#tablelayout
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Premium Quality Event Table seating charts with Fast Turnaround!

Table seating charts are essential for ensuring a smooth and organised experience for guests at weddings, corporate events, and other special occasions.At Banner House,, we can custom design and print spectacular Seating Plans as per your requirement and themes. Whether you’re looking for classic, elegant, rustic or floral we have something to suit you and your wedding. These signs are also sometimes called Seating Charts, Wedding Seating Plans, Party Seating Plan, Seating Signs etc. You can upload your own artwork ideas.Look for and add more items from the Online Shop.
Banner House, a leader in digital printing in Australia, is a premier supplier of Table seating charts , serving all major cities including Perth, Melbourne, Sydney, Brisbane, Adelaide, Hobart, Darwin, Canberra, and other regional areas.
#custom#personalised#affordable#bannerhouse#bannerhouseperth#bannerhouseaustralia#printing24hrs#cheap#partysigns#Tableseatingcharts#tableplacements#tabletop#tablelayout#table seating plans#tableseatinglayouts#printingperth
0 notes
Photo

Using up all my scraps! I saw @astitchshyofnormal was doing a scrap C2C blanket so I thought I'd do the same with mine ^^ I measured all my scraps and anything less than the length of myself T-pose fingertip to fingertip, I tossed. #tablelayout #birdseyeview #yarnporn #yarnaddict #yarnlovers #crocheter #crochetblanket #handmadeblanket #handmadecrafts #crochetwip https://www.instagram.com/p/BoxSc4_gkAq/?utm_source=ig_tumblr_share&igshid=efj9133ituoe
#tablelayout#birdseyeview#yarnporn#yarnaddict#yarnlovers#crocheter#crochetblanket#handmadeblanket#handmadecrafts#crochetwip
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
YouTube'da "Çalışma Masamı Düzenliyorum👌🏻" videosunu izleyin
#aboneol#beğen#takiptekal#shorts#kısavideo#dercalısma#Masadüzeni#tablelayout#calısmamasamıdüzenliyorum#I'morganizingmydesk
1 note
·
View note
Text
Thanksgiving 2018 Edition

How is that for your dinner plans? We hope that these have been useful to you in some ways. Feel free to mix and match these items with what you already have! Because in the end what matters is everyone being having a good time. With that said, all members of Jo Laurie Design wishes you good health, good fortune, and a Happy Thanksgiving!
See you next time.
Written by C.S
0 notes
Photo

В чем отличие сервировки стола у богатых и бедных? И как это влияет на достаток. 🔸Прежде всего, это изысканность. Например, знаменитые завтраки @rudkovskayaofficial услаждают одним своим видом) 🔸Свежесть и высочайшее качество продуктов 🔸Цветы, декор 🍀 Зачем все эти сложности? Над которыми даже пошутил @maxgalkinru 😃 🍀 На самом деле это имеет большой смысл... 🔸Многие только раз в году, на Новогодний праздник, накрывают красивый стол, закупают все самое лучшее, элитное. 🔸Зачем? Да, именно! Чтобы весь год был благополучный, богатый, счастливый. 🔸Благополучные люди ежедневно начинают свой день так. 🔸Подобное притягивает подобное, поэтому и расходуется время на ритуал сервировки стола. 🔸Где там ваши лучшие столовые приборы, тарелки? Не пора ли их достать или обновить? Чтобы каждый день, как "завтраки со звездой") ⚚Это будет магическое действие для притяжения в предстоящий день красоты и богатства. 🍀 #эзотерика #достаток #приметы #благополучие #красота #изысканность #маг #раевская #парапсихолог #обряд #ритуал #удача #magraevskaya #fortune #tablelayout #sign (at Шато де Вэссель)
#удача#приметы#magraevskaya#парапсихолог#ритуал#маг#достаток#раевская#tablelayout#эзотерика#sign#изысканность#fortune#красота#обряд#благополучие
0 notes
Text
TableLayout with Android Studio with App
The TableLayout component is an effective tool for building mobile apps that are responsive. It allows you to create layouts that work on smartphones and tablets. It supports a variety of viewport sizes and is developed using the MVVM model. In this post you'll discover how to use TableLayout as a TableLayout component to create layouts to your apps.
The Best Python Books for Beginners in 2022
1. Why do you need to use the TableLayout component?
The TableLayout component will help you create a UI that is much more organized and organized. This is especially useful when you have apps with many screens that must be separated into groups. It can also assist you to develop a user-friendly UI. ##
CCNA LAB Configuration Course Zero To Hero
2. How do you create a layout using the TableLayout component
Within Android Studio in Android Studio you are able to utilize to use the TableLayout component to design a layout for your app. In this article you'll learn how to create an outline using this component.
How To Configure Default Routing On 3 Routers
3. More advanced layouts using the TableLayout component
To design a layout that includes columns, you can use the tablelayout element. TableLayout is a TableLayout component can be described as a layout, which arranges its components into grids. It's a powerful layout that can be used to create any type of layout for user interfaces. It is not limited to the creation of tables. The TableLayout component comes with the following properties: ColumnSpan Number of Columns in the layout RowSpan The number of rows in the layout ColumnWidth is the size of a column in the layout RowHeight is the height of a row within the layout CellWidth is the width of a cell in the layout CellHeight: the height of a particular cell in the layout TableLayout uses the following methods addColumn() Adds an additional column to the added row of the layout() which adds one more row in the layout's addColumns() that adds new columns to the layout addRows(): adds new rows to the design setColumnSpan(): sets the number of columns within the layout setRowSpan() is set to how many rows within this layout's setColumnWidth():
How To Configure EIGRP in Packet Tracer - 3 Routers
4. Conclusion.
If you are running Android Studio, you can set up a TableLayout in the app. This will make it easier for your users to follow a particular layout for your app's content. This is a great way to aid users with navigation in your app.
OSI Model, Reference Model, Layer Model, 7 Layer Model
0 notes
Text
FixedHeaderTableLayout
A powerful Android library for displaying complex data structures and rendering tabular data composed of rows, columns and cells with fixed table headers and offering pan and zoom support. FixedHeaderTableLayout is similar in construction and use as to Android's TableLayout.

from The Android Arsenal https://ift.tt/31odZ8X
0 notes
Photo

Android Studio für Anfänger | FrameLayout & TableLayout | Hindi Tutorial 2019 http://androidwelt.club/android-studio-fur-anfanger-framelayout-tablelayout-hindi-tutorial-2019/?feed_id=7534&_unique_id=5f864fd13fa56
0 notes
Photo
How to create table and Format table in ms word 2010 http://ehelpdesk.tk/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/logo-header.png [ad_1] AjazComputers #MsWord #MsWord201... #dataanalysis #datamodeling #datavisualization #edittable #edittableinmsword #excel #exceldashboard #excelformulas #excelfunctions #excelmacros #excelvba #format #howtocreatetableandformattableinmsword #howtodeletetableinmicrosoftword #howtoformattableinmsword #howtoinserttableinmsword #howtomergetablesinword #inserttableinword #layout #microsoftaccess #microsoftoffice #microsoftoffice365 #microsoftpowerbi #microsoftproject #microsoftword #mswordtutorial #officeproductivity #pivottables #powerpivot #powerpoint #sap #tabel #table #tableedit #tableeditinginword #tableformattinginword #tablelayout #tablelayoutinmsword
0 notes
Text
Elegant Table Arrangements for Your Event with Banner House.

Table seating charts are meticulously crafted diagrams used to organise and designate seating arrangements for events and gatherings. Designed with precision and foresight, these charts ensure that guests are comfortably accommodated and strategically placed to facilitate interaction and flow throughout the event.
Moreover, table seating charts can be adorned with decorative elements that complement the event's theme or aesthetic, adding an extra touch of elegance or personality.
Select product from our Online Shop
Banner House is a leading supplier of high quality Table Seating Charts at affordable price across Australia.
#eventplanning#guestseating#tablelayout#eventdecor#partyplanning#bannerhouse#bannerhouseperth#welcome signs#custom
0 notes
Photo

\\WEDDING WEDNESDAY//⠀ You will fall in love all over again when you see our venue! Whether that be in person or virtually! Book a 1-1 meeting with one of our award-winning wedding coordinators and you can meet them in person or an online meeting! ⠀ Click the link to book -⠀ https://thewellbeingfarm.youcanbook.me/⠀ .⠀ .⠀ .⠀ 📸 - @slatteryphoto ⠀ #weddingwednesday #weddingplanning #tablelayout ⠀ #weddingtrends #wedding #bridestory #weddinginspiration #weddinginspo #lancsweddings #weddingday #venuestyling #uniquewedding #weddingdecor #weddingstyle #weddingplanner #weddingdesig #weddingideas #weddingtabledecor #brides #lancashireflorist #botanicalwedding #venuestyling #weddingday #rockmywedding #weddingreception #luxuryflorist #luxurycatering #luxurywedding #eventpro #lancashirewedding https://ift.tt/2WGJzO5
0 notes
Text
Free Printable December 2019 Calendar
Free Printable December 2019 Calendar - The best plan is a way to calculate your daily progress, you can if you want to change the plan. But follow your plan regularly, so track progress. It makes your life comfortable and disciplined.
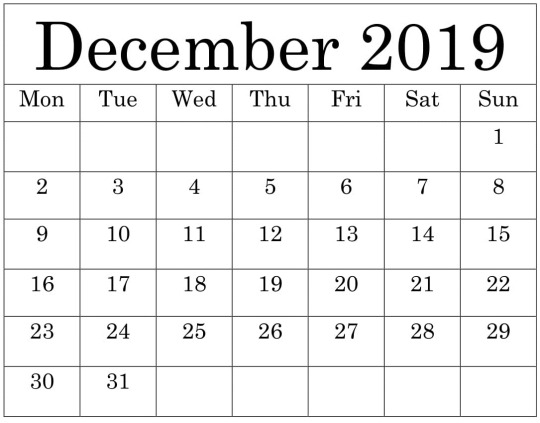
#PrintableDesign #CalendarTemplate #CuteTemplate #PrettyWallpaper #WordTemplateDesign #December2019Calendar #Holidays #Christmas #Worksheets #TableLayout
0 notes
Text
Android App Entwicklung: ESP Controller ansprechen #1

Auf dem Markt gibt es diverse ESP Controller, der Vorteil eines solchen Microcontrollers ist es, das dieser über analoge & digitale Ein/Ausgänge verfügt und als Schnittstelle WiFi besitzt.

ESP12 In diesem Tutorial möchte ich erläutern wie man für diese Microcontroller eine Android App entwickelt und verschiedene Sensoren / Aktoren ansprechen oder auch auswerten kann. Solltest du im nachfolgenden Tutorial Fehler finden, oder Fragen haben, so kannst du dich gerne per E-Mail oder über das Kontaktformular an mich wenden.
Voraussetzung
Ich setze in diesem Tutorial voraus dass, das Tool Android Studio installiert, konfiguriert und lauffähig ist. Wie man Android Studio installiert habe ich im Tutorial https://draeger-it.blog/android-app-mit-einer-mysql-datenbank-verbinden-16-01-2016/#Entwicklungsumgebung ausführlich erläutert.
leeres Projekt zum Mitmachen
Am Anfang möchte ich gerne ein leeres Projekt zum Download anbieten. Dieses Projekt kann in Android Studio importiert werden und für die nächsten Schritte weiter ausgebaut werden.
Kommunikation zwischen den Geräten
Zuerst möchte ich meine Lösung für die Kommunikation zwischen den Geräten erläutern. Sicherlich gibt es mehrere Lösung für dieses Problem, jedoch habe ich mit dieser Lösung sehr gute Erfahrungen gesammelt. Das Android Gerät sendet einen Request an den ESP in dem dieser eine HTTP Adresse aufruft. An diese Adresse können HTTP GET Parameter angehängt und vom ESP ausgewertet werden. Als Ergebnis sendet der ESP ein Respond mit einem JSON String.

Kommunikation zwischen Android & ESP Der Vorteil an einem JSON ist, das es ein kompaktes Datenformat in einer leicht lesbaren Sprache (in diesem Fall deutsch) ist. Wenn du mehr über das JSON Format erfahren möchtest so empfehle ich dir den Wikipedia Artikel Seite „JavaScript Object Notation“. In: Wikipedia, Die freie Enzyklopädie. Bearbeitungsstand: 11. Januar 2019, 11:21 UTC. URL: https://de.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=JavaScript_Object_Notation&oldid=184617074 (Abgerufen: 16. Januar 2019, 14:28 UTC)
Layout
Für dieses Tutorial nutze ich ein einfaches TableLayout mit 4 TableRows. Die erste Zeile enthält ein EditText für die IP Adresse, die zweite Zeile ein EditText für den Text welcher abgesendet werden soll und die dritte Zeile enthält eine Schaltfläche für das ausführen der Aktion zum absenden des Textes. Die letzte Zeile enthält nur eine einfache TextView für das Anzeigen des empfangenen Ergebnisses.

