#history politics and economics
Text
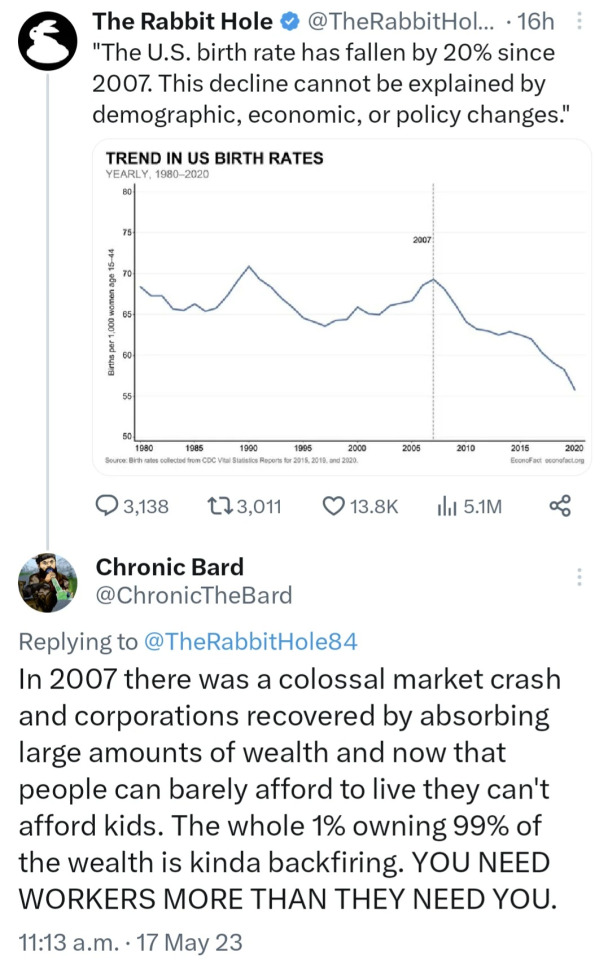
Imagine purporting to be a journalist and saying there were no economic changes after 2007.
#this is why history is important#economics#politics#also why you shouldn't trust paid-for blue checkmarks on the muskrat's birdsite
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
You’re Lucky You Have a House, Peasant!
A history of company towns
by Joyce Rice and Kevin Moore


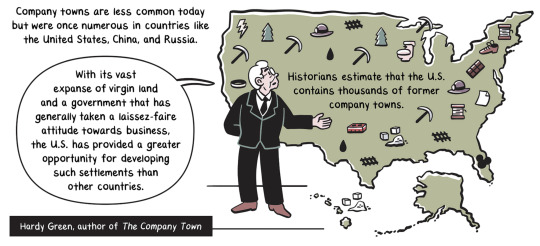












(Continue Reading)
TheNib.com
@thenib
#politics#the left#the nib#comic#webcomic#labor#Labor Unions#organized labor#history#capitalism#economic inequality#oppression#poverty#working class#long post#long reads
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
A CIA whistleblower John Stockwell (1989) giving a huge history lesson about the "CIA Economic Hit Men" 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#reeducate yourselves#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do your own research#do some research#do your research#ask yourself questions#question everything#economic hit men#cia corruption#news#history lesson#hidden history#history#political history#whistleblower#government corruption
508 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
A Warning from 1994 of a Two-Tiered Society
As secretary of labor, I thought it important to explain why the Democrats had lost both the House and the Senate in the 1994 midterm elections. I attributed it to the fact that many middle class Americans felt angry and frustrated about not getting ahead, and they took it out on Democrats who had been running Congress for many years. I took a lot of heat for this speech 29 years ago.
Watch and tell me if I was wrong.
438 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘100% feminist’: how Eleanor Rathbone invented child benefit – and changed women’s lives for ever
She was an MP and author with a formidable reputation, fighting for the rights of women and refugees, and opposing the appeasement of Hitler. Why isn’t she better known today?
Ladies please reblog to give her the recognition she deserves

By Susanna Rustin Thu 4 Jul 2024
My used copy of the first edition of The Disinherited Family arrives in the post from a secondhand bookseller in Lancashire. A dark blue hardback inscribed with the name of its first owner, Miss M Marshall, and the year of publication, 1924, it cost just £12.99. I am not a collector of old tomes but am thrilled to have this one. It has a case to be considered among the most important feminist economics books ever written.
Its centenary has so far received little, if any, attention. Yet the arguments it sets out are the reason nearly all mothers in the UK receive child benefit from the government. Its author, Eleanor Rathbone, was one of the most influential women in politics in the first half of the 20th century. She led the National Union of Societies for Equal Citizenship (Nusec, the main suffragist organisation, also formerly known as the National Union of Women Suffrage Societies) from 1919, when Millicent Fawcett stood down, until the roughly five million women who were not enfranchised in 1918 gained the vote 10 years later. In 1929, aged 57, she became an MP, and remained in parliament until her death in 1946. While there, she built up a formidable reputation based on her advocacy for women’s rights, welfare reform and the rights of refugees, and her opposition to the appeasement of Hitler.
It would not be true to say that Eleanor Rathbone has been forgotten. Her portrait by James Gunn hangs in the National Portrait Gallery. Twenty years ago she was the subject of a fine biography and she is remembered at Somerville college, Oxford – where she studied in the 1890s and ran a society called the Associated Prigs. (While the name was a joke, Rathbone did have a priggish side – as well as being an original thinker, tremendous campaigner, and stubborn, sensitive personality.) She also features in Rachel Reeves’s book The Women Who Made Modern Economics, although Reeves – who hopes shortly to become the UK’s first female chancellor – pays more attention to her contemporary, Beatrice Webb.

