#terminal value calculation dcf
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Mastering Valuation: How Discounted Cash Flow Holds the Edge

When it comes to valuing a business or an investment, few methods command the respect and widespread use as the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis. Despite the emergence of newer valuation tools and models, DCF remains a cornerstone in finance for a reason—it provides a fundamental, intrinsic value based on the actual cash the business is expected to generate over time.
In an age where markets can be volatile and speculative, understanding why DCF still reigns supreme is essential for investors, analysts, and finance professionals alike. This blog unpacks the core mechanics of DCF, its advantages, and why it continues to be a trusted valuation method in today's complex financial environment.
What is Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)?
At its essence, DCF is a valuation technique that estimates the present value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows. The key idea is simple: money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its earning potential—this is the time value of money.
The DCF formula discounts future cash flows back to the present using a discount rate, often the company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). This process accounts for risk and opportunity cost, helping investors arrive at a value that reflects both potential and uncertainty.
Why DCF is So Widely Used
Intrinsic Value Focus: Unlike market-based methods that rely on peer comparisons or multiples, DCF looks inward at the company’s own fundamentals. It isn’t swayed by market sentiment or trends.
Flexibility: DCF can be tailored to virtually any company or project, regardless of industry or size, as long as reasonable cash flow projections can be made.
Forward-Looking: Instead of relying on historical data alone, DCF forces analysts to forecast future performance, encouraging a deep understanding of the business drivers.
Risk Adjustment: By adjusting the discount rate, investors can factor in different levels of risk, making the model adaptable across sectors and economic cycles.
Breaking Down the Components of DCF
To appreciate why DCF remains a vital valuation tool, it’s important to understand its main components:
Cash Flow Projections: These are estimates of the company’s free cash flows (FCF), often forecasted over 5-10 years. Free cash flow represents the cash generated after accounting for operating expenses and capital expenditures.
Terminal Value: Since businesses often last beyond the forecast period, terminal value estimates the value of all future cash flows beyond the forecast horizon, typically calculated using a perpetuity growth model or exit multiple.
Discount Rate: This rate reflects the required return investors expect, often influenced by the risk profile of the company and market conditions.
Common Misconceptions About DCF
Many investors shy away from DCF because they view it as complicated or overly sensitive to assumptions. While it is true that small changes in inputs can significantly affect valuation, this sensitivity is a strength rather than a flaw. It forces analysts to be thorough and transparent about their assumptions.
Moreover, DCF’s complexity encourages a more disciplined investment process, one that goes beyond superficial comparisons and market hype. It demands a granular understanding of the company’s business model, competitive landscape, and growth prospects.
DCF in Today’s Market Environment
In 2025, with global markets facing inflation pressures, geopolitical tensions, and rapid technological disruptions, DCF analysis remains relevant and invaluable. Its forward-looking nature helps investors cut through noise and focus on sustainable value creation.
Recent news highlights from financial markets emphasize how volatile interest rates impact discount rates, thereby influencing valuations. For example, as central banks adjust monetary policies worldwide, companies with stable and predictable cash flows become increasingly attractive—a dynamic clearly captured in DCF models.
Additionally, sectors such as renewable energy, technology, and healthcare are seeing heightened investor interest, driven by long-term growth potential. Applying DCF analysis in these industries helps quantify that potential amid market uncertainties.

The Rise of Finance Education in the Region
With the expanding global interest in sophisticated valuation methods, the demand for finance education has surged. Professionals in regions with burgeoning financial hubs are keen to master valuation techniques like DCF.
For instance, the popularity of the online CFA course in UAE has grown remarkably, reflecting the desire among finance professionals to gain deep analytical skills that include valuation mastery. These educational programs equip candidates to confidently apply tools such as DCF in real-world scenarios, enhancing their credibility and decision-making prowess.
Practical Tips for Using DCF Effectively
To get the most out of DCF, consider these best practices:
Use Conservative Assumptions: Overly optimistic cash flow forecasts can inflate valuations. Base projections on historical data and realistic growth rates.
Stress Test Inputs: Run multiple scenarios with varying discount rates and growth assumptions to understand the range of possible valuations.
Focus on Quality of Cash Flows: Differentiate between recurring operational cash flow and one-time items.
Don’t Rely Solely on DCF: Use it in conjunction with other valuation methods to get a holistic view.
Limitations to Keep in Mind
Despite its advantages, DCF is not without limitations:
Dependence on Estimates: Future cash flows are uncertain, and errors in projections can lead to inaccurate valuations.
Terminal Value Sensitivity: Often, a large portion of valuation comes from terminal value, which can be speculative.
Complexity: Requires deep understanding and data availability, which might be challenging for some businesses.
Why DCF Remains an Authority in Valuation
The staying power of DCF comes from its grounding in finance theory and practical utility. It directly links valuation to the fundamental cash-generating capacity of the business, which is the ultimate driver of shareholder value. For finance professionals aiming to sharpen their valuation expertise, the CFA curriculum 2025 offers a deeper, more updated approach to mastering key financial concepts like DCF. With its expanded focus on practical applications and real-world case analysis, the curriculum equips candidates for roles in investment banking, equity research, and portfolio management—where valuation acumen is essential.
Final Thoughts
Discounted Cash Flow analysis is far from obsolete; in fact, it’s more relevant than ever. Its ability to adapt to various industries, incorporate risk, and provide intrinsic valuations makes it indispensable in today’s investment toolkit.
As global finance professionals increasingly embrace rigorous valuation standards, education and practical application of DCF continue to grow, especially in fast-evolving markets. Whether you are an investor, analyst, or student, mastering DCF can elevate your financial insight and decision-making.
The method’s durability proves that when it comes to valuing assets, understanding the true worth beneath market noise will always matter. DCF doesn’t just survive—it thrives as the gold standard for valuation.