ESPTutorialApp - Layout Das Layout für das Hauptfenster wird in der Datei "activity_main.xml" definiert. Damit wir die Komponenten später verwenden können legen wir uns jeweils ein Feld in der Klasse "MainActivity.java" an. Zusätzlich müssen diesen Feldern dann noch eine "Verbindung" zur Komponente mit "findViewById" in der Funktion "onCreate" hergestellt werden. private EditText ipAdressEditText; private EditText editText; private Button button; private TextView textView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ipAdressEditText = findViewById(R.id.ipAdressEditText); editText = findViewById(R.id.editText); button = findViewById(R.id.button); textView = findViewById(R.id.textView); } Da wir "nur" eine Handvoll komponenten für dieses Beispiel verwenden ersetze ich nicht die IDs durch sprechende Bezeichnungen. Jedoch empfehle ich wie bei dem Eingabefeld "ipAdressEditText" eine sprechende Bezeichnung zu wählen.
Berechtigungen der App setzen
Damit man mit einem Netzwerk kommunizieren kann, muss man der App die Berechtigung zum Zugriff auf das Internet geben. Der nachfolgende Text wird in der Datei "AndroidManifest.xml" eingetragen. Damit wir zusätzlich den Status abfragen können ob das Gerät mit einem Netzwerk verbunden ist, müssen wir die Berechtigung hinzufügen. Wenn die AndroidApp später über den GooglePlay Store ausgeliefert wird, muss der Benutzer diese Berechtigung manuell bestätigen.
Abfrage des Netzwerkstatus
Bevor wir ein Request an einen ESP Controller senden können benötigen wir eine Netzwerkverbindung. Diese baut das Handy/ Tablet in der Regel selber auf so das wir diese aus der App nutzen können. Jedoch kann es passieren das keine Netzwerverbindung besteht. Hier sollten wir den Benutzer mit einem einfachen Dialog darauf hinweisen. Wir holen uns also zuerst den "ConnectivityManager" aus den SystemServices. Der Manager kann null sein also prüfen wir zusätzlich ob dieser null ist bevor wir uns die Informationen über das aktive Netzwerk auslesen. Wenn das Gerät mit keinem Netzwerk verbunden ist so liefert die Methode "connectivityManager.getActiveNetworkInfo()" null zurück d.h. auch hier müssen wir auf null prüfen bevor wir mit der Methode "isConnected" prüfen können. Wenn keine Netzwerkverbindung besteht so wird ein Dialog angezeigt welcher den Titel "Fehlermeldung" trägt und als Text "Es besteht keine Netzwerkverbindung!" hat. Es wird für diesen Dialog nur eine Schaltfläche benötigt und beim betätigen wird der Dialog geschlossen. private boolean isNetworkAvailable() { ConnectivityManager connectivityManager = (ConnectivityManager) getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE); NetworkInfo activeNetworkInfo = null; if (connectivityManager != null) { activeNetworkInfo = connectivityManager.getActiveNetworkInfo(); } boolean available = activeNetworkInfo != null && activeNetworkInfo.isConnected(); if(!available) { AlertDialog.Builder alertDialogBuilder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); alertDialogBuilder.setTitle(getResources().getString(R.string.dialog_error)); alertDialogBuilder .setMessage(getResources().getString(R.string.msg_no_networkconnection)) .setCancelable(false) .setPositiveButton(getResources().getString(R.string.ok), new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { dialog.cancel(); } }); AlertDialog alertDialog = alertDialogBuilder.create(); alertDialog.show(); } return available; } Wenn kein WLAN aktiviert ist, wird also nun ein Dialog angezeigt. Nun muss der Benutzer die App verlassen und manuell das WLAN aktivieren. Aktivieren der WLAN Verbindung aus der App Hier können wir den Benutzer im Dialog unterstützen und die "negative Schaltfläche" für das aktivieren des WLANs benutzen. Wir holen uns zuerst wieder den "WifiManager" aus den SystemServices und aktivieren dort das Wifi über die Methode "setWifiEnabled". .setNegativeButton(getResources().getString(R.string.activate_wifi), new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { WifiManager wifi = (WifiManager) getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE); wifi.setWifiEnabled(true); dialog.cancel(); } }) Damit wir diese Funktion nutzen können müssen wir der App noch 2 zusätzliche Berechtigungen in der "AndroidManifest.xml" geben.

"Fehlermeldung keine Netzwerkverbindung" Je nach Android Version und gewählten Theme kann die Farbe und das Layout abweichen.
Absenden eines Request
Nachdem wir nun die Vorbereitungen zum erfolgreichen absenden eines Request erstellt haben möchten wir eine URLConnection zu einem Gerät aufbauen. Vorbereitungen Damit wir den Text aus dem Textfeld mit dem Button absenden können müssen wir zunächst diesem eine Aktion zuweisen. Dazu setzen wir der Funktion "setOnClickListener" das Interface "View.OnClickListener" ein. Zusätzlich prüfen wir in der Methode, ob eine aktive Netzwerkverbindung besteht. button = findViewById(R.id.button); button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (isNetworkAvailable()) { sendRequest(ipAdressEditText.getText().toString(), editText.getText().toString()); } } }); Alternativ könnten wir auch der Klasse "MainActivity" das Interface "View.OnClickListener" implementieren und somit die Funktion "onClick". Das hätte den Vorteil das bei mehr als einen Button nur eine Funktion alles Regelt. Wir rufen in der Funktion dann die weitere neue Funktion sendRequest auf, dieser Funktion übergeben wir den Text aus dem EditText. private void sendRequest(String ipAdresse, String text) {} Aufbauen einer asynchronen Verbindung Die Verbindung zum ESP wird asynchron aufgebaut. Dieses macht man immer dann wenn man Daten an einen Empfänger sendet und nicht auf das Ergebnis warten möchte. Das Ergebnis wird dann abgearbeitet wenn dieses bereit steht. Wenn nach einer bestimmten Zeit keine Antwort kommt wir ein Timeout ausgelöst. Wir benötigen zunächst eine interne Klasse welche die Abstrakte Klasse "AsyncTask" erweitert. class RequestAsyncTask extends AsyncTask {...} Und einen Konstruktor welchem wir die IPAdresse und den Text als Parameter übergeben können. private final String text; private String ipAdresse; public RequestAsyncTask(String ipAdresse, String text) { this.ipAdresse = ipAdresse; this.text = text; } Mit dem einbinden der Abstrakten Klasse müssen wir mindestens die Methode "doBackground" implementieren. protected String doInBackground(Void... voids) {...} In dieser Methode senden wir unseren Text an den ESP. Zuerst möchten wir eine einfache Begrüßung absenden und empfangen. Dazu senden wir einen Text an den ESP Controller. Dazu bauen wir uns zuerst die Adresse zusammen, diese besteht aus dem Protokoll "http" (gefolgt von einem Doppelpunkt und zwei Slashes) der IP Adresse des ESP Controllers, dem Servlet welches angesprochen werden soll, in unserem Fall heißt dieses "greeting" und dem Parameter Möchte man mehrere Parameter anhängen so müssen diese mit einem "&" getrennt werden. Dazu aber später mehr. @Override protected String doInBackground(Void... voids) { try { StringBuffer urlBuffer = new StringBuffer(); urlBuffer.append("http://"); urlBuffer.append(ipAdresse); urlBuffer.append("/greeting"); urlBuffer.append("?text="); urlBuffer.append(text); URL url = new URL(urlBuffer.toString()); URLConnection conn = url.openConnection(); conn.setDoOutput(true); return readResult(conn); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return ""; } Da bei der Verbindung eine Exception auftreten kann muss diese abgefangen werden. Hier könnte man diese Fehlermeldung noch an die Oberfläche mit einem Dialog weitergeben. Als erstes erzeugen wir uns ein neues Feld vom Typ "String" um die ggf. auftretende Fehlermeldung zu speichern. private String errorMsg; Dieses Feld befüllen wir dann in dem Catch Block mit der Fehlermeldung: ... } catch (Exception e) { errorMsg = e.getMessage(); e.printStackTrace(); } ... Ich gebe zusätzlich den Stacktrace auf der Console aus. Die Fehlermeldung wird dann ausgewertet wenn das Ergebnis der Asyncronen Verbindung ausgewertet wird. Wenn keine Fehlermeldung aufgetreten ist so wird von der URLConnection das Ergebnis gelesen. private String readResult(URLConnection conn) throws IOException { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream())); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { sb.append(line); } return sb.toString(); } Dieses Ergebnis geben wir dann in der Methode "doInBackground" zurück, die Verarbeitung dieses Ergebnisses wird dann in der Methode "onPostExecute" verarbeitet. Wir haben uns im Catch Block beim absenden uns eine ggf. auftretende Fehlermeldung gespeichert, nun prüfen wir also ob dieses Feld befüllt ist. Da das Feld initial mit "null" belegt ist machen wir einen einfachen Null Check und prüfen zusätzlich ob das "result" nicht leer ist. (Wir sollten ja ein JSON vom ESP Controller erhalten.) Wenn das Feld "errorMsg" jedoch befüllt ist so zeigen wir die Fehlermeldung an. @Override protected void onPostExecute(String result) { super.onPostExecute(result); if (errorMsg == null && result.trim().length() > 0) { textView.setText(result); } else if (errorMsg != null) { showErrorMessage(errorMsg); } } Anzeigen der Fehlermeldung in einem Dialog Die neue Methode baut dann die Fehlermeldung auf und zeigt diese an. private void showErrorMessage(String message) { AlertDialog.Builder alertDialogBuilder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); alertDialogBuilder.setTitle(getResources().getString(R.string.dialog_error)); alertDialogBuilder .setMessage(message) .setCancelable(false) .setPositiveButton(getResources().getString(R.string.ok), new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { dialog.cancel(); } }); AlertDialog alertDialog = alertDialogBuilder.create(); alertDialog.show(); } Sollte also nun zbsp. eine Verbindung nicht aufgebaut werden können, so wird eine Fehlermeldung angezeigt.

Fehlermeldung beim aufbau einer Verbindung zu einem Gerät
Sketch für den ESP Controller
Nachdem wir unsere AndroidApp geschrieben haben wollen wir uns nun dem ESP Controller widmen. Dieser muss den Request annehmen, verarbeiten und eine Antwort (Respond) an das Android Gerät senden. Wir benötigen zunächst einen Microcontroller mit einem WiFi Chip, zumeist ist dieses ein ESP8266 oder ähnliches. Diese Microcontroller gibt es günstig bei ebay.de zu kaufen zbsp. den NodeMCU, WemosD1Mini.

Wemos D1 Mini mit ESP8266 Chip Ich verwende in diesem Tutorial den WittyCloud , dieser Microcontroller verfügt neben den üblichen Ein/Ausgängen noch zusätzlich über einen Fotowiderstand und einem NeoPixel. //Bibliotheken für die Kommunikation mit WiFi Geräten #include #include const char* ssid = ""; //SSID aus dem Router const char* password = ""; //Passwort für den Zugang zum WLAN ESP8266WebServer server(80); //Port auf welchem der Server laufen soll. void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); //Baudrate für die Serielle Geschwindigkeit. delay(10); //10ms. Warten damit die Seriele Kommunikation aufgebaut wurde. Serial.print("Aufbau der Verbindung zu: "); //Ausgabe der SSID auf der Seriellen Schnittstelle. Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, password); //Initialisieren der Wifi Verbindung. while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { //Warten bis die Verbindung aufgebaut wurde. delay(500); //kleine Pause von 500ms. Serial.print("."); } //Wenn eine Verbindung erfolgreich aufgebaut wurde, //werden die Daten auf dem seriellen Ausgang ausgegeben. Serial.println(""); Serial.print("Mit "); Serial.print(ssid); Serial.println(" erfolgreich verbunden!"); //Wenn der Server angewiesen wird das Servlet mit der Bezeichnung "greeting" bereitzustellen //so wird die Funktion "callGreeting" aufgerufen. server.on("/greeting", callGreeting); server.begin(); // Starten des Servers. Serial.println("Server gestartet"); //Ausgabe auf der Seriellen Schnittstelle das der Server gestartet wurde. // Ausgabe der IP Adresse Serial.print("Adresse : http://"); Serial.print(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println("/"); } void loop() { //alle Anfragen der Clients verarbeiten. server.handleClient(); //Hier wird keine Pause eingelegt da dieses sonst die Verarbeitung stören würde. } void callGreeting(){ //Eine Variable zum speichern des gelesenen Wertes. String text = "-undefined-"; //Über alle möglichen Parameter iterieren. for (int i = 0; i //Zuweisen der Schlüssel/Wertepaare String parameterName = server.argName(i); String parameterValue = server.arg(i); //Wenn der Parametername gleich "text" ist dann... if(parameterName == "text"){ //zuweisen des Wertes zu unserer Variable text = parameterValue; } } //Absenden eines JSONS mit einer Begrüßung und unseres gelesenen Textes. sendResult("{\"msg\": \"Hello from ESP8266!- "+text+"\"}"); } //Diese Funktion sendet eine Antwort an den Client. void sendResult(String content){ //200 ist die Antwort das alles OK ist, //text/html ist der MimeType //content ist unser Text server.send(200, "text/html", content); }

