#medical and clinical writing services
Text
The Pathophysiology Of Spondylitis
Spondylitis is a comprehensive term used to describe a group of chronic inflammatory diseases that primarily affect the joints of the spine and the sacroiliac region, which includes the pelvis and lower spine. These conditions are characterized by arthritis-like symptoms and can lead to significant discomfort, reduced mobility, and other systemic complications. This detailed exploration will indulge into the nature of spondylitis, how it differs from the related condition known as spondylosis, the various types of spondylitis, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and complementary therapies.
What is Spondylitis?
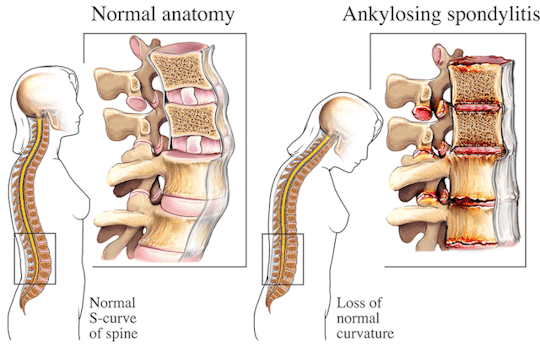
Spondylitis involves inflammation of the joints, tendons, and ligaments within the spine and sacroiliac region. Tendons are connective tissues that attach muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones. This inflammation can result in the fusion of bones (ankylosis) and the formation of new bone, leading to stiffness and reduced flexibility in the spine. In severe cases, excessive bone growth can cause significant curvature of the spine, known as kyphosis.
Spondylitis vs. Spondylosis
While both spondylitis and spondylosis cause pain in the hip and back, they are distinct conditions with different etiologies and characteristics.
Spondylitis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation, bone fusion, and excessive bone formation. This condition typically develops in teenagers and young adults and can affect multiple organs and systems within the body.
Spondylosis, on the other hand, is a degenerative condition associated with aging and the natural wear and tear of the spine. It involves the degeneration of spinal joints and discs, often accompanied by the formation of bone spurs (osteophytes). Spondylosis primarily affects older individuals, with more than 85% of people over the age of 60 experiencing this condition.
Types of Spondylitis
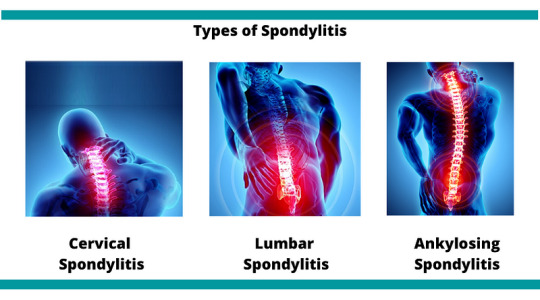
Medical professionals categorize spondylitis using two primary classification systems: the traditional system and the newer system. The traditional system recognizes six specific types of spondylitis, whereas the newer system categorizes spondylitis into two broad types based on the affected body region.
Traditional Spondylitis Classifications:
a) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Symptoms: Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, causing symptoms such as fatigue, chronic back pain, stiffness, and inflammation in various areas of the body, including joints and tendons. Over time, the vertebrae may fuse, leading to reduced mobility and flexibility.
Causes: The exact cause of AS is unknown, but a strong genetic association exists with the HLA-B27 gene. Approximately 90% of individuals with AS carry this gene, although not all carriers develop the disease.
b) Reactive Arthritis
Symptoms: Reactive arthritis typically presents with a triad of symptoms including arthritis (swelling and pain in joints), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyes with a sticky discharge), and urethritis (genital and bladder inflammation with painful urination). However, not all patients exhibit all three symptoms.
Causes: often follows a gastrointestinal infection or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The immune system overreacts to the initial infection, leading to inflammation and joint pain. The HLA-B27 gene is also strongly linked to ReA, with 30–50% of affected individuals carrying this gene.
c) Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Symptoms: Psoriatic arthritis is associated with the inflammatory skin condition psoriasis. Symptoms include dactylitis (swelling in toes and fingers), changes in nails (such as pitting), eye pain, joint pain, reduced range of motion, and fatigue. PsA typically affects people aged 30–50.
Causes: PsA often follows psoriasis, but it can also develop in individuals without skin symptoms. There is a genetic predisposition to PsA, with at least 10% of the population inheriting genes that increase susceptibility to psoriasis and PsA.
d) Enteropathic Arthritis (EnA)
Symptoms
Enteropathic arthritis is linked to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and joint swelling and pain.
Causes
The precise cause of EnA is unclear, but it is associated with chronic inflammation in the bowel. This inflammation may allow bacteria to penetrate the bowel wall, triggering an immune response that leads to joint inflammation. The HLA-B27 gene is also linked to EnA.
d) Juvenile Spondyloarthritis (JSpA)
Symptoms
Juvenile spondyloarthritis begins in individuals aged 16 or younger and typically affects the leg joints. Symptoms include joint pain, tenderness, and bowel inflammation.
Causes
Similar to adult spondylitis, JSpA is often associated with the HLA-B27 gene. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetic and environmental factors likely play a role.
e)Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis (USpA)
Symptoms
USpA is characterized by a variety of symptoms that do not fit neatly into a specific rheumatoid disorder. Symptoms may include persistent lower back pain, joint pain in small and large joints, heel pain, swelling in hands and feet, general stiffness, eye inflammation, rash, urinary tract symptoms, and intestinal inflammation.
Causes
The causes of USpA are diverse and not fully understood. It encompasses a range of symptoms that do not meet the criteria for other specific types of spondylitis.
Newer Spondylitis Categorizations
Peripheral Spondyloarthritis (pSpA)
Peripheral spondyloarthritis affects joints and tendons outside the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, and feet. It includes forms of spondylitis such as reactive arthritis, enteropathic arthritis, and undifferentiated arthritis.
2. Axial Spondyloarthritis (AxSpA)
Axial spondyloarthritis involves inflammation and pain in the pelvis and spine. This category covers a broad range of spondylitis types and includes individuals with and without sacroiliac joint fusion. AxSpA is further subdivided into non-radiographic AxSpA (without visible joint damage on X-rays) and radiographic AxSpA (visible joint damage).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing spondylitis involves abroad approach, combining physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests. There is no single definitive test for spondylitis, making a comprehensive evaluation essential.
a) Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history of autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and spondyloarthritis. The examination may include evaluating joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
b) Diagnostic Tests
Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation, such as elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Testing for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene can also provide valuable information, although not all individuals with spondylitis carry this gene.
Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques are crucial for diagnosing spondylitis and assessing the extent of joint and bone damage.
X-rays: X-rays can reveal changes in the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as joint fusion and bone spurs.
MRI Scans: MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues and can detect early signs of inflammation and joint damage that may not be visible on X-rays.
Ultrasound Scans: Ultrasound scans can be used to assess inflammation in peripheral joints and tendons.
Genetic Testing: Testing for the HLA-B27 gene can support the diagnosis, particularly in cases where clinical symptoms and imaging findings are inconclusive.
Treatment
While there is no cure for spondylitis, various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and disease severity.
Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are commonly used to reduce inflammation and pain in spondylitis patients. Examples include ibuprofen and naproxen.
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can be prescribed for short-term use to control severe inflammation and pain.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression in some types of spondylitis.
Biologic Agents: Biologic agents, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, etanercept) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors (e.g., secukinumab), target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
Analgesics: Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, may be used to manage pain when inflammation is not the primary issue.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing spondylitis by improving and maintaining spine flexibility and overall mobility. Techniques may include:
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain.
Spinal Manipulation: Performed by a trained physical therapist or chiropractor, spinal manipulation can enhance mobility and reduce pain.
Exercises: Tailored exercise programs can help strengthen muscles, improve posture, and enhance flexibility. Stretching exercises are particularly beneficial for maintaining spine and joint flexibility.
Breathing Exercises: Breathing exercises are essential for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis, as the condition can affect chest expansion and respiratory function. These exercises help maintain normal lung function and prevent restrictive lung disease.
