#united mine workers of america
Photo

“Violence that has cost two lives, listed 14 wounded, and brought National Guard troops to the Taylorville, III., mine area, was heightened by bombing of the home of John Corbo, union miner. Wreckage of the Corbo home is shown above. The family, who were In the home at the time, narrowly escaped injury. Snipers’ shots killed a woman and a man before Illinois troops reached the area.”
- from the North Bay Nugget. January 9, 1933. Page 1.
#taylorville#springfield illinois#mine war#coal miners#coal mining#union politics#union men#strike#strike violence#national guard#united mine workers of america#working class struggle#working class politics#the great depression#illinois history
1 note
·
View note
Text
This American Life
Pacific Grove, California, 10 June 2023. Photo by the Russian Reader
Jose Martinez has lived and worked in the United States since he was 14 years old. Now 67, he drives around the Yakima Valley in Washington state checking on fellow workers.
“When it’s hot, do you have a place to protect yourself from the sun and heat?” he calls out to some workers on the side of an apple orchard on a sunny…

View On WordPress
#Barbie#farmworkers in US#Redneck Army#Starbucks#Starbucks Workers United#Tanya Tuzova#union busting#unionization campaigns in US#United Farm Workers#United Mine Workers of America#West Virginia mine wars
0 notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #14
April 12-19 2024
The Department of Commerce announced a deal with Samsung to help bring advanced semiconductor manufacturing and research and development to Texas. The deal will bring 45 billion dollars of investment to Texas to help build a research center in Taylor Texas and expand Samsung's Austin, Texas, semiconductor facility. The Biden Administration estimates this will create 21,000 new jobs. Since 1990 America has fallen from making nearly 40% of the world's semiconductor to just over 10% in 2020.
The Department of Energy announced it granted New York State $158 million to help support people making their homes more energy efficient. This is the first payment out of a $8.8 billion dollar program with 11 other states having already applied. The program will rebate Americans for improvements on their homes to lower energy usage. Americans could get as much as $8,000 off for installing a heat pump, as well as for improvements in insulation, wiring, and electrical panel. The program is expected to help save Americans $1 billion in electoral costs, and help create 50,000 new jobs.
The Department of Education began the formal process to make President Biden's new Student Loan Debt relief plan a reality. The Department published the first set of draft rules for the program. The rules will face 30 days of public comment before a second draft can be released. The Administration hopes the process can be finished by the Fall to bring debt relief to 30 million Americans, and totally eliminate the debt of 4 million former students. The Administration has already wiped out the debt of 4.3 million borrowers so far.
The Department of Agriculture announced a $1 billion dollar collaboration with USAID to buy American grown foods combat global hunger. Most of the money will go to traditional shelf stable goods distributed by USAID, like wheat, rice, sorghum, lentils, chickpeas, dry peas, vegetable oil, cornmeal, navy beans, pinto beans and kidney beans, while $50 million will go to a pilot program to see if USAID can expand what it normally gives to new products. The food aid will help feed people in Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Haiti, Kenya, Madagascar, Mali, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Yemen.
The Department of the Interior announced it's expanding four national wildlife refuges to protect 1.13 million wildlife habitat. The refuges are in New Mexico, North Carolina, and two in Texas. The Department also signed an order protecting parts of the Placitas area. The land is considered sacred by the Pueblos peoples of the area who have long lobbied for his protection. Security Deb Haaland the first Native American to serve as Interior Secretary and a Pueblo herself signed the order in her native New Mexico.
The Department of Labor announced new work place safety regulations about the safe amount of silica dust mine workers can be exposed to. The dust is known to cause scaring in the lungs often called black lung. It's estimated that the new regulations will save over 1,000 lives a year. The United Mine Workers have long fought for these changes and applauded the Biden Administration's actions.
