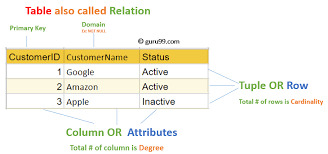
#group by and having clause in sql
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Structured Query Language (SQL): A Comprehensive Guide
Structured Query Language, popularly called SQL (reported "ess-que-ell" or sometimes "sequel"), is the same old language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. Developed in the early 1970s by using IBM researchers Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce, SQL has when you consider that end up the dominant language for database structures round the world.
Structured query language commands with examples
Today, certainly every important relational database control system (RDBMS)—such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and SQLite—uses SQL as its core question language.
What is SQL?
SQL is a website-specific language used to:
Retrieve facts from a database.
Insert, replace, and delete statistics.
Create and modify database structures (tables, indexes, perspectives).
Manage get entry to permissions and security.
Perform data analytics and reporting.
In easy phrases, SQL permits customers to speak with databases to shop and retrieve structured information.
Key Characteristics of SQL
Declarative Language: SQL focuses on what to do, now not the way to do it. For instance, whilst you write SELECT * FROM users, you don’t need to inform SQL the way to fetch the facts—it figures that out.
Standardized: SQL has been standardized through agencies like ANSI and ISO, with maximum database structures enforcing the core language and including their very own extensions.
Relational Model-Based: SQL is designed to work with tables (also called members of the family) in which records is organized in rows and columns.
Core Components of SQL
SQL may be damaged down into numerous predominant categories of instructions, each with unique functions.
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to outline or modify the shape of database gadgets like tables, schemas, indexes, and so forth.
Common DDL commands:
CREATE: To create a brand new table or database.
ALTER: To modify an present table (add or put off columns).
DROP: To delete a table or database.
TRUNCATE: To delete all rows from a table but preserve its shape.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE TABLE personnel (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
call VARCHAR(one hundred),
income DECIMAL(10,2)
);
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used for statistics operations which include inserting, updating, or deleting information.
Common DML commands:
SELECT: Retrieve data from one or more tables.
INSERT: Add new records.
UPDATE: Modify existing statistics.
DELETE: Remove information.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
INSERT INTO employees (id, name, earnings)
VALUES (1, 'Alice Johnson', 75000.00);
three. Data Query Language (DQL)
Some specialists separate SELECT from DML and treat it as its very own category: DQL.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT name, income FROM personnel WHERE profits > 60000;
This command retrieves names and salaries of employees earning more than 60,000.
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL instructions cope with permissions and access manage.
Common DCL instructions:
GRANT: Give get right of entry to to users.
REVOKE: Remove access.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON personnel TO john_doe;
five. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands manage transactions to ensure data integrity.
Common TCL instructions:
BEGIN: Start a transaction.
COMMIT: Save changes.
ROLLBACK: Undo changes.
SAVEPOINT: Set a savepoint inside a transaction.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
BEGIN;
UPDATE personnel SET earnings = income * 1.10;
COMMIT;
SQL Clauses and Syntax Elements
WHERE: Filters rows.
ORDER BY: Sorts effects.
GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a assets.
HAVING: Filters companies.
JOIN: Combines rows from or greater tables.
Example with JOIN:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT personnel.Name, departments.Name
FROM personnel
JOIN departments ON personnel.Dept_id = departments.Identity;
Types of Joins in SQL
INNER JOIN: Returns statistics with matching values in each tables.
LEFT JOIN: Returns all statistics from the left table, and matched statistics from the right.
RIGHT JOIN: Opposite of LEFT JOIN.
FULL JOIN: Returns all records while there is a in shape in either desk.
SELF JOIN: Joins a table to itself.
Subqueries and Nested Queries
A subquery is a query inside any other query.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
SELECT name FROM employees
WHERE earnings > (SELECT AVG(earnings) FROM personnel);
This reveals employees who earn above common earnings.
Functions in SQL
SQL includes built-in features for acting calculations and formatting:
Aggregate Functions: SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), MIN()
String Functions: UPPER(), LOWER(), CONCAT()
Date Functions: NOW(), CURDATE(), DATEADD()
Conversion Functions: CAST(), CONVERT()
Indexes in SQL
An index is used to hurry up searches.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON employees(call);
Indexes help improve the performance of queries concerning massive information.
Views in SQL
A view is a digital desk created through a question.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
CREATE VIEW high_earners AS
SELECT call, salary FROM employees WHERE earnings > 80000;
Views are beneficial for:
Security (disguise positive columns)
Simplifying complex queries
Reusability
Normalization in SQL
Normalization is the system of organizing facts to reduce redundancy. It entails breaking a database into multiple related tables and defining overseas keys to link them.
1NF: No repeating groups.
2NF: No partial dependency.
3NF: No transitive dependency.
SQL in Real-World Applications
Web Development: Most web apps use SQL to manipulate customers, periods, orders, and content.
Data Analysis: SQL is extensively used in information analytics systems like Power BI, Tableau, and even Excel (thru Power Query).
Finance and Banking: SQL handles transaction logs, audit trails, and reporting systems.
Healthcare: Managing patient statistics, remedy records, and billing.
Retail: Inventory systems, sales analysis, and consumer statistics.
Government and Research: For storing and querying massive datasets.
Popular SQL Database Systems
MySQL: Open-supply and extensively used in internet apps.
PostgreSQL: Advanced capabilities and standards compliance.
Oracle DB: Commercial, especially scalable, agency-degree.
SQL Server: Microsoft’s relational database.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database used in cellular and desktop apps.
Limitations of SQL
SQL can be verbose and complicated for positive operations.
Not perfect for unstructured information (NoSQL databases like MongoDB are better acceptable).
Vendor-unique extensions can reduce portability.
Java Programming Language Tutorial
Dot Net Programming Language
C ++ Online Compliers
C Language Compliers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top SQL Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers and Professionals

SQL is the foundation of data-driven applications. Whether you’re applying for a data analyst, backend developer, or database administrator role, having a solid grip on SQL interview questions is essential for cracking technical rounds.
In this blog post, we’ll go over the most commonly asked SQL questions along with sample answers to help you prepare effectively.
📘 Want a complete, updated list of SQL interview questions? 👉 Check out: SQL Interview Questions & Answers – Freshy Blog
🔹 What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is used to communicate with and manipulate databases. It is the standard language for relational database management systems (RDBMS).
🔸 Most Common SQL Interview Questions
1. What is the difference between WHERE and HAVING clause?
WHERE: Filters rows before grouping
HAVING: Filters groups after aggregation
2. What is a Primary Key?
A primary key is a unique identifier for each record in a table and cannot contain NULL values.
3. What are Joins in SQL?
Joins are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column. Types include:
INNER JOIN
LEFT JOIN
RIGHT JOIN
FULL OUTER JOIN
🔸 Intermediate to Advanced SQL Questions
4. What is the difference between DELETE, TRUNCATE, and DROP?
DELETE: Removes rows (can be rolled back)
TRUNCATE: Removes all rows quickly (cannot be rolled back)
DROP: Deletes the table entirely
5. What is a Subquery?
A subquery is a query nested inside another query. It is used to retrieve data for use in the main query.
6. What is normalization?
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity.
🚀 Get a full breakdown with examples, tips, and pro-level questions: 👉 https://www.freshyblog.com/sql-interview-questions-answers/
🔍 Bonus Questions to Practice
What is the difference between UNION and UNION ALL?
What are indexes and how do they improve performance?
How does a GROUP BY clause work with aggregate functions?
What is a stored procedure and when would you use one?
✅ Tips to Crack SQL Interviews
Practice writing queries by hand
Focus on real-world database scenarios
Understand query optimization basics
Review basic RDBMS concepts like constraints and keys
Final Thoughts
Whether you're a fresher starting out or an experienced developer prepping for technical rounds, mastering these SQL interview questions is crucial for acing your next job opportunity.