A thrilling tome … The Disinherited Family by Eleanor Rathbone. Photograph: Alicia Canter/The Guardian
But Rathbone, who came from a wealthy dynasty of nonconformist merchants, does not have anything like the name-recognition of the Pankhursts or Millicent Fawcett, or of pioneering politicians including Nancy Astor and Ellen Wilkinson. Nor does she enjoy the cachet of writers such as Virginia Woolf, whose polemic about women’s opportunities, A Room of One’s Own, was published five years after Rathbone’s magnum opus.
There are many reasons for Rathbone’s relative obscurity. One is that she was the first woman elected to parliament as an independent (and one of a handful of men at the time). Thus there is no political party with an interest in turning her into an icon. Having spent the past three years writing a book about the British women’s movement, I am embarrassed to admit that when I started, I didn’t know who she was.
Rathbone was not the first person to propose state benefits paid to mothers. The endowment of motherhood or family allowances, as the policy was known, was written about by the Swedish feminist Ellen Key, and tried out as a project of the Fabian Women’s Group, who published their findings in a pamphlet in 1912. But Rathbone pushed the idea to the forefront. A first attempt to get Nusec to adopt it was knocked back in 1921, and she then spent three years conducting research. The title she gave the book she produced, The Disinherited Family, reflected her view that women and children were being deprived of their rightful share of the country’s wealth.
The problem, as she saw it, was one of distribution. While the wage system in industrialised countries treated all workers on a given pay grade the same, some households needed more money than others. While unions argued for higher wages across the board, Rathbone believed the state should supplement the incomes of larger families. She opened the book with an archly phrased rhetorical question: “Whether there is any subject in the world of equal importance that has received so little consideration as the economic status of the family?” She went on to accuse economists of behaving as if they were “self-propagating bachelors” – so little did the lives of mothers appear to interest them.
Rathbone’s twin aims were to end wives’ dependence on husbands and reward their domestic labour. Family allowances paid directly to them could either be spent on housekeeping or childcare, enabling them to go out to work. Ellen Wilkinson, the radical Labour MP for Middlesbrough (and future minister for education), was among early supporters. William Beveridge read the book when he was director of the London School of Economics, declared himself a convert and introduced one of the first schemes of family-linked payments for his staff.
But others were strongly opposed. Conservative objections to such a radical expansion of the state were predictable. But they were echoed by liberal feminists including Millicent Fawcett, who called the plan “a step in the direction of practical socialism”. Trade unions preferred to push for a living wage, while some male MPs thought the policy undermined the role of men as breadwinners. Labour and the Trades Union Congress (TUC) finally swung behind family allowances in 1942. As the war drew to a close, Rathbone led a backbench rebellion against ministers who wanted to pay the benefit to fathers instead.

Rathbone celebrates the Silver Jubilee of the Women’s Vote in London, 20 February 1943. Photograph: Picture Post/Getty Images
It is for this signature policy that she is most often remembered today. At a time when hundreds of thousands of children have been pushed into poverty by the two-child limit on benefit payments, Rathbone’s advocacy on behalf of larger families could hardly be more relevant. The limit, devised by George Osborne, applies to universal and child tax credits – and not child benefit itself. But Rishi Sunak’s government announced changes to the latter in this year’s budget. From 2026, eligibility will be assessed on a household rather than individual basis. This is intended to limit payments to better-off, dual-income families. But the UK Women’s Budget Group and others have objected on grounds that child benefit should retain its original purpose of directly remunerating primary carers (the vast majority of them mothers) for the work of rearing children. It remains to be seen whether this plan will be carried through by the next government.
Rathbone once told the House of Commons she was “100% feminist”, and few MPs have been as single-minded in their commitment to women’s causes. As president of Nusec (the law-abiding wing of the suffrage campaign), she played a vital role in finishing the job of winning votes for women.
The last few years have seen a resurgence of interest in women’s suffrage, partly due to the centenary of the first women’s suffrage act. Thanks to a brilliant campaign by Caroline Criado Perez, a statue of Millicent Fawcett, the nonmilitant suffragist leader, now stands in Westminster, a few minutes walk from the bronze memorial of Emmeline Pankhurst erected in 1930. Suffragette direct action has long been a source of fascination. What is less well known is that militants played little part in the movement after 1918. It was law-abiding constitutionalists – suffragists rather than suffragettes – who pushed through the 1920s to win votes for the younger and poorer women who did not yet have them. Rathbone helped lead this final phase of the campaign, along with Conservative MP Nancy Astor and others.
Rathbone was highly critical of the militants, and once claimed that they “came within an inch of wrecking the suffrage movement, perhaps for a generation”. Today, with climate groups including Just Stop Oil copying the suffragette tactic of vandalising paintings, it is worth remembering that many women’s suffrage campaigners opposed such methods.
Schismatic though it was, the suffrage movement at least had a shared goal. An even greater challenge for feminists in the 1920s was agreeing on future priorities. Equal pay, parental rights and an end to the sexual double standard were among demands that had broad support. After the arrival in the House of Commons of the first female MPs, legislative successes included the removal of the bar on women’s entry to the professions, new rights for mothers and widows’ pensions. But there were also fierce disagreements.
Tensions between class and sexual politics were longstanding, with some on the left regarding feminism as a distraction. The Labour MP Marion Phillips, for example, thought membership of single-sex groups placed women “in danger of getting their political opinions muddled”. There was also renewed conflict over protective legislation – the name given to employment laws that differentiated between men and women. While such measures included maternity leave and safety rules for pregnant women, many feminists believed their true purpose was to keep jobs for men – and prevent female workers from competing.
Underlying such arguments was the question of whether women, once enfranchised, should strive for equal treatment, or push for measures designed to address their specific needs. As the debate grew more heated, partisans on either side gave themselves the labels of “old” and “new” feminists. While the former, also called equalitarians, wanted to focus on the obstacles that prevented women from participating in public life on the same terms as men, the new feminists led by Rathbone sought to pioneer an innovative, woman-centred politics. Since this brought to the fore issues such as reproductive health and mothers’ poverty, it is known as “maternalist feminism”.

