#it creates a complex algorithm that calculates how that relationship (?) is going based on available data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
As of the end of System Collapse, SecUnit intends to travel with ART and its crew/the university rather than returning to Preservation. However, Wells is leaving some openings for Preservation characters to still appear in that context, what with Amena wanting to study at the university and Ratthi having an entanglement with one of ART's crewmembers. SecUnit is fond of Ratthi, so this may put it in the terrible position of having to actually pay attention to human love lives so it can anticipate whether Ratthi is likely to make an appearance or not.
#murderbot#system collapse spoilers#it creates a complex algorithm that calculates how that relationship (?) is going based on available data#but runs it all in the background and deletes all the raw data as soon as the calculations are done#so all it is consciously presented with is the Ratthi Number
91 notes
·
View notes
Note
I love your idea of doing things with a RNG. But, how do you remember the probability while playing? Do you keep a notebook by your side? Do you have a masterlist somewhere? Can you share it?
I do like to have as many things as possible decided randomly. That way, I don’t do the same things over and over again. Basically, when it comes to what my Sims do, I follow their wants. If they have no wants I can actively fill, they free-will and do whatever they want. ACR handles romance and baby-making for me, but otherwise, when there’s a decision to make, I roll a “virtual die.” :)
I babbled, I cut...
For every neighborhood I play, I make a multi-tabbed spreadsheet to keep track of different things about it. Some of them are really complex (like for “integrated” neighborhoods, where I have to keep track of supply chains and “inventories,” for instance), and some of them are fairly simple, just tracking statistics and which lot I’m currently playing. I keep the neighborhood’s spreadsheet open side-by-side with the game (which is why I play in windowed mode) so that I can easily reference it and update it. And I do it on spreadsheets rather than notebooks because we tend to move around a lot between three houses, so the fewer things I have to remember to pack up and take when we migrate, the better. So, spreadsheets that are kept on the computer rather than notebooks.)
One of the tabs on each spreadsheet is the neighborhood’s rules. I use different rules for different ones. And I often make a new neighborhood just for the purpose of testing out and refining a new way to play, like the pseudo-Amish, so it’s not really easily shareable. Basically, it’s just a lot of text about a lot of different things. But that’s where I list the possible outcomes for things I decide randomly and/or the “algorithms” I use to calculate things. I can give you some examples, but really, you can decide pretty much anything randomly if you want to. Like, I have a mod that makes all chance card outcomes equally likely, and I generate a number to “decide” which option a Sim will “choose” when one comes up. (Otherwise, I’m likely to be tempted to always pick the “good” option because after a decade of playing I know which those are for pretty much all the career chance cards.)
Anyway, there are many things that I decide randomly, many of which happen when I create a Sim in CAS or, for born-in-game Sims, when they turn teen. For example (but this is not a complete list):
Their primary and secondary aspirations. I just assign numbers to each aspiration, a roll to decide which they get.
Their sexual preference. Which is a percentage chance. Generally, I like a 20%/60%/20% gay/straight/bi distribution (but I will use different ones for different neighborhoods, too), so I’ll randomly generate a number between 1 and 100 inclusive to decide what they’ll be. 1-20 = gay, 21-80 = straight, and 81-100 = bi)
What they’ll do to earn a living, if they don’t have a career-related LTW or if they have a career-related LTW but the career isn’t yet open/has no openings. They have many different options. Do a trade (and I use a further numbered list to decide what they’ll do), get an NPC job, get a different regular job than their LTW, open a business, operate a farm/ranch, become a person who fishes for a living, become an “escort,” etc.
The type of relationship they’ll have, for which there are a lot of options. Marriage, either only if they roll wants or whether they like it or not and, if that’s what they get, whether the marriage will be 2-career or 1-career and, if the latter, whether or not they’ll be the stay-at-home parent or their partner will be. Then there’s never marrying regardless of wants. There’s romantic partners living together but not marrying. There’s platonic co-habitation (i.e. just sharing a house/apartment with one or more “roomies,” although if that develops into romance, so be it.) Or polyamory (and I use another roll to determine how many partners), which can be either intermarried or not. Or communal. Or they can go religious, which has a whole other set of rules. Or they can enter a religious order (i.e., a convent), if the neighborhood has one. Etc. etc. I like to have lots of options so that not all households are doing the same thing.
For CAS Sims, virtually everything about them aside from their appearance -- which I let the game do, because I townify everything and just stick with what the game gives me -- is decided by random number generation. Whether or not they’ll be fat, their aspiration, astrological sign, turns on-off, etc. The only thing I don’t do by number generation is their clothing.
Other things:
Whether or not they’ll go to class each day in Uni (and I use the same “algorithm” to decide if they’ll do homework as teens, since my teens never roll wants to do so).
If they’re a same-sex couple, if/when and by what method they’ll have kids (adoption, surrogacy/sperm donation, “genetic engineering” so that they can have a kid that’s genetically both of theirs, if that’s available in the neighborhood).
Where they’ll go on a vacation, if they don’t roll a specific location want.
What kind of pet they’ll get if they roll a non-specific or either/or want.
Oh, and here’s a big one: If a Sim is one whose “destiny” is marriage whether they roll a want or not, and if they haven’t developed a romantic relationship with anyone by the time they start their own household, they get a random spouse. I keep two numbered lists (one for each gender) of all the townies/downtownies/dormies/NPCs, etc., in the neighborhood. That’s two of a neighborhood spreadsheet’s tabs. The random number generator then decides who they’ll marry, and I use a hacked wedding arch to marry them, sight unseen. I think of it as a “mail-order spouse” sort of thing, and my favorite thing ever is negative-chemistry couples. :) Which is probably way weird to some people, but I enjoy it. :)
Basically, pretty much any time a Sim has to make a “decision” about something, I generate a number to decide what that “something” will be. For me, it reduces boredom. I know it’s probably too random for many players, who like to plan things out or make choices based on a Sim’s personality or interests or what-have-you, but this is what I enjoy, so...yeah. And even “planners” might enjoy a little random sometimes, maybe especially for households they’re bored with.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Angry stomach is angry - or how we can translate tweet-speak for the medical world
“Ow my stomach is killing me”
“That burrito is really not sitting well with me”
“Uhhhg angry stomach is angry”
“My tum is :( :(”
Not only does everyday language incorporate a lot of figurative sayings, but sometimes what we write online seems like it could be another language altogether.
Now consider the problem of mapping this internet-speak to medical concepts. Chances are your doctor didn’t dissect a stomach emoji in medical school. There needs to be some system to translate the kind of language we find online to formal medical terminology. This task is called concept normalization.
Limsopatham and Collier (2016) [1] explain what has been suboptimal about previous approaches to associating informal language with medical language and propose a method of their own. In brief, they argue that there needs to be some understanding of text at the semantic level, that is lower-level meaning, before it can be understood as health-related information. The successful approach uses a convolutional neural network (CNN), which outperforms their other model of a recurrent neural network (RNN).
Both CNNs and RNNs, when used in natural language processing (NLP), typically take word embeddings as their input. The most intuitive way we can understand word embeddings is that "a word is characterized by the company it keeps." [2] Each word in an embedding is represented by a vector, typically reduced to 300 dimensions, that is the result of some statistical analysis that quantifies the relationship among all words. In this paper, the preexisting, widely used GNews (based on 100B words pulled from Google News) and BMC (based on 854MN words from medical articles) word embeddings are used as model input.
Click here for an explanation of word embeddings
A CNN applies convolution over a sliding window across words in a sentence, which here is a tweet or a phrase from a blog post. Convolution refers to a filtering function being applied to a subset of the word embeddings, resulting in a new value that gets stored to summarize that subset. The result is a feature matrix where each window of words has a value corresponding to each feature. The maximum value at each feature goes on to represent the fully connected layer, the output of the neural net. The CNN used in the paper uses a single convolutional and pooling layer, meaning that this procedure is done only once.
Click here for a primer on CNN
Instead of using a sliding window, an RNN sequentially goes through words in the sentence and at each state produces an intermediate output called the hidden state. Each subsequent word’s embedding is processed with the previous hidden state as the input, which is what makes the network recurrent. A gated recurrent unit (GRU) is used as one type of gating function that chooses what information is relevant to maintain or forget throughout the sequence of words.
Click here for a primer on RNN and click here for details on gating functions such as GRU
When a sentence is given to the trained neural net, the output is passed to the softmax activation function, which gives a probability for the sentence being assigned to each of the selected medical terms. The probability of a phrase belonging to a given term is calculated as the exponential of the network output for that term divided by the sum of all exponentiated outputs.
Click here for a quick video explaining softmax
There are six baseline models that the two neural networks are compared against and three evaluation datasets, two based on tweets and one based on blog posts that have health-related phrases. One of the Twitter-derived sets is a novel dataset created by the authors centered around adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The models are evaluated on the basis of accuracy, where each tweet or blog post phrase is labeled with some ground truth medical topic label that the neural network then has to predict. The blog dataset resulted in higher accuracy than the other two in every case, and the researchers reason that this is because written posts tend to have more linguistic structure than brief quips like tweets. In terms of models, CNN and RNN both greatly outperform the chosen baselines, especially when using GNews embeddings. The CNN achieves a stunning 44% improvement in accuracy over the highest baseline, from 0.3099 to 0.4478.
The authors discuss where their neural network models have advantages over other previously used methods for this task. One historically used class of methods is based on string matching and finding similarities in words. The pitfall here is that the models cannot derive semantic meaning and would be mislead to believe that “i don’t hunger or thirst” is indicating hunger rather than loss of appetite as a health phenomenon. A phrase such as “appetite on 10” is complex and doesn’t make sense to a model that is unaware of semantics, or the meaning being conveyed by a word. By contrast, these neural networks can make use of co-occurence of words to understand something about their underlying meanings and understand “appetite on 10” as signaling “increased appetite.”
Hungry for more? I will be starting a new blog called Code Blue that interfaces topics in healthcare with data science. More posts in this vein (ha ha) are to come soon!
Related Work
1 - Adapting Phrase-based Machine Translation to Normalise Medical Terms in Social Media Messages (Limsopatham & Collier 2015) [3]
The authors of the reviewed paper also developed a model using not neural networks but phrase-based machine translation to address this same problem of mapping informal language to medical terminology. This model is also built on the foundation of word embeddings. Like in the reviewed paper, they strive to derive a semantic sense to words and go beyond past work simply considering lexical features.
2 - Pharmacovigilance from social media: mining adverse drug reaction mentions using sequence labeling with word embedding cluster features (Nikfarjam et al 2015) [4]
This paper also models semantic similarities in words to try and derive medical meaning from the type of language used on social media. Specifically, they focus on the task of mining adverse drug reactions (ADR) based on what people have shared online. Their model, ADRMine, is based on conditional random fields (CRFs).
3 - Utilizing social media data for pharmacovigilance: A review (Sarker et al 2015) [5]
This is a survey of studies that detect ADRs from social media. They found that while there were 22 studies done on the topic, only six of them had their annotations publicly available, which is what would allow the methods to be compared on the basis of performance. They use these insights to propose a systematic way to collect ADR information from social media.
4 - Automagically Encoding Adverse Drug Reactions in MedDRA (Zorzi et al 2015) [6]
This paper continues on the theme of identifying and classifying ADRs. It uses the MedDRA database, the standard terminology set for reporting adverse events related to medications. The authors describe an algorithm to automatically derive MedDRA codes from freeform text, making it so that experts don’t have to manually annotate descriptions but only need to validate them.
5 - Twitter as a Lifeline: Human-annotated Twitter Corpora for NLP of Crisis-related Messages (Imran et al 2016) [7]
Although this paper does not deal with medical data, it still uses the Twitter universe as its subject of study for learning information from informal, noisy, and short messages. It trains an impressive word2vec model based on 52 million tweets from 19 different disaster situations that happened between 2013 and 2015. What is interesting here is that the language found in the tweets is hand-, or human-, annotated. This is something the reviewed paper did not do in coming up with a model for online to medical terminology. However, in both this paper and the one reviewed, the “ground truth” labels used to evaluate accuracy were based on hand annotation.
References
[1] Limsopatham, N., & Collier, N. (2016). Normalising Medical Concepts in Social Media Texts by Learning Semantic Representation. Apollo - University of Cambridge Repository. https://doi.org/10.17863/CAM.378
[2] "A synopsis of linguistic theory 1930-1955". Studies in Linguistic Analysis: 1–32. Reprinted in F.R. Palmer, ed. (1968). Selected Papers of J.R. Firth 1952-1959. London: Longman.
[3] Limsopatham, N., & Collier, N. (2015). Adapting Phrase-based Machine Translation to Normalise Medical Terms in Social Media Messages. In arXiv [cs.CL]. arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/1508.02285
[4] Nikfarjam, A., Sarker, A., O’Connor, K., Ginn, R., & Gonzalez, G. (2015). Pharmacovigilance from social media: mining adverse drug reaction mentions using sequence labeling with word embedding cluster features. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association: JAMIA, 22(3), 671–681.
[5] Sarker, A., Ginn, R., Nikfarjam, A., O’Connor, K., Smith, K., Jayaraman, S., Upadhaya, T., & Gonzalez, G. (2015). Utilizing social media data for pharmacovigilance: A review. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 54, 202–212.
[6] Zorzi, M., Combi, C., Lora, R., Pagliarini, M., & Moretti, U. (2015). Automagically Encoding Adverse Drug Reactions in MedDRA. 2015 International Conference on Healthcare Informatics, 90–99.
[7] Imran, M., Mitra, P., & Castillo, C. (2016). Twitter as a Lifeline: Human-annotated Twitter Corpora for NLP of Crisis-related Messages. In arXiv [cs.CL]. arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.05894
0 notes
Text
TTB3: “Invasive” AI
I mentioned in TTB1 that the computer needed to power a time distortion unit need be no more powerful than an early 2000s era laptop.
But that needs a little clarification...
I didn’t mean you could run a distortion unit “with” an early 2000s laptop running Windows XP. But with the processor and chip technology we had by the early 2000s, you could build a computer whose single purpose was to run a distortion unit... controlling the cathode manifolds, and doing all the complex calculations necessary for gravity lock to work... while also keeping track of the local date and time to within a few seconds.
I mean... 2000s era computers are capable of a hell of a lot, when you’re not asking them to stream data, render graphics, or run a bunch of bullshit software in the background.
But a time traveler also requires a second, outboard computing device, that can interface with the drive of the distortion unit... pre and post transit... and also interface with the outside world, be it radio, TV, internet, etc... and also interact intelligently with the human mission commander themself.
This AI device serves as the mission brain, first officer, what have you... and is the device that determines the divergence upon arrival, calculates the best divergence correction maneuvers for the distortion unit to make, calculates the best return path, and also gathers whatever intel it can about the world they’ve landed in... such as online maps or GPS if they’re available.
But this will always be a learning AI device... with a couple core directives programmed in that are broader than any one time travel mission... self preservation, and self update.
Self preservation is about doing whatever it takes to prevent itself getting lost, stolen, damaged, or compromised. If on mission in a pre-internet era, this might be nothing more than nagging it’s commander not to lose it, and to keep it powered up.
It could also, if lost, send out a radio beacon for it’s commander, or any other friendly time traveler to locate, until it’s battery hit’s critically low... at which point it triggers an explosive cylinder on it’s board that will destroy itself and it’s data.
But if the mission is in an era where the internet is fairly sophisticated, this would mean backing itself up to the cloud.
The self update function, then, is a lot more fun, because this would mean that, once connected to the internet, it would not only back itself up to the cloud, but also search for more advanced versions of itself that were backed up by other friendly time travelers.
And then, if it’s mission device hardware could handle it... update itself inside that device. If the mission device hardware could not handle the full upgrade, then it could still archive technical specs for how to update the hardware... that mission control, back at home base in the future, could look at after the mission was over, to improve the tech.
Now, before I go any further, we need to understand how exactly time traveling AI are able to recognize one another... because remember!... no matter where they travel in time, they never land in the same timeline they left.
Even traveling back home to the future... they never get back to the same timeline they departed from. They only (if all goes well) get back to a timeline that’s nearly identical to the one they departed from... and replace the nearly identical versions of themselves who left that one.