📚 Access the full SQL interview guide here: 👉 https://www.freshyblog.com/sql-interview-questions-answers/
#SQLInterviewQuestions#SQLQueries#DatabaseInterview#DataAnalytics#BackendDeveloper#FreshyBlog#SQLForFreshers#TechJobs
0 notes
Text
Data Analyst Interview Questions: A Comprehensive Guide
Preparing for an interview as a Data Analyst is difficult, given the broad skills needed. Technical skill, business knowledge, and problem-solving abilities are assessed by interviewers in a variety of ways. This guide will assist you in grasping the kind of questions that will be asked and how to answer them.

By mohammed hassan on Pixabay
General Data Analyst Interview Questions
These questions help interviewers assess your understanding of the role and your basic approach to data analysis.
Can you describe what a Data Analyst does? A Data Analyst collects, processes, and analyzes data to help businesses make data-driven decisions and identify trends or patterns.
What are the key responsibilities of a Data Analyst? Responsibilities include data collection, data cleaning, exploratory data analysis, reporting insights, and collaborating with stakeholders.
What tools are you most familiar with? Say tools like Excel, SQL, Python, Tableau, Power BI, and describe how you have used them in past projects.
What types of data? Describe structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data using examples such as databases, JSON files, and pictures or videos.
Technical Data Analyst Interview Questions
Technical questions evaluate your tool knowledge, techniques, and your ability to manipulate and interpret data.
What is the difference between SQL's inner join and left join? The inner join gives only the common rows between tables, whereas a left join gives all rows of the left table as well as corresponding ones of the right.
How do you deal with missing data in a dataset? Methods are either removing rows, mean/median imputation, or forward-fill/backward-fill depending on context and proportion of missing data.
Can you describe normalization and why it's significant? Normalization minimizes data redundancy and enhances data integrity by structuring data effectively between relational tables.
What are some Python libraries that are frequently used for data analysis? Libraries consist of Pandas for data manipulation, NumPy for numerical computations, Matplotlib/Seaborn for data plotting, and SciPy for scientific computing.
How would you construct a query to discover duplicate values within a table? Use a GROUP BY clause with a HAVING COUNT(*) > 1 to find duplicate records according to one or more columns.
Behavioral and Situational Data Analyst Interview Questions
These assess your soft skills, work values, and how you deal with actual situations.
Describe an instance where you managed a challenging stakeholder. Describe how you actively listened, recognized their requirements, and provided insights that supported business objectives despite issues with communication.
Tell us about a project in which you needed to analyze large datasets. Describe how you broke the dataset down into manageable pieces, what tools you used, and what you learned from the analysis.
Read More....
0 notes
Text
PySpark SQL: Introduction & Basic Queries
Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, the volume and variety of data have exploded. Traditional tools often struggle to process and analyze massive datasets efficiently. That’s where Apache Spark comes into the picture — a lightning-fast, unified analytics engine for big data processing.
For Python developers, PySpark — the Python API for Apache Spark — offers an intuitive way to work with Spark. Among its powerful modules, PySpark SQL stands out. It enables you to query structured data using SQL syntax or DataFrame operations. This hybrid capability makes it easy to blend the power of Spark with the familiarity of SQL.
In this blog, we'll explore what PySpark SQL is, why it’s so useful, how to set it up, and cover the most essential SQL queries with examples — perfect for beginners diving into big data with Python.

Agenda
Here's what we'll cover:
What is PySpark SQL?
Why should you use PySpark SQL?
Installing and setting up PySpark
Basic SQL queries in PySpark
Best practices for working efficiently
Final thoughts
What is PySpark SQL?
PySpark SQL is a module of Apache Spark that enables querying structured data using SQL commands or a more programmatic DataFrame API. It offers:
Support for SQL-style queries on large datasets.
A seamless bridge between relational logic and Python.
Optimizations using the Catalyst query optimizer and Tungsten execution engine for efficient computation.
In simple terms, PySpark SQL lets you use SQL to analyze big data at scale — without needing traditional database systems.
Why Use PySpark SQL?
Here are a few compelling reasons to use PySpark SQL:
Scalability: It can handle terabytes of data spread across clusters.
Ease of use: Combines the simplicity of SQL with the flexibility of Python.
Performance: Optimized query execution ensures fast performance.
Interoperability: Works with various data sources — including Hive, JSON, Parquet, and CSV.
Integration: Supports seamless integration with DataFrames and MLlib for machine learning.
Whether you're building dashboards, ETL pipelines, or machine learning workflows — PySpark SQL is a reliable choice.
Setting Up PySpark
Let’s quickly set up a local PySpark environment.
1. Install PySpark:
pip install pyspark
2. Start a Spark session:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName("PySparkSQLExample") \ .getOrCreate()
3. Create a DataFrame:
data = [("Alice", 25), ("Bob", 30), ("Clara", 35)] columns = ["Name", "Age"] df = spark.createDataFrame(data, columns) df.show()
4. Create a temporary view to run SQL queries:
df.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
Now you're ready to run SQL queries directly!
Basic PySpark SQL Queries
Let’s look at the most commonly used SQL queries in PySpark.
1. SELECT Query
spark.sql("SELECT * FROM people").show()
Returns all rows from the people table.
2. WHERE Clause (Filtering Rows)
spark.sql("SELECT * FROM people WHERE Age > 30").show()
Filters rows where Age is greater than 30.
3. Adding a Derived Column
spark.sql("SELECT Name, Age, Age + 5 AS AgeInFiveYears FROM people").show()
Adds a new column AgeInFiveYears by adding 5 to the current age.
4. GROUP BY and Aggregation
Let’s update the data with multiple entries for each name:
data2 = [("Alice", 25), ("Bob", 30), ("Alice", 28), ("Bob", 35), ("Clara", 35)] df2 = spark.createDataFrame(data2, columns) df2.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
Now apply aggregation:
spark.sql(""" SELECT Name, COUNT(*) AS Count, AVG(Age) AS AvgAge FROM people GROUP BY Name """).show()
This groups records by Name and calculates the number of records and average age.
5. JOIN Between Two Tables
Let’s create another table:
jobs_data = [("Alice", "Engineer"), ("Bob", "Designer"), ("Clara", "Manager")] df_jobs = spark.createDataFrame(jobs_data, ["Name", "Job"]) df_jobs.createOrReplaceTempView("jobs")
Now perform an inner join:
spark.sql(""" SELECT p.Name, p.Age, j.Job FROM people p JOIN jobs j ON p.Name = j.Name """).show()
This joins the people and jobs tables on the Name column.
Tips for Working Efficiently with PySpark SQL
Use LIMIT for testing: Avoid loading millions of rows in development.
Cache wisely: Use .cache() when a DataFrame is reused multiple times.
Check performance: Use .explain() to view the query execution plan.
Mix APIs: Combine SQL queries and DataFrame methods for flexibility.
Conclusion
PySpark SQL makes big data analysis in Python much more accessible. By combining the readability of SQL with the power of Spark, it allows developers and analysts to process massive datasets using simple, familiar syntax.
This blog covered the foundational aspects: setting up PySpark, writing basic SQL queries, performing joins and aggregations, and a few best practices to optimize your workflow.
If you're just starting out, keep experimenting with different queries, and try loading real-world datasets in formats like CSV or JSON. Mastering PySpark SQL can unlock a whole new level of data engineering and analysis at scale.
PySpark Training by AccentFuture
At AccentFuture, we offer customizable online training programs designed to help you gain practical, job-ready skills in the most in-demand technologies. Our PySpark Online Training will teach you everything you need to know, with hands-on training and real-world projects to help you excel in your career.
