#page level restore in sql server
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India | NRS Infoways
In today’s hyper‑connected marketplace, a website is far more than a digital brochure—it is the beating heart of your brand experience, your lead‑generation engine, and your most valuable sales asset. Yet many businesses still treat their sites as “launch‑and‑forget” projects, only paying attention when something breaks. At NRS Infoways, we understand that real online success demands continuous care, proactive monitoring, and seamless enhancements. That’s why we’ve built our Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India to deliver round‑the‑clock peace of mind, bulletproof performance, and measurable ROI for forward‑thinking companies like yours.
Why Website Maintenance Matters—And Why “Reliable” Makes All the Difference
Search engines reward fast, secure, and regularly updated sites with higher rankings; customers reward them with trust and loyalty. Conversely, a sluggish, outdated, or vulnerable site can cost you traffic, conversions, and brand reputation—sometimes overnight. Our Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India go beyond the basic “fix‑it‑when‑it‑breaks” model. We combine proactive health checks, performance tuning, security hardening, and content optimization into a single, cohesive program that keeps your digital storefront open, polished, and ready for growth.
What Sets NRS Infoways Apart?
1. Proactive Performance Monitoring
We leverage enterprise‑grade monitoring tools that continuously scan load times, server resources, and user journeys. By identifying bottlenecks before they escalate, we ensure smoother experiences and higher conversion rates—24/7.
2. Robust Security & Compliance
From real‑time threat detection to regular firewall updates and SSL renewals, your site stays impervious to malware, SQL injections, and DDoS attacks. We align with global standards such as GDPR and PCI‑DSS, keeping you compliant and trustworthy.
3. Seamless Content & Feature Updates
Launching a new product line? Running a seasonal promotion? Our dedicated team updates layouts, landing pages, and plugins—often within hours—to keep your messaging sharp and relevant without disrupting uptime.
4. Data‑Driven Optimization
Monthly analytics reviews highlight user behavior, bounce rates, and conversion funnels. We translate insights into actionable tasks—A/B testing CTAs, compressing heavy images, or refining navigation—all folded into our maintenance retainer.
5. Transparent Reporting & SLAs
Every client receives detailed monthly reports covering task logs, incident resolutions, and performance metrics. Our Service Level Agreements guarantee response times as low as 30 minutes for critical issues, underscoring the “Reliable” in our Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India.
Real‑World Impact: A Success Snapshot
A Delhi‑based B2B SaaS provider reached out to NRS Infoways after repeated downtime eroded user trust and slashed demo bookings by 18 %. Within the first month of onboarding, we:
Migrated their site to a high‑availability cloud cluster
Deployed a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to fend off bot attacks
Compressed multimedia assets, cutting average load time from 4.2 s to 1.3 s
Implemented weekly backup protocols with versioned restores
Result? Organic traffic climbed 27 %, demo sign‑ups rebounded 31 %, and support tickets fell by half—proving that consistent, expert care translates directly into revenue.
Flexible Plans That Scale With You
Whether you manage a lean startup site or a sprawling enterprise portal, we offer tiered packages—Basic, Professional, and Enterprise—each customizable with à‑la‑carte add‑ons like e‑commerce catalog updates, multi‑language support, or advanced SEO audits. As your business evolves, our services scale seamlessly, ensuring you never pay for overhead you don’t need or sacrifice features you do.
Partner With NRS Infoways Today
Your website is too important to leave to chance. Join the growing roster of Indian businesses that rely on NRS Infoways for Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India and experience the freedom to innovate while we handle the technical heavy lifting. Ready to protect your digital investment, delight your visitors, and outpace your competition?
Connect with our maintenance experts now and power your growth with reliability you can measure.
0 notes
Text
Jobs Portal Nulled Script 4.1

Download the Best Jobs Portal Nulled Script for Free Are you looking for a powerful, customizable, and free job board solution to launch your own employment platform? The Jobs Portal Nulled Script is your ideal solution. This fully-featured Laravel-based job board script offers premium functionality without the high cost. Whether you're building a local job site or a global hiring platform, this nulled script gives you everything you need—completely free. What is the Jobs Portal Nulled Script? The Jobs Portal Nulled Script is a premium Laravel-based job board application designed for businesses, HR agencies, and entrepreneurs who want to build a seamless job posting and recruitment website. The script comes packed with advanced features like employer and candidate dashboards, resume management, email notifications, location-based job search, and more—all without any licensing fees. Why Choose This Nulled Script? Unlike expensive premium plugins or themes, this Jobs Portal Nulled Script offers unmatched value. It provides a user-friendly interface, customizable design, and enterprise-level tools to make recruitment easier for both job seekers and employers. Plus, it's completely free to download from our site, allowing you to save money while building a professional job board. Technical Specifications Framework: Laravel 8+ Database: MySQL 5.7 or higher Language: PHP 7.4+ Responsive Design: Fully mobile-optimized API Ready: RESTful API endpoints available SEO Optimized: Built-in tools for on-page SEO Top Features and Benefits Employer & Candidate Dashboards: Tailored experiences for recruiters and job seekers. Smart Resume Management: Easily manage and filter resumes by job category and skills. Advanced Job Search: Location and keyword-based filtering for accurate results. Email Alerts: Automated job notifications for registered users. Payment Integration: Support for paid job postings with multiple gateways. Multi-language Support: Reach users across the globe effortlessly. Who Can Use This Script? The Jobs Portal Nulled Script is versatile and ideal for: HR agencies wanting a digital recruitment platform. Startups looking to monetize job listings or applications. Universities or colleges offering campus recruitment tools. Freelancers who want to provide job board services to clients. How to Install and Use Installing the Jobs Portal Nulled Script is straightforward: Download the script from our website. Upload the files to your server using FTP or a file manager. Create a MySQL database and import the provided SQL file. Edit the .env file to include your database credentials. Run the Laravel migration and seed commands to set up the tables. Visit yourdomain.com to start configuring your job portal! No technical expertise? No worries. The documentation provided makes it easy even for beginners to set up a complete job board system. FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions Is the Jobs Portal Nulled Script safe to use? Yes, we carefully scan and verify all files to ensure they are free of malware or backdoors. However, always install scripts in a secure environment. Can I customize the script? Absolutely. Since it’s built on Laravel, you have full control to customize routes, models, views, and controllers to fit your unique business model. Does the script support third-party integrations? Yes. You can integrate third-party services like payment gateways, newsletter tools, and analytics platforms with ease. Is it legal to use a nulled script? While we provide the script for educational and testing purposes, always ensure you comply with local software laws and licensing terms if you go live. Recommended Tools for WordPress Users If you're managing your site with WordPress, we recommend using UpdraftPlus Premium nulled for effortless backups and restoration. For search engine optimization, All in One SEO Pack Pro is a must-have tool to help your website rank faster and more effectively.
Take your online recruitment platform to the next level today. Download the Jobs Portal and build a modern, scalable, and highly effective job board without spending a dime!
0 notes
Text
Blog Post 1
It holds true that for most of 19th and 20th century, in the business world, there were two resources that influence most, if not all of decision and moves being made. These two resources were time and money. With enough of both of these resources, any business (with a healthy amount of hard work) could, and would succeed. In the 21st century, the business world has started to really concentrate on a third resource (previously important, but not so much as the former two). This third resource is of course Information, which is really starting to define who has power and influence; and who doesn’t; mainly based on the capacity of storage, processing speed, accessibility and reliability of the information they handle.
Information is really dictating a lot of market trends, because the main idea is that, the more a business knows, the better it can predict. And they can predict a lot, well anything (to a certain degree of course, but the accuracy is sort of scary and surprising). A strong proven practice are personalized ads on the internet; like the ads one can see on the sidebar when you are messing around Facebook and not doing homework, or whatever. The only real bottleneck with all of this, is how do you create what is called “relevant information”. Well, that is actually kind of easy, all you need is data, lots and lots of data, like massive amounts of data and an analyst (read: my dream job).
Now getting data might be relatively easy; every nowadays is outputting data in some way, shape or form (just need to know what or where to look for). The true challenge here is how to organize and store said data, to be used later to create the previously mentioned “relevant information”. Why is it challenging? Well, its because not all data is same; and this has nothing to do with its important, all data is important (until it isn’t), its more about its digital attributes and composition.
What do I mean by, not all data is same? The data produced from different unique sources is going to look very different, and that makes storage a challenge. Data could be different documents in various formats, an array of numbers, several different pictures, even a collection of keystrokes are considered value data to some individuals. So, storing all this different type of data types can be difficult, if a corporation is interested in one than one of these data types. Relational style databases did pretty well at the beginning.
But a relational style database, or SQL databases, can only go so far when tackling this problem because of the ridged way everything is structured, and by its nature the defined structure isn’t really mutable (like it is, but really its every costly time wise to do so, and you might end up just creating a new database). Non-relational style database, also called NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases are in a way much more flexible in the way the store data.
But we aren’t talking about a few tables, second challenge of SQL databases, they aren’t really scalable, corporation handle data on a much large scale; an estimate by priceonomis is 7.5 septillions (that’s 21 zeros) gigabytes of data. Oh, and this is what they generate in a day, granted I will say that only about half of this data is usable but still, that a whole lot of data!
Before we jump more into NoSQL, lets compare for a bit the two different styles of database.
https://youtu.be/LA5gY-LH63E
https://youtu.be/mqV-zYQhavc
Getting back on topic, that being NoSQL, which offers corporation the way to actually manage all this data. I am going to focus on one particular NoSQL database, Cassandra (created in 2008 by Apache). Why Cassandra? There are others such as MongoDB and Couchbase (very popular in the industry right now) but Cassandra offers two distinct advantages (in my opinion):
1. Cassandra has its on language, CQL, or Cassandra query language; which is very close to SQL, they aren’t really close enough to be siblings more like cousins. It is very easy for someone that has SQL knowledge to pick up CQL. Because of the way data is organized in a non-structured way, there is no support in CQL for things like “JOIN”, “GROUP BY”, or “FOREIGN KEY”. A great thing is that CQL can actual actually handle object data. This is probably due to the fact that Cassandra was written in Java.
2. The asynchronous masterless replication that Cassandra employs. The basic concept (its not super complex but it ain’t a cake walk either) is through this style of replication, this database model offers a high availability or accessibility to data with no single point of failure. This is due to data clusters.
https://youtu.be/zk00Bu8s4p0
Before we tackle replication together (because its what I really want to showcase), we need to cover a few concepts, just to make sure we are all on the same page.
Database Clusters
this is an industry standard practice for corporation and business that handle data in large quantities (so basically every corporation really). The idea is that there are two or more servers or nodes running together, servicing the same data sets, in both read and write requests. Why do this? Why have two very expensive pieces of equipment ($1000 to $2500 on the enterprise level) doing the same thing? Redundancy. Meaning that all nodes have the same data, this ensures that backups, restoration and data accessibility is almost a guarantee. The multiple servers also help with load balancing and scaling, because there are more nodes, more users can access the same data across the different nodes. And because of the larger network of nodes within the database, a lot of process can be automated. There can be one node just dedicate to being a coordinator/manager node (this is not a master node in anyway), which would run specific scripts and subprograms for the entire network.
Database Replication
ok, ok, there idea is simple its just copying data from one node to another in a database cluster. And you are right, but the process behind it is what truly impressive (at least to me). By the way a database that has replication added to it, is called a distributed database management system or DDBMS. So, database replication will track any changes, additions, or deletions made to any data point, will perform the same operation on the same data point in all other locations. There are several different replication techniques and models (will be explored in future posts). The key of database replication is the set up of them, several steps must be properly followed and understood for the overall set up to work. Replication is not the same as backing up data, because the replicated data is still within the network, connected to the original data; while backing up data is usually stored offsite.
Single Point of Failure
In the business world, having the lights on and getting/keeping everything running is a great concern, because it affects the bottom line. But let’s be realistic, something is going to fail at some point (its inevitable). And one of the goals of a database (based on the CAP theorem) is availability, so having a point of failure within a database system is not something most companies are looking for. This is solved by using database clusters, and replication, since they create a failsafe through redundancy. And it does it on several levels, between the load balancing, the multiple servers, and the multiple levels of access to data.
https://youtu.be/l0IQDSdVcs4
1 note
·
View note
Text
Data Recovery : Page level restore in SQL Server
Data Recovery : Page level restore in SQL Server

In this article, we shall discuss the importance of understanding the internals of the page restoration for a database administrator. Most of the time, performing a page-level restore suffices for database availability. A good backup strategy is a key to recovery or restoration, and SQL Server provides us with an option to fix database pages at a granular level. Performing a page level restore in…
View On WordPress
#dbcc checkdb#dbcc examples#dbcc ind#dbcc page#page level restore in sql server#restore page using SSMS#restore page using T-SQL
0 notes
Text
Top Sql Server Database Choices
SQL database has become the most common database utilized for every kind of business, for customer accounting or product. It is one of the most common database servers. Presently, you could restore database to some other instance within the exact same subscription and region. In the event the target database doesn't exist, it'll be created as a member of the import operation. If you loose your database all applications which are using it's going to quit working. Basically, it's a relational database for a service hosted in the Azure cloud.