Ausführen der App - Absenden eines Request an den WittyCloud
Download
Review & Ausblick
Die erste Ausbaustufe ist geschafft und als nächstes folgt nun die Umwandlung des JSONs mit Hilfe von Google Gson. Und da der WittyCloud mit einem Sensor & einen Aktor daherkommt wollen wir diese verwenden und die Daten senden bzw. empfangen. D.h. den Fotowiderstand auslesen und dem NeoPixel einen Farbwert zuzuweisen. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
android brush up from book ( development tips )
Extending the Binder classstopSelfstopSelfwidget : 사용자 interface를 구성한다. View를 extends한다.
각각의 element는 xml attributes set을 가질수 있으며 이는 widget을 configuration하는데 사용된다.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" >
최상단에 위치한 element를 root element라고 하며 xmlns 속성을 가진다.
LinearLayout 은 ViewGroup의 하나이며 이또한 View를 extends 한다. ViewGroup은 다른 View를 포함할수 있다. FrameLayout, TableLayout, RelativeLayout도 같은 종류에 속한다.
android: layout_width 와 android: layout_height은 match_parent, wrap_content로 지정될수 있다.
dp 는 density-independent pixel을 말한다.
android:oriention 설정을 통해 childs element가 상하로 또는 옆으로 출력되게 한다.
android:text를 통해 어떤내용을 widget에 표시할지를 정할수 있다.
strings.xml 이름의 화일안에 xml에서 사용될 hard coded string을 정의하여 사용한다. 이를 string resource라고 부른다. app/res/values 폴더 안에 위치해 있다. 다른 이름의 화일이 되어도 괜찮으며 여러개이어도 괜찮다.
java file은 app/java에 저장한다.
AppCompatActivity를 이용 오래된 버전의 기기에서도 최신의 기능을 사용할수 있게 한다.
activity에서는 setContentView(리소스ID)를 통해 widget을 instantiate한다.
code가 아닌 다른 모든 화일은 resource라고 한다. layout 의 경우 app\res\layout에 위치한다. code에서 resource를 사용하기 위해서는 resource ID를 이용한다.
xml file내에서는 android:id=“@+id/이름” 을 통해 새로운 resource id를 만든다.
code에서 Button을 사용하는 경우 import android.widget.Button을 통해 import한다.
editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.id_number_custom);
와 같은 형태로 widget ref를 얻을수 있다.
listener 연결 예시
android:onClick="onClick"
Or, remove this:
modelTextview.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { } });
toast 사용 예시
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "This is my Toast message!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
code에서 memeber variable이름에는 m prefix를 붙이는 것이 convention이다.
android 개발에서 activity, fragment, service는 controller의 역할을 한다. xml file은 view에 해당한다.
string special character escape은 \ 을 이용한다.
resource file name에는 대문자를 사용하지 않는다.
화면 회전 단축키 fn+control+f12 / ctrl+f12
activity는 lifecycle내에서 running, paused. stopped 와 같이 3가지 상태중 하나의 상태로 존재한다.
onCreate()은 activity instance가 만들어진후 화면에 출력전에 호출된다. 이함수내에서는
inflating widgets and putting them on display ( setContentView() )
getting refs to inflated widgets
setting listener
connecting models
를 수행한다.
android.util.Log를 import하고 Log.d() 를 이용 log를 작성한다. 보통은 code file 상단에 private static final String TAG = “화일이름” 을 통해 tag를 만들어 Log.d() 에 첫번째 parameter로 전달한다.
activity가 paused, stopped 상태로 되는 경우
사용자가 home 버튼을 누른경우
다른 popup에 의해 activity가 화면에서 가려진 상태
device configuration
screen orientation
screen density
screen size
keyboard type
dock mode
language
runtime 중에 몇몇 configuration은 변경될수 있다.
또 각각의 configuration 별로 다른 resource를 사용하게 할수 있다.
device configuration이 run-time에서 바뀌는 경우 activity 는 destroy된다. 그리고 config에 맞는 새로운 resource을 이용 새로 activity를 만들게 된다.
run-time에서 변경된 configuration으로 인한 refreshed activity가 기존의 views의 정보를 그대로 유지하기 위해서는 onSaveInstanceState()를 이용한다. views의 정보는 Bundle의 형태로 저장되었다가 다시 이용된다. 단 id를 가지고 있는 views의 정보만 유지된다.
configuration변화후에도 특정 데이터를 추가로 유지하고 싶은 경우 onSaveInstanceState()에서 아래와 같이 데이터를 추가로 저장해 주면된다.
@Override public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onSaveInstanceState(savedInstanceState); // Save UI state changes to the savedInstanceState. // This bundle will be passed to onCreate if the process is // killed and restarted. savedInstanceState.putBoolean("MyBoolean", true); savedInstanceState.putDouble("myDouble", 1.9); savedInstanceState.putInt("MyInt", 1); savedInstanceState.putString("MyString", "Welcome back to Android"); // etc. }
primitive type데이터나 Serializable, Parcelable 인터페이스를 제공하는 데이터타입만 Bundle을 이용해 저장할수 있다.
데이터를 저장하는 경우 onPaused() onSaveInstanceState()를 이용한다. onDestroy()는 호출되지 않는 경우도 발생함으로 사용하지 않는다.
home 버튼을 누르면 activity는 paused, stopped상태로 들어간다. back 버튼을 누르면 activity는 destroy 된다.
android studio 는 logcat, android lint를 debug tool로 제공한다.
하나의 activity를 시작한다 과정에는 activity java class file, xml layout, application manifest가 관여한다.
AndroidManifest.xml 화일
android os에게 application을 기술하는 metadata가 들어 있다.app/manifest 에 위치한다. 모든 activity, service, broadcast receiver 가 기술되어야 한다.
manifest file의 예시
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="net.simplifiedlearning.volleymysqlexample"> <!-- the internet permission --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application>
android:name 속성은 필수이며 <manifest>안에서 정의된 package내부의 activity인경우 . 으로 시작함으로써 fully qualified 속성을 사용하지 않아도 된다.
한 activity내에서 다른 activity를 시작하기 위해서는 startActivity( 인텐트obj )를 사용한다. 호출하면 인텐트obj의 정보에 따라 android OS의 ActivityManager가 새로운 activity를 시작하게 된다.
activity, service, broadcast receiver, content provider 는 component라 불린다. component는 OS와 communicate하기 위해서 intent를 사용한다.
intent를 만들시 context와 class를 이용해서 같은 application 내의 component로 향하는 explicit intent를 만들수 있다. 다른 application의 component를 위한 경우 implicit intent를 만들어야 한다.
intent에 추가 정보를 넣어서 전달할수 있다. putExtra() 를 이용해 key, value 형태의 추가 data를 넣을 수 있으며 이 함수는 다시 intent obj를 리턴함으로 연속해서 putExtra()를 호출할수 있다. 이때 key에 package이름을 넣어서 만들어 다른 key와의 충돌을 막는다.
액티버티obj.getIntent() 를 통해 activity가 만들어 질때 사용된 intent를 얻을수 있다.
액티버티obj.getIntent().getBooleanExtra( 키값, 디폴트값 ) 를 통해 추가로 전달된 data를 얻을수 있다.
잠시 다른 activity으로( child activity ) 이동하고 작업. 그후에 다시 계산 결과를 본래 activity로 ( parent activity ) 가져오는 경우 startActivityForResult( 인텐트obj, 리퀘스트코드 ) 를 이용해 다른 activity를 시작한다.
child activity에서 결과를 parent activity로 되돌리는 경우 보통은 setResult( 리절트코드, 인텐트obj ) 를 이용한다. result code는 보통 RESULT_OK, RESULT_CANCELED 를 되돌린다. 개발자가 정의한 코드를 되돌리는 경우 RESULT_FIRST_USER가 되기도 한다. intent obj에 추가로 되돌려줄 data를 덧붙일수 있다.
child activity에서 결과값을 되돌리면 parent activity의 onActivityResult( 리퀘스트코드, 리절트코드, 인텐트obj ) 가 호출된다.
ActivityManager는 back stack을 관리한다. 이안에는 여러 application의 activity가 존재한다.
sdk version과 API level은 의미가 같은 용어이다.
minimum supported version, target version , build version 은 build.gradle에 정의 되어있다. 단 minimum supported version, target version 은 AndroidManifest.xml에서 재정의 될수 있다.
build.gradle 예시
android { compileSdkVersion 23 buildToolsVersion “23.0.1” defaultConfig { applicationId “com.example.checkyourtargetsdk" minSdkVersion 7 targetSdkVersion 23 versionCode 1 versionName “1.0” } }
참조) https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26694108/what-is-the-difference-between-compilesdkversion-and-targetsdkversion
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT 는 android device version을 알려준다.
support library를 사용함으로써 오래된 버전의 android 기기에서도 최신의 기능을 이용할수 있게 된다. support library를 사용하기 위해서는 app\build.gradle에 필요한 library를 기입해야 한다. 그러나 File-> Project Structure 메뉴를 이용한다. app module의 Dependencies tab을 이용한다.
fragment를 사용하기 위해서는 activity는 FragmentActivity를 extends한다. fragment도 activity와 유사한 lifecycle을 가진다. activity와 마찬가지로 running, paused, stopped의 상태를 가진다. fragment가 activity와 비슷한 lifecycle 관련 함수를 가지고 있으나 다른 점이 있다면 activity의 lifecycle함수는 android OS에 의해 관리되고 fragment의 경우는 activity가 호출한다는 점이다. OS는 fragment에 관해 전혀 모른다. activity가 fragment를 관리한다.
fragment를 사용하는 두가지 방법
add fragment to activity’s layout ( inflexible, 변화불가능 )
add fragment in the activity code ( fragment교환 가능 )
creating ui fragment
app\res\layout 에 fragment xml 을 만든다
fragment java code file을 만든다. ( Fragment는 extends 한다 )
android:hint = “스트링” 을 통해 EditText의 가이드 텍스트를 제공할수 있다.
fragment는 public, activity는 protected를 사용한다.
public class FooFragment extends Fragment { @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup parent, Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... } }
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { } }
activity와 마찬가지로 configuration change간에도 유지하고 싶은 data가 있다면 onSaveInstanceState()에서 Bundle obj에 data를 추가로 저장한다.
fragment는 onCreateView()에서 views를 inflating한다.
onCreateView(레이아웃인플레이터, 뷰그룹, 번들)
인플레이터 : xml화일에서 views를 생성하는데 사용
뷰그룹: fragment가 첨부될 parent 뷰
번들 : views 생성하는데 필요한 추가 정보
fragment onCreateView()의 예시
@Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup parent, Bundle savedInstanceState) { getActivity().getActionBar().setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true); View rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_single_image, parent, false); ImageView imageView = (ImageView)rootView.findViewById(R.id.currentImage); imageView.setImageBitmap(currentImage); return rootView; }
EditText 에 listener설치하는 예시
et1.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() { @Override public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } });
FragmentManager는 fragments를 관리하고 fragment를 activity에 첨부하는 역할을 담당한다. FragmentManager는 list of fragments와 back stack of fragment transactions을 관리한다. getSupportFragmentManager() 를 통해 FragmentManager obj를 얻을수 있다.
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_crime); FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager(); Fragment fragment = fm.findFragmentById(R.id.fragment_container); if (fragment == null) { fragment = new CrimeFragment(); fm.beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commit(); } }
하나의 activity에 여러개의 fragment를 표시하기 위해서는 여러개의 구별된 container가 있어야 한다.
버튼obj.setEnabled(false) 버튼을 disable하게 한다.
CheckBox에 checked changed listener연결하는 예시
checkBox = (CheckBox)v.findViewById(R.id.approved_checkbox); checkBox.setChecked(true); checkBox.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener() { public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) { // update your model (or other business logic) based on isChecked } });
style xml화일은 res\values안에 만든다. theme은 style의 collection이다. 구조적으로 theme은 다른 style resources를 가리키는 style 화일이다.
참고) https://code.tutsplus.com/tutorials/android-from-scratch-creating-styles-and-themes--cms-26942
density-independent 을 통해 다른 screen densities에도 불구하고 view의 속성을 같은 크기로 지정 사용가능하다.
dp : 1 dp 는 항상 1/160 inches를 표시한다.
sp : scale-independent pixel. 사용자 font size preference가 적용된 density-independent이다.
attributes중에 layout으로 시작하는 속성은 widget’s parent에 대한 지시속성이며 layout parameters라고 불린다. 없는 경우는 widget자체에대한 지시속성이다.
Margin은 layout parameter이다. Padding은 layout parameter가 아니다.
LinearLayout에서 width를 정할때는 두가지 순서를 거치게 된다. 우선 layout_width를 기준으로 element를 배열하고 나서 나머지부분을 layout_weight을 고려해서 나머지 부분을 각 element에게 추가 배분한다. 그냥 두 element에게 반반 나누어주고 싶다고 한다면. layout_width=“0dp” 로하고 layout_weight를 같은 숫자로 맞춘다.( 같은 비율로 가진다는 의미 )
singleton obj는 한 application내에서 단 하나만 존재하게 된다.
예시)
public class SingletonClass { private static SingletonClass sSoleInstance; private SingletonClass(){} //private constructor. public static SingletonClass getInstance(){ if (sSoleInstance == null){ //if there is no instance available... create new one sSoleInstance = new SingletonClass(); } return sSoleInstance; } }
resource의 이름을 수정하는 경우 Refactor-> Rename을 통해 다른 references도 같이 수정한다.
시작 activity의 manifest 화일 내용
<activity android:label="Logo" android:name=".logoActivity" > <intent-filter > <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
여러개의 list, grid를 효율적으로 만들때 RecyclerView 를 이용한다.
RecyclerView, RecyclerView.ViewHolder, RecyclerView.Adapter 로 구성된다. custom 형태의 list, grid cell이 필요한 경우 ViewHolder에 해당하는 xml화일이 추가로 필요하게 된다. RecyclerView 를 사용하기 위해서는 support libarary를 추가해주어야 한다. 출력한 데이터 숫자가 많지 않는 경우 효율성이 중요하지 않는 경우 ListView, GridView를 대신 사용가능
RecyclerView.Adapter.notifyDataSetChanged() 호출을 통해 새로 update된 data를 새로 적용해서 recyclerview를 새로 고침 가능하다.
ios에서 dynamic layout를 구현하기 위해서는 auto layout을 사용했는데 이에 비슷한 기능을 하는 것이 android의 ConstraintLayout 과 RelativeLayout 이다. ( 둘의 차이점 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37321448/differences-between-constraintlayout-and-relativelayout )
fragment에서 다른 activity를 시작하는 경우 Fragment.startActivity( 인텐트obj ) 를 이용한다. 추가 data를 넣어서 전달하려는 경우 intent obj에 putExtra()를 이용해서 추가해준다. 이 data를 activity에서 접근하려는 경우 getIntent().getSerializableExtra(키이름) 을 통해 접근 가능하다.
fragment 와 activity간의 통신
https://developer.android.com/training/basics/fragments/communicating
