#outsourced labeling of data
Photo
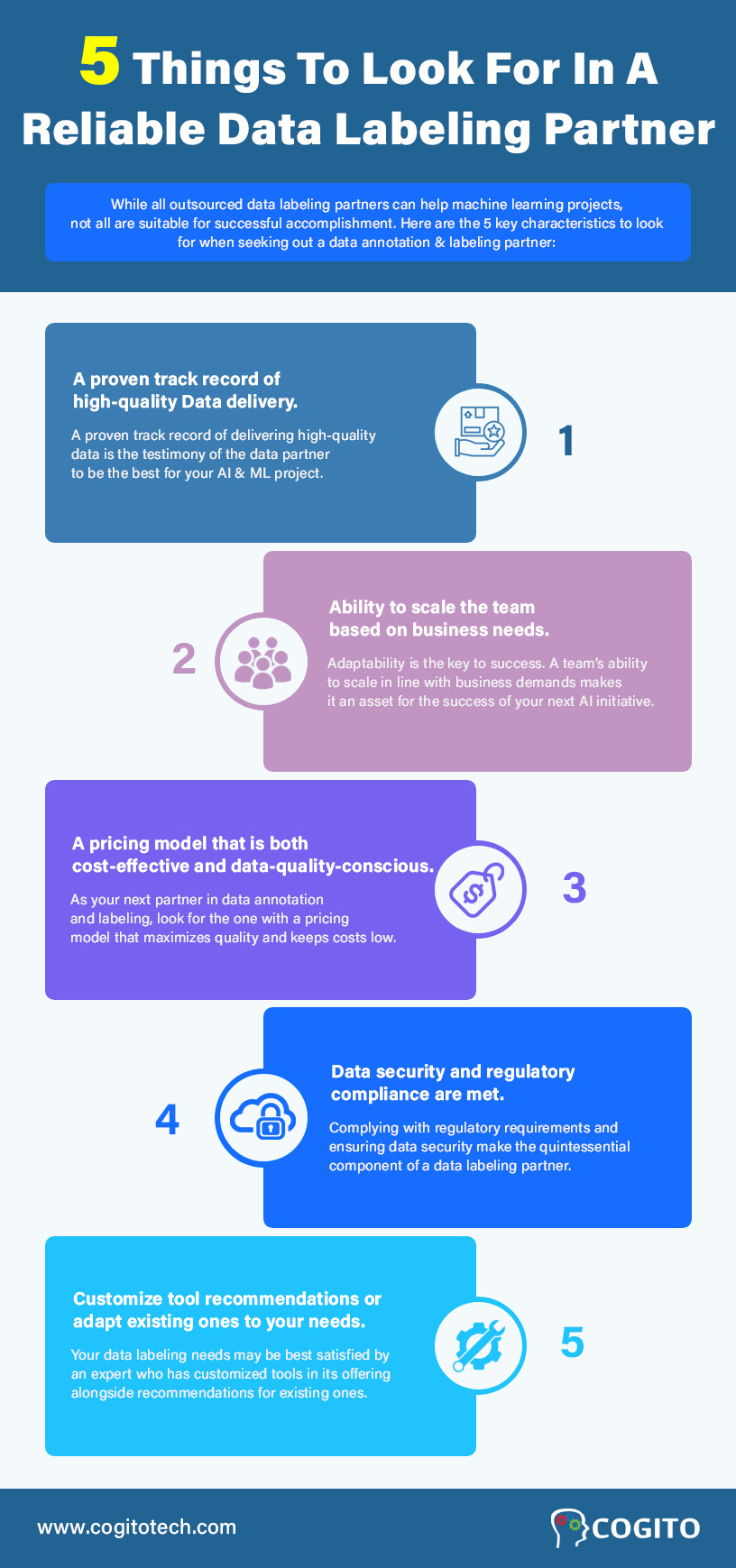
The outsourced labeling of data is popular with machine learning projects, but not every data labeling partner is suitable for successfully completing a machine learning project. Check out these five key characteristics when searching for a data annotation & labeling partner.
