#pipeline monitoring system
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
0 notes
Link
Rising oil & gas demand from developing countries, coupled with the ongoing proliferation across automation and Internet of Thing (IoT) will stimulate the...
0 notes
Text
https://allventurehub.com/pipeline-monitoring-system-market-share-analysis-and-key-developments/
Pipeline Monitoring System Market
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Importance of Water Utility Surveys
Water is a fundamental resource that sustains life, and the infrastructure supporting its supply and distribution is a critical component of urban and rural development. A water utility survey plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient and sustainable management of water resources.
Learn more at https://www.cyberswift.com/blog/water-utility-solution-detailed-overview/

#3D mapping for water utilities#Digital mapping for water utilities#GIS-based water utility mapping#Hydrographic utility surveys#Remote sensing for water pipelines#Surveying for water utility systems#Underground water pipeline surveys#Utility mapping for water projects#Water distribution network survey#Water distribution system assessment#Water infrastructure surveys#Water leakage detection surveys#Water pipeline mapping#Water pipeline monitoring solutions#Water supply network survey#Water utility asset management#Water utility inspection surveys#Water utility network monitoring#Water utility survey services
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Pipeline Monitoring System Market#Trends#Growth#Opportunities Analysis Forecast Report By 2032 | 195 Pages Report#intellectualmarketinsights
0 notes
Text
Although dam removals have been happening since 1912, the vast majority have occurred since the mid-2010s, and they have picked up steam since the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which provided funding for such projects. To date, 806 Northeastern dams have come down, with hundreds more in the pipeline. Across the country, 2023 was a watershed year, with a total of 80 dam removals. Says Andrew Fisk, Northeast regional director of the nonprofit American Rivers, “The increasing intensity and frequency of storm events, and the dramatically reduced sizes of our migratory fish populations, are accelerating our efforts.”
Dam removals in the Northeast don’t generate the same media attention as massive takedowns on West Coast rivers, like the Klamath or the Elwha. That’s because most of these structures are comparatively miniscule, built in the 19th century to form ponds and to power grist, textile, paper, saw, and other types of mills as the region developed into an industrial powerhouse.
But as mills became defunct, their dams remained. They may be small to humans, but to the fish that can’t get past them “they’re just as big as a Klamath River dam,” says Maddie Feaster, habitat restoration project manager for the environmental organization Riverkeeper, based in Ossining, New York. From Maryland and Pennsylvania up to Maine, there are 31,213 inventoried dams, more than 4,000 of which sit within the 13,400-square-mile Hudson River watershed alone. For generations they’ve degraded habitat and altered downstream hydrology and sediment flows, creating warm, stagnant, low-oxygen pools that trigger algal blooms and favor invasive species. The dams inhibit fish passage, too, which is why the biologists at the mouth of the Saw Kill transported their glass eels past the first of three Saw Kill dams after counting them...
Jeremy Dietrich, an aquatic ecologist at the New York State Water Resources Institute, monitors dam sites both pre- and post-removal. Environments upstream of an intact dam, he explains, “are dominated by midges, aquatic worms, small crustaceans, organisms you typically might find in a pond.” In 2017 and 2018 assessments of recent Hudson River dam removals, some of which also included riverbank restorations to further enhance habitat for native species, he found improved water quality and more populous communities of beetles, mayflies, and caddisflies, which are “more sensitive to environmental perturbation, and thus used as bioindicators,” he says. “You have this big polarity of ecological conditions, because the barrier has severed the natural connectivity of the system. [After removal], we generally see streams recover to a point where we didn’t even know there was a dam there.”

