#production of pharmaceutical compounds
Text
The global pharmaceutical processing seals market is projected to grow from USD 2.1 billion in 2021 to USD 3.3 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 10.0% during the forecast period. The favorable rules and regulations for pharmaceutical manufacturing in the developing regions such as APAC, the Middle East & Africa, and South America are expected to drive the pharmaceutical processing seals market. The consumption of pharmaceutical drugs is rapidly increasing at the global level especially, in the rapidly growing economies in APAC. In order to cater to the increasing demand for pharmaceutical drugs, there is an increase in the investments made in the pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment industry for capacity expansions and R&D activities. Expansion of the healthcare sector due to increasing population and improved awareness about quality healthcare are expected to drive the pharmaceutical industry and thus, boost the demand for pharmaceutical processing seals, globally.
There are various types of pharmaceutical processing seals available in the market, namely, O-rings, gaskets, lip seals, and D seals. These seals are available in different grades, shapes, and sizes. The O-rings segment dominated the pharmaceutical processing seals market owing to its high demand in pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. O-rings are used in pharmaceutical industry for applications such as cryogenic, bioprocessing, cleaning, and sterilization. These seals are used in pharmaceutical industry in agitators and hydraulic cylinders. The reason for the growth of the O-rings segment is its cost-effectiveness and wide range of applications.
The pharmaceutical processing seals market in APAC is projected to register the highest CAGR between 2020 and 2026. The region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for pharmaceutical processing seals due to the growth of the healthcare sector in the region. In addition, the huge capital investment in capacity expansions, R&D, and new product developments across the pharmaceutical industry is boosting the demand for pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment, which will subsequently drive the pharmaceutical processing seals market in the region. The growth of the pharmaceutical industry is attributed to the shifting focus of pharmaceutical manufacturers toward the region owing to favorable regulatory conditions, developing healthcare industry, increasing population, and incidences of chronic diseases. Owing to the increased demand from the APAC market, Saint-Gobain S.A., Morgan Advanced Materials PLC and Garlock have expanded their sealing solution business in the region. These expansions are expected to help the company cater to the growing pharmaceutical processing seals market in the region.
The companies are constantly exploring opportunities for expansion in the APAC region due to favorable trade initiatives proposed by the governments of the countries in the region for the expansion of pharmaceutical industry. These initiatives will open new opportunities for pharmaceutical processing seals manufacturers in the region.
#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market#COVID 19 impact on Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals#MarketsandMarkets#Global Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market#pharmaceutical processing seals#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals industry#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market Growth#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market Forecast#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Demand#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Sales#pharmaceutical processing seals market size#production of pharmaceutical compounds
0 notes
Text
Thermoplastic Polyester Engineering Resins Market is Led by APAC
The thermoplastic polyester engineering resins market was USD 3,912.2 million in 2022, and it will touch USD 5,896.6 million, advancing at a 5.4% compound annual growth rate, by 2030.
The growth of the industry is attributed to the increasing utilization of these resins for various nonstructural applications as they can be utilized without filters and are usually tougher and more ductile than thermoset resins. Furthermore, they are extensively accessible to meet domestic requirements and are easy to recycle. The rising need from the automobile and electronic sectors is also propelling the advancement of the industry.

The polybutylene terephthalate category will advance at a steady rate in the years to come. This is because of the growing requirement for PBT in the electrical and automobile sectors. PBT has unique features, including heat resistance, semi-crystalline, and lightweight, because of which conventional materials including bronze, ceramics, and cast iron in the automotive sector are getting replaced.
In 2022, the automotive category, based on application, led the thermoplastic polyester engineering resins market, with 40% share, and it will remain leading in the years to come. The automotive sector has gained momentum, over the past few years, and key manufacturers of automobiles are utilizing thermoplastic polyester to produce parts of vehicles, which benefits them to lessen the overall weight of the automobiles.
North America is likely to observe significant growth in the years to come. This is primarily because of the mounting need for recycled plastics, the existence of major players, and the growing emphasis on fuel-efficient vehicles, because of which manufacturers are extensively utilizing TPER to make their automobiles lightweight.
With the mounting utilization of such resins for numerous industrial applications, the thermoplastic polyester engineering resins industry will continue to advance in the years to come.
#acetic anhydride market#chemical industry#industrial applications#acetic anhydride production#market analysis#chemical compounds#acetic anhydride uses#pharmaceutical intermediates#chemical synthesis#chemical innovation
0 notes
Text
Global Glycolic Acid Market: Trends, Growth, and Future Prospects
The glycolic acid market was valued at USD 309.3 million in 2021, and it is set to reach USD 604.4 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.7% between 2021 and 2030, according to a research report by a market research company P&S Intelligence.
In 2021, the personal care and cosmetics category held the largest market share at 58.2%. this is due to glycolic acid being extensively utilized in…

View On WordPress
#Alpha hydroxy acids#Biodegradable compounds#Chemical exfoliation#chemical industry#Chemical peels#Cosmetic chemistry#Cosmetic formulations#Dermatological treatments#Glycolic acid#Industrial applications#market analysis#market growth#market trends#Organic acids#Pharmaceutical additives#Product innovation#Skin care industry#Sustainable sourcing#Textile industry
0 notes
Text
Scripps Research chemists have accomplished a long-elusive feat in synthetic chemistry: the invention of a broadly useful method for constructing "gamma chiral centers" on simple starting compounds called carboxylic acids. The method significantly extends the ability of chemists to build and modify complex pharmaceutical molecules and other valuable chemical products.
The paper, "Enantioselective Remote Methylene C−H (Hetero)Arylation of Cycloalkane Carboxylic Acids," has been published in the journal Science.
The term chiral refers to a type of asymmetry that allows some chemical compounds to exist in left-handed and right-handed forms. Often, only one of these forms has the desired biochemical activity, but for synthetic chemists, stereoselective reactions—those that yield just the desired form—are almost always challenging.
Continue Reading.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

Researchers create new chemical compound to solve 120-year-old problem
For the first time, chemists in the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics. The study is published in Science.
For decades, researchers have been investigating molecules called N-heteroarenes, which are ring-shaped chemical compounds that contain one or more nitrogen atoms. Bio-active molecules having a N-heteroarene core are widely used for numerous medicinal applications, lifesaving pharmaceuticals, pesticides and herbicides, and even electronics.
"While the average person does not think about heterocycles on a daily basis, these unique nitrogen-containing molecules are widely applied across all facets of human life," said Courtney Roberts, the senior author of the study and a University of Minnesota Department of Chemistry assistant professor who holds the 3M Alumni Professorship.