The easiest way to communicate between your activity and fragments is using interfaces. The idea is basically to define an interface inside a given fragment A and let the activity implement that interface.
Once it has implemented that interface, you could do anything you want in the method it overrides.
The other important part of the interface is that you have to call the abstract method from your fragment and remember to cast it to your activity. It should catch a ClassCastException if not done correctly.
There is a good tutorial on Simple Developer Blog on how to do exactly this kind of thing.
I hope this was helpful to you!
참고로 읽으면 좋은 android doc
https://developer.android.com/training/basics/fragments/communicating.html
fragments간의 통신 방법은 아래를 참고
android programming -big nerd ranch p224
activity의 Bundle에 있는 data를 fragment에서 접근하려는 경우 getActivity().getIntent().getSerializableExtra( 키이름 ) 을 통해서 직접 접근 가능하나 이 것은 fragment 사용의 유연성을 떨어뜨린다. 그러므로 해당 data를 activity내에서 먼저 구어하고 이를 이용해서 fragment를 생성할수있는 다른 constructor를 만들어 사용하는것이 좋다. android programming big nerd book p198
fragment는 fragment 자신의 startActivityForResult()와 onActivityResult() 함수를 가지고 있으나 setResult()는 가지고 있지 않다. 그래서 activity의 것을 대신 사용한다. getActivity().setResult( Activity.RESULT_OK, null ) 와 같이 사용한다.
ViewPager를 이용하기위해서는 FragmentActivity, ViewPager in xml file, FragmentStatePagerAdapter 또는 FragmentPagerAdapter가 필요하다. view pager를 이용하기 위해서는 support library가 필요하다.
AlertDialog는 Dialog의 subclass 이다. AlertDialog라고 하더라도 최신 버전의 것을 이용하고 싶다면 AppCompat library를 이용한다. 일반 fragment를 이용해서 alert dialog를 만들수도 있지만 약간불편함이 있다. DialogFragment를 이용하는 것을 추천한다. hosting activity의 FragmentManager가 DialogFragment의 onCreateDialog()를 호출함으로 alert dialog를 만든다.
DialogFragment를 extends한 alert dialog fragment에 작성할 내용
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { String title = getArguments().getString("title"); AlertDialog.Builder alertDialogBuilder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); alertDialogBuilder.setTitle(title); alertDialogBuilder.setMessage("Are you sure?"); alertDialogBuilder.setPositiveButton("OK", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // on success } }); alertDialogBuilder.setNegativeButton("Cancel", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { if (dialog != null && dialog.isShowing()) { dialog.dismiss(); } } }); return alertDialogBuilder.create(); }
hosing activity에서 alert dialog fragment가 표시되게 하는 작업
DialogFragment에 FragmentManager obj와 key로 사용될 고유 string을 pass한다.
private void showAlertDialog() { FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager(); MyAlertDialogFragment alertDialog = MyAlertDialogFragment.newInstance("Some title"); alertDialog.show(fm, "fragment_alert"); }
parent fragment에서 child fragment를 생성하고 추가data를 전달하고 싶은 경우는 child fragment에 data를 parameter로 받을수 있는 constructor를 만든다. 그리고 받은 data는 Bundle형태로 해서 fragment의 setArguments()를 이용해서 덧붙인다.
activity들간에 통신에서 parent activity가 startActivityForResult()를 호출하면 ActivityManager가 parent-child activity relationship을 관리,추적한다. child activity가 작업을 마치고 destroy될때 ActivityManager는 어떤 것이 parent activity인지 알고 있으며 그 parent activity의 onActivityResult()를 호출한다. fragment간의 통신도 이와 비슷하다. parent fragment file안에서 child fragment를 생성했을때 그 child fragment obj의 setTargetFragment( 프레그먼트obj, 리퀘스트넘버 ) 를 통해 child fragment 에서의 작업후 되돌려올 parent fragment 정보를 FragmentManager가 관리할수 있게한다. child fragment내에서는 getTargetFragment(), getTargetRequestCode()를 통해 언제는 parent fragment가 어떤 것인지 request code가 무엇인지 알아 낼수 있다. parent fragment로 처리결과를 되돌리려는 경우 child fragment에서 getTargetFragment().onActivityResult( getTargetRequestCode(), 리절트코드, 인텐트obj ) 를 호출한다.
android 5이전에는 action bar , 그 이후에는 tool bar 를 사용 navigation, actions ui를 구현했다.
toolbar를 사용하기 위해서는 AppCompat dependency가 필요하며 AppCompat theme을 사용해야 하며 모든 activity는 AppCompatActivity를 extends해야 한다.
theme은 AndroidManifest.xml 에서 지정되며 application 전반에 적용되게 할수도 있고 각 activity별로 각기 다르게 적용되게 할수도 있다.
AppTheme은 res/values/style.xml에 정의 되어 있다.
AppCompatActivity는 FragmentActivity의 child activity이므로 기본적으로 fragment사용이 가능하다. 즉 toolbar와 fragment는 사용하는 프로젝트의 경우 AppCompatActivity를 사용한다고 생각하면 된다.
toolbar의 우측상단은 toolbar menu가 사용한다. menu는 action items으로 ( menu items이라고도 불림 ) 구성된다. action items은 현재 activity에 특정 작업을 수행하거나 app에 관련된 다른 작업을 하기도 한다. menu는 layout과 비슷하게 xml로 만들어 진다. 이는 res/menu에 저장된다.
menu item 의 예시
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <item android:id="@+id/action_favorite" android:orderInCategory="300" android:title="User" android:icon="@drawable/ic_favorite" app:showAsAction="ifRoom"></item> </menu>
icon을 만들어 사용하는 경우 android asset studio를 이용해 제작하느것이 좋다. 여러 device display에 맞게 다양한 크기의 icon이 자동으로 만들어 진다. drawable 폴더에서 오른쪽 클릭한후 New->Image Asset 메뉴를 이용한다.
activity에서 menu를 만드는 경우 onCreateOptionMenu( 메뉴obj, 메뉴인플레이터obj ) 를 이용한다. fragment의 경우도 같은 onCreateOptionMenu( 메뉴obj, 메뉴인플레이터obj ) 를 이용한다. 다만 사용전에 onCreate() 안에서 setHasOptionsMenu()를 통해 메뉴가 있음을 명시해준다.
사용자의 메뉴선택 이벤트 처리는 onOptionsItemSelected( 메뉴아이템obj ) 을 통해서 한다. 어느 메뉴아이템에서 발생한 이벤트 인지는 ID를 확인해서 알아낸다음 처리한다.
@Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { switch (item.getItemId()) { // Respond to the action bar's Up/Home button case android.R.id.home: NavUtils.navigateUpFromSameTask(this); return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); }
hierarchical navigation을 사용하기 위해서는 하위 activity에 parentActivityName attribute를 설정해 주어야 한다. 하위 activity에서 상위 activity로 가기위한 <- 버튼을 누르면 FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP 효과가 발생한다. 즉 activity stack에서 상위 activity 위에 쌓여있던 다른 activity들 다 popout 시키고 바로 상위 activity로 이동하게 된다.
앱컴팻액티버티obj.getSupportActionBar().setSubtitle( 스트링 ) 을 통해 toolbar에 subtitle을 지정할수 있다.
getString( 플레이스홀더를가지고있는String, 플이스홀더를대채할objs ) 를 이용 interpolation을 이용한 string을 만들수 있다.
toolbar는 action bar와는 달리 유연하다. 여러개의 toolbar를 한꺼번에 사용가능하기도 하고 높이조정도 가능하고 toolbar안에 다른 view를 넣을수도 있다.
각각의 application은 다른 app으로부터 구분된 각자의 sandbox를 가진다. data/data/펙키지이름 의 위치에 sandbox를 가진다.
sqlite사용시 schema 예시
public final class FeedReaderContract { // To prevent someone from accidentally instantiating the contract class, // make the constructor private. private FeedReaderContract() {} /* Inner class that defines the table contents */ public static class FeedEntry implements BaseColumns { public static final String TABLE_NAME = "entry"; public static final String COLUMN_NAME_TITLE = "title"; public static final String COLUMN_NAME_SUBTITLE = "subtitle"; } }
SQLiteOpenHelper의 예시
private static final String SQL_CREATE_ENTRIES = "CREATE TABLE " + FeedEntry.TABLE_NAME + " (" + FeedEntry._ID + " INTEGER PRIMARY KEY," + FeedEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE + " TEXT," + FeedEntry.COLUMN_NAME_SUBTITLE + " TEXT)"; private static final String SQL_DELETE_ENTRIES = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + FeedEntry.TABLE_NAME;
public class FeedReaderDbHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper { // If you change the database schema, you must increment the database version. public static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1; public static final String DATABASE_NAME = "FeedReader.db"; public FeedReaderDbHelper(Context context) { super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION); } public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) { db.execSQL(SQL_CREATE_ENTRIES); } public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) { // This database is only a cache for online data, so its upgrade policy is // to simply to discard the data and start over db.execSQL(SQL_DELETE_ENTRIES); onCreate(db); } public void onDowngrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) { onUpgrade(db, oldVersion, newVersion); } }
application을 지우면 app과 관려있던 database도 같이 삭제 된다.
database의 write, update 작업은 ContentValues class를 이용한다. 이는 HashMap, Bundle 과 비슷한 key-vlue store class 이다.
insert 작업의 예시
// Gets the data repository in write mode SQLiteDatabase db = mDbHelper.getWritableDatabase(); // Create a new map of values, where column names are the keys ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); values.put(FeedEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, title); values.put(FeedEntry.COLUMN_NAME_SUBTITLE, subtitle); // Insert the new row, returning the primary key value of the new row long newRowId = db.insert(FeedEntry.TABLE_NAME, null, values);
updata 작업의 예시
SQLiteDatabase db = mDbHelper.getWritableDatabase(); // New value for one column String title = "MyNewTitle"; ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); values.put(FeedEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, title); // Which row to update, based on the title String selection = FeedEntry.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE + " LIKE ?"; String[] selectionArgs = { "MyOldTitle" }; int count = db.update( FeedReaderDbHelper.FeedEntry.TABLE_NAME, values, selection, selectionArgs);
sqlite cursor 를 이용해 data 추출하는 작업 예시
SQLiteDatabase db = getDatabase(); String[] columns = {"first_name", "last_name", "id"}; Cursor cursor = db.query("people", columns, null, null, null, null, null); while(cursor.moveToNext()) { int index; index = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow("first_name"); String firstName = cursor.getString(index); index = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow("last_name"); String lastName = cursor.getString(index); index = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow("id"); long id = cursor.getLong(index); //... do something with data }
The Cursor class provides the following methods to manipulate its internal position:
boolean Cursor.move(int offset): Moves the position by the given offset
boolean Cursor.moveToFirst(): Moves the position to the first row
boolean Cursor.moveToLast(): Moves the position to the last row
boolean Cursor.moveToNext(): Moves the cursor to the next row relative to the current position
boolean Cursor.moveToPosition(int position): Moves the cursor to the specified position
Cursor.moveToPrevious(): Moves the cursor to the previous row relative to the current position
cursor작업후에는 close() 를 통해 마무리해야 한다.
implicit intent를 통해 특정 작업을 수행 가능한 다른 app의 activity을 시작되게 할수 있다.
formatted string 만드는 예시
<resources> <string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have <b>%2$d new messages</b>.</string> </resources> Resources res = getResources(); String text = String.format(res.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), username, mailCount); CharSequence styledText = Html.fromHtml(text);
implicit intent의 구성
action : 어떤 작업인지에 대한 지정한다. Intent class내의 constant로 지정한다. 예를 들어 url을 보기 위해서는 Intent.ACTION_VIEW, 다른 예로 data를 보내기 위해서는 Intent.ACTION_SEND 를 이용한다.
location of data : 기기 외부의 url, file 시스템 내의 file 경로, ContentProvider 내의 content URI
type : MIME type. 예를 들어 text/html , audio/mpeg3
categories : 보통 action이 언제 , 어디서, 어떻게 수행 되는지에 대한 설명. 예로 android.intent.category.LAUNCHER
특정 implicit intent에 대응하는 activity를 만드느경우 manifest xml 화일안에 intent-filter를 이용한다. 이때 category 는 android.intent.category.DEFAULT 로 지정이 되어야 한다.
implicit intent도 explicit intent와 마찬가지로 추가 data를 전달할수 있다.
implicit intent 만드는 예시
Intent i = new Intent(); i.setAction(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); i.setData(Uri.parse("content://media/external/images/media/")); startActivity(i);
Intent의 createChooser를 이용하는 예시
Intent i = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND); i.setType( "message/rfc822"); startActivity(Intent.createChooser(i, "Send mail..."));
contact로 부터 정보를 가져오기 위한 intent 예시
// Start the intent of fetch a contact Intent contactPickerIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_PICK, ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI); startActivityForResult(contactPickerIntent, CONTACT_PICKER_RESULT);
ContentProvider를 통해 contact infomation에 접근이 가능하며 이를 마치 database 처럼 쉽게 접근하기 위해 ContentResolver를 이용한다. intent를 통해 외부 activity에서 작업하고 되돌아온 data는 onActivityResult에서 접근 가능하다. ContentResolver 는 getActivity.getContentResolver() 통해 얻을수 있다.
implicit intent를 이용하면 자기 자신 app이 가지고 있지 않은 permission을 요구하는 작업을 permission을 가진 다른 app이 작업을 수행하고 data만 되돌리게 할수있다.
혅 device내에 특정 intent 를 수행할수 있는 activity가 있는지 확인하는 작업

