#hepatitis- c structure
Text
The Physiology Of The Liver
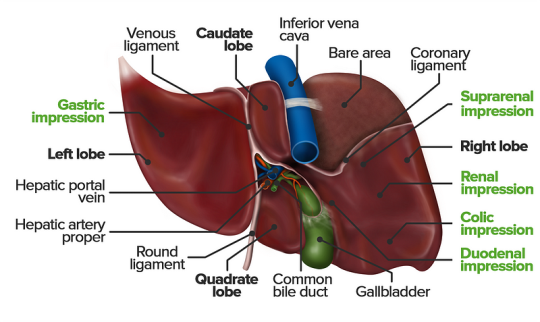
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous functions including metabolism, immunity, digestion, detoxification, and vitamin storage. It weighs around 2% of an adult’s body weight and is unique due to its dual blood supply from the portal vein (75%) and the hepatic artery (25%).
Cellular Structure
The liver’s functional unit is the lobule, which is hexagonal in shape. Each corner of the hexagon has a portal triad consisting of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. The lobule is composed mainly of hepatocytes, which have distinct apical and basolateral membranes. Hepatocytes are categorized into three zones based on their function and blood supply:
Zone I (periportal region): Closest to the blood supply, involved in oxidative metabolism (e.g., gluconeogenesis, bile formation).
Zone II (pericentral region): Sits between Zones I and III.
Zone III: Farthest from the blood supply, primarily involved in detoxification and biotransformation.
Blood and bile flow in opposite directions within the liver. The space of Disse, between the hepatocytes and the sinusoidal lumen, contains Kupffer cells (macrophages) and Ito cells (fat-storing stellate cells).
Development
The liver develops from endodermal cells of the foregut as the hepatic diverticulum around the fourth week of embryonic development. It undergoes complex differentiation influenced by various pathways (e.g., Wnt/β-catenin, FGF). By the sixth week, the liver participates in hematopoiesis, and hepatocytes begin bile production by the 12th week.
Organ Systems and Functions
The liver interacts with multiple body systems:
Digestive and Metabolic Roles: Aids in digestion, stores fat-soluble vitamins, and handles cholesterol.
Hematological Functions: Produces clotting factors and proteins.
Detoxification: Metabolizes drugs and other xenobiotics through phase I (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) and phase II (conjugation) reactions.
Bilirubin Metabolism: Converts heme to unconjugated bilirubin, then conjugates it for excretion.
Hormonal and Protein Synthesis: Involved in thyroid hormone activation and synthesis of nearly all plasma proteins.
Related Testing
Liver function tests (LFTs), including ALT, AST, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), help assess liver health. Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI are also employed to identify liver abnormalities.
Pathophysiology
Cirrhosis results from chronic liver injury (e.g., due to alcoholism, hepatitis B and C), leading to fibrosis and necrosis. It causes symptoms like portal hypertension, coagulopathy, and jaundice. Hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E), autoimmune diseases (e.g., primary biliary cholangitis), and metabolic conditions (e.g., non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) also contribute to liver pathology.
Clinical Significance
Understanding liver physiology helps manage conditions like viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, benign liver lesions, and liver cancers. Early detection through appropriate testing and management strategies is essential for preventing end-stage liver disease and improving patient outcomes
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at [email protected] and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#medical help#academic assignments#university student#medical university#university life#university#studying#study motivation#study blog#studyblr community#study inspiration#studyspo#studyblr#student#study aesthetic#medical student#aesthetic#medical school#case study
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hepcdac

Hepcdac is an antiviral medicine that can be used to deal with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. It is a direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medication that works by inhibiting the nonstructural protein HCV NS5A, Essential for the duplication of the virus. By blocking NS5A, Hepcdac can prevent the virus from multiplying and spreading in the body.
Hepcdac is usually used in combination with other antiviral medications, such as sofosbuvir or ribavirin, to form a complete treatment regimen for HCV infection. Combination therapy helps to increase the effectiveness of the treatment and reduce the risk of developing drug resistance.
Hepcdac is taken orally, typically once a day, with or without food. The amount and the dose of Hepcdac HCV are dependent on the genotype of the patient, liver function, and other factors. It is important to take the medication exactly as prescribed and to avoid missing doses to ensure the treatment’s effectiveness.
Hepcdac may cause side effects such as headache, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea, although these are generally mild and temporary. In rare cases, more severe side effects may occur, such as anemia, liver toxicity, or allergic reactions. If you experience any concerning side effects, you should contact your healthcare provider immediately
We are providing all the category of life saving drugs such as Temonat 100mg, Antreol, Rifagut 550mg, Entehep 0.5mg, Hepcinat and Lamivir HBV 100mg.
Why You Must Consider It?
Daclatasvir is a medicine that can treat infection in adults called HCV. Daclatasvir is often used in a blend with other medications such as sofosbuvir, ribavirin, or asunaprevir. Some of the reasons why you should consider Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) if you have chronic hepatitis C infection are that Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) has been shown to have a high cure rate for HCV infection when used in combination with other medications.
In clinical trials, Reports found that it can treat HCV infection. Fewer Side Effects: Compared to older HCV treatments, Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) has minimum reactions which are generally mild and well-tolerated. Convenient Dosage: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is available in an oral tablet form, which makes it easy to take. The recommended dosage is one tablet per day, with or without food.
Shorter Treatment Duration: Daclatasvir has a shorter treatment duration compared to older HCV treatments. The treatment duration ranges from 8 to 24 weeks, depending on the severity of the HCV infection and other factors. Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is available in many countries and is regulatory authorities approved such as the) European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In summary, Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is an effective and convenient treatment option for chronic hepatitis C infection. It has a high cure rate, fewer side effects, a convenient dosage form, a shorter treatment duration, and is widely available. If you have a chronic hepatitis C infection, you should consider talking to your healthcare provider about whether Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is right for you.
Some Interesting Insights About it?
Here are some interesting insights about Daclatasvir that you may find helpful:
Mechanism of Action: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) works by inhibiting the non-structural HCV protein 5A, which is important for the duplication of the virus. By inhibiting NS5A, Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) prevents the virus from replicating and spreading in the body.
Combination Therapy: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is often used in combination with other medications such as sofosbuvir, ribavirin, or asunaprevir. These combinations have been known to be highly active in treating HCV infection, even in patients having advanced disease in the liver.
Drug Relations: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) can interact with other medications, including certain HIV medications, and some cholesterol-lowering medications such as atorvastatin and simvastatin. Therefore, it is important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking before starting treatment with Hepcdac (Daclatasvir).
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: There is limited data on the safety of Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) in pregnant and breastfeeding women. Therefore, it is important to inform your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or breastfeeding before starting treatment with Hepcdac (Daclatasvir).
Cost: The cost of Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) can vary depending on the country and the healthcare system. In some countries, such as India, generic versions of the medication are available at a lower cost than the brand-name version.
0 notes
Text
TUDCA Benefits for Health