Rathbone and other Liverpool suffragettes campaigning in 1910. Photograph: Shawshots/Alamy
The faultline extended beyond Britain. But Rathbone and her foes had some of the angriest clashes. At one international convention, Lady Rhondda, a wealthy former suffragette, used a speech to deride rivals who chose to “putter away” at welfare work, instead of the issues she considered important.
The specific policy points at issue have, of course, changed over the past century. But arguments about how much emphasis feminists should place on biological differences between men and women carry on.
Eleanor Rathbone did not live long enough to see the welfare state, including child benefit paid to mothers, take root in postwar Britain. Her election to parliament coincided with the Depression, and the lengthening shadows of fascism and nazism meant that she, like her colleagues, became preoccupied with foreign affairs. In the general election of 1935, the number of female MPs fell from 15 to nine, meaning Rathbone’s was one of just a handful of women’s voices. She used hers to oppose the policy of appeasement, and support the rights of refugees, including those escaping Franco’s Spain. During the war she helped run an extra-parliamentary “woman-power committee”, which advocated for female workers.
She also became a supporter of Indian women’s rights, though her liberal imperialism led to tensions with Indian feminists. During the war she angered India’s most eminent writer, Rabindranath Tagore, and its future prime minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, when she attacked the Congress party’s policy of noncooperation with Britain’s war effort. Tagore criticised what he called the “sheer insolent self-complacency” of her demand that the anti-colonial struggle should be set aside while Britain fought Germany.
Rathbone turned down a damehood. After their first shared house in Westminster was bombed, she and her life partner, the Scottish social worker Elizabeth Macadam, moved around the corner to a flat on Tufton Street (Macadam destroyed their letters, meaning that Rathbone’s intimate life remains obscure, but historians believe the relationship was platonic). From there they moved to a larger, quieter house in Highgate. On 2 January 1946, Rathbone suddenly died.

Rathbone’s blue plaque at Tufton Court. Photograph: PjrPlaques/Alamy
A blue plaque on Tufton Street commemorates her as the “pioneer of family allowances” – providing an alternative claim on posterity for an address more commonly associated with the Brexit campaign, since a house a few doors down became its headquarters. She is remembered, too, in Liverpool, where her experience of dispersing welfare to desperately poor soldiers’ wives in the first world war changed the course of her life, and where one of her former homes is being restored by the university.
I don’t believe in ghosts. But walking in Westminster recently, I imagined her hastening across St James’s Park to one of her meetings at Nancy Astor’s house near the London Library. Today, suffragettes are celebrated for their innovative direct action. But Rathbone blazed a trail, too, with her dedication as a campaigner, writer, lobbyist and “100% feminist” parliamentarian.
Sexed: A History of British Feminism by Susanna Rustin is published by Polity Press (£20). To support the Guardian order your copy at guardianbookshop.com. Delivery charges may apply
#Eleanor Rathbone#The Disinherited Family#Books by women#Books about women#Child benefit#National Union of Societies for Equal Citizenship (Nusec)#Rachel Reeve#The Women Who Made Modern Economics#Women in politics#UK#Seed: A History of British Feminism#Susan Rustin
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
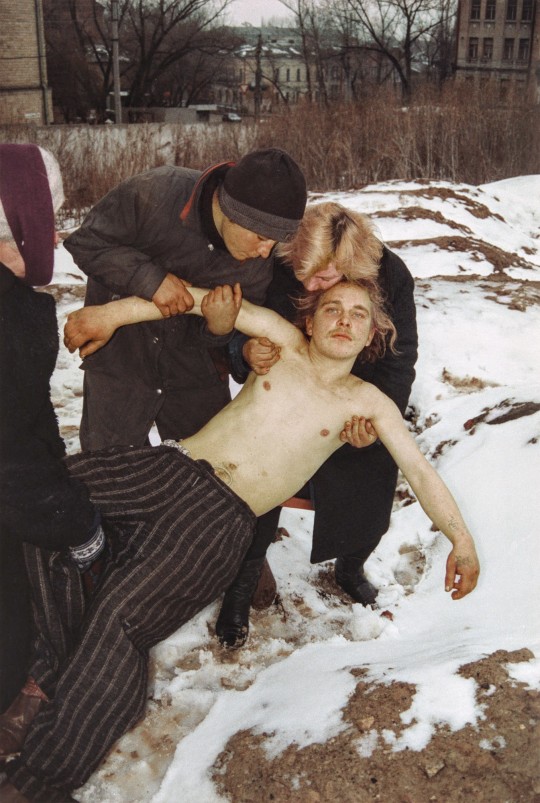

