#payment processing software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Billing Software Development Services IBR Infotech
IBR Infotech specializes in providing custom billing software development services designed to streamline your invoicing, payment processing, and transaction management. Our solutions offer seamless integration with existing systems, ensuring accurate, automated billing processes that enhance financial operations.
With a focus on user-friendly interfaces and robust security, our billing software helps businesses reduce manual errors, improve cash flow, and maintain compliance. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, our scalable solutions can be tailored to meet your specific needs, ensuring efficiency and accuracy across your billing cycles. Let IBR Infotech transform your billing system into a powerful tool for financial management and business growth. Read more -https://www.ibrinfotech.com/solutions/custom-billing-software-development #BillingSoftware #SoftwareDevelopment #CustomBilling #InvoicingSoftware #PaymentProcessing #TransactionManagement #AutomatedBilling #FinancialManagement #SecureBilling #BillingSolutions #ScalableSoftware #BusinessSoftware #CashFlowManagement #BillingSystem #TechSolutions #EnterpriseSoftware #BillingServices #FinancialTech #SoftwareDevelopmentServices
#billing software development#custom billing software#invoicing software solutions#payment processing software#transaction management system#automated billing#secure billing software#financial management software#billing system integration#custom invoicing software#user-friendly billing system#billing software for businesses#financial operations software#automated invoicing solutions
0 notes
Text
Explore the importance of cloud billing software for businesses. Discover the key reasons why integrating billing software is crucial for enhancing efficiency, accuracy and financial management in your organization. From faster invoicing to improving customer experience, learn how this essential tool can streamline processes and drive growth. Unlock insights into the benefits and features of online billing & accounting software to make informed decisions for optimizing your business operations.
#billing software#invoicing software#accounting software#online billing#invoice generator#small business billing#cloud billing software#automated billing#subscription billing#payment processing software
0 notes
Text
All-in-One Payment Solutions for Any Business
What Are Payment Solutions?
Imagine a world where transactions were clunky, slow, and insecure. Not only would businesses struggle, but customers would also be frustrated. That’s where payment solutions come in.
They are the backbone of the modern commerce experience, facilitating smooth, secure, and efficient money exchanges in a world that demands speed and reliability.
From in-store purchases to digital subscriptions, payment solutions enable every kind of business transaction.
At Valor, we understand that payments are not just about exchanging money – they’re about ensuring a seamless, secure, and smart transaction every time. This is why we’re constantly evolving to offer payment solutions that help businesses thrive.
#payment solutions#payment gateway#payment processor#payment processing#payments#credit card#POS#pos software#pos system#pos machine#pos solutions
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Procure-to-Pay (P2P) is a process

Procure-to-Pay (P2P) is a process that manages the purchase of goods and services in a business, from requesting items to making payments. Here are the key steps involved:
Identifying Needs: Recognising the requirement for goods or services.
Requisition Approval: Approval of purchase requests by relevant authorities.
Supplier Selection: Choosing suppliers based on price, quality, and delivery time.
Purchase Order Creation: Issuing a formal order to the supplier with details.
Receiving Goods/Services: Inspecting goods upon arrival to ensure accuracy.
Invoice Matching: Verifying the supplier’s invoice against the order and receipt.
Payment Approval: Reviewing and approving the payment.
Payment Execution: Processing payment to the supplier.
Record Keeping: Storing transaction records for compliance and future reference.
P2P helps businesses control costs, improve efficiency, and maintain compliance with policies. Automation of this process, through systems like SAP or Oracle, can further streamline operations.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
AR Analytics: Leveraging Accounts Receivable Analytics for Actionable Insights
Efficient Accounts Receivable (AR) is an essential component of any organization’s financial health. Effective management of AR ensures that the company maintains a healthy cash flow, minimizes the risk of bad debt, and fosters strong customer relationships. One of the most powerful tools at a company’s disposal to enhance AR processes is analytics. By leveraging AR analytics, businesses can gain actionable insights into payment behaviors and collection effectiveness. This blog explores how AR analytics can be used to optimize financial operations.
Understanding AR Analytics
AR analytics involves the systematic use of data and statistical analysis to understand and improve accounts receivable processes. This includes tracking payment patterns, predicting future payment behaviors, identifying potential risks, and measuring the effectiveness of collection strategies.
By implementing AR analytics, businesses can transition from reactive to proactive management of their accounts receivable. Instead of waiting for payment issues to arise, companies can anticipate potential problems and take preemptive measures to address them.