TUDCA supports liver health and detoxification.
It improves bile flow and digestion.
TUDCA has neuroprotective properties.
It aids in managing metabolic disorders.
TUDCA supports overall cellular health.
Liver Health and Detoxification
TUDCA (tauroursodeoxycholic acid) is a bile acid derivative known for its liver health benefits. It detoxifies the liver, promoting the elimination of toxic bile acids.
This protection reduces the risk of liver diseases like cirrhosis and hepatitis.
Improved Bile Flow and Digestion
TUDCA enhances bile flow, aiding the emulsification and absorption of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
Improved bile flow also helps prevent the formation of gallstones.
Neuroprotective Properties

Research indicates that TUDCA offers neuroprotective effects, benefiting brain health. It reduces cell death and inflammation in the brain, which is valuable for managing conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Reduction in endoplasmic reticulum stress plays a significant role in its neuroprotective properties.
Managing Metabolic Disorders
TUDCA helps manage metabolic disorders, including diabetes and obesity.
It improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation, critical for controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy weight. Enhanced liver function also supports overall metabolic health.
Cellular Health Support

TUDCA supports cellular health by protecting cells from apoptosis (programmed cell death) and reducing oxidative stress. This protection is crucial for maintaining healthy tissues and organs.
TUDCA’s ability to stabilize cellular membranes and improve mitochondrial function further enhances its role in promoting overall cellular health.
Conclusion
TUDCA offers a wide range of health benefits, particularly for liver health, digestion, brain protection, and managing metabolic disorders. Its ability to support cellular health makes it a valuable supplement for overall well-being.
FAQs
What is TUDCA?
TUDCA (tauroursodeoxycholic acid) is a bile acid derivative known for its liver-protective properties.
How does TUDCA improve liver health?
TUDCA promotes the elimination of toxic bile acids, protecting liver cells and reducing the risk of
liver diseases.
Can TUDCA help with digestion?
Yes, TUDCA enhances bile flow, aiding in the digestion and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
Is TUDCA beneficial for brain health?
TUDCA has neuroprotective properties, reducing cell death and inflammation in the brain, beneficial for
neurodegenerative conditions.
Can TUDCA help with metabolic disorders?
TUDCA improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation, supporting the management of diabetes
and obesity.Research
Albanese, A., Ludolph, A. C., McDermott, C. J., Corcia, P., Van Damme, P., H., L., Hardiman, O., Rinaldi, G., Vanacore, N., Dickie, B., Group, A. S., Tornese, P., Cocco, A., Giudice, M. L., Matteoli, M., Lauranzano, E., Malosio, M. L., Adriana Elia, C., Lombardo, F., . . . Obáin, N. N. (2022). Tauroursodeoxycholic acid in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: The TUDCA-ALS trial protocol. Frontiers in Neurology, 13, 1009113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.1009113
Berger, E., & Haller, D. (2011). Structure–function analysis of the tertiary bile acid TUDCA for the resolution of endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 409(4), 610-615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.05.043
Cabrera, D., Arab, J.P., Arrese, M. (2019). UDCA, NorUDCA, and TUDCA in Liver Diseases: A Review of Their Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. In: Fiorucci, S., Distrutti, E. (eds) Bile Acids and Their Receptors. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol 256. Springer, Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2019_241
Cardoso, I., Martins, D., Ribeiro, T. et al. Synergy of combined Doxycycline/TUDCA treatment in lowering Transthyretin deposition and associated biomarkers: studies in FAP mouse models. J Transl Med 8, 74 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-8-74
Lee, Y. Y., Hong, S. H., Lee, Y. J., Chung, S. S., Jung, H. S., Park, S. G., & Park, K. S. (2010). Tauroursodeoxycholate (TUDCA), chemical chaperone, enhances function of islets by reducing ER stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 397(4), 735-739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.022
Lu, Q., Jiang, Z., Wang, Q., Hu, H., & Zhao, G. (2021). The effect of Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) and gut microbiota on murine gallbladder stone formation. Annals of Hepatology, 23, 100289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aohep.2020.100289
Ma, H., Zeng, M., Han, Y., Yan, H., Tang, H., Sheng, J., Hu, H., Cheng, L., Xie, Q., Zhu, Y., Chen, G., Gao, Z., Xie, W., Wang, J., Wu, S., Wang, G., Miao, X., Fu, X., Duan, L., Xu, J., Wei, L., Shi, G., Chen, C., Chen, M., Ning, Q., Yao, C. and Jia, J., 2016. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial comparing the efficacy and safety of TUDCA and UDCA in Chinese patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Medicine, [online] 95(47), p.e5391.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27893675/.
Mantopoulos, D., Murakami, Y., Comander, J., Thanos, A., Roh, M., Miller, J. W., & Vavvas, D. G. (2011). Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid (TUDCA) Protects Photoreceptors from Cell Death after Experimental Retinal Detachment. PLOS ONE, 6(9), e24245.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024245
Nunes, A.F., Amaral, J.D., Lo, A.C., Fonseca, M.B., Viana, R.J.S., Callaerts-Vegh, Z., D’Hooge, R. and Rodrigues, C.M.P., 2012. TUDCA, a Bile Acid, Attenuates Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing and Amyloid-β Deposition in APP/PS1 Mice. Molecular Neurobiology, [online] 45(3), pp.440–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8256-y.
Noailles, A., Fernández-Sánchez, L., Lax, P. et al. Microglia activation in a model of retinal degeneration and TUDCA neuroprotective effects. J Neuroinflammation 11, 186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0186-3