유사한 다른 코드
List<ResolveInfo> infos = packageManager .queryIntentActivities(intent, MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY);
다른 layout을 include하는 방법
<include android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" layout="@layout/yourlayout" />
include할때 기존의 attributes를 override해서 수정된 attributes를 적용시켜 사용 가능하다.
자기 본인 app만 접근할수 있는 internal storage관련 함수들
You can save and read files in the internal storage as private files which only your app can see except for other apps with root privileges. The absolute path of this folder is data\data\[your app package]\files The class Context provides some methods which help you to make operations such as:
openFileInput(String name) Open a private file associated with this Context’s application package for reading
openFileOutput(String name, int mode) Open a private file associated with this Context’s application package for writing
getFilesDir() Gets the absolute path to the filesystem directory where your internal files are saved
getDir() Creates (or opens an existing) directory within your internal storage space
deleteFile() Deletes a file saved on the internal storage
fileList() Returns an array of files currently saved by your application
and you don’t need to have special permissions in order to use these methods.
다른 app과 같이 공유하는 external storage에 관련된 함수
getExternalCacheDir()
getExternalCacheDirs()
getExternalFilesDir()
getExternalFilesDirs()
getExternalMediaDirs()
media 관련 작업은 MediaStore class를 통해서 한다. images, videos, musics에 관한 작업은 media store class를 통해서 한다. MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE와 함께 intent를 만들면 camera를 이용해 사진을 찍을수 있다.
external storage를 이용하기 위해서는 permission이 필요하다.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
sdk 버전에 따라 permission이 필요하기도 하고 아니기도 하므로 확인하고 각 버전별 대응코드를 만들어야 한다.
ACTION_CAPTURE_IMAGE를 통한 사진 촬영후 intent에는 thumnail의 작은 크기 이미지만 포함되어 되돌려진다. 본래크기의 image는 따로 저장되며 저장된 위치만 Uri 형태로 포함되어 전달 된다.
image 촬영 예제 코드
public void onLaunchCamera(View view) { // create Intent to take a picture and return control to the calling application Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE); // Create a File reference to access to future access photoFile = getPhotoFileUri(photoFileName); // wrap File object into a content provider // required for API >= 24 // See https://guides.codepath.com/android/Sharing-Content-with-Intents#sharing-files-with-api-24-or-higher Uri fileProvider = FileProvider.getUriForFile(MyActivity.this, "com.codepath.fileprovider", photoFile); intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, fileProvider); // If you call startActivityForResult() using an intent that no app can handle, your app will crash. // So as long as the result is not null, it's safe to use the intent. if (intent.resolveActivity(getPackageManager()) != null) { // Start the image capture intent to take photo startActivityForResult(intent, CAPTURE_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE); } }
bitmap image를 가져오는 방법
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile( 파일obj.getPath() )
camera, NFC등과 같이 특정 기능이 필요한 app의 경우 사용자가 app 설치시 어떤기능이 필요한지 알리거나 해당 기능이 없는 기기를 사용하는 사용자가 설치하는것을 막을수도 있다. 이는 AndroidManifest.xml에 uses-feature 를 이용한다.
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="false" />
creating asset folder
app module위에서 오른쪽 클릭 New-> Folder-> Assets Folder 선택 change folder location은 언첵, target source set은 main으로 한다. assets 폴더안의 모든 것은 app에 포함되어서 deploy된다. assets의 접근은 AssetManager를 통해서 한다. context obj는 기본적으로 AssetManager, 기본 sqlite methods, file 관련 methods를 제공한다. AssetManager는 콘텍스트obj.getAssets() 를 통해 얻는다. 에셋메니저obj.list( 폴더경로스트링 ) 을 통해 폴더안의 화일이름들을 확인할수 있다.
asset file은 반드시 AssetManager를 이용 열어야 한다. File로 열수 없다. 에셋매니저obj.open( 경로스트링 ) 을 통해 InputStream 을 얻을수 있다. 때로는 FileDescriptors가 필요하기도 한데 이때는 에셋매니저obj.openFd( 스트링 ) 을 통해 얻을수 있다.
소리 관련 작업은 SoundPool, AudioManager를 통해서 한다.
fragment의 setRetainInstance( true ) 로 설정한 경우 configuration change 이벤트가 발생하면 fragment의 view는 삭제하지만 다른 property는 그대로 유지된다. activity의 onSaveInstanceState()에 의해서는 view만 그대로 유지되고 serial 가능한 data는 Bundle에 추가로 넣어서 보존할수 있지만 serializable 하지 않는 data는 유지 할수가 없는것과 다른 것에 유의한다. 그래서 음악재생 app에서 발생하는 configuration change 는 fragment로 해결해야한다.
color resources
res/values안에 colors.xml화일안에 app에서 사용되는 색들을 지정한다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <color name="white">#FFFFFF</color> </resources>
styles
a style is set of attributes that can be applied to a widget. res/values/styles.xml에 저장한다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <style name="CustomFontStyle"> <item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item> <item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:capitalize">characters</item> <item name="android:typeface">monospace</item> <item name="android:textSize">12pt</item> <item name="android:textColor">#00FF00</item>/> </style> </resources>
<TextView android:id="@+id/text_id" style="@style/CustomFontStyle" android:text="@string/hello_world" />
style inheritance의 예시 ( parents style에 . notation을 통해 지정할수도 있다 )
<resources> ... <style name="MyCustomTheme" parent="android:style/Theme"> <item name="android:textColorPrimary">#ffff0000</item> </style> ... </resources>
theme allows you to define a set of attributes in one place and then apply them to as many widgets as you want.
apply theme to entire app
<manifest ... > <application android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat" ... > </application> </manifest>
apply theme to one activity
<manifest ... > <application ... > <activity android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light" ... > </activity> </application> </manifest>
defining theme ( colorPrimary, colorPrimaryDark, colorAccent are basic attributes which will affect entire app )
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar"> <!-- Customize your theme here. --> <item name="colorPrimary">@color/colorPrimary</item> <item name="colorPrimaryDark">@color/colorPrimaryDark</item> <item name="colorAccent">@color/colorAccent</item> </style>
theme can be inherited. normally, theme that we use is inherited as multiple layered. we can track which theme is the original theme at top by ctrl+click on the name of theme. this process is called as “Theme spelunking”
we can override attribute which is defined parent theme as below, pay attention on starting name of item with “android”
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar"> ... <item name="android:windowBackground">@color/activityBackground</item> </style>
android:background=“?attr/colorAccent” the ? notation says to use the resource that the colorAccent attribute on your theme points to
https://stackoverflow.com/a/2733998
android calls anything that s intended to be drawn to the screen drawable.
drawable 은 display size에 따라서 스스로 변경되므로 display크기를 신경쓸필요가 없다. 즉 drawable xml 화일은 res/drawable안에 만든다.
drawable 사용예시
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@drawable/hello" android:text="@string/hello_world" />
drawable xml file예시
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="rectangle"> <stroke android:width="2dp" android:color="#FFFFFFFF" /> <gradient android:endColor="#DDBBBBBB" android:startColor="#DD777777" android:angle="90" /> <corners android:bottomRightRadius="7dp" android:bottomLeftRadius="7dp" android:topLeftRadius="7dp" android:topRightRadius="7dp" /> </shape>
state list drawable의 예시 ( item의 각각의 상태에 따라 적용되는 drawable이 달라진다. 이 file도 res/drawable 안에 작성하고 각각 적용될 drawable도 res/drawable에 저장한다. )
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:state_enabled="false" android:drawable="@drawable/bttn_grey_disabled"/> <item android:state_pressed="false" android:drawable="@drawable/bttn_orange_normal" /> <!-- pressed --> <item android:state_pressed="true" android:drawable="@drawable/bttn_orange_selected" /> <!-- focused --> <item android:state_enabled="true" android:drawable="@drawable/bttn_orange_normal"/> <!-- idle state --> </selector>
drawable item을 여러겹으로 겹처서 사용가능하다. layer list drawables allow you to combine two xml drawables into one.