0 notes
Text
Understanding DCF Valuation: A Comprehensive Guide by CompaniesNext
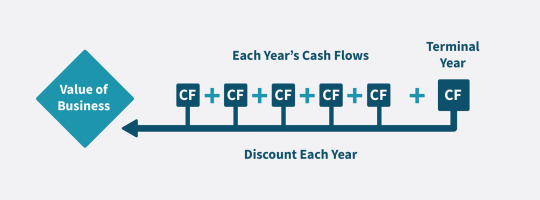
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) valuation is one of the most widely used methods for determining the intrinsic value of a business. At CompaniesNext, we aim to empower entrepreneurs, investors, and analysts with clear, actionable financial insights. In this guide, we’ll break down what DCF valuation is, why it matters, and how to perform one.
What is DCF Valuation?
DCF (Discounted Cash Flow) valuation is a financial model used to estimate the value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows. These cash flows are projected and then discounted back to their present value using a discount rate that reflects the investment’s risk.
Why Use DCF Valuation?
Accurate Reflection of Future Potential
Unlike other valuation methods, DCF focuses on the fundamentals of a business rather than market trends or comparables. It provides a more accurate view of what a company is truly worth based on its future performance.
Ideal for Long-Term Decision Making
DCF is especially useful for investors and business owners with a long-term view, as it considers the entire life cycle of a business or project.
Key Components of a DCF Model
1. Forecasted Free Cash Flows (FCFs)
Free Cash Flow is the cash a company generates after accounting for capital expenditures. It represents the cash available to investors and is the foundation of any DCF model.
2. Discount Rate
The discount rate is typically the company’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC). It reflects the opportunity cost of investing capital elsewhere at a similar risk level.
3. Terminal Value
Since it's difficult to forecast cash flows indefinitely, the terminal value estimates the business’s value beyond the forecast period. It usually accounts for a large portion of the total valuation.
Steps to Perform a DCF Valuation
Step 1: Project Free Cash Flows
Start by estimating the company’s free cash flows for the next 5–10 years based on historical performance, growth expectations, and industry trends.
Step 2: Calculate the Discount Rate
Determine the WACC by factoring in the cost of equity and the cost of debt, weighted by their respective portions in the company’s capital structure.
Step 3: Estimate the Terminal Value
Use either the Gordon Growth Model or Exit Multiple Method to estimate the terminal value.
Step 4: Discount the Cash Flows
Bring all future cash flows and the terminal value to present value using the WACC. Sum them to arrive at the total enterprise value.
Limitations of DCF Valuation
While DCF is powerful, it relies heavily on assumptions. Minor changes in growth rate, discount rate, or cash flow projections can significantly affect the final valuation.
Conclusion
DCF valuation is a cornerstone of corporate finance and investment analysis. At CompaniesNext, we help businesses and investors leverage this method to make informed, forward-thinking decisions. Whether you're assessing a startup, planning a merger, or investing in a new venture, a solid DCF model is a valuable tool in your financial toolkit.
0 notes
Text
Medical Associates is a large for-profit group practice. Its dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 7% per year into the foreseeable future. The firm's last dividend (D0) was $2, and its current stock price is $23. The firm's beta coefficient is 1.6; the rate of return on 20-year T-bonds currently is 9%; the expected rate of return is 13%. The firm's target capital structure calls for 50% debt financing, the interest rate required on the business's new debt is 10%, and its tax rate is 40%. You are to write a report that answers the following: Calculate Medical Associates' cost of equity estimate using the DCF method. Next years expected dividend = $2 * 1.07 = 2.14 Current Stock Price = $ E (Rc) = 2.14/23 + .07 = .1630 = 16.3% Calculate the cost of equity estimate using CAPM. R (Rc) = .09 + (1.6 * .013) = .1108 = 11.1% On the basis of your answers to #1 & #2, what is your final estimate for the firm's cost of equity? The two approaches have produced what can be considered a range for the actual cost of equity. A more accurate estimate would be the mean of the two numbers which is 13.7%. 3. Calculate the firm's estimate for corporate cost of capital. CCC = (.5 * .137) * (1-.4) + (.5 * .163) CCC = .0411 + .0815 CCC = .1226 = 12.26% 4. Describe the four (4) steps of capital budgeting analysis. 1) Cash flow estimation phase -- the capital outlay, operating cash flows, and terminal cash flows must be estimated; basically a summary of all the capital that will be required and when it will be spent. 2) Project riskiness -- the risks involved the project must be weighed based on the probability of success. 3) The project cost of capital is assessed -- the firm's average risk is generally used to provide a premium over the risk free rate. 4) Financial attractiveness -- financial information can be plugged into different models such as the breakeven analysis or net present value to determine what the project might look like to an investor. 5. Describe how is project risk is incorporated into a capital budgeting analysis. There three different types of risks that is dependent on one's perspective. The first risk measure is the stand alone risk that is estimated as if that were your only investment. This would represent the risk of the specific project. The next perspective of risk would be the corporate risk. This type of risk includes the corporations or organization's portfolio of various project and holding risks all combined into one number. The next risk takes and even broader perspective and is known as the market risk. This perspective is used when someone has a well-diversified portfolio generally with aspirations of a beta roughly equal to one. https://www.paperdue.com/customer/paper/medical-associates-is-a-large-for-profit-84534#:~:text=Logout-,MedicalAssociatesisalargeforprofitgroup,-Length2pages Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Mergers and Acquisitions Valuation: A Comprehensive Guide for Indian Businesses
In the dynamic landscape of the Indian economy, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) have become vital strategies for growth, diversification, and innovation. However, navigating this complex process requires a solid understanding of mergers and acquisitions valuation. This article will delve into the intricacies of M&A valuation, offering insights tailored to the Indian business environment.
Understanding Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions refer to the processes through which companies consolidate their assets, operations, and market presence. A merger typically involves two companies agreeing to combine into a single entity, while an acquisition entails one company purchasing another. Both strategies aim to enhance market competitiveness, achieve economies of scale, and increase shareholder value.
In India, the M&A landscape has evolved significantly over the past two decades, driven by factors such as globalization, technological advancements, and regulatory reforms. Understanding the valuation aspect is crucial for companies looking to engage in M&A, as it directly impacts the decision-making process and potential success of the deal.