Oveson, B. C., Iwase, T., Hackett, S. F., Lee, S. Y., Usui, S., Sedlak, T. W., Snyder, S. H., Campochiaro, P. A., & Sung, J. U. (2011). Constituents of bile, bilirubin and TUDCA, protect against oxidative stress-induced retinal degeneration. Journal of Neurochemistry, 116(1), 144-153. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07092.x
Rani, S., Sreenivasaiah, P. K., Kim, J. O., Lee, M. Y., Kang, W. S., Kim, Y. S., Ahn, Y., Park, W. J., Cho, C., & Kim, D. H. (2017). Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLOS ONE, 12(4), e0176071. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176071
Yanguas-Casás, N., Barreda-Manso, M. A., Nieto-Sampedro, M., & Romero-Ramírez, L. (2017). TUDCA: An Agonist of the Bile Acid Receptor GPBAR1/TGR5 With Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Microglial Cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 232(8), 2231-2245. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25742
Zangerolamo, L., Vettorazzi, J.F., Rosa, L.R., Carneiro, E.M. and Barbosa, H.C., 2021. The bile acid TUDCA and neurodegenerative disorders: An overview. Life sciences, 272, p.119252.
0 notes
Text
If You Have Cirrhosis and Continue to Drink: What Happens?
Cirrhosis is a severe liver condition characterized by the scarring of liver tissue, which disrupts its normal structure and function. Continued alcohol consumption after being diagnosed with cirrhosis can exacerbate the condition and lead to serious health complications. This article explores the consequences of if you have cirrhosis liver and continue to drink and emphasizes the importance of abstaining from alcohol to manage the disease effectively.
Understanding Cirrhosis and Alcohol
What is Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is the result of long-term liver damage and scarring caused by various factors, including chronic alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis (such as hepatitis B and C), fatty liver disease, and autoimmune conditions. Over time, the liver's ability to function properly diminishes, affecting its crucial roles in metabolism, detoxification, and protein synthesis.
Impact of Alcohol on Cirrhosis
Exacerbating Liver Damage
Continued alcohol consumption further damages liver cells and exacerbates existing liver inflammation and scarring. This accelerates the progression of cirrhosis, leading to irreversible liver damage and complications such as liver failure or hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
Increased Risk of Complications
Alcohol abuse in individuals with cirrhosis increases the risk of developing complications such as:
Ascites: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
Hepatic Encephalopathy: Brain dysfunction due to the liver's inability to detoxify harmful substances.
Variceal Bleeding: Rupture of enlarged veins in the esophagus or stomach.
Coagulopathy: Impaired blood clotting function.
Increased Mortality: Higher risk of death due to liver-related complications.
Managing Cirrhosis: Importance of Abstinence
Benefits of Abstaining from Alcohol
Slowing Disease Progression
Abstinence from alcohol is crucial in slowing or halting the progression of cirrhosis. It allows the liver to heal to some extent and reduces the risk of further damage, improving overall liver function.
Preventing Complications
By avoiding alcohol, individuals with cirrhosis can reduce their risk of developing severe complications associated with advanced liver disease. This includes improving quality of life and potentially extending life expectancy.
Treatment and Support
Medical Management
Consult with healthcare providers specializing in liver diseases for proper management of cirrhosis. This may involve medications to manage symptoms, dietary changes, and monitoring for complications.
Supportive Care
Engage in supportive care measures such as regular medical check-ups, vaccinations for hepatitis and influenza, and nutritional counseling to support liver health.
Seeking Help and Support
Behavioral Changes
Seeking Professional Help
If struggling with alcohol dependence or addiction, seek professional help from healthcare providers, counselors, or support groups specializing in addiction recovery.
Support Networks
Join support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or other addiction recovery programs to connect with peers facing similar challenges and receive encouragement and guidance.
Conclusion
Continuing to drink alcohol after being diagnosed with cirrhosis liver poses serious risks to health and well-being, accelerating the progression of liver damage and increasing the likelihood of severe complications. By prioritizing abstinence from alcohol and seeking medical guidance and support, individuals with cirrhosis can manage their condition effectively, improve liver function, and enhance their overall quality of life. Remember, making positive lifestyle changes and accessing appropriate healthcare resources are essential steps towards managing cirrhosis and promoting long-term health.
0 notes
Text
Conformational Dynamics of the Hepatitis C Virus 3'X #RNA [Article]
The 3' end of the hepatitis C virus genome is terminated by a highly conserved, 98-nucleotide sequence called 3'X. This untranslated structural element is thought to regulate several essential RNA-dependent processes associated with infection. 3'X has two proposed conformations comprised of either three- or two stem-loop structures that result from different base pairing interactions within the first 55 nucleotides. Here, we used single-molecule FRET spectroscopy to monitor the conformational status of fluorescently labeled constructs that isolate this region of the RNA (3'X55). We observed that 3'X55 can adopt both proposed conformations and the relative abundance of them can be modulated by either solution conditions or nucleotide deletions. Furthermore, interconversion between the two conformations is slow and takes place over the course of several hours. The simultaneous existence of two slowly interconverting conformations may help prime individual copies of the viral genome for either viral protein or RNA synthesis, thereby minimizing conflicts between these two competing processes. http://rnajournal.cshlp.org/cgi/content/short/rna.079983.124v1?rss=1&utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
The Hidden Dangers of Bile Duct Diseases and Cirrhosis: Protecting Your Liver Health

