#king manuel of portugal
Text
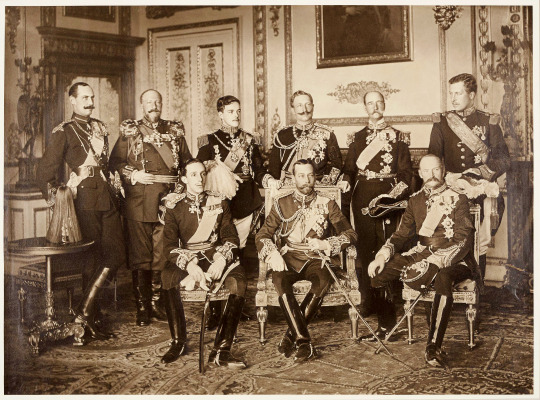

Nine European Sovereigns at Windsor Castle for the funeral of King Edward VII of the United Kingdom (Photo courtesy of Royal Collection Trust) | May 20, 1910
Standing (left to right): King Haakon VII of Norway, King Ferdinand of Bulgaria, King Manuel of Portugal, Emperor William II of Germany, King George I of the Hellenes, King Albert of the Belgians
Seated (left to right): King Alfonso XIII of Spain, King George V, King Frederick VIII of Denmark
#royaltyedit#theroyalsandi#george v#king george v#king george v of the united kingdom#haakon vii of norway#king ferdinand of bulgaria#king manuel of portugal#king william ii of germany#king george of hellenes#king albert of the belgians#king alfonso xiii of sapin#king frederick viii of denmark#british royal family#my edit
75 notes
·
View notes
Text

Manuel Maria Filipe Carlos Amélio Luís Miguel Rafael Gabriel Gonzaga Xavier Francisco de Assis Eugénio, King Manuel II of Portugal
British vintage postcard
#vintage#tarjeta#francisco#maria#xavier#briefkaart#manuel maria filipe carlos amélio luís miguel rafael gabriel gonzaga xavier francisco de assis eugénio#amlio#postcard#photography#gonzaga#assis#postal#gabriel#carte postale#filipe#sepia#eugnio#ephemera#portugal#historic#british#manuel ii#carlos#king#ansichtskarte#postkarte#rafael#manuel#postkaart
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

“He doesn’t get much credit because he was deposed and most of his descendants married into other deposed or minor royal families, but Manuel I of Portugal has many royal descendants from the deposed Habsburgs to reigning families like Belgium, Luxembourg, and Liechtenstein.” - Submitted by Anonymous
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Manuel II, King of Portugal, in Paris with Alfonso XIII, King of Spain, the two youngest sovereigns in Europe, front cover illustration from 'Le Petit Parisien', supplemnet litteraire illustre, 5th December 1909 (photolitho)
French School
#dianthus#carnation#portrait#1900s art#1900s fashion#Manuel II#King of Portugal#Alfonso XIII#King of Spain
3 notes
·
View notes
Text



