex AI’s extensive toolkit, which includes LangChain on Vertex AI, create and manage agents driven by Mistral AI models. Use Genkit’s Vertex AI plugin to incorporate Mistral AI models into your production-ready AI experiences.
Transition from experiments to real-world use
Use pay-as-you-go pricing to deploy your Mistral AI models at scale without having to worry about infrastructure management. Additionally, you may keep capacity and performance constant with Provisioned Throughput, which will be accessible in the upcoming weeks. Naturally, make use of top-notch infrastructure that was designed with AI workloads in mind.
Deploy with confidence
Use Google Cloud’s strong security, privacy, and compliance protections to deploy with confidence, knowing that your data and models are protected at every turn.
Start Using Google Cloud’s Mistral AI models now
Google is dedicated to giving developers simple access to the most cutting-edge AI features. Google Cloud collaboration with Mistral AI is evidence of both companies’ dedication to provide you access to an open and transparent AI ecosystem together with cutting-edge AI research. To maintain their customers at the forefront of AI capabilities, we’ll keep up Google Cloud tight collaboration with Mistral AI and other partners.
Visit Model Garden (Codestral, Large 2, Nemo) or the documentation to view the Mistral AI models. To find out more about the new models, see Mistral AI’s announcement. The Google Cloud Marketplace (Codestral, Large 2, and Nemo) offers the Mistral AI models as well.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#MistralAI#AI#Codestral#AIapplication#VertexAI#generativeAI#AIapps#largelanguagemodels#llm#AImodel#AIplatform#news#technews#technology#technologynews#technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
The Evolution and Impact of Software Technology
Software technology has undergone a remarkable evolution, fundamentally transforming the way we live, work, and interact. From the early days of simple programs to the complex systems we rely on today, the advancements in software technology have brought about significant changes across various sectors.
Historical Development
The journey of software technology began in the mid-20th century with the advent of the first computers. These early machines were programmed using binary code, a laborious and error-prone process. As computing technology advanced, so did programming languages, leading to the creation of assembly language and subsequently higher-level languages like FORTRAN and COBOL. These languages made programming more accessible and efficient, allowing for the development of more complex software applications.
Modern Software Development
Today, software development is a sophisticated field involving numerous languages, tools, and methodologies. Object-oriented programming (OOP), introduced in the 1980s, marked a significant shift, enabling developers to create modular, reusable code. This approach laid the groundwork for modern software engineering practices, emphasizing maintainability and scalability.
The rise of the internet in the 1990s brought about another paradigm shift. Web development became a critical area of focus, leading to the creation of languages and frameworks specifically designed for the web, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and later, more advanced frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue.js. These technologies have enabled the development of dynamic, interactive web applications that are integral to modern digital experiences.
Software in Everyday Life
Software technology permeates almost every aspect of our daily lives. Smartphones, powered by sophisticated operating systems like iOS and Android, run countless applications that assist us with everything from communication and navigation to entertainment and productivity. Cloud computing has revolutionized how we store and access data, making it possible to work from anywhere with an internet connection.
In the business world, enterprise software solutions streamline operations, enhance productivity, and provide valuable insights through data analytics. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, and other business intelligence tools have become essential components of modern business strategy.
Emerging Trends
The field of software technology is continually evolving, with several emerging trends poised to shape the future. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are at the forefront, enabling the development of intelligent applications that can learn and adapt over time. These technologies are being integrated into various industries, from healthcare and finance to transportation and entertainment, providing new capabilities and efficiencies.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another significant trend, connecting everyday devices to the internet and enabling them to communicate and interact. This technology has applications in smart homes, industrial automation, and healthcare, among other areas, creating a more interconnected and efficient world.
Blockchain technology, initially known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is now being explored for its potential to provide secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions in various fields, including supply chain management, finance, and digital identity verification.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous advancements, software technology also faces challenges. Security remains a critical concern, with cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated. Ensuring the privacy and protection of data is paramount, requiring continuous innovation in security measures.
Moreover, the rapid pace of technological change can lead to obsolescence, requiring organizations and individuals to continuously update their skills and systems to stay relevant. The ethical implications of AI and automation, such as job displacement and decision-making accountability, also need to be carefully considered and addressed.