#outsourced labeling of data#data security#data quality#Data Collection#datasets#machine learning project#machine learning#cogito#annotation
1 note
·
View note
Text
Explore how data labeling services are revolutionizing AI models with these six key use cases. From improving image recognition to enhancing natural language processing, data labeling is crucial for accurate AI performance. Learn how industries leverage these services for better decision-making and efficiency. Visit our blog to delve deeper into the transformative impact of data labeling on AI development and implementation. Engage with cutting-edge insights today.
#data labeling services#data labeling#outsource data labeling services#data annotation#data annotation services.
0 notes
Text

Data labeling in machine learning involves the process of assigning relevant tags or annotations to a dataset, which helps the algorithm to learn and make accurate predictions.
Learn more
0 notes
Text

Any AI model is as smart as the data it is fed with. Data labeling outsourcing helps you get pixel-perfect and semantically segmented accurately labeled training datasets to fuel the smart models. Get in touch with professionals today.
#Data labeling outsourcing#data labelling#data labeling companies#data labeling for machine learning
1 note
·
View note
Link
You cannot prioritize your AI model’s precision and accuracy without ensuring quality in your image datasets. Here we help you develop understanding into how to effectively manage recurring challenges by prescribing quality solutions and best practices.
#label images#label images properly for ai#top label images challenges for ai#data annotation tools#outsource image labeling#image labeling practice#image annotation quality
0 notes
Text
#AI-based models depend heavily on accurate data labeling of training data sets. As the backbone of successful AI training processes#data labeling helps advanced algorithms to use unstructured data as input.#🌐 https://www.triyock.com/#📞 +15519984727#managedservices#businessprocessoutsourcing#bpo#outsourcing#outsourcingservices#business#bposervices#businessprocess
0 notes
Text
AI projects like OpenAI’s ChatGPT get part of their savvy from some of the lowest-paid workers in the tech industry—contractors often in poor countries paid small sums to correct chatbots and label images. On Wednesday, 97 African workers who do AI training work or online content moderation for companies like Meta and OpenAI published an open letter to President Biden, demanding that US tech companies stop “systemically abusing and exploiting African workers.”
Most of the letter’s signatories are from Kenya, a hub for tech outsourcing, whose president, William Ruto, is visiting the US this week. The workers allege that the practices of companies like Meta, OpenAI, and data provider Scale AI “amount to modern day slavery.” The companies did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
A typical workday for African tech contractors, the letter says, involves “watching murder and beheadings, child abuse and rape, pornography and bestiality, often for more than 8 hours a day.” Pay is often less than $2 per hour, it says, and workers frequently end up with post-traumatic stress disorder, a well-documented issue among content moderators around the world.
The letter’s signatories say their work includes reviewing content on platforms like Facebook, TikTok, and Instagram, as well as labeling images and training chatbot responses for companies like OpenAI that are developing generative-AI technology. The workers are affiliated with the African Content Moderators Union, the first content moderators union on the continent, and a group founded by laid-off workers who previously trained AI technology for companies such as Scale AI, which sells datasets and data-labeling services to clients including OpenAI, Meta, and the US military. The letter was published on the site of the UK-based activist group Foxglove, which promotes tech-worker unions and equitable tech.
In March, the letter and news reports say, Scale AI abruptly banned people based in Kenya, Nigeria, and Pakistan from working on Remotasks, Scale AI’s platform for contract work. The letter says that these workers were cut off without notice and are “owed significant sums of unpaid wages.”
“When Remotasks shut down, it took our livelihoods out of our hands, the food out of our kitchens,” says Joan Kinyua, a member of the group of former Remotasks workers, in a statement to WIRED. “But Scale AI, the big company that ran the platform, gets away with it, because it’s based in San Francisco.”
Though the Biden administration has frequently described its approach to labor policy as “worker-centered.” The African workers’ letter argues that this has not extended to them, saying “we are treated as disposable.”
“You have the power to stop our exploitation by US companies, clean up this work and give us dignity and fair working conditions,” the letter says. “You can make sure there are good jobs for Kenyans too, not just Americans."
Tech contractors in Kenya have filed lawsuits in recent years alleging that tech-outsourcing companies and their US clients such as Meta have treated workers illegally. Wednesday’s letter demands that Biden make sure that US tech companies engage with overseas tech workers, comply with local laws, and stop union-busting practices. It also suggests that tech companies “be held accountable in the US courts for their unlawful operations aboard, in particular for their human rights and labor violations.”
