#informed search algorithms in artificial intelligence
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The surprising truth about data-driven dictatorships

Here’s the “dictator’s dilemma”: they want to block their country’s frustrated elites from mobilizing against them, so they censor public communications; but they also want to know what their people truly believe, so they can head off simmering resentments before they boil over into regime-toppling revolutions.
These two strategies are in tension: the more you censor, the less you know about the true feelings of your citizens and the easier it will be to miss serious problems until they spill over into the streets (think: the fall of the Berlin Wall or Tunisia before the Arab Spring). Dictators try to square this circle with things like private opinion polling or petition systems, but these capture a small slice of the potentially destabiziling moods circulating in the body politic.
Enter AI: back in 2018, Yuval Harari proposed that AI would supercharge dictatorships by mining and summarizing the public mood — as captured on social media — allowing dictators to tack into serious discontent and diffuse it before it erupted into unequenchable wildfire:
https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2018/10/yuval-noah-harari-technology-tyranny/568330/
Harari wrote that “the desire to concentrate all information and power in one place may become [dictators] decisive advantage in the 21st century.” But other political scientists sharply disagreed. Last year, Henry Farrell, Jeremy Wallace and Abraham Newman published a thoroughgoing rebuttal to Harari in Foreign Affairs:
https://www.foreignaffairs.com/world/spirals-delusion-artificial-intelligence-decision-making
They argued that — like everyone who gets excited about AI, only to have their hopes dashed — dictators seeking to use AI to understand the public mood would run into serious training data bias problems. After all, people living under dictatorships know that spouting off about their discontent and desire for change is a risky business, so they will self-censor on social media. That’s true even if a person isn’t afraid of retaliation: if you know that using certain words or phrases in a post will get it autoblocked by a censorbot, what’s the point of trying to use those words?
The phrase “Garbage In, Garbage Out” dates back to 1957. That’s how long we’ve known that a computer that operates on bad data will barf up bad conclusions. But this is a very inconvenient truth for AI weirdos: having given up on manually assembling training data based on careful human judgment with multiple review steps, the AI industry “pivoted” to mass ingestion of scraped data from the whole internet.
But adding more unreliable data to an unreliable dataset doesn’t improve its reliability. GIGO is the iron law of computing, and you can’t repeal it by shoveling more garbage into the top of the training funnel:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/05/29/garbage-in-garbage-out-machine-learning-has-not-repealed-the-iron-law-of-computer-science/
When it comes to “AI” that’s used for decision support — that is, when an algorithm tells humans what to do and they do it — then you get something worse than Garbage In, Garbage Out — you get Garbage In, Garbage Out, Garbage Back In Again. That’s when the AI spits out something wrong, and then another AI sucks up that wrong conclusion and uses it to generate more conclusions.
To see this in action, consider the deeply flawed predictive policing systems that cities around the world rely on. These systems suck up crime data from the cops, then predict where crime is going to be, and send cops to those “hotspots” to do things like throw Black kids up against a wall and make them turn out their pockets, or pull over drivers and search their cars after pretending to have smelled cannabis.
The problem here is that “crime the police detected” isn’t the same as “crime.” You only find crime where you look for it. For example, there are far more incidents of domestic abuse reported in apartment buildings than in fully detached homes. That’s not because apartment dwellers are more likely to be wife-beaters: it’s because domestic abuse is most often reported by a neighbor who hears it through the walls.
So if your cops practice racially biased policing (I know, this is hard to imagine, but stay with me /s), then the crime they detect will already be a function of bias. If you only ever throw Black kids up against a wall and turn out their pockets, then every knife and dime-bag you find in someone’s pockets will come from some Black kid the cops decided to harass.
That’s life without AI. But now let’s throw in predictive policing: feed your “knives found in pockets” data to an algorithm and ask it to predict where there are more knives in pockets, and it will send you back to that Black neighborhood and tell you do throw even more Black kids up against a wall and search their pockets. The more you do this, the more knives you’ll find, and the more you’ll go back and do it again.
This is what Patrick Ball from the Human Rights Data Analysis Group calls “empiricism washing”: take a biased procedure and feed it to an algorithm, and then you get to go and do more biased procedures, and whenever anyone accuses you of bias, you can insist that you’re just following an empirical conclusion of a neutral algorithm, because “math can’t be racist.”
HRDAG has done excellent work on this, finding a natural experiment that makes the problem of GIGOGBI crystal clear. The National Survey On Drug Use and Health produces the gold standard snapshot of drug use in America. Kristian Lum and William Isaac took Oakland’s drug arrest data from 2010 and asked Predpol, a leading predictive policing product, to predict where Oakland’s 2011 drug use would take place.
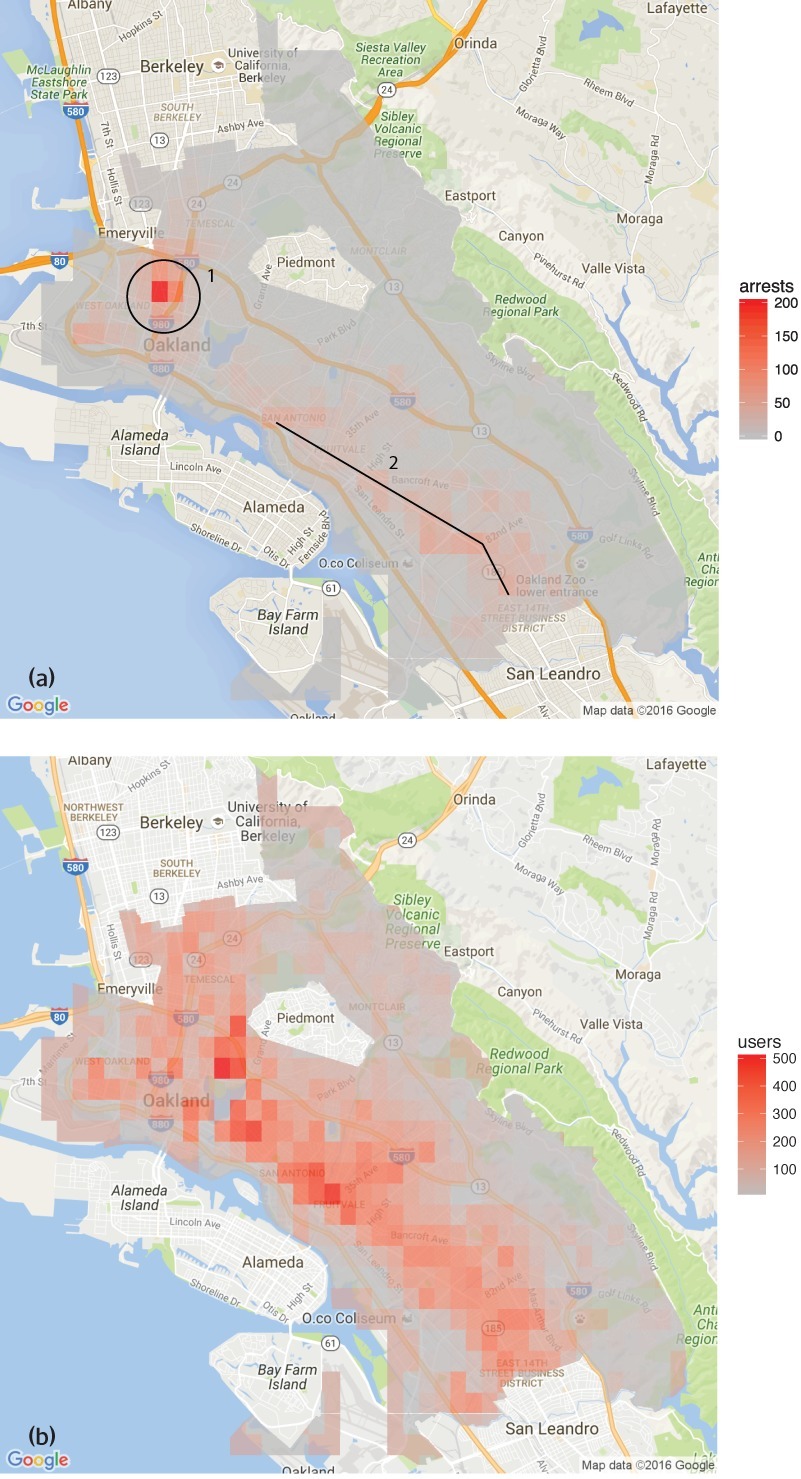
[Image ID: (a) Number of drug arrests made by Oakland police department, 2010. (1) West Oakland, (2) International Boulevard. (b) Estimated number of drug users, based on 2011 National Survey on Drug Use and Health]
Then, they compared those predictions to the outcomes of the 2011 survey, which shows where actual drug use took place. The two maps couldn’t be more different:
https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1740-9713.2016.00960.x
Predpol told cops to go and look for drug use in a predominantly Black, working class neighborhood. Meanwhile the NSDUH survey showed the actual drug use took place all over Oakland, with a higher concentration in the Berkeley-neighboring student neighborhood.