Elvas Castle situated in Elvas, Portugal, was first built during the Moorish period of rule and occupation of the area between the 8th and 12th centuries. The castle was fought over repeatedly between Moors and Christians and changed hands several times. Afonso Henriques took the castle around 1166 but it was subsequently retaken, then lost, then retaken again. Elvas Castle was eventually abandoned by the Moors in 1230 when their base in Mérida (Spain) was under threat.
Elvas Castle was also besieged in the 14th century, this time by the armies of Castile. As a result of these attacks from the across the border with Spain, Elvas was reinforced with a taller keep and artillery positions in the 15th century. King Manuel I further strengthened the castle during his reign in the early 16th century adding towers to the walls.
In the 16th century Elvas Castle became part of the ever more sophisticated walls and fortifications of Elvas built to withstand attack from neighboring Spain. Elvas Castle resisted many attempts to take it but was eventually stormed after an attack by the French in 1807 during the Peninsular War (1807-1814). However, a year later the castle was back in the combined hands of the British and Portuguese armies opposing Napoleon's forces.
#philosophy#renaissance#sculpture#architecture#italy#rome#19th century#art history#italian art#venice#academia#dark academia#archaeology#art#castle#cultural revolution#cathedral#empire#geology#geography#history#landscape#m
47 notes
·
View notes
Photo
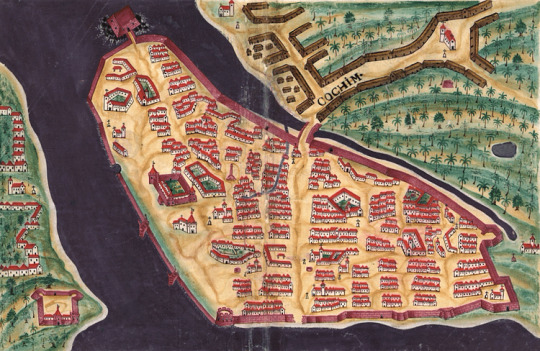
Portuguese Cochin
Cochin, located on the southwest coast of India, was a Portuguese colony from 1503 to 1663. Known to the Portuguese as Cochim, it was one of several important cities on India’s Malabar Coast and a great trade centre for spices like pepper. Cochin was the administrative capital of Portuguese India until it was replaced by Goa in 1530.
A fort was built at Cochin in 1503, the first in Portuguese India, as the Europeans used the city as their first headquarters in the East. The great explorer Vasco da Gama (c. 1469-1524) spent his last days in the city, and it remained a lucrative hub of the spice trade into the 17th century. The city was taken over by the Dutch in 1663, then the English in 1814, and finally gained independence with the rest of India in 1947. Today, the city is known as Kochi and is the most prosperous port in the Kerala region of India.
Vasco da Gama
In the 15th century, the Portuguese colonization of Madeira in the North Atlantic from 1420 was the first in a series of colonial stepping stones that eventually led to India. The treacherous Cape Bojador in West Africa was negotiated in 1434, the Azores were colonised from 1439, Cape Verde from 1462, and São Tomé and Principe from 1486. In 1488 Bartolomeu Dias sailed down the coast of West Africa and made the first voyage around the Cape of Good Hope, the southern tip of the African continent (now South Africa).
The famed Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama followed in Dias’ wake and pioneered a maritime route from Portugal to India when in 1497-9, he sailed around the Cape of Good Hope, went up the coast of East Africa, and crossed the Indian Ocean to arrive at Calicut (now Kozhikode) on the south-west coast of India. His voyage, supported by King Manuel I of Portugal (r. 1495-1521), was intended to find a legendary Christian kingdom in the East and to give Portugal direct access to the Eastern spice trade and cut out the Arab middlemen traders. The first aim ended up being an illusion but the second was indeed achieved. For the first time, Europe could access by sea a trade which had been going on for centuries but which channelled luxury goods through the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf to be then taken by camel caravan to the Mediterranean. Such goods as pepper, ginger, cloves, and cinnamon were immensely popular in Europe and expensive.
Vasco da Gama, through a mix of inexperience, lack of trade goods, and Indian confidence in the status quo, failed to establish friendly trading relations with Calicut. A second Portuguese expedition, this time with 13 ships and 1500 men and commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral, set off to repeat da Gama’s feat in March 1500 and was given the brief of muscling-in on Muslim trade by sinking any Arab ships they came across. Vasco da Gama sailed for a second time to India in 1502-3, this time with 15 ships. A result of this voyage was more trouble with the ruler of Calicut, but a trade treaty was agreed with Cochin further down the coast.
Continue reading...
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today I woke up really loving my country, my language, my people and our culture, so I decided to make a few posts about it, bear with me
The first thing I'd like to talk about is one of my favorite saying (dictation?) in portuguese: Agora Inês é morta ou Agora é tarde, Inês é morta
Translating it literally to English it would be: Now Inês is dead or Now it's too late, Inês is dead. This saying mean that doing something is futile, useless, it's too late now.
I grew up with my parents (especially my dad) saying this, so I say it often, but I decided to talk about this saying in specific instead of so many other popular saying because of the history behind it:
So, Inês de Castro was a Galician noblewoman, who was very loved by D. Pedro I, Portugal's future king. She was also Constança Manuel's lady-in-waiting, who was married with D. Pedro I. His father disapproved their relationship and ordered the exiled of Inês to the Albuquerque Castle. But their love was too strong, so they continued to correspond each other and had four children together. When D. Constança died, D. Pedro ordered, without his father's permission, that Inês de Castro returned and they started to live together. His father, D. Afonso IV, afraid of the repercussions, ordered Inês's death when D. Pedro was away. D. Pedro I was furious and after D. Afonso IV's death, he is declared the eighth king of Portugal. After this, he persecuted and killed cruelly two of the men responsible for Inês's death. He revealead that he and Inês secrectly married before her death, which legitimized their four children. D. Pedro I granted Inês de Castro the posthumous title of queen of Portugal and he certainly would like to have reigned alongside his beloved, but that is no longer possible, because now Inês is dead.
#langblr#brazilian portuguese#portuguese langblr#language learning#learning portuguese#learning brazilian portuguese#portuguese vocabulary#brazilian portuguese vocab
18 notes
·
View notes
Text








AU: Valois House. Children Francis I and Claude Valois.
Luisa(1515 - 1576). Queen of Spain and Empress of the Holy Roman Empire. Wife of Charles V. Despite the fact that the age difference between the spouses was 16 years, they loved each other. Charles treated his young wife with tenderness. She was interested in music, dancing and writing. Luisa and Charles had 7 children: John III, Claude, Philip, Ramiro, Ferdinand, Joana, Charles.
Charlotte(1516 - 1570). Queen of Portugal. Wife of Juan III and mother of 6 children: José I, Manuel, Isabella, Sancho, Aldegunda, Mary. Charlotte devoted much time to the education of her children and the enlightenment of the Portuguese court. She was the favorite sister of Francis II and maintained a close relationship with his wife.
Francis II(1518 - 1590). King of France. Husband of Mary Tudor. Francis loved his wife. Unlike his father and brothers, he never had mistresses or children out of wedlock. The reign of Francis II was an era of prosperity and rise. Father of 8 children: Claude, Francis III, Catherine, Charlotte, Tristan, Raoul, Adele, Henry.
Henry(1519 - 1587). Duke of Orleans. Husband of Catherine de Medici and father of 10 children: Francis, Elizabeth, Claude, Louis, Charles, Henry, Margaret, Hercule, Victoria and Jeanne. All his life loved only his mistress Diana de Poitiers, even wanted to marry her, but because of pressure from his father did not do it.
AU: дом Валуа. Дети Франциска I и Клод Валуа.
Луиза(1515 - 1576). Королева Испании и императрица Священной римской империи. Жена Карла V. Несмотря на то, что разница в возрасте между супругами была 16 лет, они любили друг друга. Карл с нежностью относился к молодой жене. Интересовалась музыкой, танцами и писательством. У Луизы и Карла родилось 7 детей: Хуан III, Клод, Филипп, Рамиро, Фердинанд, Хуана, Карл.
Шарлотта(1516 - 1570). Королева Португалии. Жена Жуана III и мать 6 детей: Жозе I, Мануэль, Изабелла, Саншу, Альдегунда, Мария. Шарлотта уделяла много времени образованию своих детей и просвящению Португальского двора. Была любимой сестрой Франциска II и поддерживала близкие отношения с его женой.
Франциск II(1518 - 1590). Король Франции. Муж Марии Тюдор. Франциск любил свою жену. В отличие от отца и братьев у него никогда не было любовниц и внебрачных детей. Правление Франциска II было эпохой процветания и подъёма. Отец 8 детей: Клод, Франциск III, Екатерина, Шарлотта, Тристан, Рауль, Адель, Генрих.
Генрих(1519 - 1587). Герцог Орлеанский. Муж Екатерины Медичи и отец 10 детей: Франциск, Елизавета, Клод, Людовик, Карл, Генрих, Маргарита, Эркюль, Виктория и Жанна. Всю жизнь любил только свою любовницу Диану де Пуатье, даже хотел на ней жениться, но из-за давления отца не стал этого делать.
Part 1.
#history#history au#royal family#royalty#au#france#france history#History of France#French royal family#french#french royalty#french royal family#French royal#Royal#Royals#the tudors#henryviii#mary tudor#the serpent queen#catherine de medici#mary stuart#Henryii#francis valois#The reign#elizabeth i#15th century#16th century#Francis i#Francisii#French kings
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