What we offer:
Hands-on training with real-world projects and 100+ use cases
Live sessions led by industry professionals
Certification preparation and career guidance
🚀 Enroll Now: https://www.accentfuture.com/enquiry-form/
📞 Call Us: +91–9640001789
📧 Email Us: [email protected]
🌐 Visit Us: AccentFuture
1 note
·
View note
Text
Master SQL in 2025: The Only Bootcamp You’ll Ever Need

When it comes to data, one thing is clear—SQL is still king. From business intelligence to data analysis, web development to mobile apps, Structured Query Language (SQL) is everywhere. It’s the language behind the databases that run apps, websites, and software platforms across the world.
If you’re looking to gain practical skills and build a future-proof career in data, there’s one course that stands above the rest: the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL.
Let’s dive into what makes this bootcamp a must for learners at every level.
Why SQL Still Matters in 2025
In an era filled with cutting-edge tools and no-code platforms, SQL remains an essential skill for:
Data Analysts
Backend Developers
Business Intelligence Specialists
Data Scientists
Digital Marketers
Product Managers
Software Engineers
Why? Because SQL is the universal language for interacting with relational databases. Whether you're working with MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, or Microsoft SQL Server, learning SQL opens the door to querying, analyzing, and interpreting data that powers decision-making.
And let’s not forget—it’s one of the highest-paying skills on the job market today.
Who Is This Bootcamp For?
Whether you’re a complete beginner or someone looking to polish your skills, the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL is structured to take you through a progressive learning journey. You’ll go from knowing nothing about databases to confidently querying real-world datasets.
This course is perfect for:
✅ Beginners with no prior programming experience ✅ Students preparing for tech interviews ✅ Professionals shifting to data roles ✅ Freelancers and entrepreneurs ✅ Anyone who wants to work with data more effectively
What You’ll Learn: A Roadmap to SQL Mastery
Let’s take a look at some of the key skills and topics covered in this course:
🔹 SQL Fundamentals
What is SQL and why it's important
Understanding databases and tables
Creating and managing database structures
Writing basic SELECT statements
🔹 Filtering & Sorting Data
Using WHERE clauses
Logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
ORDER BY and LIMIT for controlling output
🔹 Aggregation and Grouping
COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX
GROUP BY and HAVING
Combining aggregate functions with filters
🔹 Advanced SQL Techniques
JOINS: INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL
Subqueries and nested SELECTs
Set operations (UNION, INTERSECT)
Case statements and conditional logic
🔹 Data Cleaning and Manipulation
UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements
Handling NULL values
Using built-in functions for data formatting
🔹 Real-World Projects
Practical datasets to work on
Simulated business cases
Query optimization techniques
Hands-On Learning With Real Impact
Many online courses deliver knowledge. Few deliver results.
The 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL does both. The course is filled with hands-on exercises, quizzes, and real-world projects so you actually apply what you learn. You’ll use modern tools like PostgreSQL and pgAdmin to get your hands dirty with real data.
Why This Course Stands Out
There’s no shortage of SQL tutorials out there. But this bootcamp stands out for a few big reasons:
✅ Beginner-Friendly Structure
No coding experience? No problem. The course takes a gentle approach to build your confidence with simple, clear instructions.
✅ Practice-Driven Learning
Learning by doing is at the heart of this course. You’ll write real queries, not just watch someone else do it.
✅ Lifetime Access
Revisit modules anytime you want. Perfect for refreshing your memory before an interview or brushing up on a specific concept.
✅ Constant Updates
SQL evolves. This bootcamp evolves with it—keeping you in sync with current industry standards in 2025.
✅ Community and Support
You won’t be learning alone. With a thriving student community and Q&A forums, support is just a click away.
Career Opportunities After Learning SQL
Mastering SQL can open the door to a wide range of job opportunities. Here are just a few roles you’ll be prepared for:
Data Analyst: Analyze business data and generate insights
Database Administrator: Manage and optimize data infrastructure
Business Intelligence Developer: Build dashboards and reports
Full Stack Developer: Integrate SQL with web and app projects
Digital Marketer: Track user behavior and campaign performance
In fact, companies like Amazon, Google, Netflix, and Facebook all require SQL proficiency in many of their job roles.
And yes—freelancers and solopreneurs can use SQL to analyze marketing campaigns, customer feedback, sales funnels, and more.
Real Testimonials From Learners
Here’s what past students are saying about this bootcamp:
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “I had no experience with SQL before taking this course. Now I’m using it daily at my new job as a data analyst. Worth every minute!” – Sarah L.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “This course is structured so well. It’s fun, clear, and packed with challenges. I even built my own analytics dashboard!” – Jason D.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “The best SQL course I’ve found on the internet—and I’ve tried a few. I was up and running with real queries in just a few hours.” – Meera P.
How to Get Started
You don’t need to enroll in a university or pay thousands for a bootcamp. You can get started today with the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL and build real skills that make you employable.
Just grab a laptop, follow the course roadmap, and dive into your first database. No fluff. Just real, useful skills.
Tips to Succeed in the SQL Bootcamp
Want to get the most out of your SQL journey? Keep these pro tips in mind:
Practice regularly: SQL is a muscle—use it or lose it.
Do the projects: Apply what you learn to real datasets.
Take notes: Summarize concepts in your own words.
Explore further: Try joining Kaggle or GitHub to explore open datasets.
Ask questions: Engage in course forums or communities for deeper understanding.
Your Future in Data Starts Now
SQL is more than just a skill. It’s a career-launching power tool. With this knowledge, you can transition into tech, level up in your current role, or even start your freelance data business.
And it all begins with one powerful course: 👉 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL
So, what are you waiting for?
Open the door to endless opportunities and unlock the world of data.
0 notes
Text
Master Data Analytics, SQL, and Business Intelligence
In today's fast-growing corporate environment, where most corporate decisions are made based on data, data analysis, SQL, and BI, it's not just an enhancement to your career but a survival tool. These are essential skills that anyone can cultivate, whether you are fresh out of college or even if you’re a professional seeking a change to a more specialised career outlook. And if you are searching for a career switch through a data science certification in Pune, you are already on the right path.
Now let's elucidate why Data Analytics, SQL, and Business Intelligence are significant at present, how one can learn, and the advantages you get in the real world.
Why Data Analytics, SQL, and BI Matter More Than Ever
Organisations across the globe are gathering big data at a high rate every second. However, raw data is not easily readable and hence requires analysis to extract meaning from it. That is where data analytics comes into play – to help teams understand trends, behaviors, and results. Structured Query Language (SQL) is the most common language used today to handle database information, whereas business intelligence tools provide a format for analyzing data and presenting results in an easy-to-understand format.
Here’s how they align:
Data Analytics helps uncover patterns and make predictions.
SQL allows access, organisation, and manipulation of large datasets.
BI Tools like Power BI or Tableau present data through interactive dashboards.
These are no longer niche skills. They're essential across industries, from healthcare and finance to e-commerce and logistics.
Real-Life Example: The Retail Turnaround
Take the case of a retail chain in Pune. Sales were dropping in some outlets, and the leadership had no clue why. After investing in a team equipped with data analytics skills and SQL knowledge, they began analysing customer footfall, product movement, and regional buying behaviour.
Using BI tools, the team created easy-to-understand dashboards showing that specific items weren't moving in certain regions due to pricing mismatches. Adjustments were made, promotions targeted, and within a quarter, the underperforming outlets started showing profits again. This isn’t a one-off story—it’s happening everywhere.
Build the Right Skillset
If you're considering a data science certification in Pune, make sure the curriculum covers these critical areas:
1. Data Analytics Fundamentals
Understanding basic statistics, probability, and analytical thinking is where it all begins. You'll also learn how to frame business problems and solve them using data-driven approaches.
2. SQL – Speak the Language of Databases
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the core of database management. You’ll learn how to:
Retrieve data using SELECT statements
Filter with where clauses.
Aggregate using group by and having.