The letter comes just over a year after 150 workers formed the African Content Moderators Union. Meta promptly laid off all of its nearly 300 Kenya-based content moderators, workers say, effectively busting the fledgling union. The company is currently facing three lawsuits from more than 180 Kenyan workers, demanding more humane working conditions, freedom to organize, and payment of unpaid wages.
“Everyone wants to see more jobs in Kenya,” Kauna Malgwi, a member of the African Content Moderators Union steering committee, says. “But not at any cost. All we are asking for is dignified, fairly paid work that is safe and secure.”
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Though the Biden administration has frequently described its approach to labor policy as “worker-centered.” The African workers’ letter argues that this has not extended to them, saying “we are treated as disposable.”
“You have the power to stop our exploitation by US companies, clean up this work and give us dignity and fair working conditions,” the letter says. “You can make sure there are good jobs for Kenyans too, not just Americans."
Tech contractors in Kenya have filed lawsuits in recent years alleging that tech-outsourcing companies and their US clients such as Meta have treated workers illegally. Wednesday’s letter demands that Biden make sure that US tech companies engage with overseas tech workers, comply with local laws, and stop union-busting practices. It also suggests that tech companies “be held accountable in the US courts for their unlawful operations aboard, in particular for their human rights and labor violations.”
The letter comes just over a year after 150 workers formed the African Content Moderators Union. Meta promptly laid off all of its nearly 300 Kenya-based content moderators, workers say, effectively busting the fledgling union. The company is currently facing three lawsuits from more than 180 Kenyan workers, demanding more humane working conditions, freedom to organize, and payment of unpaid wages.
“Everyone wants to see more jobs in Kenya,” Kauna Malgwi, a member of the African Content Moderators Union steering committee, says. “But not at any cost. All we are asking for is dignified, fairly paid work that is safe and secure.”
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
1800 Ghosts, and counting.
So, 1800 or so ghosts live in my brain. I put them there, not on purpose, but they lodged in my mind during the course of my daily work as I found them, checked, referenced, located and georeferenced their ends. Most are pretty quiet, and really only pop up when I do something that specifically reminds me of them. But some of them are quite active, and pop into my head whenever I pass near where they died or touch on some aspect of the subject of their death.
They all died in some sort of landslide, avalanche, debris flow or rockfall, both natural or anthropogenic. Some of them I know next to nothing about. Others of them I know how they died, graphically, medically accurate details in both time, place, physics and biology. At length. Some I stood nearby as they were exhumed. I Smelt them, I stood by as they took their last journey. I looked into the faces of those who had to find, pack, lift and move them. Very occasionally I have to talk to their families. I'm not good at that.
Some of them are close relatives and ancestors of mine, but most are not. They are just people, who were doing the things that just people do.
But having them there, and knowing their story, stories, makes me a bit twitchy. There are some areas of my country, towns, cities, mountains, farmlands, forests, rivers, that I can't be in without thinking of these ghosts. Some of them are so active in my head that certain streets, certain valleys or hills, make me so uncomfortable it feels like there's someone with a rifle focussed on me, just out of sight. Because I know how dangerous the geography is, and who died there, when, and how often. Often in graphic detail.
Most of the time I'm not close in to these ghosts unless there's a major emergency response, which I am part of. Most of the work is dry, digital, old documents, GIS software, geomorphology and weather and rainfall and rock strata and pore pressure and earthquake and clay and Gravity. Gravity.
I _Enjoy_ this work. I do it for public service, because it leads into maps, risks, hazards, fatality risks, etc, making things safer for people in the future. But it leaves ghosts in my head. So I'm a bit fucked up by it.
So I now look at the people who do this day in, day out, for our soulless social media landscape. The contracted mechanical turks behind the trust and security teams, the people who classify images and videos and media behind the term 'AI' (and what an ugly term that is, because there is not yet any AI worthy of the name), as it hoses through our social media feeds straight from warzones and every other zone where something awful happens, and think how much worse this is than what I do, for better money, shorter hours, and with actual recourse to professional medical help when I need it:
Outsourcing the hard bits to where it's cheaper, to where the jurisdiction is more lenient, to where it raises less waves, is not going to help anyone in the long run. It's abdication of our own humanity made possible by corporate structure.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
#ai#cogitotech usa#annotation#data annotation#data collection#machine learning#content#data annotation companies#cogito ai#data quality#Outsourcing Data Labeling
0 notes
Text
📍 Collaborate With Top Data Labeling Companies and Ensure Precision in AI/ML Implementation
📌 Elevate your AI projects with top-notch data annotation and labeling services. Our expert team ensures accurate and reliable data tagging, empowering your Machine Learning models with precision. Explore innovative solutions and streamline your data workflow for unparalleled performance in the realm of Artificial Intelligence. Damco, a leading data annotation company, supports businesses by providing AI data annotation and labeling services, enhancing the accuracy of their Machine Learning algorithm predictions.