This rhino, which seems not to have been given a name, was the first to arrive in Europe since the Roman empire. It showed up in Lisbon, Portugal in 1515, a gift from an Indian leader.
King Manuel of Portugal enjoyed having the rhino in his collection — he apparently tried, unsuccessfully, to make it fight an elephant who we’ll meet later — but he seems to have realized that he could use it to strengthen his political position. So he soon packed the animal up and shipped it off to Pope Leo X, in the hopes that the Pope would continue to sanction Portugal’s imperial adventures. Unfortunately, the ship sank in a storm off of the Italian coast; the chained-up rhino sank with the ship. There are some sources that tell us that Manuel tried to stuff the rhino and send it to the Pope again, but it’s unclear if that ever happened.
This rhino was a sensation in its day, but it’s mostly remembered because of a man who never even saw it — Albrecht Dürer, one of the titans of the Northern Renaissance. Dürer, in the Netherlands, heard descriptions of the rhino and decided to make a woodcut of it.
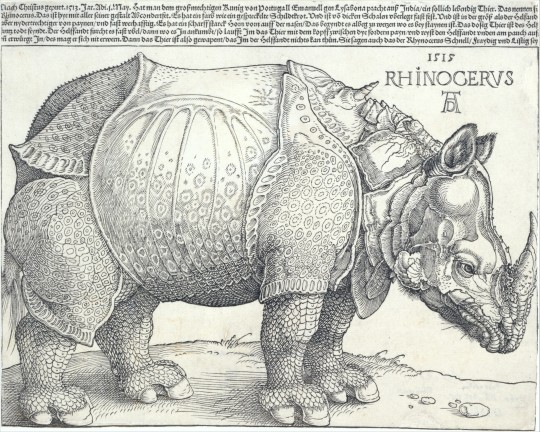
The image isn’t an accurate one, but it’s compelling and was widely copied. Dürer’s interpretation was most Europeans’ idea of what a rhinoceros looked like for two centuries.
{WHF} {Ko-Fi} {Medium}
113 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! I don't know how much you're interested in the subject today, but considering how i really adored a lot of your opinions/views of the Wars of the Roses and some people involved, especially Richard III, i was wondering how you think a scenerio where Richard remained King for more time or simply won Bosworth would be
Thank you for the teresting question.
Contrary to historical fiction works that portray him as desperate at the Battle of Bosworth, I think it's more likely Richard was hoping to get rid of Henry Tudor quickly and saw him as just a temporary nuisance. If only the battle had happened a couple of days later, when Richard got reinforcements from the North, or if William Stanley had not made the decision to definitely switch sides to Henry, the battle would've probably gone completely differently.
Below is my speculation of what happens if Richard wins:
The immediate outcome seems relatively clear - we know now that Richard was in the middle of secret negotiations with the royal family of Portugal for a double marriage between him and Infanta Joanna, and Elizabeth of York and King's 16-year old cousin Manuel, Duke of Beja, which were apparently going very well. It seems unlikely that Joanna, who had been refusing to get married for so long, would accept, but supposedly the negotiations were going well. We know Richard had sent her a personal letter, so it's fun to speculate what he said that would make her reconsider. I'm thinking he may have talked about religion (as they were both known to be pious) and pitched the marriage in terms of a partnership, and how she could do good for peace and the people of England through charity work (which she was known to do) and maybe even assured her that she wouldn't have to keep having children after she gave birth to an heir? Richard was expected to remarry and have a son after his only legitimate son and his wife died, but going by his choice of bride, he was looking for a great Queen and political partner above all, and not a broodmare - I can't imagine Joanna, who wanted to be a nun and was against marriage, agreeing to keep popping up a child every year or two until she hits menopause. He also may not have been two concerned because he had an heir and spares already, even though not 'of his body'- - his adult nephew John de La Pole and his younger brothers William, Edmund and Richard. The Portugal double marriage would've been a genius political move for many reasons: it would allow Richard to claim that he was ending the York/Lancaster rift for good by marrying Joanna, since the Portuguese royal family were through the female line the main surviving Lancastrian branch; it would fulfil his promise to Elizabeth Woodville that he would find good matches for her daughters in spite of their new 'bastard' status - and how! a Portuguese royal marriage was worthy of a princess* - and could be seen as healing the rift between the Yorkists too (and would at the same time make it impossible for Henry Tudor or anyone else to try to claim the throne of England by marrying her); and it would give England a great, intelligent and respectable Queen, who had experience in ruling as regent and could rule in RIchard's absence when he spent time abroad in wars, and whose reputation for piety and charity for people would help restore his tarnished reputation.
One interesting consequence of his marriage alliance is that Elizabeth of York would eventually have become a Queen Consort, but of Portugal, as Manuel eventually became King.Manuel I in 1495.
Once the situation became more stable, Richard would've probably focused on the things he had already started to do during his short reign - legal reforms aimed mostly at bettering the judiciary and the status of common people, and he would no doubt also want to curtail the power of major noblemen of questionable loyalty such as the Stanleys - and things he is known to have enthusiastically talked about planning to do, such as trying to convince other European countries to mount a campaign to stop the Ottoman Empire's conquests in Europe. (France would be an unlikely ally, Portugal and Burgundy would be obvious ones, and he'd no doubt try to pitch it to the Holy Roman Empire.)
I don't know whether he'd be successful at that, or how long he would live, but a few most obvious historical consequences would be:
the way the previous few decades were remembered in history would be very different, and no one would ever call them the "Wars of the Roses" - which was a name given by Walter Scott in the 19th century based on the fact that Henry VII used the red-white Tudor rose as his sigil, promoting it as a sign of supposed unity between the Lancaster and York dynasties - in spite of the fact that the Lancasters didn't actually use a red rose, or any kind of rose, as their sigil. Henry VII also presented the conflicts that had gone on as a part of one ongoing conflict that he ended with the Battle of Bosworth and by marrying Elizabeth of York. In reality, these were a few conflicts separated by years or even decades in between, and before the battle of Bosworth, the last actual armed conflict fought over the throne of England had been 14 years earlier, when Edward IV won his second and decisive war over the Lancasters. The conflict between the two Yorkist factions after Edward's death did not result in any actual battle (in 1783, Buckingham failed to ignite a rebellion, and his ally Henry turned back to France, realizing the war was lost before it began), so Henry basically 'ended the Wars of the Roses' only after he restarted them in 1485. (Not to mention that Henry had to fight another battle two years later against the Yorkists led by Jon de la Pole, which is always conveniently left out in history books, and had to catch, exile or execute various Yorkist pretenders throughout his reign.) If Henry loses the battle, he becomes only a footnote in history. Edward IV remains considered the one who ended the Lancaster-York conflicts with his decisive victory in 1471. Richard probably manages to be popular and respected king (much more than Henry was with his notorious tax laws) and would likely have claimed to have 'united the York and Lancaster branches' with his marriage to Joanna (though he probably wouldn't have made a huge deal out of it as Henry did, since Henry was promoting himself as the founder of a new dynasty that would start a new era). But what of the Princes in the Tower? Well, we don't know what happened to them and Richard may be suspected to have murdered them, but Henry definitely did imprison 11 year old Edward of Warwick and keep him locked up in the Tower until he was 25 and then executed him on trumped up treason charges just because he was another pretender to the throne, but barely anyone talks about it or cares, so... (insert something about history being written by the winners)
Scotland and England remain separate independent countries. It's very unlikely that the same chain of events would happen where the daughter of a king of England marries a king of Scotland, and then a century later her descendant becomes not just the king of Scotland but also the heir to the throne of England because the ruling dynasty of England died out. There is never a Tudor dynasty, never a Stuart dynasty, never a Hanover dynasty. And there's never a United Kingdom.
There is never such a thing as Anglicanism/the Church of England, with the monarch as its head. Mind you, this doesn't necessarily mean that England remains fully or predominantly Catholic - Protestantism was gaining popularity not just in England (even when Henry was still a devout Catholic) but also in Scotland, which didn't have a Henry VIII splitting with the Pope so he could annul his marriage. It's impossible to tell how exactly the Reformation and Counter-reformation would've affected England under different monarchs and a different dynasty, since so much of the religious strife in the 16th century was linked to Henry's decisions, his break from the Pope, his marriages and annulments and his succession issues, and then with the personalities and backgrounds of his children: Edward as a staunch Protestant (just like his mother's family), Mary as a staunch Catholic (completely unsurprising with her background and the fact that her father broke from the Pope so he could annul his marriage to her mother, proclaiming her a bastard), and then Elizabeth, who couldn't be tolerant to Catholics even if she didn't care about religion, since the Pope and therefore all Catholics considered her a bastard and an illegitimate monarch. How would elderly Richard, and/or his heirs, treat Protestants? What would they think of Martin Luther, or of William Tyndale? It's impossible to tell. He was a devout Catholic, but Protestantism didn't exist at the time, and would he (who was the first of English kings to publish official state documents in English) hate the idea of translating the Bible into English so ordinary people could understand it without the help of clergy? I really don't know, and it's even harder to tell what his heirs would be like in that regard. Would there be more religious tolerance in England? For all we know, it might even be less if a particularly fanatical monarch ended up on a throne... but at least I think I can say with some certainty that English monarchs of this hypothetical York dynasty would have no personal and dynastic reasons to persecute either Protestants or Catholics the way monarchs of the Tudor dynasty had due to their specific circumstances.
#richard iii#english history#henry vii#the wars of the roses#battle of bosworth#the tudor dynasty#edward iv#elizabeth of york#henry viii#church of england#english reformation#wars of the roses
13 notes
·
View notes
Note