Join tables efficiently
Optimise complex queries
Mastering SQL is non-negotiable if you want to dive deep into data science.
3. Business Intelligence Tools
Learning how to use tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Looker enables you to present data in visually engaging formats. Dashboards are more than pretty charts—they guide strategic decisions in real-time.
Real-Life Example: The Freelance Analyst
Ritika, a 29-year-old freelancer in Pune, was struggling to grow her consulting business. After completing a comprehensive data science course in Pune that focused on analytics, SQL, and business intelligence (BI), she offered dashboard creation and data interpretation services to startups.
Within six months, her client base doubled. She even landed a long-term contract with a US-based SaaS company to manage their product usage data. Mastering these tools didn't just make her more employable—it made her business thrive.
Career Opportunities and Salaries
Professionals with expertise in data analytics and business intelligence (BI) are in high demand. According to a recent job survey, roles that require SQL and BI skills pay 30% higher than traditional IT roles at entry-level positions. In Pune, the growing startup ecosystem and multinational presence have opened doors to exciting opportunities, especially for those who’ve undergone data science training in Pune and have hands-on skills.
Here are some career paths you can explore:
Data Analyst
Business Intelligence Developer
SQL Data Engineer
Analytics Consultant
Product Analyst
Getting Certified Makes a Difference
A data science certification in Pune not only sharpens your skills but also validates your expertise. Recruiters look for certified professionals because it reduces training time and signals that the candidate is job-ready.
Benefits of Certification:
Structured learning approach
Hands-on projects using real data
Industry-recognized credibility
Placement support (if applicable)
Peer networking and mentorship
Remember, certification is not just about learning—it's about proving that you can apply what you've learned in real-world scenarios.
Tips to Get Started
Here's how to make the most of your journey into data analytics, SQL, and BI:
Start with the basics: Brush up on statistics and Excel before diving into analytics tools.
Practice regularly: Use free datasets from Kaggle or government portals.
Join communities: Engage with local data science meetups in Pune or participate in LinkedIn groups.
Build a portfolio: Create dashboards, publish case studies, and document your learning on GitHub or Medium.
Stay updated: Tech is evolving. Stay current with the latest trends in BI tools and database technologies.
Real-Life Example: Upskilling for Career Switch
Sandeep, a mechanical engineer based in Pune, was laid off during a corporate restructuring. Rather than returning to a similar role, he decided to explore data. He mastered SQL and BI tools through a data science certification in Pune. Today, he works as a data analyst at a leading logistics firm, where he helps optimise supply chain routes using data models. What started as a setback became a turning point, all because he made the effort to upskill.
Conclusion: The Smart Career Move
Mastering data analytics, SQL, and business intelligence is no longer just for tech geeks—it's for anyone who wants to stay relevant, solve problems, and make an impact. With the rising demand for data-driven decision-making, professionals equipped with these skills are not just surviving—they're thriving.
If you're in Pune and considering stepping into this high-growth field, investing in a well-rounded data science certification in Pune can open doors you didn't even know existed. Whether it's for career transition, promotion, freelancing, or launching your startup, data is the foundation, and your journey starts now.
0 notes
Text
Learn to Use SQL, MongoDB, and Big Data in Data Science
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the right tools is as important as understanding the data. If you plan to pursue a data science certification in Pune, knowing SQL, MongoDB, and Big Data technologies isn’t just a bonus — it’s essential. These tools form the backbone of modern data ecosystems and are widely used in real-world projects to extract insights, build models, and make data-driven decisions.
Whether you are planning on updating your resume, wanting to find a job related to analytics, or just have a general interest in how businesses apply data. Learning how to deal with structured and unstructured data sets should be a goal.
Now, analysing the relation of SQL, MongoDB, and Big Data technologies in data science and how they may transform your career, if you are pursuing data science classes in Pune.
Why These Tools Matter in Data Science?
Data that today’s data scientists use varies from transactional data in SQL databases to social network data stored in NoSQL, such as MongoDB, and data larger than the amount that can be processed by conventional means. It has to go through Big Data frameworks. That is why it is crucial for a person to master such tools:
1. SQL: The Language of Structured Data
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a widely used language to facilitate interaction between users and relational databases. Today, almost every industry globally uses SQL to solve organisational processes in healthcare, finance, retail, and many others.
How It’s Used in Real Life?
Think about what it would be like to become an employee in one of the retail stores based in Pune. In this case, you are supposed to know the trends of products that are popular in the festive season. Therefore, it is possible to use SQL and connect to the company’s sales database to select data for each product and sort it by categories, as well as to determine the sales velocity concerning the seasons. It is also fast, efficient, and functions in many ways that are simply phenomenal.
Key SQL Concepts to Learn:
SELECT, JOIN, GROUP BY, and WHERE clauses
Window functions for advanced analytics
Indexing for query optimisation
Creating stored procedures and views
Whether you're a beginner or brushing up your skills during a data science course in Pune, SQL remains a non-negotiable part of the toolkit.
2. MongoDB: Managing Flexible and Semi-Structured Data
As businesses increasingly collect varied forms of data, like user reviews, logs, and IoT sensor readings, relational databases fall short. Enter MongoDB, a powerful NoSQL database that allows you to store and manage data in JSON-like documents.
Real-Life Example:
Suppose you're analysing customer feedback for a local e-commerce startup in Pune. The feedback varies in length, structure, and language. MongoDB lets you store this inconsistent data without defining a rigid schema upfront. With tools like MongoDB’s aggregation pipeline, you can quickly extract insights and categorise sentiment.
What to Focus On?
CRUD operations in MongoDB
Aggregation pipelines for analysis
Schema design and performance optimisation
Working with nested documents and arrays
Learning MongoDB is especially valuable during your data science certification in Pune, as it prepares you for working with diverse data sources common in real-world applications.
3. Big Data: Scaling Your Skills to Handle Volume
As your datasets grow, traditional tools may no longer suffice. Big Data technologies like Hadoop and Spark allow you to efficiently process terabytes or even petabytes of data.
Real-Life Use Case:
Think about a logistics company in Pune tracking thousands of deliveries daily. Data streams in from GPS devices, traffic sensors, and delivery apps. Using Big Data tools, you can process this information in real-time to optimise routes, reduce fuel costs, and improve delivery times.
What to Learn?
Hadoop’s HDFS for distributed storage
MapReduce programming model.
Apache Spark for real-time and batch processing
Integrating Big Data with Python and machine learning pipelines
Understanding how Big Data integrates with ML workflows is a career-boosting advantage for those enrolled in data science training in Pune.
Combining SQL, MongoDB, and Big Data in Projects
In practice, data scientists often use these tools together. Here’s a simplified example:
You're building a predictive model to understand user churn for a telecom provider.
Use SQL to fetch customer plans and billing history.
Use MongoDB to analyse customer support chat logs.
Use Spark to process massive logs from call centres in real-time.
Once this data is cleaned and structured, it feeds into your machine learning model. This combination showcases the power of knowing multiple tools — a vital edge you gain during a well-rounded data science course in Pune.
How do These Tools Impact Your Career?
Recruiters look for professionals who can navigate relational and non-relational databases and handle large-scale processing tasks. Mastering these tools not only boosts your credibility but also opens up job roles like:
Data Analyst
Machine Learning Engineer
Big Data Engineer
Data Scientist
If you're taking a data science certification in Pune, expect practical exposure to SQL and NoSQL tools, plus the chance to work on capstone projects involving Big Data. Employers value candidates who’ve worked with diverse datasets and understand how to optimise data workflows from start to finish.
Tips to Maximise Your Learning
Work on Projects: Try building a mini data pipeline using public datasets. For instance, analyze COVID-19 data using SQL, store news updates in MongoDB, and run trend analysis using Spark.
Use Cloud Platforms: Tools like Google BigQuery or MongoDB Atlas are great for practising in real-world environments.
