#ugaritic
Text
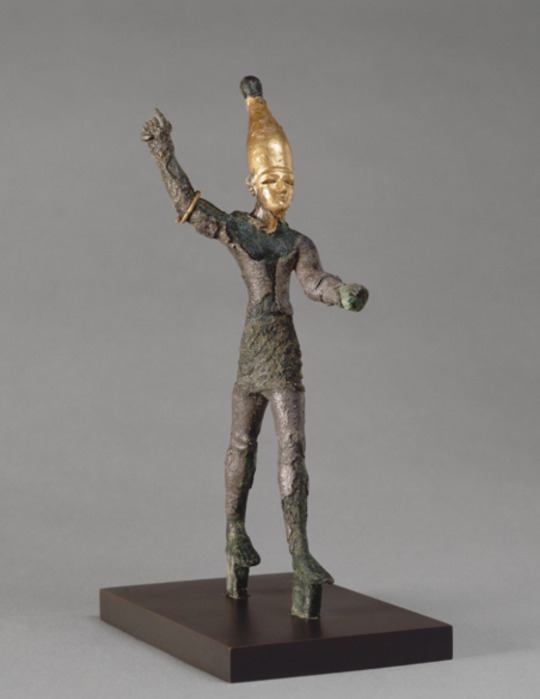

Bronze statue of Baal Hadad
Ugarit, Syria
c. 1200 BCE
Source: The Louvre
#canaan#canaanite#canaanite paganism#canaanite polytheism#canaanite gods#phoenician#phoenician paganism#phoenician polytheism#phoenician gods#ugarit#ugaritic#aramean#aramean paganism#aramean polytheism#aramean gods#natib qadish#pagan#paganism#polytheism#magic#witchcraft#occult#baal#balu#hadad#hadu#baal hadad
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
ANATOLIA & LEVANT RESOURCES
The Anthropological Masterlist is HERE.
Anatolia, or Asia Minor, is a historical West Asian peninsula that constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey.
HITTITE ─ “The Hittites, or the Empire of Hattusa, were an Anatolian people that lived during the Bronze Age, from 1650 B.C.E. to 1190 B.C.E. At their height, the empire encompassed the majority of modern-day Turkey, Lebanon, and Syria.”
─ Hittite Cuneiform Script
─ Hittite Grammar
─ The Chicago Hittite Dictionary Project
HURRIAN ─ “The Hurrians, or Khurrites, were a Near East people that lived from 3000 B.C.E. to 1300 B.C.E. They lived in Anatolia and Mesopotamia.”
─ The Mitanni Empire
─ Hurrian Culture
─ Hurrian Mythology
LUWIAN ─ “The Luwians are a group of Anatolian people that lived from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. They lived in modern-day Turkey.”
─ Luwian Studies
─ Luwian Dictionary
PHRYGIA ─ “The Phrygian people were an Anatolian people that lived from 1200 B.C.E. to 700 B.C.E. They lived in central Anatolia.”
─ Phrygian Language
─ Phrygian Inscriptions
THRACIA ─ “The Thracians were an Indo-European people that lived from the 8th century B.C.E. to 1st century C.E. They lived in the Balkans and Anatolia.”
─ Thracian Information
─ Thracian Culture
─ Thracian Language
UGARIT ─ “Ugarit was an Anatolian civilization that lived from 6000 B.C.E. to 1185 B.C.E. They lived in modern-day northern Syria.”
─ Ugaritic Information
─ Ugarit in the Bible
─ El in Ugaritic Texts
The Levant is a historical West Asian region in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Asia. It spans from the western part of the Arabian Peninsula to northeast Africa.
CARTHAGE ─ “Ancient Carthage, or the Carthaginian Empire, was a Mediterranean civilization that lived from 814 B.C.E. to 146 B.C.E. They lived in modern-day Tunisia.”
─ Carthage Information
─ Carthaginian Religion
─ Carthaginian Archaeology
EGYPT ─ “The Ancient Egyptians were a northeastern African people. They lived in the Nile Valley in Egypt.”
─ Egyptian Information
─ Ancient Egyptian Art
─ Women in Ancient Egypt
PHOENICIA ─ “The Phoenician people were a Mediterranean people that lived from 2500 B.C.E. to 64 B.C.E. They lived in modern-day Lebanon.”
─ Phoenician History
─ Phoenician Alphabet
─ Phoenician and Punic Languages
SYRIA ─ “The Syrians are an Eastern Mediterranean people that share the Syrian culture. They are native to Syria.”
─ Syria Information
─ Syria from 1700 C.E to 1920 C.E.