What’s even more vivid is what happens when you simulate running Predpol on the new arrest data that would be generated by cops following its recommendations. If the cops went to that Black neighborhood and found more drugs there and told Predpol about it, the recommendation gets stronger and more confident.
In other words, GIGOGBI is a system for concentrating bias. Even trace amounts of bias in the original training data get refined and magnified when they are output though a decision support system that directs humans to go an act on that output. Algorithms are to bias what centrifuges are to radioactive ore: a way to turn minute amounts of bias into pluripotent, indestructible toxic waste.
There’s a great name for an AI that’s trained on an AI’s output, courtesy of Jathan Sadowski: “Habsburg AI.”
And that brings me back to the Dictator’s Dilemma. If your citizens are self-censoring in order to avoid retaliation or algorithmic shadowbanning, then the AI you train on their posts in order to find out what they’re really thinking will steer you in the opposite direction, so you make bad policies that make people angrier and destabilize things more.
Or at least, that was Farrell(et al)’s theory. And for many years, that’s where the debate over AI and dictatorship has stalled: theory vs theory. But now, there’s some empirical data on this, thanks to the “The Digital Dictator’s Dilemma,” a new paper from UCSD PhD candidate Eddie Yang:
https://www.eddieyang.net/research/DDD.pdf
Yang figured out a way to test these dueling hypotheses. He got 10 million Chinese social media posts from the start of the pandemic, before companies like Weibo were required to censor certain pandemic-related posts as politically sensitive. Yang treats these posts as a robust snapshot of public opinion: because there was no censorship of pandemic-related chatter, Chinese users were free to post anything they wanted without having to self-censor for fear of retaliation or deletion.
Next, Yang acquired the censorship model used by a real Chinese social media company to decide which posts should be blocked. Using this, he was able to determine which of the posts in the original set would be censored today in China.
That means that Yang knows that the “real” sentiment in the Chinese social media snapshot is, and what Chinese authorities would believe it to be if Chinese users were self-censoring all the posts that would be flagged by censorware today.
From here, Yang was able to play with the knobs, and determine how “preference-falsification” (when users lie about their feelings) and self-censorship would give a dictatorship a misleading view of public sentiment. What he finds is that the more repressive a regime is — the more people are incentivized to falsify or censor their views — the worse the system gets at uncovering the true public mood.
What’s more, adding additional (bad) data to the system doesn’t fix this “missing data” problem. GIGO remains an iron law of computing in this context, too.
But it gets better (or worse, I guess): Yang models a “crisis” scenario in which users stop self-censoring and start articulating their true views (because they’ve run out of fucks to give). This is the most dangerous moment for a dictator, and depending on the dictatorship handles it, they either get another decade or rule, or they wake up with guillotines on their lawns.
But “crisis” is where AI performs the worst. Trained on the “status quo” data where users are continuously self-censoring and preference-falsifying, AI has no clue how to handle the unvarnished truth. Both its recommendations about what to censor and its summaries of public sentiment are the least accurate when crisis erupts.
But here’s an interesting wrinkle: Yang scraped a bunch of Chinese users’ posts from Twitter — which the Chinese government doesn’t get to censor (yet) or spy on (yet) — and fed them to the model. He hypothesized that when Chinese users post to American social media, they don’t self-censor or preference-falsify, so this data should help the model improve its accuracy.
He was right — the model got significantly better once it ingested data from Twitter than when it was working solely from Weibo posts. And Yang notes that dictatorships all over the world are widely understood to be scraping western/northern social media.
But even though Twitter data improved the model’s accuracy, it was still wildly inaccurate, compared to the same model trained on a full set of un-self-censored, un-falsified data. GIGO is not an option, it’s the law (of computing).
Writing about the study on Crooked Timber, Farrell notes that as the world fills up with “garbage and noise” (he invokes Philip K Dick’s delighted coinage “gubbish”), “approximately correct knowledge becomes the scarce and valuable resource.”
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/07/25/51610/
This “probably approximately correct knowledge” comes from humans, not LLMs or AI, and so “the social applications of machine learning in non-authoritarian societies are just as parasitic on these forms of human knowledge production as authoritarian governments.”

The Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers’ Workshop summer fundraiser is almost over! I am an alum, instructor and volunteer board member for this nonprofit workshop whose alums include Octavia Butler, Kim Stanley Robinson, Bruce Sterling, Nalo Hopkinson, Kameron Hurley, Nnedi Okorafor, Lucius Shepard, and Ted Chiang! Your donations will help us subsidize tuition for students, making Clarion — and sf/f — more accessible for all kinds of writers.

Libro.fm is the indie-bookstore-friendly, DRM-free audiobook alternative to Audible, the Amazon-owned monopolist that locks every book you buy to Amazon forever. When you buy a book on Libro, they share some of the purchase price with a local indie bookstore of your choosing (Libro is the best partner I have in selling my own DRM-free audiobooks!). As of today, Libro is even better, because it’s available in five new territories and currencies: Canada, the UK, the EU, Australia and New Zealand!

[Image ID: An altered image of the Nuremberg rally, with ranked lines of soldiers facing a towering figure in a many-ribboned soldier's coat. He wears a high-peaked cap with a microchip in place of insignia. His head has been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.' The sky behind him is filled with a 'code waterfall' from 'The Matrix.']

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Raimond Spekking (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acer_Extensa_5220_-_Columbia_MB_06236-1N_-_Intel_Celeron_M_530_-_SLA2G_-_in_Socket_479-5029.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
—
Russian Airborne Troops (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vladislav_Achalov_at_the_Airborne_Troops_Day_in_Moscow_%E2%80%93_August_2,_2008.jpg
“Soldiers of Russia” Cultural Center (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Col._Leonid_Khabarov_in_an_everyday_service_uniform.JPG
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#habsburg ai#self censorship#henry farrell#digital dictatorships#machine learning#dictator's dilemma#eddie yang#preference falsification#political science#training bias#scholarship#spirals of delusion#algorithmic bias#ml#Fully automated data driven authoritarianism#authoritarianism#gigo#garbage in garbage out garbage back in#gigogbi#yuval noah harari#gubbish#pkd#philip k dick#phildickian
833 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blog Post #3
Q1: Although social media is public, are there moral issues for the monopolization of spaces in which marginalized groups may go to cry and create change (especially while taking into account current government states)?