The Importance of Valuation in M&A
Mergers and acquisitions valuation plays a crucial role in determining the fair price for a target company. Accurate valuation helps both buyers and sellers understand the economic worth of the business, ensuring that neither party is overpaying or undervaluing the deal. Additionally, effective valuation helps in:
Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks associated with the target company, including financial health, market position, and operational efficiency.
Negotiation Leverage: Providing a solid basis for negotiations, ensuring that both parties can engage in informed discussions about price and terms.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting legal and regulatory requirements related to valuations, particularly in cases involving public companies or significant market impact.
Strategic Planning: Aligning the valuation with the acquiring company’s strategic objectives, ensuring the deal supports long-term growth.
Key Methods of Mergers and Acquisitions Valuation
Image-by-DjMiko
Several valuation methods are commonly used in the context of mergers and acquisitions. Each method offers unique insights and is suited for different types of businesses. Here are the most prevalent approaches:
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
The DCF method estimates the present value of expected future cash flows generated by the target company. This approach is particularly effective for companies with stable cash flows. In India, where many businesses are transitioning to a more predictable revenue model, DCF can provide a comprehensive view of a company’s value.
Key Steps in DCF Valuation:
Forecast Cash Flows: Estimate future cash flows for a specific period, typically five to ten years.
Determine the Discount Rate: Calculate the appropriate discount rate, reflecting the risk of the investment.
Calculate Terminal Value: Estimate the value of the business at the end of the projection period.
Compute Present Value: Discount future cash flows and the terminal value to their present value.
2. Comparable Company Analysis (Comps)
The comps method involves comparing the target company to similar firms in the industry. This valuation technique is widely used in the Indian market, where companies often operate within competitive sectors. By analyzing key financial metrics such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, enterprise value (EV), and EBITDA multiples, businesses can derive a fair valuation.
Key Considerations:
Select a peer group of companies operating in the same industry and geographical region.
Analyze historical and projected financial metrics to establish a valuation range.
Adjust for differences in size, growth rates, and market positioning.
3. Precedent Transaction Analysis
This method evaluates past transactions involving similar companies to derive a valuation multiple. By analyzing the terms of previous M&A deals, companies can gain insights into market trends and pricing strategies.
Key Steps:
Identify relevant transactions in the same industry.
Analyze the deal structure, including purchase price and payment terms.
Calculate valuation multiples based on historical transactions to estimate the value of the target company.
Challenges in Mergers and Acquisitions Valuation
Image-by-Remitski
While mergers and acquisitions valuation is essential, it comes with its set of challenges. In the Indian context, these challenges include:
Lack of Reliable Data: Access to accurate and comprehensive financial data can be limited, particularly for smaller companies. This can hinder effective valuation.
Market Volatility: The Indian market is subject to fluctuations, making it difficult to predict future cash flows and growth rates.
Cultural Differences: M&A transactions often involve integrating different corporate cultures, which can impact the overall success of the deal.
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape in India can be complex, requiring careful consideration of compliance issues.
Best Practices for Effective Valuation
Image-by-wichayada-suwanachun
To overcome these challenges and enhance the effectiveness of mergers and acquisitions valuation, consider the following best practices:
Engage Professional Valuation Experts: Collaborate with financial advisors or valuation specialists who understand the Indian market and can provide objective insights.
Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Perform comprehensive due diligence to gather relevant data and assess the target company’s financial health.
Use Multiple Valuation Methods: Employ a combination of valuation methods to triangulate and validate the final valuation figure.
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor industry trends, economic indicators, and regulatory changes to ensure valuations remain relevant.
Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions valuation is a critical component of the M&A process, particularly in the Indian business landscape. By understanding the various valuation methods and best practices, companies can make informed decisions that drive growth and success. As the Indian economy continues to evolve, effective M&A strategies, underpinned by accurate valuations, will be essential for businesses looking to thrive in a competitive environment.
Understanding mergers and acquisitions valuation not only helps companies navigate complex deals but also positions them for future success in an ever-changing market.
#businesstips#sellmybusiness#tax#businessadvice#businessforsale#venturecapital#marketing#valuation#corporatelawyer#management#businessopportunities#corporate#legaljobs#commerce#fintech#merge#consultinglife#companylaw
0 notes
Text
Top Methods Used in Business Valuation Services
Business valuation is a critical process that determines the economic value of a company. This valuation is essential for various purposes, such as mergers and acquisitions, investment analysis, financial reporting, and strategic planning. In this article, we will explore the top methods used in business valuation services, providing insights into how professionals assess the worth of a business.

Why Business Valuation Services are Important
Before diving into the methods, it's important to understand why business valuation services are essential. Accurate business valuation services help:
Facilitate informed decision-making: Business owners and investors rely on accurate valuations to make strategic decisions.
Support negotiations: Whether buying, selling, or merging businesses, knowing the accurate value helps in negotiations.
Ensure regulatory compliance: Accurate valuations are crucial for financial reporting and tax compliance.
Top Methods Used in Business Valuation Services
Several methods are employed by professionals to determine the value of a business. The choice of method depends on the nature of the business, the purpose of the valuation, and available data. Here are the top methods used in business valuation services:
1. Income Approach
The income approach values a business based on its ability to generate future income. This method is particularly useful for businesses with consistent and predictable earnings.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
How it Works: DCF analysis estimates the present value of expected future cash flows, discounted back to their value today.
Key Components: Projected cash flows, discount rate (usually the weighted average cost of capital), and terminal value.
Advantages: Provides a detailed understanding of the business’s future earning potential.
Disadvantages: Requires accurate projections and appropriate discount rates, which can be challenging to determine.
2. Market Approach
The market approach determines a business's value based on the selling price of similar businesses in the market. This method is effective when there is ample market data available.
Comparable Company Analysis (CCA)
How it Works: CCA involves comparing the target business to similar companies (peers) that have been recently sold or are publicly traded.
Key Components: Financial ratios such as price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-sales (P/S), and enterprise value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA).
Advantages: Reflects current market conditions and provides a market-based perspective.
Disadvantages: Finding truly comparable companies can be difficult, and market conditions can fluctuate.
Precedent Transactions Analysis
How it Works: This method looks at past transactions of similar companies to gauge valuation multiples and trends.