Boris Mikhailov Untitled (Kharkiv, Ukraine 1998). Life-size photograph [236 × 126 cm / 93 × 50 in.] from the 2019 "Forbidden Image" exhibition in Kyiv, Ukraine.
#photography#boris mikhailov#dark#city#kharkiv#ukraine#art history#politics#economics#life#humanity#hard times#art#1990s#surreal#history#people#urban#sociology#activism#📚
141 notes
·
View notes
Note
If management finds a way to automate jobs during a strike, is that scabbing?
Peripherally.
The automation itself is more part of the general category of management strategies to restructure workflow and production methods in order to reduce the need for, and thus the power of, labor. This dates back to the origins of Taylorism itself in the 1890s as an effort to “steal the brains from underneath the cap of labor” and through to the emergence of Human Relations and Industrial Psychology in the early 20th century as a means to better control workers. So I think you could see in as essentially equivalent to classic speed-up and stretch-out efforts to maintain production at as low a cost as possible during a strike, and thus break the union.
However, the dirty truth of automation is that there is no clean way to fully substitute machinery for labor. Due to the inherent limitations of technology at any stage of development, you need labor to repair and maintain and monitor automated systems, you need labor to install and operate the machines, you need labor to design and program and manufacture the machines. (This is one reason why the job-killing predictions around automation often fall flat, because the supposedly superior new technology often requires a significant increase in human labor to service the new technology when it breaks. For example, this is why automation in fast food has proven to be so difficult and partial than expected: it turns out that self-checkout machines are actually very expensive to operate in terms of skilled manpower.) And to the extent that a given automation contract or project is being undertaken during a strike in order to break that strike, that’s absolutely scabbing.
#labor#labor history#trade unions#unions#strikes#automation#Taylorism#political economy#economic history#scabbing#labor studies
133 notes
·
View notes
Text

131 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Deep State Mafia is running both political parties" Journalist Whitney Webb reveals
youtube
#politics#j d vance#trump#deep state#maga#history#peter thiel#palantir#big brother#new world order#globalism#2024 rnc#dnc 2024#world economic forum#never trump#paypal#wal mart#amazon#CIA#war on terror#george w bush#propaganda#covid 19#9/11#operation warp speed#Israel#benjamin netanyahu#jeffrey epstein
41 notes
·
View notes
Text

41 notes
·
View notes
Text





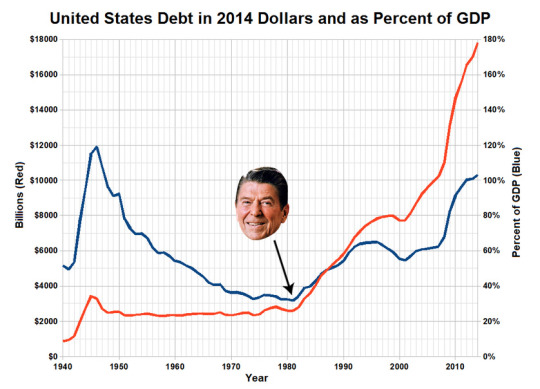

And possibly the most important one that explains the rest
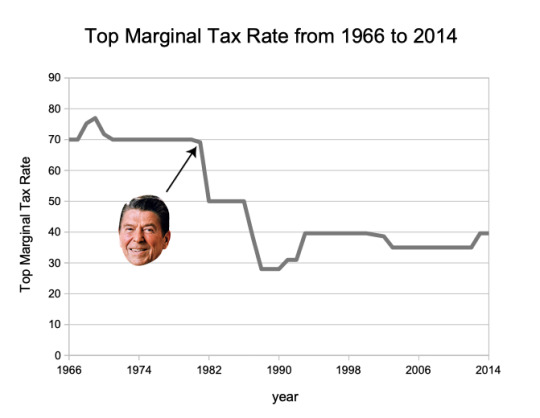
Happy July 5th
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
how to study for social studies subjects
I’d like to think that one of my strongest focuses is social studies. I love learning about history, economics, government, e.t.c. and I do well on tests! I thought that most people had it easy when it came to these subjects, but throughout working with peers and friends, I realized that wasn’t true, so here are some tips to get through those subjects:
Memorizing will be your friend: This is one of my biggest tips that I still use for my social studies subjects. Memorize, memorize, memorize! Of course, you should first understand a concept or term before memorizing it, but it helps so much to know words. I use quizlet and knowt.io to help me memorize, but you can use a variety of ways to remember. This is especially helpful for tests, as you can help fill in the blank when reading through questions and other readings.
Trick your brain: One of the reasons I was so good at social studies subjects was because I was interested in politics and government. I’m really interested in the controversial aspect of politics, which helped me understand forms and branches of government, how the economy works, e.t.c. I’ve recently heard this tip on the internet, where people trick their brain into thinking that the subject they are learning is like lore for a tv show or novel, and it worked. Your brain will probably be more likely to learn if you make it enjoyable.
Use a variety of resources: A lot of social studies subjects will have more interesting and engaging resources to use, rather than like physics with a boring textbook and some reference videos. Topics like politics will have a wide variety of books, articles, news reports, movies, and even TV shows covering them. After understanding the concepts and things you may need to know, watching a political TV show can be a form of studying! You can learn to apply, discuss, and critique different forms and resources to apply to the thing you are studying.
Find ways to connect to the modern world: Social studies subjects are one of the easiest to connect to the media and the news; you will often find articles and reporters speaking about the economy, what's going on in the supreme court, and who is voting or pushing for what agenda. If you ever need to find examples to help you learn and study, just watch the news! It’s a great resource, and can help you apply what you are learning to the real world. Oftentimes, test-makers will give a question set in a scenario, where a country is going into a recession and you may have to explain ways to solve or help it e.t.c. so the news is a great resource to see it real time.
#studyblr#study blog#studying#study#study tips#studying tips#aesthetic#social studies#economics#government#psychology#politics#ap comp gov#ap government#ap classes#ap courses#geography#history#apush#ap us history#q#queue
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