Key Metrics in AR Analytics
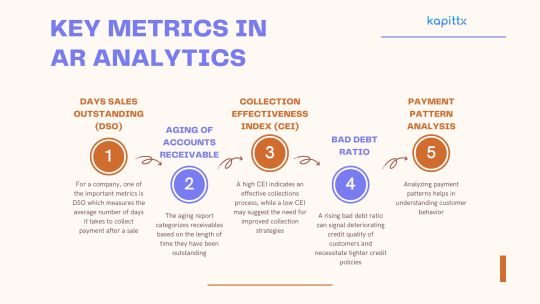
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): For a company, one of the important metrics is DSO which measures the average number of days it takes to collect payment after a sale. A lower DSO indicates faster collection of receivables and better liquidity. Monitoring DSO trends can help identify inefficiencies in the collection process and prompt corrective actions.
Aging of Accounts Receivable: The aging report categorizes receivables based on the length of time they have been outstanding. This allows for the identification of overdue accounts and prioritizes collection efforts. By analyzing aging trends, businesses can also uncover patterns that may indicate underlying issues with certain customers or products.
Collection Effectiveness Index (CEI): The Collection Effectiveness Index (CEI) gauges the efficiency of the collections process by calculating the percentage of receivables collected within a specific timeframe. A high CEI indicates an effective collections process, while a low CEI may suggest the need for improved collection strategies.
Bad Debt Ratio: This ratio compares the amount of bad debt to total sales. A rising bad debt ratio can signal deteriorating credit quality of customers and necessitate tighter credit policies.
Payment Pattern Analysis: Analyzing payment patterns helps in understanding customer behavior. By identifying customers who consistently pay late, businesses can implement targeted strategies to encourage timely payments, such as offering early payment discounts or setting stricter credit terms.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics, an advanced form of AR analytics, leverages historical data and statistical algorithms to anticipate future payment behaviors. By leveraging predictive analytics, businesses can:
Identify At-Risk Accounts: Predictive models can flag accounts that are likely to become delinquent, allowing companies to proactively engage with these customers and negotiate payment plans before issues escalate.
Optimize Credit Policies: By understanding the factors that contribute to late payments, businesses can refine their credit policies to mitigate risks. For example, adjusting credit limits based on predictive insights can help balance sales growth with credit risk.
Enhance Cash Flow Forecasting: Accurate cash flow forecasting is essential for financial planning. Predictive analytics can improve the accuracy of these forecasts by accounting for anticipated payment delays and bad debts.
Enhancing Collection Strategies

Segmentation of Receivables: Segmenting receivables based on various criteria, such as customer size, industry, and payment history, allows for tailored collection strategies. For instance, high-value customers with good payment records may be handled differently from smaller accounts with inconsistent payment patterns.
Prioritization of Collection Efforts: Using AR analytics, businesses can prioritize their collection efforts based on the likelihood of recovery. Accounts with a high probability of payment can be targeted for softer collection tactics, while accounts with lower probabilities may require more intensive follow-up.
Monitoring Collection Performance: Regularly tracking collection performance through analytics ensures that the chosen strategies are effective. By comparing the success rates of different methods, businesses can continually refine their approach.
Case Study: AR Analytics in Action
Consider a mid-sized manufacturing company that implemented AR analytics to improve its cash flow management. Prior to leveraging analytics, the company struggled with high DSO and a significant amount of overdue receivables.
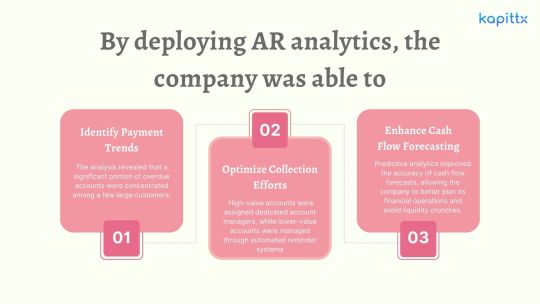
Identify Payment Trends: The analysis revealed that a significant portion of overdue accounts were concentrated among a few large customers. By addressing these accounts directly, the company was able to negotiate more favorable payment terms and reduce its DSO.
Optimize Collection Efforts: The company segmented its receivables and tailored its collection strategies accordingly. High-value accounts were assigned dedicated account managers, while lower-value accounts were managed through automated reminder systems. This resulted in a 20% improvement in the CEI.