Key Components: Analysis of past deals, transaction multiples, and market trends.
Advantages: Provides a historical perspective and helps understand market trends.
Disadvantages: Past transactions may not always reflect current market conditions or specific circumstances of the target business.
3. Asset-Based Approach
The asset-based approach values a business based on the sum of its individual assets minus liabilities. This method is often used for companies with significant tangible assets.
Book Value
How it Works: Book value calculates the value of a business based on its balance sheet, considering assets and liabilities at their historical cost.
Advantages: Simple and straightforward; useful for businesses with significant tangible assets.
Disadvantages: Does not account for the current market value of assets and may undervalue businesses with substantial intangible assets valuation.
Liquidation Value
How it Works: Liquidation value estimates the net cash that would be received if all assets were sold and liabilities paid off.
Advantages: Useful for distressed businesses or liquidation scenarios.
Disadvantages: Often lower than going concern value and may not reflect the true ongoing value of a business.
4. Hybrid Approaches
Sometimes, a combination of methods is used to arrive at a more comprehensive valuation. These hybrid approaches can provide a balanced view by incorporating multiple perspectives.
Weighted Average Method
How it Works: This method assigns different weights to various valuation methods and calculates an average based on these weights.
Advantages: Combines the strengths of different methods for a more nuanced valuation.
Disadvantages: Requires careful consideration of appropriate weights for each method.
Conclusion
Understanding the top methods used in business valuation services is crucial for business owners, investors, and financial professionals. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific context and purpose of the valuation. Whether using the income approach, market approach, asset-based approach, or a hybrid method, accurate business valuation services are essential for making informed decisions and achieving strategic goals.
By employing professional business valuation services, companies can gain a clear and accurate picture of their worth, enabling them to navigate the complexities of the business world with confidence and clarity.
0 notes
Text
Equations for the stock market Pt. 2
The discounted cash flow (DCF) model involves estimating future cash flows, determining a discount rate, calculating present value, projecting a terminal value, and summing these to find a stock's true value.
Let’s delve deeper into the discounted cash flow (DCF) model and provide a more detailed explanation along with examples. 1. Estimate Future Cash Flows: To calculate the true value of a stock using the DCF model, you need to estimate the future cash flows the company is expected to generate. These cash flows can be in the form of dividends, earnings, or free cash flow. It’s essential to be as…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Link
A DCF Model is now one of the most commonly used valuation methods for determining the value of a company or an asset. Discounted Free Cash Flow analysis is part of the income approach and thus one of the most theoretically sound valuation methods because the value is determined by the expected income from a business or asset.
Building a Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model is a very popular financial valuation method and widely used among professional investors to derive the value of a company and base their decision-making on such analysis.
A DCF model is mostly built with a spreadsheet program such as MS Excel. It requires a projection of the company’s Free Cash Flows to Firm and then discounts them to their present values. Please see here for an Example DCF Valuation Model.
#terminal value calculation dcf#discounted cash flow valuation method#discounted cash flow valuation calculator#sample dcf model
1 note
·
View note
Text
Easy to Download Formats for Sum Formula in Excel and DCF Method

Are you looking for the right excel sheets that are easy to download and can be turned into any formula to calculate anything or make an impressive sheet for representation?
Depending on your budget model, type of industry and the way of representing your reports and analysis, you will get the right solutions with easy to download for the following sheets that include Sum Formula in Excel, Discounted Cash flow valuation example, DCF method, terminal value formula in Excel and a lot more. You will learn from experts, “How to calculate DCF or How to Calculate Payback period”.
Go Online to Follow Easy Steps to Download Excel Format
Go online and you will find a number of top platforms that are offering easy to download options for DCF Method, terminal value formula in Excel, discounted cash flow valuation example and download formulas to calculate DCF. You can also download Excel budget spreadsheet, sum formula in Excel and IRR Formula.
There are a number of renowned names in this domain providing you with some of the best sheets. You have to download the right one of your choice, go through the details and
You will get a lot more like DCF Method, terminal value formula excel, Financial Ratios Analysis, excel budget spreadsheet, how to calculate payback period, sum formula in excel, IRR formula, discounted cash flow valuation example, and how to calculate DCF. Follow a few simple steps and you will be able to download the right format of your choice and within seconds.
#DCF Method#DCF Model#Terminal value formula excel#Discounted cash flow valuation example#How to calculate dcf#How to make a dcf
0 notes
Text

When it comes to valuing companies, analysts use various models to work out the total value of a business or project. Analysts use financial models, such as discounted cash flow (DCF), to do so.
Discounted cash flow is a popular method used in business valuation. It is based on the theory that an asset's value is equal to all future cash flows derived from that asset. These cash flows must be discounted to the present value at a discount rate representing the cost of capital, such as the interest rate.
Terminal value is the estimated value of an asset at the end of its useful life. It is used for computing depreciation and is also a crucial part of DCF analysis. Terminal value can be calculated using two methods: the perpetual growth method or the exit multiple methods. Get your basics right and learn more finance-related terms only with FMI online.
For more - fmi.online/all-courses/investment-banking-pathway/
0 notes
Text
Startup Valuation
Startup valuation is the process of determining the economic value of a company that has recently been formed and is yet to generate significant revenue. Valuation is critical for startups as it determines the amount of equity they can offer to investors in exchange for funding.
There are various methods used for startup valuation, including discounted cash flow (DCF), comparables, and the venture capital (VC) method. Here are some of the key factors that influence startup valuation:
Market size: The potential market size is a significant factor in startup valuation. Investors are often looking for companies that have the potential to address a large market and generate substantial revenue.
Growth potential: Investors want to see that the startup has the potential to grow rapidly and become a market leader. The more significant the growth potential, the higher the valuation.
Intellectual property: Startups that have patents or proprietary technology that offer a competitive advantage can command higher valuations.
Revenue and financials: While startups typically do not have substantial revenue or profits in the early stages, investors will still want to see financial projections and a clear path to profitability.
Team and management: Investors look for experienced and talented management teams that have a track record of success. Having a strong team can lead to a higher valuation.
Competitive landscape: Investors will consider the startup's competition and how the company is positioned to succeed in a competitive market.