#data annotation and labeling services#data annotation outsourcing#data annotation companies#data annotation services#data annotation for ml
0 notes
Text
Why Outsourcing Can Help With Data Labeling Companies
The effectiveness of artificial intelligence and robotic process automation depends on the quality of training data. Data labeling, the process of assigning labels to data samples, is crucial for creating machine learning models that can learn from data. In this article, we discuss the importance of data labeling for companies and explore the benefits of outsourcing this task to specialists.
The Use of Data Labeling on Companies
Machine learning algorithms require labeled data and tags attached to raw data samples like visuals, sounds, and texts. Companies can enhance their decision-making processes using machine learning algorithms with better-trained models. When fed more data, a well-trained machine learning system can create more complex forecasting models.
The Importance of Outsourcing Data Labeling
High-quality data is essential for efficient machine learning models. Many businesses prefer to outsource the labeling of their data to specialists to reap the benefits of their machine-learning models. Outsourcing data labeling can save time and produce better results than in-house data labeling.
Comparing In-house, Crowdsourcing, and Outsourcing Data Labeling:
In-house data labeling involves employing data scientists and infrastructure within the organization. Crowdsourcing recruits regular people to perform tasks like labeling data. Outsourcing data labeling to specialists can be a better option due to the following reasons:
Required Time - Outsourcing data labeling is preferable to doing it in-house because it takes time to train a team and construct the infrastructure needed for data labeling. Crowdsourcing can also be slow due to the internet.
Price - Outsourcing produces better results than in-house data labeling because outsourcing firms spend less on technology and hire fewer data scientists to focus on the labeling process. However, crowdsourcing is more expensive than outsourcing.
Data Quality in Terms of Labeling - Outsourcing and in-house data labeling produce higher quality results than crowdsourcing because trained professionals are used. However, different outsourcing businesses may have varying degrees of expertise regarding data labeling.
Security - Outsourcing offers less security than in-house but more than crowdsourcing. Outsourcing organizations have certifications and various security procedures that lessen the likelihood of data exploitation.
Conclusion
Outsourcing data labeling can significantly reduce costs while still producing high-quality results. Professional firms like Springbord can safely outsource annotation work and complete complex, diverse projects of significant scale. Outsourcing data labeling provides businesses access to highly qualified workers, cutting-edge technology, and rigorous quality assurance procedures.
0 notes
Text

Data labeling outsourcing is a time and cost-effective way to get quality training sets at your disposal. So, let the professionals at Damco assist you with this!
#data labeling companies#ai data labeling companies#data labeling for machine learning#data labeling#data labeling outsourcing
0 notes
Text
Across a sterile white table in a windowless room, I’m introduced to a woman in her forties. She has a square jaw and blonde hair that has been pulled back from her face with a baby-blue scrunchie. “The girls call me Marmalade,” she says, inviting me to use her prison nickname. Early on a Wednesday morning, Marmalade is here, in a Finnish prison, to demonstrate a new type of prison labor.
The table is bare except for a small plastic bottle of water and an HP laptop. During three-hour shifts, for which she’s paid €1.54 ($1.67) an hour, the laptop is programmed to show Marmalade short chunks of text about real estate and then ask her yes or no questions about what she’s just read. One question asks: “is the previous paragraph referring to a real estate decision, rather than an application?”
“It’s a little boring,” Marmalade shrugs. She’s also not entirely sure of the purpose of this exercise. Maybe she is helping to create a customer service chatbot, she muses.
In fact, she is training a large language model owned by Metroc, a Finnish startup that has created a search engine designed to help construction companies find newly approved building projects. To do that, Metroc needs data labelers to help its models understand clues from news articles and municipality documents about upcoming building projects. The AI has to be able to tell the difference between a hospital project that has already commissioned an architect or a window fitter, for example, and projects that might still be hiring.