Enhance Cash Flow Forecasting: Predictive analytics improved the accuracy of cash flow forecasts, allowing the company to better plan its financial operations and avoid liquidity crunches.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive business environment, leveraging AR analytics is no longer optional—it is a necessity. By gaining actionable insights into payment behaviors and collection effectiveness, businesses can significantly enhance their accounts receivable processes. This enhances cash flow, lowers the risk of bad debt, fortifies customer relationships, and promotes overall financial health.
Implementing AR analytics requires a commitment to data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement. With the right tools and strategies in place, businesses can transform their AR operations and achieve sustainable growth.
#ai based accounts receivable#Accounts receivable analytics#ar collection#cashflow management#ar management#ai in accounts receivable#payment reminder#cash application process#ai powered accounts receivable#accounts receivable automation software
0 notes
Text
POS Implementation
POS Implementation: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s fast-paced retail and service environments, implementing a Point of Sale (POS) system can significantly streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and improve overall efficiency. Whether you’re upgrading from a traditional cash register or installing your first POS system, proper implementation is crucial to maximizing its benefits. This guide will walk you through the essential steps of POS implementation.
Step 1: Identify Business Needs
Before selecting a POS system, assessing your business requirements is important. Consider the following:
The size and type of your business.
Specific features you need (e.g., inventory tracking, customer loyalty programs).
Budget constraints.
Integration requirements with existing software and hardware.
Step 2: Choose the Right POS System
Not all POS systems are created equal. Here’s how to select one that fits your needs:
Research and compare various providers.
Look for scalability to accommodate future growth.
Ensure it supports multiple payment methods.
Check reviews and testimonials from similar businesses.
Step 3: Hardware and Software Setup
A POS system consists of hardware (like barcode scanners, receipt printers, and card readers) and software. Ensure you:
Acquire hardware compatible with your chosen POS software.
Install and configure the software according to your operational needs.
Test all components to ensure they work seamlessly together.
Step 4: Data Migration
If you’re transitioning from an older system, data migration is a critical step:
Back up your existing data.
Transfer inventory, sales history, and customer information to the new system.
Verify the accuracy of migrated data.
Step 5: Employee Training
Proper training ensures your team can effectively use the POS system:
Organize hands-on training sessions.
Provide user manuals and support materials.
Address common troubleshooting scenarios.
Step 6: Pilot Testing
Before full-scale implementation, conduct a pilot test:
Use the system in a controlled environment.
Monitor for any issues or inefficiencies.
Gather feedback from staff and customers.
Step 7: Go Live
Once testing is complete, it’s time to roll out the system:
Schedule the launch during a low-traffic period to minimize disruptions.
Ensure on-site support is available for the initial days.
Communicate the change to your team and customers.
Step 8: Monitor and Optimize
Implementation doesn’t end with the launch. Regular monitoring is essential:
Analyze performance metrics (e.g., transaction times, error rates).
Update the system as needed to fix bugs and improve features.
Seek ongoing feedback from employees and customers.
Conclusion
Implementing a POS system is an investment in your business's future. With proper planning and execution, it can simplify daily operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive growth. By following the steps outlined above, you can ensure a smooth and successful implementation.
#POS System Implementation#Point of Sale Guide#Retail Technology#Business Efficiency#POS Hardware and Software#Data Migration Tips#Employee Training for POS#Pilot Testing POS#POS System Optimization#Small Business Solutions#Inventory Management#Customer Loyalty Programs#Payment Integration#Retail Operations#Streamlining Business Processes
0 notes
Text
Efficient Payroll Management Solutions for Accurate and Timely Employee Compensation
Efficient payroll management is essential for maintaining employee trust and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Payroll software simplifies the process by automating salary calculations, tax deductions, and payment scheduling. This technology reduces errors, saves time, and provides detailed reports for compliance and transparency. A modern payroll solution integrates seamlessly with other HR functions, offering scalability and customization to meet the unique needs of businesses. Streamline your payroll process to enhance accuracy, reduce administrative burden, and ensure timely employee payments.