Funding history: Startups that have already secured funding from reputable investors can command higher valuations.
There are several methods used for startup valuation, but the most common method used by venture capitalists is the VC method. This method values a startup based on its future potential earnings and the amount of equity the investor will receive in exchange for their investment.
The VC method involves three key components:
Expected future earnings: This is the expected future revenue of the company. Investors will consider factors such as market size, competition, and growth potential to determine this value.
Discount rate: The discount rate is used to calculate the present value of future earnings. The higher the risk associated with the investment, the higher the discount rate.
Terminal value: The terminal value is the estimated value of the company at the end of the investment horizon. This value is based on the expected future earnings of the company beyond the investment horizon.
Using these three components, the investor can determine the company's pre-money valuation. The pre-money valuation is the company's value before the investor's investment is added to the equation. The post-money valuation is the pre-money valuation plus the amount of the investor's investment.
In conclusion, startup valuation is a critical process that determines the value of a company in its early stages. Investors use various methods to determine a company's value, including the VC method, comparables, and DCF. Valuation is influenced by factors such as market size, growth potential, intellectual property, revenue and financials, team and management, competitive landscape, and funding history. Startups that can demonstrate strong growth potential and a clear path to profitability can command higher valuations.
0 notes
Text
Investment banking pathway - FMI.online
When it comes to valuing companies, analysts use various models to work out the total value of a business or project. Analysts use financial models, such as discounted cash flow (DCF), to do so.
Discounted cash flow is a popular method used in business valuation. It is based on the theory that an asset's value is equal to all future cash flows derived from that asset. These cash flows must be discounted to the present value at a discount rate representing the cost of capital, such as the interest rate.
Terminal value is the estimated value of an asset at the end of its useful life. It is used for computing depreciation and is also a crucial part of DCF analysis. Terminal value can be calculated using two methods: the perpetual growth method or the exit multiple methods.
Get your basics right and learn more finance-related terms only with FMI online.
0 notes
Text
Fundamental Analysis with Python: A Data-Driven Approach
Do you want to learn how to do fundamental analysis with Python? In this blog post, we will walk through a data-driven approach to analyzing stocks. We will use the Pandas library to load data into a data frame, and then use various techniques to analyze the data. We also use the Fundamental Analysis package to obtain fundamental data. This approach can be used for stocks.
Stock data
Gathering the data and importing it into Python is the first step. After that, we need to do some data wrangling to get it into the right format. We will then use a variety of technical indicators to do the analysis. Finally, we will backtest our trading strategy on historical data to see how it would have performed.
The first step is to import the data into a Python pandas data frame. To do this, we will use the pandas_datareader library. This library allows us to load data from a variety of sources, including Yahoo Finance. We will also need to import the DateTime library, which we will use to set the start and end dates for our data.
We will use the following code to import the data:
import pandas_datareader.data as web
from datetime import datetime
start = datetime(2016, 12, 31)
end = datetime(2017, 12, 31)
df = web.DataReader("AAPL", "yahoo", start, end)
This code will load the data for Apple Inc. (AAPL) from Yahoo Finance into a pandas data frame. The data will be downloaded for the period from December 31, 2016 to December 31, 2017.
Once the data is loaded, we can start doing some analysis. The first thing we will do is calculate the stock's return over the period. To do this, we will use the pct_change() method. This method calculates the percentage change between the current row and the previous row. We will also use the head() method to print out the first five rows of the data frame, including the calculated return column.
df['return'] = df['Adj Close'].pct_change()
df.head()
We can see from the output that Apple's stock return was positive in four out of the five days in our data sample. The largest one-day return was about 0.84%.
Fundamental data
Fundamental data can be downloaded and analyzed using the Fundamental Analysis package
To install it, type
pip install fundamentalanalysis
into your Terminal.
After we have installed the Fundamental Analysis package and imported the data, we can start to collect different fundamental metrics. For example, we can collect the market cap and enterprise value. We can also show recommendations of analysts. In addition, we can obtain DCFs over time and collect the balance sheet statements.
# Collect market cap and enterprise value
entreprise_value = fa.enterprise(ticker, api_key)
# Show recommendations of Analysts
ratings = fa.rating(ticker, api_key)
# Obtain DCFs over time
dcf_annually = fa.discounted_cash_flow(ticker, api_key, period="annual")
# Collect the Balance Sheet statements
balance_sheet_annually = fa.balance_sheet_statement(ticker, api_key, period="annual")
Closing thoughts
This is just a brief introduction to how you can do fundamental analysis with Python. In future blog posts, we will go into more detail on how to use the Fundamental Analysis package and other Python libraries to do more sophisticated fundamental analysis.
Post Source Here: Fundamental Analysis with Python: A Data-Driven Approach
from Harbourfront Technologies - Feed https://harbourfronts.com/fundamental-analysis-with-python/
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Look At The Fair Value Of Euronet Worldwide, Inc. (NASDAQ: EEFT)

With the stock down -12.5% over the prior six months, investors may be tempted to sell shares of Euronet Worldwide, Inc. (NASDAQ: EEFT). In this article, I am going to calculate the fair value of Euronet Worldwide by forecasting its future cash flows and discounting them back to today’s value. Investors may find the results of the analysis surprising.
DCF Methodology
The basic philosophy behind a DCF analysis is that the intrinsic value of a company is equal to the future cash flows of that company, discounted back to present value. The general formula is provided below. The intrinsic value is considered the actual value or “true value” of an asset based on an individual’s underlying expectations and assumptions.

Cash flows into the firm in the form of revenue as the company sells its products and services, and cash flows out as it pays its cash operating expenses such as salaries or taxes (taxes are part of the definition for cash operating expenses for purposes of defining free cash flow, even though taxes aren’t generally considered a part of operating income). With the leftover cash, the firm will make short-term net investments in working capital (an example would be inventory and receivables) and longer-term investments in property, plant and equipment. The cash that remains is available to pay out to the firm’s investors: bondholders and common shareholders.