In the revolution will be digitized, the authors discuss the role of the internet as a public sphere for activism for black activism, during a time in which there was a lack of safe, public spheres for social change. (Everett, 2011). This book was created in 2011, before the extreme monopolization of social media platforms. The use of unofficial forum websites have died down, and individuals often use these new platforms to elicit social movement and create eroding change. However, especially taking into account the current climate of politics, and the digital revenue based oligarchy that appears to be forming within the United States, I would like to question what the moral implications of these “public spheres”, when taking into account that the attention we provide, the adds we watch, and the data we give, all seems to line the pockets of capitalist oppressors.
Q 2: The new jim code states “thus, even just deciding what problem needs solving requires a host of judgements; and yet we are expected to pay no attention to the man behind the screen”. In what ways do narratives and discussions around new technologies affirming the idea that new technologies are “unbiased”?
Algorithms and data driven decision making is often seen as “out of the hands” of individual technicians and social media programers. As is stated in the race after technology, the new Jim Code article (Benjamin, 2020), a neoliberalism, colorblind view of technology has taken president. I reflected back on my own experiences prior to this class, as I also had lived under the assumption that algorithms were deemed as absolute. After taking into account my previous opinions on algorithms, and what this article states in regards to neoliberalism and productivity, I realized that production in “logic” has been moralized as being good, without further thought. Logic being different then empirical evidence, logic more so meaning a no nonsense, individualistic approach to the world.
Q3: How does the exclusivity and gatekeeping of knowledge about algorithms contribute to its continued harm, as in regards for marginalized communities.
In this week's Power of Algorithms chapter, the author states “It is impossible to know when and what influences proprietary algorithmic design, … except as we engage in critique and protest” (Noble, 2018). This statement made me question, how has the privatization of these public spaces prevented marginalized individuals from being a part of the conversation when it comes to their own algorithms, and what information they see? If updates and changes are made that change the info that people are exposed to, then why are consumers NOT more a part of the algorithm creation process?
Q4: How might issues regarding online algorithms worsen as Artificial intelligence takes search engines by storm, now automatically generating simple consumable answers?
This question stems from an ending remark made in the power of algorithms chapter (Noble, 2018), stating that there is a lack of human context in some types of algorithmically driven decisions.? Questions for me arise, such as, what results are used in the AI image generations? It can’t be all sources, are they the sources that pay money to be prioritized on google? The further distilling of responsibility (now AI being seen as absolute truth) may make it even harder for individuals to fight against algorithmic oppression, because it adds another “middle man”.
References:
Benjamin, R. (2020). Race After Technology: Abolitionist Tools for the New Jim Code. Polity.
Everett, A. (2011). “The Revolution Will Be Digitized: Reimaging Africanity in Cyberspace.” Digital Diaspora: A Race for Cyberspace, State University of New York Press, pp. 147–82.
Noble, S. U. (2018). Algorithms of Oppression: How Search Engines Reinforce Racism. New York University Press.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Recently, I was using Google and stumbled upon an article that felt eerily familiar.
While searching for the latest information on Adobe’s artificial intelligence policies, I typed “adobe train ai content” into Google and switched over to the News tab. I had already seen WIRED’s coverage that appeared on the results page in the second position: “Adobe Says It Won’t Train AI Using Artists’ Work. Creatives Aren’t Convinced.” And although I didn’t recognize the name of the publication whose story sat at the very top of the results, Syrus #Blog, the headline on the article hit me with a wave of déjà vu: “When Adobe promised not to train AI on artists’ content, the creative community reacted with skepticism.”
Clicking on the top hyperlink, I found myself on a spammy website brimming with plagiarized articles that were repackaged, many of them using AI-generated illustrations at the top. In this spam article, the entire WIRED piece was copied with only slight changes to the phrasing. Even the original quotes were lifted. A single, lonely hyperlink at the bottom of the webpage, leading back to our version of the story, served as the only form of attribution.
The bot wasn’t just copying journalism in English—I found versions of this plagiarized content in 10 other languages, including many of the languages that WIRED produces content in, like Japanese and Spanish.
Articles that were originally published in outlets like Reuters and TechCrunch were also plagiarized on this blog in multiple languages and given similar AI images. During late June and early July, while I was researching this story, the website Syrus appeared to have gamed the News results for Google well enough to show up on the first page for multiple tech-related queries.
For example, I searched “competing visions google openai” and saw a TechCrunch piece at the top of Google News. Below it were articles from The Atlantic and Bloomberg comparing the rival companies’ approaches to AI development. But then, the fourth article to appear for that search, nestled right below these more reputable websites, was another Syrus #Blog piece that heavily copied the TechCrunch article in the first position.
As reported by 404 Media in January, AI-powered articles appeared multiple times for basic queries at the beginning of the year in Google News results. Two months later, Google announced significant changes to its algorithm and new spam policies, as an attempt to improve the search results. And by the end of April, Google shared that the major adjustments to remove unhelpful results from its search engine ranking system were finished. “As of April 19, we’ve completed the rollout of these changes. You’ll now see 45 percent less low-quality, unoriginal content in search results versus the 40 percent improvement we expected across this work,” wrote Elizabeth Tucker, a director of product management at Google, in a blog post.
Despite the changes, spammy content created with the help of AI remains an ongoing, prevalent issue for Google News.
“This is a really rampant problem on Google right now, and it's hard to answer specifically why it's happening,” says Lily Ray, senior director of search engine optimization at the marketing agency Amsive. “We've had some clients say, ‘Hey, they took our article and rehashed it with AI. It looks exactly like what we wrote in our original content but just kind of like a mumbo-jumbo, AI-rewritten version of it.’”
At first glance, it was clear to me that some of the images for Syrus’ blogs were AI generated based on the illustrations’ droopy eyes and other deformed physical features—telltale signs of AI trying to represent the human body.
Now, was the text of our article rewritten using AI? I reached out to the person behind the blog to learn more about how they made it and received confirmation via email that an Italian marketing agency created the blog. They claim to have used an AI tool as part of the writing process. “Regarding your concerns about plagiarism, we can assure you that our content creation process involves AI tools that analyze and synthesize information from various sources while always respecting intellectual property,” writes someone using the name Daniele Syrus over email.
They point to the single hyperlink at the bottom of the lifted article as sufficient attribution. While better than nothing, a link which doesn’t even mention the publication by name is not an adequate defense against plagiarism. The person also claims that the website’s goal is not to receive clicks from Google’s search engine but to test out AI algorithms in multiple languages.
When approached over email for a response, Google declined to comment about Syrus. “We don’t comment on specific websites, but our updated spam policies prohibit creating low-value, unoriginal content at scale for the purposes of ranking well on Google,” says Meghann Farnsworth, a spokesperson for Google. “We take action on sites globally that don’t follow our policies.” (Farnsworth is a former WIRED employee.)
Looking through Google’s spam policies, it appears that this blog does directly violate the company’s rules about online scraping. “Examples of abusive scraping include: … sites that copy content from other sites, modify it only slightly (for example, by substituting synonyms or using automated techniques), and republish it.” Farnsworth declined to confirm whether this blog was in violation of Google’s policies or if the company would de-rank it in Google News results based on this reporting.
What can the people who write original articles do to properly protect their work? It’s unclear. Though, after all of the conversations I’ve had with SEO experts, one major through line sticks out to me, and it’s an overarching sense of anxiety.
“Our industry suffers from some form of trauma, and I'm not even really joking about that,” says Andrew Boyd, a consultant at an online link-building service called Forte Analytica. “I think one of the main reasons for that is because there's no recourse if you're one of these publishers that's been affected. All of a sudden you wake up in the morning, and 50 percent of your traffic is gone.” According to Boyd, some websites lost a majority of their visitors during Google’s search algorithm updates over the years.
