#monocular microscope
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Motorized monocular microscope
Motorized monocular microscope is a unit with excellent zoom magnification optical system and precision electromechanical system. The motorized 3D attachment can observe the specimen from 360° with high-resolution, high contrast, large depth of field, long working distance and high zoom ratio
0 notes
Text
Best Student Monocular Microscope Manufacturers in India

A Student Monocular Microscope manufacturer is a company that specializes in designing, producing, and distributing monocular microscopes specifically for educational purposes. These manufacturers offer products specifically tailored to the needs of students, providing them with reliable and affordable instruments to aid their scientific studies. Coslab India is a renowned manufacturer of high-quality student monocular microscopes. With years of experience in the industry, Coslab India has established itself as a trusted brand among educational institutions and laboratories. Contact: +91-9416113230 Mail: [email protected]
#Student Monocular Microscope Manufacturers#Best Student Monocular Microscope Manufacturers#Top Student Monocular Microscope Manufacturers#Student Monocular Microscope Manufacturers in India
0 notes
Text
Word List: Eye

beautiful words with "eye" to try to include in your poem/story
Bird's-eye - any of numerous plants with small bright-colored flowers; an allover pattern for textiles consisting of a small diamond with a center dot; having or involving a bird's-eye view
Deadeye - a rounded wood block encircled by a rope or an iron band and having holes to receive the lanyard that is used especially to set up shrouds and stays; an unerring marksman
Eye-beam - archaic: a radiant glance of the eye
Eye-opener - a drink intended to wake one up; something startling, surprising, or enlightening
Eyeable - archaic: that may be seen; visually attractive
Eyeberry - partridgeberry; wintergreen
Eyebright - any of a genus (Euphrasia) of semiparasitic herbs of the snapdragon family with spikelike racemes
Eyecup - a small oval cup with a rim curved to fit the orbit of the eye used for applying liquid remedies to the eyes
Eyedness - preference for the use of one eye instead of the other (as in using a monocular microscope)
Eyeful - a full or completely satisfying view; one that is visually attractive
Eyelet - a small hole designed to receive a cord or used for decoration (as in embroidery); peephole, loophole
Eyen - archaic plural of eye
Eyeroot - goldenseal (i.e., a perennial North American herb (Hydrastis canadensis) of the buttercup family with large leaves and a thick knotted yellow rhizome sometimes used medicinally)
Eyeshade - a visor that shields the eyes from strong light and is fastened on with a headband
Eyeshine - reflection of light from the inner surface of an eye through the pupil so that the eye has a luminous appearance (as in a cat)
Eyespot - a usually small spot of color (as on the wing of a butterfly) that resembles an eye
Eyestalk - one of the movable peduncles bearing an eye at the tip in a decapod crustacean
Eyestrain - weariness or a strained state of the eye
Eyestrings - obsolete: organic eye attachments formerly believed to break at death or blindness
Eyetooth - a canine tooth of the upper jaw
Eyewash - an eye lotion; misleading or deceptive statements, actions, or procedures
Eyewater - archaic: tears; aqueous humor
Eyewink - look, glance
Fish-eye - being, having, or produced by a wide-angle photographic lens that has a highly curved protruding front, that covers an angle of about 180 degrees, and that gives a circular image
Goldeneye - either of two diving ducks (genus Bucephala) with small yellow eyes; especially: a large-headed swift-flying Holarctic diving duck (B. clangula) with the male having a green head and striking black-and-white markings
Hawkeyed - having keen sight
Mooneye - a silvery North American freshwater bony fish (Hiodon tergisus of the family Hiodontidae)
Oxeye - any of several composite plants (as of the genera Chrysanthemum or Heliopsis) having heads with both disk and ray flowers
Shut-eye - sleep
Tigereye - a usually yellowish to brown chatoyant stone that consists of silicified crocidolite and is much used for ornament
Walleye - an eye with a whitish or bluish-white iris
If any of these words inspire your writing, do tag me or send me a link. I'd love to read your work!
More: Word Lists
#word list#eye#spilled ink#dark academia#writing reference#writeblr#langblr#words#linguistics#literature#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#poetry#poets on tumblr#writing inspiration#writing inspo#writing ideas#creative writing#m.c. escher#surrealism#art#writing resources
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
biology !
✧ THE MICROSCOPE !
microscope - tool used by scientists to view objects to small to be seen with the naked eye
allows view of a magnified version of microscopic organisms or cells
most cells studied under microscopes are measured in micrometers (μm) equal to 0.001 millimeter
details of cells can be studied
mid-1660s - dutch scientist antonie van leeuwenhoek invented first practical microscope
used this to examine protozoans, bacteria, and other microscopic organisms
compound light microscope
most common microscope used in laboratories
two lenses - objective and ocular
monocular microscope - one ocular lense
binocular microscope - two ocular lense
has several objective lenses with different magnification power
scanner - 4x
low power objective (LPO) - 10x
high power objective (HPO) - 40x
oil immersion objective (OIO) - 100x
can be used to examine both living and nonliving specimens