I will take you through my own expectations for Euronet Worldwide as well as explain how I arrived at certain assumptions. The full analysis was completed on Monday, March 19. An updated analysis using real-time data can be viewed in your web browser at finbox.io's Euronet Worldwide DCF analysis page. The steps involved in the valuation are:
1. Forecast Free Cash Flows
Create a revenue forecast
Forecast EBITDA profit margin
Calculate free cash flow
2. Select a discount rate
3. Estimate a terminal value
4. Calculate the equity value
Step 1: Forecast Free Cash Flows
The key assumptions that have the greatest impact on cash flow projections are typically related to growth, profit margin and investments in the business. The analysis starts at the top of the income statement by creating a forecast for revenue and then works its way down to net operating profit after tax (NOPAT), as shown below.

From NOPAT, deduct cash outflows like capital expenditures and investments in net working capital and add back non-cash expenses from the income statement such as depreciation and amortization to calculate the unlevered free cash flow forecast (shown above).
Create A Revenue Forecast
When available, the finbox.io’s pre-built models use analyst forecasts as the starting assumptions. To forecast revenue, analysts gather data about the company, its customers and the state of the industry. I typically review the analysts’ forecast and modify the growth rates based on historical performance, news and other insights gathered from competitors. Note that if a company only has a small number of analysts giving projections, the consensus forecast tends to not be as reliable as companies that have several analysts’ estimates. Another check for reliability is to analyze the range of estimates. If the range is really wide, it may be less accurate.
Euronet Worldwide provides payment and transaction processing and distribution solutions to financial institutions, retailers, service providers, and individual consumers worldwide. The company was founded in 1994 and is headquartered in Leawood, Kansas. Analysts covering the stock often compare the company to a peer group that includes DST Systems, Inc. (NYSE: DST), Global Payments Inc. (NYSE: GPN), Total System Services, Inc. (NYSE: TSS), and Western Union Company (NYSE: WU).

source: Benchmarks: Forecasted 5yr Revenue CAGRs
The company's 5-year revenue CAGR of 12.2% is above its selected comparable public companies: DST (-3.0%), GPN (10.8%) and WU (-0.5%) and only below TSS (22.4%). The company's projected 5-year revenue CAGR of 11.4% is above all of its selected comparable public companies.
As highlighted below, Euronet Worldwide's revenue growth has ranged from 6.5% to 17.8% over the last five fiscal years.

Going forward, analysts forecast that Euronet Worldwide's total revenue will reach $3,869 million by fiscal year 2022 representing a five-year CAGR of 11.4%. However, I conservatively adjusted my growth estimates lower as illustrated in the table below.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi Market Q2 Data Insight
With the birth of encrypted capital assets, some convincing token valuation models have emerged. Since the agreement can track revenue in real time and contains actual value flowing through them, we are able to use old-fashioned valuation practices, such as for instance price-to-earnings ratio, DCF, along with other models to measure these tokens so as to look for a relatively fair valuation. Since the last time we reported on crypto capital assets in-may, DeFi has witnessed the explosion of a wave of new tokens in the field, the most known being Compound's native governance token, COMP, which now has got the highest market value DeFi assets. Through the SAFG framework, the agreement can compliantly allocate tokens to users who provide value-added services to the agreement in nearly every jurisdiction. These can be quite simple operations: such as for instance simply using applications, providing liquidity, or participating in governance. The caveat of the SAFG token model is that tokens usually do not represent economic rights at the beginning. On the other hand, the agreement must first decentralize its own rights, and governance eventually decides to provide the asset economic rights through the worth flowing through the agreement. This trend will not disappear anytime soon. Actually , it may have just begun. DeFi protocol The next is a quick introduction to the DeFi protocols included in this article and their respective profit mechanisms.
* 0x-Liquidity Agreement-Market fees are allotted to ZRX token holders/liquidity providers.
* Aave-Lending Agreement-Part of the accrued interest is distributed to LEND token holders through destruction.
* Augur-Derivatives Agreement-Fees from the prediction market are allotted to REP token holders to participate.
* Bancor-Liquidity Agreement-Part of the transaction fee is allotted to BNT's liquidity provider.
* Compound--Lending Agreement--The accrued interest is allotted to the fund pool provider.
* Kyber-Liquidity Protocol-Part of the transaction fee is distributed to KNC token holders through token destruction or as dividends for participating in governance (Katalyst upgrade).
* Maker-Loan Agreement-The interest generated by the unexpired Dai is distributed to MKR holders in the form of token destruction.
* Synthetix-Derivatives Agreement-Transaction fees are allotted to the pledger of SNX to mint Synths.
* Ren-decentralized exchange-cross-chain exchange fees are allotted to Ren's Darknodes.
* Loopring-Liquidity Agreement-Part of the transaction fee is going to be allotted to LRC token holders.
* Gnosis-Decentralized Exchange-There happens to be no value accumulation, but it could be generated from transaction fees in the foreseeable future.