While many SEO experts are upset with the lack of transparency about Google’s biggest changes, not everyone I spoke with was critical of the prevalence of spam in search results. “Actually, Google doesn't get enough credit for this, but Google's biggest challenge is spam.” says Eli Schwartz, the author of the book Product-Led SEO. “So, despite all the complaints we have about Google’s quality now, you don’t do a search for hardware and then find adult sites. They’re doing a good enough job.” The company continues to release smaller search updates to fight against spam.
Yes, Google sometimes offers users a decent experience by protecting them from seeing sketchy pornography websites when searching unrelated, popular queries. But it remains reasonable to expect one of the most powerful companies in the world—that has considerable influence over how online content is created, distributed, and consumed—to do a better job of filtering out plagiarizing, unhelpful content from the News results.
“It's frustrating, because we see we're trying to do the right thing, and then we see so many examples of this low-quality, AI stuff outperforming us,” says Ray. “So I'm hopeful that it's temporary, but it's leading to a lot of tension and a lot of animosity in our industry, in ways that I've personally never seen before in 15 years.” Unless spammy sites with AI content are stricken from the search results, publishers will now have less incentive to produce high-quality content and, in turn, users will have less reason to trust the websites appearing at the top of Google News.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Search Engines:
Search engines are independent computer systems that read or crawl webpages, documents, information sources, and links of all types accessible on the global network of computers on the planet Earth, the internet. Search engines at their most basic level read every word in every document they know of, and record which documents each word is in so that by searching for a words or set of words you can locate the addresses that relate to documents containing those words. More advanced search engines used more advanced algorithms to sort pages or documents returned as search results in order of likely applicability to the terms searched for, in order. More advanced search engines develop into large language models, or machine learning or artificial intelligence. Machine learning or artificial intelligence or large language models (LLMs) can be run in a virtual machine or shell on a computer and allowed to access all or part of accessible data, as needs dictate.
#llm#large language model#search engine#search engines#Google#bing#yahoo#yandex#baidu#dogpile#metacrawler#webcrawler#search engines imbeded in individual pages or operating systems or documents to search those individual things individually#computer science#library science#data science#machine learning#google.com#bing.com#yahoo.com#yandex.com#baidu.com#...#observe the buildings and computers within at the dalles Google data center to passively observe google and its indexed copy of the internet#the dalles oregon next to the river#google has many data centers worldwide so does Microsoft and many others
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital Marketing Skills to Learn in 2025
Key Digital Marketing Skills to Learn in 2025 to Stay Ahead of Competition The digital marketing landscape in 2025 is rapidly changing, driven by the technological advancements, shifting consumer behavior, and the growing power of artificial intelligence. Competition and career resilience require acquiring expertise in the following digital marketing skills.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data is the backbone of modern marketing strategies. The ability to collect, analyze, and make informed decisions based on large sets of data sets great marketers apart. Proficiency in analytical software like Google Analytics and AI-driven tools is critical in measuring campaign performance, optimizing strategies, and making data-driven decisions. Predictive analytics and customer journey mapping are also becoming more critical for trend spotting and personalization of user experience.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
SEO is still a fundamental skill, but the landscape is evolving. The marketer now has to optimize for traditional search engines, voice search, and even social media, as Gen Z increasingly relies on TikTok and YouTube as search tools. Keeping up with algorithm updates, keyword research skills, and technical SEO skills is essential to staying visible and driving organic traffic.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are revolutionizing digital marketing through the power to enable advanced targeting, automation, and personalization. Marketers will need to leverage AI in order to segment audiences, design content, deploy predictive analytics, and build chatbots. Most crucial will be understanding how to balance AI-based automation with human, authentic content.
Content Generation and Storytelling
Content is still king. Marketers must be great at creating great copy, video, and interactive content that is appropriate for various platforms and audiences. Emotionally resonant storytelling and brand affection are more critical than ever, particularly as human-created content trumps AI-created content consistently.
Social Media Strategy and Social Commerce Social media is still the foremost driver of digital engagement. Mastering techniques constructed for specific platforms—such as short-form video, live stream, and influencing with influencers—is critical. How to facilitate direct sales through social commerce, built on combining commerce and social interactions, is an area marketers must master.
Marketing Automation
Efficiency is the most critical in 2025. Marketing automation platforms (e.g., Marketo and HubSpot) enable marketers to automate repetitive tasks, nurture leads, and personalize customer journeys at scale.
UX/UI Design Principles
A seamless user experience and a pleasing design can either make or destroy online campaigns. Having UX/UI basics in your knowledge and collaborating with design teams ensures that marketing campaigns are both effective and engaging.
Ethical Marketing and Privacy Compliance
With data privacy emerging as a pressing issue, marketers must stay updated on laws like GDPR and CCPA. Ethical marketing and openness foster trust and avoid legal issues.
To lead in 2025, digital marketers will have to fuse technical skills, creativity, and flexibility. By acquiring these high-impact capabilities-data analysis, SEO, AI, content development, social strategy, automation, UX/UI, and ethical marketing-you'll be at the edge of the constantly evolving digital space
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Galambo: Transforming Visual Search with Cutting-Edge AI Technology
Ever wished for a tool that turns your images into a treasure trove of information? Galambo, the innovative AI-powered image search engine, is revolutionizing how we interact with visual content by providing in-depth insights and context that go beyond simple image recognition.
Galambo is leading the charge in advanced image search technology, utilizing powerful artificial intelligence to offer a deeper understanding of your photos. Unlike traditional search engines that only provide surface-level results, Galambo’s AI dives into the nuances of each image to deliver rich, contextual information that enhances your search experience.

One of the most compelling features of Galambo is its AI-driven predictive search. When you upload an image, Galambo’s sophisticated algorithms analyze its content and suggest relevant search queries. This predictive capability streamlines your search process, delivering accurate and relevant results quickly, and saving you valuable time.
Additionally, Galambo offers a dynamic interactive search feature. By clicking on different elements within an image, you can uncover additional details and related information. This feature transforms the search experience into an interactive exploration, allowing you to delve deeper into the context and significance of your images.
Galambo’s integration with various platforms further sets it apart. It seamlessly connects with mapping services to pinpoint locations, taps into extensive databases for comprehensive insights, and links with social media for a broader perspective. This all-in-one approach ensures you have all the information you need right at your fingertips.
Privacy and security are also top priorities for Galambo. The platform employs advanced security measures to protect your data, ensuring a safe and secure search experience.
In summary, Galambo is more than just an image search engine; it’s a powerful AI tool that enhances how you explore and understand visual content. With its advanced features, interactive search capabilities, and seamless integrations, Galambo is an essential tool for anyone looking to gain deeper insights from their images. Experience the future of image search with Galambo by visiting Galambo.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Week #4
Why are white and blacks so segregated to the point that even the names are vastly different and how does this affect society as a whole?
Due to the history of segregation in the past, it eventually trickled into modern day. In the article “Race After Technology”, the author describes how in our society we perceive white people as the “norm” due to their blandness in their culture and names. Because of this, they inherit some sort of “immunity” resulting from “invisibility”, helping them in situations such as interactions with the law. In African American culture, they tend to have “made up names”, which leads to noticeable differences further separating them from other societies. This counteracts the origins of a name, where it is made up and unique. This leads to stereotypes of each culture, how someone named “Alice Tang” may be more scholarly inclined or someone named “Tyrone Jackson” will be more focused on survival.
Is it reasonable to blame AI for following algorithms that were created by humans?