parts and functions include:
mechanical
draw tube - holds ocular lens
body tube - connects ocular lens to the revolving nosepiece
coarse adjustment knob - moves either the body tube or stage upward or downward in greater increments to bring specimen into initial focus and should only be used with the scanner or lpo
fine adjustment knob - moves either the body tube or stage upward or downward in lesser increments to bring the specimen into sharp focus and used with hpo or oio
arm - supports body tube and is used to carry microscope
revolving nosepiece - circular and revolving part holding objectives
stage - flat platform to hold specimen slide
stage clips - secures specimen slide
inclination joint - attaches arm to pillar
pillar - provides support above base
base - provides firm and steady support
magnifying
ocular lens/eyepiece - detachable cylinder, capable of magnifying objects to 10x
objective lens - used to magnify the specimen under study, has LPO, HPO, and OIO
illuminating
condenser - concentrates light onto specimen
iris diaphragm - regulates how much light passes through the specimen
mirror - reflects light and directs it to the object
light source - sometimes replaces mirror, usually a small electric lamp
✧ CELLS !
1839 - matthias schieden, theodor schwann formulated cell theory
all living things are made of cells
new cells come from pre-existing cells
energy flows within cells
cells contain dna passed on from parent cell/s
all cells have basically the same chemical composition and metabolic activities
cell activity depends on the activities of subcellular structures within the cell
two main cell types :
prokaryotic cells
lack nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
eukaryotic cells
have both a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
includes both animal and plant cells
three main parts of a cell include:
cell membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
cell membrane
outermost boundary
separates cells
regulates movement of materials in/out of cell (semipermeable)
nucleus
membrane-bound structure at the center of the cell
contains dna (deoxyribonucleic acid)
nuclear membrane: gateway to nucleus and separates nucleus from cytoplasm
chromosomes: carriers of the genes, made up of dna
nucleolus: center for ribosomal activity, usually contains protein and ribonucleic acid (rna)
cytoplasm
largest part of the cell in terms of volume
composed of membrane-bound organelles
supports and suspends organelles and cellular molecules
protein synthesis
organelles
endoplasmic reticulum: channel for transport
quality control unit of cell
rough er: presence of ribosomes
smooth er: no ribosomes, site of lipid and steroid synthesis
number of ribosomes depend on activities of the cell
golgi body: packaging of secretory materials
proteins from ribosomes are chemically modified, packed, and sealed off in vesicles
lysosome: breakdown & degradation of substances by digestive enzyme + aptosis (cell suicide)
peroxisome: detoxification of harmful compounds + helps with oxygen
mitochondria: energy generators
produces adenosine triphosphate
number of mitochondrion varies depending on function/cell type
vacuole: for storage and support, filled with fluids and soluble molecules, bigger in plant cells
organelles found in specific cells
plastid: found in only plant cells, double-membrane-bound organelles
called chloroplast if containing chlorophyll
centriole: formation of spindle fibers, only in animal cells
cell wall: for protection and coverage and defines shape of plant cells
cell junction: for cell connections in only animal cells
other cytoplasmic inclusions
ribosome: protein factory, site of protein synthesis in all cells
recieve genetic info from rna and translates into amino acids
cytoskeleton: cellular strength and matility
plant cell

animal cell

✧ LEVELS OF ECOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION !
most cells look the same in early stages
new cells become specialized to carry out specific functions
tissues - cells grouped together to perform certain functions
animal tissues:

epithelial
cover the outermost part of the body
found lining the walls of digestive and respiratory tubes
protect underlying tissues
absorb nutrients
secretion of wastes
classified in number of layers:
simple
composed of one layer of cells
stratified
composed of two or more layers
muscular
ability to contract and relax
enables body movement
give shape to the body
classified according to structure:
striated
found in skeletal ad cardiac muscles
unstriated
smooth muscles found in some internal organs
classified according to movement:
voluntary
if its movement can be controlled
involve skeletal muscles
involuntary
when movement is beyond conscious control
controlled by involuntary muscles (e.x smooth muscles of the heart, esophagus, and urinary bladder)
connective
connect, bind, and pack body parts together
classified as loose and dense:
loose connective tissues
most common type
usually elastic
e.x areolar, adipose, and reticular tissues
dense connective tissues
have fibers as main matrix
composed of inelastic collagenous fibers
compactly arranged
designed for strength and support
e.x tendons, ligaments, cartilages
specialized connective tissues (e.x blood and bone) are not classified
nervous
responsible for the reception of stimuli and conduction of impulses in the body
neuron - nerve cell, basic functional unit of the nervous system
three types:
sensory neuron
reveive impulses from the different sense organs of the body
carry these impulses toward the central nervous system
motor neuron
carry impulses away from the central nervous system to muscle tissues and glands
located in the peripheral nervous system
interneuron
also called associative neurons
link the sensory neurons to motor neurons
plant tissues:
meristematic or embyronic tissues
made up of young, actively dividing cells
small, six-sided, and boxlike
transform into many different shapes and sizes according to function during maturity
usually found at the tips of roots and stems/shoots
types of meristematic tissues:
apical meristems
located at the plant shoot and root tips
produce three tissues:
protoderm
gives rise to the epidermis, the outer protective covering of a plant
ground meristem
produces ground tissues that form the bulk of the interior of a plant
procambium
produces vascular tissues that are responsible for the transport of water and nutrients
lateral meristems
located on the sides of a plant’s stem and in most plant’s roots
cause secondary growth, characterized by an increase in diameter
have two types:
vascular cambium
produces secondary tissues that induce secondary growth
extends throughout plant axis
cork cambium
produces the cork cells of the bark
located in the outer layer of the stems of woody plants and originates under the epidermis
intercalary meristems
located at the internodes or bases of leaves
help increase the length of internodes by pushing newly produced cells upward
nonmeristematic or permanent tissues
composed of mature (nondividing) and differentiated cells
two types:
simple nonmeristematic tissues
composed of only one kind of cell
perform several functions (e.x support, protection and secretion)
complex nonmesterimatic tissues
two types of complex tissues
xylem
aid in upward distribution of water and minerals
phloem
transport the food produced during photosynthesis to other parts of the plant
organs - a group of tissues working together to perform a particular function
made up of cells and tissues which carry out processes that keep animals alive


organ system - several organs working together to perform particular tasks


organ systems of plants are classified as the shoot and root systems
shoot system - usually above ground, and comprised of several organs that work together to perform specific functions (e.x buds, leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits)
root system - comprised of the roots and other associated parts, and is usually found underground, function is to anchor the plant in soil and absorb water and nutrients
organism - life-form composed of related parts that maintain different essential processes
population - group of organisms that belong to the same species living in the same geographical area
community - different populations of different species interacting with one another and their environment
ecosystem - smallest functional unit of ecology, consisting of all living organisms in a given area and nonliving factors in the environment
biome - major ecosystem type characterized by its distinct flora and fauna, which are adapted to their particular environment
biosphere - considered the highest level of ecological hierarchy, as it includes the xones of land, air and water where organisms live
✧ DOMAINS OF LIFE !
swedish taxonomist carolus linnaeus proposed only two kingdoms: plant and animal
the new six kingdoms include:
archaebacteria
eubacteria
fungi
protista
plantae
animalia
1990 - american microbiologist car woese introduce three domains of life:
archaea
consists of extremophiles or prokaryotic microorganisms that live in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperature, pH, and salinity
diverse microorganisms that can adapt to harsh environments
proteins on the gene sequences found in archaebacteria are mostly stable at extreme temperatures
classified based on their habitat and metabolism
archaebacteria - similar to eubacteria, is prokaryotic, but is more similar to eukaryotic cells, and lacks peptidogylcan made of carbohydrates, and cell membranes contain different kinds of lipid
methanogens
strictly anaerobic organisms (don’t need oxygen) whose metabolic activities produce methane
found in lake and swamp sediments, where decompose dead vegetation
found in the rumens of some herbivores where they help digest cellulose
found deep in the oceans where they thrive in undersea volcanic vents, where they synthesize organic molecules from carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas
abundant in dumpsites and raw sewage
e.x methanosarcina
methanotrix
halophiles
live in environments where salt concentration is high
found in tidal pools that have dried up over time
e.x halobacterium, halococcus, and salinivibrio
thermophiles
lack cell walls and a nucleus
usually live in hot and highly acidic conditions (e.x coal refuse piles)
also found in sulfur-rpoducing envronments such as sulfur vents or hydrothermal vents
survival in anaerobic environments depends on sulfur respiration
e.x thermoplasma acidophilum and thermoplasma volcanium
hyperthermophiles
thrive in the deep parts of the ocean
temperature and pressure are high
reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide in oil-rich environments
also live in locations rich in sulfide deposits, hot springs, and thermal vents
these places are acidic due to the production of sulfuric acid by hyperthermophiles
bacteria
consists of proteobacteria, cyanobacteria, spirochetes, and gram-positive bacteria
eubacteria - the true bacteria
organisms under this domain are almost everywhere
one of the oldest and most abundant organisms on earth due to their ability to survive in various environments or conditions
has existed for more or less 3.5 billion years
classified based on shape:

can live as a single cell or in colonies
colony - group of identical bacterial cells closely associated with one another
may join together in clusters or chains
prokaryotic
cell wall
rigid, outermost protective covering of a bacterial cell and is composed of peptidoglycan
peptidoglycan - molecule made of polysaccharides (carbohydrates) and amino acids (proteins)
maintains the shape and structure of the cell
site where viruses and antibiotics attach
cell membrane
thin, flexible, and semipermeable material that regulates the flow of materials into and out of the cells
has inward-folding membranes called mesosomes where cellular respiration takes place
nucleoid
where the genetic material is located
usually at the of the cell
not bound by a nuclear membrane
easily distinguished from the other parts of the bacterial cell
cytoplasm
occupies largest part of the cell
semiliquid portion that houses all the cytoplasmic inclusions such as the plasmid
site of essential processes needed for the cell growth, metabolism, and replication
ribosome
same function as those found in other cells
usually smaller
protein factories that translate the genetic codes from messenger rna (mrna) into proteins
pilus or fimbria
hollow hairlike structures made of proteins located on the surface of most species of bacteria
fimbriae allow bacteria to attach themselves to their host
pili are used for bacterial conjugation
flagellum
long appendage that propels the cell by spinning in a corkscrew motion
located at the terminal end of the cell membrane
capsule
serves as the outermost protective covering of some species of bacteria
composed of a slimy gelatinous substance
shields pathogenic bacteria from harsh environments and phagocytosis (also known as cell eating)
endospores
formed by some bacteria
highly resistant to harsh conditions
bacteria are nourished via the same food we eat
they spoil the food, and a change in smell and taste usually indicates their presence
some can make their own food through:
photosynthesis - a special type of chlorophyll is used to produce food (cyanobacteria)
chemosynthesis - converting inorganic compounds from their surroundings into organic materials
some bacteria are decomposers, who break down wastes and dead organisms into usable forms of energy
eukarya
includes most of the living organisms on earth, such as animals, plants, protists, and fungi
protists
eukaryotic organisms that can be unicellular or multicellular
grouped into:
plantlike or algae
diverse and widely distributed
range from single-celled to colonial and multicellular forms
not considered plants due to lack of protective structures for their reproductive cells
not classified as animals because they do not use cilia or flagella for movement
not considered fungus for lack of chitin in cell wall
some phytoplankton are protists
unicellular photosynthetic organisms that float on the surface of fresh water and salt
responsible for 50 to 85% of the oxygen in atmosphere
golden algae - diatoms
brown algae - kelp
red algae - gracilaria verrucosa
dinoflagellates - have two flagella in each cell and are found in marine environments
can grow bloom rapidly, turning water along coasts reddish-brown (red tide)
produces large amount of neurotoxins that harm marine organisms
animallike or protozoans
heterotrophic (depend on other organisms for food)
include zooflagellates
amoeba - one of the simplest known protozoans
consists of a nucleus and all other cellular parts present in a eukaryotic cell
crawls using pseudopodia (false feet)
powered by a protein called actin
eats tiny food particles
amoebiasis/amoebic dysentery - usually acquired in crowded and unsanitary areas
funguslike or slime molds
saprophytic (derive food and energy by breaking down dead organic matter)

fungi
includes wide variety of species
four major groups of fungi:
zygomycetes
rapid growers in soil/dead plants
asomycetes
parasitic and takes over their brains
basidiomycetes
spores develop in basidia
chytridiomycetes
live in soil, fresh water, and saline estuaries
found in dark, moist and humid environments
have eukaryotic cells with chitin cell walls
lack chlorophyll and procures food from other sources
some fungi obtain nutrients through parasitism
a few fungi are unicellular, most are multicellular
hyphae - threadlike filaments present in some species of fungi
elongated, tubular, and have branching filaments from the mycelium
the hyphae of the mycelium secrete enzymes that digest the food
horizontal hyphae grow across the surface of moldy food, making it appear moldy
rhizoids grows into the food
molds can reproduce asexually by growing vertical hyphae, where sporangium disperse individual spores that can develop into a new mycelium
other parts include:
cap - top part of the mushroom that protects the gills and spores
gills - found on the underside of the cap where the special structures called basidia are found
basidia - found on the gills, microscoping club-shaped reproductive structures that bear spores
stalk/stipe - supports the cap
annulus - ringlike structure along the stipe
mycelium - a mass of branching hyphae below the soil or growth medium that absorbs nutrients