Around the world, millions of so-called “clickworkers” train artificial intelligence models, teaching machines the difference between pedestrians and palm trees, or what combination of words describe violence or sexual abuse. Usually these workers are stationed in the global south, where wages are cheap. OpenAI, for example, uses an outsourcing firm that employs clickworkers in Kenya, Uganda, and India. That arrangement works for American companies, operating in the world’s most widely spoken language, English. But there are not a lot of people in the global south who speak Finnish.
That’s why Metroc turned to prison labor. The company gets cheap, Finnish-speaking workers, while the prison system can offer inmates employment that, it says, prepares them for the digital world of work after their release. Using prisoners to train AI creates uneasy parallels with the kind of low-paid and sometimes exploitive labor that has often existed downstream in technology. But in Finland, the project has received widespread support.
“There's this global idea of what data labor is. And then there's what happens in Finland, which is very different if you look at it closely,” says Tuukka Lehtiniemi, a researcher at the University of Helsinki, who has been studying data labor in Finnish prisons.
For four months, Marmalade has lived here, in Hämeenlinna prison. The building is modern, with big windows. Colorful artwork tries to enforce a sense of cheeriness on otherwise empty corridors. If it wasn’t for the heavy gray security doors blocking every entry and exit, these rooms could easily belong to a particularly soulless school or university complex.
Finland might be famous for its open prisons—where inmates can work or study in nearby towns—but this is not one of them. Instead, Hämeenlinna is the country’s highest-security institution housing exclusively female inmates. Marmalade has been sentenced to six years. Under privacy rules set by the prison, WIRED is not able to publish Marmalade’s real name, exact age, or any other information that could be used to identify her. But in a country where prisoners serving life terms can apply to be released after 12 years, six years is a heavy sentence. And like the other 100 inmates who live here, she is not allowed to leave.
When Marmalade first arrived, she would watch the other women get up and go to work each morning: they could volunteer to clean, do laundry, or sew their own clothes. And for a six hour shift, they would receive roughly €6 ($6.50). But Marmalade couldn’t bear to take part. “I would find it very tiring,” she says. Instead she was spending long stretches of time in her cell. When a prison counselor suggested she try “AI work,” the short, three-hour shifts appealed to her, and the money was better than nothing. “Even though it’s not a lot, it’s better than staying in the cell,” she says” She’s only done three shifts so far, but already she feels a sense of achievement.
This is one of three Finnish prisons where inmates can volunteer to earn money through data labor. In each one, there are three laptops set up for inmates to take part in this AI work. There are no targets. Inmates are paid by the hour, not by their work’s speed or quality. In Hämeenlinna, around 20 inmates have tried it out, says Minna Inkinen, a prison work instructor, with cropped red hair, who sits alongside Marmalade as we talk. “Some definitely like it more than others”. When I arrive at the prison on a Wednesday morning, the sewing room is already busy. Inmates are huddled over sewing machines or conferring in pairs over mounds of fabric. But the small room where the AI work takes place is entirely empty until Marmalade arrives. There are only three inmates in total who regularly volunteer for AI shifts, Inkinen says, explaining that the other two are currently in court. “I would prefer to do it in a group,” says Marmalade, adding that she keeps the door open so she can chat with the people sewing next door, in between answering questions.
Those questions have been manually written in an office 100 kilometers south of the prison, in a slick Helsinki coworking space. Here, I meet Metroc’s tall and boyish founder and CEO, Jussi Virnala. He leads me to a stiflingly hot phone booth, past a row of indoor swings, a pool table, and a series of men in suits. It’s an exciting week, he explains, with a grin. The company has just announced a €2 million ($2.1 million) funding round which he plans to use to expand across the Nordics. The investors he spoke with were intrigued by the company’s connection to Finland’s prisons, he says. “Everyone was just interested in and excited about what an innovative way to do it,” says Virnala. “I think it’s been really valuable product-wise.”