Pictured: Quassaick Creek flows freely after the removal of the Strooks Felt Dam, Newburgh, New York.
American Rivers estimates that 85 percent of U.S. dams are unnecessary at best and pose risks to public safety at worst, should they collapse and flood downstream communities. The nonprofit has been involved with roughly 1,000 removals across the country, 38 of them since 2018. This effort was boosted by $800 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. But states will likely need to contribute more of their own funding should the Trump administration claw back unspent money, and organizations involved in dam removal are now scrambling to assess the potential impact to their work.
Enthusiasm for such projects is on the upswing among some dam owners — whether states, municipalities, or private landholders. Pennsylvania alone has taken out more than 390 dams since 1912 — 107 of them between 2015 and 2023 — none higher than 16 feet high. “Individual property owners [say] I own a dam, and my insurance company is telling me I have a liability,” says Fisk. Dams in disrepair may release toxic sediments that potentially threaten both human health and wildlife, and low-head dams, over which water flows continuously, churn up recirculating currents that trap and drown 50 people a year in the U.S.
Numerous studies show that dam removals improve aquatic fish passage, water quality, watershed resilience, and habitat for organisms up the food chain, from insects to otters and eagles. But removals aren’t straightforward. Federal grants, from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or the Fish and Wildlife Service, favor projects that benefit federally listed species and many river miles. But even the smallest, simplest projects range in cost from $100,000 to $3 million. To qualify for a grant, be it federal or state, an application “has to score well,” says Scott Cuppett, who leads the watershed team at the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation’s Hudson River Estuary Program, which collaborates with nonprofits like Riverkeeper to connect dam owners to technical assistance and money...

All this can be overwhelming for dam owners, which is why stakeholders hope additional research will help loosen up some of the requirements. In 2020, Yellen released a study in which he simulated the removal of the 1,702 dams in the lower Hudson watershed, attempting to determine how much sediment might be released if they came down. He found that “the vast majority of dams don’t really trap much sediment,” he says. That’s good news, since it means sediment released into the Hudson will neither permanently worsen water quality nor build up in places that would smother or otherwise harm underwater vegetation. And it shows that “you would not need to invest a huge amount of time or effort into a [costly] sediment management plan,” Yellen says. It’s “a day’s worth of excavator work to remove some concrete and rock, instead of months of trucking away sand and fill.” ...
On a sunny winter afternoon, Feaster, of Riverkeeper, stands in thick mud beside Quassaick Creek in Newburgh, New York. The Strooks Felt Dam, the first of seven municipally owned dams on the lower reaches of this 18-mile tributary, was demolished with state money in 2020. The second dam, called Holden, is slated to come down in late 2025. Feaster is showing a visitor the third, the Walsh Road Dam, whose removal has yet to be funded. “This was built into a floodplain,” she says, “and when it rains the dam overflows to flood a housing complex just around a bend in the creek.” ...
On the Quassaick, improvements are evident since the Strooks dam came out. American eel and juvenile blue crabs have already moved in. In fact, fish returns can sometimes be observed within minutes of opening a passageway. Says Schmidt, “We’ve had dammed rivers where you’ve been removing the project and when the last piece comes out a fish immediately storms past it.”
There is palpable impatience among environmentalists and dam owners to get even more removals going in the Northeast. To that end, collaborators are working to streamline the process. The Fish and Wildlife Service, for example, has formed an interagency fish passage task force with other federal agencies, including NOAA and FEMA, that have their own interests in dam removals. American Rivers is working with regional partners to develop priority lists of dams whose removals would provide the greatest environmental and safety benefits and open up the most river miles to the most important species. “We’re not going to remove all dams,” [Note: mostly for reasons dealing with invasive species management, etc.] says Schmidt. “But we can be really thoughtful and impactful with the ones that we do choose to remove.”
-via Yale Environment 360, February 4, 2025
#rivers#riparian#united states#north america#northeast#pennsylvania#massachusetts#new york#dam#dam removal#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - April 1-7
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles! Last month’s Doodles are free to the public, so go take a look :D
1. Galapagos tortoises at Philadelphia Zoo become first-time parents at nearly 100