─ Syrian Cultural Zones
#resources#anatolia#levant#hittite#hurrian#luwian#phrygian#thracian#ugaritic#carthaginian#ancient egyptian#phoenician#syria
56 notes
·
View notes
Text



the Tale of Aqhat, abridged and summarized
note: originally Aqhat is murdered by a devotee of Anat for this slight and eaten by vultures, but getting Smote and the family guy death pose is funnier out of context and for the uninitiated
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
academic writing is starting out w one thesis and landing somewhere totally different
#somehow I've written like 13 pages so far abt what deities and stories were absorbed into the mythology of god#that wasn't the intent it was just going to be a look at the connections between the ugaritic texts and the tanakh but well. here we are.#capstone of my entire BA being the thesis that God is made up of 2 goddesses and 2 gods.#he's slaying in a bigender manner or whatever#actually more than that bc this is just the ugaritic texts but you can find other gods that got absorbed into god from other nearby#or more ancient traditions#which to Me is very lovely and kind of poetic but that's on a personal spiritual belief note#(not the historical absorption being lovely but rather the spiritual idea that god IS every god. one that has always appealed to me)
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
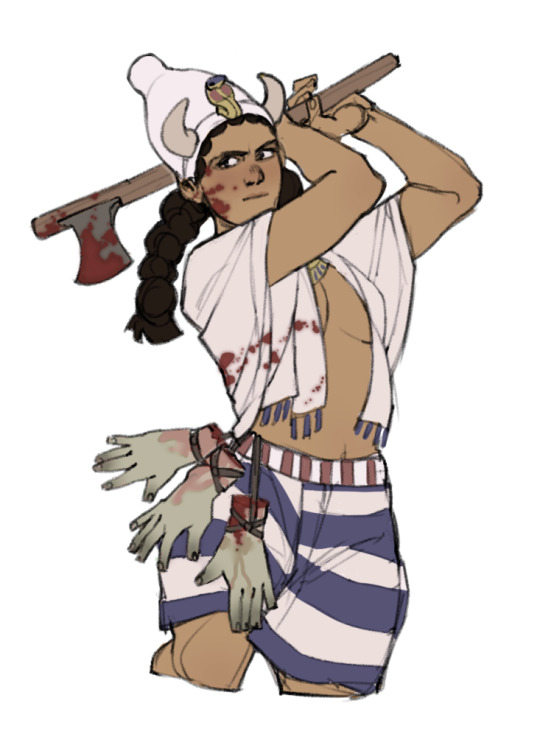

She seized divine Mot,
With a sword she split him,
With a sieve she winnowed him,
With fire she burnt him,
With mill-stones she ground him,
In a field she scattered him;
His flesh indeed the birds ate,
His limbs indeed the sparrows consumed.
Flesh cried out to flesh!
#anat is a non-binary icon#'anat‚ the victorious goddess‚ the woman who acts like a warrior‚ who wears a skirt like men and a sash like women'#ugaritic mythology#canaanite mythology#ancient egyptian mythology#ba'al cycle#levantine mythology#speaking of mythological figures‚ i... er... i seem to like them violent‚ huh#tw blood#tw light gore#art tag
108 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, sorry if this has been asked before, but do you have any reliable sources that talk about Ashtar? I'm also looking for articles that talk about El/Ilu; and Shalim and Shahar as well. I appreciate any form of help.
I've answered a similar Ashtar question a few months ago, refer to the bibliography here.
I do not have much to offer when it comes to Shahar and Shalim because as far as I can tell most scholarship focuses on exegesis of the Bible, which is something I have next to no interest in. I've answered a question about them here; the main source to depend on is Pardee's Ritual and Cult in Ugarit.
When it comes to El, the basic selection of sources dealing with Ugaritic religion should obviously be the start: Smith's Baal Cycle commentaries, Pardee's aforementioned book, Rahmouni's Divine Epithets in the Ugaritic Alphabetic Texts, Handbook of Ugaritic Studies, etc. For more specialized information I recommend:
a) Il in Personal Names by Alfonso Archi (early history, and why names with the element il and its cognates do not necessarily refer to a specific deity in pre-Ugaritic sources)
b) West Semitic god El in Anatolian Hieroglyphic Transmission by Ilya Yakubovich for the first millennium BCE
c) The God Eltara and the Theogony by Anna Maria Polvani for El's Hurro-Hittite career (there's also the Elkunirsa myth but I do not think there's any recent treatment of it, so your best bet is to just read the translation in Hoffner's Hittite Myths from the 1990s)
d) The Dwelling of ˀIlu in Baˁlu and ˀAqhatu by Madadh Richey for some lexical considerations regarding El's residence
e) God (Ilu) and King in KTU 1.23 by Theodore J. Lewis for El's role as the king of the gods
Also, it's worth checking out Wiggins' monograph A reassessment of Asherah: with further considerations of the goddess since while hardly focused on El, it does discuss Athirat's relationship with him in the Ugarit section. Similarly, might be worth looking into this author's Shapash article.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
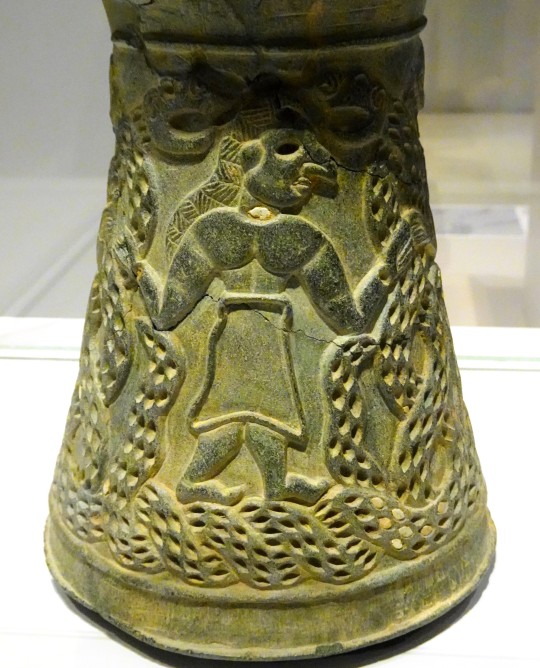






Il y a une petite quinzaine, je suis allé avec Julien et Katie, au Louvre-Lens. Ici l'expo permanente, la Galerie du Temps :
socle d'obélisque en granite, babouins - Louxor, 1250 av. J-C.