This is an imagen of María of Aragón, Queen of Portugal, from the Tríptico de Nuestra Señora de la Misericordia, Jan Provost, c. 1515.

I presume you wish to hear my thoughts about this painting, since no question was written.
Despite Jan Provoost never provenly leaving Low Countries, surprisingly not so small amount of his art are on Iberian peninsula.
Some of them provenly there since not long after their making, presumably comissioned directly. Not really sure how that comission process exactly worked.
Probably the best quality photos I could find of it are from this webpage.
Which also sheds bit of light about its history.
This painting is believed to be comissioned by Nuno Fernandes Cardoso and his wife Leonor Dias in 1511 when they had ordered construction of Chapel called la Capilla de San Juan de Letrán including the triptych for its altar. Thus it is presumed the painting was comissioned between years 1512-1515, not long after.
I have some issues regarding the royals within.
Number 1 all photos ignore the fifth presumed member of royal family-The girl in red dress on right.


(and fact two more figures are partially hiden behind the altar.)
It is believed by some that from left to right these are Manuel I, Maria of Aragon-his wife, Isabella of Portugal-his eldest daughter, Eleanor of Viseu(Dowager Queen of Portugal-wife of his predecessor) and Beatrice of Portugal-his younger daughter.
Not sure about costumes of everybody, but presumed daughters are dressed in Netherlandish outfits.
While i cannot rule out he was sent some sketches, the faces of these women are consistent with generic figures from other paintings by same artist. With designs which he was reusing.
Thus even if identification as royals is correct, it is not likely for it to be true likeness. (However in some cases, the artists were chosen because their already existing work reminded people of their loved ones. )
But the question on my mind seeing this triptych is-Where the heck are his sons? The painting is believed to be made in betwen 1512-1515.
By this point Manuel and Maria had 3 daughters and 5 boys. People were sexist back then, so idea King Manuel got depicted with wifey and daughters only is cute...but unrealistic.

While we have 7 male figures on left, one is pope(on right), one is old man, then there is monk(infante Henry was cardinal), and 4 more figures, not all of them even showing full face. They are not at front, but at back. Like is it symbolical...or were those boys not important?
Secondly, why would every royal except Manuel be depicted in clothes better fitted for somebody of lesser status?
Another depiction of the same royal family by Netherlandish artist Colijn de Coter is called Fons Vitae, and there despite outfits being netherlandish at least they were what we would expect from depiction of royalty.

Ermine, cloth of gold, crimson also popular with plenty of royals. But here only Manuel wears such suptuous robes.
(the other male with fur-that is not ermine, they specifically sewn those so that the tails appeared regularly.)
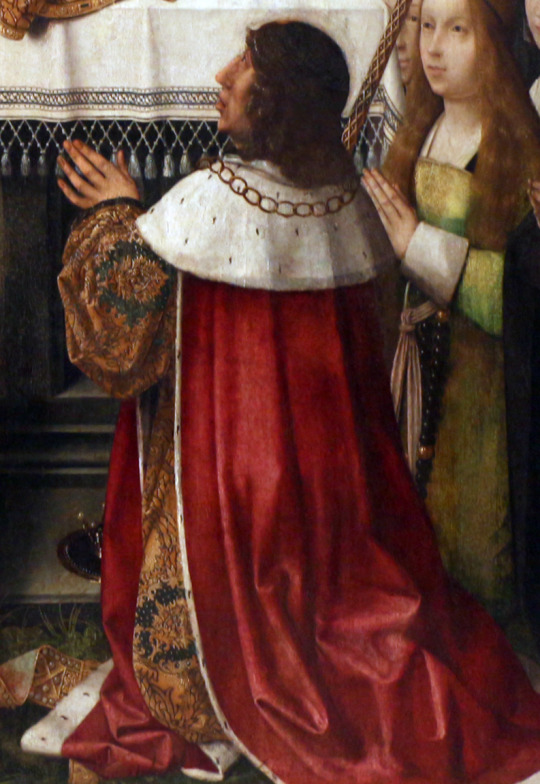


Thus i fear, it might be the case that Manuel is the sole royal depicted.

And that we have pope and king in central positions beneath Virgin Mary and people on sides will be the patrons and the family.
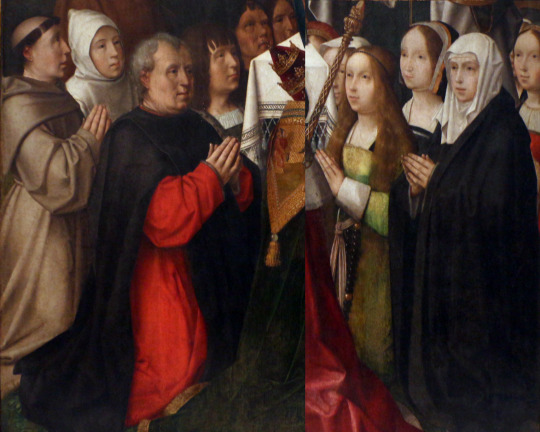

Possibly people who had the painting comissioned. Which would mean the grey-haired man in red and black is ment to represent Nuno Fernandes Cardoso(with his male relatives behind him).
And his wife Leonor Dias, is represented by either the woman in green or the woman in black with white headwear-which is also positioned probably the most at front(with the female relatives behind her.)
Thus in my opinion it could be the case of wrong identification, based upon proximity to the figure of the king and the fact the woman has golden hair (or at least i think she might have) and ribbon on upper part of forehead is bit similiar to how cofia the tranzado was worn with ribbon across forehead.
But even if i was wrong about this female not being ment to represent Maria, the face matches rest of generic saints by this artist. (for example the one on left)