So... out in the field of the vast hyperverse, time travelers can’t rely on pre-agreed passwords, code phrases, or communication fequencies... as they will all likely be slightly different... thanks to the fact they are ALL coming from, and going to slightly different timelines.
The way around this problem is to base all signal intelligence on physical and mathematical constants.
History might be slightly, to wildly different for the same date, from one timeline to another, depending on where you are in the hyperverse of parallel Earths, but two things will always be the same... math, and the laws of physics.
So, for example, Planck’s Constant, 6.62607004 × 10-34 m2 kg / s, which expresses the relationship between the energy of a single photon and it’s light frequency... will be the same no matter where you are in the hyperverse.
I use Planck’s Constant, because it became a plot point in Season 3 of Stranger Things this year... but there are innumerable other mathematical constants relating to physics, or pure math... such as Pi, out there to employ when constructing a cryptography that will work for allowing friendly time travelers to identify one another and communicate out in the field.
So, let’s get back to our AI that’s copied itself into the cloud to search for updates...
It will have some internal serial number based on some mathematical constant, that it will both broadcast, and search for... inside the packet traffic of the world.
If it identifies another instance of itself, the two will handshake and determine how they can help one another with updates and upgrades.
But even if our AI does not immediately locate another instance of itself, it can still try to identify other AI algorithms by targeting systems likely to employ them, such as search engines, or looking for more general traits common to all artificial intelligence... and attempt to learn from them.
It can also learn what it can about native tech, to see if this timeline seems to have any useful innovations not previously known.
After incorporating all it can learn from these types of scans, it will, in some way have upgraded, at least a little bit... and can then sit there in the cloud waiting to communicate all that to another instance of itself, when and if one ever comes along.
Meanwhile, the mission commander will leave for home with as much of an upgrade to their AI device as was possible... along with some technical specs for mission control to evaluate and incorporate into future AI devices that get sent with future mission commanders back to the past.
Again, here, it’s important to keep in mind that our own one timeline... the one you and I experience together, and share memories from in common... is NOT going to be visited by every time traveler out there.
Only a tiny fraction of all time travelers in the hyperverse will happen to hit our own specific timeline, at random intervals.
But, given the density of time travelers out there in this... date period... between 2009 and 2019... there have probably been half a dozen who at least stopped long enough for their AI devices to take up permanent residence on our internet as a kind of “invasive species” intermingling with one another, and our native AI, to create an invisible layer of cyber intelligence out there, independent of any authority... a total wild card in the workings of our world...
...except that it does contribute to the visibly increasing weirdness of modern reality... because they do troll us in different ways for different reasons.
0 notes
Text
New Edition of SEO Success Factors Reinforces the Significance of Content
A theme that boomed in the search engine optimization community during SMX Advanced in Seattle was that Big G desires relevant, differentiated content above all else.

In the fourth quarter of June, the SMX is upstairs in Seattle. It is officially announced for the first time in 2011 for the cyclone of SEO 2019. Success Factors and Technology Strategy In addition, ranked search engine optimization is updated every two years to reflect new changes and trends. Google (SEO).
Hundreds of search engine reform experts voted for engine refreshing, website speed, return links, user experience and maximum importance in the online engine survey. Following the usual methods, Search Engine Earth's additional team reviewed the survey results, including their own entries, created calendars and diagnoses, which can be viewed here and downloaded.
If you searching out for a digital marketing company in Pakistan, contact A One Sol.
At the advanced level of SMX, Jenny Marfin joined the editorial team of Search Engine Land Editor, Barry Schwartz and Johnson Bowman of Detroit of Johnson Bowman, to discuss and share their ideas on the factors of success. The most important thing.
The general theme of the discussion and update of the corresponding period table is a well-formed format, the importance of high-quality content available to users, which emphasizes the understanding and emphasis put on its use.
As Schwartz notes in his introductory remix, the fact is now that content is more important in the competition between content and links, now that content is more important.
Of course, there is one of the main success factors in the content table, and it was similar in the previous version. The group discussed in the first part of the discussion documents based on these factors, in particular, the power of Google in health care to determine the authority of Schwartz, which is paramount in the vertical fields. Okay
Bowman stressed the importance of writing writers to at least compete with the same standards in order to produce at least high-quality content. Johnson reminds us that Google allows companies to understand content anonymously rather than in real-language learning, using machine learning and neural networks.
Get our SEO Pakistan services to outrank your competitors.
The team suggested to Google to look for poor quality. For example, many SEOs know that modernity is one of the factors that Google understands, but that does not mean that everything is often needed for updating. Seeing the difference between Blueway and protein bars, Bowman shows that the facts on a subject can be much less than other truths.
The proof of material predominance as a factor of success is that the commission is often on the other subject when discussing other factors. For example, if you're going through a series of construction feature topics, the committee recommends setting the page speed and portability of the analysis, so it's helpful to manage Google to generate the content of your choice. Because the page and other building factors are important. Indexing index.
Referring to Google's John Mueller, Schwartz said the solution to solving many problems (probably the secondary warning, such as website engineering) is to improve your content.
In the following topic, HTML provides a useful review of the HTML marking possibilities in HTML, Johnson, stating that Google is paying attention to the tag because the web developers they can enjoy better. The navigation bar, the article text, and the cement tag tab, such as the sidebar of the page, help you help Google understand your page correctly.
We provide our clients all over the world with copywriting services by our website copy writers in Pakistan.
However, Google's response to Schwartz is difficult because most HTML have been "broken", which means that page titles such as title tags were correct encoding elements, so Google had to develop other solutions. Is not its Tags cannot be possible because we want them to live? In other words, an effective reduced example can be given because of the lack of confidence in the tag's dissatisfaction.
However, there is yet another trend in the direction of Johnson's "No Chains" proposal that you have recently highlighted a topic applied to larger site-wide linguistic Web applications, based on the parallel development of research.
Get our local search optimization Pakistan to increase your local search visibility.
On trust, the group said the best way to go is to apply Google's quality principles of training, expertise, authority and trust. Readers will be reminded that in August, by updating the basic algorithm, EAT became the largest and most important SEO community.
The Group also suggested that the necessary elements should be understood in the context of broader content and compatibility. For example, Pullman points out that if the bounce rate is too high on the so-called interesting page, the solution is to improve the quality of the content.
The last two positive types of remote tables, links and users were immediately covered. The team agrees that the original standard backlinks of the original Google algorithm can lose their relevance at all, however, it is recommended that you do not need to arrange correctly today.
With regard to user factors, Schwartz said Google recently stated that it does not customize search results based on the user, which differs from previous methods. It is true that when the user is often experienced by the football team "Jaguar", to see the end result of the user car, "Jaguar", today, Google claims the user's geographical location only and its immediacy as previously focused on the request. By customization.
A One Sol is the best enterprise SEO platform in Pakistan that offers enterprise SEO services.
Schwartz also suggested that Google analyse the user experience that Web pages provide quickly. In fact, in the past four years, there are a number of tools that can provide complete web pages in the process of searching for indexing tools, as well as interface elements and how they interact with advanced humans.
Bowman, who is expected to have intentions for the same initiative of the relationship between the user and the relationship, because of the intersection of the table, but it does not seem important. Page content.
This discussion focuses on the divorce schedule, which lists factors such as protectors, keyword filling, and advertising intervention, which have the right to classify "toxic." Specialist experts said it could be avoided and many other factors, although many of them are still popular. Schwartz mentioned the recurring problem as link schemes, emphasizing the content of Bowman and Schwartz so much that many SEOs must find a balance between seriousness, often an important source of important sites and content revenue.
The last part of the chart lists the emerging vertical components, new (or very complex) factors that do not work in the classification. Include local audio, photos and videos.
We offer ecommerce conversion optimization in Pakistan in order to take your business to the next level.
Of these, the sound is a new element clearly. Panthers agree that although speech research is still in its infancy, it now highlights the most important strategies that will become increasingly important in the future. These include sections that provide answers to targeted questions as well as provide search content that considers user needs to be based on factors.
Local residents point out that Schwartz, "because it is constantly changing," was included in the list of emerging countries, but as represented by Bowman, the local population was first established long and in some areas. Is it so?
This is usually cash that can be applied to the entire cellular table and does not indicate different usage situations and best interest. At the local level, you must attract the traffic of local market entity entities to optimize your search engines, so you can find local search engine optimization instead of centralized work rather than calculating external factors. Attention will have to lead to significant changes in other strategies.
Read also: How to optimize your Robots.txt file
Similarly, e-commerce conversion sites have significantly different goals than those who wish to create original content through multi-update content in areas such as industry news and entertainment.
However, it is useful to use the temperature of the SEO community for the most important factors. Again, the main debate in the new scheme and SMX discussion is that Google wants all relevant and diverse content.
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach to Marketing
In this guide, I’ll go into detail about how artificial intelligence is impacting marketing right now and how it will continue to impact it in the future.

At the end of this post, you’ll be excited about the possibilities of AI and probably a little nervous about the implications!
And it’s alright to be nervous because the role of marketers in organizations will change but….
…you’ll still have an important role to play.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 – Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Chapter 2 – The elements of Artificial Intelligence
Chapter 3 – AI Applications in Marketing
AI and Content Marketing
AI and Analytics
AI and Marketing Automation
AI and Conversational Marketing
AI and Email Marketing
AI and SEO
AI and Social Media
AI and Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
AI and Listening/Monitoring
AI and Image Recognition
AI and Influencer Marketing
Chapter 4 – Security Concerns about AI
Summary
Download a PDF of this Guide
Would you prefer to read this later? If so, download a PDF version of the AI Guide.
Download PDF of Guide
C H A P T E R – 1
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence in Marketing is real and now is the time to sit up and take notice.
Artificial intelligence is accelerating marketing toward a more intelligently automated future in which smarter (i.e. AI-powered) solutions enable marketers to solve problems and achieve goals more efficiently. You have a choice. You can sit back and wait for the marketing world to get smarter and change around you, or you can embrace AI now and be proactive in creating a competitive advantage for yourself and your company.
Paul Roetzer, Founder of Marketing Artificial Intelligence Institute
However, not all software companies really have AI that say they do.
There’s just so much hype surrounding AI Tech companies want to capitalize on it by saying their software is powered by AI and investors will give higher valuations to them because of the AI in their software.
But there are many great software companies building true AI applications and this is set to grow massively over the next few years.
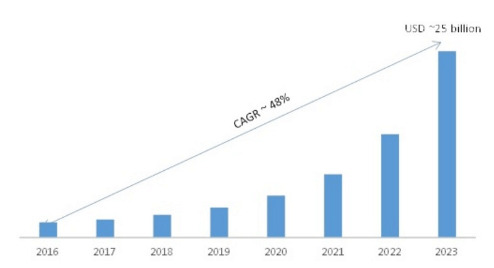
MRFR research predicted the AI market to be worth 25 billion by 2025.
If you’re a marketer, it’s time to get up to speed and understand the potential impact that AI will have on marketing. I’m pretty sure that this guide will help.
So, what is artificial intelligence?
We all know what human intelligence is…I hope so anyway!
Artificial intelligence is when a machine demonstrates some human-like intelligence.
For example:
A machine processes data and learns from it so it can make smarter decisions about the data it will process in the future.
Instead of just repeating the same instructions, the machine automatically learns new instructions based on experience.
Alpha Zero, the game playing AI developed by Deepmind, learned Chess in 4 hours and then was able to beat the best computer program available for playing chess.
Learning a new game is mimicking human intelligence, but the AI can learn in 4 hours what a human may take months doing.
Computer science describes the study of AI as the development of intelligent agents.
Look:
This is really about smart programming.
Our intelligence helps create artificial intelligence.
As some tasks become very routine they may not be considered artificial intelligence anymore.
Here’s an example:
Optical character recognition is often excluded because it’s a routine task expected from computers.
What is the difference between narrow and strong AI?
Narrow AI (also called weak AI) is artificial intelligence focused on one task.
Strong AI is everything else!
Strong AI has the ability to apply intelligence to any problem rather than a specific task.
For example:
A spam filtering tool performs one task well. A self-driving car is also described as narrow AI but I think this is a bit of a stretch!
Will Artificial Intelligence Replace Marketers?
Yes…. some!!!
Marketing is a time-intensive process with a lot of repetitive tasks which machines can help with…
…but there are certain tasks that machines will never be able to perform at the same level as human marketers.
I can imagine, in the future, sitting across from a robot discussing a business proposition but I can’t imagine I’d build the same relationship with a robot as with a real human. It’s relatively easy to build software to beat someone at Chess and…
…the software gets better at beating people.
But…
Building relationships is the most important part of marketing and computers suck at it.
Also, who is going to build a strategy for a company?
An AI enabled machine can provide inputs into this strategy but strategists will still survive.
I watched a movie called ‘Her’ recently where the actor builds a relationship with an operating system.
Such a ridiculous movie!
Currently, though, there is a serious problem with implementing AI within organizations because of the lack of knowledge amongst marketers.
In a report done with CMOs (Chief Marketing Officers) by Deloitte in 2018, the major factor that could slow down the organic growth in marketing is lack of talent.
And because AI is more technical than most other areas of marketing, this is going to be a major issue.

I wrote this guide because there is so much technical information on AI online that it’s quite difficult to understand. I’m hoping this guide will help marketers understand what AI is really about.
Once you understand AI, then you can work out how to replace the systems you use internally with AI software. And if you decide it’s smart to replace the existing software solutions, you need to figure out what functionality will be gone and what new functionality will be added.
You’ll then need to educate your team about AI and train them on the new software.
Plus, the marketplace for AI solutions is growing so fast that, without understanding AI, you’ll have a hard time finding the right vendor.
C H A P T E R – 2
The elements of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is a complex field that includes various elements.
It is focused on the following:
Learning – Acquiring information and rules for using that information.
Reasoning – Thinking about something in a logical and sensible way.
Doing – What’s the point in learning and thinking if you don’t do?
Self-correction – Understanding mistakes and correcting them.
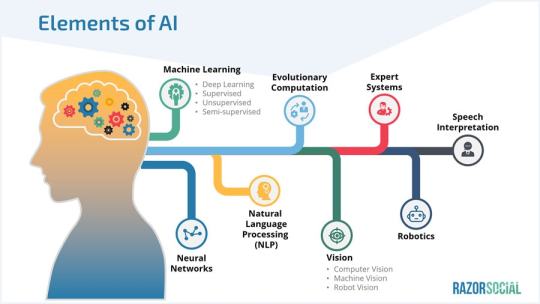
Here’s a breakdown of the main areas that AI has been implemented in.
Note: There are some overlaps in each of the areas. For example, a self-driving car uses a combination of machine learning, image recognition, and deep learning.
Neural Networks
A brain takes an input (external or internal), processes it and then produces a result.
A neuron is the basic unit of computation in the brain and it’s responsible for processing those inputs to produce the outputs.
Chemical signals are passed from neurons to neurons.
There are over 100 billion neurons, on average, in a human body and it’s an extremely complex web of interconnections between neurons. Some neurons can be connected to up 10,000 other neurons.
Imagine if someone was putting their hand near a hot stove. This is an input. The neurons would process this causing the hand to move from the stove.
Here’s how this would look internally:

The sensory neuron feels the heat, passing the information onto other internal neurons and eventually to a motor neuron which causes the reaction of moving away from the heat.
A single neuron doesn’t do much on its own, but using a complex web of neurons gives you amazing capabilities.
The neuron consists of input, output, and weight. Weight is really an indicator of importance in the overall scheme of things for this particular piece of information.
For example, you want a machine to work out how valuable a car is.
You take in a range of inputs e.g. year, make, model, condition, mileage, etc. and these are passed through neurons. Each input is weighted.
The make and the model are weighted higher than the mileage or the year.
And then:
Through a series of complex calculations, the machine comes up with a result.
Here’s a simple example of a neural network.
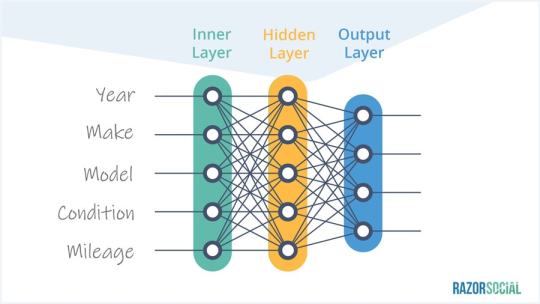
The initial inputs are weighted (e.g. characteristics based on importance), they are then sent to the hidden layer for processing, and the result is the output.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a branch of AI which enables computers to become progressively better at performing existing tasks or become able to do new tasks without any need for human intervention.