Focus on how long your query requires to execute. Your default database may be missing. In terms of BI, it's actually not a database, but an enterprise-level data warehouse depending on the preceding databases. Make certain your Managed Instance and SQL Server don't have some underlying issues that may get the performance difficulties. It will attempt to move 50GB worth of pages and only than it will try to truncate the end of the file. If not, it will not be able to let the connection go. On the other hand, it enables developers to take advantage of row-based filtering.
If there's a need of returning some data fast, even supposing it really isn't the whole result, utilize the FAST option. The use of information analysis tools is dependent upon the demands and environment of the company. Moreover partitioning strategy option may also be implemented accordingly. Access has become the most basic personal database. With the notion of data visualization, it enables the visual accessibility to huge amounts of information in easily digestible values. It is not exactly challenging to create the link between the oh-so hyped Big Data realm and the demand for Big Storage.
Take note of the name of the instance that you're attempting to connect to. Any staging EC2 instances ought to be in the identical availability zone. Also, confirm that the instance is operating, by searching for the green arrow. Managed Instance enables you to pick how many CPU cores you would like to use and how much storage you want. Managed Instance enables you to readily re-create the dropped database from the automated backups. In addition, if you don't want the instance anymore, it is possible sql server database to easily delete it without worrying about underlying hardware. If you are in need of a new fully-managed SQL Server instance, you're able to just visit the Azure portal or type few commands in the command line and you'll have instance prepared to run.
Inside my case, very frequently the tables have 240 columns! Moreover, you may think about adding some indexes like column-store indexes that may improve performance of your workload especially when you have not used them if you used older versions of SQL server. An excellent data analysis is liable for the fantastic growth the corporation. In reality, as well as data storage, additionally, it includes data reporting and data analysis.
Microsoft allows enterprises to select from several editions of SQL Server based on their requirements and price range. The computer software is a comprehensive recovery solution with its outstanding capabilities. Furthermore, you have to learn a statistical analysis tool. It's great to learn about the tools offered in Visual Studio 2005 for testing. After making your database, if you wish to run the application utilizing SQL credentials, you will want to create a login. Please select based on the edition of the application you've downloaded earlier. As a consequence, the whole application can't scale.
What Is So Fascinating About Sql Server Database?
The data is kept in a remote database in an OutSystems atmosphere. When it can offer you the data you require, certain care, caution and restraint needs to be exercised. In addition, the filtered data is stored in another distribution database. Should you need historical weather data then Fetch Climate is a significant resource.
Storage Engine MySQL supports lots of storage engines. Net, XML is going to be the simplest to parse. The import also ought to be completed in a couple of hours. Oracle Data Pump Export is an extremely strong tool, it permits you to pick and select the type of data that you would like. Manual process to fix corrupted MDF file isn't so straightforward and several times it's not able to repair due to its limitations. At this point you have a replica of your database, running on your Mac, without the demand for entire Windows VM! For instance, you may want to make a blank variant of the manufacturing database so that you are able to test Migrations.
The SQL query language is vital. The best thing of software development is thinking up cool solutions to everyday issues, sharing them along with the planet, and implementing improvements you receive from the public. Web Designing can end up being a magic wand for your internet business, if it's done in an effective way. Any web scraping project starts with a need. The developers have option to pick from several RDBMS according to certain requirements of each undertaking. NET developers have been working on that special database for a very long moment. First step is to utilize SQL Server Management Studio to create scripts from a present database.
youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Is openGauss?
openGauss is a user-friendly, enterprise-level, and open-source relational database jointly built with partners. openGauss provides multi-core architecture-oriented ultimate performance, full-link service, data security, AI-based optimization, and efficient O&M capabilities. openGauss deeply integrates Huawei's years of R&D experience in the database field and continuously builds competitive features based on enterprise-level scenario requirements. For the latest information about openGauss, visit https://opengauss.org/en/.
openGauss is a database management system.
A database is a structured dataset. It can be any data, such as shopping lists, photo galleries, or a large amount of information on a company's network. To add, access, and process massive data stored in computer databases, you need a database management system (DBMS). The DBMS can manage and control the database in a unified manner to ensure the security and integrity of the database. Because computers are very good at handling large amounts of data, the DBMS plays a central role in computing as standalone utilities or as part of other applications.
An openGauss database is a relational database.
A relational database organizes data using a relational model, that is, data is stored in rows and columns. A series of rows and columns in a relational database are called tables, which form the database. A relational model can be simply understood as a two-dimensional table model, and a relational database is a data organization consisting of two-dimensional tables and their relationships.
In openGauss, SQL is a standard computer language often used to control the access to databases and manage data in databases. depending on your programming environment, you can enter SQL statements directly, embed SQL statements into code written in another language, or use specific language APIs that contain SQL syntax.
SQL is defined by the ANSI/ISO SQL standard. The SQL standard has been developed since 1986 and has multiple versions. In this document, SQL92 is the standard released in 1992, SQL99 is the standard released in 1999, and SQL2003 is the standard released in 2003. SQL2011 is the latest version of the standard. openGauss supports the SQL92, SQL99, SQL2003, and SQL2011 specifications.
openGauss provides open-source software.
Open-source means that anyone can use and modify the software. Anyone can download the openGauss software and use it at no cost. You can dig into the source code and make changes to meet your needs. The openGauss software is released under the Mulan Permissive Software License v2 (http://license.coscl.org.cn/MulanPSL2/) to define the software usage scope.
An openGauss database features high performance, high availability, high security, easy O&M, and full openness.
High performance
It provides the multi-core architecture-oriented concurrency control technology and Kunpeng hardware optimization, and achieves that the TPC-C benchmark performance reaches 1,500,000 tpmC in Kunpeng 2-socket servers.
It uses NUMA-Aware data structures as the key kernel structures to adapt to the trend of using multi-core NUMA architecture on hardware.
It provides the SQL bypass intelligent fast engine technology.
It provides the USTORE storage engine for frequent update scenarios.
High availability (HA)
It supports multiple deployment modes, such as primary/standby synchronization, primary/standby asynchronization, and cascaded standby server deployment.
It supports data page cyclic redundancy check (CRC), and automatically restores damaged data pages through the standby node.
It recovers the standby node in parallel and promotes it to primary to provide services within 10 seconds.
It provides log replication and primary selection framework based on the Paxos distributed consistency protocol.
High security
It supports security features such as fully-encrypted computing, access control, encryption authentication, database audit, and dynamic data masking to provide comprehensive end-to-end data security protection.
Easy O&M
It provides AI-based intelligent parameter tuning and index recommendation to automatically recommend AI parameters.
It provides slow SQL diagnosis and multi-dimensional self-monitoring views to help you understand system performance in real time.
It provides SQL time forecasting that supports online auto-learning.
Full openness
It adopts the Mulan Permissive Software License, allowing code to be freely modified, used, and referenced.
It fully opens database kernel capabilities.
It provides excessive partner certifications, training systems, and university courses.
0 notes
Text
Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiWeb 6.1 NSE6_FWB-6.1 Practice Test Questions
If you want to clear Fortinet NSE6_FWB-6.1 exam on the first attempt, then you should go through PassQuestion Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiWeb 6.1 NSE6_FWB-6.1 Practice Test Questions so you can easily clear your exam on the first attempt. Make sure that you are using our NSE6_FWB-6.1 questions and answers multiple times so you can avoid all the problems that you are facing. It is highly recommended for you to use NSE6_FWB-6.1 Practice Test Questions in different modes so you can strengthen your current preparation level. Moreover, it will help you assess your preparation and you will be able to pass your Fortinet NSE6_FWB-6.1 exam successfully.
Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiWeb 6.1 (NSE6_FWB-6.1)
Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiWeb 6.1 exam will prepare you for the FortiWeb 6.1 Specialist Exam. The FortiWeb Specialist exam counts toward one of the four NSE 6 specializations required to get the NSE 6 certification.You will learn how to deploy,configure, and troubleshoot Fortinet's web application firewall: FortiWeb. Networking and security professionals involved in the administration and support of FortiWeb can attend this NSE6_FWB-6.1 exam to get certified.
Exam Details
Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiWeb 6.1 Exam series: NSE6_FWB-6.1 Number of questions: 30 Exam time: 60 minutes Language: English and Japanese Product version: FortiWeb 6.1 Status: Available
Prerequisites
Knowledge of OSI layers and the HTTP protocol
Basic knowledge of HTML, JavaScript, and server-side dynamic page languages, such as PHP
Basic experience using FortiGate port forwarding
Exam Topics
Integrating Front-End SNAT and Load Balancers Machine Learning and Bot Detection Signatures and Sanitization DoS and Defacement SSL/TLS Authentication and Access Control PCI DSS Compliance Caching and Compression HTTP Routing, Rewriting, and Redirects Troubleshooting
View Online Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiWeb 6.1 NSE6_FWB-6.1 Free Questions
What key factor must be considered when setting brute force rate limiting and blocking? A.A single client contacting multiple resources B.Multiple clients sharing a single Internet connection C.Multiple clients from geographically diverse locations D.Multiple clients connecting to multiple resources Answer: D
What role does FortiWeb play in ensuring PCI DSS compliance? A.It provides the ability to securely process cash transactions. B.It provides the required SQL server protection. C.It provides the WAF required by PCI. D.It provides credit card processing capabilities. Answer: D
What must you do with your FortiWeb logs to ensure PCI DSS compliance? A.Store in an off-site location B.Erase them every two weeks C.Enable masking of sensitive data D.Compress them into a .zip file format Answer: C
Which two statements about the anti-defacement feature on FortiWeb are true? (Choose two.) A.Anti-defacement can redirect users to a backup web server, if it detects a change. B.Anti-defacement downloads a copy of your website to RAM, in order to restore a clean image, if it detects defacement. C.FortiWeb will only check to see if there are changes on the web server; it will not download the whole file each time. D.Anti-defacement does not make a backup copy of your databases. Answer: CD
When viewing the attack logs on FortiWeb, which client IP address is shown when you are using XFF header rules? A.FortiGate public IP B.FortiWeb IP C.FortiGate local IP D.Client real IP Answer: D
0 notes
Text
Install Docker On Windows 2019

Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
NOTE: Currently not compatible with Apple Silicon (ARM). This project relies on Docker which has not been ported to Apple Silicon yet. If you are running Windows, download the latest release and add the binary into your PATH. If you are using Chocolatey then run: choco install act-cli. If you are using Scoop then run: scoop install act.
Nov 07, 2019 Here’s how you can install Docker on Windows 10 64-bit: Enable Hyper-V in your system. Download Docker Desktop for Windows and open the Docker for Windows Installer file. In the Configuration dialog window, check or uncheck the boxes based on your preferences.
This will install the Docker-Microsoft PackageManagement Provider from the PowerShell Gallery. Sample output is as shown below: Step 2: Install Docker on Windows Server 2019. Once the Containers feature is enabled on Windows Server 2019, install the latest Docker Engine and Client by running the command below in your PowerShell session.
Docker Desktop for Windows is the Community version of Docker for Microsoft Windows.You can download Docker Desktop for Windows from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
System requirements
Your Windows machine must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop.
Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, or Education (Build 17134 or higher).
For Windows 10 Home, see System requirements for WSL 2 backend.
Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run ClientHyper-V on Windows 10:
64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
4GB system RAM
BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in theBIOS settings. For more information, seeVirtualization.
WSL 2 backend
Windows 10 64-bit: Home, Pro, Enterprise, or Education, version 1903 (Build 18362 or higher).
Enable the WSL 2 feature on Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully runWSL 2 on Windows 10:
64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
4GB system RAM
BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in theBIOS settings. For more information, seeVirtualization.
Download and install the Linux kernel update package.
Note
Docker supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine,Docker CLI client, Docker Compose,Notary,Kubernetes,and Credential Helper.

Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between alluser accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windowsaccounts use the same VM to build and run containers. Note that it is not possible to share containers and images between user accounts when using the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend.
Nested virtualization scenarios, such as running Docker Desktop on aVMWare or Parallels instance might work, but there are no guarantees. Formore information, see Running Docker Desktop in nested virtualization scenarios.
About Windows containers
Looking for information on using Windows containers?
Switch between Windows and Linux containersdescribes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above.
Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab)provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It shows you how to use a MusicStore applicationwith Windows containers.
Docker Container Platform for Windows articles and blogposts on the Docker website.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
If you haven’t already downloaded the installer (Docker Desktop Installer.exe), you can get it from Docker Hub. It typically downloads to your Downloads folder, or you can run it from the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser.
When prompted, ensure the Enable Hyper-V Windows Features or the Install required Windows components for WSL 2 option is selected on the Configuration page.
Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to authorize the installer and proceed with the install.
When the installation is successful, click Close to complete the installation process.
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group. Run Computer Management as an administrator and navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users. Right-click to add the user to the group.Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
Start Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop, search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
When the whale icon in the status bar stays steady, Docker Desktop is up-and-running, and is accessible from any terminal window.
If the whale icon is hidden in the Notifications area, click the up arrow on thetaskbar to show it. To learn more, see Docker Settings.
When the initialization is complete, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop on Windows.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows machine:
From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Apps > Apps & features.
Select Docker Desktop from the Apps & features list and then select Uninstall.
Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Important
Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, andother Docker related data local to the machine, and removes the files generatedby the application. Refer to the back up and restore datasection to learn how to preserve important data before uninstalling.
Where to go next
Getting started introduces Docker Desktop for Windows.