15 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
My Ultimate History Crash Course
Are we in a second Gilded Age? Is Trump really a Fascist? Why are we so politically polarized? How did corporations take over our politics?
To understand the present, study the past.
Please join me as I share 6 crucial lessons from history.
284 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries that are no more: Republic of Venice (697AD-1797AD)
The first in a series I hope to feature on providing high level overviews of countries that existed and were influential to history or obscure and lost to most memory in time. The first up is the Republic of Venice.
Name: Serenisma Republega de Venesia (Venetian). In English this translates to the state's official name The Most Serene Republic of Venice. Also referred to as the Venetian Republic, Republic of Venice or just Venice.
Language: The official languages were the Romance languages of Latin, Venetian & later Italian. The regional dialect of Vulgar Latin in Northeastern Italy known as Veneto was the original language of Venice. This evolved in Venetian which was attested to as a distinct language as early as the 13th century AD. Venetian became the official language and lingua franca of the everyday Venetians and across parts of the Mediterranean although Latin would still be used in official documents and religious functions. Overtime, modern Italian was spoken in Venice though the Venetian language remains technically a separate language in Italy's Veneto region and the surrounding areas to this day.
Minority languages across the republic's territory included various Romance languages such as Lombard, Friulian, Ladin, Dalmatian and non-romance languages such as Albanian, Greek & Serbo-Croatian.
Territory: The republic was centered on the city of Venice founded in the Venetian lagoon on the north end of the Adriatic Sea to the northeast coast of the Italian peninsula. It also included the surrounding regions of mainland northeast Italy in the regions of Veneto and Friuli and parts of Lombardy. This became known as the terraferma or the mainland holdings of the republic. It also possessed overseas holdings in modern day Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Albania, Greece & Cyprus.
Symbols & Mottos: The main symbol of Venice was its flag which had the famed Winged Lion of St. Mark. This represented the republic's patron saint, St. Mark. Mark the Evangelist after whom the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament in the Bible is named. Mark's body and holy relics were taken by Venice and said to be housed in the Basilica di San Marco (St. Mark's Basilica) in Venice itself. Variations of this flag differed during times of peace & war. During peace the winged lion is seen holding an open book and during war flags depicted the lion with its paw upon a bible and an upright sword held in another paw.
The republic's motto in Latin was "Pax tibi Marce, evangelista meus" or in English "Peace be to you Mark, my evangelist."
Religion: Roman Catholicism was the official religion of the state but Venice did have minorities of Eastern Orthodox & Protestant (usually foreign) Christian denominations at times in its territory and it also had small populations of Jews and Muslims to be found in Greek and Albanian territories during the wars with the Ottoman Empire.
Currency: Venetian ducat and later the Venetian lira.
Population: Though population varied overtime for the republic due to a variety of factors such as war & changing territory and disease & its subsequent effects. There was rough population recorded of 2.3 million people across all of its holdings in the mid sixteenth century (circa 1550-1560). The vast majority of its population was found in the terraferma of northern Italy and the city of Venice itself with its concentrated population on the islands within the Venetian Lagoon. The Greek island of Crete and the island of (Greek speaking) Cyprus were the most populous overseas possessions of the republic's territory. The rest of the population was found its various holdings in the Balkans mostly along the Adriatic coastline.
Government: The republic followed a complex mixed model of government. Essentially it could be characterized as a mixed parliamentary constitutional republic with a mercantile oligarchy ruling over it in practice. It had no formal written constitution, and this led to a degree of evolution without exactly defined roles often in reaction to happenings in its history. The resulting government became more complex overtime as institutions became increasingly fragmented in their size, scope and duties, some almost obsolete but still retained and others not fully defined. Yet, the republic managed to function quite well for most of its history. It incorporated elements of oligarchy, monarchy & limited democracy.
It's head of state and government was known as the Doge which is akin to the term of Duke. Though this similarity of name ends there. The Doge was neither similar to a duke in the modern sense nor was it meant as a hereditary position. The doge was rather a lifetime appointment much like the Pope for the Roman Catholic Church. Furthermore, doges were elected by the ruling elite of Venice, namely its wealthy oligarchy merchant class. The doge didn't have well defined & precise powers throughout the republic's 1,100-year history. It varied from great autocracy in the early parts of the republic to increasing regulation and restriction by the late 13th century onward. Though the doge always maintained a symbolic and ceremonial role throughout the republic's history. Some doges were forcibly removed from power and post-1268 until a new doge could be elected, the republic's rule transferred to the most senior ducal counsellor with the style of "vicedoge". After a doge's death following a commission was formed to study the doge's life and review it for moral and ethical transgressions and placed judgment upon him posthumously. If the commission found the deceased doge to have transgressed, his estate could be found liable and subject to fines. The doge was given plenty of ceremonial roles such as heading the symbolic marriage of Venice to the sea by casting a marriage ring into the sea from the doge's barge (similar to a royal yacht). Additionally, the doge was treated in foreign relations akin to a prince. It's titles and styles include "My Lord the Doge", "Most Serene Prince" and "His Serenity". The doge resided in the ducal palace (Palazzo Ducale) or Doge's Palace on the lagoonfront in Venice next St. Mark's Basilica and St. Mark's Square.
While the doge remained the symbolic and nominal head of the government, the oligarchy remained supreme overall. The supreme political organ was the 480-member Great Council. This assembly elected many of the office holders within the republic (including the doge) and the various senior councils tasked with administration, passing laws and judicial oversight. The Great Council's membership post 1297 was restricted to an inheritance by members of the patrician elite of the city of Venice's most noble families recorded in the famed Golden Book. This was divided between the old houses of the republic's earliest days and newer mercantile families if their fortunes should attain them property ownership and wealth. These families usually ranged between 20-30 total. They were socially forbidden from marrying outside their class & usually intermarried for political and economic reasons. Their economic concerns were chief to the whole of the republic and most centered on Eurasian & African trade throughout the Mediterranean Sea's basin. Members of these families served in the military and eventually rose to prominent positions of administration throughout the republic.