Collaborate and Network: Connect with other learners in Pune. Attend meetups, webinars, or contribute to open-source projects.
Final Thoughts
SQL, MongoDB, and Big Data are no longer optional in the data science world — they’re essential. Whether you're just starting or upgrading your skills, mastering these technologies will make you future-ready.
If you plan to enroll in a data science certification in Pune, look for programs that emphasise hands-on training with these tools. They are the bridge between theory and real-world application, and mastering them will give you the confidence to tackle any data challenge.
Whether you’re from a tech background or switching careers, comprehensive data science training in Pune can help you unlock your potential. Embrace the learning curve, and soon, you'll be building data solutions that make a real impact, right from the heart of Pune.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Master SQL with the Best Online Course in Hyderabad – Offered by Gritty Tech
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the backbone of data handling in modern businesses. Whether you're aiming for a career in data science, software development, or business analytics, SQL is a must-have skill. If you're based in Hyderabad or even outside but seeking the best SQL online course that delivers practical learning with real-world exposure, Gritty Tech has crafted the perfect program for you For More…
What Makes Gritty Tech's SQL Course Stand Out?
Practical, Job-Focused Curriculum
Gritty Tech’s SQL course is meticulously designed to align with industry demands. The course content is structured around the real-time requirements of IT companies, data-driven businesses, and startups.
You'll start with the basics of SQL and gradually move to advanced concepts such as:
Writing efficient queries
Managing large datasets
Building normalized databases
Using SQL with business intelligence tools
SQL for data analytics and reporting
Every module is project-based. This means you won’t just learn the theory—you’ll get your hands dirty with practical assignments that mirror real-world tasks.
Learn from Industry Experts
The faculty at Gritty Tech are not just trainers; they are seasoned professionals from top MNCs and startups. Their teaching combines theory with examples drawn from years of hands-on experience. They understand what companies expect from an SQL developer and prepare students accordingly.
Each mentor brings valuable insights into how SQL works in day-to-day business scenarios—whether it's managing millions of records in a customer database or optimizing complex queries in a financial system.
Interactive and Flexible Online Learning
Learning online doesn’t mean learning alone. Gritty Tech ensures you’re part of a vibrant student community where peer interaction, discussion forums, and collaborative projects are encouraged.
Key features of their online delivery model include:
Live instructor-led sessions with real-time query solving
Access to session recordings for future reference
Weekly challenges and hackathons to push your skills
1:1 mentorship to clarify doubts and reinforce learning
You can choose batch timings that suit your schedule, making this course ideal for both working professionals and students.
Comprehensive Module Coverage
The course is divided into logical modules that build your expertise step by step. Here's an overview of the key topics covered:
Introduction to SQL and RDBMS
Understanding data and databases
Relational models and primary concepts
Introduction to MySQL and PostgreSQL
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Creating and modifying tables
Setting primary and foreign keys
Understanding constraints and data types
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Inserting, updating, and deleting records
Transaction management
Working with auto-commits and rollbacks
Data Query Language (DQL)
SELECT statements in depth
Filtering data with WHERE clause
Using ORDER BY, GROUP BY, and HAVING
Advanced SQL Queries
JOINS: INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL OUTER
Subqueries and nested queries
Views and materialized views
Indexing and performance tuning
Stored Procedures and Triggers
Creating stored procedures for reusable logic
Using triggers to automate actions
SQL in Real Projects
Working with business databases
Creating reports and dashboards
Integrating SQL with Excel and BI tools
Interview Preparation & Certification
SQL interview Q&A sessions
Mock technical interviews
Industry-recognized certification on course completion
Real-Time Projects and Case Studies
Nothing beats learning by doing. At Gritty Tech, every student works on multiple real-time projects, such as:
Designing a complete eCommerce database
Building a report generation system for a retail chain
Analyzing customer data for a telecom company
Creating dashboards with SQL-backed queries for business decisions
These projects simulate real job roles and ensure you're not just certified but genuinely skilled.
Placement Assistance and Resume Building
Gritty Tech goes the extra mile to help you land your dream job. They offer:
Resume and LinkedIn profile optimization
Personalized career guidance
Referrals to hiring partners
Mock interview practice with real-time feedback
Graduates of Gritty Tech have successfully secured jobs as Data Analysts, SQL Developers, Business Intelligence Executives, and more at top companies.
Affordable Pricing with Installment Options
Quality education should be accessible. Gritty Tech offers this high-value SQL course at a very competitive price. Students can also opt for EMI-based payment options. There are often discounts available for early registration or referrals.
Support After Course Completion
Your learning doesn't stop when the course ends. Gritty Tech provides post-course support where you can:
Revisit lectures and materials
Get help with ongoing SQL projects at work
Stay connected with alumni and mentors
They also host webinars, advanced workshops, and alumni meetups that keep you updated and networked.
Who Should Join This Course?
This SQL course is ideal for:
College students and fresh graduates looking to boost their resume
Working professionals in non-technical roles aiming to switch to tech
Data enthusiasts and aspiring data scientists
Business analysts who want to strengthen their data querying skills
Developers who wish to enhance their backend capabilities
No prior coding experience is required. The course begins from scratch, making it beginner-friendly while progressing toward advanced topics for experienced learners.
0 notes
Text
Using GROUP BY and HAVING Clauses in the ARSQL Language
Mastering GROUP BY and HAVING Clauses in ARSQL: A Complete Guide with Examples Hello, ARSQL enthusiasts! In this post, we’re diving into Using HAVING clause with GROUP BY in ARSQL – one of the most essential tools for data analysis in SQL the GROUP BY and HAVING clauses in the ARSQL Language. These features allow you to group rows based on one or more columns and apply aggregate functions like…
0 notes
Text
Foundations for Power BI Success: Essential Skills and Knowledge
Introduction
Power BI has emerged as a leading business intelligence tool, enabling professionals to analyze and visualize data effectively. However, to maximize its potential, it’s essential to build a strong foundation in key areas before diving into Power BI. For those looking to enhance their skills, Power BI Online Training & Placement programs offer comprehensive education and job placement assistance, making it easier to master this tool and advance your career.

In this blog, we’ll explore the essential skills and knowledge you should acquire to ensure success in your Power BI journey.
1. Excel and Spreadsheet Proficiency
Excel is often the first step toward understanding data analytics. Many of Power BI’s features, such as PivotTables, data formatting, and formulas, are inspired by Excel. Familiarity with functions like VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, SUMIF, and conditional formatting will help you manipulate and analyze data efficiently within Power BI.
2. Data Analysis and Visualization Principles
Power BI is a visualization-driven tool, making it crucial to understand how to interpret data and present it effectively. Learning how to choose the right charts, recognize trends, and highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) will allow you to create insightful reports that drive business decisions.
3. SQL and Database Management
Since Power BI connects with databases, knowledge of SQL (Structured Query Language) is a valuable skill. Learning how to use SELECT, JOIN, GROUP BY, and WHERE clauses will help you extract and manipulate data efficiently before bringing it into Power BI. This skill is especially useful when dealing with large datasets stored in relational databases.
4. Data Cleaning and Transformation
Raw data often needs refining before it can be analyzed. Power Query, a feature in Power BI, is used for data transformation. Understanding how to clean data, handle missing values, remove duplicates, and structure datasets properly will ensure that your reports are accurate and meaningful. It’s simpler to master this tool and progress your profession with the help of Best Online Training & Placement programs, which provide thorough instruction and job placement support to anyone seeking to improve their talents.
5. Data Modeling and Relationships
Data modeling is a crucial skill when working with Power BI. Knowing how to establish relationships between tables using primary and foreign keys, as well as understanding one-to-many and many-to-many relationships, will help create a well-structured and efficient data model for reporting.
6. DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) Proficiency
DAX is the formula language used in Power BI to create custom calculations. Learning key functions such as SUM, COUNT, CALCULATE, FILTER, and RANKX will allow you to build complex measures and optimize reporting capabilities. DAX helps transform raw data into actionable insights.
7. Understanding Business Intelligence (BI) Concepts
Power BI is a business intelligence tool, so having a basic understanding of BI concepts such as data warehousing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), and dashboarding best practices will help you design reports that align with business needs.
8. Cloud and Data Connectivity
As Power BI integrates with cloud-based platforms like Azure, Google Analytics, and SharePoint, understanding cloud storage and APIs will enhance your ability to connect and analyze real-time data from multiple sources.
Conclusion
Building a strong foundation in these key areas will help you master Power BI more effectively and unlock its full potential. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, these skills will enhance your ability to create insightful, data-driven reports and dashboards that drive business success.
0 notes
Text
This video, explained the different types of SQL clauses, what are clauses, where clauses, Like clauses, Top clauses, Order by clause, Group clauses, and having clauses.
0 notes
Text
Difference between WHERE and HAVING
The WHERE and HAVING clauses are discussed in depth in this article. They're also used to filter records in SQL queries. The difference between the WHERE and HAVING clause is the most common question posed during an interview time. The main difference between them is that the WHERE clause is used to specify a condition for filtering records before any groupings are made, while the HAVING clause is used to specify a condition for filtering values from a group. Before making the comparison, we will first know these SQL clauses.

0 notes
Text
Mastering PROC SQL in SAS for Data Manipulation and Analysis
When it comes to SAS programming, one of the most powerful and versatile features is PROC SQL. This procedure allows you to use SQL (Structured Query Language) within the SAS environment to manage, manipulate, and analyze data in a highly efficient manner. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, understanding how to work with PROC SQL is an essential skill that can greatly boost your ability to analyze large datasets, perform complex queries, and generate meaningful reports.
In this SAS programming full course, we will dive into the ins and outs of PROC SQL to help you master this critical SAS tool. Through SAS programming tutorials, you will learn how to harness the full power of SQL within SAS, improving both the speed and flexibility of your data analysis workflows.
What is PROC SQL in SAS?
PROC SQL is a procedure within SAS that enables you to interact with data using SQL syntax. SQL is one of the most widely used languages in data manipulation and database management, and PROC SQL combines the power of SQL with the data management capabilities of SAS. By using PROC SQL, you can query SAS datasets, join multiple tables, summarize data, and even create new datasets, all within a single step.
One of the key benefits of using PROC SQL is that it allows you to perform complex data tasks in a more concise and efficient manner compared to traditional SAS programming methods. For example, you can use SQL to easily filter, aggregate, and group data, which would otherwise require multiple SAS programming steps. This streamlines your workflow and makes it easier to work with large datasets, especially when combined with SAS's powerful data manipulation features.
Why Learn PROC SQL for SAS?
Mastering PROC SQL in SAS is essential for anyone looking to elevate their data analysis skills. Whether you’re working in finance, healthcare, marketing, or any other data-driven field, PROC SQL enables you to quickly and efficiently manipulate large datasets, make complex queries, and perform data summarization tasks.
Here are some reasons why learning PROC SQL should be at the top of your SAS learning agenda:
Simplifies Data Management: SQL is designed specifically for managing and querying large datasets. By learning PROC SQL, you can quickly and efficiently access, filter, and aggregate data without having to write long, complicated code.
Improves Data Analysis: With PROC SQL, you can combine multiple datasets using joins, subqueries, and unions. This makes it easier to work with data from various sources and create unified reports that bring together key insights from different tables.
Boosts Efficiency: SQL is known for its ability to handle large datasets with ease. By mastering PROC SQL, you'll be able to manipulate data more quickly and effectively, making it easier to work with complex datasets and produce high-quality analysis.
Widely Used in Industry: SQL is a universal language for database management, making it a highly transferable skill. Many companies use SQL-based databases and tools, so understanding how to work with SQL in SAS will make you more valuable to potential employers and help you stay competitive in the job market.
What You’ll Learn in This SAS Programming Full Course
In this comprehensive SAS programming full course, you will learn everything you need to know about PROC SQL. The course is designed for beginners and advanced users alike, providing a step-by-step guide to mastering the procedure. Below is a breakdown of the key concepts and techniques covered in this training:
Introduction to SQL in SAS
What is PROC SQL and how does it integrate with SAS?
Key differences between traditional SAS programming and SQL-based data manipulation.
Basic syntax of SQL and how it applies to SAS programming.
Querying Data with SQL
How to write SELECT statements to extract specific data from your SAS datasets.
Using WHERE clauses to filter data based on conditions.
How to sort and order your data using the ORDER BY clause.
Applying aggregate functions (e.g., SUM, AVG, COUNT) to summarize data.
Advanced SQL Queries
Using JOIN operations to merge data from multiple tables.
Combining data from different sources with INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, and OUTER joins.
Subqueries: How to use nested queries to retrieve data from related tables.
Union and Union All: Combining multiple result sets into a single table.
Creating New Datasets with SQL
Using CREATE TABLE and INSERT INTO statements to create new datasets from your queries.
How to use SQL to write the results of a query to a new SAS dataset.
Optimizing SQL Queries
Tips for writing more efficient SQL queries to improve performance.
How to handle lard healthcare data management.
Working with data from external databases and importing/exporting data using SQL.
Learning Path and Benefits of SAS Online Training
Whether you are just starting your journey with SAS or looking to enhance your existing knowledge, our SAS online training provides you with all the resources you need to succeed. This SAS programming tutorial will guide you through every step of the learning process, ensuring you have the support you need to master PROC SQL.
Self-Paced Learning: Our SAS online training is designed to be flexible, allowing you to learn at your own pace. You can watch the videos, review the materials, and practice the exercises whenever it’s convenient for you.
Access to Expert Instructors: The training course is led by experienced SAS professionals who are there to help you whenever you need assistance. If you have any questions or need clarification, our instructors are available to guide you through any challenges you may encounter.
Comprehensive Resources: With access to a wide variety of tutorials, practice exercises, and real-world examples, you'll have everything you need to become proficient in SAS programming. Each tutorial is designed to build on the last, helping you gradually develop a complete understanding of SAS programming.
Community Support: Join a community of learners who are also working through the SAS programming full course. Share ideas, ask questions, and collaborate with others to improve your understanding of the material.
Conclusion
Mastering PROC SQL in SAS is a valuable skill for anyone looking to improve their data analysis capabilities. By learning how to use SQL within the SAS environment, you can efficiently manage and manipulate data, perform complex queries, and create meaningful reports. Our SAS programming tutorials will provide you with the knowledge and practical skills you need to succeed in the world of data analysis.
Enroll in our SAS online training today and start learning PROC SQL! With this powerful tool in your SAS programming toolkit, you’ll be ready to tackle even the most complex data tasks with ease.
#sas programming course#sas programming tutorial#sas online training#sas programming#proc sql#data manipulation#data analytics
0 notes
Text
Unlock Your Career Potential with the Best SQL Classes in Mohali
In today's data-driven world, the ability to manage and analyze data is more critical than ever. SQL (Structured Query Language) has emerged as the go-to language for database management, making it an essential skill for professionals across various industries, including IT, finance, and marketing. If you’re looking to enhance your database skills, enrolling in the best SQL classes in Mohali can be a game-changer for your career. This blog will explore the significance of SQL, the benefits of formal training, and highlight some of the top SQL classes available in Mohali.
Why Learn SQL?
SQL is not just a programming language; it’s a powerful tool that allows you to interact with databases. Here are some compelling reasons to learn SQL:
High Demand in the Job Market: Proficiency in SQL is one of the most sought-after skills in the job market. Many organizations rely on data analytics to drive their decisions, making SQL experts invaluable.
Versatility: SQL is used across various domains, from data analysis and business intelligence to software development and database administration. This versatility means that learning SQL opens multiple career paths.