Read more.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
White Board, TOWL 6 Promo
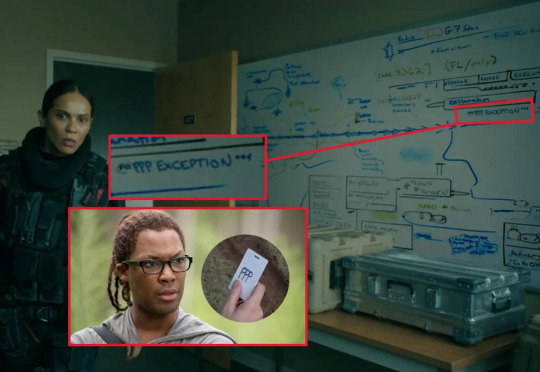
Focusing on the very bottom right of the board, it says "Refinery" C2H5OH which is a chemical formula for ethyl hydrate or ethanol.
The CRM is possibly making ethanol in their refineries, and this is possibly related to the current theories circulating about Pharmakon which can be a "poison or a cure"
Ethanol is present in alcoholic drinks (beer, wine, spirits) when diluted. It is used as a topical agent to prevent skin infections, in pharmaceutical preparations (e.g. rubbing compounds, lotions, tonics, colognes), cosmetics, and in perfumes. https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/protection/npi/substances/fact-sheets/ethanol-ethyl-alcohol#:~:text=Ethanol%20is%20present%20in%20alcoholic,%2C%20cosmetics%2C%20and%20in%20perfumes.
This prompted me to look up what moonshine is:
The fermentation process used to make moonshine produces alcohol in two forms: methanol and ethanol. Ethanol is the drinkable version. Methanol, known as wood alcohol, is a byproduct that’s toxic when large amounts end up in the finished product.
The distillation process that follows produces concentrated ethanol by boiling the fermented product. The problem moonshiners run into is ethanol has a boiling point of 173.1 degrees Fahrenheit while methanol’s boiling point is 148.5 degrees Fahrenheit. This means methanol evaporates at a faster rate than ethanol and can become concentrated. When done correctly, it only forms in small amounts and is easily separated out and discarded. Without the right equipment, high concentrations of methanol can end up in the drink.
What makes methanol so dangerous is the human body converts it to formaldehyde, an ingredient used to make embalming fluid. The body then converts formaldehyde into formic acid, a material that poisons the body’s cells. In large enough amounts, death is a real possibility. Not surprisingly, most of the dangers of drinking moonshine stem from the amount of methanol that may be present.
https://sunshinebehavioralhealth.com/alcohol-addiction/moonshine/
Ok, so back to Pharmakon, the poison or the cure, remember when Beth said "My dad used to say bad moonshine can make you go blind"
Also, bad moonshine can basically be formaldehyde, the chemical used in embalming fluid. Remember the funeral home in alone?
The dots, they are connecting. I am getting sooo excited.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, my long overdue infodump about yokai medicine/painkillers is here. Just as a heads up, there will be discussion of and reference to a variety of drugs, drug use, and addiction.
There are three main forms of treatment used to deal with pain: pharmaceutical drugs similar or identical to the ones used by humans, potions, and spells. For now, I'll focus on pharmaceutical type medications.
So, to begin, I do need to address the fact that the yokai population has an immense level of biodiversity, from skeletons to insects to dragons. This means that the use of medicine is probably incredibly complicated, as a given substance can has wildly different effects on different species--not to mention that even within a species a compound can have different results (see: stimulants and how they have drastically different effects for people with ADHD than for neurotypicals).
Add to that the fact that we also see a large variety of sizes for different yokai, from Exploding Frankie (maybe a foot tall) to the colossal building-sized creatures we see walking around int he first episode of the show, and you've got a very complex problem. (Size is relevant in figuring out dosages because drugs often have different effects at different doses, but also because larger people tend to need more to have an effect in the first place. A dose that would kill a mouse probably wouldn't kill a 6 foot tall man, for example, but depending on the exact drug it might still mess him up a lot.)
This means that it would be very difficult to, if not impossible, to properly categorize a chemical based on its effects. Sure, they know Adderall works as a stimulant and opiates are painkillers for humans, but how does that translate to a slime yokai who doesn't even have a nervous system? How do you effectively (and ethically) figure that out when the population of slime yokai is extremely limited? In all honesty, you probably don't.
(As a side note, it's fairly important that for the drugs humans use, they go through large amounts of animals trials before ever being tested on people to a) make sure the drug actually has the effect it's meant to, b) figure out what potential side effects might crop up, and c) find out what a lethal dose is. That's because we can reasonably compare the reactions of animals to what we might see in a human body. For large amounts of the yokai population, that comparison probably does not work.)
So yokai can, in dire circumstances, use substances that humans would (as painkillers, sedatives, etc) but it would be very difficult to know what dosages are safe for a given species, if any are. This would also mean that the Hidden City probably has a very different approach to drug education: less "ooh these drugs are evil and you'll get addicted immediately if you ever try them" and more "just because meth acts as a stimulant for humans doesn't mean it can't kill you at half the dose it takes them to even get an effect so be fucking careful".
I would imagine that drug regulation works very differently in the Hidden City out of necessity. After all, you can't even reliably say what effects a given chemical has, let alone recommend a dose for people to use. In a lot of cases, the best that the HC can do is probably enforce purity standards and proper labeling of products so that at the very least, people know what chemical they're actually getting and how much of it.
Which of course means that their legal system is entirely different when it comes to drug related crimes, because the use/possession of drugs is something that cannot effectively be criminalized when a pill that would cause an overdose in one person would act as a mild cough suppressant in another. (That and the whole idea behind making drugs illegal in the first place is to prevent addiction by making access harder, which... is a bit of a weird premise in the first place? but that's a whole other rant. Yes, use declines somewhat when the drug is made illegal, but it also makes it much harder for addicts to get the treatment they need when drug use is criminalized.)
Given the length of this post I think I'll cut it off here and edit with links when I get the other topics covered lmao.
Part 2 Part 3
#rottmnt#tw drugs#tw drugs mention#minor interference au#minor interference lore#bambi's rambling#this post brought to you by the fact that i'm a psych major and addiction psychology is my favorite class this semester lmao#also it's entirely possible that this post isn't fully accurate for how drugs work/are tested irl so like. don't quote me on this#i'm just pretending to know what i'm talking about
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Atlantis Expedition: Science Division Departments - Life Sciences Department
We're a bit further from the original post, having already done the medical department, so now it's time for the Life Sciences.
Much like the medical department, the notes for this underwent significant revision (nearly entirely re-done), to better granulate expectations for the department's duties and how they interact, primarily, with the medical department. Below is the original estimation, with struck text indicating revisions:
> Head: OC
> Contains: Earth biologists, bio- & biochemical engineers, astro/xeno-biologists, botany, environmental chemistry, zoology, microbiology
> Function: Auxiliary to Medical Department needs
> Examples of function: pharmaceutical synthesis, analysis of unknown species, biological database creation, gene therapies (pharmaceutical adjacent)
> Personnel quantity: 1 (Head) + 2 (Earth biologists) + 2 (bioE & biochemE) + 1 2 (astro/xenobio) + 1 (botany) + 1 (envchem) + 1 (zoo) + 2 1 (microbio) = 11
> Personnel quantity: 1 (Head) + 1 (physiologist) + 1 (geneticist) + 1 (astrobiologist) + 1 (xenobiologist) + 1 (microbiologist) + 1 (botanist) + 1 (zoologist) + 1 (biomedical engineer) + 1 (biochemical engineer) + 3 (medical laboratory scientists) = 13
> A/N: Both biologists also have training/specialization in genetics/gene mapping (assists both Carson and Katie), some input in requesting gate missions based on in-house needs
> A/N: Focus is on medical logistics and supporting Medical Department needs, research parameters fulfill SGC outlines of studying microevolutions and drug technology development.