✧ REPRODUCTION !
NTO DONE WIP DOSRYR GUS IM NOT DONE WITH MY NTOES
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Look at this lamp my sister made. She rewired an old monocular microscope to hold a light bulb

and then she made a lampshade out of glass histology slides, which are framed by prints of antique drawing of retina histology

I now have the most coveted lamp in the history of all of pathology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Atico Export: Trusted Student Microscope Suppliers for Educational Excellence

Atico Export is a leading student microscope supplier, offering a wide range of high-quality microscopes that are perfect for educational purposes. Designed with young learners in mind, our microscopes combine ease of use with robust performance, making them ideal for students exploring the world of science. We understand that students need reliable, affordable, and durable tools to help them excel in their studies, which is why we provide microscopes that meet the highest standards of optical clarity and ergonomic design.
Our student microscopes come in a variety of models, including monocular and binocular types, each featuring high-resolution optics, adjustable focus, and bright LED illumination for clear visibility. Whether for school labs, science fairs, or personal exploration, our microscopes make learning engaging and interactive. As trusted student microscope suppliers, we provide high-quality instruments that allow students to gain hands-on experience, fostering curiosity and a deeper understanding of the natural world. Browse our selection today and invest in tools that inspire the next generation of scientists.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
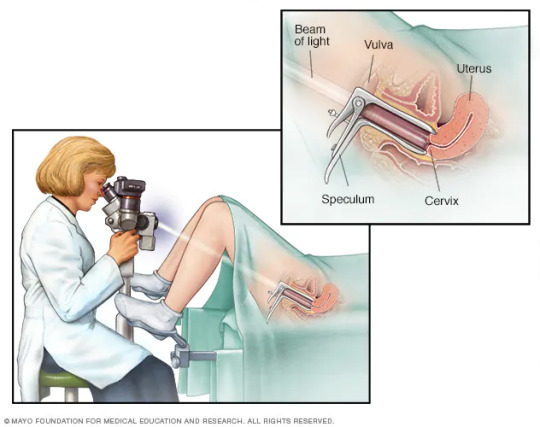
did you guys know there was a procedure where you shoot a beam of light into the vagina and look at the cervix through a microscope
A colposcope is used to identify visible clues suggestive of abnormal tissue. It functions as a lighted binocular or monocular microscope to magnify the view of the cervix, vagina, and vulvar surface. Low magnification (2× to 6×) may be used to obtain a general impression of the surface architecture. 8× to 25× magnification are utilized to evaluate the vagina and cervix. High magnification together with green filter is often used to identify certain vascular patterns that may indicate the presence of more advanced pre-cancerous or cancerous lesions.

19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Product Description If your phone with armored phone case or bulky phone case, please take it off in order to ensure the phone fits the clamp well. Not apply for rifile scope. The body is made of zinc alloy. The phone clamp is made of high strength PA Plastic. One purchase for a long-time use. Aluminum alloy shell;sturdy durable and lightweight;the phone clamp made of high strength PA plastic and features adjustable locking mechanism with a steel bolt not a spring Fits eyepiece diameter from 25 to 48mm and 1.25" telescope;not fit 2" eyepieces;compatible with microscope;telescope;binoculars;monocular;spotting scope;night vision monocular and most optical device 55 to 100mm has been tested fits for iphone;iphone 5;5s;6;6 plus;7;7plus;Sony;Sony Xperia Z;Samsung Note;Samsung Galaxy S7;Galaxy 7;Galaxy 5;Galaxy Note 5;Samsung Note 4;ECT;Moto G5+ and many other brands Works great for the phone in the up and down position taking pictures and recording sideways or in distant;keys capture the best videos of world successfully is practice and patience The surface to connect phone and eyepiece are covered by soft EVA pad, that prevent your device from being scratched or damaged. Tripod Mountable [ad_2]
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text

Monocular zoom microscope
Monocular zoom microscope is a precise optical system providing high resolution and sharp stereoscopic images. It is flexibly equipped with a microscopic stand. It can be integrated in a semi-conductor and integrate circuit board production line. Adapts to C-mount, and works with various digital cameras.
0 notes
Text
Inverted portable biological microscope LIBM-D10
Labtron Inverted Portable Biological Microscope features a lightweight handheld design, ideal for fieldwork and confined spaces like glove boxes or environmental cabinets. It offers high-resolution specimen observation, a monocular head, inverted stage for liquid samples, focus knob, optional camera attachment and a compact portable stand.