The Biden Administration announced its progress in closing the racial wealth gap in America. Under President Biden the level of Black Unemployment is the lowest its ever been since it started being tracked in the 1970s, and the gap between white and black unemployment is the smallest its ever been as well. Black wealth is up 60% over where it was in 2019. The share of black owned businesses doubled between 2019 and 2022. New black businesses are being created at the fastest rate in 30 years. The Administration in 2021 Interagency Task Force to combat unfair house appraisals. Black homeowners regularly have their homes undervalued compared to whites who own comparable property. Since the Taskforce started the likelihood of such a gap has dropped by 40% and even disappeared in some states. 2023 represented a record breaking $76.2 billion in federal contracts going to small business owned by members of minority communities. This was 12% of federal contracts and the President aims to make it 15% for 2025.
The EPA announced (just now as I write this) that it plans to add PFAS, known as forever chemicals, to the Superfund law. This would require manufacturers to pay to clean up two PFAS, perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. This move to force manufacturers to cover the costs of PFAS clean up comes after last week's new rule on drinking water which will remove PFAS from the nation's drinking water.
Bonus:
President Biden met a Senior named Bob in Pennsylvania who is personally benefiting from The President's capping the price of insulin for Seniors at $35, and Biden let Bob know about a cap on prosecution drug payments for seniors that will cut Bob's drug bills by more than half.
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#jobs#Economy#student loan debt#Environment#PFAS#politics#US politics#health care
763 notes
·
View notes
Text
Currently rereading Eric Flint's 1632 and reflecting on just how influential Flint was to me and my approach to both praxis and politics as a teenager. I found Flint when I was about thirteen or fourteen, around the time I found Pratchett I think, and he's left an equally wide thumbprint on my soul. Isn't that the most wonderful thing about stories, that people you've never met can help shape our adult selves? Mother of Demons I often recommend for its SFF worldbuilding--Flint built a species with at least four genders, only some of which are reproductive, and associated "normal" sexual orientations, and then proceeded to write in a textually intersex character and queer the hell out of it.
1632, though, is the one where a little West Virginia town in 2000 gets picked up and dropped in the middle of Thuringia, Germany in the eponymous year--right in the middle of the Thirty Years War. The local United Mine Workers of America chapter plays a major role, particularly its head.
As I write this I'm listening to the scene where the little town of Grantville, having admitted after a few days that they are probably not ever going home, is crowded into the high school gymnasium listening to the mayor lay that reality out and suggesting an interim council to help the town set out a sort of constitutional convention so they can work out what on earth they're going to do moving forward--especially since there's a bunch of displaced refugees collecting in the forests nearby. Sensible of them, really; the Americans murdered the shit out of the local soldiers that displaced them, on account of how the shaken mine workers that went out to figure out WTF happened not being super down with suddenly running into a bunch of fuckheads raping the locals and torturing people to find out where their valuables might be. After that, said Americans proceeded to retreat into the town boundaries and gibber quietly to themselves. I would go lurk in their woods, too.
Anyway, the mayor sets up this proposal, everyone agrees, and a CEO who was visiting for his son's wedding at the time steps forward and says: look. I know how to lead, and I'm probably the most qualified person here. I lead a major industry corporation effectively and I did that after my time as a Navy officer. I put myself forward because I'm qualified. Now, we're going to need to circle the wagons to get through the winter, tighten our belts, but we can get through this. We can't support all these refugees, though; we'll have to seal the border so they can't bring disease--they're a drain on our resources we can't afford--
and the UMWA guy, he gets really mad listening to this. There's this Sephardic refugee woman he's real taken with who got swept up in the town first thing, and she's sitting in and listening; he's thinking about throwing her out, thinking about how much she knows about the place they're found in, and he's furious. But he gets a good grip on his anger and he marches up and he says, look. This dude has been here two days and he's already talking about downsizing?! You're going to listen to this CEO talking about cuts, cuts, cuts? Nah. Trying to circle the wagons is probably impossible, it's stupid, and if you think my men and I are going to enforce that, you can fuck off. That proposal is inside out and bass ackwards. We've got about a six mile diameter of Grantville here; how much food do YOU think we're going to grow? How about the soldiers wandering around, do you think we're going to be able to fight armies off on our lonesome? Look at the few refugees we already have in the room, they'll tell you how those armies will treat you! We could do it for a while, the amount of gun nuts here, but so what? We don't have enough people to shoot them! Not if we're going to do anything else to keep us going! We have about six months of stockpiled coal to keep going, and without another source or getting the coal mines working, we're screwed. We have technical strength but we don't have the supplies or resources we would need to maintain it. Those refugees? They're resources. We need people to do the work we will need to keep ourselves. The hell with downsizing; let's grow outwards! Bring people in, give them safety, see what they can bring to the table once they've had a moment! He invokes: send us your tired, your poor!, and the CEO yells in frustration: this isn't America! so he yells back "it will be!"