* Balancer-Liquidity Agreement-Transaction fees are allotted to Balancer liquidity providers. Quarterly earnings ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]()_(above) DeFi quarterly revenue is calculated in line with the average annualized revenue in the next quarter (according to the Token Terminal report) divided by 4. _In the next quarter, the revenue of the DeFi agreement declined, and revenue fell 42% from the previous quarter. This really is due primarily to MakerDAO's shift to a 0% SF and DSR environment, because during the Black Thursday fluctuations at the end of March, the agreement was striving to revive the pegged price of DAI to its proper position. For that reason between April and June, Maker's earnings fell to approximately US$152, 000, in comparison to US$1. 2 million in exactly the same period in the first quarter. Another major reason for the reduction in DeFi revenue is Synthetix. Once we mentioned in the last article, Synthetix is ���facing the problem of front-running attacks, so derivatives agreements have disproportionate revenue reports. After fixing the issue, Synthetix's quarterly earnings were approximately US$267, 000, or approximately US$1 million on an annual basis. The best revenues in the next quarter were Kyber, Compound and dYdX. Kyber's liquidity agreement received $634, 000 in the quarter, Compound and dYdX were slightly lower, at $624, 700 and $624, 300 respectively. Another noteworthy profit agreement in the next quarter was 0x, which brought ZRX holders a quarterly revenue of $445, 000. Even though the existing DeFi is still towards the top of the revenue ranking, the next quarter can easily see the rapid development of new entrants and the upgrade of some major agreements. Even though Uniswap, DeFi's most popular liquidity protocol, launched its V2 version in-may, we've also seen new members in the field, including Balancer, Ren, Gnosis, and Loopring. Most of these protocols have launched major upgrades or new ones. Product launches have brought new appeal (and benefits) to the agreement. For that reason we have been realizing the ecosystem of DeFi protocols getting increasingly diverse, because they are ready to compete for a few market share. Price performance and P/E ratio ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]()DeFi tokens performed perfectly in the next quarter inspite of the decline in revenue. The driving force behind the strong performance may be the launch of liquid mining, which will be now a new theme for Ethereum and DeFi. Normally, DeFi assets grew by 199% in the next quarter, somewhat surpassing ETH and BTC, which grew by 70% and 43%, respectively. The most effective performing DeFi asset this quarter is Bancor's BNT, which has skyrocketed 546% after announcing the upgrade of the liquidity protocol V2. Another outstanding performance in the next quarter was Aave's LEND, which has the strongest performance in comparison to all the DeFi tokens this year. In the next quarter alone, LEND rose by 514%, and the cash market agreement also locked its value from 30 million US dollars to over 120 million US dollars at the end of June. The mix of paid down profits and skyrocketing asset prices has led to an overall escalation in the P/E ratio of DeFi tokens. In accordance with reports, Kyber's P/E ratio in-may was ~80, Bancor's P/E ratio was ~56, and Aave's P/E ratio was ~74. Now, the P/E ratios of these tokens have risen to 134, 92, and 545, respectively. Even though Augur continues to maintain a hugely high P/E ratio of 26673, its partner 0x has paid down the P/E ratio (from 6571 reported in May) to an even more sustainable 251, as the liquidity agreement has steadily increased lately income. Alternatively, Bancor continues to maintain the lowest P/E ratio, which will be the sole DeFi agreement with a double-digit ratio in the next quarter. ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]()___(above) The P/E ratio for the next quarter is calculated by dividing the annualized income of the next quarter on July 7, 2020 by the marketplace value. _Sub-part overview: ** ** DEXs ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]() The DEX sector was the greatest winner in the next quarter, and its particular profit reached a new high, increasing by 5% from the previous quarter and 41. 9% from the next quarter of this past year. The key contribution to growth comes from Kyber, 0x, Bancor, and the newest Balancer. Kyber When it comes to revenue, Kyber is definitely the first choice in the DEX field. The recently launched Katalyst upgraded version offers a new mechanism for KNC holders: to earn element of these benefits by participating in governance. The most effective area of the upgrade is that the reward that participants earn is ETH. In line with the current quarterly earnings (634, 000 USD) and a 65% distribution ratio, Kyber is anticipated to distribute approximately USD 412, 000 of ETH to governance participants in the next quarter. On the other hand, we ought to be able to see the rise of new protocol politicians, each of whom wish to earn their very own share of revenue. Balancer Even though Balancer was launched in March, the liquidity mining introduced in late May possibly became a booster for the agreement's growth. Ever since then, this liquidity and asset management agreement has soared to new highs and ranked fifth on DeFi Pulse, locking in a high value of US$154 million. Even though Balancer currently dwarfs Uniswap when it comes to value lock-in (US$155 million vs . US$84 million, taking Uniswap V1 and v2 in to account), Uniswap plainly dominates when it comes to transaction volume because it has more than 143 million transactions before week US dollars, and Balancer is just 34 million US dollars. DEX trading volume The DEX division witnessed new transaction volume records in the next quarter. Uniswap dominates the marketplace, and this non-tokenized liquidity agreement had a trading amount of just under $1 billion in the next quarter. The trading amount of Curve and dYdX can also be considerable. Curve's AMM has a trading amount of US$436 million between April and June, ranking 2nd, while dYdX's margin trading platform is tight with US$433 million. Followed closely by. It is worth noting that the very best three DEXs ranked by transaction volume are non-tokenized, which ultimately shows that even though tokenized incentives certainly are a catalyst for growth, they are maybe not final or omnipotent. On the other hand, all this has to do with the product's market fit and intuitive user interface that may be easily mastered. Being mindful of this and calculated by quarterly trading volume, the very best tokenized DEXs are Kyber and 0x, and their cumulative trading volume in the next quarter reached 352 million US dollars and 347 million US dollars, respectively. ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]() As DEXs continue steadily to harvest increasingly more transaction volume and can reliably and continuously generate tangible income, tokenized DEXs provide more attractive investment in the DeFi field. New DEX tokens worth watching
* Curve (CRV)-Curve is among the rising stars in the DEX field, because AMM is gathering a great deal of transaction volume and ranked 2nd in the field with a transaction amount of US$436 million in the next quarter. With the launch of the CRV governance token (expected to occur in the next few weeks/months), and it will be distributed to whoever has provided liquidity for the protocol since its launch, this is a matter of concern. Borrow Even though the lending industry may be the main force in 2019, the complete industry has experienced a significant decline, which will be nearly entirely because of the loss in Maker. In the next quarter of 2019, Maker efficiently accounted for more than 99% of the earnings of the lending industry. Twelve months later, Maker's 0% SF environment brought opportunities for new players. Compound now dominates the field as the protocol chose to raise the reserve factor of the primary tokenized assets to 50% (that is, BAT, ZRX, and REP), and USDT to 20%. For that reason Compound took the lead in the lending field for the very first time in the next quarter, with quarterly earnings of $624, 000, in contrast to $152, 000 for Maker and $114, 000 for Aave. Maker One good thing about Maker's 0% stability fee is that Dai's circulating supply is hitting a new high. In the next quarter alone, Dai's supply increased by 90%, reaching 184. 9M in blood circulation. The recent surge in supply is because of the fact Compound recently changed just how that COMP is issued, resulting in a "rotation" in support of Dai. For that reason users flocked to cast new Dai to be able to deposit it in Compound and maximize their COMP revenue. ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight] () As the method of getting Dai reaches a new high, the Maker agreement has huge profit potential. But with Dai's peg (peg) above $1, it's hard to assume that the adjustment will come soon, as the Maker governance is still exploring new mechanisms to greatly help stabilize the peg of the very popular stable currency on DeFi. Loan tokens worth watching
* BZRX-After the flash loan event in February 2020, bZx is straight back on course with the launch of the BZRX token. The token model is characterized by governance rights and liquidity mining incentives, so after the launch of its native token and restart in August, the performance of this lending agreement is going to be worth attention.