Surgery: Surgery is generally considered a last resort and is reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed. Surgical options include:
Joint Replacement: For patients with severe joint damage, joint replacement surgery (e.g., hip or knee replacement) can restore function and relieve pain.
Spinal Surgery: In cases of severe spinal deformity or nerve compression, spinal surgery may be necessary to correct curvature and alleviate pressure on nerves.
Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, complementary therapies can provide additional symptom relief and improve overall well-being. These therapies are often used alongside standard medical treatments.
Massage Therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain and stiffness in the affected areas.
Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help manage stress and reduce pain perception.
Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to improve flexibility, strength, and relaxation. Yoga can be particularly beneficial for maintaining spine flexibility and reducing pain.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and promote natural pain relief and healing.
Cupping: Cupping is a traditional therapy that involves placing suction cups on the skin to improve blood flow and reduce muscle tension. It can be used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the back and other affected areas.
Summary
Spondylitis encompasses a range of chronic inflammatory diseases that affect the spine and sacroiliac region. It is characterized by autoimmune-driven inflammation, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and potential bone fusion. Spondylitis is distinct from spondylosis, a degenerative condition associated with aging. Medical professionals classify spondylitis into various types based on symptoms and affected body regions. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, blood tests, imaging, and genetic testing. While there is no cure, treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected by spondylitis. By understanding the nature of spondylitis and the available management strategies, individuals can better navigate their condition and maintain an active, fulfilling life.
Medical students and healthcare professionals need to stay informed about the latest advancements in diagnosing and treating spondylitis. Continuous education and expert guidance are crucial for managing these complex conditions. For additional support with challenging medical units, clinical studies, research projects, assignments, and exam preparation, Expert Academic Assignment Help offers professional resources and online classes. For personalized assistance, contact [email protected] Accessing expert guidance can significantly enhance your understanding and proficiency in medical education.
#medical students#assignment help#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#healthcare#student life#medical student#studyblr#case study#student#online writing#do my online class#essay writing#phd research#clinical research#research#phd thesis writing service#phdjourney#phd life#phdblr#studying#study blog#study motivation#studyspo#study aesthetic
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Medical writing encompasses various documents, including regulatory submissions, educational materials for physicians, and public health articles. Writers must be adept in research, authoring, editing, and understanding audience-specific needs.
WorkSure® #MedicalWriting Services stands out by offering comprehensive regulatory writing support, helping clients navigate complex regulations and communicate their brand messages effectively.
Read more at: https://www.worksure.org/medical-writing-principles-scope-and-opportunities/
regulatorydocuments #researchwriting #clinicaldocuments #clinicalstudyreports
#medical writing services#medical devices#healthcare it services#clinical trials#clinical research#clinical data management services#clinical data management
0 notes
Text
Dental School Writing Services With Code Blue Essays

Embarking on a journey to dental school is both exciting and challenging. Aspiring dentists not only need to excel academically but also must craft a compelling application that sets them apart from the competition. In order to help students succeed, Code Blue Essays provides specialist dental school writing services.
Tailored Personal Statements: Dental school admissions committees seek candidates who not only have strong academic backgrounds but also possess unique qualities and motivations. The personalized personal statement editing services offered by Code Blue Essays make sure that your essay accurately conveys your enthusiasm, commitment, and qualifications.
Comprehensive Reviews: Crafting an impactful personal statement requires more than just grammar checks. Code Blue Essays' professional editors thoroughly review and provide feedback to strengthen your essay's content and structure.
Guidance and Support: Applying to dental school can be overwhelming, but with Code Blue Essays, you're not alone. Throughout the writing and editing processes, their knowledgeable editors provide direction and support, boosting your confidence in your application.
Actionable Feedback: Code Blue Essays doesn't just edit your essay; they provide actionable feedback in a supportive environment. You will gain useful information to improve your writing and overall application.
A Proven Track Record: Many successful applicants have trusted Code Blue Essays to help them secure spots in dental school. Numerous students have been able to enroll in their top-choice programs because to their services.
Reduced Stress: Crafting a strong application can be stressful, but Code Blue Essays eases the burden. They will ensure that your application is flawless while you concentrate on your education and interview preparation.
In the competitive landscape of dental school admissions, a well-crafted personal statement can make all the difference. You can get the resources you need to exhibit your best self to admissions committees from Code Blue Essays, a company that specializes in this field. Their services are intended to increase your chances of admission, regardless of whether you are experiencing writer's block or want to polish your essay.
0 notes
Text
#Clinical Evaluation Report#EU MDR#Medical Devices#Regulatory Affairs#EU MDR 2017/745#Regulatory Services#CER#Medical Writing
0 notes
Text
ACL Digital Life Sciences has a track record of partnering successfully with some leading Pharmaceuticals, Biotechs, CROs, Medical Devices and MSP companies.

We offer multiple sourcing models to suit your business needs. We work with an MSP of your choice, insourcing staff augmentation, insourcing and outsourcing FSP models and Project-based deliverables.
0 notes
Text
Medical Editing Help from Professional Medical Writer | Medical Writing Input
Medical research & medical writing are 2 time-sensitive tasks. Everything from implications, information, and results should reach the readers so that they can improve practices, and contribute to future discoveries without any delay. Hence, any mistake in the research paper is unacceptable, and one of the best ways to ensure that it is error free is to adopt medical editing services from a professional medical writer.
#Medical writing help#medical input#medical#medical writing input#medical editing services#medical writing service#scientific medical writer#clinical medical writer#thesis writing help
0 notes
Text
Here's what's going on in Ohio right now. Heavy stuff ahead.
First, I want to apologize for the misinformation in my original post. I am still learning about legislative processes. To correct: the changes to ODH and OMHAS in regards to gender therapy are not a bill, they are changes in regulations.
This is important because citizens CAN affect rule changes. There is an open commentary period where your submissions get counted and can affect how they write new regulations.
Disclaimer: I am not a lawyer, legal advocate, or medical professional. I'm just a dude who had to have it all explained to me.
The first one is Ohio Mental Health and Addiction Services. The rules proposed would make the already prohibitive process of gender transition even harder. In order to diagnose and treat gender dysphoria, a hospital needs to have a board certified psychologist per patient, a board certified endocrinologist familiar with the age group being diagnosed per patient, and a medical ethicist overseeing the hospital's plan for transition. 'Board certified' does not guarantee that the specialist is trans-friendly. It must include a detransition plan. Hospitals would have to report compliance annually. The professionals must have a contractual relationship with the patient, but do not need to offer in-person care. (In this instance, I'll get to that in the next rule change.)
This rule also deems it impermissible to prescribe gender transition care (this includes hormones, puberty blockers, or drugs) for anyone under the age of 21 without the approval of the professionals mentioned and 6 months of therapy.
There is an exception for intersex people, who may have their sex assigned to them without their consent.
The open comment period for this ends January 19 at 5pm.
Send an email to [email protected] with the subject title: "Comments on Gender Transition Care Rules."
The second one is Ohio Department of Health and it repeats a lot of the same as the first one. However, the focus is more on the regulation of doctors and paperwork. Anyone seeking transition will be put into a registry with their name redacted, but demographics like age, agab, specific diagnosis (difficult to achieve with the new regulations mentioned above), and any medications (not just related to gender transition, but any medications at all). Any cessation of care must be reported within 30 days.
This is a lot of paperwork and can overburden hospitals.
That 30 days cessation is important because if a person transfers doctors or if a clinic closes and the paperwork isn't filed, it may count as a 'detransition' when tallying demographics, even if that is not the case.
But what's curious is that the ODH regulations DO require in-person care. The rules are contradictory and vague.
The comment period for this ends Feb 5th.
Send a comment through the ODH website
Here are some important things that were mentioned at the meeting:
This is a good time to be personal with your statements. If this would disrupt your life in any way, please say so. "I fear that" "I believe this" "I worry that"- these are great ways to start your comment. An example one person gave is "I worry that this change in regulations would force me and my daughter to move out of state.'