The computers are continuously analyzing data so they can produce better results in the future. Simply put, they’re becoming smarter.
Machine learning is typically broken down into 3 parts:
Deep learning
Earlier we talked about neural networks. Deep learning uses more advanced neural networks.
So instead of an input, hidden, and output layer, you may have many hidden layers.
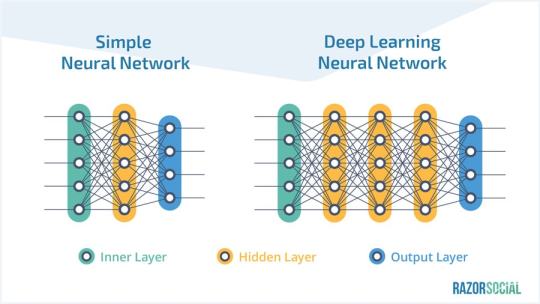
Meaning there is a lot more processing done than with a basic neural network. The same system of weights is passed between the neurons.
Deep learning is typically categorized in the following way:
Supervised
Supervised learning is where you provide the computer with input data and then the output data (i.e. the results you’d expect). You then build an algorithm around this so you can start providing new input data and the computer will automatically create the output data.
For example, imagine if you had a spam filter. Instead of giving the computer a set of rules to determine whether an email is spam or not, you provide it with a set of emails and then tell it which of those emails is spam and why. The algorithm would then be used to work out a new set of emails.
Unsupervised
With unsupervised machine learning, you provide the input data but you don’t provide the output data. The input could be a batch of test data at first.
So, the computer doesn’t have any example data to help it generate the answers. It needs to do a bit more work.
Semi-supervised
This is a happy medium. It’s not completely unsupervised but the output data is not enough to accurately predict all results.
So, the computer processes the data and uses the output data as a guideline that it improves over time as it processes more data.
You may want to use semi-supervised ML in cases when you have to manually classify the data but there’s so much to classify that you just classify a piece of it and leave the rest to the computer to deal with.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This is what natural language processing is about…

Alexa is an Amazon device.
You ask questions in a conversational way and Alexa is able to process them and give a response.
Well, it usually is…..
Natural language processing (NLP) systems have become more advanced over the last few years but there are still many challenges.
For example, it wouldn’t be unusual to say the following:
Alexa – Who are Man U playing?
Manchester United supporters often abbreviate Manchester United to Man U or the Red Devils or just saying United. There’s a slim chance that Alexa would understand these abbreviations.
Here’s another challenging example for NLP:
“I was at a pub the other night with my mates and it was deadly.”
When we use the word ‘deadly’ in this context in Ireland we mean that it was great fun. NLP systems are still not good at detecting the sentiment of text or spoken word.
So NLP will continue to evolve but it will never be perfect because of:
Accents
So many languages, variations of languages and slang used
The tone of voice and body language
Evolutionary Computation
This is the definition of evolutionary computation from Wikipedia:
“In computer science, evolutionary computation is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the sub-field of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms.”
But what does this actually mean…
It was called evolutionary because it’s a continuous process of optimization of results which ‘evolves’ better solutions over time.
It was also called evolutionary from Darwin’s theory of evolution.
For example, one of Darwin’s theories was about survival of the fittest. The weakest members of a species will die over time.
With evolutionary computing, you come up with many potential solutions to a problem. Some may be good and some may be completely random.
With testing, over time, the best solutions evolve.
With deep learning, we are focusing on models we know already. Evolutionary computing is coming up with solutions to problems where we don’t have any sample results we could use to help.
Vision
We’re talking about the ability of computers/machines or robots to see, process, and act automatically based on images.
AI for vision it’s generally split into:
Computer vision – A computer extracting information from an image to make sense of it.
Machine vision – Machines using visual methods to improve things in areas such as a production environment. They could be visually identifying faults, reviewing food labels, and/or detecting flaws in a product.
Robot vision – This is where vision is used to identify something to be worked on and the robotic capabilities perform the necessary action.
Robotics
Robots are physical machines.
Robotics is the field of study of robots.
Sometimes you’ll hear people talking about robots automatically creating content for marketers but these are not actually robots. There’s no physical robot involved.
Most robots do not have AI but this is changing.
For example, I used to own a robotic lawnmower called ‘Robomow’. The tagline was ‘It mows you don’t’. I actually used to sell them but that’s a whole different story.
Robomow sits on a charging unit and every few days it would come out and cut the grass. There was an electrical cable around the edge of the garden and the mower would go back and forth at different angles to the edges. It recorded where it had been so it knew when everywhere was cut.
It even had rain sensors so if it was raining it wouldn’t come out to cut the grass.
But it didn’t have artificial intelligence.
For example, it could have learned about obstacles in the garden and built different routes based on those obstacles.
Unfortunately, mine just kept getting stuck underneath the trampoline…
…every time…
Look:
I’m not saying these devices are not useful.
But…they could be a lot smarter.
Expert Systems
An expert system is a computer program that emulates the human ability to make decisions.
i.e. it replaces the need for or supports an existing expert.
It typically contains a knowledge base with a set of rules for applying the knowledge to each particular situation.
With machine learning capabilities, it’s building its knowledge base over time and adapting or creating new decisions based on its working knowledge.
Speech Interpretation
In the not too distant future, it will be unusual for someone not to have a device such as an Amazon Echo in their home so they can voice questions and instructions to this device and get immediate answers.
Voice interpretation is getting better all the time and some of these devices are leveraging artificial intelligence to learn over time and produce better responses.
Imagine if a speech recognition system was able to predict if a sale was going to be generated from a call center and then make suggestions to agents to improve the conversion rate?
And they did this by analyzing the conversation and the acoustics in this conversation.
A company called OTO systems studied 4,000 hours of inbound sales conversations with 50% conversion rates.
They trained their deep learning models to capture the ‘acoustic signature’ of a successful sale.
They managed to predict 94% of the call outcomes.
They then implemented this system in a call center and seen a 20% increase in engagement with a 5% increase in sales.
AI Planning
According to Wikipedia, these are strategies or sequences of actions automatically created for intelligent agents, robots or unmanned vehicles.
So, its all about analyzing a problem and producing a plan of action.
AI planning is taking into account things like:
Dependencies – does one task require another task to be completed
Milestones – specific dates that have to be met
Constraints – for example, if you only have 10 people available you can’t throw 20 people at the problem.
When the plan and the schedule are created, it is automatically adjusted based on results and changes to inputs.
For example, if a resource is not available any more then the plan has to be adjusted.
C H A P T E R – 3
AI Applications in Marketing
There are so many potential uses of AI in marketing that would make it more efficient and help deliver better results.
We have talked about 1 to 1 marketing for many years and, even with advanced marketing automation systems, this is still not a reality.
But…with artificial intelligence, we have a much better chance of delivering what feels more like a one-on-one customer communication.
Let’s take a look at some examples of how marketing can improve with AI.
AI and Content Marketing
To survive on the web we need to produce content.
Content attracts visitors, engages our audience, and gives them an incentive to come back.
Content comes in many forms:
Blog post
Testimonials
Factual data e.g. reports
Video content
Tweets
Company information
AI will never take over the full role of Content Marketer but it can certainly help.
Can computers automatically create content that doesn’t sound like it was created by a computer?
Yes!
A 2017 report by Statista found that over 90% of people surveyed said that getting personalized content was ‘very/somewhat’ appealing’.
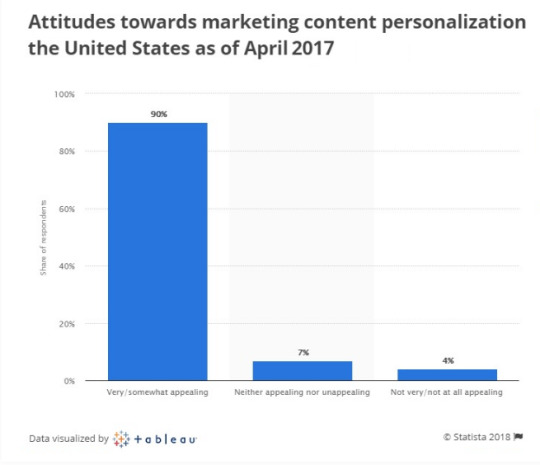
Content personalization is on the rise
Its no surprise that people want to feel like you are providing information and content that is just relevant to them. They don’t care about anyone else!!!
Marketers don’t have the time to personalize all content but luckily AI can help.
Here’s how:
Content research
MarketMuse is a software platform that gives users guidance for creating the right content. It uses big data and AI to understand how search engines rank content.
It crunches all your data and compares with other companies’ ranking for similar content.
It then organizes your content into topic clusters, defining the topics that are easy to rank for and provides recommendations on how to improve your content.
Performing a content audit is a really time-consuming process and a software like this can save you massive amounts of time.
Here’s an example where MarketMuse analyzes the top search results for marketing tools. It extracts the most relevant terms within each of the top ranking content pieces and compares this with your content.
The tool displays the number of mentions of these keywords in competitor content compared to the number of mentions in your content. You get a content score that you can improve to rank higher.
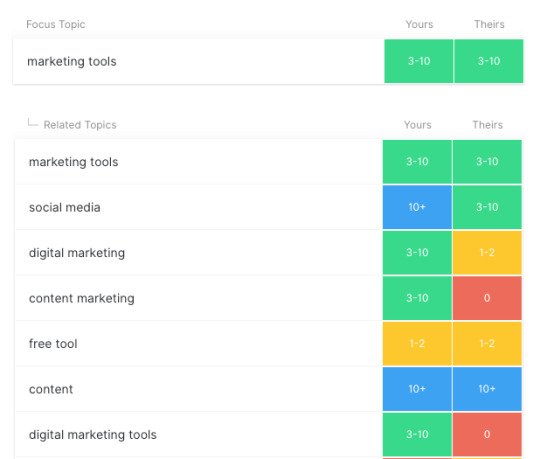
By analyzing your content, MarketMuse determines your ‘topic authority.’ These are the topics you could easily rank for by creating more content around them.
Content creation
Neurolinguistic generation (NLG) is a technology that transforms data into human-sounding narratives.
Automated Insights is a company that does exactly what their name suggests.
They analyze the data and automatically produce text that describes the data.
Imagine if you were in a stockbroking firm and you had to create 1,000 different reports for customers. That’s a dreadful thought, isn’t it?
Now, imagine clicking on a button and generating those reports automatically.
AI may not write a book or replace me as a blogger but it can certainly help a lot with content creation.
Content amplification
Content amplification is the process of promoting and distributing content through paid and unpaid tactics to achieve greater reach.
With so much noise online, even the most epic content won’t perform well unless you promote it.
Content promotion used to take up a big chunk of content marketers’ time but now there are some really smart tools out there that can help automate this process.
Here’s one example.
Inpowered is a tool that lets you select the content you want to promote across many native advertising platforms and then automates the process of placing the promotion and getting the best pay per click rates.
It will cancel promotions on certain platforms, increase promotions on other platforms, and analyze what’s working and when.
All fully automated.
This platform is interesting because the technology is very good and you only pay for engaged users. If someone views your content and immediately bounces you won’t get charged.
Content optimization
How about optimizing content to drive more traffic from Google?
In the olden days, you could stuff the same keyword many times into your article to rank.
But now…Google does semantic analysis of your content to understand what the content is about.
It uses machine learning (Rankbrain) to understand the content you write.
Also, it’s not just looking at keywords it’s looking at topic authority.
Here’s an example of how to demonstrate topic authority on your site.
You create a pillar piece of content like this piece of content.
You then create related pieces of content which link to the pillar content (and the pillar links to the related).
You may even take one step further and create guest post content on other websites linking to the related or pillar content on your site .

This shows topic authority which is more important than one post targeting a specific keyword.
Google uses AI to figure out your topic authority so it makes sense that we need tools that leverage AI to figure out if we are providing the right signals to Google.
This is what MarketMuse and other tools in this area do.
Content curation
A content curation tool is great for finding relevant content you are interested in.
For example, you set up a set of keywords and it finds content that is popular related to those keywords.
But….
…the AI version of the content curation tool takes an extra step.
Take Frase.io as an example.
This finds content but then uses AI to summarize the content so you don’t have to read it all.
I don’t know about you but that sounds awesome to me!!!
In terms of content curation, AI should assist in the following workflows: – Making more targeted queries and removing noise when monitoring the media – Summarizing information to help knowledge workers consume content faster and only dig deeper when relevant – Identifying relationships between topics and drawing trends over time Improved content curation through AI should help marketers create better newsletters, incorporate more research on their original content, scale their social media posting and create richer internal microsites. Digital publishers may use AI-driven content curation to automatically generate reports and enrich their editorial workflow.
Tomas Ratia CEO Frase.io
AI and Analytics
We typically break analytics down into descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, but let’s add a fourth dimension:
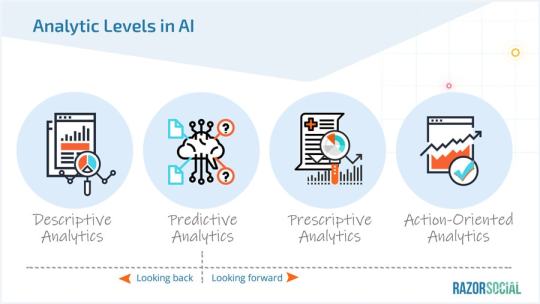
Descriptive – Looking into the past to understand what has happened
Predictive – Looking at the past and figuring out what could happen in the future
Prescriptive – Figuring out what we should do next
Action-oriented – Automatically implementing, testing, and adapting.
Descriptive analytics has been around for a long time.
An example of this would be seeing Google Analytics data but not knowing what to do with it.
Predictive analytics gives you ideas of what you might do and prescriptive tells you what you need to do.
Action-oriented analytics is where actions are automatically taken and tested based on what is prescribed.
Sometimes I log into my wife’s Netflix account by mistake and most of the recommendations are not the movies I would watch!
But when I log into my Netflix account it always shows something of interest to me.
Netflix automatically groups people into different categories and ratings are based on the feedback within the category you are placed in.
So, when I see a percentage rating indicating how likely I am to like a movie, this rating could be different for my wife as she’s in a different category.
Netflix continuously tries to provide better recommendations to market better movies to their users.
But they don’t just look at the movie/show you started watching. They will also look at:
Did you watch some of it and stopped watching
Did you watch it over a couple of nights
When you watched it i.e. a month ago, a year ago, etc.
And, of course, much more.
These are machine learning algorithms that are learning over time and automatically adjusting.
A UK company called Datalytyx have patented an AI solution which solves a major problem of analyzing large volumes of data, for example, analzying billions of records.
It’s AI software identifies the most relevant 1% of the data and you run reports based on this.
AI and Marketing Automation
A typical marketing automation task is sending a series of emails to users after they opted in to an email list.
And then, based on their interaction with emails, route people to a different path.
For example, the click on a link about a new product in the second email in a sequence triggers a different email.
This is smart email automation but it’s not AI.
AI adds a whole new layer of intelligence. Here are some examples:
Watson is an IBM platform that uses AI to learn more about your data.
‘Watson marketing‘ is a part of the Watson platform focused on…you guessed it…marketing.
One of its components is creating targeted email campaigns.
It uses AI to understand more about each individual in the campaign and tailors the communication based on this data.
For example, instead of just putting people into a bucket based on a form they fill out, it pulls the data from many sources and creates micro-segments based on lifestyle, social behavior, life stage, location, etc.
But it will also continuously evaluate this data and automatically move people between segments based on new data and performance analysis.
When you are working with large data sets you need AI to automate certain tasks and make sense of data.
For example:
Compile data from many sources and create micro-segments based on lifestyle, social behavior, life stage, location, etc.
Discover flaws in original campaigns and change segments and offers based on this.
AI and Conversational Marketing
A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate a conversation with another human.
There are many tools available (e.g. mobile monkey) which allow you to easily create a chatbot.
They have a builder program which allows you to automatically create actions based on inputs.