And of course everyone cheers. I love Flint for many reasons but he is unapologetic about affection for the America of ideals--ideals, he freely admits, that are often honored in the breach rather than the observance, ideals that are messy and flawed, but nevertheless ideals that can work to inspire us to become the best version of ourselves. For Flint, history is as valuable as a source of stories to inspire ourselves as it is a repository of knowledge, and on this I tend to agree with him. We must learn from our moments of shame but equally we must learn from moments that show us how to be our best selves.
It's been twenty three years and the text is now an interesting historical document in its own right, hitting points and rhythms in beats that are sometimes out of place today. It's not perfect. But the novel contains a commitment to joy and to emphasizing the leaps of faith and understanding that regular, everyday people make every day to try and support each other that I routinely try to match in my writing.
Anyway, one of the strengths of the novel, I think, is its gender politics: it's a very ensemble kind of novel, lots of characters, and it's preoccupied with positive masculinity in a lot of ways. There's a lot of these hyper masculine characters--Mike Stearns perhaps more than anyone else--and--and...
... And Flint's characterization of Stearns, as he sketches out who the man is--his pivotal American leader, ex boxer, working class organizer, big man.... well, it lands equally on "he is delighted and astonished to find a local woman who quickly assesses how the cushion of air in tires works," and "he considers who to set up a Jewish refugee in the middle of Germany up with and he thinks to ask the Jewish family he grew up with to host her and her ill father because he thinks she'll be most comfortable there", and "he views people as potential assets rather than potential drains." A younger man asks him for advice on whether to pursue a professional sports career because of the boxing and he says no, you're in the worst place of not being quite good enough and you'll blow out your knees without accomplishing safety. He frames that interaction such that he allows his own experiences to make him vulnerable and invite the younger man to understand when a struggle have worth it.
It's actually a really deft portrayal of intense masculinity that also makes a virtue of a bunch of traits more usually associated with women: empathy, relational sensitivity, the ability to listen. As a blueprint for what a positive masculinity can look like, vs the toxic kind, it's very well done. I think sometimes when we look at gender roles in terms of virtues, and when masculinity is defined in terms of opposition to femininity, people get lost by arguing that virtues assigned to one gender are somehow antithetical to another gender. In fact that's never been the case: virtues are wholly neutral and can appear in any gender. What the gender does is inflect the ways we expect that virtue to appear in terms of individuals' actions within their society.
Gender isn't purely an individual trait, basically; it's a product of our collective associations. Two characters with different genders can display the same virtues and strengths, but we imagine them expressed in different ways according to our cultural expectations around gender. And I just think that's neat.