Get started with Docker is a tutorial that teaches you how todeploy a multi-service stack.
Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, andhow to get support.
FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
Back up and restore data provides instructions on backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
windows, install, download, run, docker, local
Microsoft SQL Server is a database system that comprises many components, including the Database Engine, Analysis Services, Reporting Services, SQL Server Graph Databases, SQL Server Machine Learning Services, and several other components.
SQL Server 2019 has a lot of new features:
Intelligence across all your data with Big Data Clusters
Choice of language and platform
Industry-leading performance
Most secured data platform
Unparalleled high availability
End-to-end mobile BI
SQL Server on Azure
Download SQL Server 2019
Step 1 : Go to https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/evaluate-sql-server-2019.
Install Docker Engine On Windows 2019
Step 2 :To download the installer you need to fill a short form and provide your contact information.
Run the installer
Step 3 :After the download completes, run the downloaded file. Select Basic installation type.
Step 4 :Select ACCEPT to accept the license terms.
Step 5 :Accept the install location, and click INSTALL.
Step 6 :When the download completes, installation will automatically begin.
Step 7 :After installation completes, select CLOSE.
Step 8 :After this has completed, you will have SQL Server 2019 Installation Center installed.
Install SQL Server Management Studio
The steps for installing SQL Server Management Studio are as follows:
Install Docker On Windows Server 2019 Without Internet
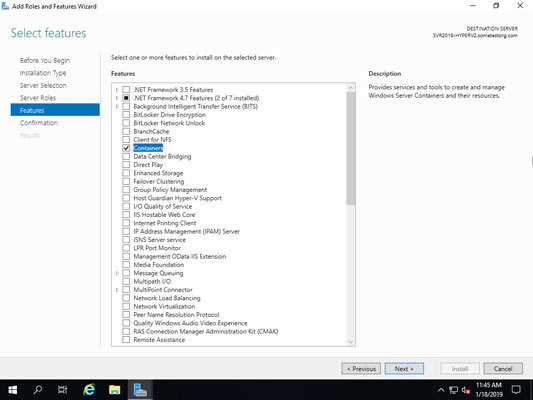
Step 9 :Open the SQL Server 2019 Installation Center application
Step 10 :Select installation on the left pane, then install SQL Server Management tools.
Step 11 :Select Download SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Step 12 :After the download completes, click RUN
Step 13 :Then INSTALL
Install Docker On Windows Server 2019 Offline
Step 14 :When installation completes, click CLOSE.
Step 15 :After this has completed, you will have several new software apps installed, including SQL Server Management Studio.
Use SQL Server Management Studio
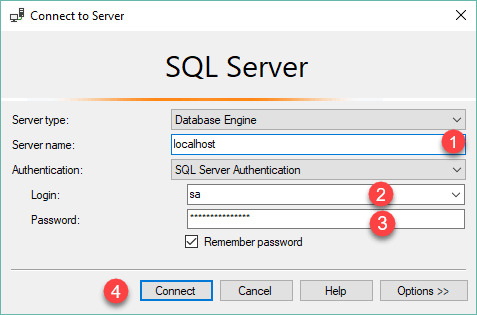
Step 16 :When you open the SQL Server Management Studio application, you’ll first see a Connect to Server window. This window allows you to establish a connection with the SQL Server instance that you already installed. The Server Name will show instance you installed, and the Authentication will show Windows Authentication. The Server Type is Database Engine.
Install Docker On Windows 2019 Iso
Step 17 :Click the CONNECT button.

0 notes
Text
Modify an Amazon RDS for SQL Server instance from Standard Edition to Enterprise Edition
Microsoft SQL Server is available in various editions, and each edition brings unique features, performance, and pricing options. The edition that you install also depends on your specific requirements. Many of our customers want to change from the Standard Edition of Amazon RDS for SQL Server to Enterprise Edition to utilize its higher memory and high-availability features. To do so, you need to upgrade your existing RDS for SQL Server instance from Standard Edition to Enterprise Edition. This post walks you through that process. Prerequisites Before you get started, make sure you have the following prerequisites: Amazon RDS for SQL Server Access to the AWS Management Console SQL Server Management Studio Walkthrough overview Amazon RDS supports DB instances running several versions and editions of SQL Server. For the full list, see Microsoft SQL Server versions on Amazon RDS. For this post, we discuss the following editions: Standard – This edition enables database management with minimal IT resources, with limited feature offerings, a lack of some high-availability features, and few online DDL operations compared to Enterprise Edition. Additionally, Standard Edition has a limitation of 24 cores and 128 GB of memory. Enterprise: This is the most complete edition to use with your mission-critical workloads. With Enterprise Edition, you have all the features with no limitation of CPU and memory. The upgrade process includes the following high-level steps: Take a snapshot of the existing RDS for SQL Server Standard Edition instance. Restore the snapshot as an RDS for SQL Server Enterprise Edition instance. Verify the RDS for SQL Server Enterprise Edition instance. Upgrade your RDS for SQL Server instance on the console We first walk you through modifying your RDS for SQL Server edition via the console. We take a snapshot of the existing RDS for SQL Server instance and then restore it as a different edition of SQL Server. You can check your version of RDS for SQL Server on the SQL Server Management Studio. On the Amazon RDS console, choose Databases. Select your database and on the Actions menu, choose Take snapshot. For Snapshot name, enter a name. Choose Take snapshot. On the Snapshots page, verify that snapshot is created successfully and check that the status is Available. Select the snapshot and on the Actions menu, choose Restore snapshot. Under DB specifications, choose the new edition of SQL Server (for this post, SQL Server Enterprise Edition). For DB instance identifier, enter a name for your new instance. Select your instance class. Choose Restore DB instance. Wait for the database to be restored. After the database is restored, verify the version of SQL Server. The following screenshot shows the new RDS for SQL Server database created from the snapshot, with all databases, objects, users, permissions, passwords, and other RDS for SQL Server parameters, options, and settings restored with the snapshot. Upgrade your RDS for SQL Server instance via the AWS CLI You can also use the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) to modify the RDS for SQL Server instance: Create a DB snapshot using create-db-snapshot CLI: aws rds create-db-snapshot ^ --db-instance-identifier mydbinstance ^ --db-snapshot-identifier mydbsnapshot Restore the database from the snapshot using restore-db-instance-from-db-snapshot CLI: aws rds restore-db-instance-from-db-snapshot ^ --db-instance-identifier mynewdbinstance ^ --db-snapshot-identifier mydbsnapshot^ --engine sqlserver-ee Clean up To avoid incurring future costs, delete your RDS for SQL Server Standard Edition resources, because they’re no longer required. On the Amazon RDS console, choose Databases. Select your old database and on the Actions menu, choose Delete. Conclusion In this post, I showed how to modify Amazon RDS for SQL Server from Standard Edition to Enterprise Edition using the snapshot restore method. Upgrading to Enterprise Edition allows you to take advantage of higher memory and the edition’s high-availability features. To learn more about most effective way of working with Amazon RDS for SQL Server, see Best practices for working with SQL Server. About the author Yogi Barot is Microsoft Specialist Senior Solution Architect at AWS, she has 22 years of experience working with different Microsoft technologies, her specialty is in SQL Server and different database technologies. Yogi has in depth AWS knowledge and expertise in running Microsoft workload on AWS. https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/database/modify-an-amazon-rds-for-sql-server-instance-from-standard-edition-to-enterprise-edition/
0 notes
Text
cPanel - Website and Hosting Management Tool
Build and Manage your WordPress Website. One Low Predictable Price!
cPanel Hosting Services will empower a Website owner with a wide variety of options at a higher level of control And automation tools designed to simplify the process of hosting a web site
With the industries best graphical interface. cPanel is an excellent option for you to consider.
cPanel's time saving automation's will make managing your Website easier than ever.
With over 80 different features which includes creating Email Accounts, Backups, File Manager, Adding Domains, MX Records, Softaculous and and the Site Publisher interface to quickly create simple websites from a variety of templates.

cPanel is the leading web hosting control panel available today
Currently in the hosting market cPanel is considered as the leading website management tool
It’s simple graphical web based interface empowers web developers, administrators and resellers to effectively develop and manage their websites
Not just for developers, even a non-professional and less technical people can easily create and manage websites and their hosting account with cPanel, you will have access to stats, disk usage and space, bandwidth usage, add, or remove email accounts, MX Records, FTP accounts.
Install different The File Manager, PHP my Sql scripts, get access to your online Web Mail
And more advanced functions, such as MIME types, cron jobs, OpenPGP keys, Apache handlers, addon domains and sub domains, password protected directories
cPanel Hosting Services is an easy to use interface for web maintenance. Even a user completely new to web hosting can easily manage their own website.
Advantages of cPanel hosting services:
Easy to use
Supports all languages
Adapts the screen size automatically, so we can use on any device
Has built-in file manager to manage the files easily
Integrated with phpMy Admin tool to manage the databases easily
Has Integrated email wizard which helps to send or receive the mails using a mail client
cPanel handles automatic upgrades of Apache, MySQL, PHP and other web applications
cPanel Features:
Looking for cPanel Hosting Services with over 80 different features?
Files
File Manager
Use the File Manager interface to manage your files. This feature allows you to upload, create, remove, and edit files without the need for FTP or other third-party applications.
Images
Use the Images interface to manage your images. You can view and resize images, or use this feature to convert image file types.
Directory Privacy
Use the Directory Privacy interface to limit access to certain resources on your website. Enable this feature to password-protect specific directories that you do not want to allow visitors to access.
Disk Usage
Use the Disk Usage interface to scan your disk and view a graphical overview of your account's available space. This feature can help you to manage your disk space usage.
Web Disk
Use the Web Disk feature to access to your website's files as if they were a local drive on your computer.
FTP Accounts
Use the FTP Accounts interface to manage File Transfer Protocol (FTP) accounts.
FTP Connections
Use the FTP Connections interface to view current connections to your site via FTP. Terminate FTP connections to prevent unauthorized or unwanted file access.
Anonymous FTP
Use the Anonymous FTP interface to allow users to connect to your FTP directory without a password. Use of this feature may cause security risks.
Backup
Use the Backup interface to back up your website. This feature allows you to download a zipped copy of your cPanel account's contents (home directory, databases, email forwarders, and email filters) to your computer.
File Restoration
Use the File Restoration interface to restore items from backed-up files.
Backup Wizard
Use the Backup Wizard interface as a step-by-step guide to assist you in backup creation.
Databases
phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a third-party tool that you can use to manipulate MySQL databases. For more information about how to use phpMyAdmin, visit the phpMyAdmin website.
MySQL Databases
Use the MySQL Databases interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, Content Management Systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
MySQL Database Wizard
Use the MySQL Database Wizard interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites with a step-by-step guide. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
Remote MySQL
Use the Remote MySQL interface to configure databases that users can access remotely. Use this feature if you want to allow applications (for example, bulletin boards, shopping carts, or guestbooks) on other servers to access your databases.
PostgreSQL Databases
Use the PostgreSQL Databases interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
PostgreSQL Database Wizard
To simultaneously create a database and the account that will access it, use the PostgreSQL Database Wizard interface. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
phpPgAdmin
phpPgAdmin is a third-party tool that you can use to manipulate PostgreSQL databases. For more information about how to use phpPgAdmin, visit the phpPgAdmin website.
Domains
Some of our Free Domain Name are mentioned and briefly mentioned for your kind regards.
Site Publisher
Use the Site Publisher interface to quickly create simple websites from a variety of templates. You can use this feature, for example, to ensure that visitors can find your contact information while you design a more elaborate website.
Addon Domains
Use the Addon Domains interface to add more domains to your account. Each addon domain possesses its own files and will appear as a separate website to your visitors.
Subdomains
Subdomains are subsections of your website that can exist as a new website without a new domain name. Use this interface to create memorable URLs for different content areas of your site. For example, you can create a subdomain for your blog that visitors can access through blog.example.com.
Aliases
Use the Aliases interface to create domain aliases. Domain Aliases allow you to point additional domain names to your account's existing domains. This allows users to reach your website if they enter the pointed domain URL in their browsers.
Redirects
Use the Redirects interface to make a specific webpage redirect to another webpage and display its contents. This allows users to access a page with a long URL through a page with a shorter, more memorable URL.
Zone Editor
Use the Zone Editor interface to add, edit, and remove A, AAAA, CNAME, SRV, MX, and TXT DNS records. It combines the functions of the Simple Zone Editor and Advanced Zone Editor interfaces.