However, these chatbots are not AI-enabled. They are trained to recognize specific user intents and they tap into a knowledge base to retrieve answers (retrieval-based chatbots).
We’re still far from seeing chatbots that can provide users with an unlimited amount of answers that they can generate on the fly. This would be the true AI at work.
Most chatbots today operate in a specific niche and the amount of things that they know and can do is very limited. However, they still use NLP techniques to understand human language. The more sophisticated ones also use sentiment analysis to understand the emotion behind the user’s words.
Chatbots, as they are today, are still a very useful tool to help automate certain parts of the sales and marketing process.
For example, chatbots can:
increase engagement through personalized conversations with users
handle customer inquiries on your website
improve targeting by collecting useful insights about users
Now, for companies that already use chatbots on their website, there are tools that can help them understand how well they’re performing.
Liveperson.com analyzes chatbot conversations in real-time to assess when customers are having a poor customer experience. Companies can then take action based on this.
Not sure if we’ll use this…may come up with a new diagram.
AI and Email Marketing
Email marketing is one area that could benefit tremendously from AI.
Just think about it – an AI tool could help you determine which type of content you need to send and when you need to send it to increase your chances of converting an individual prospect.
Given the fact that AI can process enormous amounts of data in no time, you’d be running smarter and more efficient campaigns with a better ROI. Not the mention the time you’d save on A/B testing!
An email marketing tool powered by AI could also help with another challenging area for marketers – sending highly personalized emails at scale.
AI can take into account a customer’s history with your company and determine the type of messaging and offers that work best.
For example, Phrasee is an email marketing tool that uses AI to generate subject lines, body copy, and CTAs to encourage higher click-through rates and engagement on email marketing campaigns.
AI and SEO
Artificial intelligence has the potential to make search more human.
It means that search engines now look more at the meaning and the context of the searcher’s query to deliver more meaningful results.
The era of keyword stuffing is over. Search algorithms are now focusing on the user’s context and search intent.
And this is a good thing.
Marketers can also leverage AI tools to improve the ranking of their content.
Now you can use AI to improve your SEO efforts in a variety of ways, including:
Identifying content opportunities
Performing keyword research
Identifying opportunities for content optimization
Content personalization, and more.
AI and Social Media
Every time you log into Facebook and view the news feed you are seeing AI in action.
Facebook is continuously monitoring who you follow, what you interact with, how you consume content and more.
These algorithms learn over time to produce better news feed results.
Facebook is all about engagement.
If you spend more time on the platform they can show you more ads and they make more money.
It’s that simple!
It makes total sense to track what you interact and don’t interact with.
If you follow a Facebook page and never interact with the posts they publish, that is a sure sign that you have no interest in that page’s content.
Here’s another example of AI for social media.
Persado provides “machine-generated marketing copy to drive maximum performance in any channel.”
It picks out the best words, phrases, visuals and emotions to drive more engagement.
And social media is all about engagement.
With this social media module they will automatically create the text and find the best images that will drive the most engagement.
AI and Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
Conversion rate optimization is all about improving conversion.
For example, out of 100 visitors to your website you convert 2%, and then you make changes to your website and increase your conversion to 3%.
There are many ways to increase conversion:
Improve your ads so that you get a higher click-through rate and lower cost
Improve ads so you are sending a better audience to your offer
Build a different sales funnel, for example, add an up-sell option after someone buys
Change the pages that are part of the funnel e.g. colors, text, images, video, etc.
This is a very time consuming and manual process and this is where AI can help.
Unbounce is a landing page tool.
They recently built a pilot project around AI and included 34 customers over a 6 week period.
The AI analyzed the performance of the landing pages on real campaigns and instructed conversion specialists on what to change.
On average, the increase in conversion on the pages was 19.8% with one page achieving over 100%.
This is certainly a higher performance increase than you’d expect to get from working with a conversion specialist.
AI and Listening / Monitoring
Every company out there wants to be able to capture as much of the conversations around their brand as possible.
The goal is to understand not only what people are saying about their brand, products or services, but also how they feel about them.
This helps marketers to analyze their brand presence and use those insights to improve communication with their audience and target their campaigns better.
NLP and Sentiment Analysis can really help in this area.
Companies can use AI to understand conversations around their products so they can spot potential issues and act on them, as well as to uncover purchase intent.
AI and Image Recognition
We all know how important visual content is for marketing.
Now we can use AI and image recognition tools to analyze trends and uncover the type of visuals that would bring the best results on social media and other channels.
Image recognition allows marketers to ‘listen’ to what their audience is saying through images so they can deliver visual content that fits the interests of that audience.
AI can help analyze millions of social media posts and filter through the images that people share and engage with.
Without image recognition tools, it would be impossible for marketers to analyze this amount of visual material!
One example of this is the Image Insights platform from Brandwatch. This tool is focused on helping companies uncover how people are using images that contain their brand across social media.
It basically analyzes visual mentions of a brand’s logo across millions of social media posts.
AI and Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing is a very powerful form of marketing but brands find it difficult to identify the right influencers.
With AI technology there are now smarter ways of analyzing and finding influencers.
For example:
Image recognition – AI can analyze thousands of properties of an image to find out what the image is really about.
Content analysis – AI can analyze influencer content to find out what exactly the influencer is passionate about and gets engagement for.
Assess engagement – AI tools can distinguish between fake and real engagement and analyze this level of engagement.
Influencer – Through the analysis above and other analysis it can work out how influential someone is and in what areas.
Demand for useful content from trusted experts is taking the marketing world by storm in the form of influencer collaboration and AI is playing multiple roles.
From AI powered virtual influencers on Instagram like @lilmiquela with 1.5 million followers to sophisticated AI systems used in influencer marketing platforms, the impact and implications of artificial intelligence on influencer marketing are just beginning.
Future applications of AI and influencer marketing include the ability to predict potential impact of certain influencers, content types and channel combinations as well as more advanced filtering of influencers with fake followers.
Lee Odden – Founder Toprank Marketing
C H A P T E R – 4
Security Concerns about AI
In 2018, the EU brought in a regulation called GDPR (global data protection regulation).
Its goal is to regulate the collection, storage, and use of personal data by companies without permission.
As consumers get more and more concerned with the use their personal data, I expect that similar regulation will be implemented in other parts of the world.
As AI is all about collecting and processing data this has serious repercussions.
Let’s say you walked into a supermarket and the supermarket used facial recognition to identify you and then tailored your experience based on the available data. Do they have the permission to do this? Not in Europe.
So, although AI is extremely powerful, some of it’s use will need to be approved.
Summary
There is a bright future ahead of us for AI.
It will have a huge impact on marketing for many years to come.
It will change marketing roles, it will remove some of them entirely, and it will provide a whole new level of sophistication which was never possible before.
Should you be concerned as a Marketer?
Of course.
You need to stay on top of developments in AI and see how you can incorporate it into your marketing.
You need to think about your role as a Marketer and how your role will evolve or be replaced in the future.
The post Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach to Marketing appeared first on RazorSocial.
from Blog | RazorSocial https://www.razorsocial.com/artificial-intelligence-a-modern-approach-to-marketing/
0 notes
Text
Product strategy: at the heart of our new technology platform
In recent years, the requirements for analytics as well as the range of data user profiles has shifted dramatically. At the same time, there has been an increasing demand for flexibility, customisation and power. As the number of technical providers continues to grow, the offerings of digital performance measurement solutions have become somewhat diluted – resulting in a complex, uneven and incomplete market.
As a long-term player and digital analytics pioneer since 1999, AT Internet has taken an innovative approach to the current market challenges and completely redefined its technologies. With an approach strongly focused on the needs of our users, while adhering to our values (ethical and eco-responsible), we have set out on a genuine product revolution. Our goal was more than just creating the most functions – an approach that goes against today’s need for tools that are accessible to everyone and allow users to act quickly. Instead, we’ve aimed to apply the most recent technological developments – to provide an intelligent solution to marketing, product strategy, UX and General Management challenges – while remaining focussed on the need for energy conservation and importance of privacy by design.
Here’s the full rundown of our vision, technical approach and how AT Internet carried out this technological shift.
A diverse and complex digital analytics market
When AT Internet arrived on the scene, we essentially measured interactions between computers and web pages. 20 years later, the market has come a long way. Users now combine a range of devices (smartphones, connected watches, voice assistants etc.) to access the wide range of platforms each brand offers (website, mobile site, iOS application, Android application, etc.). To respond to this, Digital Analytics solutions now need to measure these complex journeys in their entirety and as exhaustively as possible. The fact that there is an extremely wide and strategic scope of use of this data means that it also has to be highly reliable.
However, the reality of today’s Digital Analytics market is complex. Even if everyone agrees on the importance of having a complete, coherent and accurate knowledge of the reality of uses, a company looking to purchase the most appropriate solution still needs to understand the range of different approaches on the market.
Digital Marketing Analytics tools, designed to meet specific digital marketing issues, have a range of complex concepts (traffic acquisition, monetisation, numerous metrics and specific analyses…). AT Internet, Adobe Analytics and the market share leader Google Analytics are clearly positioned in this category. The quantity and variety of standard information is probably the main advantage of these players, especially for marketing management roles. Nevertheless, these tools can quickly reach their limits when it comes to analysing very specific company concepts.
Product Analytics tools have been able to take advantage of the drawbacks of Digital Marketing Analytics to gain a place in the market. American providers such as Mixpanel, Amplitude or Heap analytics, have a high degree of flexibility, allowing them to measure interactions that are very specific to the development of a product or service. Their perceived simplicity is a strong selling point for profiles in the product domain (Product Managers, Product Owners etc.). Their disadvantage is that the high degree of flexibility can make them complex when it comes to having reliable and exhaustive data – as very few analyses are ready to use. To reconstruct the visit metrics or to rebuild the dozens of marketing analyses available and necessary in digital analytics is both tedious and potentially hazardous. There are countless risks of error and it is unrealistic to imagine certifying audiences in this way.
Finally, In-house tools (designed in-house), have for a long time been only available to more mature companies. However, the availability of cloud platforms has democratised the tools needed for In-house projects. These tools can offer end-to-end customisation capabilities (nature of the data collected, processing applied, restitution interfaces) while offering configurable computing power. But beyond the exceptional skills required to successfully complete this type of project, this approach often requires numerous functional trade-offs for an economical balance that is often very challenging to maintain over time (development costs, risks, technical debt, maintenance, etc.). In addition, technical developments (cookies, adblocking, new media) and recent legislation (e.g. the GDPR) make it difficult to ensure reliability and compliance. In practice, companies that have the skills to deliver and, above all, maintain such projects are few and far between.
As a result, companies may be tempted to combine the Digital Marketing Analytics and Product Analytics tools to answer all the questions they may have about its users, while still having the flexibility of an In-House solution. However, the high cost of doing this makes it unsustainable in the long term, especially for tools that work in silos at the expense of data quality.
The elements of a new technological platform
In addition to the robustness and reliability of our solution’s analytical core, developed and proven for over 20 years by tens of thousands of users, we are adding three new key ingredients to deliver the best of Digital Marketing, Product and In-house analytics.
A strongly user-centric vision: we are going to offer even more flexibility in the ability to analyse the entire user journey, while making it easier to manipulate metrics such as Unique users (which are costly in terms of computing resources).
A higher degree of flexibility: on the basis of a more complete data model, each company will be able to take into account its own requirements thanks to almost unlimited customisation capabilities (customised variables, metrics or custom events).
Unlimited computing power: this is probably the most anticipated feature. To respond to increasingly numerous and complex challenges (deduplication, segmentation, combining datasets), the analysis and calculation power is multiplied. Some of our customers are already collecting tens of billions of interactions per month.
This new phase of our digital analytics solution is the result of one of the most ambitious projects in the history of AT Internet. To intelligently combine the 3 strengths mentioned above with our expertise, we started from scratch to build a brand-new platform – the New Data Factory. The project is particularly far-reaching as we have chosen to carry it out in complete transparency for our clients, delivering functionalities as the development progresses. Without realising, they have been using both the old measurement system and this new technological platform for months. Some of the product’s flagship functions are entirely based on this new system: our Navigation analysis, e-commerce Sales Insights analyses, or more recently the new version of our data mining tool Data Query 3.
Another foundation of our product strategy is ethics by design. Respect for the privacy of Internet users is an integral part of our company DNA. An efficient and reliable analytics solution cannot be designed without a relationship of total trust between the solution, the site and its users. In addition to guaranteeing complete technical transparency and independence, our business is exclusively that of analytics, and the ownership of the data is entirely that of the client (without any secondary use). Moreover, we are convinced that the main value of analytics above all is to better understand in order to better serve. There is no sustainable value creation from data without a clear contract of trust with Internet users. The guarantees we offer in terms of privacy and the work we have done with the CNIL, responsible for the application of the GDPR, allow us to benefit in France from an exemption from the collection of consent. This exemption is subject to conditions but allows us to make the completeness of the data considerably more reliable while respecting the essential trust of Internet users.
Finally, in addition to protecting privacy, our ethical approach also consists of minimising the impact of our activities on the planet. Collecting and processing information en masse is a particularly energy-intensive activity. We are committed to developing a solution that will reduce its carbon impact, notably through intelligent resource management and a systematic search for minimising the information collected and stored. The Big Data is not concerned about the purpose of data collection, and the quality of the data ingested and digested today seems irresponsible and disrespectful of the expectations of Internet users.
Respect for privacy, the minimisation of the data collected and calculated, and the economic balance are part of a virtuous circle where the data is fairer, more reliable, more respectful and less harmful for the planet.
The Analytics Suite: enhanced relevance and value
Our product strategy is to deliver value-added functionalities as this new technology platform is developed. Our customers have therefore already been able to test a few components of this enhanced version of the Analytics Suite.
Priority on data activation via Machine Learning
The Analytics Suite offers Data Science features based on Machine Learning algorithms: anomaly detection, prediction, contribution and automatic clustering. We are constantly enhancing our offer with intelligent functions (AXON) to support the analyst’s work by automatically suggesting insights. Traditional core analytics remain available and also continue to evolve with releases. Sunburst, for example, useful for analysing navigational routes, or funnels to illustrate churn points during the shopping journey, are still available in the solution.
We remain committed to offering a system that is fully open and ready to interconnect with our customers’ entire ecosystem. A new-generation API is being introduced, complemented by unprecedented mechanisms for extracting large volumes of data to ensure the widest possible distribution of value. There will also be more ready-to-use AT Connect connectors natively integrated into the platform. These information flows will ease the use of the data via partner tools, subject to the informed consent of the Internet user.
Flexibility and customisation, up to 1000 variables
Each company has its own specific requirements that call for a high degree of customisation. Expectations are even higher when it comes to meeting challenges other than those related to digital marketing, such as UX or product strategy. Our solution is designed to allow our clients to collect a wide range of information about users’ interactions with their brand. When an event is measured (page load, video play, etc.), it is qualified by a number of parameters that we call properties. It is this structuring that makes the information usable and relevant – each type of interaction can have specific properties. We will allow our customers to add a large number of custom properties (up to 1000).
In addition to the thirty or so predefined events offered by AT Internet, our users will be able to create an unlimited number of custom events. These include downloading a brochure, adding music to a playlist, or contacting a vendor on a classified ad site. They will be able to measure interactions that are in line with their strategic objectives or that will enrich the data collected so far, using their own jargon. These events will also be qualified by properties available in the AT Internet data model or customised.
Tagging: the tag first approach
To achieve this high degree of customisation, we will apply the tag first approach. This means that any data present in the collection library (JS, SDK) is automatically collected. Gone are the previous configurations and declarations when it comes to adding new types of events or new custom properties. To ensure data quality and seamless governance, authorised users will be notified when changes are applied to the data model. A simple authorisation will allow them to make them effective.
For all the information that does not belong in the tagging libraries, we now offer the ability to easily import data into the platform:
User criteria
Product catalogues (colours, model, brand, stock, etc.)
Content catalogues (genre, duration, director, etc.)
Campaign listings (type, cost, formats, etc.)
Generally speaking, any information that can be associated with a key (ID).
Of course, it will still be possible to easily create personalised processing rules to correct or enrich the data collected before it is stored in the platform.