Our liver, a resilient and vital organ, often works tirelessly in the background, performing numerous essential functions. However, certain conditions can severely impact its health and functionality. Among these are bile duct diseases and cirrhosis, both of which can lead to significant complications if not properly managed. This blog aims to shed light on these conditions, their symptoms, and their treatments.
What Are Bile Duct Diseases?
The bile ducts are a network of tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and the small intestine. Bile is crucial for the digestion of fats. When these ducts are compromised, it can lead to serious health issues. Here are some common bile duct diseases:
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC):
What It Is: PBC is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks the bile ducts within the liver.
Symptoms: Patients often experience fatigue, itching, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosed through blood tests for specific antibodies, liver function tests, and imaging studies. Treatment includes medications like ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and obeticholic acid. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC):
What It Is: PSC involves chronic inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, causing them to narrow.
Symptoms: This condition leads to fatigue, itching, jaundice, and abdominal pain.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosed through MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) and ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Treatment focuses on symptom management, endoscopic procedures to open blocked ducts, and potentially liver transplant.
Biliary Atresia:
What It Is: A congenital condition where the bile ducts are absent or blocked.
Symptoms: Jaundice in newborns, dark urine, pale stools, and poor growth are common signs.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Blood tests, liver biopsy, and imaging studies are used for diagnosis. Surgery (Kasai procedure) is the primary treatment, with liver transplant being necessary in some cases.
Cholangitis:
What It Is: Infection of the bile ducts, often due to gallstone obstruction.
Symptoms: This includes fever, jaundice, and abdominal pain, known collectively as Charcot’s triad.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosed through blood tests, imaging, and ERCP. Treatment involves antibiotics and procedures to relieve the obstruction.
What is Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is the end result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver, leading to permanent scarring (fibrosis). It can result from various liver diseases, including bile duct diseases.

Causes of Cirrhosis
Chronic Alcohol Abuse: Prolonged alcohol consumption can severely damage liver cells, leading to cirrhosis.
Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Hepatitis B and C infections are major contributors.
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Fat accumulation in the liver that causes inflammation and scarring.
Bile Duct Diseases: Conditions like PBC and PSC, which chronically obstruct bile flow, can also lead to cirrhosis.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
Fatigue and weakness
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Easy bruising and bleeding
Ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen)
Swelling in the legs
Itching
Hepatic encephalopathy (confusion and cognitive impairment)
Diagnosis of Cirrhosis
Physical Examination: Signs of liver disease include jaundice, spider angiomas, and ascites.
Blood Tests: Liver function tests, complete blood count, and clotting profile.
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to assess liver size, structure, and complications.
Liver Biopsy: A definitive method to diagnose cirrhosis and assess its severity.
Treatment of Cirrhosis
Medications: To manage symptoms and complications, such as diuretics for ascites and lactulose for hepatic encephalopathy.
Lifestyle Changes: Avoidance of alcohol, a healthy diet, and regular monitoring.
Management of Complications: Endoscopic procedures for varices, paracentesis for ascites, and antibiotics for infections.
Liver Transplant: Considered in advanced cases where the liver is severely damaged.
The Connection Between Bile Duct Diseases and Cirrhosis
Bile duct diseases like PBC and PSC can lead to cirrhosis by causing chronic inflammation and bile flow obstruction. Over time, this chronic damage results in liver scarring, ultimately leading to cirrhosis. Effective management of bile duct diseases is crucial to prevent or delay the onset of cirrhosis.
Conclusion
Bile duct diseases and cirrhosis are complex conditions that require careful medical management. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent progression and complications. Regular monitoring and a multidisciplinary approach involving hepatologists, gastroenterologists, and other healthcare professionals are key to optimal patient care.
Understanding these conditions and their implications can empower individuals to seek timely medical attention and make informed decisions about their health. Stay proactive about liver health, and consult healthcare providers if you notice any concerning symptoms.
Important Information:
Conference Name: 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference
Short Name: 14GHUCG2024
Dates: December 17-19, 2024
Venue: Dubai, UAE
Email: [email protected]
Visit: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/
Call for Papers: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/submit-abstract/
Register here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/registration/
Exhibitor/Sponsor: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/exhibit-sponsor-opportunities/
Call Us: +12073070027
WhatsApp Us: +442033222718
0 notes
Text
dihydrocodeine 30mg buy
Dihydrocodeine is utilized to deal with medium to critical ache. Because of the way it works on your body, even if the source of the soreness continues to be, the Mind won’t feeling it as much. It can assist clients struggling from the suffering of sciatica, arthritis during the joints, most cancers and perhaps post-operative pain.
Dayvigo has not been revealed to lead to excess weight attain in reports performed via the maker. The most common facet impact of Dayvigo is sleepiness.
Whereas converting codeine to morphine is actually a tricky and unrewarding endeavor, dihydrocodeine may be converted to dihydromorphine with incredibly superior yields (over 95%).
You will have respiratory problems or withdrawal signs if You begin or prevent taking particular other medicines. Notify your doctor if Additionally you use an antibiotic, antifungal medication, heart or blood pressure level medication, seizure medication, or drugs to take care of HIV or hepatitis C.
For more info dihydrocodeine 30mg buy.
Opioid medication can connect with all kinds of other medications and result in harmful side effects or Dying. Make certain your medical doctor understands if you also use:
All opioids can impair the mental or Actual physical skills expected for your general performance of potentially harmful tasks for example driving or operating machinery if taken in significant doses.[15][sixteen]
In the United Kingdom, dihydrocodeine is a Class B drug; but, it is available over-the-counter in small amounts (less than eight mg), when coupled with paracetamol (see co-dydramol). Dihydrocodeine is mentioned in Program five on the Misuse of Medications Restrictions 2001 whereby it truly is exempt from prohibition on possession presented that it is in the form of a single preparing not remaining suitable for injection and a lot less than one hundred mg (calculated as cost-free base) or with a total focus a lot less than two.
Don’t consider Unless of course you can stay in mattress for an entire night time (no less than seven hrs) before you decide to has to be active once more.
Consequently, the performance of the provided dose of thebacon will range among individuals, and several food stuff and drugs can have an effect on several parts of the liberation, absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination profile, and thus a variable proportion with the potency of thebacon. Thebacon is usually stated to get the six-monoacetylmorphine analog of hydrocodone, and/or maybe the 6-acetylmorphone analog of codeine. It’s also an in depth structural relative of three,fourteen-diacetyloxymorphone.
0 notes
Text
Buy Legit Methanabol Online for Superior Bodybuilding Results
Metandienone, commonly known as Methanabol, is a potent anabolic-androgenic steroid renowned for its muscle-building properties. This performance-enhancing drug, however, is subject to restrictions in many countries due to its potential to artificially enhance strength, giving users an unfair advantage over competitors. Therefore, individuals contemplating buying Methanabol online for bodybuilding pursuits should consider the implications carefully.