Following on the parameters of 1) putting people through the inter-galactic theoretical shredder is expensive, and 2) said gate shredder will only be open for a certain amount of time, the vast majority of this department's work will be geared toward the analysis, creation, testing, and preparation of pharmaceutical drugs and other inventions of medical context.
Think compounding pharmacy but better equipped, and capable of researching new things - this department specializes in medical logistics. Wikipedia has a better description of this, so I'll pull a quote:
Medical logistics is the logistics of pharmaceuticals, medical and surgical supplies, medical devices and equipment, and other products needed to support doctors, nurses, and other health and dental care providers.[1] Because its final customers are responsible for the lives and health of their patients, medical logistics is unique in that it seeks to optimize effectiveness rather than efficiency.
As with most things contrived by the SGC, there's going to be a lot of blended specialties and overlap, heavily bolstered by technological innovation. These are people Carson Beckett likely hired, or at least had a heavily-weighted opinion when Rodney was going through the application packets, because the Life Sciences is at a one-step remove from actually handling patients, and handles a significant amount of labwork and research.
The revised numbers weigh heavily in favour of biologists, due to the sheer breadth and depth of the subject, and the fact that most of these are likely to have some sort of SGC training that would make them well-versed on what to expect on the expedition in terms of disease research and thus treatment solutions.
Unlike the medical department, which handles patients directly in different aspects, this is all one "team". If you're looking for a group of scientists that can technically have the same generic appellation that would make one of them go, "Well, actually-", this is the place to look.
On to the breakdown, notes included:
> Earth biologists
» 2x of these
» Specialties?
⇛ Human physiology (academic rather than medical context)
⇛ May function as a knowledge base to study how the physiology of the expedition changes by long-term habitation in Atlantis, assists in studying long-term effects of the ATA gene therapy, development of knowledge base as Earth-based physiology changes in reaction to Pegasus galaxy habituation (exposure to local diseases, eating of local foods, etc)
⇛ Geneticist
⇛ Same as the human physiologist, but in a genetic context
⇛ Studies genetic drift of the expedition and builds knowledge base for comparisons of baseline to genetic mutations that build up over time
> Astro/xenobiology
» 2x of these
⇛ 1 of each
» SGC special
» Studies the species and speciation of non-human humanoid species
⇛ Imports from studying the Jaffa, Goa'uld, and Replicators (xenobiologist in particular)
⇛ Overlap with parasitology and immunology/histocompatibility (Goa'uld and Jaffa, respectively)
> Microbiology
» "Most microbiologists specialize in a given topic within microbiology such as bacteriology, parasitology, virology, or immunology."
» Studies the species and speciation of bacteria, algae, fungi, and some types of parasites and their vectors
> Botany
» Study of species and speciation of plant species
» Outline of botany
> Zoology
» Study of species and speciation of non-human animal species
» Outline of zoology
> Biomedical engineer
» REVAMP from bio-engineering
» Actually makes the pharmaceuticals based on the feedstocks and processes biochem engineers designed for them
⇛ Works with biochem engineers to feedback on the design process of drug manufacturing
⇛ Biologics as well as inert (in comparison) materials for drug development
⇛ Pharmacology
⟹ Most likely all drugs are powdered for shelf-stability and ease of transportation
⭆ So their responsibility in this would be referencing the SGC formulary (how many books to a Frasier) on reconstituting these drugs
➾ Compounding
⭆ What about topical prescriptions? Gel-based? Powder for gels, as well
➾ More complex formulation
⭆ What about gases, for sedation?
➾ Probably compressed canisters?
> Biochemical engineer
» Would not have existed in the early 2000s as a field related to process engineering, so an SGC special
» Also useful for researching food preservation methods
» Synthesizes information from peers in this department to create pharmaceutical drugs and their manufacturing process
> Medical Laboratory scientist
» Does the legwork of processing samples for everyone, so needs a wide range of skills
⇛ 3x of these
⇛ Specialties
⟹ Immunology/histopathology/hematology
⭆ Human tissues
⟹ Microbiology/bacteriology
⭆ Bacterial forms of infection
⟹ Virology/mycology/parasitology
⭆ Non-bacterial forms of infection
➾ Routes of non-bacterial infection
> Environmental chemistry
» Role covered under biochem engineering
» Biochem engineers can cover the study of pollution that envirochems specialize in
Environmental chemistry section preserved to properly annotate the revisions, and what their original role was supposed to be (i.e. study pollution to solve Earth's pollution issues).
It occurred to me, while revising personnel lists, that the biologists in particular will need to divide their research into some broad categories, if they want to properly develop their research topics and what category of formulations they would require from the non-biologists in the department.
We have human species, yes, but that can be parsed from Milky Way to Pegasus galaxies, and from there Earth-based humans vs Jaffa (vs Goa'uld), and Pegasus-based humans (presumably humans, as they probably wouldn't know for sure that the Ancients were the default sentient or even default humanoid species in the Pegasus galaxy).
The human microbiome is incredibly important to understanding homeostasis, disease pathology, and various other interconnected factors. Because of this, the medical laboratory scientists will be heavily relied upon to develop cultures for study. I'm willing to believe that they have some nifty adapted technology to help them study all of these subjects I've shoved under multiple umbrellas, in the form of culturing processes, reagents, microscopes, analyzing software, preserving agents/methods, and the like.
After that, testing to see how these diseases - or potential diseases, if someone in the Pegasus galaxy hosts a bacteria, virus, fungus, or parasite that their immune system is natively robust to - might infect a member of the expedition. This is where a lot of back-and-forth would be done between the Life Sciences and Medical departments, so it wouldn't be uncommon to see people like, say, Biro (pathology) and Katie Brown (botany) jointly doing research on a pathogen.
There's already a lot of canonical evidence to support this specialist overlap being a necessary concern, from the the Hoffan drug (and the subsequent Michael arc), John Sheppard's infection from an Iratus bug bite in Conversion, Asurans, Lucius' drug, the crystals of M3X-387, Kirsan fever, Jennifer Keller's infection from something that was turning her into a Wraith hiveship in The Seed, and the Second Childhood parasite.
Depending on the type of infection, a lot of the personnel in this department will coordinate with each other to develop a knowledge base, including potential therapeutic remedies. If something already in stock cannot be used (see: a potential cross-applicability of penicillin), then they might make a request to the head of the expedition for a gate team to travel based upon any information they might have (ex: Teyla and Ronon going out for samples of the Enchuri plant for treating Kirsan fever).