It was Virnala’s idea to turn to the prisons for labor. The company needed native Finnish speakers to help improve its large language model’s understanding of the construction-specific language. But in a high-wage economy like Finland, finding those data laborers was difficult. The Finnish welfare system’s generous unemployment benefits leaves little incentive for Finns to sign up to low-wage clickwork platforms like Amazon’s Mechanical Turk. “Mechanical Turk didn’t have many Finnish-language workers,” says Virnala. At the same time, he adds, automatic translation tools are still no good at Finnish, a language with only 5 million native speakers.
When Virnala pitched his idea to Pia Puolakka, head of the Smart Prison Project at Finland’s prison and probation agency, she was instantly interested, she says. Before the pandemic, another Finnish tech company called Vainu had been using prisoners for data labor. But Vainu abruptly pulled out after a disagreement between cofounders prompted Tuomas Rasila, who had been in charge of the project, to leave the company.
By the time Virnala approached her with his proposal in 2022, Puolakka was eager to resurrect the AI work. Her job is to try and make the relationship between Finnish prisons and the internet more closely resemble the increasingly digital outside world. So far, she has been installing laptops in individual cells so inmates can browse a restricted list of websites and apply for permission to make video calls. She considers data labor just another part of that mission.
The aim is not to replace traditional prison labor, such as making road signs or gardening. It’s about giving prisoners more variety. Data labeling can only be done in three-hour shifts. “It might be tiring to do this eight hours a day, only this type of work,” she says, adding that it would be nice if inmates did the data labeling alongside other types of prison labor. “This type of work is the future, and if we want to prepare prisoners for life outside prison, a life without crime, these types of skills might be at least as important as the traditional work types that prisons provide,” she says.
But how much data labeling offers inmates skills that are transferable to work after prison is unclear. Tuomas Rasila, the now estranged cofounder of Vainu, who managed the prison project there for a year, admits he has no evidence of this; the project wasn’t running for long enough to collect it, he says. “I think asking people, who might feel outside of society, to train the most high-tech aspect of a modern society is an empowering idea.”
However, others consider this new form of prison labor part of a problematic rush for cheap labor that underpins the AI revolution. “The narrative that we are moving towards a fully automated society that is more convenient and more efficient tends to obscure the fact that there are actual human people powering a lot of these systems,” says Amos Toh, a senior researcher focusing on artificial intelligence at Human Rights Watch.
For Toh, the accelerating search for so-called clickworkers has created a trend where companies are increasingly turning to groups of people who have few other options: refugees, populations in countries gripped by economic crisis—and now prisoners.
“This dynamic is a deeply familiar one,” says Toh. “What we are seeing here is part of a broader phenomenon where the labor behind building tech is being outsourced to workers that toil in potentially exploitative working conditions.”
Toh is also skeptical about whether data labor can help inmates build digital skills. “There are many ways in which people in prison can advance themselves, like getting certificates and taking part in advanced education,” he says. “But I'm skeptical about whether doing data labeling for a company at one euro per hour will lead to meaningful advancement.” Hämeenlinna prison does offer inmates online courses in AI, but Marmalade sits blank-faced as staff try to explain its benefits.
Science
Your weekly roundup of the best stories on health care, the climate crisis, genetic engineering, robotics, space, and more. Delivered on Wednesdays.
By the time I meet Lehtiniemi, the researcher from Helsinki University, I’m feeling torn about the merits of the prison project. Traveling straight from the prison, where women worked for €1.54 an hour, to Metroc’s offices, where the company was celebrating a €2 million funding round, felt jarring. In a café, opposite the grand, domed Helsinki cathedral, Lehtiniemi patiently listens to me describe that feeling.
But Lehtiniemi’s own interviews with inmates have given him a different view—he’s generally positive about the project. On my point about pay disparity, he argues this is not an ordinary workforce in mainstream society. These people are in prison. “Comparing the money I get as a researcher and what the prisoner gets for their prison labor, it doesn't make sense,” he says. “The only negative thing I’ve heard has been that there’s not enough of this work. Only a few people can do it,” he says, referring to the limit of three laptops per prison.
“When we think about data labor, we tend to think about Mechanical Turk, people in the global south or the rural US,” he says. But for him, this is a distinct local version of data labor, which comes with a twist that benefits society. It’s giving prisoners cognitively stimulating work—compared to other prison labor options—while also representing the Finnish language in the AI revolution.