Sorry. This is pretty face, but likely not Maria's.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
#JON SNOW FORTNIGHT EVENT 2023
@asoiafcanonjonsnow
DAY 10: ECHOES OF THE PAST 🗝️📜(2/2) ->
Historical parallels with Medieval bastard Kings.
John I of Portugal
To complete the the previous post of this meta, we're going to dive in the parallels and simmilarities between Jon Snow and John I of Portugal through the following points:
BASTARDY
John I of Portugal also known as John of Avis, was the bastard son of King Peter I of Portugal and Teresa Guille Lourenço, a Galician noblewoman, lady in waiting of Inês de Castro, or according to other sources, the daughter of some Lisbon merchants.
Jon Snow is officially known to be Ned Stark's bastard son, and if we consider R+L=J, he's Prince Rhaegar and Lyanna's son, and as far as we know Jon is still a bastard.
PARENT'S TRAGIC LOVE STORY
John I's father, Peter I of Portugal fell in love with Inês, a lady in waiting and cousin of Constanza Manuel de Villena (Peter's wife).
After Constanza died, they became lovers and they had four children and they wed in secret, but some Portuguese nobles and Peter's father, Afonso IV of Portugal, disliked their relationship because the possible influences of Inês' family. They plotted to kill her, Inés was killed by three of those men and it's said that when Peter became king, he put Inês' corpse in a throne next to him so that the people would swear allegiance to her as queen of Portugal and looked for revenge chasing the ones who killed Inês. John I was born a few years after Inês died when Peter I had an affair with Teresa Lourenço.
Jon's parents, Rhaegar and Lyanna met at the Harrenhal Tourney, in which both participated, Lyanna as the Knight of the Laughing Tree, Aerys sent Rhaegar some men to learn the identity of the mystery knight, so it's likely that Rhaegar figure it out and then crowned her as Queen of Love and Beauty when he won the tourney. They fell in love and run away together, Rhaegar died at the Battle of the Trident during Robert's rebellion and Lyanna died after giving birth to Jon at the Tower of Joy.
BROTHER IS THE KING
After Peter I of Portugal died, he was succeeded by his son with Constanza Manuel de Villena, Ferdinand I, and John held a prominent position during the reign of his brother.
Jon is a brother of the Night's Watch when Robb is proclaimed as King in the North and during his brief reign.
Apart from that it would be argued that Aegon VI fits here too because he's Jon's brother, but Young Griff's identity as Aegon VI is doubtful and he hasn't taken control of Westeros yet.
MILITAR EDUCATION AND CAREER
John was educated by Nuno Freire de Andrade, Master of the Order of Christ, and John became Master of the Order of Avís, one of the most important Orders in Portugal during the Middle Ages, from which he will take his last name.
Jon joined the Night's Watch, which can also be considered a militar order in which chastity is also imposed on its members just like the Order of Avis. Jeor Mormont, Lord Commander of the Night's Watch has been one of Jon's mentors, so just like John, Jon had the leader of a militar order as a mentor, and then became the head of a militar order.
RELATIONSHIPS/LOVE INTERESTS
While John formed part of the Order of Avis, despite vows of chastity, John had two bastard children with Inês Pires when he was a teenager, Beatrice and Afonso, 1st Duke of Braganza.
Jon broke his vows by falling in love and being with Ygritte, even though Jon didn't had children with Ygritte, and Jon has also expressed that he didn't want to have them because of the stigma of being a bastard and the classist Westerosi society.
POLITICAL MATCH MAKER
John was one of the negotiators of the successive marriage projects of his niece and the heiress Beatrice of Portugal, who would end up marrying John I of Castile (Henry II of Castile's son), as a way to seal peace after the Fernandine Wars, in which Ferdinand I tried to overthrow Henry II from the Castilian throne, who became king after killing his legitimate brother Peter I of Castile (who was Ferdinand I's cousin), and was supported by one of Peter I's legitimised bastard children, Constance of Castile.
In the agreements established that each one would independently reign their kingdoms and the offspring of both would inherit Portugal, although if Beatrice died without children, the heirs of her husband would inherit Portugal, and John I of Castile has children from a previous marriage to Eleanor of Aragon (this is important detail for later).
Jon has also arranged a wedding of a familiar during his time as head of the militar institucional, as the Karstarks originated as a cadet branch of the Starks, and there have been intermarriages between the two houses, so we could assume Alys and Jon are distant cousins, such as Alys and Sigorn's wedding.
PROBLEMS OF SUCESSION AND INDEPENDENCE OF THEIR KINGDOMS & THEIR RISE TO KINGSHIP
After the death of Ferdinand I, a succession crisis took place in Portugal between Beatrice, who had no offspring, and the children of Peter I of Portugal with Inés de Castro (who were considered bastards by the Portuguese nobility), and also John revolted at end of 1384 with the support of the commonfolk and the bourgeoisie, and promoted a war to maintain the independence of Portugal, adopting the title of defender of the kingdom, which he achieved by defeating Beatrice and John I of Castile, for which he was crowned king of Portugal, being the first king and founder of the House of Avis.