For more information please visit our site https://rshweb.com/blog-what-is-cpanel or https://rshweb.com/
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP Oracle ADF Interview Questions and Answers
Oracle ADF Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Oracle ADF? Oracle Application Development Framework, usually called Oracle ADF, provides a commercial Java framework for building enterprise applications. It provides visual and declarative approaches to Java EE development. It supports rapid application development based on ready-to-use design patterns, metadata-driven, and visual tools. 2. What is the ADF Features? Making Java EE Development Simpler. Oracle ADF implements the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern and offers an integrated a solution that covers all the layers of this architecture with a solution to such areas as: Object/Relational mapping, Data persistence, Reusable controller layer, Rich Web user interface framework, Data binding to UI, Security and customization. Its supports Rapid Application Development. Declarative approve (XML Driven) Reduce Maintenance Cost and time SOA Enabled 3. What is ADF BC (Business Components)? Describe them. All of these features can be summarized by saying that using ADF Business Components for your J2EE business service layer makes your life a lot easier. The key ADF Business Components that cooperate to provide the business Service implementation is: Entity Object: An entity object represents a row in a database table and simplifies modifying its data by handling all DML operations for you. It can encapsulate business logic for the row to ensure your business rules are consistently enforced. You associate an entity object with others to reflect relationships in the underlying database schema to create a layer of business domain objects to reuse in multiple applications. Application Module: An application module is a transactional component that UI clients use to work with application data. It defines an updatable data model and top-level procedures and functions (called service methods) related to a logical unit of work related to an end-user task. View Object: A view object represents a SQL query and simplifies working with its results. You use the full power of the familiar SQL language to join, project, filter, sort, and aggregate data into exactly the “shape” required by the end-user task at hand. This includes the ability to link a view object with others to create master/detail hierarchies of any complexity. When end users modify data in the user interface, your view objects collaborate with entity objects to consistently validate and save the changes. 4. How does ADF fall in MVC architecture? Oracle ADF Architecture is based on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern.MVC consists of three layers which are a model layer, view layer, controller layer. Oracle ADF implements MVC and further separates the model layer from the business services to enable service-oriented development of applications. The Oracle ADF architecture is based on four layers: The Business Services Layer This layer provides access to data from various sources and handles business logic. ADF Component comes, in this section are ViewObject, EntityObject, ViewLink, Association, etc The Model layer This layer provides an abstraction layer on top of the Business Services layer, enabling the View and Controller layers to work with different implementations of Business Services in a consistent way. ADF Component comes in this section are PageDefn, DataBindings,DataControls(AppModuleDataControl, WebServiceDataControl) The Controller layer This layer provides a mechanism to control the flow of the Web application. ADF Component comes in this section are TaskFlows(Bounded and unbounded, faces-config.xml, adfc-config.xml) The View layer This layer provides the user interface of the application. ADF components comes in this section are jsff, jspx page. 5. Oracle ADF Life Cycle Step by step It has the following phases : a) Restore view : When we hit the URL in the browser it will build the component tree corresponding to the tags given in the JSF pages. for the first time, it will build the tree and saves in the server memory. For the second time onwards, it will try to restore the existing component tree from the server memory. Otherwise, if there are any changes in the page components it will rebuild the tree again. b) Initialize Context : In this phase the databinding.cpx file will be read and the bindingcontext object will be created based on that. Binding context is nothing but a mapping of pages and page definitions. From the binding context, it will identify the page definition corresponding to the page. it will read the page definition file and creates the binding container objects. c) Prepare model : Once the binding Container is ready it will try to prepare the model objects bypassing any parameter values and if there are any task flow parameters are all evaluated in the phase d) Apply Request Values : If we enter any values in the browser against the form fields, those values will be applied against the component tree objects. e) Process validation : Once the values are applied to fields they will be validated if there any client-side validation is specified. like a mandatory min-max length. f) Update model values : Once UI validation is passed values will be applied to model objects like VO and EO g) Validate Model Updates : If there is any validation specified at entity level that will be executed. h) Invoke action : Event-related actions like the action method and action listener code will be executed i) Metadata commit : If there are any MDS related changes will be saved. j) Render response : Based on the action it will either navigate to the next page and display the response in the browser are continuing on the same page. 6. What are the various components in ADF? Oracle ADF has following components ADF Business Components: VO, EO & AM ADF Model : DataBinding (.cpx, .xml) & DataControls(.dcx) ADF View: JSP, JSF, ADF Faces etc. ADF Controller: Task flows (adf-config.xml), faces-config.xml 7. How to enable security to ADF Application? Go to the menu Application -> Secure -> Configure ADF Security and go through the wizard of creating login pages. Go to the menu Application -> Secure -> Application Roles and create an application role for this application. Create a test user and assign an application role to it. Grant all required application resources to this role. 8. How can you manage the transaction in ADF? In ADF transaction can we manage at ApplicationModule as well as task flow level. Task flow supports different mode of transaction like: No Controller transaction Always begin new transaction Always use existing transaction Use Existing Transaction if possible 9. What is the purpose of Chanage Indicator? While committing data to the table, database will check those columns to check weather we are committing on the latest data or not. 10. What is PPR in ADF? PPR means Partial Page Rendering. It means that in ADF we can refresh the portion of the page. We don't need to submit the whole page for that.

Oracle ADF Interview Questions 11. How to develop Master-details view in ADF? For Developing the Master-details view in ADF. You have to create a relationship between the 2 view object. That relationship can be created using the view link or association between entity Object. using that relationship you can create the master-details view of data. That master-details view can be Form-Form, Form-Table, Table-Table, Table-Form. 12. What is the difference between Action and ActionListener? ActionListener: ActionListener is the method which got invoked when the user clicks on the Component like button, command link, etc. Action: Action is the outcome of where you want to move once Actionlistener is completed. This can be defined in the task flow as an activity. So when listener completed application is redirected to define activity. 13. Definitions : jazn-data.xml - Store the security rules or permissions that you will create for the application, as well as providing a simple credential store for testing purposes. JDeveloper also updates the following files, which already exist: web.xml – Name of the login and error pages have been added to this file. weblogic.xml - The Section “security role assignment” of this file is used to map users (also called “principals”) to roles in WebLogic. adf-config.xml - Applications level settings like this MDS configuration, Database locking mode, View Object Max fetch size. faces-config.xml: The JSF configuration file is where you register a JSF application's resources such as custom validators and managed beans, and define all the page-to-page navigation rules. While an application can have any JSF configuration file name, typically the file name is the faces-config.xml file. Small applications usually have one faces-config.xml file.When you use ADF Faces components in your application, JDeveloper automatically adds the necessary configuration elements for you into faces-config.xml adfc-config.xml: The adfc-config.xml file is the default page flow diagram JDeveloper provided when you created an application based on the Fusion Web Application (ADF) template. adfc-config.xml is the default file name for an unbounded task flow. On this diagram, you can create a new page based on the template, which is not part of the existing orders-flow task flow. adf-settings.xml: we will register Page Phase listener 14. What Is Binding Context And Binding Container? Binding context is a runtime map between the data controls and page definition of pages in the application which is used to access the binding layer. It is accessible through the EL expression in your jspx pages. Binding container is a request-scoped map that is used to instantiate the page bindings. This is accessible through the EL expressions. Also, since it is request-scoped map, it is accessible during every page request. 15. Which component in ADF BC Manages transaction? Application Module, manages transaction. 16. Where is that we write business rules/validations in ADF and why? We should ideally be writing validations at an Entity Object level because they provide the highest degree of reuse. 17. What is the Controller in ADF in respect of MVC architecture? Controllers in the ADF framework are TaskFlows, Faces-config.xml, adfc-config.xml. In all there file you can define navigation between the pages. 18. What is an Entity object in ADF Framework? Entity object in ADF is similar to Table in the database. Any Number of view object can create on single Entity. 19. What is the View object in the ADF framework? ViewObject is representing the data collection. These view object can be created in different ways which are as follows: Entity-Based ViewObject: This view object will hold the reference of the underlying entity. These view object can hold data from single or multiple entities. While defining Viewobject based on Entity you can select the attribute which you want to keep in the entity. SQL Based ViewObject: These view objects are based on SQL quarries. This view object will have an underlying SQL Query. At runtime, they will hold data return by SQL. Programmatic View Object: User can define the view attribute which defining view object. Data will insert programmatically into these ViewObject. Static ViewObject: While defining user will define an attribute for view and in later he has to provide the values for those attribute. This kind of view object will have fixed no of rows. 20. What are Control Hints in Entity Object configuration? Control hints are associated with the current view or entity attribute. All view objects inherit the hint values at run time. Control hints for data controls and bindings, including Labels, Date & currency formatting. 21. Can an entity object be based on two Database Objects(tables/views) or two Webservices? No, Directly it's not possible to create EO using multiple tables. Entity objects will always have one to one relationship with a database object or web service. But using views you can create Entity Objects on multiple tables. 22. What is the return type of Service Methods? Service Methods can return Scalar or Primitive Datatypes. 23. How do you decide whether the application should be deployed as an EAR or a WAR? If the application contains run-time customizations using MDS, it must be bundled as an EAR. For simple WebCenter portal application with no such customizations, WAR can be created. 24. Explain Data binding & its types, sub-types? Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) provides several types of binding objects to support the attributes and operations exposed by the Oracle ADF data controls for a particular business object: ITERATOR BINDING , one per accessor attribute that your page or panel displays. Iterates over the business objects of the data collection and maintain the row currency and state. VALUE BINDINGS, one for each data-bound UI component. Provides access to data. ACTION BINDING , specifically defined for a button component. Provides access to operations defined by the business object. Value Binding Types: Attribute Value Binding Boolean Value Binding List Value Binding Range Value Binding Scroll Value Binding 25. What is Association in ADF? Association represents the relationship between 2 and more tables like a foreign key relationship. If you create Entities from the database association will automatically get created for the entity. User can also define custom association if there is no foreign-key is defined in the database. In this way, the user can handle foreign key in ADF application and can remove overhead from the database. 26. What is the view link? ViewLink represents the relationship between data of the same or multiple Entities or table. It works in the same manner as association work for the entity. While defining the ViewLink user can define the reference of the already created association if view object based on Entity Object else can manually select the column and define the link between 2 ViewObject. 27. Why we used an application module in the ADF framework? Application module is the component of ADF BC which hold the references of ViewObject and instantiate them while running the application. view object reference defines in Application Module can be used to define the JSF/JSP page. If you want to use any ViewObject on your page you must have to provide the reference in Application Module 28. What Is The Difference Between Visible Property And Render Property? The visible property is set to true/false based on the requirement whether we want to see the field on the page or not at run time. The field or component still exists on the page, though hidden. The render property is used to conditionally load the component based on a criteria. 29. How Do You Define Pagination In Adf? We define custom pagination in ADF by creating a custom table as a taskflow using the af:iterator tag. This renders the collection of data just as a table renders it. Now we bind the value property of iterator to collection model from ADF bindings declaration and set the number of visible row to, say 15. 30. Can Service Methods return type Void? Yes, Service Methods can Return type Void 31. Can Service Methods return Complex Datatypes? No, service methods can return only primitive/scalar data types. 32. What Is The Difference Between Databindings.cpx And Datacontrol.dcx? The DataBindings.cpx file contains the Oracle ADF binding context for your entire application and provides the metadata from which the Oracle ADF binding objects are created at runtime. The DataControls.dcx file is created when you register data controls on the business services. This file is not generated for Oracle ADF Business Components. It identifies the Oracle ADF model layer data control classes(factory classes) that facilitate the interaction between the client and the available business service. 33. What do you mean by Bean Scope? Bean Scope typically holds beans and other objects that need to be available in the different components of a web application. 34. SOAP Web service invocation from ADF: there are 2 options: Web service data control Web service proxy Data control : Right click on any project --> New --> Web Services --> Web service data control We need to give wsdl url and next, next ....finish... It will create web service data control almost similar to our Application module data control we can drag n drop the methods and objects on to the page. Proxy : Right click on View Controller --> New --> Web services --> Web services Proxy We need to give wsdl url and next, next ...finis... It will create java classes to invoke the web service. We will generally use that logic to invoke in button action listener or in some managed bean methods 35. What is a region in Oracle ADF? An ADF dynamic region is an ADF region where the task flow binding dynamically. Determines the value of its taskFlowId attribute at runtime. This allows the Fusion. web application to determine which bounded task flow to execute within the ADF 36. How to skip validation in ADF? Add immediate="true" to the button. This way all input fields which don't have immediate="true" will be skipped in processing. This method mainly used for view layer validation skip. 37. What Are Validators And Converters In Adf? validators : If somehow you need to create your own validation logic to meet your business needs. You can either create a validation method on the page’s backing bean (if you want custom validation for a component on a single page) or create JSF validator classes (if you want to reuse the validation logic by various pages in the application).In the real world, of course, creating the custom JSF validator classes would be adopted for ADF application for better reuse and maintenance. converters : converters are used for converting the values from one type to another, like decimal to bigdecimal or from string to date or date to string. 38. How to make any field mandatory? Add attribute required="true" to that specific field. 39. What are the various access scopes supported by ADF? ADF Faces supports the following scopes Application Scope Session Scope PageFlow Scope Request Scope BackingBean Scope. 40. How to pass ''af:selectOneChoice'' value to other page? Add valuePassThru="true" attribute to select list. 41. What are the types of ADF Faces components? ADF Faces components: Data components Input components Layout components Navigational components Output components 42. What is PPR and how do you enable Partial Page Rendering(PPR)? PPR is a feature supported by ADF Faces, using which we can render a small portion of an HTML Page, without refreshing the complete page. It is enabled by.