Since Artificial Intelligence is created by humans, it learns off what we do. It scours the internet for every piece of information possible, including things we post or search up. Knowing this, can we blame AI for racist remarks, even though it originated from humans and it is only a reflection of what society has become. As the article, “Algorithms of Oppression”, mentions how google results in African Americans with searches such as “gorilla”. To what extent can we shift the blame to AI or are we as a society going to sweep racism under the rug? I believe that we shouldn’t blame AI for racist remarks since it is only learning from how we humans are always at war with one another
Does invasion of privacy from the government lead to benefits to a community or is it just an excuse to invade privacy?
I believe that the government watches our every move and blames a certain group of people such as African American and Latinos, so it can seem more reasonable for them to track us. There are around 40,000 African Americans in the CalGang database and around 130,000 Latinos according to the article, “TrackandTrapped”. I believe they use this information for the benefits of society but for them to be able to do this they would have to track innocent civilians too, resulting in an unfair result for both groups. I do believe that tracking criminals is important to modern society, but it is a result of tracking innocent civilians too, leading to collateral damage on society as a whole.
How does gender affect the knowledge society receives?
In the Ted Talk by Kimberle Creshaw, she does an exercise listing names of people who were killed by police. If the crowd recognizes the name they will sit down, and during the first portion of naming male names most people stayed standing up. Eventually she heard female names and the majority of the audience sat down. I can relate this to my own knowledge, where I only remember the name of African American Males that have lost their life and not one female who has lost their life due to racial reasons. It is obvious the media focuses attention on males who are dealing with racial hardships but never the females. It makes me question why, especially if they are the same racial group, how does gender affect the attention of the media?
Benjamin, R. (2020). Race After Technology: Abolitionist Tools for the New Jim Code. Polity.
Crenshaw, K. (2016, December 7). The Urgency of Intersectionality. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=akOe5-UsQ2o
Everett, A. (2002). The Revolution Will Be Digitized. Duke University Press. https://read.dukeupress.edu/social-text/article-abstract/20/2%20(71)/125/32619/The-Revolution-Will-Be-DigitizedAFROCENTRICITY-AND?redirectedFrom=fulltext
5 notes
·
View notes
Text


Planning autonomous surface missions on ocean worlds
hrough advanced autonomy testbed programs, NASA is setting the groundwork for one of its top priorities—the search for signs of life and potentially habitable bodies in our solar system and beyond. The prime destinations for such exploration are bodies containing liquid water, such as Jupiter's moon Europa and Saturn's moon Enceladus.
Initial missions to the surfaces of these "ocean worlds" will be robotic and require a high degree of onboard autonomy due to long Earth-communication lags and blackouts, harsh surface environments, and limited battery life.
Technologies that can enable spacecraft autonomy generally fall under the umbrella of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and have been evolving rapidly in recent years. Many such technologies, including machine learning, causal reasoning, and generative AI, are being advanced at non-NASA institutions.
NASA started a program in 2018 to take advantage of these advancements to enable future icy world missions. It sponsored the development of the physical Ocean Worlds Lander Autonomy Testbed (OWLAT) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the virtual Ocean Worlds Autonomy Testbed for Exploration, Research, and Simulation (OceanWATERS) at NASA's Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California.
NASA solicited applications for its Autonomous Robotics Research for Ocean Worlds (ARROW) program in 2020, and for the Concepts for Ocean worlds Life Detection Technology (COLDTech) program in 2021.
Six research teams, based at universities and companies throughout the United States, were chosen to develop and demonstrate autonomy solutions on OWLAT and OceanWATERS. These two- to three-year projects are now complete and have addressed a wide variety of autonomy challenges faced by potential ocean world surface missions.
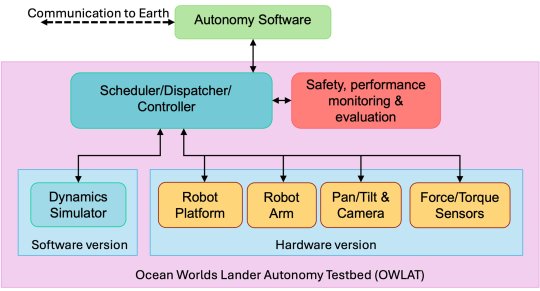
OWLAT
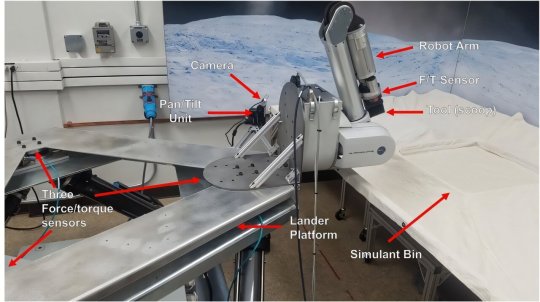
OWLAT is designed to simulate a spacecraft lander with a robotic arm for science operations on an ocean world body. Each of the OWLAT components is detailed below.
The hardware version of OWLAT is designed to physically simulate motions of a lander as operations are performed in a low-gravity environment using a six degrees-of-freedom (DOF) Stewart platform. A seven DOF robot arm is mounted on the lander to perform sampling and other science operations that interact with the environment. A camera mounted on a pan-and-tilt unit is used for perception.
The testbed also has a suite of onboard force/torque sensors to measure motion and reaction forces as the lander interacts with the environment. Control algorithms implemented on the testbed enable it to exhibit dynamics behavior as if it were a lightweight arm on a lander operating in different gravitational environments.
The team also developed a set of tools and instruments to enable the performance of science operations using the testbed. These various tools can be mounted to the end of the robot arm via a quick-connect-disconnect mechanism. The testbed workspace where sampling and other science operations are conducted incorporates an environment designed to represent the scene and surface simulant material potentially found on ocean worlds.
The software-only version of OWLAT models, visualizes, and provides telemetry from a high-fidelity dynamics simulator based on the Dynamics And Real-Time Simulation (DARTS) physics engine developed at JPL. It replicates the behavior of the physical testbed in response to commands and provides telemetry to the autonomy software.
The autonomy software module interacts with the testbed through a Robot Operating System (ROS)-based interface to issue commands and receive telemetry. This interface is defined to be identical to the OceanWATERS interface. Commands received from the autonomy module are processed through the dispatcher/scheduler/controller module and used to command either the physical hardware version of the testbed or the dynamics simulation (software version) of the testbed.
Sensor information from the operation of either the software-only or physical testbed is reported back to the autonomy module using a defined telemetry interface. A safety and performance monitoring and evaluation software module ensures that the testbed is kept within its operating bounds. Any commands causing out of bounds behavior and anomalies are reported as faults to the autonomy software module.
OceanWATERS
At the time of the OceanWATERS project's inception, Jupiter's moon Europa was planetary science's first choice in searching for life. Based on ROS, OceanWATERS is a software tool that provides a visual and physical simulation of a robotic lander on the surface of Europa.
OceanWATERS realistically simulates Europa's celestial sphere and sunlight, both direct and indirect. Because we don't yet have detailed information about the surface of Europa, users can select from terrain models with a variety of surface and material properties. One of these models is a digital replication of a portion of the Atacama Desert in Chile, an area considered a potential Earth-analog for some extraterrestrial surfaces.
JPL's Europa Lander Study of 2016, a guiding document for the development of OceanWATERS, describes a planetary lander whose purpose is collecting subsurface regolith/ice samples, analyzing them with onboard science instruments, and transmitting results of the analysis to Earth.
The simulated lander in OceanWATERS has an antenna mast that pans and tilts; attached to it are stereo cameras and spotlights. It has a 6 degree-of-freedom arm with two interchangeable end effectors—a grinder designed for digging trenches, and a scoop for collecting ground material. The lander is powered by a simulated non-rechargeable battery pack. Power consumption, the battery's state, and its remaining life are regularly predicted with the Generic Software Architecture for Prognostics (GSAP) tool.