xml drawables are density independent.
9-patch image file is specially formatted so that android knows which portions can and cannot be scaled. file name is like “ name.9.png “. this is can be made withe image editor which comes with android SDK. if i change the name into “ .9.png “ and open up by double click. it will bring editor automatically. i can see black border line around image which will be stretched.
app icon lives in res/mipmap folder
intent에 addFlags( Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TAST ) 를 이용하면 새로 열리는 activity는 새로운 task 상에서 시작하게 된다. 예를 들어 a app에서 FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TAST를 이용해 b app을 시작하는 경우 b app의 task에서 작업을 하게된다. 만약 b app이 이미 열려있는 상태라면 열린 b app이 작업을 수행하게 된다.
task and process


lollipop버전이후로는 android.intent.action.SEND 와 android.intent.action.SEND_MULTIPLE 에 의해서는 새로 구분된 task가 만들어진다. 또 Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT에 의해 multiple document작업이 가능하다.(예로 google drive docs을 생각하면 된다.)
참고사항) Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK, android:documentLaunchMode = “intoExisting” , Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT, android.documentLaunchMode = “always”
인터넷 작업에 URL obj를 이용한다. opentConnection()을 통해 URL을 지향하는 connection obj를 만들수 있다. HttpURLConnection은 connection을 represent한다. 그러나 getInputStream() 또는 getOutputStream() 호출을 하지 않는 이상 response code를 얻을수 없다. URL obj를 만들고 connection을 만들면 read()를 통해 data의 끝에 이를때 까지 data를 얻을수 있다. 이런 작업 후에는 최종적으로 ByteArrayOutputStream의 byte array를 결과로 얻을수 있다.
internet사용을 위해서는 AndroidManifest.xml에 다음 permission이 필요하다.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
asynctask의 사용 예시
public class AsyncTaskActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener { Button btn; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); // because we implement OnClickListener we only have to pass "this" // (much easier) btn.setOnClickListener(this); } public void onClick(View view) { // detect the view that was "clicked" switch (view.getId()) { case R.id.button1: new LongOperation().execute(""); break; } } private class LongOperation extends AsyncTask<String, Void, String> { @Override protected String doInBackground(String... params) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.interrupted(); } } return "Executed"; } @Override protected void onPostExecute(String result) { TextView txt = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.output); txt.setText("Executed"); // txt.setText(result); // might want to change "executed" for the returned string passed // into onPostExecute() but that is upto you } @Override protected void onPreExecute() {} @Override protected void onProgressUpdate(Void... values) {} } }
uri class를 이용 query string 만드는 예시
appendQueryParameter will do the escape process too
public String buildUrl(String picid) { Builder builder = Uri.parse(SHARE_URL).buildUpon(); builder.appendQueryParameter("title", this.mShareContent); builder.appendQueryParameter("version", "0031105000"); if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(this.mAppKey)) { builder.appendQueryParameter("source", this.mAppKey); } if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(this.mToken)) { builder.appendQueryParameter("access_token", this.mToken); } String aid = Utility.getAid(this.mContext, this.mAppKey); if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(aid)) { builder.appendQueryParameter("aid", aid); } if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(this.mAppPackage)) { builder.appendQueryParameter(REQ_PARAM_PACKAGENAME, this.mAppPackage); } if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(this.mHashKey)) { builder.appendQueryParameter(REQ_PARAM_KEY_HASH, this.mHashKey); } if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(picid)) { builder.appendQueryParameter(REQ_PARAM_PICINFO, picid); } return builder.build().toString(); }
JSONObject()를 이용 json string을 java obj로 전환 가능하다. getJSONArray()를 통해 JSONObject hierarchy navigate가 가능하다.
fragment는 isAdded() 함수를 통해 본 fragment가 activity에 attached되었는지 확인가능하다.
AsyncTask는 onPostExecute()를 제공하며 이는 doInBackground()이후에 호출되고 main thread위에서 수행된다. 그러므로 background작업후에 필요한 UI작업을 수행할수 있다.
AsyncTask.cancel( false )를 통해 부드럽게 작업을 중지하거나 AsyncTask.cancel( true )를 통해 즉시 중단시킬수 있다.
AsyncTask생성은
new AsyncTask<첫번째타입, 두번째타입, 세번째타입>( )
으로 한다. 이때 첫번째타입은 excute()에 전달될 파라미터 타입을 지정한다. 두번째타입은 onProgressUpdate()에 전달될 파라미터 타입, 세번째는 return 타입을 지정한다. AsyncTask의 작업 진행정도를 확인하고자 하는경우 doInBackground() 내에서 publishProgress()를 호출하고 나서 onProgressUpdate()를 통해 진행정도를 확인할수 있다.
AsyncTask를 이용하는 경우 activity, fragment의 lifecycle 과 configuration change등에 어떻게 대응해야할지 생각해야 한다. 보통의 경우 setRetainInstance( true ) 과 여기에 추가 data를 넣어 해결한다. 그렇지만 좀더 깊이 생각해볼 필요가 있다. 예를 들어 AsyncTask 작업중에 OS가 메모리가 필요해서 fragment를 급히 destroy하는 경우가 생길수 있다. 이런 관리가 불편해서 사용하기 힘들다면 해당 작업을 할수 있는 Loader를 사용하는 것이 편하다. 보통 disk, database, ContentProvider, network, another process등등의 작업은 Loader가 제공되어있다. 이들은 AsyncTask를 내포하고 있는 AsyncTaskLoader들이며 이들은 LoaderManager에 의해 관리되기 때문에 위에서 언급한 문제를 신경쓰지 않아도 된다.
ImageView의 android:scaleType = “centerCrop”은 image를 가운데 놓고 원래 image의 작은 변을 view의 크기만큼 확대하고 남는 부분은 잘라낸다.
android service는 main thread에서 작업을 수행한다. ( background thread에서 작업할줄 예상했지만 아니다 )
handlerthread 를 이용한 작업
참고)
https://youtu.be/Yo3VT-fZr68 ( 시리즈 동영상 2, 6번 실제 코드 )
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12877944/what-is-the-relationship-between-looper-handler-and-messagequeue-in-android ( 기본개념 )
https://medium.com/@ali.muzaffar/handlerthreads-and-why-you-should-be-using-them-in-your-android-apps-dc8bf1540341 ( 기본설명 )
handlerthread 안에는 looper obj가 이미 들어가 있다. handler는 handlerthread 안에서 만들어 진다. message는 handler를 통해 만들어진다. HandlerThread 를 시작하면( start()를 호출하고나면 ) getLooper()를 통해 Looper obj를 얻을수 있고 Handler constructor에 looper obj를 전달함으로써 looper에 연결된 handler를 얻을수있다. 만약 Handler constructor에 looper obj를 전달하지 않는면 자동으로 현 thread에 존재하는 looper를 이용한다. 만약 main thread상에서 그냥 new Handler()를 수행하면 main thread에 연결된 handler가 만들어진다.
HandlerThread handlerThread = new HandlerThread("MyHandlerThread"); handlerThread.start(); Looper looper = handlerThread.getLooper(); Handler handler = new Handler(looper);