vase, le Maître des Animaux et serpents léontocéphales - Iran du S.E., 2500 av. J-C.
statue récipient - Kaluraz, Iran, 900-600 av. J-C.
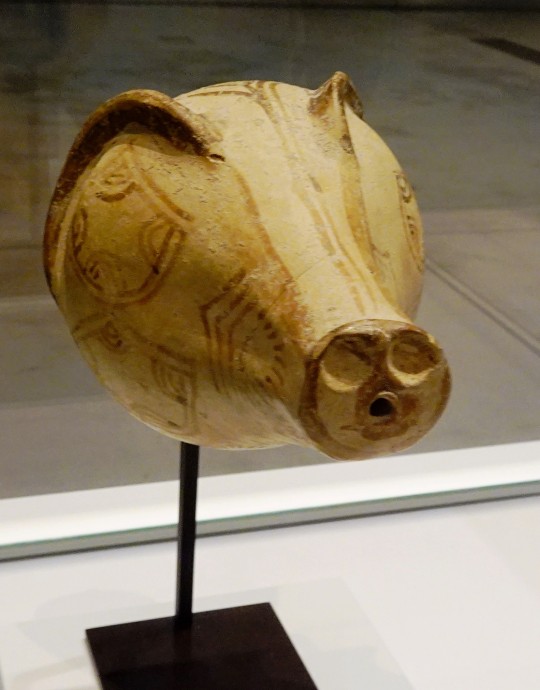
rhyton, sanglier - Ugarit, Syrie, 1200 av. J-C.
cratère mycénien avec guerriers et chars - Ugarit, Syrie, 1200 av. J-C.
hommes et chevreau - temple de déesse-mère Ninhursag, Suse, royaume d'Elam, Iran, 2700 av. J-C.
#expo#louvre-lens#archéologie#mythologie#monstre#babouin#obélisque#égypte#égypte antique#maître des animaux#léontocéphale#serpent#serpent léontocéphale#iran#perse#mésopotamie#kaluraz#rhyton#sanglier#ugarit#ougarit#syrie#phénicie#ninhursag#suse#galerie du temps#elam#cratère#mycènes#mycénien
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Zeus himself, the central character in Hesiod’s Theogony, bears some of the most easily recognizable Northwest Semitic features, in addition to those of the Indo-European Sky God inherited by the Greeks. It is not necessary, therefore, to discuss them at length. It suffices to recall that the Canaanite Storm God Baal and the homologous Greek god share a similar position in the succession of kings in Heaven, as well as the position of the youngest son. They both reign from a palace on a northern mountain (Olympos, Zapanu/Zaphon), and they wield thunder as their distinctive weapon. As with his Near Eastern counterparts, thunder, lightning, and the thunderbolt were the “missiles/shafts of great Zeus.” The position of his sister and principal consort Hera is like that of Anat, Baal’s sister and partner (though not consort). For some, this coupling “violates the incest taboo” in Greek myth but allows Hera to remain an “equal” partner according to her right of birth, as the daughter of Kronos. In Il. 4.59 she is the oldest daughter, in Il. 16.432,18.352 she is called “sister and wife” and in Hesiod Th. 454 she is the youngest daughter of Kronos, exactly as Zeus is the last son.
The list of similarities between Zeus and the different manifestations of the Canaanite god (either Baal or El or Yahweh in the later Hebrew theology) is long and has been the subject of much discussion by classicists, Semitists, and biblical scholars. Perhaps most interesting are the parallels noticeable at the level of their epithets, such as Zeus the “cloud-gatherer” (nephelegereta)or “lightener” (asteropetes), and the frequent characterization of Baal in Ugaritic poetry as the “cloud-rider” (rkb ʿrpt). Other epithets of the Northwest Semitic Storm God Adad (Haddad) are preserved in Akkadian hymns, such as “lord of lightning” or “establisher of clouds.” …
Zeus’ “high-in-the-Sky” position and Sky-nature are reflected in other epithets such as hypatos and hypsistos. At the same time, similar divine epithets meaning “the high one” (eli, elyon, and ram) are very common in Northwest Semitic religious texts, accompanying several principal divinities. For instance, this epithet is used in the Ugaritic epic for Baal, and different forms of the adjective are attested in Aramaic, as well as in the Hebrew Bible accompanying El, Yahweh, and Elohim. … The association of the Storm God in Syro-Palestine with the bull as a symbol of fertility is also present in the various mythological narratives involving Zeus, most clearly in the famous motif of Zeus’ kidnapping the Phoenician princess Europa and carrying her on his back after taking the shape of a bull.