More info: https://ahalts.com/solutions/hr-services/complete-payroll

#Payroll Management#Payroll Software#Salary Processing#Tax Deductions#Employee Compensation#Wage Calculation#Automated Payroll#Compliance Reporting#Payment Schedules#HR Payroll Solutions
0 notes
Text
#POS System#Restaurant Management#Restaurant POS#Hospitality Software#Food Service Technology#TouchBistro POS#Restaurant Software#Inventory Management#Customer Loyalty Program#Staff Scheduling#Menu Management#Point of Sale#Restaurant Analytics#Payment Processing#Table Management#Mobile POS#Restaurant Operations#Order Management#Kitchen Display System#Cloud POS
1 note
·
View note
Text
Enhancing Vendor Management Relationships through MYNDAPX
“We’re not on the same page,” “I wasn’t informed about this change,” “Our emails/calls go unanswered,” or “We’re always the last to know,” are the common statements we get to hear between a vendor and a business.
In the fast-paced world of business, the significance of strong vendor relationships cannot be overstated. They are the foundation upon which companies build their operational success and growth. Yet, managing these relationships efficiently remains a formidable challenge for many businesses. Communication gaps, inconsistencies in payments, and complexities in contracts often hinder the smooth operation of these relationships. Addressing these challenges necessitates a revolutionary approach—one that MYNDAPX offers with its cutting-edge technology aimed at streamlining processes and fostering a culture of trust and transparency.
#Vendor Management#MYNDAPX#vendor management software#vendor payment process#vendor payment system#MYNDSolution
0 notes
Text
Billing and Invoice Process for Small Business

Invoicing vs. Billing
Invoice is an office based document and process where a seller distributes a commercial document displays the profit or sale from one business to another business or consumer, owners etc. It may contain information about the particular party name, product quantity, tax, and GST and payment terms.
On the other hand, a Billing is a sales document that mostly deals with the payment for purchasing items, products or services with respect to. It’s either written in a piece of paper or in electronically format to serve as a transaction happens between the buyer and the seller or else vice-versa.
What is an invoice?
An invoice is an item or product based document that maintain track of products or services delivered to the customer, customer, total amount, dues etc.
Invoices are nothing but the commercial records that helps organizations and companies to get paid for their services.
Who uses an invoice, and what is the purpose?
Invoices are used by the small vendors.
It helps to keep an account of the sales or supplies.
To keep the track of inventory of the business.
It can also be used as historical data for future prediction.
To keep track of business income for tax purposes.
What are the best invoicing tools out there?
Creating a manually invoicing is always stressful, sending it out, and also taking the follow up too consume lot of time. Even more stressful for any business or organizations is the recurring invoices that consume lot of time and money cost.
The main benefits of choosing right billing software are to manually manage the data in a spreadsheet format. The TRIRID-Billing software is easy to use and take less time to generate receipt.
Whether you have a small, medium or large business, TRIRID-Billing software keep tabs on every transactions. It means that no need to worry about entering a tab every time on your keyboard from computer before you perform accounting transactions.
With the help of TRIRID-Billing software you can see exactly when a consumer opens the invoice a perform necessary transactions. You can easily check your transactions and other necessary tasks anytime anywhere.
With TRIRID-Billing software you can store your invoices in the form of data files on your Computer/Mobile/Tablet etc. Now you have rights to access to them without use of any paper.
For More Information:
Call @ +91 8980010210
Visit @ https://tririd.com/tririd-biz-gst-billing-accounting-software
#Benefits of Billing Software#Custom Billing Software#processing invoices for payment#TRIRID-Billing in Bopal-Ambli road-ahmedabad#TRIRID-Billing in ISCON-Ambli road-ahmedabad
0 notes
Text
#Housecall Pro review#Home service business software#Business management software#Field service management#Scheduling software for service businesses#Invoicing and payment processing tools#Customer management software#Marketing tools for service pros#Home service industry solutions#Business software for plumbers#HVAC business management#Landscaping business software#Electrical service software#Service business automation#Small business technology solutions#Streamlining business operations#Growing a service business#Software for service professionals#Home service scheduling tools#Best software for service businesses
0 notes
Text
What is EMV Software? Key Components, Types, and Global Applications

In today’s digital age, the need for secure and efficient payment systems has become paramount. EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) technology has emerged as a global standard for secure credit and debit card transactions. EMV software plays a critical role in enabling this technology, ensuring that payment systems are secure, reliable, and compliant with international standards. This blog will explore what EMV software is, its key components, the different types of EMV software, and its applications across various regions, including Türkiye, Africa, Malaysia, UAE, China, Hong Kong, Algeria, Bulgaria, Ghana, Oman, Ethiopia, Kuwait, Nigeria, Finland, Zimbabwe, Kenya, Mexico, Qatar, Singapore, and Poland.
What is EMV Software?