History
Developed by CIBA in 1955, Metandienone was initially introduced in Germany and the USA before gaining widespread popularity worldwide. Initially favored by amateur athletes, its usage later extended to professionals, contributing to a surge in Methanabol sales. Subsequently, production expanded to include several Asian countries.
Why Use Methanabol
Methanabol stands out as one of the most preferred oral steroids in history, also available in injectable form. Its introduction marked a pivotal moment in the history of steroid usage, heralding significant changes in athletic performance. Widely recognized for its ability to accelerate muscle and strength gains, Methanabol operates similarly to testosterone, enhancing libido and red blood cell production alongside muscle mass.
Potential Threats
While Methanabol offers remarkable benefits, overuse can lead to adverse effects, prompting individuals to buy legit Methanabol online cautiously. Aromatization poses significant risks, with women facing the development of masculine traits such as facial hair growth and deepening voice, while men may experience gynecomastia and fluid retention. Hepatic concerns also arise due to its C-17 AA structure, necessitating vigilance, particularly for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions.
Mitigating Risks
To minimize the potential dangers associated with Methanabol, users should prioritize liver health and consider alternate administration methods such as injectables. Injectable forms may reduce hepatic stress compared to oral ingestion. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks during Methanabol use.
In conclusion, while Methanabol offers substantial benefits for bodybuilding enthusiasts, responsible usage is paramount to avoid adverse effects. Individuals seeking to capitalize on its muscle-building properties should proceed with caution, ensuring adherence to recommended dosages and monitoring their overall health throughout the cycle.
0 notes
Text
Hepcdac
Hepcdac is an antiviral medicine that can be used to deal with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. It is a direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medication that works by inhibiting the nonstructural protein HCV NS5A, Essential for the duplication of the virus. By blocking NS5A, Hepcdac can prevent the virus from multiplying and spreading in the body.
Hepcdac is usually used in combination with other antiviral medications, such as sofosbuvir or ribavirin, to form a complete treatment regimen for HCV infection. Combination therapy helps to increase the effectiveness of the treatment and reduce the risk of developing drug resistance.
Hepcdac is taken orally, typically once a day, with or without food. The amount and the dose of Hepcdac HCV are dependent on the genotype of the patient, liver function, and other factors. It is important to take the medication exactly as prescribed and to avoid missing doses to ensure the treatment’s effectiveness.
Hepcdac may cause side effects such as headache, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea, although these are generally mild and temporary. In rare cases, more severe side effects may occur, such as anemia, liver toxicity, or allergic reactions. If you experience any concerning side effects, you should contact your healthcare provider immediately
We are providing all the category of life saving drugs such as Temonat 100mg, Antreol, Rifagut 550mg, Entehep 0.5mg, Hepcinat and Lamivir HBV 100mg.
Why You Must Consider It?
Daclatasvir is a medicine that can treat infection in adults called HCV. Daclatasvir is often used in a blend with other medications such as sofosbuvir, ribavirin, or asunaprevir. Some of the reasons why you should consider Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) if you have chronic hepatitis C infection are that Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) has been shown to have a high cure rate for HCV infection when used in combination with other medications.
In clinical trials, Reports found that it can treat HCV infection. Fewer Side Effects: Compared to older HCV treatments, Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) has minimum reactions which are generally mild and well-tolerated. Convenient Dosage: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is available in an oral tablet form, which makes it easy to take. The recommended dosage is one tablet per day, with or without food.
Shorter Treatment Duration: Daclatasvir has a shorter treatment duration compared to older HCV treatments. The treatment duration ranges from 8 to 24 weeks, depending on the severity of the HCV infection and other factors. Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is available in many countries and is regulatory authorities approved such as the) European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In summary, Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is an effective and convenient treatment option for chronic hepatitis C infection. It has a high cure rate, fewer side effects, a convenient dosage form, a shorter treatment duration, and is widely available. If you have a chronic hepatitis C infection, you should consider talking to your healthcare provider about whether Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is right for you.
Some Interesting Insights About it?
Here are some interesting insights about Daclatasvir that you may find helpful:
Mechanism of Action: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) works by inhibiting the non-structural HCV protein 5A, which is important for the duplication of the virus. By inhibiting NS5A, Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) prevents the virus from replicating and spreading in the body.
Combination Therapy: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) is often used in combination with other medications such as sofosbuvir, ribavirin, or asunaprevir. These combinations have been known to be highly active in treating HCV infection, even in patients having advanced disease in the liver.
Drug Relations: Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) can interact with other medications, including certain HIV medications, and some cholesterol-lowering medications such as atorvastatin and simvastatin. Therefore, it is important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking before starting treatment with Hepcdac (Daclatasvir).
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: There is limited data on the safety of Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) in pregnant and breastfeeding women. Therefore, it is important to inform your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or breastfeeding before starting treatment with Hepcdac (Daclatasvir).
Cost: The cost of Hepcdac (Daclatasvir) can vary depending on the country and the healthcare system. In some countries, such as India, generic versions of the medication are available at a lower cost than the brand-name version.
0 notes
Text