The final fight of Zeus with Typhon (Th. 820-880) has also been compared to the fight between Baal and Yam (the Sea) in the Ugaritic Baal Cycle and to that between Demarous and Pontos (the Sea) in Philon’s Phoenician History (P.E. 1.10.28). As mentioned earlier, the Storm God’s struggle with a monster also (albeit more distantly) resembles the clash between the Hurrian Weather God Teshub and the monsters Ullikummi, Illuyanka, and Hedammu. The figure of Typhon in Hesiod can in fact be seen as a Greek version of a “cosmic rebel” repeatedly reimagined with different characteristics in the specific versions, who endangers the Weather God’s power and generally has both marine and chthonic features. The Levantine and Greek adversaries probably have more than a merely thematic resonance, as the very name of Typhon might have a Semitic origin. It has hypothetically but quite convincingly been associated with the Semitic name Zaphon. Mount Zaphon (Ugaritic Zapunu or Zapanu) is a central point of reference in the geography and the religion of Ugarit. Known by Greeks and Romans as Kasion oros/ mons Casius (today Jebel al-Aqra), this peak on the north coast of Syria (south of the Orontes River) was also mentioned in Hurrian-Hittite myths. The mountain occupies a central spot in both the fight between Ullikummi and Teshub (as Mount Hazzi) and in the Ugaritic Baal Cycle. In the Ugaritic epic, the fight against Yam (the Sea) is not described as taking place on the mountain, but the celebration of Baal’s victory is, as it is the god’s abode overlooking the Mediterranean: “With sweet voice the hero sings / over Baalu on the summit / of Sapan (= Zaphon).” Much later, Apollodoros locates the cosmic fight with Typhon on Mons Casius precisely, which indicates that the link between Typhon and Zaphon had persisted, even though the name known to Hellenistic authors was the Greek, not the Semitic one."
- When the Gods Were Born: Greek Cosmogonies and the Near East by Carolina López-Ruiz
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
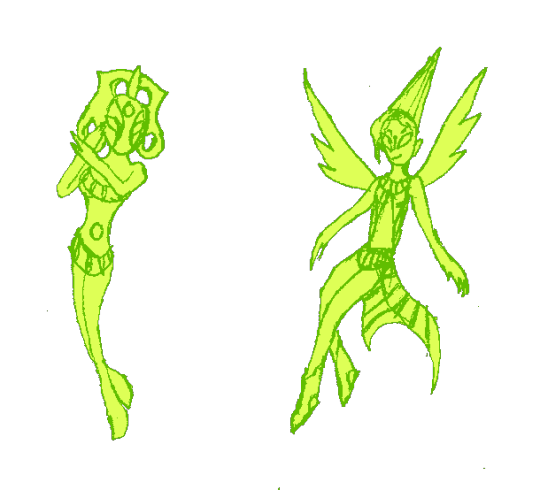

Astarte and Shaushka.
Astarte or Ashtart is an Ugaritic goddess cognate with Ishtar. She was a deity of rulership and justice and a major character in the Baal Cycle.
Shaushka is a Hurrian goddess of love and war equated with Ishtar. She is the sister of the head god Teshub and is sometimes described with both male and female characteristics.