With that being said, anything that you send to these sites will be public record, so be cautious about what you reveal about yourself in your comment.
If you are in need of help, please reach out to one of these resources:
Trans Ohio Emergency Fund Resource Page
Kaleidoscope Youth Center
If you are in need of legal advice on how to navigate all this, please call
888-LGBT-LAW
This is not everything. There is unfortunately more because Ohio decided to break a record this month with anti-trans motions. But today I'm focusing on things that we can take action on.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Research Services for Local and Global Clinical Trials - Contract Research Organisation (CRO)
CliniExperts Research Services is your one stop expert solution to conducting clinical trials in India, stress-free.
Clinical trials have several phases and must follow strict protocols all throughout, until the very end. Clear objective of the clinical trial, design, methodology, statistical considerations to the organization of the project, etc must be well-designed and equally well-executed. Errors at any step can lead to complications in the application process.
To enable a glitch-free clinical trial, we provide the following services:
Clinical Trial Management
Clinical trials are complex undertakings and effective trial management is crucial. Our experienced project and site managers along with experts in vendor and data management ensure that each phase of the trial is executed meticulously and timely.
Clinical Project Management
Our excellent team promises to deliver the project as per pre-decided timelines with all the components of the project well-aligned. We ensure this by building a strongly structured trial and executing all it just as efficiently.
Clinical Investigation
Clinical investigation refers to studies performed on live subjects. These could be studies concerning diagnosis or treatment of certain diseases or clinical drug development and methodology. We ensure that the investigative trials are carried out smoothly right from patient selection, to sample collection, testing and analysis.
Clinical Performance Evaluation
Performance evaluation of a clinical trial is all about the authenticity and accuracy of the results and the scientific validity of the results. Trial safety must be ensured at each step. Foreseeing, preventing and navigating through possible pitfalls is what ensures a well-executed Clinical performance evaluation.
#Clinical Research Services#clinical trial services#global clinical trials#local clinical trials#clinical trial solutions#Clinical Trial Management Services#Clinical Trial Registry India#Ethics Committee Registration#Contract Research Organisation#CRO#Medical Writing#Medical Monitoring
0 notes
Text
My dearest butterfly,
I usually pride myself on having a way with words, never having my tongue tied, never having to stutter or stumble, and yet, with you, I find it hard to even breathe let alone speak. Ever since the day you stepped into my clinic, stepped into my life, I’ve found myself in a fog, never able to say what I feel, to speak with confidence, like without you I'm some sort of shell of myself.
As a doctor, I assumed I was ill, sick, perhaps coming down with something that would pass with rest and time. However, I found out the truth- I was sick of course, but nothing that would be cured with needles and antibiotics.
My dear butterfly, I have come to find out, my ailment is love sickness. As cutesy as that sounds, what I mean to say is- I'm utterly obsessed with you, and cannot rest or feel alive until I see you in my sight, or feel you by my side.
The fact I am blessed enough to touch you, to examine every area, intimate or not, to be trusted with your darkest medical secrets-It fuels me more than any other patient has. With you, curing you and your health just has more meaning to me, has more depth and humanity. You have that way about you, making me feel deeper than any human ever has, reaching my core and burrowing deep within the walls of my heart.
This letter is nothing but a love filled ramble, but one I simply had to write. I can no longer hide how I feel, how I crave. I don't expect you to know what to do with all of this information right away, so, I’ll give you a few good rules to go by while everything sets in and has time to process.
This is all true. I adore you, deeper than anyone could ever adore you, and more intense than any past lover could ever dream
I refuse to let you try and deny me. You can be coy, you can be shy, you can even need time and space, but you wont be with anyone else but me in the romantic sense. I’ll take whatever precautions I need to ensure this rule is followed.
I mean you absolutely no harm, however, as mentioned above, I’ll do what I must. Just sit back and take in what you need, but know, I’m utterly sick for you darling, there’s no way you can turn me away, be your attempts silly or desperate.
I’ll be sure to send this letter over the weekend to give you more time, but, if by chance the postal service messes up, a few days letting your mind wander at your work wouldn’t be awful either.
I’ll see you soon, my love. We’ll discuss this more in person, where my words are sharper than the pen I used, and my voice will convey just how serious I am about all of this.
All yours, only yours,
-Doctor Lee.
(-Mommabean, hope you liked!)
#yandere imagines#yandere scenarios#my ocs#doctor lee my oc#dr lee my oc#yandere doctor#yandere serial killer#yandere oc#yandere letter#yandere male#yandere prompts#mommabean
473 notes
·
View notes
Text
"How will people get healthcare?
(...)
During the Spanish Civil War, Barcelona’s Medical Syndicate, organized largely by anarchists, managed 18 hospitals (6 of which it had created), 17 sanatoria, 22 clinics, 6 psychiatric establishments, 3 nurseries, and one maternity hospital. Outpatient departments were set up in all the principal localities in Catalunya. Upon receiving a request, the Syndicate sent doctors to places in need. The doctor would have to give good reason for refusing the post, “for it was considered that medicine was at the service of the community, and not the other way round.”[40] Funds for outpatient clinics came from contributions from local municipalities. The anarchist Health Workers’ Union included 8,000 health workers, 1,020 of them doctors, and also 3,206 nurses, 133 dentists, 330 midwives, and 153 herbalists. The Union operated 36 health centers distributed throughout Catalunya to provide healthcare to everyone in the entire region. There was a central syndicate in each of nine zones, and in Barcelona a Control Committee composed of one delegate from each section met once a week to deal with common problems and implement a common plan. Every department was autonomous in its own sphere, but not isolated, as they supported one another. Beyond Catalunya, healthcare was provided for free in agrarian collectives throughout Aragon and the Levant.
Even in the nascent anarchist movement in the US today, anarchists are taking steps to learn about and provide healthcare. In some communities anarchists are learning alternative medicine and providing it for their communities. And at major protests, given the likelihood of police violence, anarchists organize networks of volunteer medics who set up first aid stations and organize roving medics to provide first aid for thousands of demonstrators. These medics, often self-trained, treat injuries from pepper spray, tear gas, clubs, tasers, rubber bullets, police horses, and more, as well as shock and trauma. The Boston Area Liberation Medic Squad (BALM Squad) is an example of a medic group that organizes on a permanent basis. Formed in 2001, they travel to major protests in other cities as well, and hold trainings for emergency first aid. They run a website, share information, and link to other initiatives, such as the Common Ground clinic described below. They are non-hierarchical and use consensus decision-making, as does the Bay Area Radical Health Collective, a similar group on the West Coast.
Between protests, a number of radical feminist groups throughout the US and Canada have formed Women’s Health Collectives, to address the needs of women. Some of these collectives teach female anatomy in empowering, positive ways, showing women how to give themselves gynecological exams, how to experience menstruation comfortably, and how to practice safe methods of birth control. The patriarchal Western medical establishment is generally ignorant of women’s health to the point of being degrading and harmful. An anti-establishment, do-it-yourself approach allows marginalized people to subvert a neglectful system by organizing to meet their own needs.
After Hurricane Katrina devastated New Orleans, activist street medics joined a former Black Panther in setting up the Common Ground clinic in one of the neediest neighborhoods. They were soon assisted by hundreds of anarchists and other volunteers from across the country, mostly without experience. Funded by donations and run by volunteers, the Common Ground clinic provided treatment to tens of thousands of people.
The failure of the government’s “Emergency Management” experts during the crisis is widely recognized. But Common Ground was so well organized it also out-performed the Red Cross, despite the latter having a great deal more experience and resources.[41] In the process, they popularized the concept of mutual aid and made plain the failure of the government. At the time of this writing Common Ground has 40 full-time organizers and is pursuing health in a much broader sense, also making community gardens and fighting for housing rights so that those evicted by the storm will not be prevented from coming home by the gentrification plans of the government. They have helped gut and rebuild many houses in the poorest neighborhoods, which authorities wanted to bulldoze in order to win more living space for rich white people."