962 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1833, Parliament finally abolished slavery in the British Caribbean, and the taxpayer payout of £20 million in “compensation” [paid by the government to slave owners] built the material, geophysical (railways, mines, factories), and imperial infrastructures of Britain [...]. Slavery and industrialization were tied by the various afterlives of slavery in the form of indentured and carceral labor that continued to enrich new emergent industrial powers [...]. Enslaved “free” African Americans predominately mined coal in the corporate use of black power or the new “industrial slavery,” [...]. The labor of the coffee - the carceral penance of the rock pile, “breaking rocks out here and keeping on the chain gang” (Nina Simone, Work Song, 1966), laying iron on the railroads - is the carceral future mobilized at plantation’s end (or the “nonevent” of emancipation). [...] [T]he racial circumscription of slavery predates and prepares the material ground for Europe and the Americas in terms of both nation and empire building - and continues to sustain it.
Text by: Kathryn Yusoff. "White Utopia/Black Inferno: Life on a Geologic Spike". e-flux Journal Issue #97. February 2019.
---
When the Haitian Revolution erupted [...], slaveholding regimes around the world grew alarmed. In response to a series of slave rebellions in its own sugar colonies, especially in Jamaica, the British Empire formally abolished slavery in the 1830s. [...] Importing indentured labor from Asia emerged as a potential way to maintain the British Empire’s sugar plantation system. In 1838 John Gladstone, father of future prime minister William E. Gladstone, arranged for the shipment of 396 South Asian workers, bound to five years of indentured labor, to his sugar estates in British Guiana. The experiment [...] inaugurated [...] "a new system of [...] [indentured servitude]," which would endure for nearly a century. [...] Desperate to regain power and authority after the war [and abolition of chattel slavery in the US], Louisiana’s wealthiest planters studied and learned from their Caribbean counterparts. [...] Thousands of Chinese workers landed in Louisiana between 1866 and 1870, recruited from the Caribbean, China and California. [...] When Congress debated excluding the Chinese from the United States in 1882, Rep. Horace F. Page of California argued that the United States could not allow the entry of “millions of cooly slaves and serfs.”
Text by: Moon-Ho Jung. "Making sugar, making 'coolies': Chinese laborers toiled alongside Black workers on 19th-century Louisiana plantations". The Conversation. 13 January 2022.
---
The durability and extensibility of plantations [...] have been tracked most especially in the contemporary United States’ prison archipelago and segregated urban areas [...], [including] “skewed life chances, limited access to health [...], premature death, incarceration [...]”. [...] [In labor arrangements there exists] a moral tie that indefinitely indebts the laborers to their master, [...] the main mechanisms reproducing the plantation system long after the abolition of slavery [...]. [G]enealogies of labor management […] have been traced […] linking different features of plantations to later economic enterprises, such as factories […] or diamond mines […] [,] chartered companies, free ports, dependencies, trusteeships [...].
Text by: Irene Peano, Marta Macedo, and Colette Le Petitcorps. "Introduction: Viewing Plantations at the Intersection of Political Ecologies and Multiple Space-Times". Global Plantations in the Modern World: Sovereignties, Ecologies, Afterlives (edited by Petitcrops, Macedo, and Peano). Published 2023.
---
Louis-Napoleon, still serving in the capacity of president of the [French] republic, threw his weight behind […] the exile of criminals as well as political dissidents. “It seems possible to me,” he declared near the end of 1850, “to render the punishment of hard labor more efficient, more moralizing, less expensive […], by using it to advance French colonization.” [...] Slavery had just been abolished in the French Empire [...]. If slavery were at an end, then the crucial question facing the colony was that of finding an alternative source of labor. During the period of the early penal colony we see this search for new slaves, not only in French Guiana, but also throughout [other European] colonies built on the plantation model.
Text by: Peter Redfield. Space in the Tropics: From Convicts to Rockets in French Guiana. 2000.