#ugaritic mythology#canaanite mythology#hurrian mythology#astarte#ashtart#shaushka#ishtar#inanna#Destiny of Dionysus#oc#two posts today because i meant to post the last touhou OC yesterday but forgot
16 notes
·
View notes
Text


Ugarit
7 notes
·
View notes
Text


Stele of Baalshamin - Zeus Kyrios
Dura-Europos, aka Dura, Syria
c. 31 CE
Source: The Pantheon of Palmyra by Javier Teixidor, 1979
#baal#baalshamin#dura europos#syria#canaan#canaanite#canaanite paganism#canaanite polytheism#canaanite gods#phoenician#phoenician paganism#phoenician polytheism#phoenician gods#ugarit#ugaritic#aramean#aramean paganism#aramean polytheism#aramean gods#natib qadish#pagan#paganblr#paganism#polytheism#witchcraft#witchblr#magic#occult
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
what if the thing that is going to turn me into a manuscript tradition fucker is literally just it being hebrew bible studies instead of like catullus or whatever... i'm sorry all my classicist friends for secretly thinking it was annoying and bad when we had to learn about that stuff it turns out i too am susceptible to. Texts.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yahweh and Asherah in the Hebrew Bible
Yahweh and Asherah in the Hebrew Bible
The Death of Jezebel, by Gustave Doré, 1866. From wikipedia.org
The Hebrew Bible uniformly recognizes the unique deity of the Lord, the God of Israel who identifies himself to Moses as “I AM” transliterated as Yahweh. Only he is the God of the heavens and the earth, the creator of all things, the sole Lord of the heavenly hosts who sits on his throne ruling over the divine council. In contrast…

View On WordPress
#academic#ANE#Asherim#Asheroth#Athirat#Baal#Canaanite religion#Comparative religion#fertility#goddess#paganism#Patrick Quinn#scholarly#Take Note Of This#TNOT#Ugarit#YHWH
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
what they don't tell u abt getting into academia is sometimes getting a huge pile of books from amazon about one very niche topic for free can feel like christmas
#me like the sickos haha yesss comic as i get 10 books about the ugaritic texts monotheism and yahwism#religious studies rambling
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
pov: you pass by blackarachnia's quarters in the middle of the night while their family is still on cybertron
#eukarian music#the phonetics are slightly off#as this is based on ancient ugarit rather than any african dialect#but the vibe is there#Youtube#rp event: rebirth
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ishkur, Baal, and others: a guide to the weather gods of Mesopotamia and ancient Syria
I received an ask recently which was difficult to answer in the conventional way:
Is there any difference between Adad, Hadad, Ugaritic Baal, and Ishkur? What aspects would be specific to each? Was Dagan said to be the father of Ugaritic Baal or Hadad? Also, what sources would you recommend on the subject?
After much consideration and multiple failed attempts to write a short response I decided to present the information in the form of a proper article. You can find it under the cut.
Recommended reading
I’ll reverse the usual formula and start with literature recommendations. The most comprehensive treatment of this matter is quite literally a 1000+ pages long monograph, Daniel Schwemer’s Die Wettergottgestalten Mesopotamiens und Nordsyriens im Zeitalter der Keilschriftkulturen. Materialien und Studien nach den schriftlichen Quellen. It’s available for free, and remains reliable basically 99% of the time. I am aware reading hundreds of dense pages of academic German might be a bit much, but luckily the same author effectively wrote a two part abridged edition in English, The Storm-Gods of the Ancient Near East: Summary, Synthesis, Recent Studies. It is similarly available for free, see here for part 1 and here for part 2.
Other literature which is worth checking out, and which I also utilized here, includes Lluís Feliu’s monograph The God Dagan in Bronze Age Syria and his article Two brides for two gods. The case of Šala and Šalaš; Alfonso Archi’s Hadda of Ḫalab and his Temple in the Ebla Period; and Shana Zaia’s Adad in Assyria: Royal Authority in the Neo-Assyrian Period. Furthermore, a new desertion which seems relevant was published recently, Albert Dietz’s Der Wettergott im Bild: diachrone Analyse eines altorientalischen Göttertypus im 3. und 2. Jahrtausend v. Chr., but I did not have the opportunity to read it yet.
To properly answer the rest of the questions, the historical and environmental context of the worship of weather deities has to be addressed first.
Ishkur in Mesopotamia in the Uruk and Early Dynastic periods
At the dawn of recorded history, in lower Mesopotamia weather gods did not enjoy particular prominence. This has a lot to do with the environment - the importance of weather deities typically stems from reliance on rainfall in agriculture. As through a solid chunk of Mesopotamia irrigation mattered more, there was no real need for a major weather deity to arise. Canals were often handled by local tutelary gods, for example Shara in Umma.
The oldest attested weather deity in Mesopotamia is Ishkur, who pretty clearly already worshiped in the Uruk period, but his importance was comparatively minor. His two main spheres of influence were seemingly providing water for land which was not irrigated (for example the steppe) and presiding over the destructive side of the weather - not just heavy rainfall, but also dust storms.
Ishkur was also the main god of the city of Karkar, which has not yet been located with certainty, but presumably is to be found close to Adab on the banks of the Tigris. The fact that the logogram read as “storm” also represented this toponym in the Uruk period already is how it was possible to establish that the city was already a cult center of Ishkur at this time, and presumably earlier. The same logogram was also used to represent Ishkur’s name, for obvious reasons. However, the etymology of his proper name is unknown. It might be a Sumerian word which fell out of use before the start of recorded history otherwise, or it might come from a substrate language; this is ultimately irrelevant and has no real bearing on the tangible early history of this god.
In addition to Karkar Ishkur was worshiped in nearby Adab and even further south in Lagash, but that’s about it for the earliest sources. Worth noting that for example in Ur there was virtually no cult of any weather deity until the late third millennium BCE, and even then, in the Ur III period it was of no interest to rulers. We also do not know much about the circle of deities associated with him. Based on later evidence it is presumed that his wife might have been the goddess Medimsha (“possessing beautiful limbs”), and god lists indicate his sukkal (attendant deity) was the deified lightning, Nimgir, but that’s about it.