Without this kind of initiative, Lehtiniemi worries that non-English languages are being locked out of this next generation of technology. Smart speakers still struggle to understand Finnish dialects. “Not all Finnish people speak English very well, so there's a need for these local forms of data labeling as well,” Lehtiniemi says. Metroc isn’t the only company that has been forced to get creative about finding Finnish data labor. In 2011, the national library created a game to incentivize volunteers to help digitize its archive. In 2020, broadcaster YLE teamed up with Helsinki University and the state development company VAKE to ask volunteers to donate recordings of them speaking Finnish.
There is a sense in Finland that the prison project is just the beginning. Some are worried it could set a precedent that could introduce more controversial types of data labeling, like moderating violent content, to prisons. “Even if the data being labeled in Finland is uncontroversial right now, we have to think about the precedent it sets,” says Toh. “What stops companies from outsourcing data labeling of traumatic and unsavory content to people in prison, especially if they see this as an untapped labor pool?”
It's also not clear whether labor conditions in Finland's prisons—which famously focus on rehabilitation—could be replicated in other countries with a less progressive approach to justice. In the US, 76 percent of prisoners report that prison labor is mandatory, according to civil rights group, the ACLU. “The prison system in the United States is very, very different from what we have in Finland or Nordic countries. It's a completely different idea,” says Rasila. “In Finland, there is an exclusively positive feeling around the project because everyone knows that this is very voluntary.”
AI companies are only going to need more data labor, forcing them to keep seeking out increasingly unusual labor forces to keep pace. As Metroc plots its expansion across the Nordics and into languages other than Finnish, Virnala is considering whether to expand the prison labor project to other countries. “It’s something we need to explore,” he says.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best data extraction services in USA
In today's fiercely competitive business landscape, the strategic selection of a web data extraction services provider becomes crucial. Outsource Bigdata stands out by offering access to high-quality data through a meticulously crafted automated, AI-augmented process designed to extract valuable insights from websites. Our team ensures data precision and reliability, facilitating decision-making processes.
For more details, visit: https://outsourcebigdata.com/data-automation/web-scraping-services/web-data-extraction-services/.
About AIMLEAP
Outsource Bigdata is a division of Aimleap. AIMLEAP is an ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified global technology consulting and service provider offering AI-augmented Data Solutions, Data Engineering, Automation, IT Services, and Digital Marketing Services. AIMLEAP has been recognized as a ‘Great Place to Work®’.
With a special focus on AI and automation, we built quite a few AI & ML solutions, AI-driven web scraping solutions, AI-data Labeling, AI-Data-Hub, and Self-serving BI solutions. We started in 2012 and successfully delivered IT & digital transformation projects, automation-driven data solutions, on-demand data, and digital marketing for more than 750 fast-growing companies in the USA, Europe, New Zealand, Australia, Canada; and more.
-An ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified
-Served 750+ customers
-11+ Years of industry experience
-98% client retention
-Great Place to Work® certified
-Global delivery centers in the USA, Canada, India & Australia
Our Data Solutions
APISCRAPY: AI driven web scraping & workflow automation platform
APISCRAPY is an AI driven web scraping and automation platform that converts any web data into ready-to-use data. The platform is capable to extract data from websites, process data, automate workflows, classify data and integrate ready to consume data into database or deliver data in any desired format.
AI-Labeler: AI augmented annotation & labeling solution
AI-Labeler is an AI augmented data annotation platform that combines the power of artificial intelligence with in-person involvement to label, annotate and classify data, and allowing faster development of robust and accurate models.
AI-Data-Hub: On-demand data for building AI products & services
On-demand AI data hub for curated data, pre-annotated data, pre-classified data, and allowing enterprises to obtain easily and efficiently, and exploit high-quality data for training and developing AI models.
PRICESCRAPY: AI enabled real-time pricing solution
An AI and automation driven price solution that provides real time price monitoring, pricing analytics, and dynamic pricing for companies across the world.
APIKART: AI driven data API solution hub
APIKART is a data API hub that allows businesses and developers to access and integrate large volume of data from various sources through APIs. It is a data solution hub for accessing data through APIs, allowing companies to leverage data, and integrate APIs into their systems and applications.
Locations:
USA: 1-30235 14656
Canada: +1 4378 370 063
India: +91 810 527 1615
Australia: +61 402 576 615
Email: [email protected]
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thousands of law enforcement officials and people applying to be police officers in India have had their personal information leaked online—including fingerprints, facial scan images, signatures, and details of tattoos and scars on their bodies. If that wasn’t alarming enough, at around the same time, cybercriminals have started to advertise the sale of similar biometric police data from India on messaging app Telegram.