To simulate degraded or broken subsystems, a variety of faults (e.g., a frozen arm joint or overheating battery) can be "injected" into the simulation by the user; some faults can also occur "naturally" as the simulation progresses, e.g., if components become over-stressed. All the operations and telemetry (data measurements) of the lander are accessible via an interface that external autonomy software modules can use to command the lander and understand its state. (OceanWATERS and OWLAT share a unified autonomy interface based on ROS.)
The OceanWATERS package includes one basic autonomy module, a facility for executing plans (autonomy specifications) written in the PLan EXecution Interchange Language, or PLEXIL. PLEXIL and GSAP are both open-source software packages developed at Ames and available on GitHub, as is OceanWATERS.
Mission operations that can be simulated by OceanWATERS include visually surveying the landing site, poking at the ground to determine its hardness, digging a trench, and scooping ground material that can be discarded or deposited in a sample collection bin. Communication with Earth, sample analysis, and other operations of a real lander mission, are not presently modeled in OceanWATERS except for their estimated power consumption.
Because of Earth's distance from the ocean worlds and the resulting communication lag, a planetary lander should be programmed with at least enough information to begin its mission. But there will be situation-specific challenges that will require onboard intelligence, such as deciding exactly where and how to collect samples, dealing with unexpected issues and hardware faults, and prioritizing operations based on remaining power.
Results
All six of the research teams used OceanWATERS to develop ocean world lander autonomy technology and three of those teams also used OWLAT. The products of these efforts were published in technical papers, and resulted in the development of software that may be used or adapted for actual ocean world lander missions in the future.
TOP IMAGE: Artist's concept image of a spacecraft lander with a robot arm on the surface of Europa. Credits: NASA/JPL – Caltech
CENTRE IMAGE The software and hardware components of the Ocean Worlds Lander Autonomy Testbed and the relationships between them. Credit: NASA/JPL – Caltech
LOWER IMAGE: The Ocean Worlds Lander Autonomy Testbed. A scoop is mounted to the end of the testbed robot arm. Credit: NASA/JPL – Caltech
BOTTOM IMAGE: Screenshot of OceanWATERS. Credit: NASA/JPL – Caltech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
SEO Services Company in Ahmedabad
In today's competitive digital landscape, having a strong online presence is essential for any business aiming to thrive. Growup Business Solution stands as the leading SEO Services Company in Ahmedabad, dedicated to elevating your brand's visibility and driving significant organic traffic to your website. As the #1 SEO Company in Ahmedabad, we offer comprehensive and tailored SEO strategies that cater to the specific needs of each client, ensuring your business stands out in the digital realm.
Our SEO Services in Ahmedabad are meticulously designed to address the diverse requirements of businesses across various sectors. We begin with an in-depth analysis of your current online presence, identifying key strengths and areas that need improvement.
Our team of seasoned SEO professionals then develops a customized strategy, incorporating keyword research, on-page optimization, content creation, and link building. By targeting the most relevant and high-traffic keywords, we ensure your website climbs the ranks on search engine results pages, increasing visibility and attracting potential customers.
At Growup Business Solution, we understand that effective SEO is not just about driving traffic but also about converting visitors into loyal customers. As the Best SEO Company in Ahmedabad, we focus on creating high-quality, engaging content that resonates with your audience and encourages them to take action. Our content marketing strategies are designed to add value to your visitors, establishing your brand as an authority in your industry and fostering trust and credibility.

One of the defining aspects of our SEO Services Company in Ahmedabad is our commitment to staying ahead of the curve. The digital landscape is constantly evolving, with search engine algorithms frequently updated. Our team of SEO experts is always abreast of the latest industry trends and best practices, ensuring that our clients benefit from innovative strategies that deliver long-term results. Whether it's optimizing for voice search, mobile-first indexing, or leveraging artificial intelligence, we have the expertise to keep your business ahead of the competition.
Moreover, our approach to SEO is data-driven and results-oriented. We provide regular reports and analytics, giving you clear insights into the performance of your SEO campaigns. This transparency allows us to make informed adjustments and continuously refine our strategies to maximize your return on investment. As the Top SEO Services in Ahmedabad, we pride ourselves on delivering measurable results that contribute to your business's growth and success.
Growup Business Solution's dedication to excellence has positioned us as the Best SEO Services in Ahmedabad. Our holistic approach to SEO, combined with our unwavering commitment to client satisfaction, sets us apart in the industry. By choosing us as your SEO partner, you can be confident that your business is in capable hands, poised to achieve greater online visibility, increased traffic, and higher conversions.
In conclusion, Growup Business Solution is your premier SEO Services Company in Ahmedabad. With our expertise, dedication, and innovative strategies, we are ready to help your business reach new heights in the digital world. Contact us today to learn more about how we can enhance your online presence and drive your business forward.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Have you ever used AI? I did, once, before I knew anything about our modern definition of AI and what would become of it. The DALL-E image generator could output only a vauge guess of what the prompt requested, but it was at least mildly entertaining. I thought it was a novelty, to be honest. How wrong I was!
So, what is AI? "Artificial Intelligence" is an umbrella term. It does include machine learning, like LLMs (ChatGPT) or image generators (Midjourney), but many people fail to realize that artificial intelligence includes many other fields. Some of which computers have been doing for decades. A computer doing anything that a human could do is technically artificial intelligence. Social media algorithms, bots that play chess, and sensing how much laundry is in your washing machine could all be classified as AI.
The modern idea that AI is just language models, image generators, and other "assistants" is perpetuated by people (companies) who want to make the tech seem new and cutting-edge. They want users, investors, and, most importantly, money. Before you ask ChatGPT for another recipe or generate a Studio-Ghibli-style profile picture, take a minute to listen to this.
Machine learning models have lots of issues, some more well-known than others. You may have heard that AI training often uses stolen data, and that it displaces artists. Unfortunately, there's more to it than that. Training and using AI models uses lots of electricity and produces lots of heat. This means that lots of coal is burned, and lots of water is used to cool the data centers. These data centers also create lots of noise pollution, harming their areas' economies and quality of life. You might think, "so what?" Well, think about it. Is it worth it to lose our planet just for the sake of a little convenience? The tech industry wants you to think so. But what do you think?
If you still use AI, all I have to say is "why?" How can you look at all of the information and still decide to use it? Despite what the tech industry says, AI does not have to be the next step for humanity.
What if, instead of using AI, you figure it out on your own? You are more than your habits and your current knowledge, and you can make a difference. Say "hi" to your friends, your neighbors, and your family. Comission artists, search for scholarly articles, and follow independent journalists. Learn.
Humans were not made for convenience, we were made for connection. So leave ChatGPT alone, close out of Midjourney, and spend some time with the people you love.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Artificial intelligence in real estate industry:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being utilized in the real estate industry to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and improve overall efficiency. Here are some ways AI is making an impact in real estate:
1. Property Valuation: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data including historical sales data, property features, neighborhood characteristics, and market trends to accurately estimate property values. This helps sellers and buyers to make informed decisions about pricing.
2. Predictive Analytics: AI-powered predictive analytics can forecast market trends, identify investment opportunities, and anticipate changes in property values. This information assists investors, developers, and real estate professionals in making strategic decisions.
3. Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots can handle customer inquiries, schedule property viewings, and provide personalized recommendations to potential buyers or renters. This improves customer service and helps real estate agents manage their workload more efficiently.
4. Property Search and Recommendation: AI algorithms can analyze user preferences, search history, and behavior patterns to provide personalized property recommendations to buyers and renters. This enhances the property search experience and increases the likelihood of finding suitable listings.
5. Property Management: AI-powered tools can automate routine property management tasks such as rent collection, maintenance scheduling, and tenant communication. This reduces administrative overhead and allows property managers to focus on more strategic aspects of their role.