Because of their support role as a department, the fact that all the scientists here can be used as in-house reference for the medical department, and their unique position to recommend gate missions for consideration on the roster, this department functions well as a bridging gap for the various demands the expedition has placed on them by the IOA and the SGC.
Total Life Sciences Department Personnel
Head of Department: 1
Biologists: 5
Engineers: 2
Laboratory Scientists: 3
Botany: 1
Zoology: 1
Total total: 13
I'll be going over canonical personnel such as Katie Brown in their own posts, but for now this is a general accounting of the expedition’s life sciences department.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discussing NMN, Nutraceuticals, & Merchant Payment Processing
Article by Jonathan Bomser | CEO | Accept-Credit-Cards-Now.com

In today's ever-evolving health and business landscape, the merging of NMN, nutraceuticals, and merchant payment processing is reshaping our approach to wellness and commercial transactions. Join us as we explore the interconnectedness of these elements and their influence on our lives.
Nutraceuticals: Pioneering the Path to Optimal Health
Nutraceuticals are at the forefront of modern health and wellness trends. This blend of "nutrition" and "pharmaceuticals" encompasses products that go beyond basic sustenance, providing health benefits to enhance overall well-being. This category includes dietary supplements, vitamins, herbal remedies, and functional foods.
As health-conscious individuals continue to grow in number, the demand for nutraceuticals has skyrocketed. People are actively seeking solutions to improve their health, manage specific conditions, and enhance vitality. This burgeoning interest has given rise to a thriving industry, where businesses must implement robust merchant account processing systems to seamlessly accept credit cards and offer customers convenient payment options.
Merchant Payment Processing: The Engine of Modern Transactions
Merchant payment processing is the powerhouse driving contemporary commerce. In an era where cash transactions are dwindling, the ability to accept credit cards has become a necessity for businesses across the board. It's no longer just a matter of convenience; it's about exceeding customer expectations and driving sales.
For the nutraceutical sector, efficient payment processing is of particular significance. When customers seek health solutions, they demand a seamless, secure, and hassle-free buying experience. The capacity to accept credit cards ensures that transactions are promptly executed, nurturing trust and customer loyalty.
Selecting the Optimal Merchant Account Processing Solution
The choice of the right merchant account processing solution is a pivotal one for businesses. Factors like fees, security, customer support, and alignment with your business model must all be carefully evaluated.
Nutraceutical businesses have their unique considerations. Many of them provide subscription-based supplement plans, necessitating a payment system that adeptly manages recurring billing. Given the sensitive health information involved, security is of paramount importance. Compliance with industry standards, including the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), is non-negotiable.
NMN: A Nutraceutical Game-Changer
Now, let's cast the spotlight on NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), a star performer in the realm of nutraceuticals. NMN is a naturally occurring compound found in various foods like broccoli and avocados. Its claim to fame lies in its potential to boost NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) levels, a coenzyme critical for energy metabolism and DNA repair.
NMN has garnered substantial attention for its possible anti-aging properties. As we age, NAD+ levels decline, leading to a range of health issues. NMN supplements aim to reverse this decline, presenting a promising avenue to improved health and longevity. As the demand for NMN products continues to climb, nutraceutical businesses must have reliable merchant account processing systems in place to efficiently handle the growing demand for these life-enhancing products.
youtube
The Nexus of NMN, Nutraceuticals, and Payment Processing
The intersection of NMN, nutraceuticals, and payment processing presents a distinctive opportunity for businesses. With the health and wellness industry on the ascent, offering top-tier health products like NMN and delivering customers a seamless payment experience are pivotal.
Efficient payment processing systems aren't just transaction facilitators; they are central to customer satisfaction. When customers can make secure payments with their preferred credit cards, they are more inclined to complete their purchases and return for future transactions.
#high risk merchant account#high risk payment gateway#high risk payment processing#merchant processing#payment processing#credit card payment#credit card processing#accept credit cards#payment#youtube#Youtube
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
Could you tell us more about working in labs? What types of study are necessary and what is your daily life like? Do you like what you do? (Asking because I'm very interested in this type of area😞) Thanks😸
hi, lovely! I love this question, and it’s so nice to hear you’re interested in lab work! 🩵 and yes, i love what i do, but you know, from time to time, i think of what life would have been like if i pursued fashion or writing instead, but i’m pretty happy where i am right now yea~ means so much to me that you asked 🥹
well, as an undergrad, i took up pharmaceutical sciences (currently finishing up my masters 😭), but most of my colleagues typically graduate with degrees in biology, biochemistry, chemistry, or even, statistics.
as for my daily life…
if i’m not working on my master’s thesis or having my fave meal of chicken nuggets and iced coffee to keep me awake, i mostly spend my time in an quality control assay laboratory. the company i’m working for sends finished products and i help determine the label claim of random drugs from different market batches (say, a painkiller, and the packaging claims it has 400 mg of the active drug, i confirm if that is indeed true by subjecting it to different tests, if it ain’t, we have to get manufacturing to fix it) or more preferably, i determine the identity of unknown compounds in prototype drugs using instrumental methods like infrared spectroscopy or nuclear magnetic spectroscopy. it’s kinda similar to how a forensic scientist maps out dna samples and fingerprints!
…
i rambled *hehe*~ this was such a nice question and i really loved answering it. 🥹🫶🏻 thank you, quenn!
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The report "Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market by Material (Metals, PTFE, Nitrile Rubber, Silicone, EPDM, FKM, FFKM, UHMWPE, PU), Type (O-Ring Seals, Gaskets, Lip Seals, D Seals), Application (Manufacturing Equipment), and Region - Global Forecast to 2026", The pharmaceutical processing seals market is projected to grow from USD 2.1 billion in 2021 to USD 3.3 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 10.0% during the forecast period. The growth of pharmaceutical processing seals market is attributed to the increased demand for pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment due to the growing healthcare industry and increasing consumption of pharmaceutical drugs. In addition, the expansion of healthcare industry in APAC due to favorable trade policies proposed by the government of countries in this region is expected to drive the pharmaceutical processing seals market.
#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market#COVID 19 impact on Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals#MarketsandMarkets#Global Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market#pharmaceutical processing seals#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals industry#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market Growth#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Market Forecast#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Demand#Pharmaceutical Processing Seals Sales#pharmaceutical processing seals market size#production of pharmaceutical compounds
0 notes
Text
CBD Market and its scopes
The CBD market is a rapidly growing industry, with the potential to become one of the most significant players in the health and wellness space. With the increasing acceptance of cannabis as a viable form of medicine, more and more people are turning to CBD as a natural alternative to traditional pharmaceuticals.

CBD, or cannabidiol, is a chemical compound found in the cannabis plant. Unlike its psychoactive cousin THC, CBD does not produce a "high" or intoxicating effect. Instead, it is believed to have a range of therapeutic benefits, including reducing anxiety and inflammation and potentially even treating conditions like epilepsy and chronic pain.