핸들러obj.obtainMessage( 작업번호, 타겟obj ) 를 통해 message를 만들수 있다.
메시지obj.sendToTarget()을 통해 message queue에 message를 넣을 수 있다.
순서가 되서 message queue안의 message가 수행되려고 하면 message obj안의 target handler의 handleRequest()가 호출되어 수행된다.
SearchView는 toolbar에 들어가는 action view이다.
searchview item을 다른 toolbar menu item과 같이 menu.xml에서 만든다.
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> < menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"> < item android:id="@+id/action_search" android:icon="@android:drawable/ic_menu_search" android:title="Search" app:actionViewClass="android.support.v7.widget.SearchView" app:showAsAction="ifRoom|collapseActionView" /> < /menu>
fragment의 onCreateOptionMenu() 안에서 만들어진 toolbar menu item중에 search view item을 찾아내고 메뉴아이템obj.getActionView()를 통해 SearchView obj를 얻는다. 그리고 setOnQueryTextListener()통해 관련 listener를 연결한다.
SharedPreferences는 Bundle과 유사한 key-value store 이다. 다만 SharedPreferences 는 app이 close되고 나서도 그 값이 app sandbox에 file형태로 저장되었다가 나중에 다시 app이 작동될때 사용가능하다. 컨텍스트obj.getSharedPreferences( 스트링, 정수값 ) 을 통해 특정 SharedPreferences를 얻을수 있으나 PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences( 컨텍스트obj )를 이용해도 충분한 경우가 많다.
Save to preferences
SharedPreferences preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPrefererences(this); SharedPreferences.Editor editor = preferences.edit(); editor.putString("key","value"); editor.apply();
Retrieve a Preference
SharedPreferences preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(this); String value = preferences.getString("key", "defaultValue");
IntentService 예시
public class MyIntentService extends IntentService { public MyIntentService() { super("MyIntentService"); } // Invoked when this intent service is started. @Override protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { if (intent != null) { // Get current child thread. Thread currThread = Thread.currentThread(); // Get current thread info. String threadInfo = ThreadUtil.getThreadInfo(currThread); // Log current thread info. Log.d(MyIntentServiceActivity.TAG_INTENT_SERVICE, "MyIntentService child thread info." + threadInfo); } } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); Log.d(MyIntentServiceActivity.TAG_INTENT_SERVICE, "MyIntentService onCreate() method is invoked."); } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); Log.d(MyIntentServiceActivity.TAG_INTENT_SERVICE, "MyIntentService onDestroy() method is invoked."); } }
IntentService는 Service중의 하나이고 Service는 Context를 기반한다. service’s intent를 command라고 부른다. 첫번째 command가 IntentService를 시작하게 되면 background thread가 만들어지고 이곳에서 작업을 하게 된다. 그이후에 도착하는 command는 queue에 넣어지게 된다. queue에서 하나씩 작업을 해나가며 더이상 command가 남아 있지 않으면 stop, destroy된다. IntentServie도 Activity와 마찬가지로 AndroidManifest.xml에 정의해주어야 한다.
AndroidManifest.xml의 예시
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.dev2qa.example"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".service.intentService.MyIntentServiceActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <service android:name=".service.intentService.MyIntentService" android:exported="false" /> <service android:name=".service.intentService.MyCommonService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true"></service> </application> </manifest>
IntentService는 Service와 달리 background thread 에서 작업한다.
network 작업을 하는 경우 network가 연결되어있는지 ConnectiityManager를 통해 확인한다. 이때 android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE permission이 manifest에 정의되어 있어야 한다.
Handler.sendMessageDelayed() 또는 Handler.postDelayed()를 이용 작업을 연기할수 있다. 다만 사용자가 해당 activity에 머물어 있어야 연기가 가능하다. AlarmManager는 Intent를 스스로 보낼수 있는 system service이다.
Get AlarmManager instance from the system services
val alarmMgr = getSystemService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE) as AlarmManager
Create the Intent and PendingIntent to pass in AlarmManager
// Intent to start the Broadcast Receiver val broadcastIntent = Intent(this, AlarmBroadcastReceiver::class.java) // The Pending Intent to pass in AlarmManager val pIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this,0,broadcastIntent,0)
AlarmManager에 모드설정, 시간, pendingintent를 전달한다.
// Set an alarm to trigger 5 second after this code is called alarmMgr.set( AlarmManager.RTC_WAKEUP, System.currentTimeMillis() + 5000, pIntent ) // stop here
AlarmManager.setRepeating()
AlarmManager.setInexactRepeating()
AlarmManager.RTC --- wall clock
AlarmManager.setWindow()
AlarmManager.setExact() --- 단 한번 정확한 시간에 울림, 반복없음
등으로 알람울리는 시간 지정모드를 변경가능하다.
AlarmManager.cancel( 펜딩인덴트obj ) 를 통해 취소가능하다.
AlarmManager.ELAPSED_REALTIME ---- 기기가 boot하고 나서 지난 시간
AlarmManager.RTC ---- wall clock time
위의 둘다 기기가 sleep mode인경우 알람은 울리지 않는다. sleep mode에서 깨어나서 알람이 울리게 하기위해서는
AlarmManager.ELAPSED_REALTIME_WAKEUP
AlarmManager.RTC_WAKEUP
을 사용한다.
같은 PendingIntent를 여러번 보내면 마지막의 PendingIntent으로 대체된다.
notification 예시
// Create an explicit intent for an Activity in your app Intent intent = new Intent(this, AlertDetails.class); intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK); PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, 0); NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, CHANNEL_ID) .setSmallIcon(R.drawable.notification_icon) .setContentTitle("My notification") .setContentText("Hello World!") .setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_DEFAULT) // Set the intent that will fire when the user taps the notification .setContentIntent(pendingIntent) .setAutoCancel(true);
notify()가 호출되어야 실제 notification이 발송된다. notification id는 application전체에 걸쳐 고유한 번호가 이며 만약 같은 번호의 notification을 또 보낸다면 최신의것이 과거의 것을 교체한다.
NotificationManagerCompat notificationManager = NotificationManagerCompat.from(this); // notificationId is a unique int for each notification that you must define notificationManager.notify(notificationId, mBuilder.build());
service는 stopSelf(), stopService()가 호출되지 않는 이상 멈추지 않는다. 혹 OS에 의해서 잠시 멈춰질수 있으나 다시 service를 작동할 환경이 되면 다시 시작된다. 어떤 이유에서건 멈추어진 command 는 onStartcommand에서 지정된 flag - START_NOT_STICKY, START_REDELIVER_INVENT, START_STICKY- 에 따라서 다시 시작되기도 하고 아니기도 하게 된다.
service는 lifecycle을 가진다. onCreate(), onStartCommnad( 인텐트obj, 플래그정수, 스타트id ), onDestroy()
START_NON_STICKY service는 stopSelf() 또는 stopSelf( 스타트id인티저 ) 를 통해 멈추어질수 있다. 작업중 os에의해 갑자기 멈추어진 경우 service는 사라진다. IntentService가 대표적 START_NON_STICKY service이다.
START_REDELIVE_INTENT service는 stopSelf() 또는 stopSelf( 스타트id인티저 ) 를 통해 멈추어질수 있다. 작업중 os에의해 갑자기 멈추어진 경우 본래 가지고 있던 intent를 이용 나중에 다시 작업한다.
START_STICKY service 는 stopService( 인텐트obj ) 를 통해 정지할수 있다. 작업중 os에의해 갑자기 멈추어진 경우 null intent를 이용 나중에 다시 작업한다.
A bound service is the server in a client-server interface. A bound service allows components (such as activities) to bind to the service, send requests, receive responses, and even perform interprocess communication (IPC). When creating a service that provides binding, you must provide an IBinder that provides the programming interface that clients can use to interact with the service. There are three ways you can define the interface:
Extending the Binder class ( 같은 app에서만 사용 가능, 가장 많이 사용됨 )
Using a Messenger
Using AIDL
extending binder class 예시
service
public class LocalService extends Service { // Binder given to clients private final IBinder mBinder = new LocalBinder(); // Random number generator private final Random mGenerator = new Random(); /** * Class used for the client Binder. Because we know this service always * runs in the same process as its clients, we don't need to deal with IPC. */ public class LocalBinder extends Binder { LocalService getService() { // Return this instance of LocalService so clients can call public methods return LocalService.this; } } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return mBinder; } /** method for clients */ public int getRandomNumber() { return mGenerator.nextInt(100); } }
서비스를 이용하는 client activity
public class BindingActivity extends Activity { LocalService mService; boolean mBound = false; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); // Bind to LocalService Intent intent = new Intent(this, LocalService.class); bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); // Unbind from the service if (mBound) { unbindService(mConnection); mBound = false; } } /** Called when a button is clicked (the button in the layout file attaches to * this method with the android:onClick attribute) */ public void onButtonClick(View v) { if (mBound) { // Call a method from the LocalService. // However, if this call were something that might hang, then this request should // occur in a separate thread to avoid slowing down the activity performance. int num = mService.getRandomNumber(); Toast.makeText(this, "number: " + num, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } /** Defines callbacks for service binding, passed to bindService() */ private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) { // We've bound to LocalService, cast the IBinder and get LocalService instance LocalBinder binder = (LocalBinder) service; mService = binder.getService(); mBound = true; } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) { mBound = false; } }; }
JobScheduler는 특정 조건이 만족될 때만 작동되는 service이다.
JobScheduler 의 예시. onStartJob(), onStopJob()
public class MyJobService extends JobService { private static final String TAG = MyJobService.class.getSimpleName(); boolean isWorking = false; boolean jobCancelled = false; // Called by the Android system when it's time to run the job @Override public boolean onStartJob(JobParameters jobParameters) { Log.d(TAG, "Job started!"); isWorking = true; // We need 'jobParameters' so we can call 'jobFinished' startWorkOnNewThread(jobParameters); // Services do NOT run on a separate thread return isWorking; } private void startWorkOnNewThread(final JobParameters jobParameters) { new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { doWork(jobParameters); } }).start(); } private void doWork(JobParameters jobParameters) { // 10 seconds of working (1000*10ms) for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { // If the job has been cancelled, stop working; the job will be rescheduled. if (jobCancelled) return; try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (Exception e) { } } Log.d(TAG, "Job finished!"); isWorking = false; boolean needsReschedule = false; jobFinished(jobParameters, needsReschedule); } // Called if the job was cancelled before being finished @Override public boolean onStopJob(JobParameters jobParameters) { Log.d(TAG, "Job cancelled before being completed."); jobCancelled = true; boolean needsReschedule = isWorking; jobFinished(jobParameters, needsReschedule); return needsReschedule; } }
조건이 만족되면 onStartJob()이 main thread에서 수행되고 작업이 완료되면 false를 return한다. instentService와는 달리 개발자가 스스로 thread를 만들어 사용해야 한다. 무슨 이유에서든 작업이 중지되기 바로 직전 onStopJob()이 호출된다. 여기서 true를 return하면 작업이 마무리 되지 않았으므로 나중에 다시 실행해야한다는 의미이다.
AndroidManifest.xml
<service
android:name=".MyJobService"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_JOB_SERVICE"
android:exported = “true” />
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(this, MyJobService.class); JobInfo jobInfo = new JobInfo.Builder(12, componentName) .setRequiresCharging(true) .setRequiredNetworkType(JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_UNMETERED) .build();
JobScheduler jobScheduler = (JobScheduler)getSystemService(JOB_SCHEDULER_SERVICE); int resultCode = jobScheduler.schedule(jobInfo); if (resultCode == JobScheduler.RESULT_SUCCESS) { Log.d(TAG, "Job scheduled!"); } else { Log.d(TAG, "Job not scheduled"); }
sync adapter를 이용하면 특정한 때에 특정한 uploading, downloading 작업을 자동으로 할수 있다.
broadcast intent는 일반 intent와 비슷하나 다수의 broadcast receiver에게 알릴수 있다는 점이 다르다. 예를들어 BOOT_COMPLETED system broadcast intent가 발생하면 모든 해당 broadcast receiver가 작동하게된다.
app이 작동하지 않는 때에도 broadcast intent에 반응해서 작업을 수행하는 broadcast receiver를 standalone receiver라고 한다. app이 작동하고 있는 동안에만 작동하는 receiver를 dynamic receiver라고 한다. broadcast receiver도 manifest에 정의해 주어야한다.
system broadcast intent작업의 예시
public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { Toast.makeText(context, "Intent Detected.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }
<application android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <receiver android:name="MyReceiver"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"> </action> </intent-filter> </receiver> </application>
custom broadcast intent의 예시
public void broadcastIntent(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"); sendBroadcast(intent); }
public void broadcastIntent(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"); sendBroadcast(intent); }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <receiver android:name="MyReceiver"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"> </action> </intent-filter> </receiver> </application> </manifest>
broadcast receiver는 main thread에서 작업한다. 또 작업할 시간이 많이 주어지지 않는다. 그러므로 간단한 작업만 할수 있으며 다른 activity나 service를 가동시킬수 있다.
registerReceiver( BroadcastReceiver, IntentFilter )를 통해 유동적으로 broadcast receiver를 등록할수 있다. 또 unregisterReceiver( BroadcasetReceiver ) 를 통해 제거할수도 있다. broadcast receiver를 가변적으로 register했다가 제거할수 있는 것과 마찬가지로 IntentFilter도 code상에서 만들수 있다. addCategory( 스트링 ), addAction( 스트링 ) , addDataPathe( 스트링 ) 을 이용할수 있다. 가변적으로 등록된 broadcast receiver는 손수 제거해야 한다. 예를 들어 onStart()에서 등록되었다면 onStop()에서 제거한다. onActivityCreated()에서 등록 되었다면 onActivityDestroyed()에서 제거한다.
다른 app이 아닌 오직 자기 본인 app만 broadcast intent에 반응하게 하기위해서는 manifest file에 고유 문자열 키를 이용한 permission과 protectionLevel을 설정해주고 broadcast intent, broadcast receiver register할때 고유 문자열 키를 이용한다.
manifest file에 custom permission을 설정할때 android:protectionLevel을 설정해주어야 한다. normal, dangerous, signature, signatureOrSystem의 종류가 있고 signature를 많이 사용한다.
ordered broadcast를 통해 broadcast가 연쇄적으로 수행되게 할수 있다.
broadcast receiver는 작업을 수행하는데 길지 않은 시간을 배정받는다. 이를 극복하기 위한 두가지 방법이 있다. 1. service를 이용한다. 2. BroadcastReceiver.goAsync() 과 BroadcastReceiver.PendingResult를 이용한다.
if you want to broadcast the occurrence of an event within your app’s process only? using an event bus is the good way.
app에서 web page를 display해양 하는 경우 두가지 방법으로 처리할수 있다. 1. implicit intent Intent.ACTION_VIEW를 이용 다른 web browser app을 이용 2. web view를 이용
web view 작업 1. display할 web page url 2. enable javascript 3. web page를 render할때 접근할수 있는 interface를 제공하는 WebViewClient의 함수들을 이용
예시1.
public class MainActivity extends Activity { private WebView myWebView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview); // Configure related browser settings myWebView.getSettings().setLoadsImagesAutomatically(true); myWebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true); myWebView.setScrollBarStyle(View.SCROLLBARS_INSIDE_OVERLAY); // Configure the client to use when opening URLs myWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient()); // Load the initial URL myWebView.loadUrl("http://www.example.com"); } }
예시2 shouldOverrideUrlLoading에서 true return하면 url 주소를 개발자가 edit 하겠다는 뜻. false는 수정없이 url 주소를 그대로 이용하겠다는 의미.
private class MyWebViewClient extends WebViewClient { @Override public boolean shouldOverrideUrlLoading(WebView view, String url) { if (url.endsWith(".mp4")){ Intent in = new Intent (Intent.ACTION_VIEW , Uri.parse(url)); startActivity(in); return true; } else return false; } }
WebViewClient는 interface for responding to rendering events
WebChromeClient는 event interface for reacting to event that shoud change elements of chrome around the browser
WebChromeClient 사용예시
getWindow().requestFeature(Window.FEATURE_PROGRESS); WebView mWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.mywebview); mWebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true); final Activity activity = this; mWebView.setWebChromeClient(new WebChromeClient(){ public void onProgressChanged(WebView view, int progress) { activity.setTitle("Loading..."); activity.setProgress(progress * 100); if(progress == 100) activity.setTitle("My title"); } }); mWebView.loadUrl(URL);
뷰obj.setVisibility( View.GONE ) 으로 view를 제거할수 있다.
뷰obj.setVisibility( View.VISIBLE ) 으로 view를 보이게 할수 있다.
configuration change되면 webview가 reload 된다. 이를 onSaveInstanceState를 이용 view의 상태를 유지하려고 생각하겠지만 WebView, VideoView는 유지해야할 data가 많아서 그렇게 되지 못한다. 또 retain fragment 으로도 해결하기 힘들다.
<activity android:name=".MyActivity" android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden" android:label="@string/app_name">
위와 같이 표기함으로써 개발자가 configuration change 를 처리하겠다고 한다면 새로 reload되지 않는다. 그러나 처리과정은 개발자가 해야 한다.
addJavaScriptInterface 예시
JavaScriptInterface 안에 있는 public void showToast(String webMessage) 가 html 문서에서의 javascript obj가 된다. Wv.addJavascriptInterface(myJavaScriptInterface, "AndroidFunction") 에서 두번째 파라미터가 javascript obj의 이름이 된다.
public class JavaScriptInterfaceDemoActivity extends Activity { private WebView Wv; private TextView myTextView; final Handler myHandler = new Handler(); /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); Wv = (WebView)findViewById(R.id.webView1); myTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1); final JavaScriptInterface myJavaScriptInterface = new JavaScriptInterface(this); Wv.getSettings().setLightTouchEnabled(true); Wv.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true); Wv.addJavascriptInterface(myJavaScriptInterface, "AndroidFunction"); Wv.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/www/index.html"); } public class JavaScriptInterface { Context mContext; JavaScriptInterface(Context c) { mContext = c; } public void showToast(String webMessage){ final String msgeToast = webMessage; myHandler.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // This gets executed on the UI thread so it can safely modify Views myTextView.setText(msgeToast); } }); Toast.makeText(mContext, webMessage, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } }
<!DOCTYPE > <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" debug="true"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0"> <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes"> <meta name="viewport" content="target-densitydpi=device-dpi" /> <script type="text/javascript"> function init() { var testVal = document.getElementById('mytextId').value; AndroidFunction.showToast(testVal); } </script> </head> <body> <div style="float: left;width: 50%;"> <input type="text" style="width: 180px;" name="myText" id="mytextId" /> </div> <div style="clear: both;height: 3px;"> </div> <div> <input value="submit" type="button" name="submit" id="btnSubmit" onclick="javascript:return init();" /> </div> </body> </html>
@JavascriptInterface annotation을 사용 축약할수도 있다. ( big nerd android programming p523 참조 )
myWebView.addJavascriptInterface(new Object() { @JavascriptInterface public void anObject() { return new Object(){ @JavascriptInterface public void method() { //yay! } } } }, "plugins");
custom view를 만드는 경우. 기본적으로 적어도 두가지 constructor를 마련해주어야 한다. 하나는 view가 code에 의해서 만들어질때 또 다른 하나는 xml화일을 기반으로 만들어질때를 위한 것이다.
xml화일에서 custom view를 사용하는 경우 아래와 같이 fully qualified name을 사용한다.
<com.vogella.android.view.compoundview.ColorOptionsView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeight" custom:titleText="Background color" custom:valueColor="@android:color/holo_green_light" />
Canvas, Paint class가 android 내의 그림작업 하는데 주로 사용된다.
모든 view는 local layout rect를 가진다. 상부 layout 내부에서의 위치를 말한다.
뷰obj.getTop()
뷰obj.getBottom()
뷰obj.getRight()
뷰obj.getLeft() 를 통해 local layout rect를 구할수 있다.
objectanimator를 이용한 property animation
TimeInterpolator는 animation 변화속도를 조절한다.
ObjectAnimator anim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(myView, "rotation", 0f, 90f); anim.setDuration(2000); // Duration in milliseconds anim.setInterpolator(timeInterpolator); // E.g. Linear, Accelerate, Decelerate anim.start()
ObjectAnimator는 property animator이다. property animator는 property setter methods를 반복적으로 호출함으로써 구현한다. 예를 들어 ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( 뷰obj, “y”, 0, 1 ) 는
뷰obj.setY(0)
뷰obj.setY(0.1)
뷰obj.setY(0.2) 이런식으로 반복호출한다.
view의 transformation property를 지정함으로써 view를 이동 변형이 가능하다.
rotation에 관련된 property - rotation, pivotX, pivotY
scale에 관련된 property - scaleX, scaleY
이동에 관련된 property - translationX, translationY
각각의 property는 getter와 setter를 가진다. 예) getTranslationX(), setTranslationX()
property animation시에 시작점과 종료점이 불분명한경우 개발자가 TypeEvaluator를 새로 수정해서 만들어 연결해 주어야 한다.
AnimatorSet을 이용 여러 property animation을 순차적으로 일어나게 할수있다.
android 는 basic lodation API를 제공한다. gps, cell towers, wifi connection등을 통해 위치를 얻을수 있다.google standard library외에 Play Services를 통해 common services를 제공받는다.
google play services를 사용하기 위한 작업
Google Play Services library dependency를 project structure에서 add 한다.
Play Services 사용전에는 play service가 사용가능한지 확인하는 과정이 필요하다.
예시)
private boolean checkPlayServices(){ int resultCode = GooglePlayServicesUtil .isGooglePlayServicesAvailable(this); if(resultCode != ConnectionResult.SUCCESS){ if (GooglePlayServicesUtil.isUserRecoverableError(resultCode)){ GooglePlayServicesUtil.getErrorDialog(resultCode, this, PLAY_SERVICES_RESOLUTION_REQUEST).show(); }else { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "This device is not supported", Toast.LENGTH_LONG) .show(); finish(); } return false; } return true; }
다만 위의코드 수정이 필요하다.
GoogleApiAvailability.getInstance().isGooglePlayServicesAvailable(context)
위치정보를 이용하는 경우 permission이 필요하다
<manifest ... > <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> ... <!-- Needed only if your app targets Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher. --> <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.location.gps" /> ... </manifest>
ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION을 이용하기도 한다.
play services를 이용하기 위해서는 client를 만들어야 한다. (GoogleApiClient)
mClient = new GoogleApiCilent.Builder( getActivity() ).addApi( LocationServices.API ).build();
addConnectionCallbacks(new GoogleApiCilent.ConnectionCallbacks())
을 통해 google api가 연결 되었을때 아닐때를 알수 있다. onConnected(), onConnectionSuspended()
google에서는 activity 의 onStart()에서 client를 연결하고 onStop()에서 연결을 제거하기를 추천한다.
menu를 update하기 위해서는 getActivity().invalidateOptionsMenu() 해줘야 한다.
0 notes
Photo