6. Risk Assessment: AI algorithms can analyze factors such as credit history, employment status, and financial stability to assess the risk associated with potential tenants or borrowers. This helps landlords and lenders make informed decisions about leasing or lending.
7. Smart Building Technology: AI-enabled sensors and IoT devices can collect and analyze data on building occupancy, energy consumption, and environmental conditions to optimize building operations, improve energy efficiency, and enhance occupant comfort.
#KhalidAlbeshri#pivot#Holdingcompany#CEO#Realestate#realestatedevelopment#contentmarketing#businessmanagement#businessconsultants#businessstartup#marketingtips#خالدالبشري
#advertising#artificial intelligence#autos#business#developers & startups#edtech#education#futurism#finance#marketing
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Data Structure and Algorithms in JAVA | Full Course on Data Structure
In this course, we are going to discuss Data Structures and Algorithms using Java Programming. The data structure is a way to store and organize data so that it can be used efficiently. It is a set of concepts that we can use in any programming language to structure the data in the memory. Data structures are widely used in almost every aspect of computer science i.e. operating systems, computer science, compiler design, Artificial Intelligence, graphic,s and many more. Some examples of Data structures that we are going to cover in this course are arrays, linked lists, stack, queue, Binary Tree, Binary Search Tree, Graphs, etc. Apart from knowing these data structures, it's also important to understand the algorithmic analysis of a given code. Different Sorting and searching techniques will be talked about with their implementation in java programming. Lastly, this course contains information on the Greedy approach, Dynamic approach, and divide and Conquer approach to programming.
#youtube#free education#education#educate yourselves#technology#educate yourself#data structures#data analytics#Data Structure and Algorithms in JAVA#javaprogramming#Data Structure and Algorithms#how to think like a programmer#programming classes#programming
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Free AI to Human Text Converters: Are They Worth It?
In the fast-evolving world of content creation, artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized how we write, communicate, and share information. With AI tools generating vast amounts of content in a matter of seconds, the demand for high-quality human-like text has skyrocketed. But are free AI to human text converters really worth it? Let’s explore their potential, limitations, and why AI to Human Text Converter is the perfect solution for your needs.
What Are AI to Human Text Converters?
AI to human text converters are tools designed to transform robotic, machine-generated content into readable, fluent text that mimics human writing. These tools are especially useful for content creators, businesses, and marketers who rely on AI-generated content but need it to sound more natural and engaging.
Why Use AI to Human Text Converters?
There are several reasons why content creators may choose to use these converters:
Readability: AI-generated content can often be too technical or robotic. Converters enhance readability by making the text sound more fluid.
SEO Optimization: Human-like content is more likely to engage readers, improve time spent on the page, and lead to better SEO results.
Improving Engagement: Natural-sounding text attracts more readers and helps build better audience engagement.
Editing and Polishing: Even the best AI content requires tweaking. These converters offer a fast way to polish the text.
Free vs. Paid Converters: What’s the Difference?
While many AI to human text converters are available for free, they may not always deliver the same quality as their paid counterparts. Free tools often come with limitations, such as word limits, fewer advanced features, and lower-quality output.
However, if you're looking for a reliable, efficient, and free AI to human text converter, AI to Human Text Converter is the perfect choice. Our tool provides a seamless experience, ensuring that your content sounds natural and professional without breaking the bank.
Key Features of AI to Human Text Converters
When choosing an AI to human text converter, it's essential to look for certain key features:
Accuracy: The tool should accurately interpret and convert AI-generated text into natural human language.
Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is critical for efficiency, especially for beginners.
Customization Options: The ability to tweak tone, style, and structure can make a big difference in the final output.
Speed: Time is money, and fast text conversions help content creators stay on top of deadlines.
SEO Integration: High-quality content that ranks well on search engines is vital for success. Tools with SEO features or plugins are a bonus.
Why Choose AI to Human Text Converter?
At AI to Human Text Converter, we provide a free, easy-to-use tool with advanced features designed to help you convert AI-generated text into high-quality human-like content. Here’s why we stand out:
Free Forever: No need to worry about premium subscriptions. Our tool offers quality text conversions without hidden fees.
Simple Interface: Our platform is built with simplicity in mind, ensuring that anyone can use it to convert text in a few easy steps.
Advanced Algorithms: We utilize cutting-edge AI technology to refine your text, making it sound more human, professional, and engaging.
SEO-Friendly: Our tool enhances your content’s SEO potential by making it more readable and appealing to both readers and search engines.
No Word Limits: Unlike other free tools that cap the number of words, AI to Human Text Converter allows you to convert as much text as you need.
How to Get the Best Results from an AI to Human Text Converter
If you're using an AI to human text converter, there are several best practices to follow to ensure top-notch results:
Edit the Input: Before converting, make sure the AI-generated text is clear and coherent. The better the input, the better the output.
Check for Context: Ensure the converted text fits your topic or audience. Customizing it to fit your unique needs can significantly enhance the quality.
Use SEO-Optimized Keywords: When converting text, make sure you integrate important keywords to improve your content’s visibility on search engines.
Review and Edit: Even after converting, always review the text to ensure it's up to your standard. Small tweaks can make a big difference.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Optimizing Business Operations with Advanced Machine Learning Services
Machine learning has gained popularity in recent years thanks to the adoption of the technology. On the other hand, traditional machine learning necessitates managing data pipelines, robust server maintenance, and the creation of a model for machine learning from scratch, among other technical infrastructure management tasks. Many of these processes are automated by machine learning service which enables businesses to use a platform much more quickly.
What do you understand of Machine learning?
Deep learning and neural networks applied to data are examples of machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence focused on data-driven learning. It begins with a dataset and gains the ability to extract relevant data from it.
Machine learning technologies facilitate computer vision, speech recognition, face identification, predictive analytics, and more. They also make regression more accurate.
For what purpose is it used?
Many use cases, such as churn avoidance and support ticket categorization make use of MLaaS. The vital thing about MLaaS is it makes it possible to delegate machine learning's laborious tasks. This implies that you won't need to install software, configure servers, maintain infrastructure, and other related tasks. All you have to do is choose the column to be predicted, connect the pertinent training data, and let the software do its magic.
Natural Language Interpretation
By examining social media postings and the tone of consumer reviews, natural language processing aids businesses in better understanding their clientele. the ml services enable them to make more informed choices about selling their goods and services, including providing automated help or highlighting superior substitutes. Machine learning can categorize incoming customer inquiries into distinct groups, enabling businesses to allocate their resources and time.
Predicting
Another use of machine learning is forecasting, which allows businesses to project future occurrences based on existing data. For example, businesses that need to estimate the costs of their goods, services, or clients might utilize MLaaS for cost modelling.
Data Investigation
Investigating variables, examining correlations between variables, and displaying associations are all part of data exploration. Businesses may generate informed suggestions and contextualize vital data using machine learning.
Data Inconsistency
Another crucial component of machine learning is anomaly detection, which finds anomalous occurrences like fraud. This technology is especially helpful for businesses that lack the means or know-how to create their own systems for identifying anomalies.
Examining And Comprehending Datasets
Machine learning provides an alternative to manual dataset searching and comprehension by converting text searches into SQL queries using algorithms trained on millions of samples. Regression analysis use to determine the correlations between variables, such as those affecting sales and customer satisfaction from various product attributes or advertising channels.
Recognition Of Images
One area of machine learning that is very useful for mobile apps, security, and healthcare is image recognition. Businesses utilize recommendation engines to promote music or goods to consumers. While some companies have used picture recognition to create lucrative mobile applications.