As the popularity of CBD grows, so too does the market for CBD-based products. These products come in a variety of forms, including oils, tinctures, edibles, and topicals, and can be found in stores and online.
One of the major factors driving the growth of the CBD market is the increasing legalization of cannabis. As more and more states and countries legalize the use of marijuana for medical and recreational purposes, the market for CBD products is expected to continue to expand.
Additionally, the growing body of scientific research on the potential benefits of CBD contributes to the market's growth. As more and more studies are conducted, the evidence supporting the use of CBD for a range of conditions is becoming increasingly compelling.
However, the CBD market is not without its challenges. Despite the growing acceptance of CBD, the legal landscape surrounding the sale and use of these products is still somewhat murky. In the United States, for example, the FDA has not yet approved the use of CBD as a medical treatment, and there are strict regulations on the sale of CBD products.
Another challenge facing the CBD market is the need for more standardization in the industry. Because the market is still relatively new, there is a lack of industry-wide regulations governing the production and labeling of CBD products. This can make it difficult for consumers to know exactly what they are getting when they purchase a CBD product.
Despite these challenges, the future of the CBD market looks bright. As more and more people turn to CBD for its potential health benefits, the demand for these products is only going to continue to grow. As the market matures and the legal landscape becomes more clear, the CBD market is expected to become an increasingly important player in the health and wellness space. More Pharmas and Wellness stores are going to be adopted in the Global Market
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Kenny Stancil
Common Dreams
May 10, 2023
"We want to know why there are Americans who are dying, or are becoming much sicker than they should, because they can't afford the medicine they need," said the Vermont Independent.
U.S. Sen. Bernie Sanders on Wednesday paid his respects to the victims of insulin price gouging in front of the Big Pharma CEOs who are responsible and reiterated the need to make all lifesaving prescription drugs affordable.
Sanders (I-Vt.), chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP), opened the panel's hearing by acknowledging "the many Americans who have needlessly lost their lives because of the unaffordability of insulin" and "the thousands who wound up in emergency rooms and hospitals suffering from diabetic ketoacidosis—a very serious medical condition as a result of rationing their insulin."
"This is a problem that is unique to the United States."
Diabetes—a disease that can wreak havoc on organs, eyesight, and limbs if left unmanaged—affects more than 37 million U.S. adults and is the country's eighth leading cause of death, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Although it costs less than $10 to produce a vial of insulin required to treat diabetes, uninsured patients in the U.S. pay nearly $300 per vial of the century-old drug because Eli Lilly and Company, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi—the three pharmaceutical corporations that control 90% of the nation's lucrative insulin market—charge excessive prices with little resistance from federal lawmakers.
As Sanders noted, such corporate profiteering—a problem compounded by the widespread lack of coverage under the nation's for-profit healthcare system—forces many people to skip doses, with deadly consequences. Recent studies found that 1.3 million people in the U.S. ration insulin, including an estimated 1 in 4 people with Type 1 diabetes. People without insurance are the most likely to do so, followed by those with private insurance.
Ahead of the hearing, Sanders released a video featuring diabetes patients sharing their struggles to afford insulin in the U.S.
youtube
"Imagine just three companies having worldwide market dominance over such necessities as air and water," Steve Knievel, an advocate with Public Citizen's access to medicines program, said Wednesday in a statement. "This is what people with diabetes face with insulin."
Addressing the CEOs of the three aforementioned firms during the hearing, Sanders outlined how each has jacked up prices in recent decades:
Eli Lilly increased the price of Humalog 34 times since 1996 from $21 to $275—a 1,200% increase. The same exact product. No changes at all. The only reason for the huge increase in price during that period was that there was no legislation to stop them. In America, the drug companies could charge any price they want.
But it's not just Eli Lilly. Novo Nordisk increased the price of Novolog 28 times from $40 in 2001 to $289—a 625% increase.
And then there is Sanofi, a company that increased the price of Lantus 28 times from $35 in 2001 to $292—a 730% increase.
"In every instance it is the same exact product that rose astronomically," said Sanders. "And let's be clear. This is a problem that is unique to the United States. In France, 20 years ago, the cost of Lantus was $40. Today, it has gone down to just $24."
Sanders has famously accompanied Americans with diabetes on a two-mile trip from Detroit, Michigan to Windsor, Ontario. In Canada, people can purchase the exact same insulin product for one-tenth of the price they would pay in the U.S.
"We cannot rely on limited price concessions from insulin corporations to ensure this essential resource is accessible and fairly priced for Americans who need it."
Also in attendance at Wednesday's hearing were the leaders of CVS Health, Express Scripts, and OptumRX, three major pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs). Sanders took them to task, noting that "as insulin manufacturers continued to increase prices, PBMs signed secret deals to increase their profits by putting insulin products on their formularies not with the lowest list price but the ones that gave PBMs the most generous rebates."
Thanks to sustained public pressure and fresh policy changes—namely the Inflation Reduction Act's provision limiting Medicare beneficiaries' insulin copayments to $35 per month—Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi have all recently pledged to significantly lower the list prices for some of their insulin products. As Sanders explained:
Eli Lilly announced it would reduce the price of Humalog by 70% later this year—from $275 to $83. Eli Lilly also decreased the price of its generic Humalog to $25 per vial.
Novo Nordisk announced it would reduce the price of Novolog by 75% beginning next year—from $289 to $72.
Sanofi announced it would reduce the price of Lantus by 78% beginning next year—from $292 to $64.
While Sanders thanked the three companies for taking what he called "an important step forward," he stressed that "we must make sure that these price reductions go into effect so that every American with diabetes gets the insulin they need at an affordable price," vowing to "hold a hearing early next year to make certain that happens."
Knievel, meanwhile, said that "we cannot rely on limited price concessions from insulin corporations to ensure this essential resource is accessible and fairly priced for Americans who need it, regardless of their insurance status or age."
His message was echoed by Margarida Jorge, head of Lower Drug Prices Now.
"Certainly, these multimillion-dollar CEOs will spend their time in front of the committee patting themselves on the back for bowing to public pressure and lowering the cost of insulin," Jorge said in a statement. "But let's be clear, the tens of millions of Americans who cannot afford their prescription medication should not have to depend on the goodwill of greedy corporations who have repeatedly shown they care about profits more than people to bring them relief from skyrocketing prescription costs."
Sanders and Rep. Cori Bush (D-Mo.) recently introduced the Insulin for All Act of 2023, which would cap insulin prices at $20 per vial.
Only federal legislation of this sort can "put an end to decades of price gouging that has led to preventable suffering and costs the lives of people with diabetes who need insulin to live," Knievel emphasized.
Meanwhile, Sanders made clear that the unaffordability of insulin is part of a much broader crisis and proceeded to ask:
If Eli Lilly can lower the price of Humalog by 70%, why is it still charging the American people about $200,000 for Cyramza (CYR-AMZA) to treat stomach cancer—a drug that can be purchased in Germany for just $54,000?