I LOVE this table layout I found on Pinterest! What do you guys think? #wedding #weddinginspiration #bride #bridetobe #weddingplanner #fiance #futuremrandmrs #happycouple #weddingdecor #love #weddingideas #pinterest #atlanta #atlantawedding #atlantaweddingvendor #atlantavendor #atlantaweddingplanner #engaged #tablelayout #weddingreception #southernbride
#atlantavendor#weddingdecor#love#southernbride#pinterest#fiance#engaged#atlantaweddingvendor#atlantawedding#atlantaweddingplanner#bride#weddingideas#happycouple#weddinginspiration#wedding#weddingreception#bridetobe#weddingplanner#futuremrandmrs#atlanta#tablelayout
1 note
·
View note
Text
300+ TOP Ext JS Interview Questions and Answers
Ext JS Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Ext Js? Ext JS stands for extended JavaScript. It is a JavaScript framework to develop rich UI web based desktop applications. 2. Why did you choose Ext JS? The overall design of extjs is exemplary.One can learn a lot from it’s unified architecture – no matter which language one is programming in. Extjs requires you to start with one of their base classes – ensuring a consitent model. Consistency is extremely important for the library to be reusable. Extjs documentation seems to be very comprehensive and well maintained. key aspect of the EXTJS Library is the cross-browser support. Build rich Internet applications with Ext JS Ext JS framework is the multitude of rich UI elements provided. These elements include forms, dialog boxes, tabs, trees, and grids. The Ext JS framework includes support for Ajax implementations. Ext JS integration with other Web server frameworks. Ext JS framework development into several popular integrated development environments (IDEs), including Eclipse, Aptana, and Komodo. Ext JS provides excellent performance.The framework is fully object oriented and extensible. Because it’s written in the JavaScript language 3. What are major Web browsers supported by Ext JS framework? Windows® Internet Explorer® version 6 and later. Mozilla Firefox version 1.5 and later (PC and Macintosh). Apple Safari version 2 and later. Opera version 9 and later (PC and Mac). 4. Integration of Web development server-side frameworks with Ext JS? You can use Ext JS with other common Web development server-side frameworks, including PHP, the Java™ language, Microsoft® .NET, Ruby on Rails, and ColdFusion. 5. Where Extjs extended from ? Ext JS as a project to extend the functionality that the YUI Library.A key aspect of the YUI Library is the cross-browser support.The Extjs framework is fully object oriented and extensible. Because it’s written in the JavaScript language. 6. Extjs Ajax implementation? A typical Ext JS Ajax implementation: an HTML text field and button element that posts data in the text field to a Web server when the button is clicked. 7.Do you have any advice for developers using Ext for the first time? Ext can be used by Web Application developers who are familiar with HTML but may have little or no experience with JavaScript application development. If you are starting to build a new web application, or you are revamping an existing application, then take your time to understand the basics of the library including. 8. How to access Dom element using EXTJS? The Element API is fundamental to the entire Ext library. Using traditional Javascript, selecting a DOM node by ID is done like this: var myDiv = document.getElementById(‘myDiv’); Using Extjs: Ext.onReady(function() { var myDiv = Ext.get(‘myDiv’); }); 9. what is the purpose of Element Object in Extjs? Element wraps most of the DOM methods and properties that you’ll need, providing a convenient, unified, cross-browser DOM interface (and you can still get direct access to the underlying DOM node when you need it via Element.dom) The Element.get() method provides internal caching, so multiple calls to retrieve the same object are incredibly fast The most common actions performed on DOM nodes are built into direct, cross-browser Element methods (add/remove CSS classes, add/remove event handlers, positioning, sizing, animation, drag/drop, etc.) 10. what is syntax for Ext js Button click event? Ext.onReady(function() { Ext.get(‘myButton’).on(‘click’, function(){ alert(“You clicked the button”); }); }); ulating it. 11. what is use of Ext.onReady() function ? Ext.onReady is probably the first method that you’ll use on every page. This method is automatically called once the DOM is fully loaded, guaranteeing that any page elements that you may want to reference will be available when the script runs syntax: Ext.onReady(function() { alert(“Congratulations! You have Ext configured correctly!”); }); 12. For example, to show our message when any paragraph in our test page is clicked, what is the extjs code on paragraph click? Ext.onReady(function() { Ext.select(‘p’).on(‘click’, function() { alert(“You clicked a paragraph”); }); }); or Ext.onReady(function() { var paragraphClicked = function() { alert(“You clicked a paragraph”); } Ext.select(‘p’).on(‘click’, paragraphClicked); }); 13. List out the extjs library files to include in JSP page? ext-base.js ext-all-debug.js or ext-all.js ext-all.css base.css or examples.css 14. List out the css file required to apply Extjs Theme property? xtheme-gray.css ext-all.css 15. what is purpose of MessageBox? MessageBox is asynchronous. MessageBox call, which demonstrates the readable message to user. MessageBox used for multiple purpose like Ext.Msg.alert() Ext.Msg.prompt() Ext.Msg.show({}); Ext.Msg.wait(); 16. write syntax for MessageBox show() method? Ext.MessageBox.show({ title: ‘Paragraph Clicked’, msg: ‘User clicked on Paragraph’, width:400, buttons: Ext.MessageBox.OK, animEl: paragraph }); 17. what is method to Update the message box body text for MessageBox? updateText( ) : Ext.MessageBox 18. what is a widget? A widget is a tiny piece or component of functionality. 19.what is parent class for all stores in extjs? how many stores exists? Ext.data.Store is parent class for all stores. A Store object uses its configured implementation of DataProxy to access a data object unless you call loadData directly and pass in your data. subclasses for Store: GroupingStore, JsonStore, SimpleStore 20. How to handle event for a extjs component? using listeners config object. For ex for grid events : listeners: {rowclick: gridRowClickHandler,rowdblclick: gridRowDoubleClickHandler} using addListener( String eventName, Function handler, , ) : void Appends an event handler to this component using on( String eventName, Function handler, , ) : void Appends an event handler to this element (shorthand for addListener) For ex: store.on( “datachanged”, function( store ){ ….. }); 21. How to find no of records in a store? using store.getCount() : Gets the number of cached records. store.getTotalCount() : Gets the total number of records in the dataset as returned by the server. 22. How to handle exception while loading datastore? using loadexception event. syntax: store.loadexception() : Fires if an exception occurs in the Proxy during loading. use beforeload : ( Store this, Object options ) : Fires before a request is made for a new data object. If the beforeload handler returns false the load action will be canceled. syntax: store.on(‘loadexception’, function(event, options, response, error) { alert(“Handling the error”); event.stopEvent(); }); 23. how to handle updates for store changes? use store.commitChanges() 24. what is the purpose of each() in store? Calls the specified function for each of the Records in the cache each( Function fn, ) 25. how to get modified records using store object? store.getModifiedRecords() : Gets all records modified since the last commit. 26. how to get record using index? store.getAt( Number index ) : Get the Record at the specified index. 27. how to get record using id? store.getById( String id ) : Get the Record with the specified id. 28. what is the purpose of load() in store? store.load() : returns boolean Loads the Record cache from the configured Proxy using the configured Reader. For remote data sources, loading is asynchronous, and this call will return before the new data has been loaded. store.load({callback: fnCheckData, scope: this}); 29. what is purpose of loadData() in store? store.loadData( Object data, ) : void Loads data from a passed data block and fires the load event. loadData(storeData,false); False to replace the existing records cache. loadData(storeData,true) : True to append the new Records rather than replace the existing cache. 30. How many types of layout managers exist in extjs?what are they? Layouts fall under this package Ext.layout.* Types of layouts: Absolute Layout: This is a simple layout style that allows you to position items within a container using CSS-style absolute positioning via XY coordinates. Accordion Layout: Displays one panel at a time in a stacked layout. No special config properties are required other than the layout. All panels added to the container will be converted to accordion panels. AnchorLayout: This type of layout is most commonly seen within FormPanels (or any container with a FormLayout) where fields are sized relative to the container without hard-coding their dimensions. BorderLayout: Border layouts can be nested with just about any level of complexity that you might need. Every border layout must at least have a center region. All other regions are optional. CardLayout (TabPanel): The TabPanel component is an excellent example of a sophisticated card layout. Each tab is just a panel managed by the card layout such that only one is visible at a time CardLayout (Wizard): You can use a CardLayout to create your own custom wizard-style screen. FitLayout: A very simple layout that simply fills the container with a single panel. FormLayout: FormLayout has specific logic to deal with form fields, labels, etc.FormLayout in a standard panel, ColumnLayout: This is a useful layout style when you need multiple columns that can have varying content height.Any fixed-width column widths are calculated first, then any percentage-width columns specified using the columnWidth config TableLayout: Outputs a standard HTML table as the layout container.you want to allow the contents to flow naturally based on standard browser table layout rules. data, plus manip 31. How we can apply pagination in grid panel ? using Ext.PagingToolbar plugin, we can implement pagination to a grid panel syntax: new Ext.PagingToolbar({ pageSize: 25, store: store, displayInfo: true, displayMsg: ‘Displaying topics {0} – {1} of {2}’, emptyMsg: “No topics to display”, }) // trigger the data store load store.load({params:{start:0, limit:25}}); 32. what is xtype? The xtype will be looked up at render time up to determine what type of child Component like TextField, NumberField etc to create. i,e xtype = Class ———————- button = Ext.Button textfield = Ext.form.TextField radio – Ext.form.Radio grid = Ext.grid.GridPanel combo = Ext.form.Combobox toolbar = Ext.Toolbar 33. what is vtype? The validations provided are basic and intended to be easily customizable and extended. Few vtypes provided by extjs are as below: emailText : String, The error text to display when the email validation function returns false alphanumText : String, The error text to display when the alphanumeric validation function returns false urlText : String, The error text to display when the url validation function returns false 34.Why we need javascript Library? Javascript is an awesome language. It’s super flexible.Browsers are the modern UI paradigm. The javascript Libraries now must provide a rich set of UI Widgets. javascript libraries: JQuery Qooxdoo Dojo Prototype.js mootools extjs 35.how to get record object from store: var record = grid.getStore().getAt(rowIndex); 36. purpose of Load mask? To apply mask to page level / component level. restrict user not to access any components in page var pageProcessBox = new Ext.LoadMask( Ext.getBody(), { msg: ‘Loading Employee details.’ } ); pageProcessBox.show(); 37. purpose of renderer in grid panel? using config option, renderer: fnCellColor where fnCellColor is method to apply color to a cell. 38. how to get selection model used in a grid panel? using grid.getSelectionModel(); method 39. how to stop editing a record? newRecord.endEdit(); 40. how to start editing a record? newRecord.beginEdit(); 41. how to commit a record modification? newRecord.commit(); 42. what is use of combo select event function? To get the selected value from a combo.using getvalue(); var selectedComboValue = mycombo1.getValue(); 43. how to get a value of textfield or combo box? using getvalue(); var selectedValue = mytextfield.getValue(); 44. how to apply css on select of combo box? using config option as emptyClass : ’emptycss’, where emptycss is a css classname 45. what are components required for grid panel? store, columnmodel, id, width,height 46. how to disable menu option for header in columnModel? using menuDisabled: true 47. how to hide the column in grid panel? using hidden : true 48. How to register callbacks to the load and exception events of the JsonStore? var grid = new Ext.grid.GridPanel({ store: new Ext.data.JsonStore({ listeners: { load: this.onLoadSuccess.crateDelegate(this), exception: this.onLoadException.createDelegate(this) } }), onLoadSuccess: function () { // success }, onLoadException: function () { // error }, } 49. extjs decode() ? var json = Ext.decode(response.responseText); Ext.Msg.alert(‘Error’, json.error); 50. Extjs Vs jQuery: ExtJs and JQuery are kind of apples and oranges. You can compare Ext Core to JQuery, and ExtJs to JQuery UI. Ext JS is a full-fledged widget library while jQuery (not jQuery UI) and Mootools are JavaScript frameworks that help with DOM manipulation etc. Whilst jQuery and Mootools help with the general workings of a site. jQuery UI is a much less rich set of components. Ext JS seems to be focussed on tables and storing Ext JS Questions and Answers pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes