#learning agent in ai
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Do you ever think about how for almost 1000 years there's this story about a King named Arthur with an old man wizard advisor named Merlin and then in 2008 (and onward) it got rewired to where we're writing fanfiction and making art and edits of them kissing?
If you told someone 20 years ago that you wanted to see King Arthur and Merlin kiss they would've thought you were crazy.
#bbc merlin#bbc merthur#merlin#merthur#arthur pendragon#fanfiction#fanart#i was writing something for them and i use google docs and it tried to auto insert 'King' before Arthur at one point#and I just thought#if ai is learning to write by stealing fanfiction of these two#or if my fbi agent is watching#and they think it's the old man wizard and arthur#that's weird
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
OpenAI Releases Codex: A Software Agent that Operates in the Cloud and Can Do Many Tasks in Parallel
OpenAI has released a research preview of Codex, a cloud-based software engineering agent that's not just another code completion tool. Codex is a cloud-based software-engineering agent that turns on isolated sandboxes, pulls your repo, and chips away at features, bug fixes, test suites, and even pull-request boilerplates—often in parallel.
What is OpenAI Codex? 📌
→ Cloud-based software engineering agent
→ Can write features, answer codebase questions, run tests, and propose Pull Requests for review
→ Each task runs in its own isolated cloud environment
→ Provides detailed terminal logs, test outputs, and citations
→ Users can create AGENTS.MD files in their repository to instruct Codex on project-specific commands, testing procedures, and coding standards
→ Powered by codex-1
How to use Codex: 📌
→ Users can access Codex through the ChatGPT sidebar
→ Assign coding tasks by typing a prompt
→ Each request is handled independently
→ Codex can read and edit files and run commands like test suites, linters, and type checkers
→ Task completion generally takes between one and thirty minutes
Once done, Codex runs its changes within its sandboxed environment, which users can then review, ask for more changes, open a GitHub PR, or pull the changes into their local setup.
↗️ Full Read: https://aiagent.marktechpost.com/post/openai-releases-codex-a-software-agent-that-operates-in-the-cloud-and-can-do-many-tasks-in-parallel
Codex: Availability 📌
Codex is currently rolling out to ChatGPT Pro, Enterprise, and Team users, with access for Plus and Edu users planned to come soon.

#agentic ai#ai#ai agency#ai agents#artifical intelligence#chatgpt#codex#ChatGPT Codex#OpenAI Codex#coding#programming#engineering#software#machine learning#software engineering agent#software engineering#coding agent
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
#artificial intelligence#machine learning#marketing#technology#google#google trends#autonomous robots#emotions#finance#healthcare#agentic ai
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

AI’s Role in Business Process Automation
Automation has come a long way from simply replacing manual tasks with machines. With AI stepping into the scene, business process automation is no longer just about cutting costs or speeding up workflows—it’s about making smarter, more adaptive decisions that continuously evolve. AI isn't just doing what we tell it; it’s learning, predicting, and innovating in ways that redefine how businesses operate.
From hyperautomation to AI-powered chatbots and intelligent document processing, the world of automation is rapidly expanding. But what does the future hold?
What is Business Process Automation?
Business Process Automation (BPA) refers to the use of technology to streamline and automate repetitive, rule-based tasks within an organization. The goal is to improve efficiency, reduce errors, cut costs, and free up human workers for higher-value activities. BPA covers a wide range of functions, from automating simple data entry tasks to orchestrating complex workflows across multiple departments.
Traditional BPA solutions rely on predefined rules and scripts to automate tasks such as invoicing, payroll processing, customer service inquiries, and supply chain management. However, as businesses deal with increasing amounts of data and more complex decision-making requirements, AI is playing an increasingly critical role in enhancing BPA capabilities.
AI’s Role in Business Process Automation
AI is revolutionizing business process automation by introducing cognitive capabilities that allow systems to learn, adapt, and make intelligent decisions. Unlike traditional automation, which follows a strict set of rules, AI-driven BPA leverages machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision to understand patterns, process unstructured data, and provide predictive insights.
Here are some of the key ways AI is enhancing BPA:
Self-Learning Systems: AI-powered BPA can analyze past workflows and optimize them dynamically without human intervention.
Advanced Data Processing: AI-driven tools can extract information from documents, emails, and customer interactions, enabling businesses to process data faster and more accurately.
Predictive Analytics: AI helps businesses forecast trends, detect anomalies, and make proactive decisions based on real-time insights.
Enhanced Customer Interactions: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, improving customer service efficiency and satisfaction.
Automation of Complex Workflows: AI enables the automation of multi-step, decision-heavy processes, such as fraud detection, regulatory compliance, and personalized marketing campaigns.
As organizations seek more efficient ways to handle increasing data volumes and complex processes, AI-driven BPA is becoming a strategic priority. The ability of AI to analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and make intelligent decisions is transforming industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
“At the leading edge of automation, AI transforms routine workflows into smart, adaptive systems that think ahead. It’s not about merely accelerating tasks—it’s about creating an evolving framework that continuously optimizes operations for future challenges.”
— Emma Reynolds, CTO of QuantumOps
Trends in AI-Driven Business Process Automation
1. Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation, a term coined by Gartner, refers to the combination of AI, robotic process automation (RPA), and other advanced technologies to automate as many business processes as possible. By leveraging AI-powered bots and predictive analytics, companies can automate end-to-end processes, reducing operational costs and improving decision-making.
Hyperautomation enables organizations to move beyond simple task automation to more complex workflows, incorporating AI-driven insights to optimize efficiency continuously. This trend is expected to accelerate as businesses adopt AI-first strategies to stay competitive.
2. AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling seamless interactions with customers and employees. AI-driven conversational interfaces are revolutionizing customer service, HR operations, and IT support by providing real-time assistance, answering queries, and resolving issues without human intervention.
The integration of AI with natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis allows chatbots to understand context, emotions, and intent, providing more personalized responses. Future advancements in AI will enhance their capabilities, making them more intuitive and capable of handling complex tasks.
3. Process Mining and AI-Driven Insights
Process mining leverages AI to analyze business workflows, identify bottlenecks, and suggest improvements. By collecting data from enterprise systems, AI can provide actionable insights into process inefficiencies, allowing companies to optimize operations dynamically.
AI-powered process mining tools help businesses understand workflow deviations, uncover hidden inefficiencies, and implement data-driven solutions. This trend is expected to grow as organizations seek more visibility and control over their automated processes.
4. AI and Predictive Analytics for Decision-Making
AI-driven predictive analytics plays a crucial role in business process automation by forecasting trends, detecting anomalies, and making data-backed decisions. Companies are increasingly using AI to analyze customer behaviour, market trends, and operational risks, enabling them to make proactive decisions.
For example, in supply chain management, AI can predict demand fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, and prevent disruptions. In finance, AI-powered fraud detection systems analyze transaction patterns in real-time to prevent fraudulent activities. The future of BPA will heavily rely on AI-driven predictive capabilities to drive smarter business decisions.
5. AI-Enabled Document Processing and Intelligent OCR
Document-heavy industries such as legal, healthcare, and banking are benefiting from AI-powered Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and document processing solutions. AI can extract, classify, and process unstructured data from invoices, contracts, and forms, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy.
Intelligent document processing (IDP) combines AI, machine learning, and NLP to understand the context of documents, automate data entry, and integrate with existing enterprise systems. As AI models continue to improve, document processing automation will become more accurate and efficient.
Going Beyond Automation
The future of AI-driven BPA will go beyond automation—it will redefine how businesses function at their core. Here are some key predictions for the next decade:
Autonomous Decision-Making: AI systems will move beyond assisting human decisions to making autonomous decisions in areas such as finance, supply chain logistics, and healthcare management.
AI-Driven Creativity: AI will not just automate processes but also assist in creative and strategic business decisions, helping companies design products, create marketing strategies, and personalize customer experiences.
Human-AI Collaboration: AI will become an integral part of the workforce, working alongside employees as an intelligent assistant, boosting productivity and innovation.
Decentralized AI Systems: AI will become more distributed, with businesses using edge AI and blockchain-based automation to improve security, efficiency, and transparency in operations.
Industry-Specific AI Solutions: We will see more tailored AI automation solutions designed for specific industries, such as AI-driven legal research tools, medical diagnostics automation, and AI-powered financial advisory services.
AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s here, and it’s already transforming the way businesses operate. What’s exciting is that we’re still just scratching the surface. As AI continues to evolve, businesses will find new ways to automate, innovate, and create efficiencies that we can’t yet fully imagine.
But while AI is streamlining processes and making work more efficient, it’s also reshaping what it means to be human in the workplace. As automation takes over repetitive tasks, employees will have more opportunities to focus on creativity, strategy, and problem-solving. The future of AI in business process automation isn’t just about doing things faster—it’s about rethinking how we work all together.
Learn more about DataPeak:
#datapeak#factr#technology#agentic ai#saas#artificial intelligence#machine learning#ai#ai-driven business solutions#machine learning for workflow#ai solutions for data driven decision making#ai business tools#aiinnovation#digitaltools#digital technology#digital trends#dataanalytics#data driven decision making#data analytics#cloudmigration#cloudcomputing#cybersecurity#cloud computing#smbs#chatbots
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Inside the AI Based Contact Center with Tools Tech and Trends
Introduction

The evolution of customer service has entered a new era with the rise of the AI based contact center. No longer just a support line, today’s contact centers are intelligent, data-driven hubs that utilize artificial intelligence to deliver personalized, efficient, and scalable customer interactions. As businesses race to stay ahead of the curve, understanding the essential tools, technologies, and emerging trends that power AI-driven contact centers becomes crucial. This article explores how AI is transforming contact centers and what lies ahead for this innovative landscape.
The Rise of the AI Based Contact Center
Traditional contact centers, though essential, have long suffered from inefficiencies such as long wait times, inconsistent service, and high operational costs. AI-based contact centers are solving these issues by automating routine tasks, predicting customer needs, and delivering omnichannel support.
AI technology, such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and robotic process automation (RPA), is now integrated into contact center platforms to enhance agent productivity and customer satisfaction.
Essential Tools Driving AI Based Contact Centers
1. AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Agents
Chatbots are the most visible AI tool in contact centers. These virtual assistants handle customer queries instantly and are available 24/7. Advanced bots can handle complex conversations using NLP and deep learning, reducing human intervention for repetitive inquiries.
2. Intelligent Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems
Modern IVR systems use voice recognition and AI to route calls more accurately. Unlike traditional menu-based IVRs, intelligent IVRs can interpret natural language, making customer interactions smoother and faster.
3. Speech Analytics Tools
AI-driven speech analytics tools analyze live or recorded conversations in real time. They extract keywords, sentiments, and emotional cues, offering insights into customer satisfaction, agent performance, and compliance issues.
4. Workforce Optimization (WFO) Platforms
AI helps optimize staffing through forecasting and scheduling tools that predict call volumes and agent availability. These platforms improve efficiency and reduce costs by aligning workforce resources with demand.
5. CRM Integration and Predictive Analytics
By integrating AI with CRM systems, contact centers gain predictive capabilities. AI analyzes customer data to forecast needs, recommend next-best actions, and personalize interactions, leading to higher engagement and retention.
Core Technologies Enabling AI Based Contact Centers
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows machines to understand, interpret, and respond in human language. This is the backbone of AI-based communication, enabling features like voice recognition, sentiment detection, and conversational AI.
2. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
These technologies enable AI systems to learn from past interactions and improve over time. They are used to personalize customer interactions, detect fraud, and optimize call routing.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure for scalability and flexibility. AI contact centers hosted in the cloud offer remote access, fast deployment, and seamless integration with third-party applications.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA automates repetitive tasks such as data entry, ticket generation, and follow-ups. This frees up human agents to focus on more complex customer issues, improving efficiency.
Emerging Trends in AI Based Contact Centers
1. Hyper-Personalization
AI is pushing personalization to new heights by leveraging real-time data, purchase history, and browsing behavior. Contact centers can now offer customized solutions and product recommendations during live interactions.
2. Omnichannel AI Integration
Customers expect consistent service across channels—phone, email, chat, social media, and more. AI tools unify customer data across platforms, enabling seamless, context-aware conversations.
3. Emotion AI and Sentiment Analysis
Emotion AI goes beyond words to analyze voice tone, pace, and volume to determine a caller's emotional state. This data helps agents adapt their responses or triggers escalations when needed.
4. Agent Assist Tools
AI now works hand-in-hand with human agents by suggesting responses, summarizing calls, and providing real-time knowledge base access. These agent assist tools enhance productivity and reduce training time.
5. AI Ethics and Transparency
As AI becomes more prevalent, companies are increasingly focused on responsible AI usage. Transparency in how decisions are made, data privacy, and eliminating bias are emerging priorities for AI implementation.
Benefits of Adopting an AI Based Contact Center
Businesses that adopt AI-based contact centers experience a variety of benefits:
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Faster, more accurate responses enhance the overall experience.
Cost Reduction: Automation reduces reliance on large human teams for repetitive tasks.
Increased Scalability: AI can handle spikes in volume without compromising service quality.
Better Insights: Data analytics uncover trends and customer behaviors for better strategy.
Challenges in AI Based Contact Center Implementation
Despite the advantages, there are challenges to be aware of:
High Initial Investment: Setting up AI tools can be capital intensive.
Integration Complexities: Integrating AI with legacy systems may require customization.
Change Management: Staff may resist AI adoption due to fear of replacement or complexity.
Data Security and Compliance: AI systems must adhere to data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Future Outlook of AI Based Contact Centers
The future of AI-based contact centers is promising. As technology matures, we can expect deeper personalization, more intuitive bots, and stronger collaboration between human agents and AI. Voice AI will become more empathetic and context-aware, while backend analytics will drive strategic decision-making.
By 2030, many experts predict that AI will handle the majority of customer interactions, with human agents stepping in only for high-level concerns. This hybrid model will redefine efficiency and service quality in the contact center industry.
Conclusion
The AI based contact center is transforming how businesses interact with customers. With powerful tools, cutting-edge technologies, and evolving trends, organizations are reimagining the contact center as a strategic asset rather than a cost center. By investing in AI, companies can enhance customer experiences, improve operational efficiency, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital marketplace. The time to explore and adopt AI contact center solutions is now—because the future of customer support is already here.
#AI based contact center#contact center tools#AI contact center technology#artificial intelligence in customer service#customer service automation#chatbot integration#virtual agents#intelligent IVR systems#speech analytics#workforce optimization#predictive analytics in contact centers#CRM integration with AI#natural language processing#machine learning in call centers#robotic process automation#omnichannel support#emotion AI#agent assist tools#contact center trends#AI-powered customer experience
0 notes
Text
What can 1998 tell us about ProcureTech solutions in 2025?
#1998 RAM#2025 RAM#agent-based metaprise#agent-based model#AI#Arkestro#Artificial Intelligence#procuretech#self-learning algorithms
0 notes
Text
Explore the Open LLM Leaderboard for Smarter AI Model Selection
There are multiple AI models out there which offer different functionalities. But which one is better for you? Do you know? You can know about the performance of each LLM model and track it based on several metrics using the Open LLM Leaderboard. The Open LLM Leaderboard is an essential resource for anyone interested in large language models (LLMs). It ranks open-source language models based on a variety of benchmarks like MMLU, Hella Swag, and ARC, offering an up-to-date, transparent comparison of model performance. Whether you're a developer, researcher, or enterprise decision-maker, this leaderboard helps you evaluate which models are best suited for your applications. By tracking the latest advances, it supports better AI adoption and innovation across industries. The leaderboard also highlights emerging models, providing insights into their strengths and weaknesses. To stay ahead in the fast-moving AI landscape and make informed decisions, keep checking the latest Open LLM Leaderboard.

0 notes
Text
The Agentic Age
JB: The latest buzzword in articles about AI is “Agentic,” which asserts that AI will act as my agent to help me achieve my goals without my directly requesting or guiding said help. This is similar to human “agents.” We have real estate agents, talent agents, secret agents, etc. Can you give me a listing of six ways human agents can overstep their bounds and create problems for those they are…
#agentic#agentic ai#AI#AI agent#artificial-intelligence#chatgpt#human agent#machine-learning#secret agent#technology
0 notes
Text
Stay ahead with the latest trends in AI agents. Learn how these autonomous tools are reshaping industries, from finance to healthcare.

Discover how AI agents are transforming industries with intelligent automation, boosting efficiency, and enabling smarter decision-making in 2025 and beyond.
#AI agents#autonomous AI agents#intelligent agents#AI automation#AI-powered tools#artificial intelligence agents#AI agents in business#AI customer service agents#AI agents for startups#AI automation for enterprises#AI virtual assistants#workflow automation#generative AI#AI trends 2025#future of AI#machine learning agents#conversational AI#AI task automation#how AI agents work#benefits of AI agents#best AI agents for productivity#using AI agents in business#AI agents for process automation#top AI agents tools
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text

Agentic AI: The Next Evolution of Autonomous Business Systems
As markets evolve and competition intensifies across every industry, organizations are under immense pressure to find smarter, faster, and more adaptable solutions to stay ahead. One of the most promising developments in artificial intelligence is the rise of Agentic AI. Unlike traditional AI systems that operate under rigid instruction sets, Agentic AI exhibits autonomy, adaptability, and decision-making capabilities that mirror human-like behaviour. This transformative leap is poised to redefine how businesses operate, optimize, and scale.

What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to systems designed to act as autonomous agents capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and executing actions in pursuit of specific goals. These AI agents are not merely reactive; they are proactive, strategic, and capable of learning over time. While traditional AI relies on explicit programming to function within predefined parameters, Agentic AI systems exhibit goal-oriented behaviour and can operate independently with minimal human intervention.
Agentic AI is built upon advancements in several core areas of AI research:
Reinforcement Learning: Enables agents to learn optimal behaviours through trial and error.
Cognitive Architectures: Provides frameworks that mimic human decision-making processes.
Multi-Agent Systems: Facilitates collaboration and competition between multiple autonomous agents.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows agents to understand and communicate using human language.
Together, these technologies empower Agentic AI to engage in complex tasks such as strategic planning, resource allocation, customer interaction, and even creative problem-solving.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
Autonomy: Agentic AI systems operate independently, requiring minimal human oversight once objectives are defined.
Goal-Directed Behaviour: These systems pursue high-level objectives rather than executing narrow, task-specific instructions.
Adaptability: They adjust strategies and actions based on real-time data and evolving conditions.
Interactivity: Agentic AI can engage with users and systems through natural language and interfaces.
Self-Improvement: Through continuous learning and feedback, Agentic AI can enhance its performance over time.
Business Systems Powered by Agentic AI
Agentic AI is not just transforming individual workflows; it’s redefining entire business systems from the ground up. These agents are evolving from operational tools into dynamic components of enterprise architecture, capable of orchestrating complex interdependencies across departments.
1. Autonomous Business Operations
Agentic AI can manage end-to-end business processes with little to no human intervention. These agents are integrated into enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, turning them from static data repositories into proactive, decision-making ecosystems. For example, a procurement agent can dynamically renegotiate supplier contracts based on market fluctuations and risk analysis, while another manages compliance updates across jurisdictions.
2. Customer Experience Systems
By embedding agentic models within customer-facing systems, businesses can build AI-powered service layers that anticipate needs, resolve issues, and deliver personalized experiences. Unlike static chatbots or scripted IVRs, Agentic AI can traverse multiple customer touchpoints (email, chat, voice, social) and deliver consistent, context-aware support.
3. Sales and Marketing Platforms
Agentic AI enables continuous experimentation and optimization in marketing systems. These agents autonomously test messaging, allocate budgets across platforms, and modify content strategies based on user engagement and real-time analytics. In CRM systems, they identify upsell opportunities, draft personalized communications, and coordinate multi-channel campaigns, essentially becoming an autonomous marketing operations layer.
4. Finance and Risk Management
In finance departments, Agentic AI is reshaping systems like forecasting, budgeting, and compliance monitoring. Agents can generate real-time cash flow projections, detect anomalies in expense reports, or autonomously trigger fraud investigation protocols. As finance systems become more modular and API-driven, Agentic AI acts as the "glue" coordinating across them, making intelligent decisions without waiting on batch processes or human review.
5. Human Capital Systems
Talent management platforms infused with Agentic AI can manage workforce planning, skill development, and internal mobility. For example, an internal agent could monitor team workloads, project deadlines, and employee engagement metrics, and then recommend internal transfers or hiring actions. These agents don’t just automate HR tasks; they actively shape the workforce strategy.
The Strategic Layer: Agentic AI as Enterprise Orchestrator
Perhaps the most transformative potential lies in Agentic AI’s ability to operate as an orchestration layer across disparate business systems. Imagine a "Chief Operations Agent" that interfaces with finance, sales, HR, and logistics, balancing priorities, identifying cross-functional inefficiencies, and reallocating resources in real time.
Such a system could:
Adjust pricing models based on supply chain costs and customer demand.
Initiate hiring sprees based on projected sales pipeline activity.
Re-prioritize product development sprints based on customer feedback and competitor moves.
These agents don’t just automate; they synchronize and strategize, providing a layer of continuous enterprise optimization.
“Software is eating the world, but AI is going to eat software.” — Jensen Huang (CEO of NVIDIA)
The Benefits of Agentic AI in Business
The integration of Agentic AI into business systems offers a multitude of advantages:
Scalability: Agentic AI can manage increased workloads without proportional increases in cost or human resources.
Efficiency: By automating repetitive and complex tasks, businesses can redirect human talent to higher-value initiatives.
Resilience: These systems can quickly adapt to disruptions, making businesses more agile and robust.
Data Utilization: Agentic AI can analyze and act upon massive datasets far beyond human capabilities, uncovering hidden insights and opportunities.
Continuous Optimization: With the ability to learn and evolve, Agentic AI ensures that processes are constantly improving.
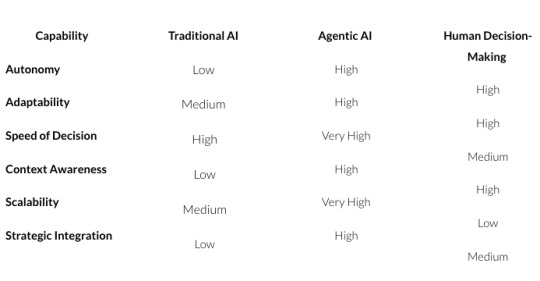
Comparison: Traditional AI vs. Agentic AI vs. Human Decision-Making
Challenges & Considerations
While the potential of Agentic AI is enormous, its adoption also presents challenges that businesses must navigate carefully:
Ethical Concerns: Autonomy raises questions about decision accountability, data use, and fairness.
Security Risks: Autonomous agents must be hardened against manipulation and breaches.
Integration Complexity: Replacing or augmenting legacy systems can be resource-intensive.
Governance and Control: Clear frameworks must define when and how AI agents act independently.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of strong internal governance, AI ethics frameworks, and next-generation IT infrastructure.
The Future of Agentic AI
The trajectory of Agentic AI suggests a future where businesses function as decentralized networks of intelligent agents collaborating in real time. Imagine a digital enterprise where finance, logistics, customer service, and strategy are orchestrated not by departments, but by autonomous agents that seamlessly integrate and adapt to changing circumstances.
We are likely to see the rise of meta-agents, which are AI systems that manage other agents, coordinate cross-domain workflows, and enforce organizational goals. These will serve as the AI equivalent of the executive suite, translating strategy into dynamic execution.
Additionally, the democratization of Agentic AI through low-code/no-code platforms will empower non-technical users to deploy and manage AI agents without technical barriers; further accelerating innovation across all levels of an organization.
We’re standing at the cusp of a new industrial revolution, one not powered by steam or silicon, but by intelligent autonomy. Agentic AI is more than just another technological advancement; it's a reimagining of how work gets done. As these systems become more capable, their role in business will shift from tool to collaborator and from support system to strategic partner.
Embracing Agentic AI requires more than investment. It demands systems thinking, executive sponsorship, and a willingness to challenge the status quo.
Learn more about DataPeak:
#factr#datapeak#saas#technology#agentic ai#artificial intelligence#machine learning#ai#ai-driven business solutions#machine learning for workflow#ai solutions for data driven decision making#ai business tools#ai agents#digital technology#digital trends#digitaltools#datadrivendecisions#data driven decision making#dataanalytics#ai platform for business process automation#ai for business efficiency#ai business solutions#ai driven business solutions#business#ai technology#techinnovation
0 notes
Text
Más allá del chatbot: construyendo agentes reales con IA
Vengo escuchando desde hace un tiempo que un modelo de lenguaje al que, usando ChatGPT o Copilot, le subes archivos y le haces preguntas sobre estos artículos, es un “agente”. A simple vista, parece solo una herramienta que responde preguntas usando texto. Eso no tiene pinta de ser un agente. Pero, ¿lo es?
Tras ver este video sobre los diferentes tipos de agentes de IA que existen, creo que ya sé por qué estamos llamando "agentes" a ese uso concreto de los modelos.
Los 5 tipos de agentes de IA
Según la teoría clásica (ver “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach”, 4th edition, de Stuart Russell y Peter Norvig, sección 2.4, "The Structure of Agents"), los agentes se clasifican así:
Reflexivo simple: responde con reglas fijas.
Basado en modelos: tiene una representación del entorno y memoria.
Basado en objetivos: toma decisiones según metas.
Basado en utilidad: evalúa opciones según preferencia/valor.
De aprendizaje: mejora con la experiencia.
¿Dónde encaja el caso que estamos analizando, ese modelo al que le subimos unos documentos y le hacemos preguntas sobre ellos? Eso que OpenAI llama GPTs y que Microsoft llama "agentes" en el Copilot Studio, ¿con cuál de los anteriores tipos de agentes se corresponde?
Si lo usamos solo para responder una pregunta directa → se parece al reflexivo simple.
Si analiza archivos cargados y extrae conclusiones dispersas → actúa como basado en modelos.
Si le damos tareas claras (resumir, estructurar, comparar) → parece el basado en objetivos.
Si optimiza claridad o formato según instrucciones → podría ser el basado en utilidad.
Si el sistema aprende de nosotros y mejora con el tiempo → sería un agente de aprendizaje.
Por lo tanto, GPT (o el mismo caso hecho en Copilot) por sí mismo no es un agente completo, pero integrado con sistemas (nosotros mismos, por ejemplo) que le dan contexto, metas, memoria y feedback, claramente se convierte en uno.
Entonces, ¿cómo sería un agente “de verdad”? Un agente de verdad es uno que actúa como un sistema autónomo inteligente, no solo uno que responde preguntas.
Para aclarar qué es un agente en términos más prácticos, vamos a intentar comprender la arquitectura MCP (Model Context Processing), propuesta por Anthropic para construir agentes y que está siendo adoptada por la industria.
MCP: Conectando agentes de IA con el mundo real
MCP (Model Context Protocol) es una infraestructura para que modelos de lenguaje puedan interactuar de forma segura y estructurada con herramientas externas, APIs, bases de datos y otros sistemas disponibles dentro de la organización.
Aunque no es una arquitectura cognitiva completa, puede servir como la “capa de integración” que permite a un agente cognitivo acceder a información en tiempo real, ejecutar acciones y trabajar sobre entornos reales. MCP es la “puerta al mundo real” para agentes que necesitan trabajar con datos y sistemas externos.
Ejemplo práctico: Un agente que resuelve problemas en una organización
Imaginemos un asistente corporativo inteligente que:
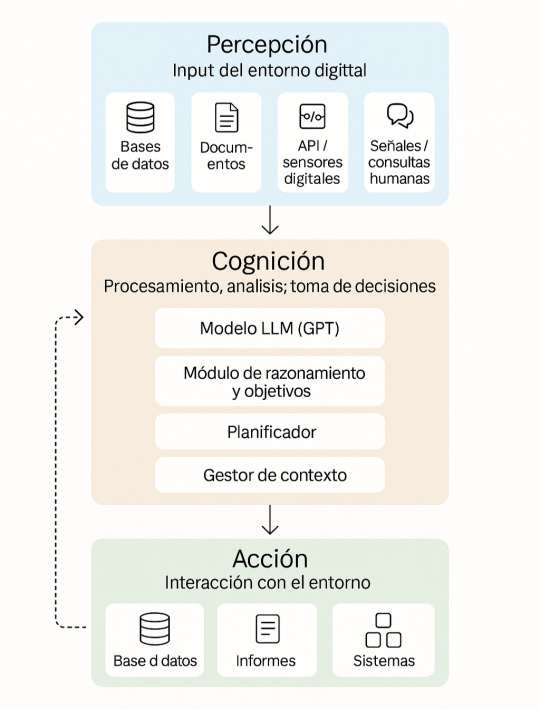
a) hemos diseñado con una arquitectura cognitiva basada en módulos (percepción, cognición, acción) y que, además,
b) se conecta al ecosistema de la empresa mediante el protocolo MCP (Model Context Protocol) de Anthropic.
Veamos qué funciones contendría cada uno de los tres módulos cognitivos que compondrían dicho asistente y cómo interactuaría con el mundo a su alrededor mediante MCP:
1. Percepción
Lee bases de datos, informes, logs, emails, APIs internas.
Recibe consultas humanas o detecta anomalías automáticamente.
2. Cognición
Usa uno o varios GPTs para interpretar texto, combinar datos y razonar.
Planea pasos: “analizar gastos”, “comparar con presupuestos”, “detectar desviaciones”.
Mantiene memoria de su contexto de trabajo, objetivos y estados intermedios.
3. Acción
Consulta sistemas, genera informes, dispara flujos de trabajo.
Toma decisiones o propone acciones con justificación.
Aprende de feedback: mejora sus planes con el tiempo.
Veamos ahora a ese agente en funcionamiento en un caso concreto:
Percibe: detecta aumento de costes en logística.
Razona: analiza contratos, identifica rutas ineficientes, predice impacto.
Actúa: propone cambios, notifica a compras, inicia seguimiento.
¿Por qué queremos construir este tipo de agentes?
Porque van más allá de un chatbot con el que conversamos, como ChatGPT.
Porque automatizan la resolución de problemas reales.
Porque combinan todos los datos de la organización, eliminándose así los silos de información aislados.
Porque actúan con propósito, objetivo. No se limitan a responder preguntas.
La IA no es solo generar texto en respuesta a una pregunta. Es una IA estructurada, autónoma y conectada. Y arquitecturas cognitivas combinadas con protocolos como MCP hacen posible que los agentes realmente trabajen con nosotros —y por nosotros— en contextos organizativos complejos. Es comportamiento estructurado, toma de decisiones, acción. Eso es un agente.

#inteligencia artificial#IA#GPT#agentes inteligentes#machine learning#MCP#Anthropic#arquitectura cognitiva#tecnología empresarial#automatización#datos empresariales#sistemas inteligentes#procesamiento multimodal#LLM#AI agents
0 notes
Text
Top AI Features Powering Next-Gen Contact Centers

Introduction
The evolution of contact centers from traditional call hubs to intelligent customer engagement platforms is being driven by artificial intelligence (AI). In a hyper-connected world where customers expect fast, personalized, and efficient service, AI is playing a transformative role. From automating routine tasks to offering real-time analytics and sentiment analysis, AI is redefining the standards of customer support. Modern contact centers, powered by AI, are becoming more responsive, proactive, and insightful—enhancing both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
This article explores the top AI features that are revolutionizing next-generation contact centers and how they are helping businesses stay competitive in today’s digital landscape.
1. AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Perhaps the most visible AI application in contact centers is the use of chatbots and virtual assistants. These tools are capable of handling thousands of customer queries simultaneously across various platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and social media.
Key Benefits:
24/7 availability
Immediate responses to FAQs
Reduced workload for human agents
Seamless integration with CRM systems
Advanced AI chatbots use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) to understand customer queries better and improve over time. They also support multilingual interactions, expanding a business’s global reach.
2. Intelligent Call Routing
Traditional call routing systems use basic algorithms like round-robin or skill-based routing. AI takes this to the next level with predictive routing, which uses historical data and real-time analytics to match customers with the most suitable agents.
Example: If a customer previously had a billing issue and rated a certain agent highly, AI can route future related calls directly to that agent, ensuring a personalized experience.
Benefits:
Enhanced customer satisfaction
Reduced average handling time
Better utilization of agent expertise
3. Speech and Sentiment Analysis
AI-driven sentiment analysis tools assess the tone, pitch, and language of customer conversations in real-time. This allows agents to adapt their approach based on the emotional state of the caller.
Key Capabilities:
Detect frustration or satisfaction
Real-time alerts for supervisors
Contextual response suggestions for agents
This not only helps in de-escalating potential conflicts but also contributes to training and performance reviews.
4. Real-Time Agent Assistance
AI can provide live suggestions, answers, and prompts to agents during customer interactions. Known as Agent Assist or Co-Pilot systems, these features boost agent efficiency and reduce error rates.
Use Cases:
Auto-suggesting answers based on past tickets or knowledge base
Providing legal or compliance language for regulated industries
Offering upsell/cross-sell suggestions during the call
This enables even less-experienced agents to perform like experts, thereby maintaining service consistency.
5. Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Modern AI systems can analyze historical customer data to predict future behaviors and offer prescriptive actions. For example, AI can forecast customer churn and suggest personalized retention strategies.
Key Features:
Trend identification
Churn prediction
Customer lifetime value estimation
Product recommendation modeling
These analytics turn contact centers from reactive to proactive units that can anticipate customer needs and take preventive measures.
6. Automated Quality Monitoring
Quality assurance (QA) in traditional contact centers involves manual listening to a random sample of calls. AI changes this by automatically analyzing 100% of customer interactions for compliance, tone, and performance metrics.
Advantages:
Scalable and unbiased QA process
Immediate feedback loops
Identification of training opportunities
This ensures consistent service quality and helps businesses remain compliant with industry standards and regulations.
7. AI-Driven Self-Service
Customers increasingly prefer solving issues on their own. AI enables robust self-service solutions through intelligent FAQs, voice assistants, and dynamic help centers.
Core Components:
AI-curated knowledge bases
Interactive voice response (IVR) systems
Visual IVRs with dynamic menus based on customer behavior
These systems can deflect a significant volume of queries, saving time and reducing contact center costs.
8. Workforce Optimization (WFO)
AI enhances workforce optimization by analyzing call volumes, customer demand patterns, and agent performance to create optimized schedules and workloads.
Capabilities Include:
Forecasting peak interaction times
Automating shift scheduling
Identifying training needs through performance data
This ensures that the right number of agents with the right skills are available at the right time.
9. Multilingual Support
With global customer bases, multilingual support is essential. AI translation engines powered by NLP enable real-time language translation, allowing agents to assist customers in multiple languages.
Benefits:
Expanded market reach
Consistent support quality
Reduced need for native-speaking agents
Advanced systems even recognize regional dialects and slang, further enhancing communication accuracy.
10. Omnichannel AI Integration
Today’s customers expect consistent service across phone, email, chat, social media, and more. AI enables omnichannel support by centralizing data and ensuring continuity in customer interactions.
Features Include:
Unified customer profiles
Context-aware responses
Seamless channel transitions (e.g., chat to call)
This creates a cohesive customer experience and provides agents with the full context of past interactions, reducing redundancy and frustration.
Conclusion
AI is not just an enhancement to traditional contact center operations—it is a fundamental driver of their transformation. From handling repetitive tasks to offering deep insights into customer behavior, AI is redefining what’s possible in customer service.
By leveraging AI-powered features like chatbots, intelligent routing, sentiment analysis, and predictive analytics, next-generation contact centers are achieving higher efficiency, better customer satisfaction, and lower operational costs. The focus is shifting from handling calls to delivering experiences, and AI is at the heart of that shift.
Businesses that invest in AI capabilities today will be better positioned to adapt to the growing demands of tomorrow’s customers. As AI continues to evolve, contact centers will become smarter, faster, and more human than ever before—setting a new standard for customer engagement in the digital era.
#AI contact centers#AI in customer service#AI-powered chatbots#virtual assistants for support#intelligent call routing#real-time agent assistance#AI sentiment analysis#predictive analytics in contact centers#AI customer experience#automated quality monitoring#AI in workforce optimization#self-service solutions AI#omnichannel customer support AI#speech analytics in call centers#AI call center solutions#AI customer engagement tools#AI-driven customer insights#machine learning in contact centers#AI customer service automation
0 notes
Text
Idea Frontier #4: Enterprise Agentics, DaaS, Self-Improving LLMs
TL;DR — Edition #4 zeroes-in on three tectonic shifts for AI founders: Enterprise Agentics – agent frameworks such as Google’s new ADK, CrewAI and AutoGen are finally hardened for production, and AWS just shipped a reference pattern for an enterprise-grade text-to-SQL agent; add DB-Explore + Dynamic-Tool-Selection and you get a realistic playbook for querying 100-table warehouses with…
#ai#AI Agents#CaseMark#chatGPT#DaaS#DeepSeek#Enterprise AI#Everstream#generative AI#Idea Frontier#llm#LoRA#post-training LLMs#Predibase#Reinforcement learning#RLHF#text-to-SQL
0 notes
Text
Smarter Business Decisions with Enterprise AI
Enterprise AI is transforming how businesses analyze data, automate processes, and scale innovation. From customer service to operational efficiency, AI-driven solutions are helping companies stay competitive. Discover tools and platforms that bring intelligent automation to the enterprise level.
For more information, Visit:
0 notes
Text
Why is achieving clean data impossible without a sound learning loopback process for self-learning algorithms?
#Agentic AI#Agentic AI Agents#clean data#loop back learning process#procurement#procuretech#self learning algorithms
0 notes