-Peter Gelderloos, "Anarchy Works" (2010)
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
GENSHIN MEN & TAKING CARE OF YOU WHEN YOU'RE SICK .
characters. xiao zhongli diluc kaeya childe alhaitham neuvillette x gn!reader
genre. romantic fluff.
an. look at the cuties taking care of u :3 | please reblog!! im getting back into writing and reblogs with tags and comments will make me want to write more :D
xiao
when you're sick, he immediately forces you to get back into bed, not moving a muscle. xiao does everything, from making you food to going out to run errands and even enduring that horrible small talk he had to go through because he hasn't interacted with the stall owner in a while. he squeezes your hands to make sure that you know that he's there! xiao won't let anything happen to you. make sure that you're all wrapped up and cuddly when he gets home, because he's sure to shower you with physical affection – even if that's something that he doesn't do very often.
zhongli
zhongli makes sure to brew his finest tea for you, as well as booking that speedy consultation with the local pharmacist. trust that with all his years of wisdom and knowledge, zhongli makes sure to pick the best traditional medicine for you: a basket of ground violetgrass and qingxins mixed with honey sometimes does the trick. he watches your poor frame tremble, and wishes that he were gifted the powers of health instead.
diluc
upon hearing that you're sick, diluc immediately calls for adelinde to make something for you – a sweet broth, that has cured all things health-related since his childhood. it's a one-pot wonder, and adelinde has to politely kick him out of the kitchen before he says too much and ruins her cooking. diluc doesn't care about getting germs, and still makes sure that you're close to him. he holds you close, and maybe that wishful thinking of you passing your germs to him will make everything better.
kaeya
trust that when you first cough, he immediately goes to albedo to ask for a cure and a medication – albedo has to remind him that he's an alchemist, not a pharmacist – and kaeya sighs and turns to his stash of medication instead. he definitely makes sure to give you extra attention during this period (extra attention? what's that, when you've always been spoilt by your boyfriend?) and gets you all the different comfort foods and all the things you want and need – kaeya is the boyfriend to be at your side, day and night, when you're sick.
childe
makes his mom's chicken noodle soup for you! it's packed with veggies you love and a hearty broth that is just perfect for your sinuses. childe definitely still wants to cuddle you, even though you're a mess ... as much as you try to push him away, he always comes back with more – you've given up trying to keep distance at this point. it's really only a matter of time now before he gets sick because of you. you make sure to do the same for him when he's sick, though ... so that's a good two and a half weeks spent together.
alhaitham
he makes you rest your head on his lap, while he reads to you –claiming that you need as much rest as you can. you're not going to complain, though ... it's comfortable, it's homely, and alhaitham is definitely being very sweet. just like the sweet and comforting honey lemon tea he just brewed for you. alhaitham definitely makes sure that you take all your medications on time, because prolonging this bout of illness won't do for anyone.
neuvillette
the first time neuvillette found out that you were sick, he didn't exactly understand what to do. a little clueless, even – dragons, or rather non-humans, just don't get sick like you did. nevertheless, after some advice from a few human friends, neuvillette got to work. his contacts offered speedy services ... imagine getting a discount at the city's clinic, as well as a basket full of fresh vegetables from the melusines! it makes you smile a little on the inside, knowing that neuvillette cares about you so much. hehe.
taglist: @tiredsleep @loptido @raincxtter @chichikoi @ladyadii @soulsanta @sheiiths @genshinparty @eowinthetraveler @moonbyunniee @legitnoi @lemontum @manager-of-the-pudding-bank @starz222 @ilyuu @cherry-colored-petals @mondaymelon @tartaglia-apologist @soleillunne @m1shapanda @aimynx @smokipoki @adeptuscharm @diorlumx @vennnnn-diagram @ryuryuryuyurboat @yuminako @st0pthatsgay @aqualesha @sixtynintharchon @supernova25 @kunikuda-simp @starglitterz (send ask/comment to be added to taglist)
reblogs w/ tags & comments help me lots !!! if you liked this and would like to support me, please consider dropping me a follow as well :-) they all go a long way!
#astronetwrk#zhongli x reader#kaeya x reader#diluc x reader#childe x reader#neuvillette x reader#zhongli fluff#kaeya fluff#diluc fluff#childe fluff#neuvillette fluff#genshin impact x reader#genshin x reader#genshin x gn reader#genshin impact x gn reader#[📝 stewardess' notepad!]#genshin fluff#domestic fluff#xiao x reader#xiao x gn reader#xiao fluff#alhaitham x reader#alhaitham x gn reader#alhaitham fluff#sickfic
893 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Pulmonary Embolism?
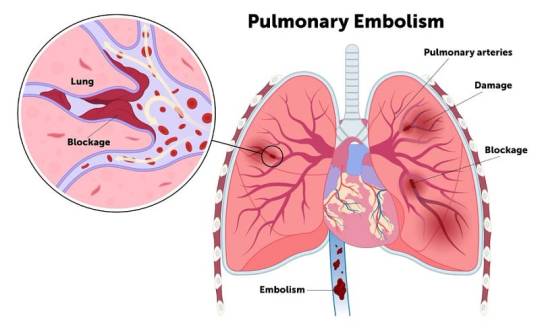
Introduction
Pulmonary embolism (PE) stands as a formidable medical concern, defined by the sudden obstruction of pulmonary arteries by blood clots or other substances. This obstruction poses a grave threat to life if not promptly addressed. In this comprehensive journey , we indulge into the technicality of PE, exploring its profound origins, clinical manifestations, predisposing factors, potential complications, and avenues for prevention.
A. Definition Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism manifests when a blood clot, typically originating from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the lower extremities, migrates to the lungs, precipitating arterial blockage.
B. Significance
PE emerges as a critical condition, triggering significant impairment of pulmonary function and predisposing individuals to severe complications, including mortality, in the absence of timely intervention.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
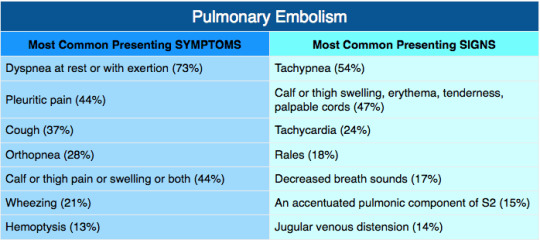
A. Common Symptoms encompass acute dyspnea, chest pain, and syncope, often manifesting abruptly and varying in intensity.
B. Additional Symptoms: Patients may also present with hemoptysis, tachycardia, dizziness, diaphoresis, pyrexia, lower limb edema, and cyanosis, reflective of diverse physiological perturbation.
Causes and Risk Factors

a. Venous Thromboembolism
Predominantly, PE ensues from embolic occlusion secondary to thrombi originating in the deep venous system of the lower extremities.
b. Diverse Etiologies
PE may arise from fat emboli, tumor emboli, or air emboli, presenting a spectrum of etiological paradigms.
C. Predisposing Factors:
Notable risk factors encompass antecedent , underlying medical conditions (e.g., cardiovascular diseases, malignancies), surgical interventions, coagulopathies, prolonged immobility, and the prothrombotic milieu associated with COVID-19 infection
Complications of Pulmonary Embolism
a). Mortality:
Untreated PE poses a grave threat to life, with mortality rates approximating one-third of cases, underscoring the exigency of timely intervention.
b). Pulmonary Hypertension
Chronic embolic burden culminates in pulmonary hypertension, engendering elevated pulmonary arterial pressures and consequent cardiac strain.
C. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Persistent emboli precipitate vascular remodeling, culminating in a debilitating condition marked by enduring pulmonary hypertension and associated morbidities.
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism
A. Pharmacological Prophylaxis
Anticoagulant prophylaxis stands as a cornerstone intervention in high-risk cohorts, mitigating thrombotic propensity perioperatively and during hospitalization.
B. Mechanical Modalities
Mechanical prophylaxis modalities encompass compression stockings, limb elevation, early mobilization, and pneumatic compression devices, fostering venous return and thwarting stasis-induced thrombogenesis.