- Setting AutoSubmit property to true on the triggering element. - Setting the PartialTriggers property of the target component to refer to the component id of the triggering element. 43. Explain Role Of Javascript In Adf? ADF Component allows JavaScript function to listen for ADF Faces component events, like select or disclosure events, and browser DOM events like focus, mouse hover, mouse click or keyboard events. The component has its client Component property set to true. 44. What is the association in ADF? Oracle ADF associations are business components that defines a relationship between two Oracle ADF entity object definitions (the "source" and "destination" entity objects) based on sets of entity attributes (the "source" and "destination" attributes) from each. 45. What are the different types/categories of Taskflows? Taskflows are of two categories : Bounded and UnBounded. 46. When we drag drop VO from DataControl which binding occurs? Value binding occurs. 47. What is a Taskflow? Taskflow is the controller of an ADF application, it provides us a declarative approach to define the control flow. It is used to define the navigation between pages and various task flow activities. 48. What is the difference between Bounded and UnBounded task flows? Differences between Bounded and UnBounded taskflows : Bounded taskflows can be secured but Unbounded can’t. Bounded taskflows can accept the parameter and return values but unbounded taskflows don’t support parameters Bounded taskflows has a single entry point or a default activity but unbounded taskflows have multiple entry points. Bounded taskflows can be called from other bounded/unbounded taskflows but unbounded cannot be called or reused. Bounded taskflows support transactions unbounded don’t 49. What Is Policy Store And Identity Store In Oid? Identity Store is used to store information about users and groups while the Policy Store is used to store information about security policies. 50. What are the Data Control scopes available in ADF? Isolate/Shared Shared : Data Control instances will be shared across the task flows Isolated: New set of data control instances will be created 51. Can bounded task flow runs on the browser? NO 52. Explain the purpose of using Controls flow in ADF? Controls flow for Navigation from one activity to other activity with in the Task flow. 53. What is the behavior of the router in ADF task flow? Based on some condition router can decide which route need to be followed. If none of the condition match in that case router will follow the default route defined by use. 54. How can navigation define in task flow? Navigation can be defined in task flow using control flows and invoked by jsff/jspx page using action event like button link etc. 55. Can ADF task flow hold more than 1 view activity? Yes. ADF task flow can have multiple view activity but 1 activity has to be defined as the default activity. 56. What is the Parent Action in ADF Taskflow? Parent action is activity using that you can invoke the Control flow define in parent task flow from child task flow. 57. What is the method activity in Adf Taskflow? Using this activity you can invoke any method defined in manage-bean. 58. How to initialize ADF Taskflow? Open the task flow in Overview Mode select general like there is initializer property. you can provide any method reference which will get invoked whenever task flow instance created. 59. What is Managed Bean? Managed bean is a java class, which is initialized by the JSF framework. It is primarily used to hold view and controller logic. It is also used to execute Java code to be executed on a user action like Button Click. 60. What is Backing Bean? Backing beans are those managed beans which have 1:1 mapping with a page. They have getters and setters for all the components in the related page. 61. What is the difference between managed and backing beans? Backing bean has 1:1 relation with page whereas managed beans can be used in multiple pages. Backing beans scope is limited to the page whereas managed beans can have other scopes too. 62. What is a different kind of resource bundle supported in ADF? ADF supports different types of resource bundle which are as follows: Property file based (text file which contains key-value pair) xliff file based (XML file which contains key-value pair) List Resource bundle 63) What is the difference between jspx and jsff? jspx and jsff file are the same in most of the manner. The only difference is that you can run jspx directly on the browser while jsff file container which will run on the browser. 64. Following three main component attributes are used to enable partial page rendering: autoSubmit: When the autoSubmit attribute of input or select component is set to true, and appropriate action takes place (such as a value change), the component automatically submits the form it is enclosed in. partialSubmit: When the partialSubmit attribute of a command component is set to true, clicking the button or link causes the page to be partially submitted. partialTriggers: All rendered components support the partialTriggers attribute. Use this attribute to list the IDs of components whose change events are to trigger this component to be refreshed. 65. ADF View Criteria View Object in ADF is representing a table database object supports Select query against the table. View Criteria is adding ‘Where clause’ to the View Objects but Unlike SQL query View Object support multiple View Criteria. The purpose of allowing multiple ADF view criteria is you can choose the ADF View Criteria you want on your pages. For example, I have an employee table has a column ‘type; with value ‘manager’ and ‘director’. I want to display the list of managers in one page and list of directors on another page. For this, I simply create two View Criteria, One for employee and another for director and use employee VC for employee page and manager VC for manager page. 66. What are the different types of bindings in ADF? ADF contains the following types of bindings: Method Bindings: This binding is used when you want to use custom methods to be executed. Attribute Bindings: This is the binding to retrieve the value of a single view attribute in the iterator binding’s current view row. For eg; #{bindings.CustomerId.InputValue} Tree Bindings: This is used for tables, tree-tables, and trees. It is used to expose rows of a table in the iterator binding’s current range. Eg; All Customers-#{bindings.AllCustomers.labels.CustomerId} Action Bindings: This binding type is used when buttons or command links are dropped on the user interface and require an action to be performed on them. We can use data control operations on them, for eg, Create, Delete, First, Last, Commit, Rollback, etc. Iterator Binding : This binding is created by the application to access the ADF binding context. It contains a reference to the page bound data collection, helps access it and iterates over its data objects. 67. Memory Scope for ADF Managed Beans Application Scope: The application scope lasts until the application stops. Values that you store in a managed bean with this scope is available to every session and every request that uses the application. Avoid using this scope in a task flow because it persists beyond the life span of the task flow. Session Scope: The session scope begins when a user first accesses a page in the application and ends when the user's session times out due to inactivity, or when the application invalidates the session. Use this scope only for information that is relevant to the whole session, such as user or context information. Avoid using it to pass values from one task flow to another. Instead, use parameters to pass values between task flows. Using parameters gives your task flow a clear contract with other task flows that call it or are called by it. Another reason to avoid the use of session scope is that it may persist beyond the the life span of the task flow. Page Flow Scope : Choose this scope if you want the managed bean to be accessible across the activities within a task flow. A managed bean that has a pageFlow scope shares state with pages from the task flow that access it. A managed bean that has a pageFlow scope exists for the life span of the task flow.If another task flow's page references the managed bean, the managed bean creates a separate instance of this object and adds it to the pageFlow scope of its task flow. View Scope : Use this scope for managed bean objects that are needed only within the current view activity and not across view activities. It defines the scope for each viewport that ADF Controller manages, for example, a root browser window or an ADF region. The life span of this scope begins and ends when the current viewId of viewport changes. If you specify a view, the application retains managed bean objects used on a page as long as the user continues to interact with the page. These objects are automatically released when the user leaves the page. Request Scope : Use request scope when the managed bean does not need to persist longer than the current request. Backing Bean Scope : A backing bean is a convention to describe a managed bean that stores accessors for UI components and event handling code on a JSF page. It exists for the duration of a request and should not be used to maintain state. Use this scope if it is possible that your task flow appears in two ADF regions on the same JSF page and you want to isolate each instance of ADF region. 68. Can we change DB connection for any particular AM? YES, follow steps to change DB connection: Double click on AM. GO to the configuration tab, click on configuration file bc4j.xml Here we have attribute JDBCName under element AppModuleConfig, change the connection which is created for other DB. 69. What is the difference between setting an immediate=true on a button and immediate=true on a text field? When immediate is true on a button, the command’s action and ActionListeners, including the default ActionListener provided by the JavaServer Faces implementation will be executed during the Apply Request Values phase of the request processing lifecycle, rather than waiting until the Invoke Application phase. In case of a text field, by default, values are converted and validated together in the Process Validators phase. However, if you need access to the value of a component during Apply Request Values – for example, if you need to get the value from an actionListener on an immediate commandButton – then setting this to “immediate” makes that possible. 70. How can one bounded task flow can call another? One task flow can call another bounded task flow using a task flow call activity or a URL. 71. Task Flow Activities: Method Call: Invokes a method, typically a method on a managed bean. A method call activity can be placed anywhere within an application’s control flow to invoke application logic based on control flow rules. Parent Action: Allows a bounded task flow to generate outcomes that are passed to its parent view activity. Router: Evaluates an EL expression and returns an outcome based on the value of the expression. For example, a router in a credit check task flow might evaluate the return value from a previous method call and generate success, failure, or retry outcomes based on various cases. These outcomes can then be used to route control to other activities in the task flow. Save Point Restore: Restores a previous persistent save point, including application state and data, in an application supporting save for later functionality. Task Flow Call: Calls abounded task flow from an unbounded task flow or another bounded task flow. Task Flow Return: Identifies when a bounded task flow completes and sends control flow back to the caller. (Available for bounded task flows only). View: Displays a JSF page or page fragment. Multiple view activities can represent the same page or same page fragment. Control Flow Case : Identifies how control passes from one activity to the next in the application. Wildcard Control Flow Rule: Represents a control flow case that can originate from any activities whose IDs match a wildcard expression. 72. What is the difference between Trinidad.config and Trinidad.skins? Trinidad.config file is created when you create a WebCenter Portal application. This is used to register the skin-family you are going to use for your entire application. Trinidad.skins are used when we use the skin as a jar file. This file provides a mapping between the skin id and the actual path where the skin exists. 73. JMS Integration with ADF: in the web logic console, we need to create JMS Server, JMS Queue. In the application, we need to create MessageDrivenBean implements MessageListener mapping the same jndi name of JMS Queue. We need to override onMessage() method. Whenever we recieve some message into the JMS queue, this onMessage() will be invoked with the Message as parameter. 74. Exception Handling : We need to extend DCErrorHandlerImpl class and override reportException() method. We need to register that class in the DataBindings.cpx file. When any exception is thrown in the ADF application, it will come to this metChod. 75. Contextual Event in ADF: Contextual Event is way to communicate between two taskflows. Sometimes we have taskflow to open in a region and have to get some values from task flow. Contextual Events have two parts : Publisher Event (Producer) : As button or any component that can raise event Handler Event (Customer) : That listines and process event published by the producer Oracle ADF Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Backend web development services with new frameworks
Nowadays, the customer experience passed on by an application picks its conspicuousness and proficiency in the more drawn out run. Thusly, it gets major for fashioners to focus on both front-end and back-finish of the application. Routinely, the customers can see, contact and experience the front-end or UI of the application earnestly.
Regardless, the front-end comprehension of an application is driven by various bits of its backend - database affiliations, business method for deduction, customer request masterminding, and execution. In that capacity, the makers as consistently as conceivable research ways to deal with oversee overhaul the introduction and nature of the backend web development services code. Most aces abuse vivacious back-end structures to make the applications pass on optional customer experience without putting extra time and effort.
Brief Overview of 12 Widely Used Back-end Web Frameworks
1) ASP.NET Core
Microsoft starting late released ASP.NET Core 1.0 with a few creative features to loosen up development, testing, and sending of both web and cloud application. Despite being an open source web application structure, ASP.NET Core invigorates three unequivocal stages Windows, OS X and Linux. Moreover, it draws in organizers to send their applications in different inclinations. The specialists have choice to consolidate ASP.NET Core with a few open source web improvement instruments, while abusing a pivotal shaped development condition (IDE) like Visual Studio.
2) Ruby on Rails
Ruby on Rails (RoR) is a completely used web application structure for Ruby programming tongues. It supports a few typically used programming improvement perfect models including MVC, and underlines on programming testing. The affiliation and-play regard gave by RoR engages aces to re-endeavor the web application as showed up by changing business necessities. The thing originators can other than misuse the code library and structure choices gave by RoR to accomplish regular web progress endeavors without making additional code. They can in like manner use RoR to make model of the application, and move from meaning to advance the time of the assignment quickly.
3) Django
Django is a hugely watched Python web application structure. Python attracts coordinators to accumulate web applications with irrelevant, legitimate and reusable code. Additionally, Django supports MVC plan structure. As such, the fashioners can keep the business reason, UI and application data confined. Simultaneously, they can misuse the trademark instruments gave by Django to accomplish customary web improvement endeavors like website page maps, customer underwriting, content alliance, and memcaching. Django further draws in programming specialists to change explicit bits of the web application as showed up by express business nuts and bolts. What's more, it gives a few packs, near to an energized ORM structure, and an earth shattering manager interface.
4) Node.js
The JavaScript library engages site experts to make server-side code in JavaScript. Various organizers use Node.js to shape both client side and server-side code in JavaScript. Node.js is in like manner used everything considered by organizers as a part of MEAN Stack close by MangoDb, Elegant.js and AngularJS. In any case, Node.js is planned as a cross-sort out runtime engine, and executes code through Google's V8 JavaScript engine. It further improves the execution speed of JavaScript code by executing headings in parallel through non-blocking limits and drawing in programming modelers to run assignments nonconcurrently. Simultaneously, Node.js goes with features to streamline fundamental web improvement assignments like record structure I/O, data spouting, parallel data and frameworks affiliation.
5) Play Framework
The open source best website development company application structure is written in Scala. It attracts coordinators to make feature rich web applications by joining Java and Scala programming tongues. As Play supports MVC course of action plan, it gets less amazing for artists to loosen up web application development by keeping business reason and UI layers kept. In addition, the non-blocking and stateless structure of Play Framework interfaces with creators to scale web applications without putting extra time and effort. The originators can in like manner assess the plausibility of the code constantly by profiting the trademark testing support and in a general sense hit restore work procedure of the Scala web framework.
6) Catalyst
Primary purpose is a for the most part used Perl web structure. As it supports MVC rule, it gets progressively immediate for specialists to assemble and keep up immense web applications by keeping their UI and business protection layers free. Moreover, the originators can profit the readied to-use modules give by Catalyst to accomplish an arrangement of web development endeavors like customer underwriting, dealing with, and session the board. Catalyst further goes with a lightweight test server and a significant database ORM, while supporting different templating vernaculars. The Perl web framework is besides sorted out with features to keep standard improvement attempts focal and clean.