---
To control the desperate and the jobless, the authorities passed harsh new laws, a legislative program designed to quell disorder and ensure a pliant workforce for the factories. The Riot Act banned public disorder; the Combination Act made trade unions illegal; the Workhouse Act forced the poor to work; the Vagrancy Act turned joblessness into a crime. Eventually, over 220 offences could attract capital punishment - or, indeed, transportation. […] [C]onvict transportation - a system in which prisoners toiled without pay under military discipline - replicated many of the worst cruelties of slavery. […] Middle-class anti-slavery activists expressed little sympathy for Britain’s ragged and desperate, holding […] [them] responsible for their own misery. The men and women of London’s slums weren’t slaves. They were free individuals - and if they chose criminality, […] they brought their punishment on themselves. That was how Phillip [commander of the British First Fleet settlement in Australia] could decry chattel slavery while simultaneously relying on unfree labour from convicts. The experience of John Moseley, one of the eleven people of colour on the First Fleet, illustrates how, in the Australian settlement, a rhetoric of liberty accompanied a new kind of bondage. [Moseley was Black and had been a slave at a plantation in America before escaping to Britain, where he was charged with a crime and shipped to do convict labor in Australia.] […] The eventual commutation of a capital sentence to transportation meant that armed guards marched a black ex-slave, chained once more by the neck and ankles, to the Scarborough, on which he sailed to New South Wales. […] For John Moseley, the “free land” of New South Wales brought only a replication of that captivity he’d endured in Virginia. His experience was not unique. […] [T]hroughout the settlement, the old strode in, disguised as the new. [...] In the context of that widespread enthusiasm [in Australia] for the [American] South (the welcome extended to the Confederate ship Shenandoah in Melbourne in 1865 led one of its officers to conclude “the heart of colonial Britain was in our cause”), Queenslanders dreamed of building a “second Louisiana”. [...] The men did not merely adopt a lifestyle associated with New World slavery. They also relied on its techniques and its personnel. [...] Hope, for instance, acquired his sugar plants from the old slaver Thomas Scott. He hired supervisors from Jamaica and Barbados, looking for those with experience driving plantation slaves. [...] The Royal Navy’s Commander George Palmer described Lewin’s vessels as “fitted up precisely like an African slaver [...]".
Text by: Jeff Sparrow. “Friday essay: a slave state - how blackbirding in colonial Australia created a legacy of racism.” The Conversation. 4 August 2022.
#abolition#tidalectics#multispecies#ecology#intimacies of four continents#ecologies#confinement mobility borders escape etc#homeless housing precarity etc#plantation afterlives#archipelagic thinking
179 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kamala Harris’s ‘Joyful’ War on Entrepreneurs
When Democrats talk about boosting the middle class, what they mean is government employees.
By Allysia Finley Wall Street Journal
Americans who tuned in to Kamala Harris’s coronation last week heard from plenty of celebrities, labor leaders and politicians. Missing from the “joyous” celebration, however, were entrepreneurs who generate middle-class jobs.
No surprise. Cheered on by the crowd, Democrats took turns whacking “oligarchs” and “corporate monopolists.” By the time Ms. Harris took the stage, the pinatas’ pickings had been splattered around. This is what Democrats plan to do if they win: destroy wealth creators so they can spread the booty among their own.
Corporate greed is “the one true enemy,” United Auto Workers President Shawn Fain proclaimed. Vermont Sen. Bernie Sanders insisted the party “must take on Big Pharma, Big Oil, Big Ag, Big Tech, and all the other corporate monopolists whose greed is denying progress for working people.” Pennsylvania Sen. Bob Casey railed against “greedflation” and accused corporations of “extorting families.”
Barack Obama lambasted Donald Trump and his “well-heeled donors.” “For them, one group’s gains is necessarily another group’s loss,” Mr. Obama said. “For them, freedom means that the powerful can do pretty much what they please, whether it’s fire workers trying to organize a union or put poison in our rivers or avoid paying taxes like everybody else has to do.”
Democrats treat wealth as a zero-sum game, and so Mr. Obama’s straw men are rich. They get richer by making everyone else poorer—and taking away from the well-off is the only way to enhance the lives of the poor and middle class. Hence, the left’s plans to raise taxes on “billionaires” and businesses to finance more welfare.