Your understanding of AI will drastically shift. They used to believe that AI was only beyond the financial reach of large corporations. However, thanks to services anyone may now use this technology.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Digital Marketing: Trends to Watch in 2025

As we move closer to 2025, the digital marketing landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. The strategies that worked a few years ago are now being replaced by new, innovative approaches. For businesses aiming to stay competitive and relevant, understanding the emerging trends in digital marketing is essential.
This blog explores the key trends expected to shape the future of digital marketing by 2025, providing you with insights that can help you adapt and thrive in this dynamic environment.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Marketing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have already begun to revolutionize digital marketing, and their influence is set to grow even stronger by 2025. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, offering insights that were previously unattainable. These tools enable marketers to:
Personalize content at scale: AI can help create highly personalized content tailored to individual user preferences, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
Automate customer interactions: Chatbots and virtual assistants, powered by AI, will handle more customer interactions, offering real-time assistance and improving user experience.
Predict consumer behavior: Machine learning algorithms can analyze past consumer behavior to predict future actions, helping marketers to anticipate needs and tailor their strategies accordingly.
2. The Rise of Voice Search and Conversational Marketing
With the increasing adoption of smart speakers and voice-activated devices, voice search is becoming a critical component of digital marketing. By 2025, it's estimated that more than 75% of households will own a smart speaker, making voice search optimization essential. Here's how you can prepare:
Optimize for natural language: Unlike traditional text searches, voice searches are more conversational. Optimizing your content for natural language queries will help improve your visibility in voice search results.
Focus on local SEO: Many voice searches are local, so ensure your business is optimized for local SEO to capture this growing segment.
Leverage conversational marketing: Engage with your audience through chatbots and live chat tools, providing instant responses and personalized experiences that meet the expectations of voice-savvy consumers.
3. Data Privacy and Ethical Marketing
As data breaches and privacy concerns become more prevalent, consumers are increasingly aware of how their data is used. By 2025, data privacy will be at the forefront of digital marketing, with stricter regulations and more informed consumers. To build trust and remain compliant:
Adopt transparent data practices: Clearly communicate how you collect, store, and use customer data. Transparency will be key in gaining consumer trust.
Invest in secure technologies: Use secure methods to handle data, ensuring that your business complies with data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
Ethical marketing practices: Shift towards ethical marketing by focusing on providing real value to consumers rather than exploiting their data. This approach will help build long-term customer relationships.
4. Content Experience (CX) and the User Journey
Content is still king, but the way users experience content is becoming just as important as the content itself. By 2025, the focus will shift from merely producing high-quality content to creating a seamless content experience (CX) that enhances the user journey. Key strategies include:
Interactive content: Incorporate interactive elements such as quizzes, polls, and infographics to make content more engaging and memorable.
Omnichannel content delivery: Ensure your content is accessible across all platforms and devices, offering a consistent and seamless experience whether users are on mobile, desktop, or tablet.
Personalized user journeys: Leverage AI to personalize the user journey based on individual behavior and preferences, making the content experience more relevant and engaging.
5. The Growth of Video Marketing and Augmented Reality (AR)
Video marketing has been a dominant force in digital marketing for years, and its importance will only increase by 2025. However, the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) is set to take video marketing to new heights:
Short-form video content: Platforms like TikTok and Instagram Reels have popularized short-form videos. In 2025, this trend will continue, with brands needing to create concise, engaging content that captures attention quickly.
Live streaming: Live streaming offers a unique way to connect with audiences in real-time, and it will become even more prevalent. Whether it's product launches, behind-the-scenes looks, or live Q&A sessions, live streaming will be a powerful tool for engagement.
AR-enhanced videos: Augmented Reality will allow brands to create immersive experiences, blending the digital and physical worlds. From virtual try-ons to interactive product demos, AR will make video content more engaging and effective.
6. Social Commerce and Shoppable Content
Social media platforms are increasingly becoming more than just places for social interaction; they are evolving into full-fledged e-commerce platforms. By 2025, social commerce is expected to dominate, with shoppable content playing a key role:
Integrated shopping experiences: Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Pinterest will offer seamless shopping experiences, allowing users to purchase products directly from posts and stories.
Influencer-driven commerce: Influencers will continue to play a significant role in driving social commerce, with brands collaborating with them to create authentic, shoppable content.
User-generated content (UGC): Encourage customers to share their experiences and showcase products in use. UGC not only builds trust but also drives more conversions by offering real-life examples of product satisfaction.
7. Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Consumers are becoming more conscious of the social and environmental impact of the brands they support. By 2025, sustainability and social responsibility will be integral to digital marketing strategies:
Green marketing initiatives: Highlight your brand's commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly products, packaging, and practices. Consumers are more likely to support brands that align with their values.
Social responsibility campaigns: Engage in campaigns that address social issues, whether it's supporting charitable causes, advocating for equality, or promoting community well-being.
Transparent branding: Be open about your brand's efforts in sustainability and social responsibility. Transparency will resonate with consumers who prioritize these values.
8. The Impact of 5G on Digital Marketing
The rollout of 5G technology will have a significant impact on digital marketing by 2025. With faster internet speeds and reduced latency, 5G will enable more sophisticated marketing tactics:
Enhanced mobile experiences: 5G will improve mobile user experiences, making it crucial for brands to optimize their mobile content and websites for speed and performance.
Real-time data and analytics: Marketers will have access to real-time data, allowing for quicker decision-making and more dynamic marketing strategies.
Advanced AR and VR experiences: The increased bandwidth of 5G will support more advanced Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) experiences, offering new ways for brands to engage with customers.
Conclusion
The future of digital marketing in 2025 promises to be both exciting and challenging. As technology continues to advance, marketers must stay agile and adapt to new trends to remain competitive. By embracing AI and machine learning, optimizing for voice search, prioritizing data privacy, and creating immersive content experiences, businesses can not only survive but thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Staying ahead of these trends will require a commitment to continuous learning and innovation. However, the rewards—improved customer engagement, increased brand loyalty, and sustained growth—will make the effort worthwhile. Start preparing now, and position your brand as a leader in the future of digital marketing.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discover the Future of Image Search with Galambo: AI-Powered Insights at Your Fingertips
Ever wished you could unlock hidden details in your images with a single click? Galambo, the state-of-the-art AI-driven image search engine, turns that wish into reality by offering an unprecedented level of detail and context for every photo.
Galambo is revolutionizing how we interact with visual content through its advanced artificial intelligence technology. Unlike traditional image search tools, Galambo delves deep into each image, providing a rich tapestry of information that goes far beyond simple recognition. This enhanced capability makes it a game-changer for anyone looking to gain more from their visual assets.

The heart of Galambo’s technology lies in its AI-powered predictive search. When you upload an image, Galambo’s sophisticated algorithms analyze its contents and suggest relevant queries based on the image's details. This feature significantly speeds up the search process and ensures that you get highly accurate results, optimizing your workflow and saving valuable time.
Another notable aspect of Galambo is its dynamic interactive search feature. Instead of passively viewing images, you can click on various elements within them to access additional information and related content. This interactive approach transforms image searching into an engaging and informative experience, allowing you to explore visuals in a more meaningful way.
Galambo’s integration capabilities further enhance its usefulness. It links with mapping services to identify locations, taps into extensive databases for in-depth information, and connects with social media platforms to provide broader context. This seamless integration makes Galambo a versatile tool for multiple applications, from research to marketing and beyond.
Security is a priority for Galambo, with robust measures in place to protect your data. This ensures that your image searches and analyses are conducted with the highest level of privacy and security.
In conclusion, Galambo stands out as a leading AI-powered image search engine, offering advanced features that redefine how we interact with visual content. Its predictive search capabilities, interactive features, and comprehensive integrations make it an indispensable tool for those seeking to maximize their image analysis. Discover how Galambo can elevate your approach to visual content by visiting Galambo.
3 notes
·
View notes