If Novo Nordisk can lower the price of Novolog by 75%, why is it still charging Americans with diabetes $12,000 for Ozempic when the exact same drug can be purchased for just $2,000 in Canada?
If Sanofi can reduce the price of Lantus by 78%, why is it still charging cancer patients in America over $200,000 for Caprelsa—a drug that can be purchased in Japan for just $37,000?
"Lowering the cost of insulin is only one part of what we must accomplish," said the senator. "This committee is determined to end the outrage in which Americans pay, by far, the highest prices in the world for virtually every brand name prescription drug on the market—whether it is a drug for cancer, heart disease, asthma, or whatever."
"We want to know why there are Americans who are dying, or are becoming much sicker than they should, because they can't afford the medicine they need," he continued. "We have got to ask, how does it happen that nearly half of all new drugs cost over $150,000? How does it happen that cancer drugs which, in some cases, cost just a few dollars to manufacture are selling on the market for over $100,000?"
"Americans die, get sicker than they should, and go bankrupt because they cannot afford the outrageous cost of prescription drugs, while the drug companies and the PBMs make huge profits. That has got to change."
"I know that our guests from the drug companies will tell us how much it costs to develop a new drug and how often the research for new cures is not successful," said Sanders. "I get that. But what they are going to have to explain to us is why, over the past decade, 14 major pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly, spent $747 billion on stock buybacks and dividends."
"They will also have to explain how as an entire industry pharma spent $8.5 billion on lobbying and over $745 million on campaign contributions over the past 25 years to get Congress to do its bidding," Sanders added. "Unbelievably, last year, drug companies hired over 1,700 lobbyists including the former congressional leaders of both major political parties—that's over three pharmaceutical industry lobbyists for every member of Congress."
In Sanders' words, "That could well explain why we pay the highest prices for prescription drugs in the world and why today drug companies can set the price of new drugs at any level they wish."
"While Americans pay outrageously high prices for prescription drugs, the pharmaceutical industry and the PBMs make enormous profits," he noted. "In 2021, 10 major pharmaceutical companies in America made over $100 billion in profits—a 137% increase from the previous year. The 50 top executives in these companies received over $1.9 billion in total compensation in 2021 and are in line to receive billions more in golden parachutes once they leave their companies. Last year, the three major PBMs in America made $27.5 billion in profits—a 483% increase over the past decade. These PBMs manage 80% of all prescription drugs in America."
"In other words, Americans die, get sicker than they should, and go bankrupt because they cannot afford the outrageous cost of prescription drugs, while the drug companies and the PBMs make huge profits," Sanders lamented. "That has got to change and this committee is going to do everything possible to bring about that change."
Jorge, for her part, described the Inflation Reduction Act as a "milestone" law that "will help tens of millions of seniors."
"But it is just the start," said Jorge. "Congress should pass legislation to bring the prescription drug reforms that are saving Medicare patients and taxpayers billions to people of all ages, so that everyone can get lower drug prices on medicines they need—including insulin."
"Congress, not greedy corporations trying to redeem their tarnished reputations, should be leading the way on reforms that put patients ahead of pharmaceutical profits," she added.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Lab to Patient – The Evolution of Medicine Production
The journey of a medicine from a research laboratory to a patient’s bedside is a complex and intricate process. It involves rigorous scientific research, extensive clinical trials, stringent regulatory approvals, and sophisticated manufacturing processes. This blog will explore the evolution of medicine production, highlighting the role of leading pharmaceutical companies in India, including Centurion Healthcare, in bringing life-saving medications to the market.

The Genesis of Medicine: Research and Development
The Role of Pharma Companies in India
The development of new medications begins with a deep understanding of diseases and the biological mechanisms that drive them. Pharmaceutical companies in India, renowned for their robust R&D capabilities, play a pivotal role in this phase. Researchers at these companies work tirelessly to identify potential therapeutic targets and develop compounds that can modulate these targets effectively.
Preclinical Research
Before a new drug can be tested in humans, it must undergo extensive preclinical research. This involves laboratory and animal studies to assess the safety and efficacy of the compound. The goal is to gather enough data to support the initiation of clinical trials. This stage is crucial for ensuring that only the most promising and safe candidates move forward.
Clinical Trials: Testing in Humans
Phase I Trials
Once a compound has shown promise in preclinical studies, it enters Phase I clinical trials. These trials involve a small number of healthy volunteers and aim to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of the drug. For a medicine manufacturing company in India like Centurion Healthcare, this phase is critical for determining the initial safety profile of the drug.
Phase II Trials
If Phase I trials are successful, the drug progresses to Phase II trials, which involve a larger group of patients who have the condition the drug is intended to treat. The focus here is on assessing the drug’s efficacy and further evaluating its safety. Pharmaceutical companies in India invest heavily in this phase to gather robust data that can support the drug’s potential therapeutic benefits.
Phase III Trials
Phase III trials are the most extensive and involve a large number of patients across multiple locations. These trials are designed to confirm the drug’s efficacy, monitor side effects, and compare it to standard treatments. For a medicine manufacturing company, this phase is critical for obtaining the data needed for regulatory approval.
Regulatory Approval
After successful Phase III trials, the data is submitted to regulatory authorities for approval. In India, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new drugs. Obtaining regulatory approval is a significant milestone for any medicine company in India, allowing the drug to be marketed and made available to patients.
Manufacturing: From Lab Bench to Production Line
Scaling Up Production
Once a drug receives regulatory approval, the focus shifts to manufacturing. Scaling up production from laboratory scale to commercial scale is a complex process that requires significant expertise and investment. Medicine manufacturing companies in India, such as Centurion Healthcare, employ state-of-the-art technologies and adhere to stringent quality control measures to ensure that every batch of medicine meets the highest standards.
Quality Assurance and Control
Quality assurance and control are paramount in medicine manufacturing. Companies implement rigorous testing protocols to ensure that each batch of the drug is consistent in terms of potency, purity, and safety. This involves testing raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products. Pharmaceutical companies in India are known for their stringent quality control measures, which are essential for maintaining the trust of healthcare providers and patients.
Packaging and Distribution
Once manufactured, the medicines are packaged in a manner that ensures their stability and safety during transportation and storage. Packaging must protect the drug from environmental factors such as light, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. After packaging, the medicines are distributed to pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics, ensuring that they are readily available to patients.
Post-Market Surveillance
The journey of a medicine does not end with its launch in the market. Post-market surveillance is crucial for monitoring the drug’s performance in the real world. This involves collecting and analyzing data on the drug’s safety and efficacy from patients and healthcare providers. Pharmaceutical companies in India are actively involved in post-market surveillance to ensure that any potential issues are identified and addressed promptly.
Pharmacovigilance
Pharmacovigilance is a key component of post-market surveillance. It involves the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problems. Medicine manufacturing companies in India have dedicated pharmacovigilance teams that monitor and report any adverse events associated with their drugs, ensuring patient safety.