C. Travel Recommendations
Travelers predisposed to thromboembolic events are counselled on hydration maintenance, periodic ambulation during prolonged periods of immobility, and the judicious utilization of compression garments to mitigate venous stasis during protracted journeys.
Conclusion
Pulmonary embolism emerges as a formidable adversary, demanding expeditious recognition and intervention to forestall catastrophic signal .A comprehensive grasp of its pathophysiological under happenings, clinical hallmarks, predisposing factors, complications, and preventive strategies is paramount for optimal management. Through concerted efforts encompassing risk mitigation and vigilant surveillance, individuals can navigate the perilous terrain of PE with greater resilience, minimizing morbidity and mortality associated with this grave condition.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at [email protected] for professional assistance.
#assignment help#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#do my online class#online writing#assignment services#academic assignments#medical school#assignmentwriting#clinicalstudy#clinical research#medication#nursing#nurse#nurses#nursingcourses#university student#pharmacy colleges#college help
0 notes
Text
WorkSure® is a Medpharma outsourcing company which offers impeccable services in #pharmacovigilance with profound experience of the team.
Read more at: https://www.worksure.org/pharmacovigilance-the-science-in-public-welfare/
Demo Video: https://youtu.be/gZ-qNxOqyWY?si=WZSqylrZrobmsNOq
#medicalaffairs #regulatoryaffairs #medicomarketing #patientsafety #healthcare
#medical devices#healthcare it services#medical writing services#clinical data management#key opinion leader#clinical data management services#clinical research#clinical trials#pharmacovigilance services#pharmacovigilance
0 notes
Text
Writing Notes: Autopsy
Autopsy - dissection and examination of a dead body and its organs and structures.
The word autopsy is derived from the Greek autopsia, meaning “the act of seeing for oneself.”
Also known as: necropsy, postmortem, postmortem examination
Why is an autopsy done?
To determine the cause of death
When a suspicious or unexpected death occurs
To observe the effects of disease; when there's a public health concern, such as an outbreak with an undetermined cause
To establish the evolution and mechanisms of disease processes
When no doctor knows the deceased well enough to state a cause of death and to sign the death certificate
When the doctor, the family or legally responsible designee of the deceased person requests an autopsy
Who does the autopsy?
Autopsies ordered by the state can be done by a county coroner, who is not necessarily a doctor
A medical examiner who does an autopsy is a doctor, usually a pathologist
Clinical autopsies are always done by a pathologist
How is an autopsy done?
After the patient is pronounced dead by a physician, the body is wrapped in a sheet or shroud and transported to the morgue, where it is held in a refrigeration unit until the autopsy.
Autopsies are rarely performed at night.
Autopsy practice was largely developed in Germany, and an autopsy assistant is traditionally honored with the title "diener", which is German for "helper".
The prosector and diener wear fairly simple protective equipment, including scrub suits, gowns, gloves (typically two pair), shoe covers, and clear plastic face shields.
The body is identified and lawful consent obtained.
The procedure is done with respect and seriousness.
The prevailing mood in the autopsy room is curiosity, scientific interest, and pleasure at being able to find the truth and share it.
Most pathologists choose their specialty, at least in part, because they like finding the real answers.
Many autopsy services have a sign, "This is the place where death rejoices to help those who live." Usually it is written in Latin ("Hic locus est ubi mors gaudet succurrere vitae").
EXTERNAL EXAMINATION
The prosector checks to make sure that the body is that of the patient named on the permit by checking the toe tag or patient wristband ID.
The body is placed on the autopsy table.
Experienced dieners, even those of slight build, can transfer even obese bodies from the carriage to the table without assistance.
Since the comfort of the patient is no longer a consideration, this transfer is accomplished with what appears to the uninitiated a rather brutal combination of pulls and shoves, not unlike the way a thug might manhandle a mugging victim.
The body is measured.
Large facilities may have total-body scales, so that a weight can be obtained.
The autopsy table is a waist-high aluminum fixture that is plumbed for running water and has several faucets and spigots to facilitate washing away all the blood that is released during the procedure.
Older hospitals may still have porcelain or even marble tables.
The autopsy table is basically a slanted tray (for drainage) with raised edges (to keep blood and fluids from flowing onto the floor).
After the body is positioned, the diener places a "body block" under the patient's back. This rubber or plastic brick-like appliance causes the chest to protrude outward and the arms and neck to fall back, thus allowing the maximum exposure of the trunk for the incisions.
Abnormalities of the external body surfaces are then noted and described, either by talking into a voice recorder or making notes on a diagram and/or checklist.
OPENING THE TRUNK
The diener takes a large scalpel and makes the incision in the trunk. This is a Y-shaped incision. The arms of the Y extend from the front of each shoulder to the bottom end of the breast bone (called the xiphoid process of the sternum). In women, these incisions are diverted beneath the breasts, so the "Y" has curved, rather than straight, arms. The tail of the Y extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic bone and typically makes a slight deviation to avoid the umbilicus (navel). The incision is very deep, extending to the rib cage on the chest, and completely through the abdominal wall below that.
With the Y incision made, the next task is to peel the skin, muscle, and soft tissues off the chest wall. This is done with a scalpel. When complete, the chest flap is pulled upward over the patient's face, and the front of the rib cage and the strap muscles of the front of the neck lie exposed. Human muscle smells not unlike raw lamb meat in my opinion. At this point of the autopsy, the smells are otherwise very faint.
An electric saw or bone cutter (which looks a lot like curved pruning shears) is used to open the rib cage. One cut is made up each side of the front of the rib cage, so that the chest plate, consisting of the sternum and the ribs which connect to it, are no longer attached to the rest of the skeleton. The chest plate is pulled back and peeled off with a little help of the scalpel, which is used to dissect the adherent soft tissues stuck to the back of the chest plate. After the chest plate has been removed, the organs of the chest (heart and lungs) are exposed (the heart is actually covered by the pericardial sac).
Before disturbing the organs further, the prosector cuts open the pericardial sac, then the pulmonary artery where it exits the heart. He sticks his finger into the hole in the pulmonary artery and feels around for any thromboembolus (a blood clot which has dislodged from a vein elsewhere in the body, traveled through the heart to the pulmonary artery, lodged there, and caused sudden death. This is a common cause of death in hospitalized patients).
The abdomen is further opened by dissecting the abdominal muscle away from the bottom of the rib cage and diaphragm. The flaps of abdominal wall fall off to either side, and the abdominal organs are now exposed.
REMOVING THE ORGANS OF THE TRUNK
The most typical method of organ removal is called the "Rokitansky method." This is not unlike field dressing a deer. The dissection begins at the neck and proceeds downward, so that eventually all the organs of the trunk are removed from the body in one bloc.
The first thing the diener does is to identify the carotid and subclavian arteries in the neck and upper chest. He ties a long string to each and then cuts them off, so that the ties are left in the body. This allows the mortician to more easily find the arteries for injection of the embalming fluids.
A cut is them made above the larynx, detaching the larynx and esophagus from the pharynx. The larynx and trachea are then pulled downward, and the scalpel is used to free up the remainder of the chest organs from their attachment at the spine.
The diaphragm is cut away from the body wall, and the abdominal organs are pulled out and down.
Finally, all of the organs are attached to the body only by the pelvic ligaments, bladder, and rectum.
A single slash with the scalpel divides this connection, and all of the organs are now free in one block. The diener hands this organ bloc to the prosector. The prosector takes the organ bloc to a dissecting table (which is often mounted over the patient's legs) and dissects it. Meanwhile, the diener proceeds to remove the brain.
Another method is called Virchow method, which entails removing organs individually.
EXAMINATION OF THE ORGANS OF THE TRUNK
At the dissection table, the prosector typically dissects and isolates the esophagus from the rest of the chest organs. This is usually done simply by pulling it away without help of a blade (a technique called "blunt dissection"). The chest organs are then cut away from the abdominal organs and esophagus with scissors. The lungs are cut away from the heart and trachea and weighed, then sliced like loaves of bread into slices about one centimeter thick. A long (12" - 18"), sharp knife, called a "bread knife" is used for this.