Conclusion
Software technology has profoundly transformed the modern world, driving innovation and efficiency across various domains. As we look to the future, continued advancements and emerging trends promise to further revolutionize the way we live and work. However, it is essential to navigate the associated challenges thoughtfully to ensure that the benefits of software technology are realized in a secure, ethical, and sustainable manner.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of Tech Roles: From Programmers to AI Specialists
The tech industry has always been at the forefront of innovation, constantly evolving and adapting to new advancements. Over the decades, the roles within this dynamic sector have undergone significant transformations. For IT hiring agencies, understanding this evolution is crucial in matching the right talent with the right opportunities. In this blog, we’ll take a journey through the evolution of tech roles, from early programmers to today's AI specialists, and explore what this means for the future of tech hiring.
The Birth of Programming
In the early days of computing, the role of a programmer was a niche, highly specialized profession. These pioneers were tasked with writing machine-level code, often for specific, single-purpose machines.
Key Characteristics:
● Skills: Proficiency in low-level languages like Assembly and machine code.
● Scope: Focused on writing basic programs for calculation and data processing.
● Environment: Primarily academic and research institutions, with limited commercial application.
As technology advanced, programming languages became more sophisticated. The development of high-level languages such as FORTRAN and COBOL in the 1950s and 60s marked a significant shift, making programming more accessible and paving the way for broader applications.
The Rise of Software Development
The 1970s and 80s saw the rise of software development as a distinct profession. With the advent of personal computers and commercial software, the demand for skilled software developers skyrocketed.
Key Characteristics:
● Skills: Knowledge of high-level programming languages like C, C++, and later Java and Python.
● Scope: Development of operating systems, software applications, and games.
● Environment: Emergence of software companies, such as Microsoft and Apple, and increased presence in various industries.
During this period, IT hiring agencies began to flourish, helping companies find developers with the skills needed to create increasingly complex software solutions.
The Internet Era and Web Development
The 1990s brought the internet revolution, drastically changing the tech landscape. The rise of the World Wide Web created new opportunities and roles, particularly in web development.
Key Characteristics:
● Skills: Proficiency in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and server-side languages like PHP and Ruby.
● Scope: Creation and maintenance of websites, e-commerce platforms, and web applications.
● Environment: Growth of tech startups, digital agencies, and IT departments within traditional companies.
The internet era emphasized the need for versatility and rapid development, leading to the adoption of Agile methodologies and the importance of user experience (UX) design.
The Mobile Revolution
The introduction of smartphones in the late 2000s marked another pivotal shift, giving rise to mobile app development as a critical tech role.
Key Characteristics:
● Skills: Expertise in mobile development frameworks such as iOS (Swift/Objective-C) and Android (Java/Kotlin).
● Scope: Development of mobile applications, including games, utilities, and social media platforms.
● Environment: Expansion of the app economy, with tech giants like Google and Apple leading the way.
Mobile app development required a focus on performance optimization and intuitive user interfaces, further diversifying the skill set needed in tech roles.
The Age of Data and AI
In recent years, data science and artificial intelligence (AI) have become the new frontiers of the tech industry. The ability to analyze vast amounts of data and create intelligent systems is transforming how businesses operate.
Key Characteristics:
● Skills: Proficiency in data analysis tools (R, Python), machine learning frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch), and big data technologies (Hadoop, Spark).
● Scope: Developing algorithms for predictive analytics, natural language processing, and autonomous systems.
● Environment: Integration of AI across various sectors, from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and retail.
The rise of AI specialists has created a high demand for professionals who can bridge the gap between theoretical research and practical applications, making them some of the most sought-after talent by IT hiring agencies.
Implications for IT Hiring Agencies
Understanding the evolution of tech roles is essential for IT hiring agencies to effectively match candidates with the right opportunities. Here are a few key takeaways:
1. Diverse Skill Sets: The tech industry now encompasses a wide range of roles requiring diverse skill sets. Agencies must stay updated on the latest technologies and trends to find suitable candidates.
2. Specialized Knowledge: As roles become more specialized, agencies need to identify candidates with specific expertise, such as AI, cybersecurity, or cloud computing.
3. Continuous Learning: The rapid pace of technological change means that continuous learning and professional development are crucial for both candidates and recruiters. Agencies should encourage and support candidates in obtaining relevant certifications and training.