In the vast landscape of medical specialties, hepatologists emerge as the guardians of liver well-being, possessing specialized knowledge and skills to diagnose and treat a wide array of liver-related conditions. Let's delve into the world of hepatology and uncover why consulting a liver specialist is paramount for optimal liver health.
Understanding Hepatology
Hepatology, a specialized branch of medicine, focuses on the study of liver function, diagnosis of liver diseases, and implementation of effective treatment strategies. Hepatologists, armed with extensive training and experience, play a pivotal role in managing liver disorders such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, and liver cancer.
The Hepatologist's Toolbox
Hepatologists utilize a range of diagnostic tools to evaluate liver health comprehensively. These may include blood tests to assess liver enzymes and function, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI to visualize the liver's structure, and liver biopsy for precise diagnosis of liver diseases and assessment of liver damage.
Holistic Liver Care
One of the key strengths of hepatology lies in its holistic approach to liver care. Hepatologists not only focus on diagnosing and treating liver conditions but also emphasize preventive measures, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing management to optimize liver function and overall health. They work closely with patients to develop personalized care plans tailored to individual needs and goals.
Advancements in Liver Treatment
The field of hepatology continues to evolve with advancements in liver treatment options. Hepatitis C, for instance, has witnessed remarkable progress with the development of direct-acting antiviral medications, leading to higher cure rates and improved outcomes. Hepatologists stay abreast of these advancements, ensuring patients have access to the most effective and innovative treatments available.
Importance of Consultation
If you experience symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, or persistent fatigue, seeking consultation with a hepatologist is crucial. Early detection and intervention can significantly impact the course of liver diseases, leading to better prognosis and enhanced quality of life.
Conclusion
In the realm of liver health, hepatologists serve as trusted guides, offering expert care, specialized treatments, and ongoing support to patients navigating liver-related challenges. By partnering with a hepatologist, individuals can proactively manage their liver health, address concerns promptly, and embark on a journey towards a healthier liver and overall well-being.
0 notes
Text

Hepatitis in Pediatric Patients:
Children represent a vulnerable demographic susceptible to hepatitis, displaying unique patterns of transmission, clinical manifestations, and long-term consequences. Hepatitis A, primarily spread through fecal-oral contamination of food and water, poses a significant threat to children, often presenting as acute illness characterized by jaundice, fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and nausea. Conversely, hepatitis B, typically transmitted from mother to child during childbirth or through blood exposure, presents distinctive challenges in pediatric healthcare, necessitating timely vaccination and careful screening of high-risk infants. The evolving landscape of pediatric hepatitis highlights the critical role of comprehensive vaccination programs, early detection, and multidisciplinary care to mitigate disease impact and prevent long-term complications in children.
Hepatitis in the Adult Population:
Adults comprise a diverse group affected by hepatitis, with hepatitis B and C emerging as prominent global concerns, particularly among high-risk groups like injection drug users, healthcare professionals, and individuals with underlying health conditions. Chronic hepatitis B, prevalent in a substantial portion of adults, underscores the importance of targeted screening, early detection, and prompt initiation of antiviral therapy to prevent disease progression and reduce the risk of liver cirrhosis and cancer. Similarly, hepatitis C, once a formidable challenge with limited treatment options, has seen a significant transformation with the introduction of direct-acting antiviral agents, offering cure rates exceeding 95% and reshaping the landscape of hepatitis management in adults. However, addressing disparities in access to screening, diagnosis, and treatment remains a critical challenge, requiring concerted efforts to improve healthcare delivery and outcomes globally.
Diagnosis and Management:
The diagnosis of hepatitis requires a systematic approach involving clinical assessment, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and histopathological examination to determine the underlying cause, assess disease severity, and guide treatment decisions. Blood tests, including serological markers and viral load assays, are essential for distinguishing between acute and chronic hepatitis, identifying viral strains, and monitoring treatment response. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI provide valuable information on liver structure, blood flow, and the presence of complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. Although invasive, liver biopsy remains valuable in certain cases, offering histological confirmation of the diagnosis and guiding treatment strategies.
Treatment options for hepatitis encompass a variety of pharmacological interventions, including antiviral drugs, immunomodulatory therapy, and supportive care measures to alleviate symptoms and promote liver health. In acute hepatitis, conservative management with rest, hydration, and dietary adjustments is often sufficient, with close monitoring of liver function and symptoms. Chronic hepatitis requires a proactive approach aimed at achieving sustained viral suppression, halting disease progression, and reducing the risk of complications. Antiviral medications targeting specific viral enzymes have revolutionized treatment, offering high efficacy and shorter durations compared to conventional therapies. Additionally, immunomodulatory agents play a role in managing autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis associated with systemic conditions.
Early diagnosis and management of hepatitis is possible by undergoing a regular full body health checkup at a good hospital.
#regular health checkups#full body health checkup#hepatitis#hepatitis A#hepatitis B#hepatitis C#pediatric hepatitis#chronic hepatitis#blood tests#CT scans#MRI scans#liver biopsy#liver health#acute hepatitis#antiviral drugs
0 notes
Text
COVID-19 naming
ADD ARTICLE DESCRIPTION
During the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, the disease and virus were sometimes called "coronavirus", "Wuhan coronavirus", or "Wuhan pneumonia".
In January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) tentatively named it "2019-nCoV", short for "2019 Novel Coronavirus", or "2019 Novel Coronavirus Acute Respiratory Disease". This naming was based on the organization's 2015 guidelines for naming novel viruses and diseases, avoiding the use of geographic locations (such as Wuhan), in part to prevent social stigma. A similar structure has also been used by the AP when referring to virus variants, for example, referring to it as the "Delta variant" rather than the "South African variant".
On 11 February 2020, the WHO named the disease COVID-19 (short for coronavirus disease 2019). That same day, the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) formally announced it had named the causative virus as SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) based upon its genetic similarity to the 2003 SARS-CoV. The separation between the disease and the causative virus is based on the same nomenclature policies that separate AIDS and the virus which causes it, HIV.
WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus explained that CO stands for coronavirus, VI for virus, and D stands for disease, while 19 stands for the year, 2019, that the outbreak was first detected. As such, there has never been a "COVID-1" or any other "COVID-" series disease with a number below 19.
Chinese virus
From January to March 2020, US President Donald Trump repeatedly described the virus as the "Chinese virus". In March 2020, the president claimed to have abandoned the term, telling Fox News "we shouldn't make any more of a big deal out of it". On March 18 and 19, 2020, Trump twice defended using the term "Chinese virus" amid instances of bigotry against Asians in the United States. Trump referred to it as "the China Virus" at least as late as January 2021.
This description was also used by members of the Spanish far-right political party Vox, especially by its leader Santiago Abascal in March 2020.
CCP virus
The Epoch Times has reportedly funded right-wing groups promoting the use of the term "CCP virus" to lay blame on the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) for the pandemic. Chinese-born New Zealand sculptor Chen Weiming created a 20-foot statue in Liberty Sculpture Park in Yermo, California, depicting Chinese leader and CCP general secretary Xi Jinping with spike proteins as his hair, naming it "CCP virus".
Stylization
Stylization of the term has varied since the virus's and disease's discovery. The World Health Organization (WHO) stylizes the disease as COVID-19 with all letters capitalized and many other organizations have followed their lead. The AP Stylebook, Chicago Manual of Style, and the Modern Language Association (MLA) have styled it similarly. Several observers have noted the importance of proper stylization, despite the seeming ridiculousness of worrying over such matters "at a time like this" (during the early days of the pandemic), recalling the confusion and prejudice which resulted from unclear or inconsistent naming as was the case with AIDS (which was called GRID/HTLV-III/LAV at various times) and non-A, non-B Hepatitis. They have also pointed out that future researchers will benefit from consistency when reviewing past data and research.
However, stylization as "Covid-19" has become common as well. Numerous news sources including The New York Times, CNN, Politico, The Wall Street Journal, NBCNews have presented the term with a capital C but all other letters as lower case. As a result, use of "Covid-19" has become commonplace and even the accepted standard in some cases. Use of "Covid-19" in news sources from the United Kingdom like The Guardian has also been the norm since most British newspapers only capitalize an entire acronym if the acronym is typically spelled out like "B-B-C" or "N-H-S" while acronyms which are pronounced as words, like "Nasa" or "Unicef" have their first letter capitalized and all subsequent letters lowercase.
While COVID-19 refers to the disease and SARS-CoV-2 refers to the virus which causes it, referring to the "COVID-19 virus" has been accepted. Reference to SARS-CoV-2 as "the coronavirus" has become somewhat accepted despite such use implying that there is only one coronavirus species. Similarly, use of "COVID" for the disease (if the first rendered as COVID-19) has been tolerated. Use of "the Coronavirus" to refer to the COVID-19 pandemic which began in December 2019 has also been accepted. Although such use does not specify the year or which coronavirus-related disease is being referred to, given its all-encompassing impact at the time, such references have been deemed justifiable. Use of "the" when referring to the disease, virus, or 2019 pandemic has been quite varied with some requiring use of "the" while others have not. The Oxford English Dictionary noted that "the" is typically not used when referring to the disease, COVID-19, but is not uncommon when referring to the virus.
Reference to the virus and/or the disease as "corona", "the corona", and "the rona" has also arisen in various parts of the world.
Colloquial names