Adad ("Hadda") in early Syrian sources
The situation was diametrically different in upper Mesopotamia and across northern Syria. In these regions agriculture did depend on rainfall, which naturally meant weather gods were present in many local pantheons for as long as evidence is available. The best early sources we have are the texts from Ebla, which are roughly contemporary with the Early Dynastic sources mentioned in the previous paragraphs.
The Eblaites evidently recognized Aleppo as the cult center of a weather god, who they referred to as Adad - or rather by a cognate of this name, which can be romanized as something like “Hadda” or "'Adda", but you get the point. It’s a derivative of the root *hdd, “to thunder”, which appears in some capacity in virtually every single language from the Semitic family. The Akkadian spelling, which is firmly Adad, seemingly reflects the weakening of the h present in Eblaite and later in a number of other languages (Ugaritic, Aramaic etc) into a glottal stop.
Despite the root *hdd itself appearing in languages spoken as far south as Ethiopia, weather gods with names derived from it were seemingly initially basically restricted to northern Syria and upper Mesopotamia. Therefore, this is another piece of evidence indicating there is hardly such a thing as a “Semitic pantheon”; languages are not religions. It is not possible to tell when his cult was originally established, and claims linking any neolithic object with worship of weather gods require a healthy dose of skepticism. What is clear is that he was already well established by the third millennium BCE.
Interestingly, despite Adad’s high status in the Eblaite pantheon, his original cult center, Aleppo, was hardly a political power in its own right in the third millennium BCE. In that regard he resembles many of the other major members of the local pantheon, like Hadabal (formerly read as Nidakul; no etymological relation to Adad or Baal) or Dagan, whose cult centers likewise did not form kingdoms in their own right .

A map of ancient Syria, showing the location of Ebla, Aleppo, Mari and other nearby cities (wikimedia commons)
All we can tell about the associations between Adad and other deities in the Ebla-Aleppo area is that he definitely had a wife, Halabatu, possibly to be understood as “she of Aleppo”. This name likely later morphed into better known Hebat. There’s no real evidence for a link between Adad and Dagan at this point in time, and Alfonso Archi went as far as arguing Dagan was not yet regarded as a senior, fatherly figure in the third millennium BCE, but this is ultimately speculative.
Adad was also worshiped midway between Ebla and lower Mesopotamia, in Mari. Local scribes were the first people on record to associate him with Ishkur, and utilized the logographic writing of the latter’s name to represent the former. Curiously in Ebla this convention was entirely unknown, even though in other cases logograms borrowed from Mesopotamia did see some usage in a similar context.
Adad and Ishkur in Mesopotamia through third and second millennia BCE
In the Sargonic period Adad started to spread to new areas. He is well attested as far east as Gasur (later Nuzi) near modern Kirkuk. Since no comparable evidence is available for the Early Dynastic period, it can be safely assumed that he was restricted to western areas earlier. However, how exactly his cult entered the east and the south remains poorly understood.
A major development for Adad in Mesopotamia was the merge between him and Ishkur. Presumably it started developing right as the southern scribal culture started to expand into areas where Adad was worshiped, like Mari. The details of this process are poorly known, but by the Ur III period Adad and Ishkur were effectively the same god in Mesopotamia.
The worship of Adad was subsequently promoted by kings of the Isin and Larsa dynasties, and by the Old Babylonian period he was recognized as a major deity. He acquired some new roles, being invoked as a god of justice and divination - perhaps these offset the environmental factors responsible for Ishkur’s lack of popularity? However, many sources also indicate that even as a weather god he was recognized in a positive, rather than exclusively destructive role, acting as a bringer of abundance. He also came to be known as the "canal inspector of the gods", ie. as a god of irrigation.
Adad's family in lower Mesopotamia

Frans Wiggermann's drawing of a seal impression showing a weather god and his spouse; reproduced here for educational purposes only.
In lower Mesopotamia, the composite “Ishkur-Adad” kept a genealogy most likely originally developed with Ishkur in mind. His father was Anu, the sky god. The relationship between them is hardly explored in myths, though an Old Babylonian flood myth has a funny passage where, to cite Schwemer, “Adad (...) is to bring about a famine for humanity through lack of rainfall, and (...) then has to be guarded in heaven by Anu because of his corruptibility”. Alas, the audience presumably didn’t think that giving him the role of a failson was funny, and this element is absent from later flood myths.
There is apparently only one source from the south which directly refers to Adad’s mother, and it places Urash in this role. This is hardly unexpected. My impression is that among online hobbyists Urash gets the least recognition of all three of Anu’s wives, but honestly prior to the “antiquarian theology” rising in late sources from Uruk, literally mere centuries before the death of cuneiform, she was -the- wife of Anu, with Ki bordering on being a non-personified concept and Antu hardly mattering. If a deity was defined as a child of Anu chances are very high Urash was the mother, basically.