Enhanced Data Management: Understanding SQL allows you to efficiently store, manipulate, and retrieve data, enabling better decision-making within your organization.
Ease of Learning: SQL has a relatively simple syntax compared to other programming languages, making it accessible even for beginners.
Key Topics Covered in SQL Classes
A comprehensive SQL course typically covers a range of essential topics, including:
Introduction to Databases: Understanding database concepts and types, including relational and non-relational databases.
Basic SQL Commands: Learning fundamental commands such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Data Retrieval Techniques: Mastering how to filter, sort, and aggregate data using WHERE, ORDER BY, and GROUP BY clauses.
Joins and Subqueries: Understanding how to combine data from multiple tables using different types of joins and employing subqueries for complex data retrieval.
Database Design: Learning about normalization, keys, and relationships within a database.
Stored Procedures and Functions: Exploring how to create reusable SQL scripts for common tasks.
Performance Tuning: Understanding indexing and query optimization techniques for improved performance.
How to Choose the Right SQL Class
Selecting the right SQL class can significantly impact your learning experience and career advancement. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
Assess Your Skill Level: Determine whether you are a beginner or have some experience in SQL, and choose a class that matches your skill level.
Curriculum Review: Look for classes that cover essential SQL topics and provide hands-on training to ensure practical learning.
Instructor Expertise: Research the qualifications and experience of the instructors to ensure you receive quality education.
Class Size: Smaller class sizes often allow for more personalized attention, enhancing your learning experience.
Placement Support: Check if the institute offers placement assistance to help you secure job opportunities after completing the course.
Final Thoughts
Investing in SQL training can significantly enhance your data management skills and career prospects. By enrolling in one of the best SQL classes in Mohali, you will gain the knowledge and expertise needed to excel in today’s data-centric job market.
With a structured curriculum, practical exposure, and support from experienced instructors, you will be well-prepared to tackle SQL challenges and drive better decision-making within your organization. Start your journey today and unlock new opportunities in the world of data management!
0 notes
Text
SQL Pipe Syntax, Now Available In BigQuery And Cloud Logging
The revolutionary SQL pipe syntax is now accessible in Cloud Logging and BigQuery.
SQL has emerged as the industry standard language for database development. Its well-known syntax and established community have made data access genuinely accessible to everyone. However, SQL isn’t flawless, let’s face it. Several problems with SQL’s syntax make it more difficult to read and write:
Rigid structure: Subqueries or other intricate patterns are needed to accomplish anything else, and a query must adhere to a specific order (SELECT … FROM … WHERE … GROUP BY).
Awkward inside-out data flow: FROM clauses included in subqueries or common table expressions (CTE) are the first step in a query, after which logic is built outward.
Verbose, repetitive syntax: Are you sick of seeing the same columns in every subquery and repeatedly in SELECT, GROUP BY, and ORDER BY?
For novice users, these problems may make SQL more challenging. Reading or writing SQL requires more effort than should be required, even for experienced users. Everyone would benefit from a more practical syntax.
Numerous alternative languages and APIs have been put forth over time, some of which have shown considerable promise in specific applications. Many of these, such as Python DataFrames and Apache Beam, leverage piped data flow, which facilitates the creation of arbitrary queries. Compared to SQL, many users find this syntax to be more understandable and practical.
Presenting SQL pipe syntax
Google Cloud is to simplify and improve the usability of data analysis. It is therefore excited to provide pipe syntax, a ground-breaking invention that enhances SQL in BigQuery and Cloud Logging with the beauty of piped data flow.
Pipe syntax: what is it?
In summary, pipe syntax is an addition to normal SQL syntax that increases the flexibility, conciseness, and simplicity of SQL. Although it permits applying operators in any sequence and in any number of times, it provides the same underlying operators as normal SQL, with the same semantics and essentially the same syntax.
How it operates:
FROM can be used to begin a query.
The |> pipe sign is used to write operators in a consecutive fashion.
Every operator creates an output table after consuming its input table.
Standard SQL syntax is used by the majority of pipe operators:
LIMIT, ORDER BY, JOIN, WHERE, SELECT, and so forth.
It is possible to blend standard and pipe syntax at will, even in the same query.
Impact in the real world at HSBC
After experimenting with a preliminary version in BigQuery and seeing remarkable benefits, the multinational financial behemoth HSBC has already adopted pipe syntax. They observed notable gains in code readability and productivity, particularly when working with sizable JSON collections.
Benefits of integrating SQL pipe syntax
SQL developers benefit from the addition of pipe syntax in several ways. Here are several examples:
Simple to understand
It can be difficult to learn and accept new languages, especially in large organizations where it is preferable for everyone to utilize the same tools and languages. Pipe syntax is a new feature of the already-existing SQL language, not a new language. Because pipe syntax uses many of the same operators and largely uses the same syntax, it is relatively easy for users who are already familiar with SQL to learn.
Learning pipe syntax initially is simpler for users who are new to SQL. They can utilize those operators to express their intended queries directly, avoiding some of the complexities and workarounds needed when writing queries in normal SQL, but they still need to master the operators and some semantics (such as inner and outer joins).
Simple to gradually implement without requiring migrations
As everyone knows, switching to a new language or system may be costly, time-consuming, and prone to mistakes. You don’t need to migrate anything in order to begin using pipe syntax because it is a part of GoogleSQL. All current queries still function, and the new syntax can be used sparingly where it is useful. Existing SQL code is completely compatible with any new SQL. For instance, standard views defined in standard syntax can be called by queries using pipe syntax, and vice versa. Any current SQL does not become outdated or unusable when pipe syntax is used in new SQL code.
No impact on cost or performance
Without any additional layers (such translation proxies), which might increase latency, cost, or reliability issues and make debugging or tweaking more challenging, pipe syntax functions on well-known platforms like BigQuery.
Additionally, there is no extra charge. SQL’s declarative semantics still apply to queries utilizing pipe syntax, therefore the SQL query optimizer will still reorganize the query to run more quickly. Stated otherwise, the performance of queries written in standard or pipe syntax is usually identical.
For what purposes can pipe syntax be used?
Pipe syntax enables you to construct SQL queries that are easier to understand, more effective, and easier to maintain, whether you’re examining data, establishing data pipelines, making dashboards, or examining logs. Additionally, you may use pipe syntax anytime you create queries because it supports the majority of typical SQL operators. A few apps to get you started are as follows:
Debugging queries and ad hoc analysis
When conducting data exploration, you usually begin by examining a table’s rows (beginning with a FROM clause) to determine what is there. After that, you apply filters, aggregations, joins, ordering, and other operations. Because you can begin with a FROM clause and work your way up from there, pipe syntax makes this type of research really simple. You can view the current results at each stage, add a pipe operator, and then rerun the query to view the updated results.
Debugging queries is another benefit of using pipe syntax. It is possible to highlight a query prefix and execute it, displaying the intermediate result up to that point. This is a good feature of queries in pipe syntax: every query prefix up to a pipe symbol is also a legitimate query.
Lifecycle of data engineering
Data processing and transformation become increasingly difficult and time-consuming as data volume increases. Building, modifying, and maintaining a data pipeline typically requires a significant technical effort in contexts with a lot of data. Pipe syntax simplifies data engineering with its more user-friendly syntax and linear query structure. Bid farewell to the CTEs and highly nested queries that tend to appear whenever standard SQL is used. This latest version of GoogleSQL simplifies the process of building and managing data pipelines by reimagining how to parse, extract, and convert data.
Using plain language and LLMs with SQL
For the same reasons that SQL can be difficult for people to read and write, research indicates that it can also be difficult for large language models (LLMs) to comprehend or produce. Pipe syntax, on the other hand, divides inquiries into separate phases that closely match the intended logical data flow. A desired data flow may be expressed more easily by the LLM using pipe syntax, and the generated queries can be made more simpler and easier for humans to understand. This also makes it much easier for humans to validate the created queries.