The heart is weighed and opened along the pathway of normal blood flow using the bread knife or scissors. Old-time pathologists look down on prosectors who open the heart with scissors, rather than the bread knife, because, while the latter takes more skill and care, it is much faster and gives more attractive cut edges than when scissors are used. The coronary arteries are examined by making numerous crosscuts with a scalpel.
The larynx and trachea are opened longitudinally from the rear and the interior examined. The thyroid gland is dissected away from the trachea with scissors, weighed, and examined in thin slices. Sometimes the parathyroid glands are easy to find, other times impossible.
The bloc containing the abdominal organs is turned over so that the back side is up. The adrenal glands are located in the fatty tissue over the kidneys (they are sometimes difficult to find) and are removed, weighed, sliced, and examined by the prosector.
The liver is removed with scissors from the rest of the abdominal organs, weighed, sliced with a bread knife, and examined. The spleen is similarly treated.
The intestines are stripped from the mesentery using scissors (the wimpy method) or bread knife (macho method). The intestines are then opened over a sink under running water, so that all the feces and undigested food flow out. As one might imagine, this step is extremely malodorous. The resultant material in the sink smells like a pleasant combination of feces and vomitus. The internal (mucosal) surface of the bowel is washed off with water and examined. It is generally the diener's job to "run the gut," but usually a crusty, senior diener can intimidate a young first- year resident prosector into doing this ever-hated chore. Basically, whichever individual has the least effective steely glare of disdain is stuck with running the gut.
The stomach is then opened along its greater curvature. If the prosector is lucky, the patient will have not eaten solid food in a while. If not, the appearance of the contents of the stomach will assure the prosector that he will not be eating any stews or soups for a long time. In either case, the smell of gastric acid is unforgettable.
The pancreas is removed from the duodenum, weighed, sliced and examined. The duodenum is opened longitudinally, washed out, and examined internally. The esophagus is similarly treated.
The kidneys are removed, weighed, cut lengthwise in half, and examined. The urinary bladder is opened and examined internally. In the female patient, the ovaries are removed, cut in half, and examined. The uterus is opened along either side (bivalved) and examined. In the male, the testes are typically not removed if they are not enlarged. If it is necessary to remove them, they can be pulled up into the abdomen by traction on the spermatic cord, cut off, cut in half, and examined.
The aorta and its major abdominal/pelvic branches (the renal, celiac, mesenteric, and iliac arteries) are opened longitudinally and examined.
Most of the organs mentioned above are sampled for microscopic examination. Sections of the organs are cut with a bread knife or scalpel and placed in labeled plastic cassettes. Each section is the size of a postage stamp or smaller and optimally about three millimeters in thickness. The cassettes are placed in a small jar of formalin for fixation. They are then "processed" in a machine that overnight removes all the water from the specimens and replaces it with paraffin wax. Permanent microscopic sections (five microns, or one two-hundredth of a millimeter thick) can be cut from these paraffin sections, mounted on glass slides, stained, coverslipped, and examined microscopically. The permanent slides are usually kept indefinitely, but must be kept for twenty years minimum.
Additional small slices of the major organs are kept in a "save jar," typically a one-quart or one-pint jar filled with formalin. Labs keep the save jar for a variable length of time, but at least until the case is "signed out" (i.e., the final written report is prepared). Some labs keep the save jar for years. All tissues that are disposed of are done so by incineration.
A note on dissection technique: All of the above procedures are done with only four simple instruments -- a scalpel, the bread knife, scissors, and forceps (which most medical people call "pick-ups." Only scriptwriters say "forceps"). The more handy the prosector, the more he relies on the bread knife, sometimes making amazingly delicate cuts with this long, unwieldy-looking blade. The best prosectors are able to make every cut with one long slicing action. To saw back and forth with the blade leaves irregularities on the cut surface which are often distracting on specimen photographs. So the idea is to use an extremely sharp, long blade that can get through a 2000-gram liver in one graceful slice. Some old-time purist pathologists actually maintain their own bread knives themselves and let no one else use them. Such an individual typically carries it around in his briefcase in a leather sheath. This would make an excellent fiction device, which, to my knowledge, has not been used. Imagine a milquetoast pathologist defending himself from a late-night attacker in the lab, with one desperate but skillful slash of the bread knife almost cutting the assailant in half!
Note on the appearance of the autopsy suite: Toward the end of the autopsy procedure, the room is not a pretty sight. Prosectors vary markedly in how neat they keep the dissection area while doing the procedure. It is legendary that old-time pathologists were so neat that they'd perform the entire procedure in a tux (no apron) right before an evening at the opera (pathologists are noted for their love of classical music and fine art). Modern prosectors are not this neat. Usually, the autopsy table around the patient is covered with blood, and it is very difficult not to get some blood on the floor. We try to keep blood on the floor to a minimum, because this is a slippery substance that can lead to falls. The hanging meat scales used to weigh the organs are usually covered with or dripping with blood. The chalk that is used to write organ weights on the chalkboard is also smeared with blood, as may be the chalkboard itself. This is an especially unappetizing juxtaposition.
Another example using the Virchow method:
After the intestines are mobilized, they may be opened using special scissors.
Inspecting the brain often reveals surprises. A good pathologist takes some time to do this.
The pathologist examines the heart, and generally the first step following its removal is sectioning the coronary arteries that supply the heart with blood. There is often disease here, even in people who believed their hearts were normal.
After any organ is removed, the pathologist will save a section in preservative solution. Of course, if something looks abnormal, the pathologist will probably save more. The rest of the organ goes into a biohazard bag, which is supported by a large plastic container.
The pathologist weighs the major solid organs (heart, lungs, brain, kidneys, liver, spleen, sometimes others) on a grocer's scale.
The smaller organs (thyroid, adrenals) get weighed on a chemist's triple-beam balance.
The next step in the abdominal dissection will be exploring the bile ducts and then freeing up the liver. The pathologist uses a scalpel or other similar tool.
After weighing the heart, the pathologist completes the dissection. There are a variety of ways of doing this, and the choice will depend on the case. If the pathologist suspects a heart attack, a long knife may be the best choice.
In the example: The liver is removed. The pathologist finds something important. It appears that the man had a fatty liver. It is too light, too orange, and a bit too big. Perhaps this man had been drinking heavily for a while.
The pathologist decides to remove the neck organs, large airways, and lungs in one piece. This requires careful dissection. The pathologist always examines the neck very carefully.
The liver in this example weighs much more than the normal 1400 gm.
The lungs are almost never normal at autopsy. In the example, the lungs are pink, because the dead man was a non-smoker. The pathologist will inspect and feel them for areas of pneumonia and other abnormalities.
The liver is cut at intervals of about a centimeter, using a long knife. This enables the pathologist to examine its inner structure.
The pathologist weighs both lungs together, then each one separately. Afterwards, the lungs may get inflated with fixative.
The rest of the team continues with the removal of the other organs. They may decide to take the urinary system as one piece, and the digestive system down to the small intestine as another single piece. This will require careful dissection.
One pathologist holds the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, duodenum, and spleen. He opens these, and may save a portion of the gastric contents to check for poison.
Another pathologist holds the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. Sometimes these organs will be left attached to the abdominal aorta. The pathologist opens all these organs and examine them carefully.
Dissecting the lungs can be done in any of several ways. All methods reveal the surfaces of the large airways, and the great arteries of the lungs.
Most pathologists use the long knife again while studying the lungs. The air spaces of the lungs will be evaluated based on their texture and appearance.
Before the autopsy is over, the brain is usually suspended in fixative for a week so that the later dissection will be clean, neat, and accurate.
If no disease of the brain is suspected, the pathologist may cut the brain fresh.
The kidneys are weighed before they are dissected.
It is the pathologist's decision as to whether to open the small intestine and/or colon. If they appear normal on the outside, there is seldom significant pathology on the inside.
One pathologist prepares the big needle and thread used to sew up the body.
When the internal organs have been examined, the pathologist may return all but the tiny portions that have been saved to the body cavity. Or the organs may be cremated without being returned.