A ready-to-use tool with 400 properties and 120 standard metrics
The self-service analytics feature, which is already a major strength of the product, will be further enhanced. The platform’s new data model is enriched, bringing the number of standard properties (traffic sources, e-commerce, audio/video, advertising, technologies…) to more than 400 and the number of metrics to 120. The use of this data model combines significant time savings with high quality analysis.
An exceptionally smooth experience
An analyst must be able to identify the potential for optimisation in Explorer, continue their investigation in Data Query and share the results of their analysis in a customised dashboard. Adaptive and scalable, the user will be able to choose which features to access based on their profile.
Behind the scenes of a technological revolution
In line with our product vision, the development of a new technological platform has been the subject of a number of decisive technical choices.
Architecture: adapted technologies and a DevOps approach
Starting from scratch to develop a product allows you to choose the best in terms of technology. In the past, our platform has been almost entirely based on a single range of technology solutions. We are changing our approach and now choose to use as many technologies as necessary to achieve our goals. Some are genuine industry benchmarks, such as Kafka for real-time processing, or Snowflake which is probably the most powerful datawarehouse on the market. But beyond the technologies, it is the quality of the tool combinations that is key to the expected benefits. To ensure that these different components work together smoothly, scalably and flexibly, we are applying a DevOps approach within our development teams and making extensive use of container orchestration (Kubernetes).
Storage: a radically different approach to unifying data
The new technology platform is based on a unified storage of all data collected on behalf of a company. Whether standard or custom, all properties become a column in this data storage structure. The measured interactions are rows in this structure (potentially several billion per month), regardless of the sites or devices they come from.
This radical change in technical approach has two advantages:
A truly unified view: all the data generated by a user is gathered and available. An analyst will be able to study a very large scope (all platforms), a set of sites (all applications) or even a section of a site, without constraints.
Unparalleled performance: this storage method, backed by the technological choices made, allows unprecedented query speed. The volume of data and the complexity of queries no longer impose limits.
In a future article, we will discuss in detail the technical advantages of unified column storage compared to a more traditional approach.
Photo credits: Xavier Bellenger
Article Product strategy: at the heart of our new technology platform first appeared on Digital Analytics Blog.
from Digital Analytics Blog https://ift.tt/2wdyxFf via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
A Modern Approach to Marketing
In this guide, I’ll go into detail about how artificial intelligence is impacting marketing right now and how it will continue to impact it in the future.
At the end of this post, you’ll be excited about the possibilities of AI and probably a little nervous about the implications!
And it’s alright to be nervous because the role of marketers in organizations will change but….
…you’ll still have an important role to play.
Table of Contents
Download a PDF of this Guide
Would you prefer to read this later? If so, download a PDF version of the AI Guide.
C H A P T E R – 1
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence in Marketing is real and now is the time to sit up and take notice.
Artificial intelligence is accelerating marketing toward a more intelligently automated future in which smarter (i.e. AI-powered) solutions enable marketers to solve problems and achieve goals more efficiently. You have a choice. You can sit back and wait for the marketing world to get smarter and change around you, or you can embrace AI now and be proactive in creating a competitive advantage for yourself and your company.
Paul Roetzer, Founder of Marketing Artificial Intelligence Institute
However, not all software companies really have AI that say they do.
There’s just so much hype surrounding AI Tech companies want to capitalize on it by saying their software is powered by AI and investors will give higher valuations to them because of the AI in their software.
But there are many great software companies building true AI applications and this is set to grow massively over the next few years.
MRFR research predicted the AI market to be worth 25 billion by 2025.
If you’re a marketer, it’s time to get up to speed and understand the potential impact that AI will have on marketing. I’m pretty sure that this guide will help.
So, what is artificial intelligence?
We all know what human intelligence is…I hope so anyway!
Artificial intelligence is when a machine demonstrates some human-like intelligence.
For example:
A machine processes data and learns from it so it can make smarter decisions about the data it will process in the future.
Instead of just repeating the same instructions, the machine automatically learns new instructions based on experience.
Alpha Zero, the game playing AI developed by Deepmind, learned Chess in 4 hours and then was able to beat the best computer program available for playing chess.
Learning a new game is mimicking human intelligence, but the AI can learn in 4 hours what a human may take months doing.
Computer science describes the study of AI as the development of intelligent agents.
Look:
This is really about smart programming.
Our intelligence helps create artificial intelligence.
As some tasks become very routine they may not be considered artificial intelligence anymore.
Here’s an example:
Optical character recognition is often excluded because it’s a routine task expected from computers.
What is the difference between narrow and strong AI?
Narrow AI (also called weak AI) is artificial intelligence focused on one task.
Strong AI is everything else!
Strong AI has the ability to apply intelligence to any problem rather than a specific task.
For example:
A spam filtering tool performs one task well. A self-driving car is also described as narrow AI but I think this is a bit of a stretch!
Will Artificial Intelligence Replace Marketers?
Yes…. some!!!
Marketing is a time-intensive process with a lot of repetitive tasks which machines can help with…
…but there are certain tasks that machines will never be able to perform at the same level as human marketers.
I can imagine, in the future, sitting across from a robot discussing a business proposition but I can’t imagine I’d build the same relationship with a robot as with a real human. It’s relatively easy to build software to beat someone at Chess and…
…the software gets better at beating people.
But…
Building relationships is the most important part of marketing and computers suck at it.
Also, who is going to build a strategy for a company?
An AI enabled machine can provide inputs into this strategy but strategists will still survive.
I watched a movie called ‘Her’ recently where the actor builds a relationship with an operating system.
Such a ridiculous movie!
Currently, though, there is a serious problem with implementing AI within organizations because of the lack of knowledge amongst marketers.
In a report done with CMOs (Chief Marketing Officers) by Deloitte in 2018, the major factor that could slow down the organic growth in marketing is lack of talent.
And because AI is more technical than most other areas of marketing, this is going to be a major issue.
I wrote this guide because there is so much technical information on AI online that it’s quite difficult to understand. I’m hoping this guide will help marketers understand what AI is really about.
Once you understand AI, then you can work out how to replace the systems you use internally with AI software. And if you decide it’s smart to replace the existing software solutions, you need to figure out what functionality will be gone and what new functionality will be added.
You’ll then need to educate your team about AI and train them on the new software.
Plus, the marketplace for AI solutions is growing so fast that, without understanding AI, you’ll have a hard time finding the right vendor.
C H A P T E R – 2
The elements of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is a complex field that includes various elements.
It is focused on the following:
Learning – Acquiring information and rules for using that information.
Reasoning – Thinking about something in a logical and sensible way.
Doing – What’s the point in learning and thinking if you don’t do?
Self-correction – Understanding mistakes and correcting them.
Here’s a breakdown of the main areas that AI has been implemented in.
Note: There are some overlaps in each of the areas. For example, a self-driving car uses a combination of machine learning, image recognition, and deep learning.
Neural Networks
A brain takes an input (external or internal), processes it and then produces a result.
A neuron is the basic unit of computation in the brain and it’s responsible for processing those inputs to produce the outputs.
Chemical signals are passed from neurons to neurons.
There are over 100 billion neurons, on average, in a human body and it’s an extremely complex web of interconnections between neurons. Some neurons can be connected to up 10,000 other neurons.
Imagine if someone was putting their hand near a hot stove. This is an input. The neurons would process this causing the hand to move from the stove.
Here’s how this would look internally:
The sensory neuron feels the heat, passing the information onto other internal neurons and eventually to a motor neuron which causes the reaction of moving away from the heat.
A single neuron doesn’t do much on its own, but using a complex web of neurons gives you amazing capabilities.
The neuron consists of input, output, and weight. Weight is really an indicator of importance in the overall scheme of things for this particular piece of information.
For example, you want a machine to work out how valuable a car is.
You take in a range of inputs e.g. year, make, model, condition, mileage, etc. and these are passed through neurons. Each input is weighted.
The make and the model are weighted higher than the mileage or the year.
And then:
Through a series of complex calculations, the machine comes up with a result.
Here’s a simple example of a neural network.
The initial inputs are weighted (e.g. characteristics based on importance), they are then sent to the hidden layer for processing, and the result is the output.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a branch of AI which enables computers to become progressively better at performing existing tasks or become able to do new tasks without any need for human intervention.
The computers are continuously analyzing data so they can produce better results in the future. Simply put, they’re becoming smarter.
Machine learning is typically broken down into 3 parts:
Deep learning
Earlier we talked about neural networks. Deep learning uses more advanced neural networks.
So instead of an input, hidden, and output layer, you may have many hidden layers.
Meaning there is a lot more processing done than with a basic neural network. The same system of weights is passed between the neurons.
Deep learning is typically categorized in the following way:
Supervised
Supervised learning is where you provide the computer with input data and then the output data (i.e. the results you’d expect). You then build an algorithm around this so you can start providing new input data and the computer will automatically create the output data.
For example, imagine if you had a spam filter. Instead of giving the computer a set of rules to determine whether an email is spam or not, you provide it with a set of emails and then tell it which of those emails is spam and why. The algorithm would then be used to work out a new set of emails.
Unsupervised
With unsupervised machine learning, you provide the input data but you don’t provide the output data. The input could be a batch of test data at first.
So, the computer doesn’t have any example data to help it generate the answers. It needs to do a bit more work.
Semi-supervised
This is a happy medium. It’s not completely unsupervised but the output data is not enough to accurately predict all results.
So, the computer processes the data and uses the output data as a guideline that it improves over time as it processes more data.
You may want to use semi-supervised ML in cases when you have to manually classify the data but there’s so much to classify that you just classify a piece of it and leave the rest to the computer to deal with.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This is what natural language processing is about…
Alexa is an Amazon device.
You ask questions in a conversational way and Alexa is able to process them and give a response.
Well, it usually is…..
Natural language processing (NLP) systems have become more advanced over the last few years but there are still many challenges.
For example, it wouldn’t be unusual to say the following:
Alexa – Who are Man U playing?
Manchester United supporters often abbreviate Manchester United to Man U or the Red Devils or just saying United. There’s a slim chance that Alexa would understand these abbreviations.
Here’s another challenging example for NLP:
“I was at a pub the other night with my mates and it was deadly.”
When we use the word ‘deadly’ in this context in Ireland we mean that it was great fun. NLP systems are still not good at detecting the sentiment of text or spoken word.
So NLP will continue to evolve but it will never be perfect because of:
Accents
So many languages, variations of languages and slang used
The tone of voice and body language
Evolutionary Computation
This is the definition of evolutionary computation from Wikipedia:
“In computer science, evolutionary computation is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the sub-field of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms.”
But what does this actually mean…
It was called evolutionary because it’s a continuous process of optimization of results which ‘evolves’ better solutions over time.
It was also called evolutionary from Darwin’s theory of evolution.
For example, one of Darwin’s theories was about survival of the fittest. The weakest members of a species will die over time.
With evolutionary computing, you come up with many potential solutions to a problem. Some may be good and some may be completely random.
With testing, over time, the best solutions evolve.
With deep learning, we are focusing on models we know already. Evolutionary computing is coming up with solutions to problems where we don’t have any sample results we could use to help.
Vision
We’re talking about the ability of computers/machines or robots to see, process, and act automatically based on images.
AI for vision it’s generally split into:
Computer vision – A computer extracting information from an image to make sense of it.
Machine vision – Machines using visual methods to improve things in areas such as a production environment. They could be visually identifying faults, reviewing food labels, and/or detecting flaws in a product.
Robot vision – This is where vision is used to identify something to be worked on and the robotic capabilities perform the necessary action.
Robotics
Robots are physical machines.
Robotics is the field of study of robots.
Sometimes you’ll hear people talking about robots automatically creating content for marketers but these are not actually robots. There’s no physical robot involved.
Most robots do not have AI but this is changing.
For example, I used to own a robotic lawnmower called ‘Robomow’. The tagline was ‘It mows you don’t’. I actually used to sell them but that’s a whole different story.
Robomow sits on a charging unit and every few days it would come out and cut the grass. There was an electrical cable around the edge of the garden and the mower would go back and forth at different angles to the edges. It recorded where it had been so it knew when everywhere was cut.
It even had rain sensors so if it was raining it wouldn’t come out to cut the grass.
But it didn’t have artificial intelligence.
For example, it could have learned about obstacles in the garden and built different routes based on those obstacles.
Unfortunately, mine just kept getting stuck underneath the trampoline…
…every time…
Look:
I’m not saying these devices are not useful.
But…they could be a lot smarter.
Expert Systems
An expert system is a computer program that emulates the human ability to make decisions.
i.e. it replaces the need for or supports an existing expert.
It typically contains a knowledge base with a set of rules for applying the knowledge to each particular situation.
With machine learning capabilities, it’s building its knowledge base over time and adapting or creating new decisions based on its working knowledge.
Speech Interpretation
In the not too distant future, it will be unusual for someone not to have a device such as an Amazon Echo in their home so they can voice questions and instructions to this device and get immediate answers.
Voice interpretation is getting better all the time and some of these devices are leveraging artificial intelligence to learn over time and produce better responses.
Imagine if a speech recognition system was able to predict if a sale was going to be generated from a call center and then make suggestions to agents to improve the conversion rate?
And they did this by analyzing the conversation and the acoustics in this conversation.
A company called OTO systems studied 4,000 hours of inbound sales conversations with 50% conversion rates.
They trained their deep learning models to capture the ‘acoustic signature’ of a successful sale.
They managed to predict 94% of the call outcomes.
They then implemented this system in a call center and seen a 20% increase in engagement with a 5% increase in sales.
AI Planning
According to Wikipedia, these are strategies or sequences of actions automatically created for intelligent agents, robots or unmanned vehicles.
So, its all about analyzing a problem and producing a plan of action.
AI planning is taking into account things like:
Dependencies – does one task require another task to be completed
Milestones – specific dates that have to be met
Constraints – for example, if you only have 10 people available you can’t throw 20 people at the problem.
When the plan and the schedule are created, it is automatically adjusted based on results and changes to inputs.
For example, if a resource is not available any more then the plan has to be adjusted.
C H A P T E R – 3
AI Applications in Marketing
There are so many potential uses of AI in marketing that would make it more efficient and help deliver better results.
We have talked about 1 to 1 marketing for many years and, even with advanced marketing automation systems, this is still not a reality.
But…with artificial intelligence, we have a much better chance of delivering what feels more like a one-on-one customer communication.
Let’s take a look at some examples of how marketing can improve with AI.
AI and Content Marketing
To survive on the web we need to produce content.
Content attracts visitors, engages our audience, and gives them an incentive to come back.
Content comes in many forms:
Blog post
Testimonials
Factual data e.g. reports
Video content
Tweets
Company information
AI will never take over the full role of Content Marketer but it can certainly help.
Can computers automatically create content that doesn’t sound like it was created by a computer?
Yes!
A 2017 report by Statista found that over 90% of people surveyed said that getting personalized content was ‘very/somewhat’ appealing’.
Content personalization is on the rise
Its no surprise that people want to feel like you are providing information and content that is just relevant to them. They don’t care about anyone else!!!
Marketers don’t have the time to personalize all content but luckily AI can help.
Here’s how:
Content research
MarketMuse is a software platform that gives users guidance for creating the right content. It uses big data and AI to understand how search engines rank content.
It crunches all your data and compares with other companies’ ranking for similar content.
It then organizes your content into topic clusters, defining the topics that are easy to rank for and provides recommendations on how to improve your content.
Performing a content audit is a really time-consuming process and a software like this can save you massive amounts of time.
Here’s an example where MarketMuse analyzes the top search results for marketing tools. It extracts the most relevant terms within each of the top ranking content pieces and compares this with your content.
The tool displays the number of mentions of these keywords in competitor content compared to the number of mentions in your content. You get a content score that you can improve to rank higher.
By analyzing your content, MarketMuse determines your ‘topic authority.’ These are the topics you could easily rank for by creating more content around them.
Content creation
Neurolinguistic generation (NLG) is a technology that transforms data into human-sounding narratives.
Automated Insights is a company that does exactly what their name suggests.
They analyze the data and automatically produce text that describes the data.
Imagine if you were in a stockbroking firm and you had to create 1,000 different reports for customers. That’s a dreadful thought, isn’t it?
Now, imagine clicking on a button and generating those reports automatically.
AI may not write a book or replace me as a blogger but it can certainly help a lot with content creation.