2022-09-13 phylogenetic tree of life of COVID-19 using the PANGO nomenclature; only a few of these variants have come to public notice
Numerous mutations and variants of SARS-CoV-2 have acquired colloquial vis-à-vis scientific labels for ease of pronunciation and usage, both in the lab and to some extent in mass media. The nomenclature draws from the corpus of mythology (both Greek and Scandinavian and astronomy.
Public messaging has been a concern given that these elements of popular reportage can be at variance with the Greek alphabet nomenclature established by the WHO; other schemes have been proposed.
Variants
Arcturus (XBB.1.16) was named on social media after the star; Kraken (XBB.1.5), Cerberus (BQ.1.1), Typhon (BQ.1), and Gryphon (XBB) were coined by evolutionary biologist T. Ryan Gregory (from his own personal nomenclature of mythical creatures); whereas Pelican, Quail, and Mockingbird (variants of 20I/501Y.V1), have not gained wider usage. The BA.2.86 variant was named 'pirola' (sic) by a group of scientists on social media in late 2023, and was brought to public attention by an August edition of the Wall Street Journal. (Inasmuch as the World Health Organization has suggested using astronomy for its plethora of names, the Twitter user @JPWeiland suggested the obscure Jovian asteroid 1082 Pirola "for its uniqueness" and the possibility of shifting the nomenclaure to Pi or Rho if needed.)
Mutations
Nicknames have also arisen for mutations such as Nelly (N501Y), Doug (and Douglas) (D614G), and even Eeek (E484K), initially meant as convenient labels in University of Bern lab discourse.
See also
Virus classification
References
ABOUT THIS ARTICLE
View edit history
Updated 50 days ago
View talk page
Discuss improvements to this article
Page issues
Alerts about subpar or problematic content
READ MORE
Shi Zhengli
Chinese researcher at the Wuhan Institute of Virology
COVID-19 pandemic
Pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2
Virus that causes COVID-19
Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted.
View article in browser










0 notes
Text
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
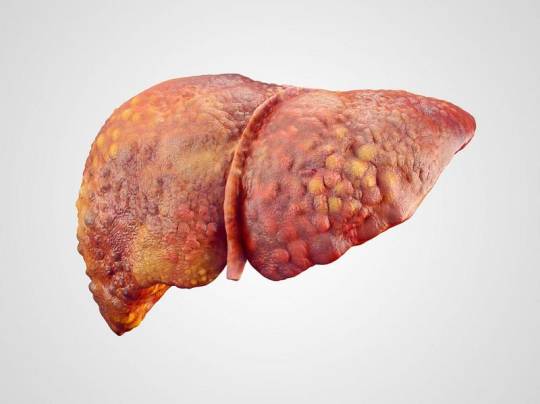
Introduction
Cirrhosis stands as a challenge in the narrative of liver disease, marking the culmination of a complex interplay of factors that converge to undermine the organ’s structural integrity and functional capacity. This condition, characterized by the progressive accumulation of scar tissue within the liver parenchyma, holds a cascade of physiological network that reverberate throughout the body, manifesting in a spectrum of symptoms and complications. From its inner onset to its profound implications for morbidity and mortality, cirrhosis generate the intricate interplay between genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and individual behaviors.
In this comprehensive discussion, we embark on an exploration of the multifaceted dimensions of cirrhosis, traversing its etiological underpinnings, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, therapeutic strategies, and avenues for prevention and self-care. By delving into the intricacies of cirrhosis, we endeavor to elucidate the imperative of early recognition, proactive intervention, and holistic management in ameliorating its adverse sequelae and fostering optimal outcomes for affected individuals
Pathophysiology of Cirrhosis

Central to the pathogenesis of cirrhosis lies a complex interplay of molecular and cellular events that precipitate the gradual transformation of healthy hepatic tissue into fibrotic scar tissue. At the heart of this process lies fibrogenesis, wherein a multitude of cellular players, including hepatic stellate cells, inflammatory mediators, and extracellular matrix proteins, triggers a profibrotic milieu in response to persistent liver injury and inflammation. The ensuing deposition of collagen-rich scar tissue disrupts the structure of the liver lobules, impeding normal hepatocellular function and vascular dynamics.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations

The clinical presentation of cirrhosis spans a broad spectrum, reflecting the diverse array of physiological derangements engendered by advanced liver disease. Early-stage cirrhosis may manifest subtly, with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, malaise, and vague abdominal discomfort, often eluding timely diagnosis. However, as the disease progresses, overt signs of hepatic decompensation emerge, including jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and gastrointestinal bleeding, heralding the onset of life-threatening complications. Moreover, cirrhosis exerts systemic effects beyond the confines of the liver, precipitating coagulopathy, renal dysfunction, and metabolic disturbances.
Etiology and Risk Factors
Cirrhosis arises from an influence of etiological insults, encompassing a diverse spectrum of predisposing factors that contribute to hepatocellular injury and fibrogenesis. Foremost among these is chronic alcohol abuse, which inflicts direct hepatotoxic effects and potentiates oxidative stress and inflammatory cascades within the liver microenvironment. Additionally, viral hepatitis infections, particularly hepatitis B and C, constitute major drivers of cirrhosis worldwide, underscoring the imperative of vaccination and antiviral therapy in disease prevention and management. Other contributing factors include nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, autoimmune disorders, hereditary hemochromatosis, and biliary tract diseases, each exerting a unique influence on cirrhosis pathogenesis.
Diagnostic Modalities

Accurate diagnosis forms the linchpin of effective cirrhosis management, necessitating a judicious amalgamation of clinical symptoms, laboratory investigations, imaging modalities, and histopathological evaluation. Liver function tests serve as indispensable tools for gauging the synthetic and metabolic capacity of the liver, while imaging studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) afford insights into hepatic morphology, vascular dynamics, and the presence of focal lesions. Despite their utility, these modalities may be supplemented by liver biopsy, which remains the gold standard for assessing the degree of fibrosis and guiding therapeutic decisions, albeit fraught with procedural risks and sampling variability.
Treatment Strategies

While cirrhosis represents a chronic and irreversible condition, therapeutic interventions are geared toward monitoring disease progression, alleviating symptoms, and forestalling the onset of complications. Pharmacological therapies, including hepatoprotective agents, antifibrotic agents, and symptom-based medications, aim to attenuate hepatic inflammation, inhibit fibrogenesis, and ameliorate symptom burden in cirrhotic patients. Furthermore, endoscopic interventions such as variceal band ligation and trans jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting play a major role in the management of portal hypertension and its sequelae, including variceal bleeding and refractory ascites. For select individuals with end-stage liver disease, liver transplantation offers a definitive therapeutic option, affording a second lease on life and circumventing the inexorable progression of cirrhosis-related complications.
Self-Care and Lifestyle

Empowering individuals with cirrhosis to adopt proactive self-care measures constitutes a cornerstone of comprehensive disease management, emphasizing the role of lifestyle modifications, dietary interventions, and preventive strategies in optimizing health outcomes. Lifestyle modifications, including abstinence from alcohol, adherence to a liver-friendly diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, are paramount in attenuating hepatic inflammation, promoting metabolic homeostasis, and mitigating cardiovascular risk factors in cirrhotic patients. Additionally, vaccination against hepatitis viruses, avoidance of hepatotoxic medications, and judicious monitoring of comorbid conditions serve as essential pillars of preventive care, safeguarding against disease exacerbations and fostering long-term wellness in individuals with cirrhosis.
Conclusion
Cirrhosis emerges as a complex and a dangerous disease, syndrome characterized by progressive hepatic fibrosis, compromised organ function, and a plethora of systemic manifestations. The etiological heterogeneity of cirrhosis underscores the need for a personalized and multidisciplinary approach to disease management, Focusing to the unique pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical manifestations inherent to each individual. Through timely diagnosis, targeted interventions, and collaborative care, healthcare providers can mitigate the burden of cirrhosis, optimize patient quality of life, and prolong survival in affected individuals. As we navigate complexities of cirrhosis, a concerted emphasis on preventive measures, patient education, and therapeutic innovations holds the key to unlocking a brighter prognosis for those afflicted by this formidable liver disease.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at [email protected]
for assistance guidance.
#assignment help#healthcare#medical students#nursing student#nursing school#medical school#medical student#homework help#academic assignments#medicine#clinical research#research#research paper#medical conditions#medical assistance#health tips#pharmacy student#pharmacology#pharmacy technician#pharmacy
0 notes