4. Adaptability: The ability to adapt to new technologies and methodologies is essential. IT hiring agencies should look for candidates who demonstrate flexibility and a willingness to learn.
5. Future Trends: Keeping an eye on emerging trends, such as quantum computing and blockchain, will help agencies anticipate future hiring needs and stay ahead of the curve.
Conclusion
The evolution of tech roles from programmers to AI specialists highlights the dynamic nature of the tech industry. For IT hiring agencies, staying informed about these changes is crucial for successfully placing candidates in roles where they can thrive. By understanding the historical context and future trends, agencies can better serve both their clients and candidates, driving innovation and growth in the tech sector.
#it staffing agency#it recruitment agency#it staffing services#it hiring agencies#it placement agencies#it employment agency#it recruiting firms
0 notes
Text
The Evolution and Impact of Software Development
Software development is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that plays a crucial role in modern society. It encompasses the processes involved in creating, designing, deploying, and maintaining software systems. From the early days of simple programming to the current landscape of complex, integrated systems, software development has transformed how businesses operate and how individuals interact with technology.

A Brief History
The history of software development dates back to the mid-20th century with the invention of early computers. The first software was written in machine language, a tedious and error-prone process. With the development of assembly languages and high-level programming languages such as Fortran, COBOL, and later, C and Java, the process became more manageable and efficient.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the rise of personal computers and the internet revolutionized software development. This era saw the birth of the software industry as we know it, with companies like Microsoft and Apple leading the charge. The introduction of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) made software more accessible to the general public, further accelerating the industry's growth.
Modern Software Development Practices
Today, software development is characterized by several key practices and methodologies that enhance productivity, quality, and collaboration. Some of the most significant advancements include:
1. Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, have transformed how software is developed. Agile emphasizes iterative development, where software is built in small, incremental steps. This approach allows for continuous feedback, rapid adaptation to changes, and early delivery of valuable features. Agile methodologies promote collaboration among cross-functional teams, ensuring that all stakeholders are involved throughout the development process.
2. DevOps
DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). It aims to shorten the software development lifecycle and deliver high-quality software continuously. DevOps practices include continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and infrastructure as code (IaC). These practices enhance collaboration between development and operations teams, automate repetitive tasks, and improve deployment processes.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized software development by providing scalable, on-demand resources. Platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer a wide range of services, from infrastructure to machine learning tools. Cloud computing enables developers to build, test, and deploy applications more efficiently and cost-effectively. It also facilitates collaboration and remote work, allowing teams to access resources and collaborate from anywhere in the world.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming integral parts of modern software development. AI and ML enable the creation of intelligent applications that can learn from data, make predictions, and automate complex tasks. These technologies are used in various domains, including healthcare, finance, and entertainment, to enhance decision-making, personalize user experiences, and optimize operations.
The Impact of Software Development
Software development has a profound impact on various aspects of society and the economy:
1. Economic Growth
The software industry is a significant driver of economic growth. It creates jobs, fosters innovation, and enables the digital transformation of businesses. Software solutions streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency, contributing to increased productivity and competitiveness.
2. Social Change
Software development has transformed how people communicate, access information, and entertain themselves. Social media platforms, messaging apps, and streaming services have reshaped social interactions and entertainment consumption. Educational software and e-learning platforms have made education more accessible, especially in remote and underserved areas.
3. Healthcare
In healthcare, software development has led to advancements in medical research, patient care, and administration. Electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and health monitoring apps are just a few examples of how software solutions improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare services.
4. Environmental Impact
Software development also plays a role in addressing environmental challenges. Smart grid technology, renewable energy management systems, and environmental monitoring applications are examples of how software solutions contribute to sustainable development and environmental conservation.
The Future of Software Development
The future of software development is exciting and full of potential. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing, blockchain, and augmented reality (AR) are poised to redefine the field. Quantum computing promises to solve complex problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. Blockchain offers new possibilities for secure and transparent transactions, while AR and virtual reality (VR) are set to revolutionize user experiences and interactions.
Moreover, the increasing focus on cybersecurity, data privacy, and ethical considerations will shape the future of software development. As technology continues to advance, developers will need to address these challenges to build secure, trustworthy, and ethical software solutions.