The Great Council overtime circumscribed the doge's power by creating councils devoted to oversight of the doge or executive and administrative functions (similar to modern executive cabinets or departments) whereas the doge became more and more a ceremonial role. The also created a senate which handled daily legislation. They also created a Council of Ten set to have authority over all government action. Other bodies were formed from this Great Council and others overtime. This resulted in intricate and overlapping yet separate bodies which found themselves subject to limitations with various checks on virtually each other's power. Essentially running as committees or sub-committees with checks on another committee's powers. These bodies weren't always completely defined in their scope and overtime their complexity led to battles to limit other's power (with limited success) along with gradual obsolescence and sometimes slow grinding administration.
Military: The military of Venice consisted of a relatively small army and a powerful navy. The famed Venetian Arsenal in Venice proper was essentially a complex of armories and shipyards to build and arm Venice's navy. The arsenal in Venice has the capacity to mass produce ships and weapons in the Middle Ages, centuries before the Industrial Revolution allowed for modern mass production in economic and military applications. Venice's military was designed towards protecting it possessions both in Italy and its overseas territories. The primary concern was to secure Venice's trade routes to the rest of Europe as well as Asia & Africa. It faced opponents' overtime ranging from the Franks, the Byzantine Empire, Bulgarians to other Italian city-states, France, Austria, the Ottoman Empire and Barbary Corsairs along with European pirates in the Adriatic and Mediterranean. It played key roles as a naval transport in other powers including throughout the Crusades. It also played a key role in the infamous Fourth Crusade which culminated in the Sack of Constantinople in 1204 AD, an event which fractured the Byzantine Empire into a half-century of civil war between successor states before a weakened revival in the mid 13th century. The Byzantine Empire would linger until the 15th century when the Ottoman Empire finally conquered its last remaining portions. Many attribute this loss to in part to its weakness still resulting from that 1204 sack lead by Venice. The Venetian military would exist until the republic's end when The French Republic's Army of Italy under Napoleon Bonaparte conquered the republic, a conquest in which the Venetians surrendered without a proper fight.
Economy: Venice's economy was based largely in trade. Namely control over the salt trade. Venice was to control salt (preservative of food) production and trade throughout the Mediterranean. It also traded in commodities associated with the salt trade routes to Eurasia and Africa. These commodities could include other foodstuffs (grains, meats & cheeses), textiles & glassware among other items.
Lifespan: 697AD-1797AD. Though the exact founding of Venice itself hasn't been determined. It is traditionally said to have taken place in the year 421 AD. At a time when Roman citizens in northeast Italy were escaping waves of Germanic & Hunnic barbarian invasions that contributed to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. The going theory is that these Romans evaded barbarian attacks by building their homes in the Venetian Lagoon by hammering wood stakes to form a foundation which sunk into the muddy shallows and petrified. Upon which they built their homes and created a cityscape marked by streets and canals interlaced. Venice remained a community of fishermen and merchants and was nominally under the control of the surviving Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire). It avoided barbarians overrunning the land but also was removed enough from Constantinople that it was relatively autonomous and became strategically important as a port. Other islands in the lagoon also banded together with Venice in a loose confederation of sorts by the 6th and 7th centuries which increased economic productivity and security for the city. The first doge was said to have been elected in 697 AD under the name Paolo Lucio Anafesto, though there is dispute about his historicity. Anafesto supposedly ruled until 717 AD. This is traditionally regarded as the foundation of the Republic of Venice.
Venice's third doge was Orso Ipato who reigned from 726-737 and he is the first undisputed historically recorded doge whose existence was confirmed. Orso also known as Ursus was known to strengthen the city's navy and army to protect it from the Lombard Germanic invaders who had overrun and ruled Italy by that time. Though nominally part of the Byzantine Empire, by 803, the Byzantine Emperors are said to have recognized Venice's de-facto independence. Though this view is disputed somewhat, it nevertheless remained virtually independent until its collapse in 1797.
Venice also partook in the slave trade of non-Christian European populations from Eastern Europe and transferred them to North Africa, selling them to the Arab and Berber (Moors) of the Islamic world.
As the 9th century progressed, the Venetian navy secured the Adriatic and various trade routes by defeating Slavic and Muslim pirates in the region. The Venetians also went onto battle the Normans who settled in southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Venice provided naval transports for Crusaders from Western Europe starting with the successful First Crusade.
The High Middle Ages (1000AD-1350AD) saw the wealth and expansion Venice increase dramatically. However, over this period Venice gradually came into mixed relations with its former ruler the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine Empire endured corruption, civil war and foreign invasion which saw it alternate between periods of waning power and restored power. Venice provided the Byzantines with an increased naval force when needed and many trading commodities. In exchange for this, Venice was granted trading rights within Byzantine territory and a place within the "Latin Quarter" for Western Europeans in Constantinople. The Byzantine populace though calling themselves "Romans" having taken on the political & cultural institutions of the Roman Empire which lived on in the East long after the Western half's collapse, were in fact mostly Greek by ethnicity, language and culture. Their religion was the Eastern Orthodox or Greek Orthodox branch of Christianity which was often at odds with Roman Catholics of Western Europe. Resentment at the religious and cultural differences along with the economic displacement the Venetians and other Italian merchants from Genoa & Pisa had caused in Constantinople's maritime & financial sectors contributed to the 1182 "Massacre of the Latins" in which the Byzantine Greek majority of the city rioted and slaughtered much of the 60,000 mostly Italian Catholics living within the city. Thousands were also sold into slavery to the Anatolian Seljuk Turks.