It isn’t enough that the top 1% of earners already pay 45.8% of federal income tax, which funds government services and welfare for the bottom half. As for poisoning rivers, perhaps Mr. Obama forgot that his own Environmental Protection Agency caused the 2015 Gold King Mine disaster, which spilled toxic waste into Colorado’s Animas River.
Quoting Abraham Lincoln, the former president invoked “the better angels of our nature” even as he appealed to America’s darker angels. His speech brought to mind a recent homily by my local parish priest about the dangers of class warfare and envy, one of the seven deadly sins.
Success, the priest explained, isn’t a zero-sum game. When a businessman succeeds, he creates jobs that help the poor. Envying and tearing down the successful makes everyone poorer. Rather than plunder the wealthy, society should celebrate success and try to help everyone prosper.
Democrats derisively refer to such ideas as “trickle-down economics.” They denounce and diminish business success, and claim the wealthy have profited from greed and government support. Who can forget Mr. Obama’s line in 2012 that “if you’ve got a business, you didn’t build that”?
Rather than try to make it easier for businesses to succeed—say, by reducing taxes or easing regulations—Democrats want to do the opposite. They call for “leveling the playing field” and “growing the middle class out,” euphemisms for taxing success so government can hand out money. But government doesn’t create wealth. People do.
While business success isn’t zero-sum, government growth can be. Its expansion makes it more difficult for business to thrive. The result is fewer jobs, lower wages and less tax revenue, which finances essential public services such as law enforcement and the “safety net” for the indigent.
Mr. Trump’s appeal in 2016 partly stemmed from slow economic growth during Mr. Obama’s presidency. The Republican promised to make all Americans richer by liberating businesses from government’s shackles. Mr. Trump’s deregulation and tax cuts worked: Average real wages increased nearly 70% faster during his first three years than during Mr. Obama’s presidency.
Yet most Americans have become poorer under Mr. Biden, as government spending has fueled inflation, which has eroded wages. Job growth has become increasingly concentrated in sectors that depend on government spending. When Democrats talk about boosting the middle class, they mean the class of government workers.
Government, education, healthcare and social assistance account for more than 60% of the new jobs added in the last year. In the 17 states where Democrats boast a “trifecta”—control of the governorship and both legislative chambers—the share is 98%. In the 23 states with Republican trifectas, it’s 47%.
Likewise, average wage growth since the start of the pandemic has been lower in high-tax states such as Illinois (13.6%), New York (14.4%) and California (17.2%) than in low-tax Florida (22.5%), Texas (23.3%) and South Dakota (26.9%). If middle-class Americans want to get richer, they ought to move to Miami, Dallas or Sioux Falls.
“As long as we look to legislation to cure poverty, or to abolish special privilege,” Henry Ford once observed, “we are going to see poverty spread and special privilege grow.” That’s the joyous future Americans can expect during a Harris presidency.
Appeared in the August 26, 2024, print edition as 'Kamala Harris’s ‘Joyful’ War on Entrepreneurs'.