7) Laravel
The PHP framework associates with modelers to accomplish significant assignments like check, session the board, planning and saving by surrounding expressive code. It further gives a strategy of mechanical assemblies to energize development of huge and complex web applications. Furthermore, it makes it progressively clear for programming experts to lead unit test to chart the impact of changes made to the code at various occasions of development. Laravel in like manner goes with an arrangement engine considered Blade that connects with programming artists to diminish execution overheads by making plain PHP code in the strategies. The clarification 5.3 of Laravel further goes with different new features like streamlined API request and choice to add WebSockets to the application.
8) Phalcon
Phalcon is a cutting edge PHP structure which is engineered with base on speed. As opposed to various structures, Phalcon is a PHP improvement written in C programming language. So it eats up lower resources while passing on improved execution. As Phalcon is estimatedly coupled, the thing assembles have decision to use the framework completely or its specific parts as glue sections. They can similarly download and show the structure as a PHP module. Phalcon further offers features to accomplish essential assignments like database get the chance to, check, trade, educating, dealing with, lining, plan engine, structure engineer, and sorting out.
9) Symfony
Symfony goes with a mix of features that help programming designers to make and keep up PHP web applications without putting extra time and effort. It interfaces with designers to add handiness to the site by switching things up of pre-amassed regions. Simultaneously, it also empowers them to use outcast programming areas. In this way, it gets less complex for fashioners to update the site's solace and execution by switching things up of programming parts. The customers furthermore have decision to perform unit testing by using adulated structures like PHPUnit. They also have decision to invigorate development of complex application by using the full-stack kind of the framework.
10) Yii Framework
Yii is one of the world class PHP structures open in the market. As it reinforces MVC plan, it gets less astounding for programming masters to diminish the development time by keeping the business backing and UI disengaged. Simultaneously, they can without a lot of a stretch lift the application's presentation by benefitting baffling holding support gave by Yii. Yii further urges coordinators to work with AJAX substantially more gainfully. It further makes customer input grouping through structures powerfully secure by giving validators, contraptions and right hand procedures. Moreover, it goes with features to shield the application from SQL mix and cross-site scripting ambushes. The organizers can also use Yii to perform unit tests and handiness testing without putting any extra time and effort.
11) CakePHP
The PHP framework goes with features to help programming engineers with making models and creation applications rapidly. The coordinators can benefit the code age feature of CakePHP to make models of the application adequately. At the same time, they can moreover abstain from making longer lines out of code by benefitting worked in features for database get to, assertion, endorsing, cognizance, and dealing with. The customers can also start using CakePHP on a very basic level in the wake of setting the database up. CakePHP further collaborators programming specialists to manage all bits of the application sensibly, while supporting MVC game plan.
12) Zend Framework 2
Close by being a full made PHP structure, Zend is also being used by a couple of colossal objectives. The open source framework enables programming organizers to make areas by using object-sorted out code. The specific structure of Zend further makes it continuously direct for customers to consolidate its structure confounds with various frameworks and libraries. As Zend is sifted through a combination of classes, the thing modelers can stack the key parts as individual libraries. Likewise, they can use ZendService to find the opportunity to without a doubt comprehended web benefits by recognizing client side libraries. Regardless, unique programming engineers feel that Zend has a diligently irritating need to hold data. Zend still goes with features to quicken improvement of tremendous scale web applications.
0 notes
Link
Daily obligations in a DBA life can be time-consuming, depending on the type of tasks needed to maintain a SQL Server. Problems that can occur range from SQL Server instance configuration to the actual databases it is facilitating. Allowing these issues to happen and persist can interfere with the overall performance of an environment and take away much needed time that can be spent differently.
ApexSQL Manage is a SQL Server instance management tool that can find and resolve potential problems in a SQL Server environment by performing regular health checks of SQL Server instances as well as discovering SQL Server instances, create instance snapshots and comparison between live SQL Server or snapshots and document SQL Server configuration.
Key areas, where potential issues with database configurations can interfere with SQL Server performance, and ApexSQL Manage can help are as following:
Full Recovery Mode issues
Database AUTO_CLOSE issues
Database AUTO_SHRINK issues
Database auto growth
Database capacity
Database compatibility value
Database collation
Databases without owners
Database files
Database Virtual log file number value
Full Recovery Mode issues
SQL Server’s Full Recovery Model enables you to recover to a point-in-time and provided complete protection against media failure or disaster incidents. To have a viable disaster recovery plan, it is recommended to set all production databases to full recovery mode. This will ensure a healthy chain of database and transaction log backups. Executing this rule will determine if there are databases on a SQL Server instance that are not set to Full recovery mode and offer a FixSQL script to immediately resolve this issue.
To resolve this issue, check the desired rule from the main grid and click on the FixSQL button of the main ribbon. The tool will instantly analyze which databases are in violation of the rule and generate a TSQL script to correct the issue. Click on the Execute button in the FixSQL window to run the query:
Database AUTO_CLOSE issues
When AUTO_CLOSE is set to ON, the database is closed when the last user disconnects from the database. This can hinder performance on high traffic production database since AUTO_CLOSE flushes procedure cache after each connection and increases overhead on the SQL Server instance when the database is repeatedly opened and closed. Best practice for production environments where a database is accessed regularly by different users is to set AUTO_CLOSE to OFF.
To determine if a database has AUTO_CLOSE set to ON, simply run a database health check on that SQL Server and check if the result of the rule is Failed. If the rule is not in compliance with best practices, check the rule and click on the FixSQL button to create a FixSQL script that will resolve the issue. The created script will be shown in the FixSQL window. To execute the script, click on the Execute button:
Database AUTO_SHRINK issues
Unless necessary, do not set the AUTO_SHRINK option to ON. While this is a tempting option that can save up valuable disk space, it has a drastic set of drawbacks, which in the majority of cases outweigh the positives. Setting AUTO_SHRINK to ON can lead to massive database fragmentation since SQL Server is constantly moving the last page in the database to the first available space. Repeating this process every time will put the pages out of order. Additionally, the read and write operations can cause performance issues on the SQL Server instance.
To determine if a database has AUTO_SHRINK set to ON, simply repeat the steps mentioned above, run a database health check, check if the result of the rule is Failed, and click on the FixSQL button from the main ribbon to fix the issue. Once the FixSQL window is opened it will show which databases are affected, click on the Execute button to run the query:
Database auto growth
Log file(s) and data file(s) must increase size with constant value . Set the FILEGROWTH of your database’s transaction log and data files to use memory units instead of a percentage. Setting the log and data file(s) to grow by a percentage can, through time, result in larger growth increments. This can cause the growth operation to slow down, which in turn can lead to slow database performance. Additionally, Auto Growth is a delicate topic, and best practices depend on the user environment. For example, if a database grows 1GB per day, and Auto Growth is set to 100MB, SQL Server will trigger 10 Auto Growth events, which will drastically impact performance on that SQL Server instance. It is important to monitor the database growth and quantity of inserts to determine the best value for Auto Growth.
To set the proper auto-growth run a database health check, check if the result of the rule is Failed, and to fix the issue, click on the FixSQL button from the main ribbon. Once the FixSQL window is opened, it will show the SQL code, which can be further modified to fit the needs of the user environment. Click on the Execute button to run the query:
Database capacity
This rule demonstrates how to check if the data and log file grow too close to full capacity and how to generate a FixSQL query for this issue. The best practice is to grow a database during maintenance periods, preferably when the database is offline. This will provide adequate time to add enough space and analyze how much space will be needed for the next maintenance period.
To check if database capacity is reaching near full, run a database health check. If the result of the database capacity rule is Fail, check the rule and click on the FixSQL button from the main ribbon. Presented FixSQL script will show the TSQL code, which can be used to grow the database. By default, the growth increment will be around 50%. This can further be modified to fit the needs of the user environment. Click on the Execute button to run the query:
Database compatibility value
Sometimes a database has been restored with a different compatibility value and hasn’t been changed since. To avoid potential performance issues where queries can take longer to execute, it is best practice to check the database compatibility with the compatibility specified version of the SQL Server and change it accordingly. Running this rule will determine which databases on the selected SQL Server instance have a mismatch of compatibility levels and provide a FixSQL to resolve the issue:
Database collation
Differences in database collation and SQL Server collation can cause issues when joining between different databases. To avoid such issues, best practice is to keep the same collation across databases and SQL Servers. Executing this rule will compare the database collations to SQL Server collation and create a FixSQL script with databases that have different collations from the SQL Server instance.
Note: In some cases, this difference is a deliberate configuration of the user environment, and executing this FixSQL script will not provide any benefit.
Databases without owners
This issue can occur when the defined owner, a Windows login, has been removed from the Active Directory group or the local machine. Now, the SQL Server instance has an unknown value, and the database has no owner. To resolve this issue, best practice is to assign a SQL Server Login dedicated to that database. Running this rule will provide a FixSQL with databases which do not have an owner and recommend to set system administrator (sa) as the owner. If the sa login is not considered the best fit for the database owner, it is up to the user preference to assign the appropriate owner:
Database files
It is considered best practice to keep the database files and transaction logs on separate drives. In case of disaster on the primary drive, all database files and logs will be lost, and data recovery will not be a viable option. For this rule, there is no FixSQL script since this is not possible with SQL code alone. Instead, the Violation tab offers advice on how to proceed in this scenario:
When a new database is created, it is recommended to specify separate drives for the data and logs. To move the files after the database is created, the database must be taken offline. Following methods can be used to successfully relocate data and log files:
Restore the database from backup by using the RESTORE DATABASE statement with the WITH MOVE option
Detach and then attach the database specifying separate locations for the data and log devices
Specify a new location by running the ALTER DATABASE statement with the MODIFY FILE option, and then restart the SQL Server instance
Database Virtual log file number value
Virtual log files are used by SQL Servers to internally manage the log file. They are separated into smaller files that contain the log data records. Whenever there is a need for new free space, or the active virtual logs are full, a new one is created. Too many virtual log files can cause transaction log backups to slow down and can additionally slow down database recovery. In extreme cases, this can lead to issues on the SQL Server instance that can affect insert/update/delete performance:
Conclusion
To summarize, executing health check analysis for database category using ApexSQL Manage can provide an easier overview of potential issues in managed SQL environments as well as solutions on how to resolve them and maintain a healthy SQL Server. By using this SQL Server instance management tool for regular analysis and best practice enforcement, issues can be detected before they cause major performance impact.
0 notes
Text
cPanel - Website and Hosting Management Tool
Build and Manage your WordPress Website. One Low Predictable Price!
cPanel Hosting Services will empower a Website owner with a wide variety of options at a higher level of control And automation tools designed to simplify the process of hosting a web site
With the industries best graphical interface. cPanel is an excellent option for you to consider.
cPanel's time saving automation's will make managing your Website easier than ever.
With over 80 different features which includes creating Email Accounts, Backups, File Manager, Adding Domains, MX Records, Softaculous and and the Site Publisher interface to quickly create simple websites from a variety of templates.
cPanel is the leading web hosting control panel available today
Currently in the hosting market cPanel is considered as the leading website management tool
It’s simple graphical web based interface empowers web developers, administrators and resellers to effectively develop and manage their websites
Not just for developers, even a non-professional and less technical people can easily create and manage websites and their hosting account with cPanel, you will have access to stats, disk usage and space, bandwidth usage, add, or remove email accounts, MX Records, FTP accounts.
Install different The File Manager, PHP my Sql scripts, get access to your online Web Mail
And more advanced functions, such as MIME types, cron jobs, OpenPGP keys, Apache handlers, addon domains and sub domains, password protected directories
cPanel Hosting Services is an easy to use interface for web maintenance. Even a user completely new to web hosting can easily manage their own website.
Advantages of cPanel hosting services:
Easy to use
Supports all languages
Adapts the screen size automatically, so we can use on any device
Has built-in file manager to manage the files easily
Integrated with phpMy Admin tool to manage the databases easily
Has Integrated email wizard which helps to send or receive the mails using a mail client
cPanel handles automatic upgrades of Apache, MySQL, PHP and other web applications

cPanel Features:
Looking for cPanel Hosting Services with over 80 different features?
Files
File Manager
Use the File Manager interface to manage your files. This feature allows you to upload, create, remove, and edit files without the need for FTP or other third-party applications.
Images
Use the Images interface to manage your images. You can view and resize images, or use this feature to convert image file types.
Directory Privacy
Use the Directory Privacy interface to limit access to certain resources on your website. Enable this feature to password-protect specific directories that you do not want to allow visitors to access.
Disk Usage
Use the Disk Usage interface to scan your disk and view a graphical overview of your account's available space. This feature can help you to manage your disk space usage.
Web Disk
Use the Web Disk feature to access to your website's files as if they were a local drive on your computer.
FTP Accounts
Use the FTP Accounts interface to manage File Transfer Protocol (FTP) accounts.
FTP Connections
Use the FTP Connections interface to view current connections to your site via FTP. Terminate FTP connections to prevent unauthorized or unwanted file access.
Anonymous FTP
Use the Anonymous FTP interface to allow users to connect to your FTP directory without a password. Use of this feature may cause security risks.
Backup
Use the Backup interface to back up your website. This feature allows you to download a zipped copy of your cPanel account's contents (home directory, databases, email forwarders, and email filters) to your computer.
File Restoration
Use the File Restoration interface to restore items from backed-up files.
Backup Wizard
Use the Backup Wizard interface as a step-by-step guide to assist you in backup creation.
Databases
phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a third-party tool that you can use to manipulate MySQL databases. For more information about how to use phpMyAdmin, visit the phpMyAdmin website.
MySQL Databases
Use the MySQL Databases interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, Content Management Systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
MySQL Database Wizard
Use the MySQL Database Wizard interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites with a step-by-step guide. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
Remote MySQL
Use the Remote MySQL interface to configure databases that users can access remotely. Use this feature if you want to allow applications (for example, bulletin boards, shopping carts, or guestbooks) on other servers to access your databases.
PostgreSQL Databases
Use the PostgreSQL Databases interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
PostgreSQL Database Wizard
To simultaneously create a database and the account that will access it, use the PostgreSQL Database Wizard interface. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
phpPgAdmin
phpPgAdmin is a third-party tool that you can use to manipulate PostgreSQL databases. For more information about how to use phpPgAdmin, visit the phpPgAdmin website.
Domains
Some of our Free Domain Name are mentioned and briefly mentioned for your kind regards.
Site Publisher
Use the Site Publisher interface to quickly create simple websites from a variety of templates. You can use this feature, for example, to ensure that visitors can find your contact information while you design a more elaborate website.
Addon Domains
Use the Addon Domains interface to add more domains to your account. Each addon domain possesses its own files and will appear as a separate website to your visitors.
Subdomains
Subdomains are subsections of your website that can exist as a new website without a new domain name. Use this interface to create memorable URLs for different content areas of your site. For example, you can create a subdomain for your blog that visitors can access through blog.example.com.
Aliases
Use the Aliases interface to create domain aliases. Domain Aliases allow you to point additional domain names to your account's existing domains. This allows users to reach your website if they enter the pointed domain URL in their browsers.
Redirects
Use the Redirects interface to make a specific webpage redirect to another webpage and display its contents. This allows users to access a page with a long URL through a page with a shorter, more memorable URL.
Zone Editor
Use the Zone Editor interface to add, edit, and remove A, AAAA, CNAME, SRV, MX, and TXT DNS records. It combines the functions of the Simple Zone Editor and Advanced Zone Editor interfaces.
For more information please visit our site https://rshweb.com/blog-what-is-cpanel or https://rshweb.com/
0 notes
Text
cPanel - Website and Hosting Management Tool
Build and Manage your WordPress Website. One Low Predictable Price!
cPanel Hosting Services will empower a Website owner with a wide variety of options at a higher level of control And automation tools designed to simplify the process of hosting a web site
With the industries best graphical interface. cPanel is an excellent option for you to consider.
cPanel's time saving automation's will make managing your Website easier than ever.
With over 80 different features which includes creating Email Accounts, Backups, File Manager, Adding Domains, MX Records, Softaculous and and the Site Publisher interface to quickly create simple websites from a variety of templates.
cPanel is the leading web hosting control panel available today
Currently in the hosting market cPanel is considered as the leading website management tool
It’s simple graphical web based interface empowers web developers, administrators and resellers to effectively develop and manage their websites
Not just for developers, even a non-professional and less technical people can easily create and manage websites and their hosting account with cPanel, you will have access to stats, disk usage and space, bandwidth usage, add, or remove email accounts, MX Records, FTP accounts.
Install different The File Manager, PHP my Sql scripts, get access to your online Web Mail
And more advanced functions, such as MIME types, cron jobs, OpenPGP keys, Apache handlers, addon domains and sub domains, password protected directories
cPanel Hosting Services is an easy to use interface for web maintenance. Even a user completely new to web hosting can easily manage their own website.

Advantages of cPanel hosting services:
Easy to use
Supports all languages
Adapts the screen size automatically, so we can use on any device
Has built-in file manager to manage the files easily
Integrated with phpMy Admin tool to manage the databases easily
Has Integrated email wizard which helps to send or receive the mails using a mail client
cPanel handles automatic upgrades of Apache, MySQL, PHP and other web applications.
cPanel Features:
Looking for cPanel Hosting Services with over 80 different features?
Files
File Manager
Use the File Manager interface to manage your files. This feature allows you to upload, create, remove, and edit files without the need for FTP or other third-party applications.
Images
Use the Images interface to manage your images. You can view and resize images, or use this feature to convert image file types.
Directory Privacy
Use the Directory Privacy interface to limit access to certain resources on your website. Enable this feature to password-protect specific directories that you do not want to allow visitors to access.
Disk Usage
Use the Disk Usage interface to scan your disk and view a graphical overview of your account's available space. This feature can help you to manage your disk space usage.
Web Disk
Use the Web Disk feature to access to your website's files as if they were a local drive on your computer.
FTP Accounts
Use the FTP Accounts interface to manage File Transfer Protocol (FTP) accounts.
FTP Connections
Use the FTP Connections interface to view current connections to your site via FTP. Terminate FTP connections to prevent unauthorized or unwanted file access.
Anonymous FTP
Use the Anonymous FTP interface to allow users to connect to your FTP directory without a password. Use of this feature may cause security risks.
Backup
Use the Backup interface to back up your website. This feature allows you to download a zipped copy of your cPanel account's contents (home directory, databases, email forwarders, and email filters) to your computer.
File Restoration
Use the File Restoration interface to restore items from backed-up files.
Backup Wizard
Use the Backup Wizard interface as a step-by-step guide to assist you in backup creation.
Databases
phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a third-party tool that you can use to manipulate MySQL databases. For more information about how to use phpMyAdmin, visit the phpMyAdmin website.
MySQL Databases
Use the MySQL Databases interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, Content Management Systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
MySQL Database Wizard
Use the MySQL Database Wizard interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites with a step-by-step guide. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
Remote MySQL
Use the Remote MySQL interface to configure databases that users can access remotely. Use this feature if you want to allow applications (for example, bulletin boards, shopping carts, or guestbooks) on other servers to access your databases.
PostgreSQL Databases
Use the PostgreSQL Databases interface to manage large amounts of information on your websites. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
PostgreSQL Database Wizard
To simultaneously create a database and the account that will access it, use the PostgreSQL Database Wizard interface. Many web-based applications (for example, bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops) require database access.
phpPgAdmin
phpPgAdmin is a third-party tool that you can use to manipulate PostgreSQL databases. For more information about how to use phpPgAdmin, visit the phpPgAdmin website.
Domains
Some of our Free Domain Name are mentioned and briefly mentioned for your kind regards.
Site Publisher
Use the Site Publisher interface to quickly create simple websites from a variety of templates. You can use this feature, for example, to ensure that visitors can find your contact information while you design a more elaborate website.
Addon Domains
Use the Addon Domains interface to add more domains to your account. Each addon domain possesses its own files and will appear as a separate website to your visitors.
Subdomains
Subdomains are subsections of your website that can exist as a new website without a new domain name. Use this interface to create memorable URLs for different content areas of your site. For example, you can create a subdomain for your blog that visitors can access through blog.example.com.
Aliases
Use the Aliases interface to create domain aliases. Domain Aliases allow you to point additional domain names to your account's existing domains. This allows users to reach your website if they enter the pointed domain URL in their browsers.
Redirects
Use the Redirects interface to make a specific webpage redirect to another webpage and display its contents. This allows users to access a page with a long URL through a page with a shorter, more memorable URL.
Zone Editor
Use the Zone Editor interface to add, edit, and remove A, AAAA, CNAME, SRV, MX, and TXT DNS records. It combines the functions of the Simple Zone Editor and Advanced Zone Editor interfaces.
For more information please visit our site https://rshweb.com/blog-what-is-cpanel or https://rshweb.com/
0 notes
Text
Orchestrating database refreshes for Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora
The database refresh process consists of recreating of a target database using a consistent data copy of a source database, usually done for test and development purposes. Fully-managed database solutions such as Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) or Amazon Aurora make it incredibly easy to do that. However, database administrators may need to run some post-refresh activities such as data masking or password changes, or they may need to orchestrate multiple refreshes because they manage several databases, each of them with more than one environment. In some cases, refreshes have to be performed frequently, even daily. In this post, we describe the features of a serverless solution that you can use to perform database refresh operations at scale, with a higher level of automation. This solution can be deployed and tested using the instructions available in the GitHub repo. In the next section, we go over what you’re going to build. Potential use cases The solution described in this post enables you to do the following: Refresh an existing database (or create a new one) using one of the four options available: Latestpoint – The data is aligned to the latest point in time. torestorepoint – The data is aligned to a specified point in time. fromsnapshot – The data is aligned at the snapshot creation time. fast-cloning (only for Aurora) – The data is aligned to the latest point in time, but it’s cloned using the fast-cloning feature provided by Aurora. Refresh an existing encrypted database (or create a new one). A cross-account use case has the following considerations: The only options available are fromsnapshot or fast-cloning (only for Aurora). The AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) primary key (managed by the source account) must be manually shared with the target AWS account before launching the refresh. Perform a cross-account refresh of an existing database (or create a new one). As a pre-requisite, the source account has to share with the target account the Amazon RDS or Aurora snapshot or the source Aurora cluster, before launching the refresh process. Run post-refresh SQL scripts against the new refreshed database (only available for Amazon RDS for MariaDB, Amazon RDS for MySQL and Aurora MySQL) to perform the following: Clearing, masking, or modifying sensitive data coming from the source production database. Deleting unnecessary data or removing unnecessary objects coming from the source production database. Customize the solution by adding or removing steps to orchestrate operations for those applications that have different requirements, using the same state machine. Keep the history of all the database refresh operations of your applications, in order to answer questions such as: When has my database last been refreshed? Does my application have all its non-production databases refreshed? Is the refresh that I launched yesterday complete? Prerequisites The solution implemented focuses on a time-consuming administrative task that DBAs have to deal with: the database refresh. The process consists of recreating an existing database. Typically, this is a copy used for test and development purposes whose data has to be “refreshed”. You can use a backup or the last available image of the related production environment to refresh a database. The solution can also be applied to scenarios when you create a new environment from scratch. The process can involve additional steps to apply different settings or configurations to the new refreshed database. The following diagram illustrates the process. The backup can be either logical (a partial or full export the source dataset) or physical (a binary copy of the database, which can be full, incremental, whole, or partial). The solution described in this post allows you to use physical backups (Amazon RDS or Aurora snapshots) during the restore process or the Aurora cloning feature in order to copy your databases. Solution overview The solution uses several AWS services to orchestrate the refresh process: Amazon Aurora – A MySQL-and PostgreSQL-compatible relational database built for the cloud. The solution uses Aurora snapshots or the fast cloning feature to restore Aurora database instances. Restores are performed using APIs provided by RDS and Aurora. Amazon DynamoDB – A fully-managed key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. We use it to keep track of all the refresh operations run by this solution. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud – Amazon EC2 provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud. The solution uses it in conjunction with AWS Systems Manager to run SQL scripts against your restored databases. AWS Lambda – Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You pay only for the compute time you consume. Lambda functions are used to implement all the steps of a database refresh. AWS Step Functions – A serverless function orchestrator that makes it easy to sequence AWS Lambda functions and multiple AWS services into business-critical applications. This is the core service of the solution, used to orchestrate database refreshes. Amazon RDS – A fully managed relational database solution that provides you with six familiar databases. The solution uses Amazon RDS snapshots to restore RDS databases instances. Restores are performed using APIs provided by RDS and Auroras. Amazon Simple Notification Service – Amazon SNS is a fully managed messaging service for both systems-to-system and app-to-person communication. We use it to notify users about the completion of refresh operations. Amazon Simple Storage Service – Amazon S3 is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security and performance. We use it to store the SQL scripts that the solution allows you to run against new restored databases. AWS Secrets Manager – Secrets Manager helps you to securely encrypt, store, and retrieve credentials for your database and other services. We use it to manage the access credentials of the databases involved in your refreshes. AWS Systems Manager – Systems Manager organizes, monitors and automates management tasks on your AWS resources. With Systems Manager Run Command, you can optionally run SQL scripts stored on Amazon S3 against your restored databases. This solution may incur costs; check the pricing pages related to the services you’re using. Architecture The architecture of the solution proposed is shown in the following diagram. The pre-restore workflow has the following steps: The end user prepares the refresh file (described later in this post) by configuring which steps have to be performed (including the optional creation of a Secrets Manager secret). If necessary, the end user can also prepare SQL scripts, stored on Amazon S3, to run as post-refresh scripts. The restore workflow has the following steps: The end user initiates the refresh process by starting the Step Functions state machine (the refresh process could be initiated automatically, if needed). The state machine manages each step of the database restore by invoking Lambda functions that are part