Due to what happened to John with the fight for the independence of Portugal against another family member, it is most likely that in TWOW when Jon arrives in Winterfell the inheritance problem between the Starklings will have to be solved, and with Robb's will and his position as the older brother and being the one with political experience, supported by the Free Folk, the Mountain Clans and some Northern Noble Houses like the recently created House of Thenn, formed by Alys and Sigorn, Jon will be named king in the North breaking relations with the Iron Throne that is under the control of the Lannisters and the North will be (for the moment) independent again. In addition, the matter of Beatrice and her husband John I of Castile reminds me a bit of the marriage of Sansa and Tyrion, being Tywin's initial plan to get the North under the rule of the Lannisters, although that did not work and the best method was having the Boltons at Winterfell. Plus both Tyrion and John I of Castile have lions in their sigils, although the Castilian lion is purple (or in some media, red) and the Lannister one is golden.
ALLIANCES, MARRIAGE & OFFSPRING/POSSIBLE MARRIAGE (SPECULATIONS)
Like his brother Ferdinand I, John supported Constance's cause, allying with her against John I of Castile, but they were defeated and Constance did not get the Castilian throne, her daughter Catherine of Lancaster married John I of Castile's son, Henry III, and their son was John II of Castile, thus uniting the two lines of succession of Alfonso XI of Castile.
As well as Peter I of Castile's two eldest surviving daughters married two of Edward III of England's sons (Constance married John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster and Isabella married Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York), John I of Portugal married Philippa of Lancaster, John of Gaunt's eldest daughter with Blanche of Lancaster, and they had a loving marriage and eight children: Blanche, Afonso, Edward I of Portugal, Peter, Henry, Isabella, John and Ferdinand.
Edward was a poet and writer, his more important books were, on good governance,'The Loyal Counselor', 'Book of Councils', 'Response, being princes, to the infant D. Ferdinand about some complaints he had of his father'; on sports and horsemanship, with educational connotations, 'Teaching book about riding well in any saddle' and "Regiment to learn to play weapons'.
It's very likely that Jon will need to make more alliances to stablish his position as King in The North and preparing for the War for the Dawn and fight against the Others, and one way to do it it would be marrying someone with a prominent influence and a big army.
And although Dany hasn't landed on Westeros yet, due to her army and her influence as queen claimant to the Iron Throne, could be a good ally, and Dany would like to help due to her care for people who are needed, so probably Jon and Dany would join forces and eventually they could fall in love, marry and rule Westeros together.
Plus, if Jon ans Dany have children, one of them could be a poet like Edward I or a music composer and a bookworm like Rhaegar.
CUNNING/KNOWLEDGE
Contemporary writers state John that his position as a master of a religious military order made him an exceptionally learned king for the Middle Ages. His love for knowledge and culture was passed down to his children, who are collectively referred to by Portuguese historians as the illustrious generation, for example, Edward I the Eloquent and Peter were considered as two of the most learned princes of their time, and Henry the Sailor invested heavily in science and in the development of nautical activities.
Although Jon is often seen as a warrior, he has shown interest on knowledge and books too and he has been showing competences and skills for being a good leader and he's cunning good at politics and a good administrator, as he has been proving during his time as Lord Commander of the Night's Watch.
DRAGON IMAGERY
John I of Portugal's sigil has some elements that make me link him with Jon, his emblem has a crest with a dragon, which was usually used in the heraldry of the Portuguese Royal family, in which a dragon appears in the Royal crest or two green dragons as the supports of coat of arms, which makes me think of Rhaegal, a green dragon, who was named after Rhaegar and most likely Jon is its dragonrider.
#jonsnowfortnightevent2023#jonsnowfortnightevent#jon snow#meta#canonjonsnow#canonjon#jon meta#asoiaf meta#day 10#echoes of the past#historical parallels#john i of portugal#João I#medieval bastard kings
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Prince Manuel Maria Filipe Carlos Amélio Luís Miguel Rafael Gabriel Gonzaga Xavier Francisco de Assis Eugénio of Bragaza, later King Manuel II of Portugal
Portuguese vintage postcard
#historic#briefkaart#maria#postkaart#carte postale#manuel#ephemera#xavier#miguel#francisco#tarjeta#photo#filipe#postcard#postal#portuguese#amlio#postkarte#assis#manuel ii#prince#later#king#ansichtskarte#rafael#bragaza#carlos#portugal#gonzaga#gabriel
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pedro & Inês (cultural ramblie)
Happy Valentine's Day!! <3<3 When I planned this post, I did not realize Carnaval and Valentine's Day were on consecutive days (catholic calendar calculations continue to kick my ass, just like every year), so you get TWO cultural ramblies for the price of one!!
This one is a bit different from the other ones. I usually talk about legends or holiday traditions but this is actually just history! Still, I felt inclined to share partly because this is a major thing in portuguese culture and partly because this is the most overdramatic historical anecdote I have ever seen and more people need to know about it. Now, let's get into it!
The Tragedy of Pedro and Inês