0 notes
Text
Polarizing Microscope 40x – 400x
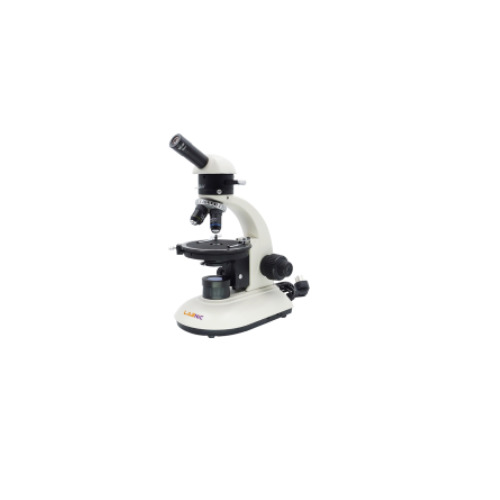

Labnic Polarizing Microscope features an achromatic optical system with a monocular head, 30° inclination, and 360° rotation. It offers a 40x–400x magnification range, a quadruple outward revolving nosepiece, and a lockable round working stage for precise and stable observations.
0 notes
Text

Explore a wide range of Microscopes for scientific, industrial, and educational use. Find top Microscopes Suppliers, Manufacturers & Exporters.
Monocular Microscope
Monocular Microscope Suppliers
Monocular Microscope Manufacturer
1 note
·
View note
Text
Microscopes Lab Equipment Manufacturers, Suppliers and Exporters in India
Welcome to Educational Equipment India, your premier destination for high-quality lab equipment tailored to meet your educational needs. As a leading lab equipment manufacturer in India, we take pride in fueling curiosity and fostering learning through our innovative products.