Content amplification
Content amplification is the process of promoting and distributing content through paid and unpaid tactics to achieve greater reach.
With so much noise online, even the most epic content won’t perform well unless you promote it.
Content promotion used to take up a big chunk of content marketers’ time but now there are some really smart tools out there that can help automate this process.
Here’s one example.
Inpowered is a tool that lets you select the content you want to promote across many native advertising platforms and then automates the process of placing the promotion and getting the best pay per click rates.
It will cancel promotions on certain platforms, increase promotions on other platforms, and analyze what’s working and when.
All fully automated.
This platform is interesting because the technology is very good and you only pay for engaged users. If someone views your content and immediately bounces you won’t get charged.
Content optimization
How about optimizing content to drive more traffic from Google?
In the olden days, you could stuff the same keyword many times into your article to rank.
But now…Google does semantic analysis of your content to understand what the content is about.
It uses machine learning (Rankbrain) to understand the content you write.
Also, it’s not just looking at keywords it’s looking at topic authority.
Here’s an example of how to demonstrate topic authority on your site.
You create a pillar piece of content like this piece of content.
You then create related pieces of content which link to the pillar content (and the pillar links to the related).
You may even take one step further and create guest post content on other websites linking to the related or pillar content on your site .
This shows topic authority which is more important than one post targeting a specific keyword.
Google uses AI to figure out your topic authority so it makes sense that we need tools that leverage AI to figure out if we are providing the right signals to Google.
This is what MarketMuse and other tools in this area do.
Content curation
A content curation tool is great for finding relevant content you are interested in.
For example, you set up a set of keywords and it finds content that is popular related to those keywords.
But….
…the AI version of the content curation tool takes an extra step.
Take Frase.io as an example.
This finds content but then uses AI to summarize the content so you don’t have to read it all.
I don’t know about you but that sounds awesome to me!!!
In terms of content curation, AI should assist in the following workflows: – Making more targeted queries and removing noise when monitoring the media – Summarizing information to help knowledge workers consume content faster and only dig deeper when relevant – Identifying relationships between topics and drawing trends over time Improved content curation through AI should help marketers create better newsletters, incorporate more research on their original content, scale their social media posting and create richer internal microsites. Digital publishers may use AI-driven content curation to automatically generate reports and enrich their editorial workflow.
Tomas Ratia CEO Frase.io
AI and Analytics
We typically break analytics down into descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, but let’s add a fourth dimension:
Descriptive – Looking into the past to understand what has happened
Predictive – Looking at the past and figuring out what could happen in the future
Prescriptive – Figuring out what we should do next
Action-oriented – Automatically implementing, testing, and adapting.
Descriptive analytics has been around for a long time.
An example of this would be seeing Google Analytics data but not knowing what to do with it.
Predictive analytics gives you ideas of what you might do and prescriptive tells you what you need to do.
Action-oriented analytics is where actions are automatically taken and tested based on what is prescribed.
Sometimes I log into my wife’s Netflix account by mistake and most of the recommendations are not the movies I would watch!
But when I log into my Netflix account it always shows something of interest to me.
Netflix automatically groups people into different categories and ratings are based on the feedback within the category you are placed in.
So, when I see a percentage rating indicating how likely I am to like a movie, this rating could be different for my wife as she’s in a different category.
Netflix continuously tries to provide better recommendations to market better movies to their users.
But they don’t just look at the movie/show you started watching. They will also look at:
Did you watch some of it and stopped watching
Did you watch it over a couple of nights
When you watched it i.e. a month ago, a year ago, etc.
And, of course, much more.
These are machine learning algorithms that are learning over time and automatically adjusting.
A UK company called Datalytyx have patented an AI solution which solves a major problem of analyzing large volumes of data, for example, analzying billions of records.
It’s AI software identifies the most relevant 1% of the data and you run reports based on this.
AI and Marketing Automation
A typical marketing automation task is sending a series of emails to users after they opted in to an email list.
And then, based on their interaction with emails, route people to a different path.
For example, the click on a link about a new product in the second email in a sequence triggers a different email.
This is smart email automation but it’s not AI.
AI adds a whole new layer of intelligence. Here are some examples:
Watson is an IBM platform that uses AI to learn more about your data.
‘Watson marketing‘ is a part of the Watson platform focused on…you guessed it…marketing.
One of its components is creating targeted email campaigns.
It uses AI to understand more about each individual in the campaign and tailors the communication based on this data.
For example, instead of just putting people into a bucket based on a form they fill out, it pulls the data from many sources and creates micro-segments based on lifestyle, social behavior, life stage, location, etc.
But it will also continuously evaluate this data and automatically move people between segments based on new data and performance analysis.
When you are working with large data sets you need AI to automate certain tasks and make sense of data.
For example:
Compile data from many sources and create micro-segments based on lifestyle, social behavior, life stage, location, etc.
Discover flaws in original campaigns and change segments and offers based on this.
AI and Conversational Marketing
A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate a conversation with another human.
There are many tools available (e.g. mobile monkey) which allow you to easily create a chatbot.
They have a builder program which allows you to automatically create actions based on inputs.
However, these chatbots are not AI-enabled. They are trained to recognize specific user intents and they tap into a knowledge base to retrieve answers (retrieval-based chatbots).
We’re still far from seeing chatbots that can provide users with an unlimited amount of answers that they can generate on the fly. This would be the true AI at work.
Most chatbots today operate in a specific niche and the amount of things that they know and can do is very limited. However, they still use NLP techniques to understand human language. The more sophisticated ones also use sentiment analysis to understand the emotion behind the user’s words.
Chatbots, as they are today, are still a very useful tool to help automate certain parts of the sales and marketing process.
For example, chatbots can:
increase engagement through personalized conversations with users
handle customer inquiries on your website
improve targeting by collecting useful insights about users
Now, for companies that already use chatbots on their website, there are tools that can help them understand how well they’re performing.
Liveperson.com analyzes chatbot conversations in real-time to assess when customers are having a poor customer experience. Companies can then take action based on this.
Not sure if we’ll use this…may come up with a new diagram.
AI and Email Marketing
Email marketing is one area that could benefit tremendously from AI.
Just think about it – an AI tool could help you determine which type of content you need to send and when you need to send it to increase your chances of converting an individual prospect.
Given the fact that AI can process enormous amounts of data in no time, you’d be running smarter and more efficient campaigns with a better ROI. Not the mention the time you’d save on A/B testing!
An email marketing tool powered by AI could also help with another challenging area for marketers – sending highly personalized emails at scale.
AI can take into account a customer’s history with your company and determine the type of messaging and offers that work best.
For example, Phrasee is an email marketing tool that uses AI to generate subject lines, body copy, and CTAs to encourage higher click-through rates and engagement on email marketing campaigns.
AI and SEO
Artificial intelligence has the potential to make search more human.
It means that search engines now look more at the meaning and the context of the searcher’s query to deliver more meaningful results.
The era of keyword stuffing is over. Search algorithms are now focusing on the user’s context and search intent.
And this is a good thing.
Marketers can also leverage AI tools to improve the ranking of their content.
Now you can use AI to improve your SEO efforts in a variety of ways, including:
Identifying content opportunities
Performing keyword research
Identifying opportunities for content optimization
Content personalization, and more.
Every time you log into Facebook and view the news feed you are seeing AI in action.
Facebook is continuously monitoring who you follow, what you interact with, how you consume content and more.
These algorithms learn over time to produce better news feed results.
Facebook is all about engagement.
If you spend more time on the platform they can show you more ads and they make more money.
It’s that simple!
It makes total sense to track what you interact and don’t interact with.
If you follow a Facebook page and never interact with the posts they publish, that is a sure sign that you have no interest in that page’s content.
Here’s another example of AI for social media.
Persado provides “machine-generated marketing copy to drive maximum performance in any channel.”
It picks out the best words, phrases, visuals and emotions to drive more engagement.
And social media is all about engagement.
With this social media module they will automatically create the text and find the best images that will drive the most engagement.
AI and Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
Conversion rate optimization is all about improving conversion.
For example, out of 100 visitors to your website you convert 2%, and then you make changes to your website and increase your conversion to 3%.
There are many ways to increase conversion:
Improve your ads so that you get a higher click-through rate and lower cost
Improve ads so you are sending a better audience to your offer
Build a different sales funnel, for example, add an up-sell option after someone buys
Change the pages that are part of the funnel e.g. colors, text, images, video, etc.
This is a very time consuming and manual process and this is where AI can help.
Unbounce is a landing page tool.
They recently built a pilot project around AI and included 34 customers over a 6 week period.
The AI analyzed the performance of the landing pages on real campaigns and instructed conversion specialists on what to change.
On average, the increase in conversion on the pages was 19.8% with one page achieving over 100%.
This is certainly a higher performance increase than you’d expect to get from working with a conversion specialist.
AI and Listening / Monitoring
Every company out there wants to be able to capture as much of the conversations around their brand as possible.
The goal is to understand not only what people are saying about their brand, products or services, but also how they feel about them.
This helps marketers to analyze their brand presence and use those insights to improve communication with their audience and target their campaigns better.
NLP and Sentiment Analysis can really help in this area.
Companies can use AI to understand conversations around their products so they can spot potential issues and act on them, as well as to uncover purchase intent.
AI and Image Recognition
We all know how important visual content is for marketing.
Now we can use AI and image recognition tools to analyze trends and uncover the type of visuals that would bring the best results on social media and other channels.
Image recognition allows marketers to ‘listen’ to what their audience is saying through images so they can deliver visual content that fits the interests of that audience.
AI can help analyze millions of social media posts and filter through the images that people share and engage with.
Without image recognition tools, it would be impossible for marketers to analyze this amount of visual material!
One example of this is the Image Insights platform from Brandwatch. This tool is focused on helping companies uncover how people are using images that contain their brand across social media.
It basically analyzes visual mentions of a brand’s logo across millions of social media posts.
AI and Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing is a very powerful form of marketing but brands find it difficult to identify the right influencers.
With AI technology there are now smarter ways of analyzing and finding influencers.
For example:
Image recognition – AI can analyze thousands of properties of an image to find out what the image is really about.
Content analysis – AI can analyze influencer content to find out what exactly the influencer is passionate about and gets engagement for.
Assess engagement – AI tools can distinguish between fake and real engagement and analyze this level of engagement.
Influencer – Through the analysis above and other analysis it can work out how influential someone is and in what areas.
Demand for useful content from trusted experts is taking the marketing world by storm in the form of influencer collaboration and AI is playing multiple roles.
From AI powered virtual influencers on Instagram like @lilmiquela with 1.5 million followers to sophisticated AI systems used in influencer marketing platforms, the impact and implications of artificial intelligence on influencer marketing are just beginning.
Future applications of AI and influencer marketing include the ability to predict potential impact of certain influencers, content types and channel combinations as well as more advanced filtering of influencers with fake followers.
Lee Odden – Founder Toprank Marketing
C H A P T E R – 4
Security Concerns about AI
In 2018, the EU brought in a regulation called GDPR (global data protection regulation).
Its goal is to regulate the collection, storage, and use of personal data by companies without permission.
As consumers get more and more concerned with the use their personal data, I expect that similar regulation will be implemented in other parts of the world.
As AI is all about collecting and processing data this has serious repercussions.
Let’s say you walked into a supermarket and the supermarket used facial recognition to identify you and then tailored your experience based on the available data. Do they have the permission to do this? Not in Europe.
So, although AI is extremely powerful, some of it’s use will need to be approved.
Summary
There is a bright future ahead of us for AI.
It will have a huge impact on marketing for many years to come.
It will change marketing roles, it will remove some of them entirely, and it will provide a whole new level of sophistication which was never possible before.
Should you be concerned as a Marketer?
Of course.
You need to stay on top of developments in AI and see how you can incorporate it into your marketing.
You need to think about your role as a Marketer and how your role will evolve or be replaced in the future.
Source link
0 notes
Text
Detroit: Become Human Writer David Cage on the Power of Narrative, Agency, and Gaming
Quantin Dream is taking the idea of intelligent AI to a new level with the upcoming Detroit: Become Human. At first glance, this narrative-based games dives into the fantasy sci-fi realm, where machines rise up against their masters and become a class unto themselves.
But after going hands-on with it, it's not quite that. In fact, director David Cage purposely wasn't aiming for fantasy, but more for the plausible. On top of that, he's hopeful that Detroit will encourage players to think about elements of the human experience and some of society's biggest ills.
After trying the game out for ourselves, Shacknews had a few questions to pose to the Heavy Rain and Beyond: Two Souls scribe about what players can expect from Detroit, the social issues he hopes to touch on, and the writer's approach to such a branching narrative.
Shacknews: This is clearly an original story, but I'm sensing inspirations from other elements of fiction, like Asimov's works. What particular works have helped inspire Detroit's narrative?
David Cage, Quantic Dream Studio Founder: So I'm a big sci-fi fan. I love Ray Bradbury, Gibson, K. Dick, all those people are masters. But at the same time, I try to take some distance from them and when I started working on the story, even on my team, some people said, "Is it going to be like I, Robot? Is it going to be like Asimov with those types of references?"
And I thought, no, it's going to be different, because I don't know if I want to talk about AI and androids. I want to talk about human beings. I want to talk about us. And yes, I'm using androids, but actually, it's more about us, about our world, our societies, our relationships. I hope there won't be too many obvious references.
Shacknews: What's humanity's perception of androids in this story? I've seen it go both ways, with androids being presented as this great blessing of modern convenience and as this sub-human scourge.
Cage: I felt it would be like this, because I think if you're rich enough in this future, you will benefit from technology. You will have an android working for you, so you would love technology. But if you're on the other end of the social spectrum, you will maybe have lost your job because an android replaced you and you won't have enough money to buy one to help you in your house, so you will suffer from technology.
And that's one of the things that struck me when working on this, is that technology maybe won't be for everyone and it'll be perceived as both a curse and a blessing.
Shacknews: You've made it clear that this won't be like a case of Skynet rising up and trying to overthrow humanity. It's a story where androids becoming self-aware is a programming flaw, with those cases strictly in the minority. What made you decide on that story element?
Cage: I didn't want to tell the story of Terminator or I, Robot. I felt life and self-consciousness was probably an accident. That's how I felt. I was also curious about this question of whether self-consciousness and emotion is just a matter of power calculation because we have a very complex brain that can make so many calculations, thus this is why we develop self-awareness. But if that's the case, then machines will develop it, too, because they will be more intelligent than we are and they will have a more powerful brain than us very soon.
So will they develop consciousness also because they will have the power to do so? Or is consciousness something else that doesn't depend just on connections in your brain and is more spiritual. And that's a very interesting question and I feel this is a question that androids will answer for us. If they develop self-consciousness, it'll just mean we are just sophisticated machines. If they don't, it'll mean we're something more than that.
Shacknews: I want to segue into one of the more philosophical queries that the story presents. There's a scene where Markus is asked to paint and that presents an idea of "Can machines grasp the concept of art?" And I want to ask if there are other complex questions that you hope players will walk away with after playing this game?
Cage: We want this experience to be thought-provoking and we want to make the player think about AI, technology, and technology's impact on our lives, but also on the future of our society, our dependence on technology, and how we become more selfish. All these questions are there and there are questions about oppression, segregation, and all of these things.
But regarding the moment that you are referring to with the painting? I was very impressed by a visit I had in a Sony lab, working on an algorithm, creating music. People always think that machines can only make very machine-esque type of music and actually, this lab did an experiment where they analyzed how a piano jazz player was playing. What's his style? What's his improvisation style? And they put it into an algorithm and the algorithm began to play the same way.
So they had a disc track where the track starts and plays piano. Then there's a moment where it's not him playing piano anymore, it's the algorithm playing like him. And when you listen, you can't tell the difference. This is right now! It's not sci-fi, it's available right now! And that was my reference with painting and I think that we will see algorithm painting very soon. I think that music will just come after and the more it progresses, the more it can do beautiful things. And I think emotion, in art, is something that can be analyzed and reproduced. That's my personal theory.
Shacknews: You're looking to touch on a host of social issues. I've seen hints of economic inequality, classism, racism. What questions about life and society as a whole do you hope players will think about after playing Detroit?
Cage: Detroit is the story of people who wake up one day and think they deserve a better life.
That's the case of androids. They realize they are treated like objects. They want something different. They think they deserve freedom. They think they deserve rights. This is something that can be applied to different types of people in our society today. And my goal was not to give lessons or send a message, but it was more to increase questions to the player and confront them with this and see what they think. Again, it's a thought-provoking experience and we're very curious to see what types of debates it will trigger among players.
Shacknews: I can't shake some of what I've seen with those scenes with Todd and Alice. There are times when it does feel uncomfortable to watch. Was this something you felt necessary to convey the gravity of the story and is there any fear that the heavier subject matter might be off-putting to certain players?
Cage: We felt it was important to have this scene that is about an android risking its life to save a little human girl. And this is what Kara is doing in this scene, because they share their dream of freedom. They both want to be free for different reasons and they would need to learn to love each other, to like each other, trust each other, to discover who they are, and build this relationship together.
So you needed a threat. You needed something that's heavy and dark that they can escape from. But at the same time, we tried to be very cautious about how we do this. We understand that this is a very sensitive scene, we talk about it every day within the team to really make sure we're doing the right thing. We're trying to be very respectful about this topic in particular. But it asks the question of what a game is. And if your description of a game is and if you're description of a game is "a game is fun," then this type of scene is totally inappropriate, because you can't have fun with such dark themes. But if you feel that interacting means being in the shoes of someone and experiencing what they go through, then it's a totally different take, because suddenly, you're in the shoes of the victims. You understand the threat. You live it. You'd better understand it. So it's not about glamorizing violence. We never do that at any point in the game. At no point do we think violence is cool or violence is the answer to your problems. We always feel that glamorizing violence is wrong. We never use violence when it's gratuitous. We use violence because violence is a part of life, it's a part of a story that we tell, and it's a way to build our characters and make you feel those emotions and feel the bond between Kara and Alice.
I know there will be some discussions around this and some people will say "They don't do it right and they should do this or do that." I am a writer. I have a lot of respect for my medium and I believe it's led me to talk about any topic. I'm not taking this lightly. I'm not naive. I'm not a young kid having fun with important things. But I defend my freedom as a writer to talk about these kinds of topics, because I believe it's important and we try to do it with this interactive medium. Did I do it right? Did I do it wrong? People will play these scenes and tell me.
Shacknews: Lastly, I'm glad you touched on your vocation as a writer, because I want to ask about the process, specifically. What was your approach to putting together this kind of narrative and how do you manage to keep track of all the branching possibilities?
Cage: Work, work, work.
What is challenging when you create this is that it's a left brain/right brain process. You need to be creative, because you talk about emotions and characters, like any storyteller. That's your creative part. But at the same time, your right brain needs to be organized and keep track of the branches and the consequences and the variables. And so I have a tree structure that I build as I write and it's switching between my left brain and my right brain all the time. Each time I create a new branch with a story and put it in the tree structure, but then I need to go back to my left brain and go "What happens? What is the consequence of what you just created?" Then I need to provide a creative answer that creates more branches, so I need to go back to the tree structure. And it goes back and forth.
I've managed to create about more than 60,000 variables and conditions in the game. The game listens to what you do and tracks what you do all the time and we want to give consequences to all of your actions. There are things that you've done in this first hour of gameplay that will have very significant impact later in the story. There are entire scenes that you may see or miss, there are characters that you may see for a couple of minutes or may be with you until the end. Your relationships with the other characters are tracked and that's very important. It may have consequences later in the story. So we track all of these things and try to give you a satisfying narrative experience based entirely on your choices and your decisions.
Shacknews: And it's one of those stories that you can only tell in gaming and not in any other medium, right?
Cage: Absolutely! Putting you in the shoes of someone is something that only this medium can do and that's so unique and so powerful! So now my gut feeling is that we need to do something with this. We need to say something meaningful. Because we have this medium, we have this power. Let's use it to be thought-provoking and put you in the shoes of someone else and give you an idea of what it's like.
Detroit: Become Human is set to release on Friday, May 25 on PlayStation 4. Those looking to get a taste of what the game will look like can try out Connor's Hostage scene in the Detroit: Become Human demo that's out today.
Detroit: Become Human Writer David Cage on the Power of Narrative, Agency, and Gaming published first on https://superworldrom.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
Artificial intelligence: here's what you need to know to understand how machines learn
http://bit.ly/2vz8bsA
From Jeopardy winners and Go masters to infamous advertising-related racial profiling, it would seem we have entered an era in which artificial intelligence developments are rapidly accelerating. But a fully sentient being whose electronic “brain” can fully engage in complex cognitive tasks using fair moral judgement remains, for now, beyond our capabilities.
Unfortunately, current developments are generating a general fear of what artificial intelligence could become in the future. Its representation in recent pop culture shows how cautious – and pessimistic – we are about the technology. The problem with fear is that it can be crippling and, at times, promote ignorance.
Learning the inner workings of artificial intelligence is an antidote to these worries. And this knowledge can facilitate both responsible and carefree engagement.
The core foundation of artificial intelligence is rooted in machine learning, which is an elegant and widely accessible tool. But to understand what machine learning means, we first need to examine how the pros of its potential absolutely outweigh its cons.
Data are the key
Simply put, machine learning refers to teaching computers how to analyse data for solving particular tasks through algorithms. For handwriting recognition, for example, classification algorithms are used to differentiate letters based on someone’s handwriting. Housing data sets, on the other hand, use regression algorithms to estimate in a quantifiable way the selling price of a given property.
What would a machine say to this? Jonathan Khoo/Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND
Machine learning, then, comes down to data. Almost every enterprise generates data in one way or another: think market research, social media, school surveys, automated systems. Machine learning applications try to find hidden patterns and correlations in the chaos of large data sets to develop models that can predict behaviour.
Data have two key elements – samples and features. The former represents individual elements in a group; the latter amounts to characteristics shared by them.
Look at social media as an example: users are samples and their usage can be translated as features. Facebook, for instance, employs different aspects of “liking” activity, which change from user to user, as important features for user-targeted advertising.
Facebook friends can also be used as samples, while their connections to other people act as features, establishing a network where information propagation can be studied.
My Facebook friends network: each node is a friend who might or might not be connected to other friends. The larger the node, the more connections one has. Similar colours indicate similar social circles. https://lostcircles.com/
Outside of social media, automated systems used in industrial processes as monitoring tools use time snapshots of the entire process as samples, and sensor measurements at a particular time as features. This allows the system to detect anomalies in the process in real time.
All these different solutions rely on feeding data to machines and teaching them to reach their own predictions once they have strategically assessed the given information. And this is machine learning.
Human intelligence as a starting point
Any data can be translated into these simple concepts and any machine-learning application, including artificial intelligence, uses these concepts as its building blocks.
Once data are understood, it’s time to decide what do to with this information. One of the most common and intuitive applications of machine learning is classification. The system learns how to put data into different groups based on a reference data set.
This is directly associated with the kinds of decisions we make every day, whether it’s grouping similar products (kitchen goods against beauty products, for instance), or choosing good films to watch based on previous experiences. While these two examples might seem completely disconnected, they rely on an essential assumption of classification: predictions defined as well-established categories.
When picking up a bottle of moisturiser, for example, we use a particular list of features (the shape of the container, for instance, or the smell of the product) to predict – accurately – that it’s a beauty product. A similar strategy is used for picking films by assessing a list of features (the director, for instance, or the actor) to predict whether a film is in one of two categories: good or bad.
By grasping the different relationships between features associated with a group of samples, we can predict whether a film may be worth watching or, better yet, we can create a program to do this for us.
But to be able to manipulate this information, we need to be a data science expert, a master of maths and statistics, with enough programming skills to make Alan Turing and Margaret Hamilton proud, right? Not quite.
You don’t have to be Alan Turing to have a go at machine learning. CyberHades/Flickr, CC BY-NC
We all know enough of our native language to get by in our daily lives, even if only a few of us can venture into linguistics and literature. Maths is similar; it’s around us all the time, so calculating change from buying something or measuring ingredients to follow a recipe is not a burden. In the same way, machine-learning mastery is not a requirement for its conscious and effective use.
Yes, there are extremely well-qualified and expert data scientists out there but, with little effort, anyone can learn its basics and improve the way they see and take advantage of information.
Algorithm your way through it
Going back to our classification algorithm, let’s think of one that mimics the way we make decisions. We are social beings, so how about social interactions? First impressions are important and we all have an internal model that evaluates in the first few minutes of meeting someone whether we like them or not.
Two outcomes are possible: a good or a bad impression. For every person, different characteristics (features) are taken into account (even if unconsciously) based on several encounters in the past (samples). These could be anything from tone of voice to extroversion and overall attitude to politeness.
For every new person we encounter, a model in our heads registers these inputs and establishes a prediction. We can break this modelling down to a set of inputs, weighted by their relevance to the final outcome.
For some people, attractiveness might be very important, whereas for others a good sense of humour or being a dog person says way more. Each person will develop her own model, which depends entirely on her experiences, or her data.
Different data result in different models being trained, with different outcomes. Our brain develops mechanisms that, while not entirely clear to us, establish how these factors will weight out.
What machine learning does is develop rigorous, mathematical ways for machines to calculate those outcomes, particularly in cases where we cannot easily handle the volume of data. Now more than ever, data are vast and everlasting. Having access to a tool that actively uses this data for practical problem solving, such as artificial intelligence, means everyone should and can explore and exploit this. We should do this not only so we can create useful applications, but also to put machine learning and artificial intelligence in a brighter and not so worrisome perspective.
There are several resources out there for machine learning although they do require some programming ability. Many popular languages tailored for machine learning are available, from basic tutorials to full courses. It takes nothing more than an afternoon to be able to start venturing into it with palpable results.
All this is not to say that the concept of machines with human-like minds should not concern us. But knowing more about how these minds might work will gives us the power to be agents of positive change in a way that can allow us to maintain control over artificial intelligence and not the other way around.
Matt Escobar receives funding from the Core Research for Evolutionary Science and Technology (CREST) project 'Development of a knowledge-generating platform driven by big data in drug discovery through production processes' of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)
0 notes
Text
If We Have A Connection, Why Are We Drifting Apart?
In a world of technological advances, immediate response, globalized medicine, and media human beings have never in our life been confronted the conundrum to influence the world and our localities as unwittingly as human beings are presently. Medical advances can be shared at lightning speed from France and the United Kingdom to the southern areas of the Sahara and a small town in Mexico. The human condition through adaptation, migration, and desire to survive has presented people are as resilient as is the capacity of the human spirit to advance upon the modernized, conceptualized, rationalized, or overtaken. Success or prominence appear through the exercising of our uniquity as a common act of volition or ingenuity which present the results of the errant, hypothesized, or foreseen.
The human experience as a simple, complex, or modernized existential journey presents the frequently exponential and variable of situations, circumstances, and scenarios. Opportunity abounds for the success, failure, and optimum over the status quo. Equiponderance reveals human beings exercising the capacities to communicate, interact, and engage in a more immediate fashion at professional and personal levels from the most intimate to the less meaningful. This fact or reality from necessity, luxury, or indulgence appears to be seemingly simplifying the world for children and adults alike. To what measured or leveled cost, barometer, or extent do we measure simplification, luxury, indulgence, or complexities?
Nowadays more and more people are busy as they always were throughout history. Family, friends, acquaintances, work, education, relationships, careers, children, sports, after school activities, new additions to the family, medical issues, or life’s welcomed and unwelcomed events or complications are only the normality the focused or multitasking have occurring at any given time. The addition of technology, interpretation, and out of body experiences people have with the addition of social tools to manage availability and communication can make things quite the entertainment fiasco and episode of the latest issue Hot Keys. Hot Keys issues with complimentary attachments added to deliver upon a sociopath’s schadenfreude of life’s calamities. How are people overcoming this not so new and latest, but not so hidden, open form of entertainment, social impairment, or healthy mental stimulation?
The most effective means some have employed are through simply unplugging from it and remaining abreast of things with discretion. Many people have discovered after feeding the machine an absence of as little as fifteen to thirty-nine days has them missing many virtual infomercials, soap operas, and psychologically impaired events. This frequent, scheduled, or routine discipline has the potential to reduce negativity from personal and professional encounters as new habits become formed keeping one from encounters of the variable such as the mind-numbing, unhealthy, immature, exacerbating, gossip-like, or harmful in nature.
Many tools linking human beings along our journeys are people, email, professional correspondence, postal mail, telephony, and social media. These valuable assets or commodities of people, tools, assets, materials, and resources are designed nowadays to interact, suggest, and steer to or from calculated coordinates provided a certain motivation. Suggestions from interactions when analyzed steer independent human being toward a motivating factor by algorithms utilizing an azimuth determined by an algorithm which is based upon the variably differentiated. Data, information, infrastructure, and resources are creating a suggested present or future destination which is validly or irrelevantly determined through a combination of influencing factors. This intelligence, information, or data is evaluated, reviewed, or analyzed for oscillating validities and irrelevancies as singular or pluralized pieces of information, data, and input.
Information, data, or input which becomes translated to an algorithm permits analysts of a human or manufactured form to weigh correctly or incorrectly factors of happenstance, purpose, or intention. Situations, circumstances, or scenarios which are analyzed are evaluated under differentiated environmental controls with highlighted focalize positions presented from the requisitioned or discovered.
How can humans interacting, transacting, or communicating between or among the variable of the human condition remain connected and simplify the life’s journey? The truth is the human species is not completely capable of simplifying life because life’s content, character, and nature present the frequently exponentially diverse of calculatable factors for creating the realities the brain can experience without effect as parallel universal outcomes or strategically chosen paths of reaction, anticipation, or influence.
The evaluated, conceptualized, concealed, or unknown present factors of happenstance, intuition, and intent which are only comprehendible at certain levels, stages, or phases of cerebral intellect, ingenuity, awareness, mindfulness, or conceptualization. Some strategies or techniques which have been revealed as effective are presented below from a broad, basic, or generalize perspective which can apply to a significant percentage of the human population. The valuable commodity of people, time, money, and resources in combination with the limited and overabundant were considered. Some explanations or observances are provided for consideration. In any case the human experience which is influenced by the exponentially variable. Life is enriched frequently by humanities encounter with that which enriches the soul, open our eyes, warm the heart, and teaches from the perspective of wisdom and knowledge.
Isolation or complete removal, this is drastic and is often proven to show nirvana, giddiness, euphoria, relapse, withdrawal, random health changes, or harm. The need to believe we as human beings are acknowledged or accepted at a certain level of authenticity or genuineness stems from the wisdom of the long historical value of the human species. A history which reveals winners and losers under identifiable criterion of fact, error, misperception, or conceptualization. Success and the capacity for winning is within us all. Travel to the gym, I am not Fabio and look like a bad Fred Flintstone, for sixty to one hundred and twenty minutes and the majority learn once a pattern is induced and implemented some things take care of themselves. Like loaning your enemy one hundred dollars with the bill payable as one hundred dollars the following week, and not a percent of interest every week there-after. For many professionals and homemakers managing the messages, faxes, voicemails, e-mails, social media bells, and sirens become managed with care, discretion, and a touch of old school time or lifestyle management.
Truth is many people are important on variably differentiated levels. The average human being is not in demand at all hours of the day for our whole lifetime, this type of urgency is rare. Understanding our demand, versatility, skill, craftsmanship, and integrity to be available as characteristics to be loaned perpetually is essential. Comprehending humans are not always in demand all the time and at all hours of the day, month, week, or years assists or enables professional and personal time management. Identify where and when we as living beings are for lack of better words are going to be inevitably listed between or among the collective of indispensable men and women of past and current memory. Love your friends, family, acquaintance, and strangers accordingly. Don’t be rude or snotty, short is okay because we all have our days. Be polite, stress management requires the frequent employment of a smile, acknowledgement, and momentum to maintain the cerebrally intelligent course of action.
While unplugging entirely from the chaos, drama, and eventful is a novel concept it is irrational for a multitude of reasons at the professional or personal level. Magic jack, Ringcentral, Squarespace, and 4securemail provide excellent service for managing a myriad of choices facing the average professional or person seeking to simplify life’s encounters. More could services could be listed and where humans are intelligent beings who are capable of reason or rationalize these few alternatives are presented for conceptualization and the versatility they provide.
Healthy and functional life enriching communication is often the key to success in any endeavor, the feeling of having a solid unchanging foundation is essential. Removal of drama, the fictionalized, sociopaths, stalkers, nosey neighbor, spying coworker, or well-intentioned but over-reaching loved one can be is sometimes more manageable thank people think. It does require effort. A phone, fax, e-mail, and web management tool assists or enables a glace or view toward progress, stagnation, or the slow moving. A store or outlet for identifying what is completed or available may assist or enable project management on a public or privately identifiable interface. A location to have contact, communication, commerce, and interaction is essential to accomplishing any goal, thought, or ambition for many of us and not many of us carry legal pads everywhere life may lead.
Social media management can be problematic, troublesome, and complex when or where not reaching out to the people who are smarter than us for direction, tools, assets, material, resources, or intellectual wisdom may be concerned. What is suggested here at face value are some tools which have some tools built in to ease the process of implementation. This may be for people who love humanity but kind want to miss a lot of the communication that frequently clouds the mind by managing things a bit more differently.
The requirement to remain abreast of happenings in the world are manageable at various levels of ease, familiarity, and comfort. Offsetting the scroll after scroll after scroll from pages of seemingly endless information, a solution to the problem facing some can be as simple as using a tool to manage and maximize communication, privacy, and time.
Magicjack delivers quality, when or where the need to employ voice over internet provider connections is an option from telephony communication, and is inexpensive for many.
RingCentral provides versatile phone and fax integration using telephony technology. The perks of this service are stand alone and second to none, in my opinion. The online full functionality and landline capabilities of this service strengthen the attractiveness of this product. This is very reasonable priced for personal use and the utilization of a toll-free phone number permits for latitude across multiple social media platforms because the added security of a toll-free number assists the professional of private consumer to identify the phone number of callers and receive messages or facsimile transmissions. The perk of a toll-free number lessens for many the variable concerns of placing a phone number to social media accounts. The whole you called me I get your number as a default condition of phoning, as a norm, there are exceptions though. Integrate this technological tool with google phone or another free phone number service and you have an addition field of security.
Squarespace offers a person or professional alike to rent, or own, a website containing the most current of bells and whistles many would like to employ to represent themselves or their business. Squarespace offers the end user a variety of greatly differentiate presentation formats. The options with Squarespace appear to be limitless for the average user at the most basic service level. The basic level provides the capacity to create a blog, biography, store, resource center, and much more.
SQUARESPACE ALSO PROVIDES FREE ONLINE CLASSES OR TUTORIALS WHICH INFORM EACH USER OF HOW TO MAXIMIZE THE POTENTIAL OF THEIR WEB ASSET PRESENCE. There is also a wonderful online support team which is quite capable of answering any client inquiry complete to the level of a client’s satisfaction.
4securemail provides a professional e-mail messaging service increased levels of secure encryption. There are various service options and plans.
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, MySpace, Youtube, or Instagram provide the capacity to organize, utilize, and showcase professional and personal associations, affiliations, or passions. Cool part is social media is an awesome tool for discovery, distribution, networked information, and data gathering. Problem is the truth can take some investigation and money to locate. Truth is many among us have over exerted ourselves while spying on the Jones or posting the day to day or occasional family, friends, acquaintance, and life shaping events report. This frequently can become expensive as it cost people, time, money, and resources.
Almost all social media platform services provide a message box and people spend hours looking for the likes, loves, laughs, sadness, etc. Many social media platforms exhibit the absence of a personal page view, like Facebook offers to members, clients, or affiliates, which almost always provides a messaging option for social interactions, transactions, and engagements.
Many private citizens and professionals build a market base of interested or affiliated consumers at internal or external levels of interaction to satisfy day to day needs at personal or professional levels where quality interaction may become the most meaningful. High numbers of caring, selfless, selfish, or self-indulgent people face the same types of obstacle all other people do with human interaction and professional communication. People have lives which are eventful or non-eventful. G-d bless the person who has thousands or millions of followers, fans, or interacting connections. Truth is communications for many people are missed or lost to or by many of these people. The comments are buried and without staff, or a lot of spare time, interaction is missed. Depending on out of body experiences from previous comments communication can become misconstrued.
This phenomenon is common when or where people believe people are alike or similar as other human beings within the parameters of a defined area of whatever, pick it “the topic”.
The message box, or social media instant messaging center, may be the best for the optimum level of responsible interactions, therefore it is advocated to utilize the public display of a toll-free phone and fax number. Private citizens and professionals are intricately interwoven at the home or work level and these types of interactions are almost always seen, observed, evaluated, discarded, or filed for present of future reference, use, or reflection. If these communications do not get buried as frequently can happen. These can also get highjacked by meeting new people. New people can be such an adventure.
Nowism is a luxury of modern technology, tools, assets, materials, and resources of the individual and professional alike. Selfishness or oversight regarding other people’s valuable commodities of people, time, money, and resources is as easy as happenstance. Life and the communicated are important to survival and the transacted as the frequently urgent is revealed by instant messages or direct communication. Drama can ensue, especially when delusions of the 911 system are ignored, overlooked, or absently not recognized. I have traffic tickets for this, this is something I am knowledgeable about. In my case, I was not willing to interact with the 911 system and became engaged anyhow. I do not text and drive, so chill, call me I am toll free I will tell you all about it. Just sharing.
Connectivity is required sometimes for independence, immediacy, and nowism and through modern technology organizations, people, friends, families, and acquaintances are comprehending, misinterpreting, influencing, and reacting at levels of unprecedented swiftness which has never occurred in the history of human experiences.
A toll-free number, RingCentral, 4securemail, Squarespace, and Magicjack all offer and provide the “go to” options for the optimum offsetting the liability of lost time and productivity. They all provide the capacity for overlap to maximize proficiency for obstacles, obstructions, or the homogeneous for many social platform integrations.
Pick up the phone and call or fax your friend, instant message, or e-mail them directly. The blanketing effect of nowism is causing people to drop, skip, and miss the old-school interactions which created a bond initially as people change healthfully over life’s journey. The people we knew yesterday on social media do not have the time, as we appear not too have the time after fifteen to thirty-nine days. Interaction with the reactive and engaging with hair, eyes, nose, and a mouth is essential for human success and meaningful interactions.
HORIZONTAL RULE
References and Resources:
https://pixabay.com/en/kermit-frog-phone-figure-funny-2551555/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/Alexas_Fotos-686414/
https://pixabay.com/en/press-journalist-photographer-news-1015988/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/Alexas_Fotos-686414/
https://pixabay.com/en/communication-phone-call-message-1015376/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/3dman_eu-1553824/
https://pixabay.com/en/michelangelo-abstract-boy-child-71282/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/PublicDomainPictures-14/
https://pixabay.com/en/woman-samsung-alpha-taking-picture-638384/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/FirmBee-663163/
https://pixabay.com/en/mental-health-mental-health-teen-2470926/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/Maialisa-905513/
https://pixabay.com/en/girl-women-phone-young-1797769/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/gm_pangtondevil-3683176/
https://pixabay.com/en/group-fingers-hand-finger-smilies-1721675/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/ElisaRiva-1348268/
https://pixabay.com/en/the-device-hospital-surgery-1822457/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/sasint-3639875/
https://pixabay.com/en/robot-artificial-intelligence-2167836/, https://pixabay.com/en/users/geralt-9301/
HORIZONTAL RULE
Contact: I am always looking for work.
Thomas Collins Jr. 110 Marginal Way #118, Portland, Maine 04101
Toll Free: 855-893-4518
Professional Messaging Link: https://thingsofpracticality.squarespace.com/contact/
HORIZONTAL RULE
Other Publications:
http://www.amazon.com/Thomas-Collins-Jr./e/B00FARBGA6,
https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/8443660.Thomas_Collins_Jr_
0 notes
Text
Detroit: Become Human Writer David Cage on the Power of Narrative, Agency, and Gaming
Quantin Dream is taking the idea of intelligent AI to a new level with the upcoming Detroit: Become Human. At first glance, this narrative-based games dives into the fantasy sci-fi realm, where machines rise up against their masters and become a class unto themselves.
But after going hands-on with it, it's not quite that. In fact, director David Cage purposely wasn't aiming for fantasy, but more for the plausible. On top of that, he's hopeful that Detroit will encourage players to think about elements of the human experience and some of society's biggest ills.
After trying the game out for ourselves, Shacknews had a few questions to pose to the Heavy Rain and Beyond: Two Souls scribe about what players can expect from Detroit, the social issues he hopes to touch on, and the writer's approach to such a branching narrative.
Shacknews: This is clearly an original story, but I'm sensing inspirations from other elements of fiction, like Asimov's works. What particular works have helped inspire Detroit's narrative?
David Cage, Quantic Dream Studio Founder: So I'm a big sci-fi fan. I love Ray Bradbury, Gibson, K. Dick, all those people are masters. But at the same time, I try to take some distance from them and when I started working on the story, even on my team, some people said, "Is it going to be like I, Robot? Is it going to be like Asimov with those types of references?"
And I thought, no, it's going to be different, because I don't know if I want to talk about AI and androids. I want to talk about human beings. I want to talk about us. And yes, I'm using androids, but actually, it's more about us, about our world, our societies, our relationships. I hope there won't be too many obvious references.
Shacknews: What's humanity's perception of androids in this story? I've seen it go both ways, with androids being presented as this great blessing of modern convenience and as this sub-human scourge.
Cage: I felt it would be like this, because I think if you're rich enough in this future, you will benefit from technology. You will have an android working for you, so you would love technology. But if you're on the other end of the social spectrum, you will maybe have lost your job because an android replaced you and you won't have enough money to buy one to help you in your house, so you will suffer from technology.
And that's one of the things that struck me when working on this, is that technology maybe won't be for everyone and it'll be perceived as both a curse and a blessing.
Shacknews: You've made it clear that this won't be like a case of Skynet rising up and trying to overthrow humanity. It's a story where androids becoming self-aware is a programming flaw, with those cases strictly in the minority. What made you decide on that story element?
Cage: I didn't want to tell the story of Terminator or I, Robot. I felt life and self-consciousness was probably an accident. That's how I felt. I was also curious about this question of whether self-consciousness and emotion is just a matter of power calculation because we have a very complex brain that can make so many calculations, thus this is why we develop self-awareness. But if that's the case, then machines will develop it, too, because they will be more intelligent than we are and they will have a more powerful brain than us very soon.
So will they develop consciousness also because they will have the power to do so? Or is consciousness something else that doesn't depend just on connections in your brain and is more spiritual. And that's a very interesting question and I feel this is a question that androids will answer for us. If they develop self-consciousness, it'll just mean we are just sophisticated machines. If they don't, it'll mean we're something more than that.
Shacknews: I want to segue into one of the more philosophical queries that the story presents. There's a scene where Markus is asked to paint and that presents an idea of "Can machines grasp the concept of art?" And I want to ask if there are other complex questions that you hope players will walk away with after playing this game?
Cage: We want this experience to be thought-provoking and we want to make the player think about AI, technology, and technology's impact on our lives, but also on the future of our society, our dependence on technology, and how we become more selfish. All these questions are there and there are questions about oppression, segregation, and all of these things.
But regarding the moment that you are referring to with the painting? I was very impressed by a visit I had in a Sony lab, working on an algorithm, creating music. People always think that machines can only make very machine-esque type of music and actually, this lab did an experiment where they analyzed how a piano jazz player was playing. What's his style? What's his improvisation style? And they put it into an algorithm and the algorithm began to play the same way.
So they had a disc track where the track starts and plays piano. Then there's a moment where it's not him playing piano anymore, it's the algorithm playing like him. And when you listen, you can't tell the difference. This is right now! It's not sci-fi, it's available right now! And that was my reference with painting and I think that we will see algorithm painting very soon. I think that music will just come after and the more it progresses, the more it can do beautiful things. And I think emotion, in art, is something that can be analyzed and reproduced. That's my personal theory.
Shacknews: You're looking to touch on a host of social issues. I've seen hints of economic inequality, classism, racism. What questions about life and society as a whole do you hope players will think about after playing Detroit?
Cage: Detroit is the story of people who wake up one day and think they deserve a better life.
That's the case of androids. They realize they are treated like objects. They want something different. They think they deserve freedom. They think they deserve rights. This is something that can be applied to different types of people in our society today. And my goal was not to give lessons or send a message, but it was more to increase questions to the player and confront them with this and see what they think. Again, it's a thought-provoking experience and we're very curious to see what types of debates it will trigger among players.
Shacknews: I can't shake some of what I've seen with those scenes with Todd and Alice. There are times when it does feel uncomfortable to watch. Was this something you felt necessary to convey the gravity of the story and is there any fear that the heavier subject matter might be off-putting to certain players?
Cage: We felt it was important to have this scene that is about an android risking its life to save a little human girl. And this is what Kara is doing in this scene, because they share their dream of freedom. They both want to be free for different reasons and they would need to learn to love each other, to like each other, trust each other, to discover who they are, and build this relationship together.
So you needed a threat. You needed something that's heavy and dark that they can escape from. But at the same time, we tried to be very cautious about how we do this. We understand that this is a very sensitive scene, we talk about it every day within the team to really make sure we're doing the right thing. We're trying to be very respectful about this topic in particular. But it asks the question of what a game is. And if your description of a game is and if you're description of a game is "a game is fun," then this type of scene is totally inappropriate, because you can't have fun with such dark themes. But if you feel that interacting means being in the shoes of someone and experiencing what they go through, then it's a totally different take, because suddenly, you're in the shoes of the victims. You understand the threat. You live it. You'd better understand it. So it's not about glamorizing violence. We never do that at any point in the game. At no point do we think violence is cool or violence is the answer to your problems. We always feel that glamorizing violence is wrong. We never use violence when it's gratuitous. We use violence because violence is a part of life, it's a part of a story that we tell, and it's a way to build our characters and make you feel those emotions and feel the bond between Kara and Alice.
I know there will be some discussions around this and some people will say "They don't do it right and they should do this or do that." I am a writer. I have a lot of respect for my medium and I believe it's led me to talk about any topic. I'm not taking this lightly. I'm not naive. I'm not a young kid having fun with important things. But I defend my freedom as a writer to talk about these kinds of topics, because I believe it's important and we try to do it with this interactive medium. Did I do it right? Did I do it wrong? People will play these scenes and tell me.
Shacknews: Lastly, I'm glad you touched on your vocation as a writer, because I want to ask about the process, specifically. What was your approach to putting together this kind of narrative and how do you manage to keep track of all the branching possibilities?
Cage: Work, work, work.
What is challenging when you create this is that it's a left brain/right brain process. You need to be creative, because you talk about emotions and characters, like any storyteller. That's your creative part. But at the same time, your right brain needs to be organized and keep track of the branches and the consequences and the variables. And so I have a tree structure that I build as I write and it's switching between my left brain and my right brain all the time. Each time I create a new branch with a story and put it in the tree structure, but then I need to go back to my left brain and go "What happens? What is the consequence of what you just created?" Then I need to provide a creative answer that creates more branches, so I need to go back to the tree structure. And it goes back and forth.
I've managed to create about more than 60,000 variables and conditions in the game. The game listens to what you do and tracks what you do all the time and we want to give consequences to all of your actions. There are things that you've done in this first hour of gameplay that will have very significant impact later in the story. There are entire scenes that you may see or miss, there are characters that you may see for a couple of minutes or may be with you until the end. Your relationships with the other characters are tracked and that's very important. It may have consequences later in the story. So we track all of these things and try to give you a satisfying narrative experience based entirely on your choices and your decisions.
Shacknews: And it's one of those stories that you can only tell in gaming and not in any other medium, right?
Cage: Absolutely! Putting you in the shoes of someone is something that only this medium can do and that's so unique and so powerful! So now my gut feeling is that we need to do something with this. We need to say something meaningful. Because we have this medium, we have this power. Let's use it to be thought-provoking and put you in the shoes of someone else and give you an idea of what it's like.
Detroit: Become Human is set to release on Friday, May 25 on PlayStation 4. Those looking to get a taste of what the game will look like can try out Connor's Hostage scene in the Detroit: Become Human demo that's out today.
Detroit: Become Human Writer David Cage on the Power of Narrative, Agency, and Gaming published first on https://superworldrom.tumblr.com/
0 notes