“Mommy, the female tortoise, is considered one of the most genetically valuable Galapagos tortoises in the Association of Zoos and Aquariums’ species survival plan. [… T]he zoo said it is “overjoyed” at the arrivals of the four hatchlings, a first in its more than 150-year history.”
2. Massachusetts home-electrification pilot could offer a national model

“In total, the program is providing free or heavily subsidized solar panels and heat pumps to 55 participating households, 12 of which also received batteries at no cost. […] It’s a strategy that program planners hope can help address the disproportionate energy burden felt by lower-income residents of the region[….]”
3. National Park Rangers rebel against queer erasure on Trans Day of Visibility

“[… A] group of over 1,000 off-duty, fired, and retired National Park Service employees launched Rangers Uncensored, an online archive that restores and amplifies LGBTQ+ stories quietly scrubbed from government websites since President Donald Trump’s second inauguration.”
4. World's largest wildlife crossing reaches critical milestone

“Over the next few days they'll be adding 6,000 cubic yards of specially manufactured soil to cover the crossing, a mix of sand, silt and clay inoculated with a bit of compost and hyperlocal mycorrhizal fungi, carefully designed and tested to mimic the biological makeup of native soils around the site.“
5. Bipartisan bill to boost green building materials glides through House

“[B]ipartisan legislation the House of Representatives passed in a 350-73 vote last week would give the Department of Energy a clear mandate to develop a full program to research, develop, and deploy clean versions of the building materials.”
6. Tribal Wildlife Grants Funding Announced
“Tribal Wildlife Grants are intended to help Tribes develop programs for the conservation of habitat and species of traditional or cultural importance[….] Typically funded projects include: conservation planning, fish and wildlife management and research, habitat mapping and restoration, inventory and monitoring, and habitat preservation. […] A total of $6.1 million is available for this round of funding[….]”
7. Germany adds another one million PV arrays to take solar total to 104 gigawatts

“Following a rapid rise in household solar panel installations, Germany’s total number of PV arrays has passed the five million “milestone[.…]” Solar systems already cover almost 15 percent of Germany’s electricity demand, BSW-Solar said. […] The total capacity of all PV systems installed in Germany surpassed 100 GW at the start of the year.”
8. Stronger together: Bilby conservation efforts enhanced by Indigenous knowledge

“Ms. Geyle said the results showed combining [conventional science and traditional tracking methods] more accurately estimated bilby abundance than using either technique individually[….] "[… ensuring] that Indigenous people remain central to decision-making about their lands and species that inhabit them," Ms. Geyle said.”
9. Lennar will build 1,500new Colorado homes with geothermal heat pumps

“The homebuilder is partnering with Dandelion Energy to install the tech, which is efficient but expensive — unless it’s built into new homes from the start. […] And by eliminating the need for new gas pipelines and reducing the peak electricity demands on the power grid, subdivisions built on this model could save a bundle on utilities as well[….]”
10. New strategy launched to protect Tanzanian biodiversity hotspot

“Conservationists have launched a 20-year-long project to protect what is arguably Tanzania’s most biologically rich landscape: the Udzungwa Mountains. The strategy places notable emphasis on communities living here, with more than half of its budget allocated to social and economic projects and managing human-wildlife conflict.”
March 22-28 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#nature#philadelphia#zoo#galapagos#tortoise#solar panels#clean energy#national park service#lgbt+#lgbt#lgbtq#park ranger#wildlife#us politics#ecology#green infrastructure#indigenous#habitat restoration#germany#solar energy#solar power#australia#geothermal#heat pump#energy efficiency#biodiversity#tanzania#animals
266 notes
·
View notes
Text

Egyptologists Clash Over ‘Underground City’ Beneath Pyramids
Claims that an “underground city” exists beneath ancient Egyptian pyramids have caused a row among experts.
Researchers from Italy say they have uncovered giant vertical shafts wrapped in “spiral staircases” under the Khafre pyramid.
They said on Sunday that they found a limestone platform with two chambers and channels that resemble pipelines for a water system more than 2,100 feet below the pyramid, with underground pathways leading even deeper into the earth.
But the claims – which have not been published or independently peer-reviewed – were labelled “false” and “exaggerated” by fellow Egyptologists.