An Entire List of Microscopes Lab Equipment and How to Use Them
1. Monocular Biological Microscope, 400x, LED:
Explore the world of microscopic organisms with our Monocular Biological Microscope, offering 400x magnification for detailed observation.
LED illumination ensures bright and clear images, ideal for educational and professional use.
Compact design for easy portability and storage.
Perfect for students, hobbyists, and professionals in biology, microbiology, and related fields.
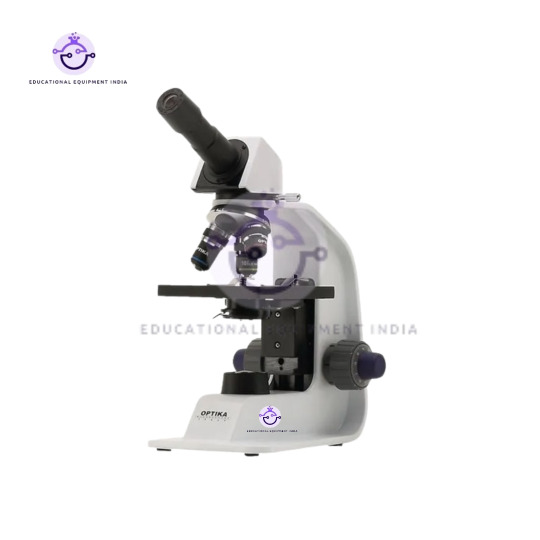
2. Binocular Microscope 1000x, LED:
Dive deeper into the microcosm with our Binocular Microscope featuring 1000x magnification, revealing intricate details with precision.
Equipped with LED illumination for enhanced visibility and clarity.
Dual eyepieces provide comfortable viewing for extended periods, perfect for research labs and educational institutions.
Robust construction ensures durability and reliability.
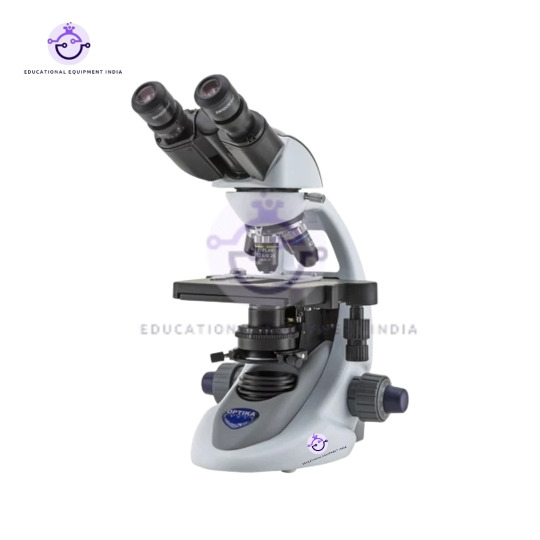
3. Monocular Biological Microscope 400x – Mirror:
Experience versatility with our Monocular Biological Microscope offering 400x magnification, supplemented by mirror illumination for flexible usage in various environments.
Ideal for fieldwork and outdoor exploration, eliminating the need for external power sources.
Compact and lightweight design for on-the-go observations.
Suitable for students, field researchers, and enthusiasts.
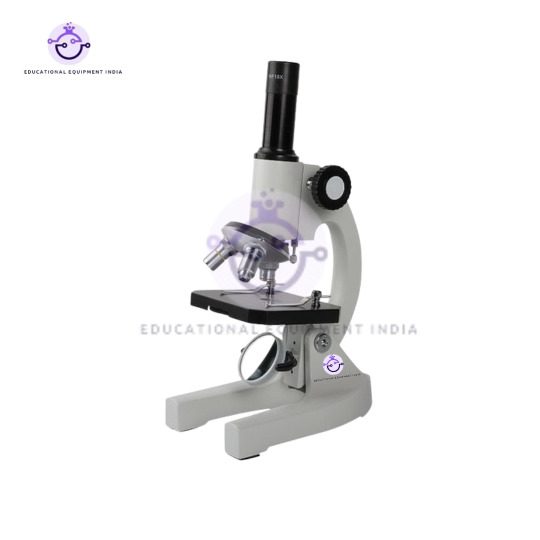
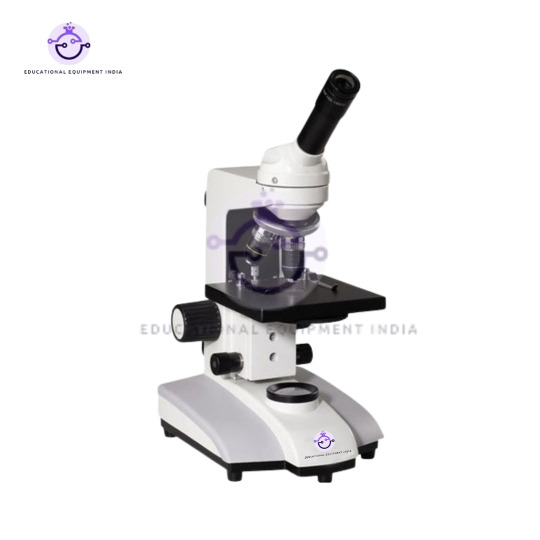
4. Monocular Microscope:
Discover the unseen world with our Monocular Microscope, a versatile tool for scientific exploration and educational purposes.
Adjustable magnification options cater to a wide range of applications, from basic observation to detailed analysis.
Compact and user-friendly design suitable for beginners and professionals alike.
Compatible with various accessories for expanded functionality.
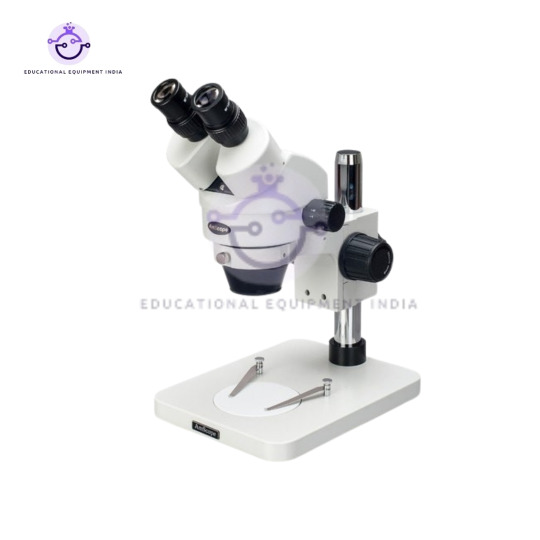
5. Stereo Binocular Microscope:
Gain a three-dimensional perspective on specimens with our Stereo Binocular Microscope, offering enhanced depth perception and spatial awareness.
Designed for intricate tasks such as dissection, soldering, and jewelry making, providing precision and clarity.
Binocular eyepieces ensure comfortable viewing, reducing eye strain during prolonged use.
Perfect for hobbyists, artisans, and professionals in fields requiring precise visualization.
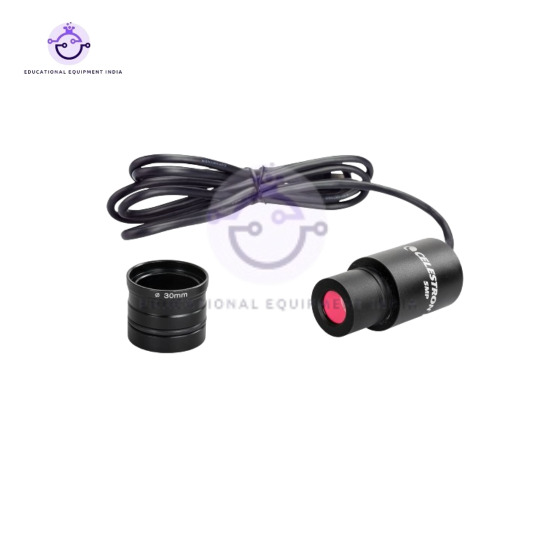
6. Microscope Digital Camera, 5MP:
Capture and document your microscopic discoveries with our Microscope Digital Camera, boasting 5MP resolution for high-quality images.
Easily attachable to most microscopes, transforming your device into a digital imaging system.
User-friendly software allows for image processing, measurement, and sharing.
Ideal for research, education, and documentation purposes.