of this solution The post-restore workflow includes the following steps: When the restore is complete, the state machine runs the post-restore SQL scripts. It provides two options: The state machine can run the scripts, stored on Amazon S3, through a Lambda function. If configured, you can use Secrets Manager to store and manage the database credentials. The state machine can run the scripts, stored on Amazon S3, using an EC2 instance, through Systems Manager Run Command. The state machine uses a DynamoDB table to store information about the process and its status. The state machine notifies the end user about the process final status using Amazon SNS. Steps of a database refresh Before describing in more detail what the solution looks like and how it works, it’s important to understand at a high level the main steps that are part of a database refresh: A backup of the source database is created. If the target database already exists, it’s stopped or, in most of the cases, deleted. The target database is re-created through a database restore operation, using the backup from Step 1. Post-restore scripts are run against the new restored target database. The Step Functions state machine implemented for this solution is composed by several states; most of them are related to specific steps of a database refresh operation. In particular, some states are required only for Amazon RDS, others only for Aurora, and others are required for both. The following table lists the main steps related to a refresh of an RDS DB instance performed by our solution. Step # Step Name Description 1 delete-replicas Deletes the existing read replicas of the target database 2 stop-old-database Stops the existing target database 3 perform-restore Performs the restore 4 delete-old-database Deletes the old target database 5 rename-database Renames the new target database 6 fix-tags Updates the tags of the new target database 7 create-read-replicas Re-creates the read replicas previously deleted 8 change-admin-pwd Changes the admin password of the new target database 9 rotate-admin-pwd Rotates the admin password within the secret for the new target database 10 runscripts Runs SQL scripts against the new target database 11 update-dynamodb Updates a DynamoDB table with some information about the refresh completed 12 send-msg Sends an SNS notification (e-mail) about the completion of the refresh The following table lists the main steps related to a refresh of an Aurora cluster performed by our solution. Step # Step Name Description 1 delete-replicas Deletes the existing read replicas of the target database 2 perform-restore Performs the restore (it only creates the cluster) 3 create-instance Creates a new instance within the cluster restored at Step 2 4 delete-old-database Deletes the old target DB instance 5 delete-old-cluster Deletes the old target cluster 6 rename-cluster Renames the new target cluster 7 rename-database Renames the new target database 8 fix-tags Updates the tags of the new target database 9 create-read-replicas Re-creates the read replicas previously deleted 10 change-admin-pwd Changes the admin password of the new target database 11 rotate-admin-pwd Rotates the admin password within the secret for the new target database 12 runscripts Runs SQL scripts against the new target database 13 update-dynamodb Updates a DynamoDB table with some information about the refresh completed 14 send-msg Sends an SNS notification (e-mail) about the completion of the refresh The graphic representation of the Step Function state machine that contains all the states mentioned above is available on the GitHub repo. You can use it on RDS DB instances, Aurora clusters, or both. The job poller strategy One of the main challenges of implementing an orchestrator with serverless services is to manage their stateless nature. When a certain operation is performed by a Lambda function against a database, how can we know when the operation is complete? The job poller strategy is a good solution. The following image is an extract from the solution showing this mechanism: For most of the steps that are part of a database refresh, we implement the same strategy: Step Functions invokes a Lambda function that performs a certain operation (such as restore a database). Step Functions waits a certain number of seconds (you configure) using the state of “Wait”. Step Functions invokes a Lambda function that checks if the operation has completed (if the database has been restored and its status is “available”). Step Functions verifies the results of the previous check using the state type “Choice”. Step Functions goes to the next state if the operation has completed; otherwise it waits again (returns to Step 2). Configuring your database refresh The steps of the database refresh are orchestrated by a Step Functions state machine based on an input file provided – the “refresh file”. It’s a JSON document containing all the input parameters for the state machine (in particular for the Lambda functions associated to the state machine states) which determines the characteristics of the refresh. A refresh file contains information about a specific refresh, so ideally for a single production database with two different non-production environments (one for development and one for test), a DBA has to prepare two refresh files. After these files are defined, they’re ready to be used and the related refresh can be scheduled or automated. The following code is the high-level structure of a refresh file: { "comment": "", "": { "": "", "": "", "": "", [..] "wait_time": , "check": { "": "", "": "", "checktodo": "", "torun": "true|false" }, "torun": "true|false" }, "": { "": "", "": "", "": "", [..] "wait_time": , "torun": "true|false" }, [..] } The file contains an element for every state machine’s state that needs an input. For more information about defining it, see the GitHub repo. Keep in mind the following about the refresh file: Not all the elements are required; some of them are related to steps that you may not want to run during a database refresh. Some elements are only related to Amazon RDS, others only to Aurora. Each element has a “torun” attribute that you can set to “false” in case you want to skip the related step. Each element has a “wait_time” attribute that determines for how long the state machine has to wait before checking whether the related operation or step is complete. Some elements have a “check” section that contains the input parameters for the Lambda function that verify whether a certain step completed successfully. This section has a “torun” parameter as well. Within an element, some parameters are required and others are optional. Within an element, some parameters are related to each other; if one has a value, the other one will become is also required. In this post, we show you three examples of elements related to three different steps of a database refresh. The following code shows a refresh of an RDS DB instance to the latest point: [..] "restore": { "dbservice": "rds", "source": "mysqlinstp", "target": "mysqlinstd", "restoretype": "latestpoint", "application": "app1", "environment": "development", "port": 3307, "subgrp": "db-sub-grp-virginia", "iamdbauth": "False", "cwalogs": "audit,error,general,slowquery", "copytagstosnap": "True", "dbparamgrp": "default.mysql5.7", "deletionprotection": "False", "secgrpids": "sg-03aa3aa1590daa4d8", "multiaz": "False", "dbname": "mysqlinstd", "dbclass": "db.t3.micro", "autominor": "False", "storagetype": "gp2", "wait_time": 60, "check": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mysqlinstdtemp", "checktodo": "checkrestore", "torun": "true" }, "torun": "true" } [..] The preceding section of the refresh file indicates that an RDS for MySQL DB instance “mysqlinstp” must be used as the source for the refresh to the latest point of the DB instance “mysqlinstd”. The section includes other information about the new database to be restored, including the security group ID, the storage type, the DB instance class. The state machine verifies every 60 seconds whether the restore operation is complete. In the “check” section, you can notice that a database is always restored with a name ending with the suffix “%temp”. This suffix is removed later with another step. The following code illustrates how to rename an RDS for MySQL DB instance once restored: [..] "rename": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mysqlinstdtemp", "wait_time": 10, "check": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mysqlinstd", "checktodo": "checkrename", "torun": "true" }, "torun": "true" } [..] The preceding section of the refresh file indicates that the new restored RDS DB instance “mysqlinstdtemp” must be renamed to “mysqlinstd”. The state machine verifies every 10 seconds whether rename operation is complete. The following code runs post-refresh SQL scripts against a new restored RDS DB instance: [..] "runscripts": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mysqlinstd", "engine": "mysql", "access": "secret", "secretname": "/development/app1r/mysqlinstd", "method": "lambda", "bucketname": "awsolproj", "prefix": "rdsmysql/mysqlinstd", "keys": "00test.sql,01test.sql", "wait_time": 10, "check": { "dbservice": "rds", "bucketname": "awsolproj", "prefix": "rdsmysql/mysqlinstd", "checktodo": "runscripts", "torun": "true" }, "torun": "true" } [..] The preceding section of the refresh file indicates that the scripts “00test.sql” and “01test.sql” stored on Amazon S3 in the bucket “awsolproj” must be run through Lambda against the RDS for MySQL DB instance “mysqlinstd”. Database credentials are retrieved using Secrets Manager, and the status of the operation is verified every 10 seconds. Managing secrets At the end of the restore, the new database has the same passwords for all the users within the database, including the primary user. This situation could represent a problem from a security standpoint, and for this reason the Step Functions state machine includes the following two states: change-admin-pwd and rotate-admin-pwd. With change-admin-pwd, the password of the primary user is automatically changed with a new one specified in the refresh file. If a Secrets Manager secret is configured for that database, the secret can be synchronized as well. See the following code: [..] "changeadminpwd": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mysqlinstd", "temppwd": "temppwd123", "secret": "true", "secretname": "/development/app1/mysqlinstd", "wait_time": 15, "check": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mysqlinstd", "checktodo": "checkpwd", "torun": "true" }, "torun": "true" } [..] With rotate-admin-pwd, if a Secrets Manager secret is configured and it has the rotation settings enabled, the secret containing the primary user password is rotated: "rotateadminpwd": { "dbservice": "rds", "dbinstance": "mybetainstd", "secretname": "/development/gamma/mybetainstd", "wait_time": 15, "check": { "dbservice": "rds", "secretname": "/development/gamma/mybetainstd", "temppwd": "temppwd123", "checktodo": "rotatepwd", "torun": "true" }, "torun": "true" } The solution allows you to run post-refresh SQL scripts in two ways: Using Lambda Using Systems Manager Run Command and EC2 The first option is more suitable if you’re more familiar with Lambda and want to keep the solution’s infrastructure completely serverless. Otherwise, DBAs who are used to directly managing SQL scripts on a server can easily manage them through Systems Manager: scripts are downloaded from Amazon S3 to the EC2 instance that is part of the solution and run from there. In both cases, you have to store the scripts on Amazon S3. The following code is the section of the refresh file related to the “run-script-” state: "runscripts": { "dbservice": "aurora|rds", "cluster": "", "dbinstance": "", "engine": "aurora-mysql|mysql|mariadb|oracle|aurora-postgresql|postgresql", "access": "pwd|secret", "temppwd": "", "secretname": "", "method": "lambda|ec2", "bucketname": "", "prefix": "/", "keys": ",,", "wait_time": , "check": { "dbservice": "aurora|rds", "bucketname": "", "prefix": "/", "checktodo": "runscripts", "torun": "true" }, "torun": "true" } Within a SQL script, you can run SELECT, DDL (Data Definition Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language), and DCL (Data Control Language) statements. As of this writing, this feature is available only for MySQL-related databases (Amazon RDS for MySQL, Amazon RDS for MariaDB, and Aurora MySQL) Tracking and troubleshooting your database refresh Keeping track of database refreshes is important especially when you have to manage hundreds of production databases plus the related non-production ones. This solution uses an encrypted DynamoDB table to record information about databases refreshes, giving you the ability to quickly answer questions like the following: Which date is the data of this database aligned to? When was the last time we refreshed this database? From which source did this database copy? Did the refresh of this database run successfully yesterday? Considering the production database, what’s the status of the refreshes of its non-production databases? The current structure of the DynamoDB table is the following: Table name – dbalignement-awssol Partition key – dbinstance Sort key – restoredate Additional attributes – appname,environment,recordingtime,restoretype,snapshot,source,status As of this writing, the solution doesn’t provide any local secondary index (LSI) or global secondary index (GSI) for the table, but you can easily add new GSIs to increase the number of access patterns that can be satisfied based on your needs. If a database refresh fails for any reason, you can use different services to understand the reasons. You can easily monitor the runs of your state machines through the Step Functions API or through its dashboard. The graph inspector can immediately tell you at which state there was a failure or at which state the state machine got stuck. If you choose a state, you can also take a look at the related input and output. You can also monitor the output of the Lambda functions associated with the states of the solution. Lambda logs information about its runs in Amazon CloudWatch Logs, from which you can get more details about what happened during a certain operation. Get notified or verify the database refresh completion The solution uses Amazon SNS to send emails about the success or failure of the database refreshes performed. In case of success, some details about the database just refreshed are included in the message sent. The following code is the section of the refresh file related to the “sendmsg” state: "sendmsg": { "dbservice": "aurora|rds", "application": "", "environment": "", "dbinstance": "", "source": "", "restoretype": "fromsnapshot|restorepoint|latestpoint|fastcloning", "topicarn": "", "torun": "true|false" } This feature is optional. What’s next The solution could be improved in some aspects, especially in the submission of the information about the database refresh. As of this writing, the input to provide must be manually prepared, but in the future we’re thinking about providing a user interface through which you can create the related JSON files and immediately perform some pre-checks that can validate the information provided. Notifications are sent to users via Amazon SNS but another option could be to use Amazon Simple E-mail Service (Amazon SES) to get more detailed information about the refreshes performed by sending formatted e-mails with additional information attached about the new database just restored. As of this writing, the solution doesn’t support Amazon RDS for SQL Server, and running post-refresh SQL scripts is available only for MySQL-related engines. We’re working to include those features in the remaining engines. Conclusion In this post, we showed how you can automate database refresh operations using serverless technology. The solution described can help you increase the level of automation in your infrastructure; in particular it can help reduce the time spent for an important and critical maintenance activity such as database refreshes, allowing DBAs to focus more on what matters when they manage their Amazon RDS and Aurora databases on AWS. We’d love to hear what you think! If you have questions or suggestions, please leave a comment. About the Authors Paola Lorusso is a Specialist Database Solutions Architect based in Milan, Italy. She works with companies of all sizes to support their innovation initiatives in the database area. In her role she helps customers to discover database services and design solutions on AWS, based on data access patterns and business requirements. She brings her technical experience close to the customer supporting migration strategies and developing new solutions with Relational and NoSQL databases. Marco Tamassia is a technical instructor based in Milan, Italy. He delivers a wide range of technical trainings to AWS customers across EMEA. He also collaborates in the creation of new courses such as “Planning & Designing Databases on AWS” and “AWS Certified Database – Specialty”. Marco has a deep background as a Database Administrator (DBA) for companies of all sizes (included AWS). This allows him to bring his database knowledge into classroom brining real world examples to his students. https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/database/orchestrating-database-refreshes-for-amazon-rds-and-amazon-aurora/
0 notes