Researchers claim they have discovered eight cylinder-shaped structures below the Khafre - Khafre Project.
Prof Corrado Malanga and his team from the University of Pisa used radar pulses to create high-resolution images deep into the ground, similar to how sonar radar maps the ocean.
In a statement, he said: “When we magnify the images [in the future], we will reveal that beneath it lies what can only be described as a true underground city.”
The scientists have also said there is “an entire hidden world of many structures’’ and that “the Pyramid of Khafre might conceal undiscovered secrets, notably the fabled Hall of Records”.
The Hall of Records, a concept popularised in ancient Egyptian lore, is believed to be an ancient library beneath the Great Pyramid or the Sphinx, with vast amounts of information about the ancient civilisation.
Prof Lawrence Conyers, a radar expert at the University of Denver who focuses on archaeology, told the Daily Mail it was not possible for the technology to penetrate that deeply into the ground.
He said the idea that it proves an underground city existed is “a huge exaggeration”.
But he said it was conceivable small structures, such as shafts and chambers, may be present from before the pyramids were built.
He highlighted how “the Mayans and other peoples in ancient Mesoamerica often built pyramids on top of the entrances to caves or caverns that had ceremonial significance to them”.
The work by Prof Malanga and fellow researchers Filippo Biondi and Armando Mei was previously discussed during a briefing in Italy last week.
The project’s spokesman, Nicole Ciccolo, shared a video on Saturday of the trio discussing the findings that are yet to be published in a scientific journal.
Tomographic images could indicate internal artificial structures under the pyramid - Khafre Project.
The team focused on the Khafre pyramid, which, along with Khufu and Menkaure pyramids, make up the three in the Giza complex.
The pyramids are thought to have been built some 4,500 years ago and sit on the west bank of the Nile river in northern Egypt.
The vertical shafts identified below the ground were about 33 to 39 feet in diameter, located at a depth of at least 2,130 feet, the researchers said, adding that they may support the pyramid, which needs “a strong foundation, otherwise it may sink”.
The team showed an image created by using the pulses which they claim includes “a complex, luminous structure with distinct vibrations” they believe is “an actual underground city”.
“The existence of vast chambers beneath the earth’s surface, comparable in size to the pyramids themselves, have a remarkably strong correlation between the legendary Halls of Amenti,” Ms Ciccolo said.
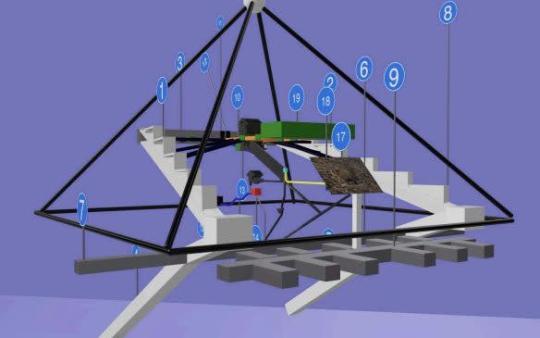
A 3D model displays the structures inside the central part of the Pyramid of Khafre - Khafre Project.
Prof Malanga and Mr Biondi published a separate peer-reviewed paper in October 2022 in the scientific journal Remote Sensing, which found hidden rooms and ramps inside Khafre, along with evidence of a thermal anomaly near the pyramid’s base.
The new study used similar technology but with extra help from satellites orbiting Earth.
Radar signals from two satellites about 420 miles above Earth were directed into the Khafre pyramid.
The experts then monitor how they bounce back and convert the signals into sound waves, which allows them to “see” through the solid stone and map out underground structures in 3D.
Prof Malanga claimed the results had been “completely consistent” and using two satellites ruled out the chance of “misinterpretation”.
By Michael Searles.

View of the ancient crypt inside the Great step pyramid of Djoser, Saqqara. Cairo.
#Egyptologists Clash Over ‘Underground City’ Beneath Pyramids#Scientists using new radar technology find 'vast city' beneath pyramids#Khafre pyramid#Khafre Project#The Hall of Records#ancient artifacts#archeology#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient Egypt#egyptian history
165 notes
·
View notes
Text




I have said this before, and I will say it again: the us, israel and turkey are the wombs of evil—warmongering, unscrupulous, immoral killing machines wreaking havoc, desolation, and death anywhere they tread.
My heart goes out to Palestinians, and I dread what this means for us Armenians. In case you didn't know, israel, supported by the us in all its military "endeavors," is heavily supporting the azeris (thus the us-israel-azeri military pipelines). And what are the azeris doing with all those weapons?
On March 5 [2023], the Israeli Haaretz newspaper published an astounding article titled, “92 Flights from Israeli Base Reveal Arms Exports to Azerbaijan.” The article reported that on March 2, Azerbaijan’s Silk Way Airlines’ cargo plane landed in Israel’s Ovda military airport. Two hours later, it returned to Baku via Turkey and the Georgian Republic. In the last seven years, this is the 92nd cargo flight from Baku to Ovda, the only airfield in Israel that is allowed to export explosives. These military shipments increased substantially during Azerbaijan’s attacks on Armenia/Artsakh in 2016, 2020, 2021 and 2022. President Ilham Aliyev of Azerbaijan has described Israel’s covert relations with Azerbaijan as being like an iceberg – nine-tenths of it is below the surface. Israel supplies almost 70-percent of Azerbaijan’s weapons and in return receives about half of its imported oil. Haaretz quoted foreign media sources disclosing: “Azerbaijan has allowed the Mossad [Israel’s intelligence agency] to set up a forward branch [in Azerbaijan] to monitor what is happening in Iran, Azerbaijan’s neighbor to the south, and has even prepared an airfield intended to aid Israel in case it decides to attack Iranian nuclear sites. Reports from two years ago stated that the Mossad agents who stole the Iranian nuclear archive smuggled it to Israel via Azerbaijan. According to official reports from Azerbaijan, over the years Israel has sold it the most advanced weapons systems, including ballistic missiles, air defense and electronic warfare systems, kamikaze drones and more.” Haaretz revealed that Azerbaijan’s Silk Way Airlines “operates three weekly flights between Baku and [Israel’s] Ben-Gurion International Airport with Boeing 747 cargo freighters.” In addition, some Eastern European countries circumvent the ban on the sale of weapons to Azerbaijan by shipping them via Israel. The restriction of the sale of weapons by Europe and the United States to Armenia and Azerbaijan created an opportunity for Israel to earn billions of dollars in weapons’ sales to Azerbaijan. Haaretz reported that “Israel has exported a very wide range of weapons to the country [Azerbaijan] – starting with Tavor assault rifles all the way to the most sophisticated systems such as radar, air defense, antitank missiles, ballistic missiles, ships and a wide range of drones, both for intelligence and attack purposes. Israeli companies have also supplied advanced spy tech, such as communications monitoring systems from Verint and the Pegasus spyware from the NSO Group – tools that were used against journalists, the LGBT community and human rights activists in Azerbaijan, too.”