How to use them and where:
Monocular Biological Microscope (400x, LED): Start by placing the specimen on the stage and adjusting the focus using the coarse and fine adjustment knobs. Illuminate the specimen with the LED light source for enhanced visibility. Ideal for educational institutions, laboratories, and field research.
Binocular Microscope (1000x, LED): Similar to the monocular microscope, adjust focus and illumination for clear observation. Dual eyepieces provide a comfortable viewing experience, making it suitable for advanced research, medical laboratories, and professional settings.
Monocular Biological Microscope (400x – Mirror): Utilize the mirror illumination for outdoor exploration and fieldwork. Its portable design makes it perfect for on-the-go observations in environments without access to power sources, such as forests, fields, and remote areas.
Monocular Microscope: As a versatile tool, this microscope can be used in various settings, including classrooms, home laboratories, and hobbyist workshops. Adjust the magnification according to your observation needs and explore the microscopic world with ease.
Stereo Binocular Microscope: Employ this microscope for tasks requiring depth perception and spatial awareness, such as dissection, soldering, and jewelry making. Its ergonomic design and comfortable eyepieces make it suitable for prolonged use in workshops, artisan studios, and manufacturing facilities.
Microscope Digital Camera (5MP): Attach the digital camera to your microscope to capture high-resolution images of microscopic specimens. Use the accompanying software for image processing, measurement, and sharing. Ideal for documentation, research, and educational purposes in laboratories, universities, and medical institutions.
0 notes
Text
Stereo Microscope

A stereo microscope, also known as a dissecting microscope or stereoscopic microscope, is an optical microscope variant designed for low-magnification observation of three-dimensional objects. Unlike compound microscopes, which use a single objective lens to magnify the specimen, stereo microscopes have two separate optical paths with two eyepieces (binocular) or one eyepiece (monocular), providing a three-dimensional view of the sample.
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Product Description Phone adapter for telescope Installation Procedure Microscope Mobile Holder 【Enjoy Exploring Fun】 This Telescope Phone Mount Allows You To Capture The Beauty Of The World Easily Through Your Screen. Connect Your Phone With Telescope Or Microscope To Explore Far Beautiful Scene And Amazing Micro World. 【Widely Range Applications】 The smartphone photo adapter holder is suitable for eyepieces with 25mm-48mm outer diameter and can be mounted on spotting scopes, monocular, binoculars, astronomical telescopes, and microscope eyepieces. Compatible with Android and iPhone smartphones with a width of 56-99mm / 2.2-3.9", Fits eyepieces with 25-48mm / 1-1.9" diameter. You can capture photos & videos through eyepieces. 【Applicable Cellphone】 This microscope phone adapter ONLY works with the phone width range: 56-99 mm / 2.2-3.9 inch. 【Easy To Use】 Simply Place Your Phone In The Adapter, Center Your Phone’s Camera Over The Eyepiece, And Use The Knobs To Secure The Adapter In Place. 【Safe & Durable】 Telescope Adapter For Mobile Is Zinc Alloy Shell, Sturdy Durable And Lightweight. The Phone Clamp Made Of High Strength Pa Plastic And Features Adjustable Locking Mechanism With a Steel Bolt Not a Spring. [ad_2]
0 notes