* Aave's upgrade: This growing lending agreement has additionally been heralding the upgrade of tokens and governance. In view of Aave's growth in 2020 and its particular recently announced credit authorization, it's expected that the Aave camp may have major moves in the coming weeks. Derivatives ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]() So far, Synthetix is still the sole major player in the derivatives field. But Synthetix appears to be being a de-derivatives agreement (due to disproportionate gains), and recent fixes have caused a substantial drop in agreement revenue. Fortuitously, Synthetix has been iterating and releasing new products at the fastest speed. The DeFi Derivatives Agreement recently introduced binary options, allowing users to position bets on the near future price of any supported asset on the agreement inside a predetermined period of time. The team will also launch futures contracts later this year. Given the direct success of binary options and the nearly unlimited market potential in Ethereum futures contracts, we are able to expect that the Synthetix camp may have a lot of appeal. Equally important, the blood circulation method of getting Synthetix's native encrypted U. S. dollar sUSD in the next quarter increased by 379%, reaching a total level of 22. 7 million U. S. dollars, and so the blood circulation of sUSD is consistently refreshing its historical record. Even though sUSD has some way to go before it competes with other stablecoins in market capitalization, the growth in the next quarter is a positive sign and indicates the next development trend (especially if Synthetix follows around reduce c-ratio and increase ether Fang collateral). ![Exclusive丨Which potential projects deserve attention? DeFi market Q2 data insight]()Augur also lacks substantial use, making the revenue of this prediction market agreement nearly stagnant, bringing quarterly revenue of only two thousand one hundred dollars. But the upcoming Augur V2 should (hopefully) bring recovery to at least one of Ethereum's OG gaming platform currency protocols. Interestingly, while Augur is busy building V2, we've also seen notable new players in the prediction market, including Gnosis's Omen and Polymarket-these two prediction market platforms have brought competition to Augur V2. An appealing aspect of Augur is that the protocol can realize liquidity mining, making a strong motivation for market participants to actively use and guide the newest protocol. However now you can find forget about details in this regard, and we'll continue steadily to focus on whether this can eventually work. Derivative tokens worth watching
* UMA-UMA agreement has good reasons to be a competitor in the derivatives field since it provides an attractive modular design. Simply speaking, anyone can use UMA to produce any synthetic asset collateralized with ETH or DAI. The agreement also strongly signifies that there exists a mechanism for liquidity mining, that'll provide attractive incentives for users to cast synthetic assets on the agreement. Conclusion Even though earnings declined in the quarter, DeFi tokens have continued to improve to new highs predicated on liquid mining. Even though the price-to-earnings ratio reaches hundreds, relatively speaking, this is actually maybe not too high. Compared with old-fashioned capital markets, Tesla will not even have an optimistic income, along with other large technology companies such as for instance Netflix have a price-earnings ratio that is a few hundred lower. The reason being the P/E ratio is approximately future growth potential. Tesla has first-class electric cars. This is a company that builds clean energy for future years. And clean energy may be the future. For that reason investors' valuation of this potential is really as high as $286 billion, and will maybe not be shaken as the company has never made any money. DeFi is on a similar path. The long run direction just isn't more banks, but fewer banks. Now they're all early-stage digital technologies that are used to construct a totally open financial system that anyone in the world can access. The long run growth potential is very good. Ethereum's currency agreement is preparing to disrupt the trillion-dollar financial market. Inspite of the great potential, we've only seen one DeFi unicorn so far (congrats Compound! ). For that reason because so many well-known DeFi agreements are valued at less than US$500 million and their price-to-earnings ratios are mostly in the reduced hundreds, we've only scratched the surface of the huge development that's coming in the near future.
#earn cryptocurrency#earn free bitcoins instantly#bitcoin cloud mining free#earn free crypto#free btc
0 notes
Text
Building a DCF Model

Discounted cash flow (DCF) model is one of the most used valuation methods to determine the value of a company or any cash flowing asset. Normally, a DCF model is an add-on to an existing, working financial model as to calculate the net present value by discounting the projected cash flows. There are three important elements that you need to consider when calculating the DCF value.
· Free Cash Flow to Firm (projected cash flows)
· Weighted Average Cost of Capital (discount rate)
· Time period used for valuation
The main concept of the DCF Model is to consider the time value of money. As you already know, as time passes by, the value of money constantly changes. Basically, what used to be less might be more in the future and vice versa. The DCF Model will be helpful in calculating of what could be expected in the future such as potential investment opportunities and other interests.
Most users prefer using the DCF Model due to its straightforward approach on calculating the present value. For example, if a company purchases an asset with an expected life of 5 years, the model will then calculate the future value of said asset by discounting it to find the present value. In cases for business acquisition, the need to determine a terminal value is essential as to put an end period of the DCF Model.
Though it may sound simple enough to build a DCF model, you would still need the required know-how as to ensure that the model is according to the state of the economy, trends, and other factors that could affect the variables in the model. To get a better understanding on how to build a DCF Model, you can take a look at eFinancialModels. There, you’ll be able to acquire and download industry-specific DCF model templates which you can use as a reference once you build your very own DCF valuation model.
0 notes
Text
Valuation – Finance Technical Interview Questions
Valuation – Finance Technical Interview Questions
What are the different ways to value a company?
Walk me through a DCF valuation. What is free cash flow and how is it calculated? What would you use for a discount rate? How do you determine the terminal value?
How do you calculate WACC?
What is the formula for CAPM?
What is beta? How and why do you unlever a beta?
What is the current market risk premium? What is the current risk-free rate?
What…
View On WordPress
0 notes