The Stockholm International Peace Institute wrote: “Israel’s defense exports to Azerbaijan began in 2005 with the sale of the Lynx multiple launch rocket systems by Israel Military Industries (IMI Systems), which has a range of 150 kilometers (92 miles). IMI, which was acquired by Elbit Systems in 2018, also supplied LAR-160 light artillery rockets with a range of 45 kilometers, which, according to a report from Human Rights Watch, were used by Azerbaijan to fire banned cluster munitions at residential areas in Nagorno-Karabakh,” even though Israel and 123 other countries have banned the use of cluster bombs. Haaretz reported: “In 2007, Azerbaijan signed a contract to buy four intelligence-gathering drones from Aeronautics Defense Systems. It was the first deal of many. In 2008 it purchased 10 Hermes 450 drones from Elbit Systems and 100 Spike antitank missiles produced by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and in 2010 it bought another 10 intelligence-gathering drones. Soltam Systems, owned by Elbit, sold it ATMOS self-propelled guns and 120-millimeter Cardom mortars, and in 2017 Azerbaijan’s arsenal was supplemented with the more advanced Hanit mortars. According to the telegram leaked in Wikileaks, a sale of advanced communications equipment from Tadiran was also signed in 2008.”
According to Haaretz, “Israel and Azerbaijan took their relationship up a level in 2011 with a huge $1.6 billion deal that included a battery of Barak missiles for intercepting aircraft and missiles, as well as Searcher and Heron drones from Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). It was reported that near the end of the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War in 2020, a Barak battery shot down an Iskander ballistic missile launched by Armenia. Aeronautics Defense Systems also began cooperating with the local arms industry in Azerbaijan, where some of the 100 Orbiter kamikaze (loitering munitions) drones were produced – drones that Azerbaijan’s defense minister called ‘a nightmare for the Armenian army.’” In 2021, “an indictment was filed against [Israel’s] Aeronautics Defense Systems for violating the law regulating defense exports in its dealing with one of its most prominent clients. A court-imposed gag order prevents the publication of further details. A project to modernize the Azerbaijani army’s tanks began in the early 2010s. Elbit Systems upgraded and equipped the old Soviet T-72 models with new protective gear to enhance the tanks’ and their crews’ survivability, as well as fast and precise target acquisition and fire control systems. The upgraded tanks, known as Aslan (Lion), starred in the 2013 military parade. Azerbaijan’s navy was reinforced in 2013 with six patrol ships based on the Israel Navy’s Sa’ar 4.5-class missile boats, produced by Israel Shipyards and carrying the naval version of the Spike missiles, along with six Shaldag MK V patrol boats with Rafael’s Typhoon gun mounts and Spike missile systems. Azerbaijan’s navy also bought 100 Lahat antitank guided missiles.”
In 2014, “Azerbaijan ordered the first 100 Harop kamikaze drones from IAI, which were a critical tool in later rounds of fighting. Azerbaijan also purchased two advanced radar systems for aerial warning and defense from IAI subsidiary Elta that same year…. Two years later, Azerbaijan bought another 250 SkyStriker kamikaze drones from Elbit Systems. Many videos from the areas of fighting showed Israeli drones attacking Armenian forces…. In 2016, during Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s visit to Baku, Aliyev revealed that contracts had already been signed between the two countries for the purchase of some $5 billion in ‘defensive equipment.’ In 2017, Azerbaijan purchased advanced Hermes 900 drones from Elbit Systems and LORA ballistic missiles from IAI, with a range of 430 kilometers. In 2018, Aliyev inaugurated the base where the LORA missiles are deployed, at a distance of about 430 kilometers from Yerevan, Armenia’s capital. During the war in 2020, at least one LORA missile was launched, and according to reports it hit a bridge that Armenia used to supply arms and equipment to its forces in Nagorno-Karabakh. More advanced Spike missiles were sent in 2019 and 2020.”
#what can men do against such reckless hate#politics#us politics#gaza#all eyes on palestine#armenia#azeri crimes#israeli crimes#turkish crimes#world politics#war crimes#genocide#artsakh is armenia
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
As is turning disturbingly into custom, I have a paper to write and I can't think unless I start writing to somebody first.
The topic is the Flint Water Crisis. Our focus, corrosion and why it happened. The nuance I'm adding for spice: Ancient plumbing.
So, in Flint, Michigan, the major players are the Detroit Water and Sewerage Department (DWSD) and the City of Flint (Flint). The City of Flint is in a $25 million deficit and their contract with DWSD to supply water expires in 2014. In 2011, the state has put the city under Emergency Management, which is trying to decrease spending, essentially. Additionally, since 2004, DWSD has been upping their service rates at a yearly 6.2%, or 62% total (expensive). And kind of an asshole move since Flint has been buying water from DWSD since 1967.
Flint has their own water treatment plant that's been an emergency backup to the DWSD-supplied water, but it is only operated 4 times a year just to ensure it can function.
Flint says Fuck This Actually, and in 2013, decides to pull water from Lake Huron; but this pipeline is still being developed and only due to be online in 2017. So Flint decides for the 2-3 year period, they can pull water from the Flint River and treat it in their own treatment plant. They hire an engineering firm to retrofit the plant and email Michigan Department of Environmental Quality (MDEQ) for quality guidelines to follow during plant startup.
At this point, Flint was incorrectly told by MDEQ they DID NOT have to continue adding phosphates to the water as corrosion control, which the previous plant had been doing. They could start up as normal, and check every six months for any lead issues. Additionally, to control the amount of trihalomethanes (fancy word for a gas molecule with three halogens, a hydrogen, and a carbon) already in the water, the plant added FeCl3 as a disinfectant and flocculant (purifies water via latching onto other molecules and allowing them to be filtered out) instead; FeCl3 is non-toxic, but increases the water corrosivity in an already corrosive system.
This is where the more known portion of the story begins: people immediately notice the changes in the water, including increasing discoloration and are concerned. It's policy to have a monitoring pool of homes for quality control, and Flint had that, but it's also policy to have 50% of those homes contain lead service lines and none on the Flint circuit were. They also didn't sample the homes that were on the circuit properly to pick up lead in the system, so the lead numbers that were picked up, were likely minimized.
So on one hand, you have people (and a whole lot of visual evidence) pointing to a damaged, polluted water supply, and test results that don't show anything abnormal.
Resident Zero took water samples to show to the city, and then independently sent them to Virginia Tech. The minimum concentration of lead in all the samples was 217 ug/L, 14.5 times the EPA action level of 15 ug/L. And as the sampling occurred, lead levels increased in the last five samples, so not even flushing the pipes (common precautionary treatment for any nasty buildup in pipes while water hasn't been moving) was adequate protection for any home inhabitants.
The reason this occurred was the corrosion of lead scaling that had built up on steel service lines outside homes (Fig 1). Typically, when phosphate is used as a corrosion inhibitor, soluble metals precipitate and create a scale on the pipe. Nothing goes into solution or the house, and things are fine and dandy. Without corrosion inhibitors, not only was the original corrosive contact occurring between the steel and lead pipes, but the scale was being removed and carried into the system. 99% of the contamination was due to this scale, as noted when solid filtration was used on the water samples and lead values decreased.


(Pieper, et al 2017)
+ Findings
+ Corrections/future learnings
+ Rome
29 notes
·
View notes
Text

Extensive damage to an undersea gas pipeline and communications cable connecting Finland and Estonia “could not have occurred by accident” and appears to be the result of a “deliberate … external act”, Finnish authorities have said.
“It is likely that the damage to both the gas pipeline and the communication cable is the result of external activity,” the Finnish president, Sauli Niinistö, said on X, formerly Twitter, on Tuesday, adding that the cause of the damage was not yet clear.

Local media cited unnamed government sources as saying Russian sabotage was suspected, while regional security experts said a Russian survey vessel had recently been observed making repeated visits to the vicinity of the Balticconnector pipeline.
Niinistö said the government was “in contact with our allies and partners” and that Finland was “prepared, and our readiness is good”, adding that the incident, uncovered early on Sunday morning, had “no effect on our energy supply security”.
Nato’s secretary general, Jens Stoltenberg, said the transatlantic military alliance was “ready to share information about the destruction of Finnish and Estonian underwater infrastructure” and to “support its allies”.
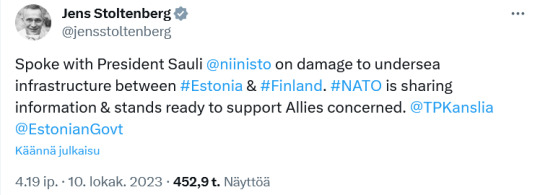
Markku Hassinen, of the Finnish border guard, said no seismic activity had been recorded in the Gulf of Finland before the discovery of the Balticconnector damage, but “vessels from several different countries” had been monitored in the area. But seismologists at Norsar, Norway’s national datacentre for the comprehensive nuclear test ban treaty (CTBT), confirmed late on Tuesday that they had registered a “probable explosion” at 1.20 am on Sunday.
Both countries’ gas network operators on Sunday reported an unusual drop in pressure in the bi-directional, 48-mile (77km) pipeline, which runs across the seabed of the Gulf of Finland from Inkoo in Finland to Paldiski in Estonia. The state-owned Finnish operator, Gasgrid, said the pipeline had been shut down immediately because of a suspected leak, adding that the country’s gas system was stable, with supply secured through a floating liquefied fossil gas terminal.
Read full article by The Guardian
134 notes
·
View notes
Text

Enhancing Gas Pipeline Management with GIS: Key Benefits and Applications
In the energy and utilities sector, gas pipeline management is complex, requiring precision, safety, and a clear strategy for both existing infrastructure and future expansion. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized pipeline management by providing a spatially accurate, data-rich view of assets. From asset management and leak detection to route planning and demand forecasting, GIS is becoming indispensable for gas companies. This blog delves into the ways GIS transforms gas pipeline management, delivering benefits across safety, efficiency, cost-saving, and planning.
#benefits of using gis for gas pipelines#ensuring gas pipeline safety with gis tools#gas network analysis#gas pipeline asset management#gas pipeline gis mapping services#gas pipeline leak detection using gis#gas pipeline management in gis#gas pipeline mapping software#gas pipeline monitoring tools#gas pipeline risk assessment#gis applications in energy sector#gis for gas pipeline monitoring#gis for infrastructure management#gis in oil and gas industry#gis pipeline maintenance software#gis pipeline monitoring system#gis pipeline route planning#gis software for gas pipeline route optimization#victoryofgoodoverevil#gis solutions for pipeline maintenance and monitoring#gis-based pipeline integrity management#pipeline data management#pipeline geographic information systems#pipeline management solutions#remote sensing for gas pipelines#spatial analysis for gas pipelines#spatial data for gas pipelines
0 notes
Text

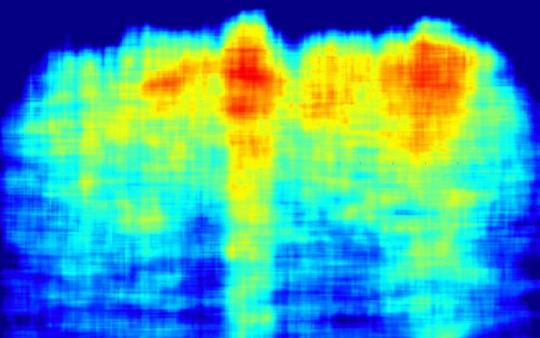
Scan Do Attitude
Being able to monitor brain changes in mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's disease at point-of-care is desirable but, because of their necessarily lower magnetic field strength, portable MRI scanners have resolution limitations due to a lower signal-to-noise ratio. Here, combination with a machine learning pipeline overcomes disadvantages and renders the portable system more freely available and cost-effective
Read the published research article here
Selection from an image from work by Annabel J. Sorby-Adams and colleagues
Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution – NonCommercial – NoDerivs (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Published in Nature Communications, December 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#biology#brain#neuroscience#neurodegeneration#alzheimer's#mri#brain scan#medical imaging
12 notes
·
View notes