This event lingered in Venice's memory as its trade in the city was reduced for awhile. Though trade resumed between the Byzantines and the West again shortly thereafter, the event soured the perception of the Greeks to Western Europeans. This along with a subsequent power struggle for the throne of the Eastern Roman Emperor fell into Venice & Western Crusader's hands in 1202. Looking to originally ferry Western Crusaders to the Levant against the Islamic Ayyubid Sultanate of Egypt & Syria. Events transpired that devolved into Venice conspiring under its doge Enrico Dandalo along with other Western leaders and a Byzantine claimant to the throne that resulted in the first successful sacking of Constantinople in 1204. The city was ransacked, some Greek citizens murdered by the Crusaders & classical works of art destroyed or looted (most famously the four bronze horses of St. Marks in Venice) and politically, the Byzantine Empire would be temporarily fractured between competing Greek dynasties while the Crusaders along with Venice created the short-lived Latin Empire, which controlled Constantinople and its environs while Venice also acquired Greek territories which it was to hold for centuries. Venice also came into conflict with the Second Bulgarian Empire at this time as its support of the Latin Empire of Constantinople encroached on the Bulgarian's land. Eventually by the mid 13th century the Latin Empire (never fully stable) collapsed, and the Byzantine Empire was restored until the mid-15th century but forever weakened as a result of the 1204 sacking of its capital.
Venice reached trade deals with the Mongol Empire in 1221. As the century wore on, it also engaged its rival in Western Italy Genoa in some warfare.
The 14th century is generally regarded as Venice at its peak as it faced down Genoa in a number of battles and came to be the most dominant trading power in the Mediterranean, though it was impacted by the Black Death plague. Nevertheless, into the 15th and even 16th centuries, it partook in a number of wars which saw it gain territory on the Italian mainland, establishing its terraferma domain.
By the 16th late 15th and into the 16th century new threats had emerged such as the Turkish Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman capture of Constantinople in 1453 is seen as the end of the Middle Ages as the last political vestiges of the Roman Empire vanished from the world stage. However, a number of Byzantine Greeks escaped on Italian ships during the conquest of the city and others escaped Greece in subsequent years. These refugees brought with them artistic and cultural heritages that reemphasized the classical forms of Ancient Greece and Rome and lead to the Italian Rennaisance in art & other forms of culture. Ideas which emphasized humanism and spread to elsewhere in Europe overtime.
While there was a cultural flourishing in Venice and elsewhere due to the Rennaisance. There was also the first signs of economic and political decline as well from the 16th century onwards. The Ottoman dominance in the Eastern Mediterranean meant the traditional trade routes to the East were cut off by an often-hostile Muslim power. Additionally, other maritime powers in the West namely Spain & Portugal had recently begun exploring the continents of South & North America and in time France, England & the Netherlands would join in them. This decline in Eastern trade and the newfound trade routes dominated by other European states in the Americas and Asia (by way of rounding Africa) would render trade with Venice gradually obsolete. Venice would still maintain what trade it could in the Mediterranean, but it also focused on production and placed increasing importance on its Italian mainland possessions rather than just its declining position overseas in Greek territories, including the loss of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571. Though the Venetian navy with other Christian powers won the notable naval victory against the Ottomans in 1570 at Lepanto.
It was also involved in the Italian Wars between various rival city states and the power struggle between the Papacy, France and the Hapsburg realms of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain.
Other factors that impacted the declining trade in the 17th century included an inability to keep up in the textile trade elsewhere in Europe, closure of the spice trade to all but the Spanish, Dutch, Portuguese, French and English and the Thirty Years War (1618-1648) which impacted Venice's trade partners.
Ongoing wars including a 21-year siege of Crete by the Ottomans saw further losses. Although Venice partook in the Holy League headed by the Holy Roman Empire (under Hapsburg Austria) which saw some minor temporary gains from the Ottomans in southern Greece before losing them again in the early 18th century.
War and loss of overseas territories along with a stagnant economy was slightly offset by a somewhat strong position in northern Italy. Nevertheless, its maritime fleet was reduced to a mere shadow of its former glory and it found itself sandwiched still between Austria and France. Over the rest of the 18th century, economic stagnation and social stratification remained prevalent while Venice remained in a quiet peace. However, the French Revolution reignited war in Italy and while Venice remained neutral, it would soon get caught up in events.
The Austrians and the Piedmontese (Italian) allies were beaten by the French Republic's Army of Italy headed by an up-and-coming general named Napoleon Bonaparte. Bonaparte and the French army crossed the borders of northern Italy into Venetian neutral territory to pursue the Austrians. Eventually half of Venice's territory was occupied by France and the remainder of the mainland was occupied by Austria. By secret treaty the French and Austrians were to divide the territory between themselves (Venice was consulted in the matter). Bonaparte gave orders to Venetian doge Ludovico Manin to surrender the city to French occupation to which he abdicated his power. The republic's Major Council met one last time to officially declare an end to republic on May 12th, 1797, after 1,100 years. Venice was placed under a provisional government and ironically the French looted Venice stripping it of artworks to grace the Louvre Museum in Paris along with the Arc d'Triomphe, taking the famed four bronze horses of St. Mark's to adorn the triumphal arch in Paris, the very same horses Venice had confiscated from Constantinople in 1204. It was a symbolic end to the republic, the irony of which did not escape commentators at the time. Following Napoleonic France's final defeat in 1815 the horses were returned to Venice and St. Mark's where they remain today. Venice itself was given over to the Austrian Empire.
The Republic of Venice has a historical legacy in terms of its economic accomplishments through control of trade and its innovative mass production of ships, armaments & trade commodities. It also holds a political legacy worthy of study given it was a unique and enduring polity for 1,100 years. One that maintained a complex and at times chaotic form of government that still managed to function and endure for centuries.
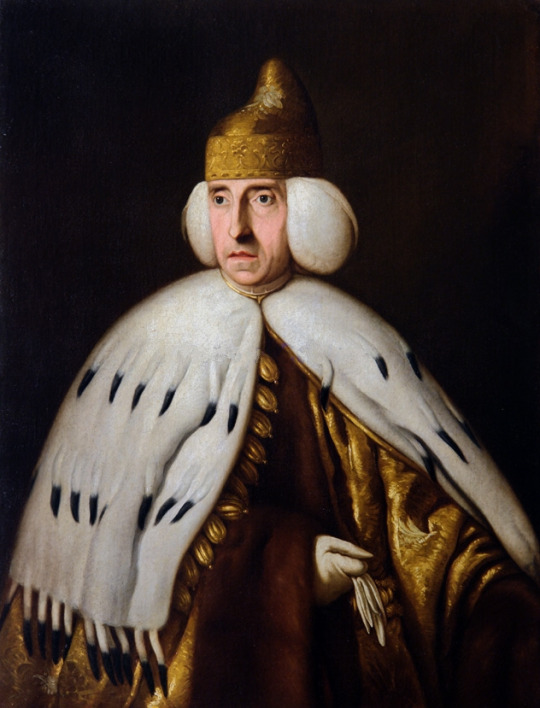
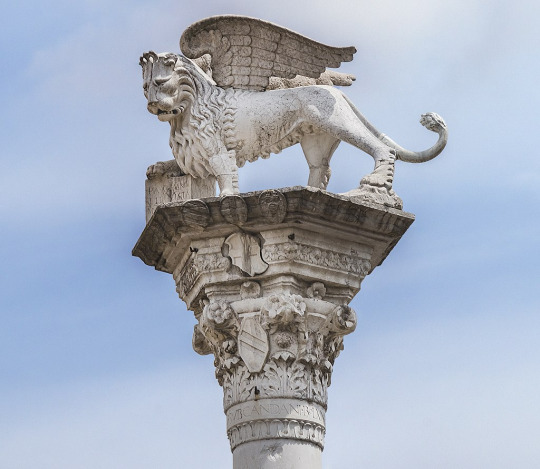