Last month, security researcher Jeremiah Fowler spotted the sensitive files on an exposed web server linked to ThoughtGreen Technologies, an IT development and outsourcing firm with offices in India, Australia, and the US. Within a total of almost 500 gigabytes of data spanning 1.6 million documents, dated from 2021 until when Fowler discovered them in early April, was a mine of sensitive personal information about teachers, railway workers, and law enforcement officials. Birth certificates, diplomas, education certificates, and job applications were all included.
Fowler, who shared his findings exclusively with WIRED, says within the heaps of information, the most concerning were those that appeared to be verification documents linked to Indian law enforcement or military personnel. While the misconfigured server has now been closed off, the incident highlights the risks of companies collecting and storing biometric data, such as fingerprints and facial images, and how they could be misused if the data is accidentally leaked.
“You can change your name, you can change your bank information, but you can't change your actual biometrics,” Fowler says. The researcher, who also published the findings on behalf of Website Planet, says this kind of data could be used by cybercriminals or fraudsters to target people in the future, a risk that’s increased for sensitive law enforcement positions.
Within the database Fowler examined were several mobile applications and installation files. One was titled “facial software installation,” and a separate folder contained 8 GB of facial data. Photographs of people’s faces included computer-generated rectangles that are often used for measuring the distance between points of the face in face recognition systems.
There were 284,535 documents labeled as Physical Efficiency Tests that related to police staff, Fowler says. Other files included job application forms for law enforcement officials, profile photos, and identification documents with details such as “mole at nose” and “cut on chin.” At least one image shows a person holding a document with a corresponding photo of them included on it. “The first thing I saw was thousands and thousands of fingerprints,” Fowler says.
Prateek Waghre, executive director of Indian digital rights organization Internet Freedom Foundation, says there is “vast” biometric data collection happening across India, but there are added security risks for people involved in law enforcement. “A lot of times, the verification that government employees or officers use also relies on biometric systems,” Waghre says. “If you have that potentially compromised, you are in a position for someone to be able to misuse and then gain access to information that they shouldn’t.”
It appears that some biometric information about law enforcement officials may already be shared online. Fowler says after the exposed database was closed down he also discovered a Telegram channel, containing a few hundred members, which was claiming to sell Indian police data, including of specific individuals. “The structure, the screenshots, and a couple of the folder names matched what I saw,” says Fowler, who for ethical reasons did not purchase the data being sold by the criminals so could not fully verify it was exactly the same data.
“We take data security very seriously, have taken immediate steps to secure the exposed data,” a member of ThoughtGreen Technologies wrote in an email to WIRED. “Due to the sensitivity of data, we cannot comment on specifics in an email. However, we can assure you that we are investigating this matter thoroughly to ensure such an incident does not occur again.”
In follow-up messages, the staff member said the company had “raised a complaint” with law enforcement in India about the incident, but did not specify which organization they had contacted. When shown a screenshot of the Telegram post claiming to sell Indian police biometric data, the ThoughtGreen Technologies staff member said it is “not our data.” Telegram did not respond to a request for comment.
Shivangi Narayan, an independent researcher in India, says the country’s data protection law needs to be made more robust, and companies and organizations need to take greater care with how they handle people’s data. “A lot of data is collected in India, but nobody's really bothered about how to store it properly,” Narayan says. Data breaches are happening so regularly that people have “lost that surprise shock factor,” Narayan says. In early May, one cybersecurity company said it had seen a face-recognition data breach connected to one Indian police force, including police and suspect information.
The issues are wider, though. As governments, companies, and other organizations around the world increasingly rely on collecting people’s biometric data for proving their identity or as part of surveillance technologies, there’s an increased risk of the information leaking online and being abused. In Australia, for instance, a recent face recognition leak impacting up to a million people led to a person being charged with blackmail.
“So many other countries are looking at biometric verification for identities, and all of that information has to be stored somewhere,” Fowler says. “If you farm it out to a third-party company, or a private company, you lose control of that data. When a data breach happens, you’re in deep shit, for lack of a better term.”
10 notes
·
View notes