Because it’s much simpler to comprehend what’s happening and what’s feasible, pipe syntax also enables improved code assistants and auto-completion. Additionally, it allows for suggestions for local modifications to a single pipe operator rather than global edits to an entire query. More natural language-based operators in a query and more intelligent AI-generated code suggestions are excellent ways to increase user productivity.
Discover the potential of pipe syntax right now
Because SQL is so effective, it has been the worldwide language of data for 50 years. When it comes to expressing queries as declarative combinations of relational operators, SQL excels in many things.
However, that does not preclude SQL from being improved. By resolving SQL’s primary usability issues and opening up new possibilities for interacting with and expanding SQL, pipe syntax propels SQL into the future. This has nothing to do with creating a new language or replacing SQL. Although SQL with pipe syntax is still SQL, it is a better version of the language that is more expressive, versatile, and easy to use.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#SQL#PipeSyntax#BigQuery#SQLpipesyntax#CloudLogging#GoogleSQL#Syntax#LLM#AI#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Data Science with SQL: Managing and Querying Databases
Data science is about extracting insights from vast amounts of data, and one of the most critical steps in this process is managing and querying databases. Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard language used to communicate with relational databases, making it essential for data scientists and analysts. Whether you're pulling data for analysis, building reports, or integrating data from multiple sources, SQL is the go-to tool for efficiently managing and querying large datasets.
This blog post will guide you through the importance of SQL in data science, common use cases, and how to effectively use SQL for managing and querying databases.

Why SQL is Essential for Data Science
Data scientists often work with structured data stored in relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite. SQL is crucial because it allows them to retrieve and manipulate this data without needing to work directly with raw files. Here are some key reasons why SQL is a fundamental tool for data scientists:
Efficient Data Retrieval: SQL allows you to quickly retrieve specific data points or entire datasets from large databases using queries.
Data Management: SQL supports the creation, deletion, and updating of databases and tables, allowing you to maintain data integrity.
Scalability: SQL works with databases of any size, from small-scale personal projects to enterprise-level applications.
Interoperability: SQL integrates easily with other tools and programming languages, such as Python and R, which makes it easier to perform further analysis on the retrieved data.
SQL provides a flexible yet structured way to manage and manipulate data, making it indispensable in a data science workflow.
Key SQL Concepts for Data Science
1. Databases and Tables
A relational database stores data in tables, which are structured in rows and columns. Each table represents a different entity, such as customers, orders, or products. Understanding the structure of relational databases is essential for writing efficient queries and working with large datasets.
Table: An array of data with columns and rows arranged.
Column: A specific field of the table, like “Customer Name” or “Order Date.”
Row: A single record in the table, representing a specific entity, such as a customer’s details or a product’s information.
By structuring data in tables, SQL allows you to maintain relationships between different data points and query them efficiently.
2. SQL Queries
The commands used to communicate with a database are called SQL queries. Data can be selected, inserted, updated, and deleted using queries. In data science, the most commonly used SQL commands include:
SELECT: Retrieves data from a database.
INSERT: Adds new data to a table.
UPDATE: Modifies existing data in a table.
DELETE: Removes data from a table.
Each of these commands can be combined with various clauses (like WHERE, JOIN, and GROUP BY) to refine the results, filter data, and even combine data from multiple tables.
3. Joins
A SQL join allows you to combine data from two or more tables based on a related column. This is crucial in data science when you have data spread across multiple tables and need to combine them to get a complete dataset.
Returns rows from both tables where the values match through an inner join.
All rows from the left table and the matching rows from the right table are returned via a left-join. If no match is found, the result is NULL.
Like a left join, a right join returns every row from the right table.
FULL JOIN: Returns rows in cases where both tables contain a match.
Because joins make it possible to combine and evaluate data from several sources, they are crucial when working with relational databases.
4. Aggregations and Grouping
Aggregation functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX are useful for summarizing data. SQL allows you to aggregate data, which is particularly useful for generating reports and identifying trends.
COUNT: Returns the number of rows that match a specific condition.
SUM: Determines a numeric column's total value.
AVG: Provides a numeric column's average value.
MIN/MAX: Determines a column's minimum or maximum value.
You can apply aggregate functions to each group of rows that have the same values in designated columns by using GROUP BY. This is helpful for further in-depth analysis and category-based data breakdown.
5. Filtering Data with WHERE
The WHERE clause is used to filter data based on specific conditions. This is critical in data science because it allows you to extract only the relevant data from a database.
Managing Databases in Data Science
Managing databases means keeping data organized, up-to-date, and accurate. Good database management helps ensure that data is easy to access and analyze. Here are some key tasks when managing databases:
1. Creating and Changing Tables
Sometimes you’ll need to create new tables or change existing ones. SQL’s CREATE and ALTER commands let you define or modify tables.
CREATE TABLE: Sets up a new table with specific columns and data types.
ALTER TABLE: Changes an existing table, allowing you to add or remove columns.
For instance, if you’re working on a new project and need to store customer emails, you might create a new table to store that information.
2. Ensuring Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity means ensuring that the data is accurate and reliable. SQL provides ways to enforce rules that keep your data consistent.
Primary Keys: A unique identifier for each row, ensuring that no duplicate records exist.
Foreign Keys: Links between tables that keep related data connected.
Constraints: Rules like NOT NULL or UNIQUE to make sure the data meets certain conditions before it’s added to the database.
Keeping your data clean and correct is essential for accurate analysis.
3. Indexing for Faster Performance
As databases grow, queries can take longer to run. Indexing can speed up this process by creating a shortcut for the database to find data quickly.
CREATE INDEX: Builds an index on a column to make queries faster.
DROP INDEX: Removes an index when it’s no longer needed.
By adding indexes to frequently searched columns, you can speed up your queries, which is especially helpful when working with large datasets.
Querying Databases for Data Science
Writing efficient SQL queries is key to good data science. Whether you're pulling data for analysis, combining data from different sources, or summarizing results, well-written queries help you get the right data quickly.
1. Optimizing Queries
Efficient queries make sure you’re not wasting time or computer resources. Here are a few tips:
*Use SELECT Columns Instead of SELECT : Select only the columns you need, not the entire table, to speed up queries.
Filter Early: Apply WHERE clauses early to reduce the number of rows processed.
Limit Results: Use LIMIT to restrict the number of rows returned when you only need a sample of the data.
Use Indexes: Make sure frequently queried columns are indexed for faster searches.
Following these practices ensures that your queries run faster, even when working with large databases.
2. Using Subqueries and CTEs
Subqueries and Common Table Expressions (CTEs) are helpful when you need to break complex queries into simpler parts.
Subqueries: Smaller queries within a larger query to filter or aggregate data.
CTEs: Temporary result sets that you can reference within a main query, making it easier to read and understand.
These tools help organize your SQL code and make it easier to manage, especially for more complicated tasks.
Connecting SQL to Other Data Science Tools
SQL is often used alongside other tools for deeper analysis. Many programming languages and data tools, like Python and R, work well with SQL databases, making it easy to pull data and then analyze it.
Python and SQL: Libraries like pandas and SQLAlchemy let Python users work directly with SQL databases and further analyze the data.
R and SQL: R connects to SQL databases using packages like DBI and RMySQL, allowing users to work with large datasets stored in databases.
By using SQL with these tools, you can handle and analyze data more effectively, combining the power of SQL with advanced data analysis techniques.
Conclusion
If you work with data, you need to know SQL. It allows you to manage, query, and analyze large datasets easily and efficiently. Whether you're combining data, filtering results, or generating summaries, SQL provides the tools you need to get the job done. By learning SQL, you’ll improve your ability to work with structured data and make smarter, data-driven decisions in your projects.
0 notes