Conclusion
Software development is a cornerstone of the digital age, driving innovation and transformation across all sectors. From its humble beginnings to its current state as a sophisticated and essential industry, software development continues to evolve, pushing the boundaries of what is possible. As we look to the future, the potential for further advancements and their impact on society is limitless, promising a world where technology continues to enhance and enrich our lives.
Get in touch today to kickstart your digital journey with AYB Infotech!
Email: [email protected] Phone: 02030265160 Website: www.aybinfotech.com Address: - 167-169 Great Portland street, 5th Floor, London, W1W 5PF
#appdevelopment#applaunch#appstore#digitalstrategy#digitaltransformation#mobilemarketing#mobiletech#onlinebusiness#digitalmarketing#innovation#Website Development#Mobile App Development#eCommerce Website Development#Software development
0 notes
Text
Constructing the Future One Line at a Time: Digital Dream Builders
Overview
Our world has changed in ways we could never have imagined due to the speed at which technology is developing. Software development, a profession that has transformed industries and our everyday lives, is at the center of this change. Software engineers, the architects of this digital revolution, are frequently compared to contemporary architects since they create complex structures with code. This article explores the history, significance, difficulties, and prospects of the field of software development.
A Synopsis of Software Development's Past
Though she is frequently credited as the first computer programmer, Ada Lovelace started the route towards software creation in the early 19th century. Lovelace developed the first algorithm meant for machine processing while working on Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine. The emergence of the first high-level programming languages, such as FORTRAN and COBOL, in the middle of the 20th century set the foundation for contemporary software engineering.
The introduction of personal computers in the 1980s, which democratized access to computing power, marked the next step in the progression. During this time, software behemoths like Apple and Microsoft rose to prominence, becoming well-known for their operating systems and apps. The internet boom of the late 20th and early 21st centuries gave rise to web-based applications and Silicon Valley's emergence as the world's tech center.
Software Developers' Role
Programmers, often known as coders or software developers, are the people who create and maintain software applications. They work in a variety of fields, including as game creation, systems programming, mobile app development, and web development. A wide range of programming languages, tools, and frameworks are used by developers to create software that satisfies user needs and advances organizational goals.
A software developer's responsibilities extend beyond simple coding. It calls for critical thinking, problem-solving, and ongoing learning. It is essential for developers to comprehend customer needs, create effective algorithms, produce readable code, and conduct thorough testing on their systems. Since most software projects are built by teams rather than by individuals, collaboration is also essential.
Software Development's Effects
Software development has a significant and wide-ranging impact on society. Software programs improve productivity, simplify processes, and facilitate data-driven decision-making in the business sector. The operation of contemporary firms depends on enterprise software solutions like enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
Software programs have become essential in daily life. Software connects us through social networking sites like Facebook and Instagram as well as messaging apps like Zoom and WhatsApp. Digital entertainment services like Netflix and Spotify have revolutionized media consumption, while e-commerce behemoths like Amazon and Alibaba have changed how we shop.
Software development has also greatly aided the healthcare sector. Systems for electronic health records (EHRs) facilitate better patient care by making medical histories easily accessible. Applications for telemedicine make healthcare more accessible by enabling remote consultations. Furthermore, the diagnosis and creation of individualized treatment regimens are being accomplished through the use of software-driven technologies such as machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI).
Difficulties in Software Development
Even with all of its benefits, software development is not without its difficulties. Handling complexity is one of the main issues. These days, software systems include millions of lines of code and several interrelated components, making them extremely complicated. It's a big job to make sure these systems work properly and are bug-free.
Another big worry is security. Software is a target for cyberattacks as it becomes more and more essential to our daily life. Throughout the development process, developers must put security first and put strong authentication, authorization, and encryption systems in place. Even with the greatest of intentions, vulnerabilities can still be used to cause security incidents and data breaches.
Another issue is the speed at which technology is changing. To stay up to date with new frameworks, tools, and programming languages, developers need to constantly upgrade their skill set. It might be difficult and time-consuming to meet this requirement for ongoing learning. Additionally, developers may experience burnout due to the requirement for quick innovation and the desire for faster development cycles, which are driven by agile approaches.
Software Development's Future
Software development is expected to have an exciting and demanding future. The sector will probably be shaped by a few trends in the upcoming years.
AI and ML: These two technologies have the potential to completely transform the software development industry. By automating repetitive processes like code generation and testing, these technologies allow developers to concentrate on more intricate and imaginative areas of their work. Additionally, intelligent recommendations and error detection can be provided via AI-driven development tools, enhancing productivity and code quality.