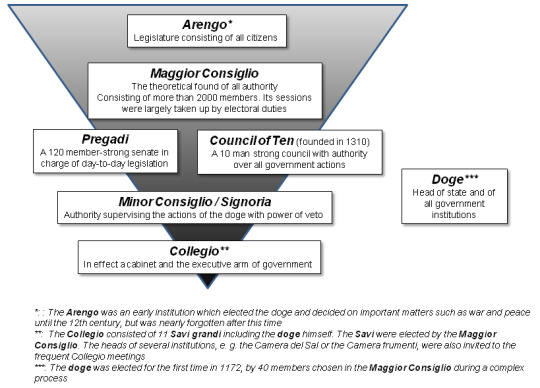






#military history#middle ages#venice#venetian republic#italy#politics#political history#trade#economics#governance#commerce#ottoman empire#spain#byzantine empire#napoleon#doge#republic
73 notes
·
View notes
Text

Conclusion: May Day today
The Haymarket Tragedy remains a symbol of countless struggles against capitalism, the State and oppression. Freedoms won in recent times rest on the sacrifices of martyrs like the IWPA anarchists, and the Malawian workers of 1959, 1992 and 1993.
May Day is a symbol of the unshakeable power of working class solidarity, and of remembrance for martyrs. It can serve as a rallying point for new anti-capitalist, participatory-democratic left resistance.
We need to defend and extend the legacy of the Haymarket affair, and to build the working class as a power-from-below for social change.
#history#Malawi#May Day#labor#malawian politics#anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#community building#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#anarchy#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economics#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment
17 notes
·
View notes