The Role of Technology in Medicine Production
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
The pharmaceutical industry has embraced advanced manufacturing technologies to enhance efficiency and product quality. Techniques such as continuous manufacturing, automation, and advanced analytics are revolutionizing the way medicines are produced. These technologies enable medicine manufacturing companies to produce drugs more efficiently, reduce waste, and ensure consistent product quality.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is playing a significant role in the evolution of medicine production. Pharmaceutical companies in India are leveraging digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics to streamline their operations. These technologies are used in various stages of drug development and manufacturing, from identifying new drug targets to optimizing production processes and ensuring quality control.
Sustainability in Medicine Production
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the pharmaceutical industry. Companies are adopting environmentally friendly practices and technologies to minimize their environmental footprint. This includes using renewable energy sources, reducing waste, and implementing green chemistry principles. Medicine manufacturing companies in India are at the forefront of this movement, striving to make their production processes more sustainable.
Centurion Healthcare: Leading the Way
As a leading medicine manufacturing company in India, Centurion Healthcare is dedicated to advancing the field of medicine production. Our commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability sets us apart in the industry. Here is how we are contributing to the evolution of medicine production:
Cutting-Edge Research and Development
Our R&D team is at the heart of our success. We invest heavily in research to discover and develop new therapeutic agents that address unmet medical needs. Our state-of-the-art facilities and collaboration with leading research institutions enable us to stay at the forefront of medical innovation.
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities
At Centurion Healthcare, we utilize advanced manufacturing technologies to produce high-quality medicines efficiently. Our manufacturing facilities are equipped with the latest equipment and adhere to international standards of quality and safety. We are committed to continuous improvement and innovation in our production processes.
Comprehensive Quality Control
Quality is our top priority. We have established rigorous quality control measures to ensure that every product we manufacture meets the highest standards. From raw material testing to final product release, our quality assurance team meticulously monitors every step of the production process.
Commitment to Sustainability
We are committed to making our production processes more sustainable. We have implemented various initiatives to reduce our environmental impact, including energy-efficient practices, waste reduction programs, and sustainable sourcing of raw materials. Our goal is to contribute to a healthier planet while providing high-quality medicines to patients.
Conclusion
The evolution of medicine production is a testament to the dedication and innovation of pharmaceutical companies in India. From the initial stages of research and development to the manufacturing and distribution of life-saving medications, every step in this journey is crucial. At Centurion Healthcare, we are proud to be a part of this dynamic industry, contributing to the health and well-being of patients worldwide.
As a leading medicine company in India, we remain committed to advancing the field of medicine production through cutting-edge research, advanced manufacturing technologies, and a steadfast commitment to quality and sustainability. Our journey from the lab to the patient’s bedside is driven by a passion for excellence and a desire to make a meaningful impact on global health.
#Medicine manufacturing company in India#Pharma companies in India#Medicine company in India#Pharmaceutical companies in India#Medicine manufacturing company
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
CoX: Polysynthesis
This is an explanatory writeup of one of my Original Characters (OCs). Nothing here is necessarily related to a meaningful fiction you should recognise and is shared because I think my OCs are cool and it’s cool to talk about OCs you make.
“I know what it takes to be a top hero.”
When your powers involve the ability to synthesise together chemicals into other objects, there are a lot of routes you can take them. You could invest heavily in engineering and mechanisation and make guns or bombs. Or you could dive deep into studying pharmaceuticals and synthetic chemistry and make a whole bunch of chemical compounds, like riot foam, tailored vision-warping drugs, and degrading crystal blades.
Polly to her fans, Syn to her friends, she’s a firm believer in study, theory, and then practical applications. You might know her because of fan pages, interviews or podcasts she’s done, her discussion of Identity Management or Chemical Innovation.
Polysynthesis has a very clear, crisp, public hero persona when she’s interacting with other heroes in most work settings. This is a woman who knows that she could be on the record and on camera and she is clear about communicating that whenever she can. Science talk, hero talk, the persona that many heroes consider On, that’s what most people encounter when they deal with her; Polly in action is very On. This means very rarely is she critical of others, and likes to highlight the ways she’s using complex chemistry or the like to defeat her opponents.
Which is a little at odds with the ways she does that, which can be flooding small spaces with toxic gases or riot foam and stabbing into things with knives that she routinely discards as she moves through a scene. There’s a lot of very tangible, physical violence, brutish almost, as she espouses specific chemical agents that she’s using to break through armour or immobilise enemies harmlessly.
Stepping back from public events, she’s much more relaxed, but still has a public persona; That persona is a science communicator, someone who lives in the overlap of nerd and jock, who goes to talk about ways that scientific devices and problem solving applications work together, but she’s very tangible, very material; not dimensional science or big power manufacturers but rather a fascination with chemistry in people’s everyday lives. Things you can do and make with stuff around your home.
Because that’s what she can do. Polly can synthesise anything she wants, from chemicals in her body, and then create them and hold them in her hand. She’ll tell you how hard it is to make something like an iphone because there’s a lot of literally microscopic action in the process and then she’ll do it anyway because she wants you to know she’s really good. But the problem is that’s a party trick – the phone is one design she knows how to make, and they’re not just easily transferred; making an iphone with a slightly different case? Easy enough. Changing the architecture inside it? The software? Absolutely not. That’s why she relies on making things that are fungible and simple most of the time – drugs, poisons, chemical agents and knives. It’s also part of her training regimen: she generates synthetic compounds for her own body, that let her create and maintain optimal states. It’s why she’s tall, strong and jacked.
This has also a related oddness regarding her and food, which is you’ll never see her eating food in public. She drinks – usually water – but in public spaces she’s very deliberate to never be seen eating anything in public. This is because when she revealed on a podcast to an interviewer that she synthesises food products in her body to make her created objects, and that means she consumes a lot of food, she found out there was a large body people on the internet who were suddenly Very Interested in her in ways she found a little uncomfortable, and wanted to discourage.
Polly believes firmly in not devaluing others’ work with her own powers. When she gets a new outfit, she pays the designer a user’s fee and then replicates her own copy of the outfit with her powers. This vision of not devaluing work disappears when she’s making things like a smartphone or a tracking device, and when pressed as to why she mostly shrugs about it. There’s a conversation about depriving value from artists versus depriving value from corporations, but she’s not likely to get into it.
Build
Polly’s a tank! A bio armour/claws tank. That means she’s got a build that focuses on being tough and being able to spam her area affect attacks in order to grab and hold aggro, and then it doesn’t matter if she does lots of single target damage as long as she can do it indefinitely. Her build has:
45+% defense to Smashing, Lethal, Fire, Cold and Melee damage
41% defence to Energy and Negative
90% resistance to smashing and lethal damage
80% global recharge
the ability to double-stack Follow Up for a 60% global damage buff
The ludicrous survivability and auras of Bio Armour.
I like this build a lot, no link at the moment because exports still don’t work. I like how her build can use Musculature to improve its damage output, and run Assault as well, because Bio Armour has so much recovery.