In the Old Babylonian period the southern version of Adad also gained a spouse, Shala, a fellow weather deity. This goddess must be categorically distinguished from Shalash known from earlier sources, who will be discussed later. We do not really know particularly well where she came from. Today the most common assumption is that her name is Hurrian and can be translated as “daughter”. This would point at origin in some part of Upper Mesopotamia. Lluis Feliu suggests that she might have originally been the spouse of the Hurrian weather god Teshub in a tradition perhaps centered on hitherto unidentified cities on the Tigris, though while plausible, this is ultimately purely speculative. Shala is very sparsely attested in Hurrian context, but to be fair most evidence we have comes from the west of the Hurrian sphere, and not from the east where she theoretically would be present.
Mesopotamian god lists indicate that Shala was equated with Medimsha, presumably in a similar manner as Adad was with Ishkur. There is no independent evidence for Medimsha being Ishkur’s wife beyond texts which equate them with Adad and Shala, but the conclusion she held such a status even before the conflation is widely accepted, and I see no real reason to dispute it.
Adad and Shala also had a number of children. The best attested ones are Misharu (“justice”), originally an independent god perhaps integrated into Adad’s circle because his name sounds similar to the akkadian word for wind, and Usur-amassu (“heed his - ie. Adad’s - word”). There isn’t much of a reason to discuss them in detail here since they were not weather deities; Usur-amassu is a fascinating figure though, and while initially male, they are mostly notable due to switching gender in the first millennium BCE as a new courtier of Inanna/Ishtar in Uruk, without losing the connection to her parents.
Western views on Adad’s genealogy and marital status
While Shala was firmly the wife of the Mesopotamian Adad in Babylonia and Assyria, and Anu was equally firmly his father, the situation was different over in Aleppo and around it. As I mentioned before, the weather god of Aleppo already had a wife in the third millennium BCE, Halabatu. While many deities worshiped in Syria in the third millennium BCE later vanished, she remained a member of the local pantheon under the shortened name Hebat, and her position did not change. To my best knowledge the eastern limit for her recognition as the spouse of the weather god was Mari. The west is more complicated, though she pretty firmly appears in this role in Alalakh. The complex case of Ugarit will be discussed later.
The different circles of associated deities make it pretty easy to separate Mesopotamian and western traditions. I would argue that a formal distinction between the Mesopotamian Adad and the “Aleppine” original is attested in the god list K 2100 (no catchier name for now), which lists “Ilhallabu”, “god of Aleppo”, among Adad’s foreign counterparts.
Mari is somewhat of an oddity in that western and southern traditions pertaining to the weather god of Aleppo and the Mesopotamian Adad probably coexisted there. The Mariote kings recognized the weather god of Aleppo, but we also have some evidence that his peer from Karkar had some presence in the kingdom. For instance, Shala appears in personal names, and a seal refers to Anu as the weather god’s father. However, it is possible that a distinct western tradition regarding his parentage was followed in this area.
While we do not know if Dagan was regarded as the father of the weather god of Aleppo in the third millennium BCE, it does appear that a connection between them was recognized in the Old Babylonian period. A mystery which for now cannot be solved is whether Dagan became the father of the weather god because his Hurrian counterpart Kumarbi was, or the other way around. Until more textual sources dealing with the theology of northern Syria surface it probably will remain impossible to answer this question for certain.
Regardless of how the weather god came to be Dagan’s son, his mother in this situation would be Shalash. Her name is accidentally similar to Shala’s, but she has a distinct origin. In a ritual preserved in the Mari corpus but originating in Aleppo, Dagan and Shalash both appear alongside Hebat, which is generally taken as an indication they were regarded as members of one family.
Weather gods of Kumme and Arrapha in Mari (and beyond): enter Teshub

A late Bronze Age relief depicting Teshub (center left) and his wife Hebat (center right) alongside their family and court (wikimedia commons)
A further Mariote curiosity are references to weather gods of Kumme and Arrapha, to whom kings also paid respect. Both of these cities were Hurrian, and it is quite likely that the deity designated by the logogram normally read as Adad was in fact Teshub in these cases.
Teshub was seemingly also starting to approach on the turf of the original weather god of Aleppo in the Old Babylonian period, as Hebat already shows up as his wife at this time. Eventually he fully replaced him, becoming the new weather god of Aleppo due to growing Hurrian cultural influence in Syria, though he did not hold this title forever. After the bronze age collapse local Luwian princes referred to the weather god of Aleppo as Tarhunza, and eventually the old name returned, with Arameans in the first millennium BCE worshiping Hadad in Aleppo. It’s worth noting a Neo-Assyrian treaty invokes the god of Aleppo separately from the Mesopotamian Adad, which indicates in this period the two were also viewed as separate. As a further Assyrian curiosity it might be worth bringing up “Adad of Kumme”, more or less the last reference to Teshub; see here for more information, in addition to Schwemer’s monograph.
It is agreed the pairing Hebat with Teshub was adopted by Hurrians from northern Syria based on parallels between him and the local weather god, but it is not clear if he had a wife earlier. There is a theory that Shaushka, who in later sources firmly appears as his sister, was originally his spouse, but I will admit I do not fully get the reasoning, it’s not like anyone sensible advocates that Utu and Inanna were originally a couple. Feliu’s Shala theory strikes as much more plausible: Shaushka is firmly unmarried, Shala is firmly the wife of a weather god.
Coastal novelties, or the rise of Baal in Ugarit

Detail of the Baal stele from Ugarit (wikimedia commons).
The overlap between the weather god of Aleppo and Teshub was not the only western development in the second millennium BCE. Thai was the creation of Baal. The title designated the western weather god from the Mediterranean coast to roughly the middle Euphrates, though it only replaced the basic name, Hadad, in coastal areas. While the epithet Baal -or rather its cognates - already occurs in the third millennium BCE (for example in titles of Dagan), its use to specifically designate a distinct weather god was a novelty.
While it seems the use of the title Baal to designate a god derived from Hadad was widespread on the Mediterranean coast, this phenomenon is best attested from Ugarit. Baal had the standard responsibilities of a weather deity there, but also acquired the unique role of a protector of sailors. Rather fittingly, in the Baal Cycle his enemy is the personified sea, Yam.
We know there already was a myth dealing with the conflict between a weather god and the sea before in the tradition of Aleppo, but I do not think there’s any real consensus over what it entailed. I’m under the impression that since Dagan was ultimately the supreme deity, and there’s no real indication his relationship with his children was negative, it is not impossible that what unfolded was more similar to the various myths about Ninurta’s exploits, where the hero acts on behalf of his father. This is ultimately pure speculation, though.
Baal was associated neither with Shala nor with Hebat. The latter was only worshiped in Ugarit as the spouse of Teshub, recognized as the god of Aleppo. Baal himself seemingly had no permanent spouse, though Ugaritic literature might point at informal links between him and Anat and/or Ashtart. Ugaritic tradition recognized Dagan as his father, in line with the views popular further inland, though the matter is pretty complicated as the supreme coastal god El could also be referred as his father. This remains a matter of heated debate, and the fact “father” was also effectively a generic honorific does not really help. Multiple nondescript minor goddesses were recognized as Baal’s daughters, though their mother is left unspecified. Pidray is by far the best attested, and a recent discovery indicates she was already worshiped by Amorites in the Old Babylonian period, presumably in relation to the weather god of Aleppo.
Aramaic Ramman
The last distinct name which needs to be briefly discussed here is Ramman(u), which in Mesopotamia earlier on was primarily a title of the god Amurru, who can be best described as a divine redneck stereotype. However, in the first millennium BCE Arameans used to refer to their version of Hadad, worshiped in Damascus arguably effectively as a distinct deity. For more on this topic, which I am actually not very well-versed in, see here.
Other Mesopotamian weather deities
While Adad was obviously THE Mesopotamian weather god, a second figure of analogous character, Wer, was worshiped in the north and west. The origin of his name is uncertain. The first consonant behaves in wildly unpredictable ways which do not really match the phonology of any known language spoken in ancient Mesopotamia which might mean it originates in a hitherto unknown extinct substrate.
Wer is relatively sparsely attested in literature, but in the Old Babylonian version of the Epic of Gilgamesh he is referenced as the master of Humbaba, something unparalleled both in earlier and later versions of Gilgamesh narratives. We never actually encounter him in the surviving fragments, but Enkidu basically hypes him up as if he was an overarching shonen antagonist:

This passage is sourced from Andrew R. George's edition.
There’s a back and forth argument in scholarship over whether Wer/Mer can be identified with Itur-Mer, the tutelary god of Mari. I personally lean towards the view that he cannot, and that the competing view is more plausible. Said alternative relies on the structure of the name, which seems to be theophoric; in the light of this peculiarity it has been argued Itur-Mer was a deified ancestor or culture hero simply bearing a theophoric name invoking Mer. For a detailed discussion of this god see here.
In the Lament for Sumer and Ur, the destructive aspects of the weather are “outsourced” to a deity named Kingaludda, “director of the storm”. He is otherwise pretty much only attested in An = Anum, where he occurs far away from Adad’s section. He gets glossed as “evil god”, ilu lemnu. Another antagonistic figure related to the weather is Bilulu from the myth Inanna and Bilulu.
The rainbow was deified separately from other weather phenomena under the name Manzat. She for the most part had no real connection to Adad and his circle, though it has been noted temples dedicated to Adad and Shala and to Manzat were juxtaposed in Chogha Zanbil in Elam in modern Iran. All three appear there presumably because they were worshiped in heavily Mesopotamia-influenced Susa. I wrote about her extensively in the past, both here and on wikipedia, so while she is one of my favorite minor goddesses I do not think there is a need to say more here.
A mistaken assumption common in older publications and online is that Enlil, the standard head of the pantheon, was a weather god. For his character see this article and this monograph in particular. Another common mistake is interpreting gods poetically compared to storms or fighting using weather phenomena in a single myth or two as weather gods. These are just poetic topoi and there’s no real reason to assert Ninurta, Tishpak or Inanna had much to do with the weather.
51 notes
·
View notes