EMV software is a specialized application that facilitates secure payment transactions using EMV chip technology. Unlike traditional magnetic stripe cards, EMV chip cards store data on a microprocessor chip, which generates a unique transaction code for every payment. This makes it nearly impossible for fraudsters to clone cards or steal sensitive information.
EMV software is integrated into payment terminals, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and ATMs to enable communication between the chip card and the payment network. It ensures that transactions are authenticated, encrypted, and processed securely. The software also supports compliance with EMV standards, which are mandated by card networks like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express.
Why is EMV Software Important?
Enhanced Security: EMV software reduces the risk of card-present fraud by using dynamic authentication for each transaction.
Global Compliance: It ensures that payment systems adhere to international EMV standards, enabling seamless cross-border transactions.
Customer Trust: Secure transactions build trust among consumers, encouraging the use of digital payments.
Fraud Prevention: By replacing static magnetic stripe data with dynamic transaction codes, EMV software significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and copyright fraud.
Key Components of EMV Software
EMV software is a complex system that relies on several key components to function effectively. These components work together to ensure secure, efficient, and compliant payment processing.
1. Chip Card Interface
The chip card interface is the foundation of EMV software. It enables communication between the EMV chip card and the payment terminal. This interface supports the exchange of data, including transaction details, authentication codes, and encryption keys.
2. Cryptographic Algorithms
EMV software uses advanced cryptographic algorithms to secure transaction data. These algorithms encrypt sensitive information, such as cardholder data and transaction amounts, to prevent unauthorized access. Common algorithms include RSA, AES, and SHA.
3. Transaction Processing Engine
The transaction processing engine is the core of EMV software. It handles the entire transaction lifecycle, from card authentication to authorization and settlement. This component ensures that transactions are processed quickly and accurately.
4. Authentication Protocols
EMV software supports multiple authentication protocols to verify the legitimacy of the card and the transaction. These include:
Static Data Authentication (SDA): Verifies that the card data has not been altered.
Dynamic Data Authentication (DDA): Uses cryptographic methods to validate the card and transaction.
Combined Data Authentication (CDA): Combines SDA and DDA for enhanced security.
5. Terminal Management System
The terminal management system allows businesses to configure, monitor, and update payment terminals remotely. This component ensures that terminals are always running the latest version of EMV software and are compliant with current standards.
6. Risk Management Tools
EMV software includes risk management tools to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions. These tools analyze transaction patterns, flag suspicious activities, and implement additional security measures when necessary.
7. Compliance Modules
Compliance modules ensure that the software adheres to EMV standards and regional regulations. These modules are regularly updated to reflect changes in industry requirements.
8. User Interface
The user interface (UI) is the front-end component of EMV software that allows merchants and customers to interact with the payment system. A well-designed UI ensures a smooth and intuitive payment experience.
Types of EMV Software
EMV software can be categorized based on its application, functionality, and deployment model. Below are the main types of EMV software:
1. EMV Payment Terminal Software
EMV terminal software is installed on payment terminals and POS systems. It enables these devices to read EMV chip cards, process transactions, and communicate with payment networks. This type of software is widely used in retail stores, restaurants, and other merchant locations.
2. EMV ATM Software
EMV ATM software is designed for automated teller machines (ATMs). It allows ATMs to accept EMV chip cards for cash withdrawals, balance inquiries, and other banking services. This software is essential for reducing ATM fraud and ensuring compliance with EMV standards.
3. EMV Mobile Payment Software
With the rise of mobile payments, EMV software has been adapted for smartphones and other mobile devices. This type of software enables contactless payments using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. Examples include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay.
4. EMV Card Issuance Software
EMV card issuance software is used by banks and financial institutions to personalize and issue EMV chip cards. This software encodes cardholder data onto the chip and generates cryptographic keys for secure transactions.
5. EMV Host System Software
EMV host system software is deployed on the backend of payment networks. It handles transaction authorization, settlement, and fraud detection. This software is critical for ensuring the smooth operation of large-scale payment systems.
6. EMV Testing and Certification Software
Before EMV software can be deployed, it must undergo rigorous testing and EMV certification to ensure compliance with industry standards. EMV testing software simulates real-world transaction scenarios to identify and resolve potential issues.
7. EMV Cloud-Based Software
Cloud-based EMV software is hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. This type of software offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for businesses with multiple locations or those looking to reduce hardware costs.