History
Okay, so there’s this twist in Polysynthesis’ story. That is, part of what helps her maintain her secret identities, is that Polysynthesis isn’t a hero from Primal Earth. She started her life on Praetoria, as a completely different person, who looked different and had a different gender. That old identity doesn’t have a lot to build a story out of, because and this is very important, I don’t ever want to do anything with that old identity. It’s a deadname, and a dead identity. The important thing about it is to explain how Polly looks at the world around her now.
She was used to partying and enjoying herself and indulging and making the coolest drugs for rich and elite people, far away from the real problems real people dealt with in their real lives. The realisation after the fall of Praetoria of how much that old life of casual joy and pleasure was built on neglecting good she could do in a community of people who could suffer was part of what shocked her into making herself into a heroine – and she’s very much trying to jump to the top step here, which is why there’s this drive to succeed to excess.
And also why she uses an alternate identity to go out and party and get high and vent the anxiety of someone who struggles with the trauma of having her whole world ended. And that’s just part of the history of this character. Because, that’s all stuff that flowed from conversations with friends, while the start for her story, well, the start was something I think of as very important to almost all forms of OC creation, and that is, blatant and unapologetic theft.
I watched too much of My Hero Academia which I would say now is ‘more than just the first Gentle story arc.’ It’s not a good show. It’s a show about superheroes that doesn’t understand what superheroes are or what superheroes are for and largely thinks that Japan’s school system is good for educational outcomes and also good for students. The show nonetheless has a bunch of popular and well-known characters that mean there’s a ton of fanart of these characters that look cool. In the context of roleplay, being able to grab art and use it to highlight or emphasise moments in storytelling, that’s great fun and valuable, so having a character who looks like someone where there’s a ton of existing fanart in different contexts is really useful!
In My Hero Academia there’s a character named Momo Yaoyorozu. She’s the superhero Creati, and if you’ve been having your nose twitch while I described Momo and her powers, yeah, this is why. I made Polly as a whole-character reference to Momo. Momo’s powers are interesting and cool but also not central to the story so it doesn’t matter how many times a problem could be solved by having Momo come up with a solution for it but instead the story needs Momo to be very limited and kinda stupid. Momo at one point uses her powers to create a chain gun that she then uses to not shoot at things and just as a dead weight, and that’s… so silly.
Also, she’s a woman in My Hero Academia so her life is going to suck anyway, because that anime sucks at writing women, period.
There’s also stuff about Momo that doesn’t make sense? Like her body and her attitude and the way she models is all very strange when it’s meant to be a what fifteen years old? That seems wildly ridiculous given just how she looks. And she’s meant to be smart, a highly skilled student, but her ability to conceive of solutions to problems in the series is preposterously basic, because the story doesn’t ever want her solutions to be good ones.
Polly was originally going to go by ‘Syn’ socially, because I like when a character’s appellation is a little more challenging than just the most obvious one. It shows when a player has done a little extra and remembers a detail like that dealing with a character, right? But then a friend’s character, a very sweet Starfire like, pointed out that ‘Polly’ is cute. And well, damnit, it is, and fine. She’s Polly now.
There’s also the way that I didn’t want Polly to be too omnidisciplinary. If she’s doing a ton of research into engineering and chemistry regularly, and then praciticing using those powers and working out, there’s going to be stuff she’s not an expert in, especially when she’s trying to project an entire upbringing in a world where she’s an interloper. To that she recruited a ‘social media manager’ whose job it is to present her pictures and manage her appointments on podcasts and stuff like that, and that’s Mac.
Mac has to deal with all sorts of things, because Polly as a hero is great, Polly as a public science communicator is amazing, and Polly as a social media management client is a nightmare. She doesn’t get the memes, she doesn’t know what she should set up, and she doesn’t look at the product either. Which means that Mac wakes up to a phone upload of thousands of photos and a calendar and then has to try and wrangle Polly to make her appointments (with the always very understandable interruption of hero work), while also dealing with Polly’s own difficulty being, well, normal. Mac is constantly frustrated by Polly missing opportunities and being unavailable when she needs to be (because there’s a nonzero chance she was sleeping in because she’s still going out and partying).
And all this is because a friend, hearing about Polly, who doesn’t even play City of Heroes, went ‘I bet her social media manager’s job sucks’ and we talked about it!
Polly’s background, of a terrible self-centered drug dealer to the privileged elite who shifts into a heroic chemistry teacher was literally a reference to a Breaking Bad meme another friend shared when she heard about the concept of Polysynthesis. This same friend also had the same opinion of Creati, and helped kick off the idea of how to use the same powerset without being focused on technically challenging creations that aren’t meaningfully useful.
I like hanging on to these details about how a character was shaped by my friends, because my friends are cool, and OCs are like dolls that we can play with together. It’s nice to have creative play narratives with people you care about! It’s cool and I recommend it!
Check it out on PRESS.exe to see it with images and links!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Scientists help unravel life's cosmic beginnings
Knowledge about the early forms of life in the universe that may have led to the development of life on Earth remains largely unknown. However, a group of scientists at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa are attempting to change that.
In a newly published paper in Nature Astronomy, researchers in the Department of Chemistry have discovered how some crucial molecules can form in space, which could lead to significant developments about how life may have originated on Earth.
The molecules in question are called nitrogen carrying aromatic molecules, which are important in many areas of chemistry and biology. They serve as the building blocks for a wide range of compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, plastics, and natural products. Aromatic molecules are also found in important biomolecules such as amino acids, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and vitamins.
Using molecular beams, the UH chemistry team, led by Professor Ralf I. Kaiser, recreated the environments of the Taurus Molecular Cloud (dense region of interstellar gas and dust located in the Taurus constellation, where new stars are actively forming) and of Titan's atmosphere (resembles Earth's early conditions due to its nitrogen-rich composition and presence of methane). Titan is Saturn's largest moon.
In combination with electronic structure calculations by Professor Alexander M. Mebel (Florida International University), along with interstellar (Professor Xiaohu Li, Chinese Academy of Sciences) and atmospheric modeling (Professor Jean-Christophe Loison, University of Bordeaux), postdoctoral fellow Zhenghai Yang was able to pinpoint fundamental structural units of aromatic molecules, which offer new paths to understanding how the building blocks of DNA and RNA might have formed in space, reshaping our ideas about how life's ingredients originated throughout the galaxy.
"The study suggests that nitrogen carrying aromatic molecules—pyridine, pyridinyl, and (iso)quinoline—could have been synthesized in environments that scientists are really honing in on due to their similarities to Earth," Kaiser said. "Understanding how these molecules form is vital for unraveling the mysteries of life's origins. Findings like these could have future implications, including for practical applications not only in biotechnology and synthetic biology, but also in combustion sciences."
IMAGE....CM functions of the C–ND3 and C2–NH3 reactions. Credit: Nature Astronomy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02267-y
4 notes
·
View notes