#wall street journal#kamala harris#tim walz#obama#schumer#pelosi#AOC#Democrats#Biden#trump 2024#trump#president trump#repost#america first#americans first#america#donald trump#ivanka
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
okay
For decades, nuclear power has been the largest source of clean energy in the United States, accounting for 19% of total energy produced last year
false. first sentence. off to a great start. you may notice this is a 2022 chart but i can tell you the only new reactors started since then are vogtle 3 and 4 (you may notice that's not a new power plant but new reactors at an existing plant), years late and $17b over budget, vogtle as a whole produces 1.1gwh, we use about 29 million annually. point being: it has not risen to 19%, the last reactor since vogtle was watts bar in 2016 and since then we've decommissioned 14 of them
The industry directly employs nearly 60,000 workers in good paying jobs
weirdly low estimate, almost by half
maintains these jobs for decades
"maintains" is doing a lot of work here, does that include toxic exposure payouts? because they are still fighting pretty hard to get those in the world's first nuclear contamination site, hanford
and supports hundreds of thousands of other workers
✅ true! 475,000 according to the NEI link above
In the midst of transformational changes taking place throughout the U.S. energy system
sure
the Biden-Harris Administration is continuing to build on President Biden’s unprecedented goal of a carbon free electricity sector by 2035
have they developed carbon free cement yet? (yes.) at scale? (no.) are we just not counting construction emissions because they're one-time emissions investments or how does this work exactly, i would love to know because i think we're also not counting emissions from waste transport to longterm storage because we haven't started doing that. anyway they've built a train for it even though we don't have a storage site so that's umm. that's uhh. fine i'm sure
while also ensuring that consumers across the country have access to affordable, reliable electric power
i guess you can still say "across the country" if you exclude texas as an outlier
and creating good-paying clean energy jobs.
i guess you can still call them good paying clean energy jobs if everybody who mines and refines the uranium dies of cancer because you just pulled out of the largest disarmament program in history due to it being geopolitically inadmissible (for russia... to continue... selling us the uranium from decommissioning...? i'm still trying to figure out the optics of that one but anyway as i have previously stated we didn't actually stop buying it in cases where it's "liable to cause supply chain issues")
Alongside renewable power sources like wind and solar, a new generation of nuclear reactors is now capturing the attention of a wide range of stakeholders
weird way to say that
for nuclear energy’s ability to produce clean, reliable energy and meet the needs of a fast-growing economy, driven by President Biden’s Investing in America agenda and manufacturing boom.
this is a carrier sentence to inject the president's name, but i would like to question which sectors of the growing economy are driving the most energy demand because i'm sure there are no nasty truths being elided there (it's computing)
The Administration recognizes that decarbonizing our power system, which accounts for a quarter of all the nation’s greenhouse gas emissions, represents a pivotal challenge requiring all the expertise and ingenuity our nation can deliver.
it's time once again for... the energy flow sankey chart! the reason the power system accounts for a quarter of greenhouse gas emissions is in no small part because 67% of it is lost to waste heat. has the nation's expertise and ingenuity started working on that yet

The Biden-Harris Administration is today hosting a White House Summit on Domestic Nuclear Deployment, highlighting the collective progress being made from across the public and private sectors
oh boy! a summit! talking about it is the same as doing it
Under President Biden’s leadership, the Administration has taken a number of actions to strengthen our nation’s energy and economic security by reducing – and putting us on the path to eliminating – our reliance on Russian uranium for civil nuclear power and building a new supply chain for nuclear fuel
gosh, i got ahead of myself and already criticized both of those things
including: signing on to last year’s multi-country declaration at COP28 to triple nuclear energy capacity globally by 2050
everybody criticized that
developing new reactor designs
which ones, the bill gates project that just got cancelled because utilities pulled out (edit: that's nuscale, the bill gates project is terrapower), the rolls royce submarine, or the one that just got regulatory approval (edit: this is also nuscale)
extending the service lives of existing nuclear reactors
yep! you sure showed the embrittlement at diablo canyon by doing nothing about it
and growing the momentum behind new deployments
nonsense clause, but it has this really ominous undercurrent due to its vagueness
Recognizing the importance of both the existing U.S. nuclear fleet and continued build out of large nuclear power plants, the U.S. is also taking steps to mitigate project risks associated with large nuclear builds and position U.S. industry to support an aggressive deployment target.