(portraits of Pedro and Inês, made centuries after their deaths)
In 1340, Prince Pedro of Portugal, son of King Afonso the 4th, married Constança Manuel of Aragon. When she moved to Portugal, Constança brought along her lady-in-waiting, Inês de Castro. You can already see where this is going.
Pedro and Inês fell madly in love and began a secret relationship (which seems to not have been that secret at all). In 1344, Afonso the 4th exiled Inês to the castle of Albuquerque, near the border, out of fear that this affair would sour diplomatic relationships with Castille.
It just so happens that Constança died in childbirth one year later. Despite his father's requests, Pedro refused to remarry, claiming that he was still too overcome with grief over his wife's death. Instead, he had Inês's exile annulled and began living with her. During this period in which they lived together, they had 4 children.
In 1355, five years later, King Afonso the 4th ordered the assassination of Inês de Castro. She was killed in Coimbra, in Quinta das Lágrimas, where legend says you can still hear her crying at the fountain where she lost her life, later named Fonte das Lágrimas ("Fountain of Tears"). This moment, along with another one further ahead, is the one all the poets go crazy for.
Inês's death triggered a revolt against the king, led by Pedro. However, there was never an actual physical confrontation, since the queen-mother was able to stop it in time.
In 1357, Pedro rose to the throne, becoming King Pedro the 1st. He claimed that he had married Inês in secret around 1354, legitimizing their children and making her possibly the only posthumous queen in history (someone fact-check me on this). For avenging her death, he was dubbed "Pedro, the Just".
He had matching tombs made for him and Inês so she could be buried as queen by his side. They still stand today in the Monastery of Alcobaça, where you can visit them. They were placed on opposite ends of the transept, facing each other, so that they could be face to face when they rose from their graves. The inscription on Pedro's tomb is thought to read "Until the ends of the world". I'll show pics later, don't worry.
You thought I was done? I haven't even gotten to the overdramatic part! (Ok, the tomb thing was pretty dramatic, but this part is extra as hell)
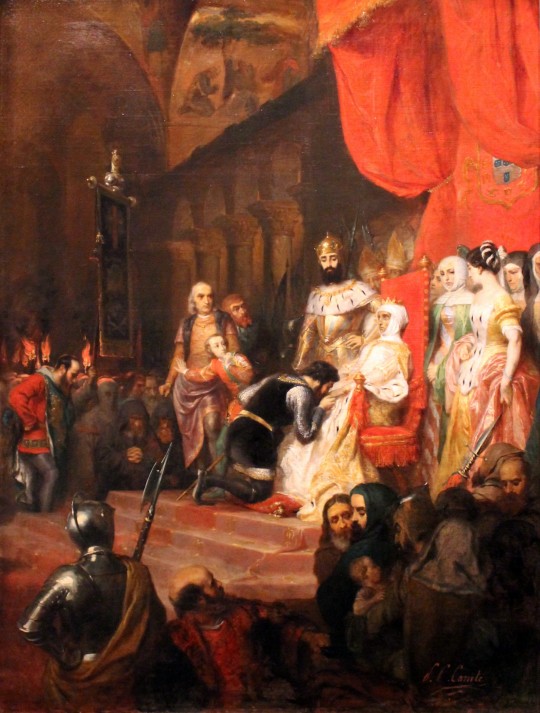
As King Pedro the 1st, he had Inês's two assassins executed. According to a somewhat contemporary chronicle by Fernão Lopes (still Middle Ages but a century later), he had their hearts ripped out, one through the chest and another through the back. Sources seem to disagree on whether this actually happened or not, but Fernão Lopes was a pretty reliable guy in other parts of his chronicle. And, this being strictly myth, it is said that he made those two assassins kiss the hand of Inês's corpse as they would the queen's. For this, he was dubbed "Pedro, the Cruel", on top of his other title. Perfectly balanced and whatnot.
Here's a painting by Pierre-Charles Comte about it:

The Tombs
I saw them in early November of last year and I cannot overstate how amazing they are in real life. The whole church they're in is beautiful but the tombs are just breathtaking, especially knowing the story behind them.
They're the reason I wanted to make this post. They are considered some of the greatest masterpieces of portuguese gothic sculpture. They are full of intricate carvings and, despite missing a few pieces here and there, are still in amazingly good condition today. You can visit them for free any time.
Here are the pictures I promised. The last 2 are taken by me!



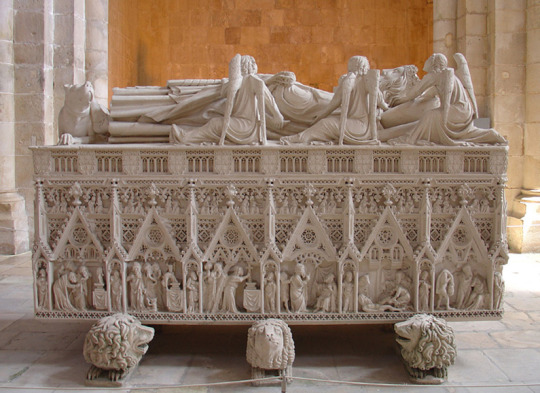


Some historical notes (cool facts)
This is mostly about the corpse coronation part because I found it in my research and thought it was cool.
The first dynasty of portuguese kings didn't have coronations. They were seen as warrior kings first and foremost, and therefore felt no need to pledge their allegiance to Christianity. If they did swear over something, it was a shield. They did not have the fancy ceremony.
What can we learn from all this, you ask?
Write that overdramatic romance you've been wanting to. You'll never out-drama queen King Pedro the 1st.
#as a kid i always felt really bad for Constança#she literally got pushed aside in the history she was a part of#no one cares about her???#all she is is “a woman who got cheated on”?? she deserves better!!!#anyways Pedro is the greatest drama queen to ever live#imagine being so extra about your girlfriend's death your tombs become some of the most famous sculptures in Portugal#and also the heart thing#the Middle Ages really were a time huh#portugal ramblies#portuguese history#portuguese legend#pedro e inês#happy valentine's day#<3 <3 <3#i'm not translating the names. fuck that.#i refuse to look up what the english equivalent of “Inês” is
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Portugal, Manuel I (1495-1521)
Portugues of 10 Cruzados, Lisbon
Manuel I (31 May 1469 – 13 December 1521), known as the Fortunate (Portuguese: O Venturoso), was King of Portugal from 1495 to 1521.
#Portugal#Manuel I#Portugues of 10 Cruzados#cpon#gold coin#collectable coin#metal detector#metal detecting finds#ancient artifacts#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations
138 notes
·
View notes
Text

Henrique Medina - Portrait of His Majesty Manuel ll - Last King of Portugal
27 notes
·
View notes