Cloud Computing: Software development, deployment, and maintenance are changing as a result of the move to cloud computing. With the help of scalable infrastructure provided by cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, developers can create apps that can manage massive amounts of data and traffic. With serverless computing, developers can concentrate only on developing code because the cloud provider handles the infrastructure.
The goal of DevOps is to produce high-quality software continuously while also reducing the length of the development lifecycle. It is a collection of methods that combines software development with IT operations. Pipelines for continuous delivery (CD) and continuous integration (CI) automate the development, testing, and launch of applications, cutting down on time to market and enhancing reliability.
Quantum computing is still in its infancy, but it has the potential to tackle issues that classical computers are unable to handle at the moment. Quantum algorithms have the potential to transform domains including material science, encryption, and optimization. For software developers to fully utilize the potential of quantum computers, they will need to acquire new concepts and approaches.
Regulation and Ethics: As software becomes more widely used in society, it will be important to comply with regulations and take ethical considerations into account. It is necessary to address concerns like algorithmic unfairness, data privacy, and the environmental impact of software development. It will be the responsibility of developers to follow moral standards and collaborate with legislators to guarantee that software advances the common good.
The Human Factor in Software Engineering
The human aspect is still fundamental to software development, even though technology and tools play a significant role. What really propels innovation is the creativity, problem-solving aptitude, and teamwork skills of developers. To encourage innovation and protect developers' well-being, development teams must establish a welcoming and positive culture.
Cooperation and Communication: The success of every software project depends on efficient cooperation and communication. People with a variety of backgrounds and skill sets, such as developers, designers, testers, and project managers, frequently make up development teams. Collaboration is made easier by tools like communication platforms, project management software, and version control systems, but team members' interpersonal abilities really shine through.
Growth and Continuous Learning: Because the IT sector moves quickly, developers must participate in ongoing learning. Numerous organizations encourage engagement in open-source projects, attend conferences, and provide training programs in order to promote this. Developers themselves frequently take the initiative to enrol in online courses, coding bootcamps, and professional networks in order to acquire new languages, frameworks, and best practices.
Work-Life Balance: Software development is a hard field that can result in long hours and high levels of stress. Prioritizing work-life balance is crucial for organizations and developers alike in order to avoid burnout. A better work environment can be achieved with the assistance of mental health resources, remote work opportunities, and flexible working hours. Creating a culture that prioritizes quality over quantity and encourages reasonable project deadlines can also lessen stress and increase job satisfaction.
Case Studies: Software Development Pioneers
To demonstrate the revolutionary potential of software development, let us examine some innovative companies and projects through case studies.
Google: Information access was transformed by Google's search engine. Its enormous infrastructure and intricate algorithms, which index and retrieve data from billions of web sites, conceal its complexity. Google's inventiveness goes beyond
GitHub: Using GitHub has completely changed the way engineers work together on software projects. Through the provision of a collaborative coding and version control platform, GitHub has made it possible for developers worldwide to share and contribute to open-source projects. The software development process has been expedited by the platform's interaction with project management applications and CI/CD pipelines.
Tesla: The Company’s software developments are just as important as its progress with electric cars. With no need to visit a service center, Tesla vehicles can now get new features and enhancements thanks to the company's over-the-air software updates. Tesla's cutting-edge driver-assistance technology, Autopilot, interprets data from cameras, sensors, and radar using complex algorithms so that it can navigate and drive on its own.
Conclusion
Our world is still being shaped by the dynamic and ever-evolving industry of software development. Software development has come a long way from its modest beginnings with Ada Lovelace's early algorithms to the complex applications of today. Software's significance is highlighted by the ways it affects numerous industries, businesses, and everyday life.
The difficulties of handling complexity, guaranteeing security, and keeping up with technological advancements will not go away in the future. But there are also a ton of amazing opportunities brought about by AI, cloud computing, DevOps, and quantum computing. Through adoption of these technologies and adherence to ethical principles, software developers can persist in creating software that propels advancements and enhances people's lives.
In the end, how creative, collaborative, and lifelong learners software developers are will define the industry's destiny. They create the future one line at a time as digital dream builders, bringing concepts to life and expanding the realm of the conceivable. Software development is a never-ending journey, with the upcoming chapter expected to be just as thrilling and revolutionary as the previous ones.
#habilelabs#ethics first#crmsoftware#aws cloud#amazon web services#softwaredeveloper#softwareenginner#software development
0 notes
Text
Defining IT Legacy Systems: Origins, Evolution, and Current Relevance

In the fast-paced world of technology, where innovations occur at lightning speed, the term "legacy system" often carries a connotation of obsolescence. However, understanding the origins, evolution, and current relevance of IT legacy systems is crucial for businesses aiming to balance modern advancements with reliable infrastructure. This blog explores the journey of legacy systems from their inception to their role in today's digital landscape.
Origins of IT Legacy Systems
The Dawn of Computing
The concept of legacy systems dates back to the early days of computing in the mid-20th century. During this period, large mainframe computers, such as IBM's System/360, became the backbone of corporate IT infrastructure. These systems were designed to handle vast amounts of data and perform complex calculations, making them indispensable for large organizations.
Custom-Built Solutions
In the 1970s and 1980s, many companies invested heavily in custom-built software tailored to their specific needs. These systems, often written in programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN, were robust and reliable. They powered critical business operations, from financial transactions to inventory management.
Evolution of Legacy Systems
The Rise of Personal Computing
The 1980s and 1990s saw the advent of personal computers and the proliferation of client-server architectures. While PCs brought computing power to individual desks, many organizations continued to rely on their legacy mainframes and custom-built solutions for core functions. The client-server model introduced new challenges in integrating legacy systems with emerging technologies.
The Internet Era
With the rise of the internet in the late 1990s and early 2000s, businesses began to adopt web-based applications. Legacy systems, originally designed for isolated environments, faced new demands for connectivity and interoperability. Middleware solutions and enterprise application integration tools emerged to bridge the gap between old and new technologies.
Cloud Computing and Beyond
The last two decades have been characterized by rapid advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. Despite these innovations, many organizations still rely on legacy systems for critical operations. The challenge has shifted from merely maintaining these systems to integrating them with cutting-edge technologies and ensuring their security in an increasingly interconnected world.
Current Relevance of IT Legacy Systems
Stability and Reliability
One of the main reasons legacy systems persist is their proven stability and reliability. These systems have been tested over decades and are often the backbone of critical operations, such as banking transactions and airline reservations. Their reliability is unmatched, making them indispensable in industries where downtime is not an option.
High Cost of Replacement
Replacing a legacy system is not a trivial task. The cost, both in terms of money and time, can be prohibitive. New systems require significant investment in hardware, software, and training. Additionally, the risk of disruption during the transition period can be a major deterrent for businesses.
Customization and Integration
Many legacy systems are highly customized to meet the specific needs of the organizations that use them. This customization, while beneficial, also makes replacement difficult. Instead of complete overhauls, many companies opt for integrating legacy systems with modern applications using APIs and other middleware solutions.
Regulatory and Compliance Factors
In some industries, regulatory requirements and compliance standards make it challenging to replace legacy systems. These systems often have built-in compliance features that newer solutions may lack. Ensuring that a new system meets all regulatory requirements can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Balancing Legacy Systems with Modern Innovations
Incremental Modernization
Rather than replacing legacy systems entirely, many organizations are adopting an incremental approach to modernization. This involves gradually updating components of the system, integrating them with modern technologies, and phasing out outdated parts over time. This approach minimizes risk and allows for a smoother transition.
Leveraging Cloud Technologies
Cloud computing offers scalable and flexible solutions for modernizing legacy systems. By migrating certain functions to the cloud, organizations can reduce infrastructure costs, improve data accessibility, and enhance collaboration. Hybrid cloud environments, where legacy systems coexist with cloud-based solutions, are becoming increasingly popular.
Focus on Cybersecurity
As legacy systems continue to play a crucial role in business operations, ensuring their security is paramount. Regular security audits, updates, and the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
Conclusion
IT legacy systems, despite their age, remain vital components of many organizations' IT infrastructures. Understanding their origins, evolution, and current relevance is crucial for businesses aiming to strike a balance between leveraging reliable, time-tested technology and embracing modern innovations. By adopting strategic modernization approaches and focusing on integration and security, organizations can ensure that their legacy systems continue to support their growth and success in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
0 notes