Applications of EMV Software Across Regions
EMV software and EMV Kernel is used globally to enhance payment security and streamline transaction processing. Below is an overview of its applications in various regions:
1. Türkiye
In Türkiye, EMV software is widely adopted in retail, hospitality, and banking sectors. The country has seen a significant reduction in card fraud since implementing EMV technology.
2. Africa
African countries, including Ghana, Nigeria, Kenya, and Zimbabwe, are increasingly adopting EMV software to combat fraud and promote financial inclusion. Mobile payment solutions powered by EMV technology are particularly popular in this region.
3. Malaysia
Malaysia has a well-established EMV infrastructure, with most payment terminals and ATMs supporting chip card transactions. EMV software is also integrated into the country’s popular e-wallet services.
4. UAE
The UAE is a leader in adopting advanced payment technologies. EMV software is used in retail, transportation, and government services to ensure secure and efficient transactions.
5. China and Hong Kong
China and Hong Kong have embraced EMV technology, particularly for contactless payments. EMV software is integrated into mobile payment platforms like Alipay and WeChat Pay.
6. Algeria
Algeria is transitioning from magnetic stripe cards to EMV chip cards, with EMV software playing a key role in this shift. The technology is helping to reduce fraud and improve payment security.
7. Bulgaria
Bulgaria has adopted EMV software across its banking and retail sectors. The country’s payment infrastructure is fully compliant with EMV standards.
8. Oman
Oman has implemented EMV software in its payment terminals and ATMs to enhance security and support the growing adoption of contactless payments.
9. Ethiopia
Ethiopia is in the early stages of adopting EMV technology. EMV software is being introduced to modernize the country’s payment systems and reduce fraud.
10. Kuwait
Kuwait has a robust EMV infrastructure, with most payment terminals and ATMs supporting chip card transactions. EMV software is also used in the country’s popular mobile payment apps.
11. Finland
Finland is a pioneer in digital payments, with EMV software widely used in retail, transportation, and online transactions. The country’s payment systems are known for their security and efficiency.
12. Mexico
Mexico has adopted EMV software to combat card fraud and improve payment security. The technology is widely used in retail, hospitality, and banking sectors.
13. Qatar
Qatar has implemented EMV software across its payment infrastructure to support secure and seamless transactions. The country is also exploring the use of EMV technology in government services.
14. Singapore
Singapore is a global leader in payment innovation, with EMV software integrated into its advanced payment systems. The country’s payment terminals and ATMs are fully EMV-compliant.
15. Poland
Poland has a well-established EMV infrastructure, with most payment terminals and ATMs supporting chip card transactions. EMV software is also used in the country’s popular mobile payment apps.
EMV software is a critical component of modern payment systems, enabling secure, efficient, and compliant transactions. Its key components, including chip card interfaces, cryptographic algorithms, and transaction processing engines, work together to ensure the integrity of payment data. With various types of EMV software available, businesses can choose the solution that best meets their needs.
As the adoption of EMV technology continues to grow globally, regions like Türkiye, Africa, Malaysia, UAE, China, Hong Kong, Algeria, Bulgaria, Ghana, Oman, Ethiopia, Kuwait, Nigeria, Finland, Zimbabwe, Kenya, Mexico, Qatar, Singapore, and Poland are benefiting from enhanced payment security and reduced fraud. By leveraging EMV software, businesses and financial institutions can build trust with customers, comply with international standards, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of digital payments.
0 notes
Text
#Choosing veterinary software#pet appointment booking India#Pet appointment software#Pet clinic booking software#Pet clinic payment processing#Pet clinic software#Pet clinic software India#Pet healthcare software#Pet management software#Top tips for veterinary software#vet appointment software#vet clinic software#Vet practice software India#Vet Software#Veterinary appointment booking#Veterinary appointment booking India#Veterinary Billing Software Suriname#Veterinary billing system#Veterinary clinic management software tips#veterinary clinic software#Veterinary clinic software India#Veterinary EMR software#veterinary management software#veterinary practice form#Veterinary practice management India#Veterinary Practice Management software#Veterinary Software
1 note
·
View note
Text
Faster Withdrawals, Happier You: Streamline Your Finances with PayTrackster
PayTrackster, payment analytics software is not just an automated payment processor, but something more enduring. It’s a one-and-only solution that keeps you under control of e-commerce finances, expedites PayPal’s withdrawal approval, and allows you to save on chargebacks and other costly inconveniences. Through automating processes, eliminating errors and providing real-time insights, PayTrackster saves you valuable time and resources so you can focus on fundamentals — your business growth and success.
0 notes