The appropriate laws, and the wishes of the family, are obeyed.
The breastbone and ribs are usually replaced in the body.
The skull and trunk incisions are sewed shut ("baseball stitch").
The body is washed and is then ready to go to the funeral director.
These notes do not show all the steps of an autopsy, but will give you the general idea.
During the autopsy, there may be photographers, evidence technicians, police, hospital personnel, and others.
In the example, the pathologists submit the tissue they saved to the histology lab, to be made into microscopic slides.
When these are ready, they will examine the sections, look at the results of any lab work, and draw their final conclusions.
The only finding in this sample autopsy was fatty liver. There are several ways in which heavy drinking, without any other disease, can kill a person. The pathologists will rule each of these in or out, and will probably be able to give a single answer to the police or family.
CLOSING UP AND RELEASING THE BODY
After all the above procedures are performed, the body is now an empty shell, with no larynx, chest organs, abdominal organs, pelvic organs, or brain. The front of the rib cage is also missing. The scalp is pulled down over the face, and the whole top of the head is gone. Obviously, this is not optimal for lying in state in public view. The diener remedies this problem. First, the calvarium is placed back on the skull (the brain is not replaced), the scalp pulled back over the calvarium, and the wound sewn up with thick twine using the type of stitch used to cover baseballs. The wound is now a line that goes from behind the ears over the back of the skull, so that when the head rests on a pillow in the casket, the wound is not visible.
The empty trunk looks like the hull of a ship under construction, the prominent ribs resembling the corresponding structural members of the ship. In many institutions, the sliced organs are just poured back into the open body cavity. In other places, the organs are not replaced but just incinerated at the facility. In either case, the chest plate is placed back in the chest, and the body wall is sewn back up with baseball stitches, so that the final wound again resembles a "Y."
The diener rinses the body off with a hose and sponge, covers it with a sheet, and calls the funeral home for pick- up. As one might imagine, if the organs had not been put back in the body, the whole trunk appears collapsed, especially the chest (since the chest plate was not firmly reattached to the ribs). The mortician must then remedy this by placing filler in the body cavity to re-expand the body to roughly normal contours.
Ultimately, what is buried/cremated is either 1) the body without a brain and without any chest, abdominal, or pelvic organs, or 2) the body without a brain but with a hodgepodge of other organ parts in the body cavity.
FINISHING UP
After the funeral home has been called, the diener cleans up the autopsy suite with a mop and bucket, and the prosector finishes up the notes and/or dictation concerning the findings of the "gross exam" (the part of the examination done with the naked eye and not the microscope; this use of the term "gross" is not a value judgement but a direct German translation of "big" as opposed to "microscopic").
For some odd reason, many prosectors report increased appetite after an autopsy, so the first thing they want to do afterwards is grab a bite to eat.
The whole procedure in experienced hands, assuming a fairly straightforward case and no interruptions, has taken about two hours.
Complicated cases requiring detailed explorations and special dissections (e.g., exploring the bile ducts, removing the eyes or spinal cord) may take up to four hours.
AFTER THE AUTOPSY
Days to weeks later, the processed microscopic slides are examined by the attending pathologist, who renders the final diagnoses and dictates the report.
A final report is ready in a month or so. The glass slides and a few bits of tissue are kept forever, so that other pathologists can review the work.
Only the pathologist can formally issue the report, even if he or she was not the prosector (i.e., the prosector was a resident, PA, or med student).
The report is of variable length but almost always runs at least three pages. It may be illustrated with diagrams that the prosector draws from scratch or fills in on standard forms with anatomical drawings.
The Joint Commission for the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO), which certifies hospitals, requires the final report to be issued within sixty days of the actual autopsy.
The College of American Pathologists, which certifies medical laboratories, requires that this be done in thirty days.
Nevertheless, pathologists are notorious for tardiness in getting the final report out, sometimes resulting in delays of years.
Perhaps the non-compensated nature of autopsy practice has something to do with this. Pathologists are otherwise very sensitive to turnaround times.
THE BRAIN-CUTTING
The examiner returns to the brain left suspended in a big jar of formalin for a few weeks. After the brain is "fixed," it has the consistency and firmness of a ripe avocado.
Before fixation, the consistency is not unlike that of three-day- old refrigerated, uncovered Jello.
Infant brains can be much softer than that before fixation, even as soft as a flan dessert warmed to room temperature, or worse, custard pie filling. Such a brain may be difficult or impossible to hold together and can fall apart as one attempts to remove it from the cranium.
Assuming good fixation of an adult brain, it is removed from the formalin and rinsed in a running tap water bath for several hours to try to cut down on the discomforting, eye-irritating, possibly carcinogenic formalin vapors.
The cerebrum is severed from the rest of the brain (brainstem and cerebellum) by the prosector with a scalpel.
The cerebellum is severed from the brainstem, and each is sliced and laid out on a tray for examination.
The cerebrum is sliced perpendicularly to its long axis and laid out to be examined.
Sections for microscopic processing are taken, as from the other organs, and a few slices are held in "save jars."
The remainder of the brain slices is incinerated.
Sources: 1 2 3 4
If these notes help with your poem/story, do tag me, or leave a link in the replies. I would love to read them!
#writing notes#spilled ink#dark academia#writing prompt#writers on tumblr#poetry#poets on tumblr#literature#writeblr#fiction#creative writing#writing reference#studyblr#langblr#linguistics#words#writing resources
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Medical Writing Services#Medical Writing#Regulatory Medical Writing#Artificial Intelligence#AI#Automate Manual Process#Life Sciences#Product documentation#Clinical Study Reports#Clinical Data#Clinical Studies#Clinical Research#Content Authoring
0 notes
Text
Monsters in the Dark | Nikto x Reader | Part 1

First "official" part of Nikto x Reader fic set in the cowboy AU originally created by @ghouljams once again staring our darling Sputnik. Makes a lot more sense if you read the prologue which can be found linked below.
A/N: Did I spend several hours watching Kevin Richardson videos with him hanging out with his hyenas while writing this? Yes. Do I regret it? Absolutely not. This also ended up a lot longer than I was expecting lmao.
Warnings: Depictions of Minor Medical Procedures.
Masterlist: CoD Masterlist
Prev Part | Next Part
When working as a rural vet there’s a surprising amount of driving involved. Travelling from the clinic to farms and huge properties miles and miles away for in-person appointments and consultations can understandably take several hours out of your day. Most of the time you don’t even have working cell service to help guide you to your destination and you’re forced to either memorise the route beforehand or turn to your old reliable map.
You’re new to the area, having decided to spend some time travelling across the US for the potential experience it could offer you. You’ve done plenty of work on stations in the north of Australia, helping jackaroos to manage any illness within their herds, always moving from place to place, and so Texas seemed like the perfect place to start your travels.
While training, however, you had been given an offer to travel to South Africa to work with the numerous wildlife there both on reserves and in zoos. It was the best year of your life and ignited a passion for working with exotic animals.
Travelling the US for work was an exciting opportunity to help rural communities with their livestock and to work with the numerous native species you’ve never had the chance to encounter in your everyday life. This little town was just another step on your travels and, so far, hadn’t really stood out to you more than any other small town.
So, it isn’t out of place for you to be driving down a lengthy driveway through the woods and pulling up to a rundown old house. What is strange, is the huge creature sitting at the top of the porch.
The hyena is massive. It’s powerfully built with pure muscle, and no doubt would be able to tear you to pieces if it chose to. It’s so distracting that for a long time you don’t even notice the huge man standing beside your car. He looks just as strong as the hyena sitting behind him and you’re not sure how you missed his approach.
When the lady at the front desk informed you that there was a gentleman asking for a veterinarian with experience handling exotics, you were thinking perhaps a rare lizard, or an uncommon species of parrot. What you weren’t expecting was to see an adult hyena staring you down.
You’re more than a little reluctant to leave the safety of the vehicle, but upon receiving a jerk of the head from the man, you cautiously exit the car. Not once do you take your eyes off the predator while you quickly grab your bag from the backseat.
Having dealt with hyenas before, you know better than to show any kind of fear, forcing your shoulders down from your ears and starting to take calm, deep breaths. You offer your name to who you presume is the animal’s owner and hold out a hand for him to shake.
The man, “Nikto,” as he grunts to you, takes your hand after a moment and gives it a firm shake. You’re used to farmers having a strong grip, so you simply offer the man a bright grin. “I take it this is the patient?” you ask, nodding your head toward the hyena in question.
The man is clad head to toe in all-black clothing. Typical cowboy hat, black denim jeans, and a shirt that has a high collar and sleeves that reach all the way down to his wrists where they meet with a pair of leather gloves. All regular clothing, albeit a little dark for such a hot climate, but what really sets him apart is the dark neck gaiter covering most of his features.
You would think it odd for him to be hiding his face on his own property, but you’ve heard that there’s several other ex-military men in the town that also prefer bandanas or masks to showing their bare faces. It looks intimidating, especially given just how huge the guy is, but at the end of the day he’s your client and it isn’t your place to judge.
“да,” Nikto nods, “this is Sputnik.” He looks you up and down, before asking, “you are comfortable with her, yes?”
“Uh, yeah, I’ve worked with hyenas before,” you confirm. That, unfortunately, doesn’t make it any easier or less nerve-wracking to be so close to an unrestrained predator. Normally, there’s at least a fence between you and any of the wildlife you’re treating, but hopefully the animal is somewhat friendly given it’s allowed to roam free.
At your confirmation, he lets out a sharp whistle and snaps out a harsh, “КО МНЕ!” Causing the animal to leap to her feet and sprint across the grass to her owner’s side.
You try not to jump when Sputnik runs directly toward you but manage to keep a handle on your reactions. Much to your relief, however, rather than tackling you to the floor and tearing your throat out, the hyena starts laughing excitedly and running circles around you. She’s clearly very curious, stopping every few seconds to try and sniff at you from a distance.
You can imagine it would be an intimidating sight for anyone who has never encountered a hyena before, but she’s clearly just excited to meet someone new. “Is she normally this excited to meet new people?” you ask, unable to resist the smile that grows on your face as Sputnik starts to playfully nip at Nikto’s legs.
The man huffs, crossing his arms over his chest, “no.”
You’re beginning to understand that Nikto is not one for making conversation.
As Sputnik calms again, you watch her wander around the area. The issue becomes clear to you quite quickly in the form of a slight limp on one of her hind legs. She seems to otherwise be bright, alert and responsive, only the sore leg causing her problems.
You run through the basic questions about the problem, how long it’s being going on, and how her behaviour has been recently. You quickly take notes on her previous medical history while keeping an eye on Sputnik. After taking down her information, you ask Nikto to bring her to one of the old sheds so you can begin the exam.
She’s a beautiful hyena, and despite not having the behaviour of a domesticated dog, she can somewhat follow her owner’s commands. After seeing Nikto tapping the top of one of the tables, she hops up into a bench for you to more easily inspect her body.
With Sputnik firmly restrained by her owner, you gently reach out for her hind paw. You softly palpate the area, taking note of the large amount of swelling, particularly in the area between two of her toes. After glancing up to ensure she isn’t getting too stressed, you pull apart the toes, spotting a nasty yellow lump of what is presumably infection.
As you check over the area, you notice something black sticking out of the wound. With your trusty pair of tweezers you take hold of the object and begin to gently tease it out of the swollen mass. Sputnik’s leg twitches slightly, clearly not happy about someone touching her sore paw, but after a few soft words of encouragement she settles once again.
Your grip on the object slips a few times, but eventually you’re able to pull it free. It’s a nasty thorn, a whole inch in length that was buried in the poor animal’s foot. Just removing it causes a flood of pus to begin squirting from the wound and you’re thankful for the medical gloves you’re wearing, because it is far from a pleasant smell.
Sputnik whines, trying to pull her paw away again, but with your client still holding her head in place you can continue to express the rest of the fluid without causing her much more distress. With a small syringe of saline, you quickly flush out the remaining chunks of hardened infection until the liquid runs clear.
It’s a small enough opening that she won’t need the wound packed or any stitches to keep it closed. Instead, you spray the area with a thick layer of Blu-Kote to prevent any further infection.
“I'll need to give her a quick antibiotic injection to make sure it won’t come back, just make sure she’s restrained, okay?” You receive a grunt of acknowledgement, then provide the needed shot. Sputnik tries to turn and snap at you, but with Nikto in the way she ends up biting at thin air and growling in frustration.
You gently rub at the hyena’s back with a loving coo, “what a brave girl, you did so well!”
After being released she turns to regard you for a moment, before squealing happily and trying to lick at your face. It seems you’re already forgiven for your cruel transgressions against the poor girl. “Looks like this was the cause of the trouble,” you explain, briefly showing Nikto the old thorn you’d removed.
Nikto turns his gaze to Sputnik, rolling his eyes before gently cuffing her around the back of the head. “Долбоеб,” he mutters, ignoring the way she starts to playfully bite at one of his gloved hands.
You’re not entirely sure what he said, but no doubt it’s some sort of insult. Not that Sputnik seems to care, hopping down from the table and trotting around the barn as if the last ten minutes didn’t occur.
“I gave her a strong antibiotic, but spotted hyenas are pretty notorious for their infections being resistant to treatment, so if she starts getting worse or isn’t improving then be sure to give me a call and we’ll look at if there’s anything we need to do,” you explain, keeping an eye on how Sputnik moves on her feet now.
“Understood,” the man nods, standing ramrod straight with his arms crossed over his chest.
Clearly this man still isn’t very interested in a conversation, given he has nothing further to add and almost seems to be pointedly ignoring you. It’s a little uncomfortable, but he’s certainly not the first... interesting character you’ve dealt with in your career and he won’t be the last. “Do you have any other questions about the treatment?” you ask.
“нет,” he grunts, before quickly adding, “no.”
You nod, offering the man a genuine smile, “well, I’m glad I could help out.” You remove your gloves and quickly start packing away the tools you’d been using, “the office will send through an invoice to your email, so you can pay online or head down to the clinic to pay in person.”
He just nods, watching you silently as you finish up collecting your tools and placing them back away into your bag. His eyes seem to burn into you, his icy gaze piercing through your body and directly into your very soul. You’re not sure how comfortable you are having your innermost self so openly exposed to someone you’ve only just met, but quickly shake off the feeling.
As soon as you’re finished packing, you pull out one of your personal cards, handing it to Nikto. He stares at the piece of cardboard for a long moment, and you quickly explain, “my card, it’s got my number on it in case you ever need help.” You can’t imagine how difficult it must be for him to find someone with genuine experience treating large predatory animals and you’re more than happy to offer as much of your expertise as he wants.
Nikto awkwardly goes to reach for the card with one of his hands, only to pause midway and reach for it with the other one. He fleetingly glances over the card, then tucks it into one of his shirt pockets.
While you make your way back to your car, Nikto calls Sputnik back over and ensures the animal walks at his heels. She doesn’t seem happy with this command, whining and laughing as she looks between her master and you. She very obviously wants to run after you and play but knows better than to ignore her owner.
Sputnik sits next to Nikto as the man watches you quickly pack everything back into your car. She keeps looking between you and Nikto, as if silently begging him to allow her to go back to you for more attention, but he stands strong against her sad eyes. It’s cute, really, since it likely means that weaponized puppy dog eyes are an effective tool in getting the stoic man to crumble if she’s still attempting to use them against him.
Before you hop into the car you give Sputnik a wave, laughing when she cries at you. “Bye, sweetheart!” you coo again, before offering her owner a wave and a smile.
Looking into the rear-view mirror on your way back toward the main road, you can see both Nikto and Sputnik watching you leave. They’re an odd pair, but it’s been a while since you had the chance to work with such a beautiful animal and you can’t help looking forward to seeing both her and her strange human again sometime soon.
#writing#call of duty modern warfare#reader insert#fanfic#call of duty nikto#nikto x reader#cowboy au
209 notes
·
View notes