this one is not nonsense but they can't just out and out say "we are deregulating the industry because opening the process for public comment is most often the thing that slows it down" because then somebody might realize they're bulldozing ahead no matter what any constituent says, does, or actually wants
To help drive reactor deployment while ensuring ratepayers and project stakeholders are better protected, theAdministration is announcing today the creation of a Nuclear Power Project Management and Delivery working group that will draw on leading experts from across the nuclear and megaproject construction industry to help identify opportunities to proactively mitigate sources of cost and schedule overrun risk
i'm sure a revolving door working group packed with industry insiders can solve this without compromising their commitment to the profit motive, not that it particularly matters since the cost is passed on to the consumer in the form of fees on the electric bill
The United States Army is also announcing that it will soon release a Request for Information to inform a deployment program for advanced reactors to power multiple Army sites in the United States
good god... that is a fresh nightmare i did not see coming
Additionally, the Department of Energy released today a new primer highlighting the expected enhanced safety of advanced nuclear reactors
"expected" really serves to demonstrate several points i've made
i'm going to stop going line by line here because i know this is already too boring and long for anyone to read this far, unless anybody wants to know what i think about parts 50, 52, and 53 of the NRC licensing guidance -- which many of you have very clearly stated over the years that you don't -- and while i do want to acknowledge that it does go into more detail and even answer some of the questions i raised (vogtle comes up, diablo canyon comes up, a list of which SMR designs is given, or at least a list of the companies responsible for them),
what i would like to focus on is one conspicuous absence:
the reason we need a new fleet of reactors is because they are an essential part of the bomb production chain. they are the beginning of the refinement process, and we cannot carry out the plan (already underway) to replace the minutemen missiles currently in silos with sentinel missiles without significant new construction. we cannot start the president's desired wars with russia and china without the new sentinels. he's not going to be the one to carry this out, he's ensuring whoever is his successor in about 2030 or more likely 2040 will be armed to do so. limited amount of time left to prevent that
93 notes
·
View notes
Photo
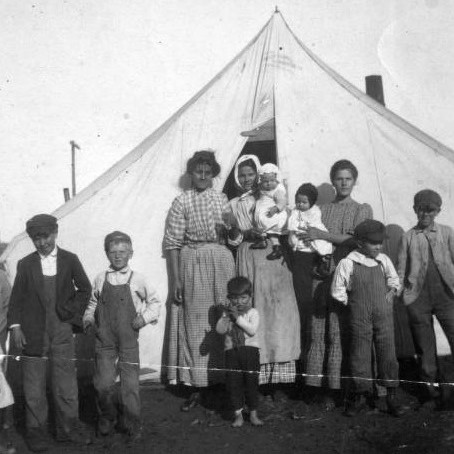

On this day, 20 April 1914, the Ludlow massacre took place when US troops opened fire with machine guns on a camp of striking miners and their families in Ludlow, Colorado. 12,000 miners had gone out on strike the previous September against the Rockefeller family-owned Colorado Fuel and Iron Corporation (CF&I) following the killing of an activist of the United Mine Workers of America (UMWA). They then demanded better safety at work, and to be paid in money, instead of company scrip (tokens which could only be redeemed in the company store). The Rockefellers evicted the striking miners and their families from their homes, and so they set up "tent cities" to live in collectively, which miners' wives helped run. Company thugs harassed strikers, and occasionally drove by camps riddling them with machine-gun fire, killing and injuring workers and their children. Eventually the national guard was ordered to evict all the strike encampments, and the morning of April 20 they attacked the largest camp in Ludlow. They opened fire with machine guns on the tents of the workers and their families, who then returned fire. The main organiser of the camp, Louis Tikas, went to visit the officer in charge of the national guard to arrange a truce. But he was beaten to the ground then shot repeatedly in the back, killing him. That night, troops entered the camp and set fire to it, killing 11 children and two women, in addition to 13 other people who were killed in the fighting. The youngest victim was Elvira Valdez, aged just 3 months. Protests against the massacre broke out across the country, but the workers at CF&I were defeated, and many of them were subsequently sacked and replaced with non-union miners. Over the course of the strike 66 people were killed, but no guardsmen or company thugs were prosecuted. More information, sources and map: https://stories.workingclasshistory.com/article/9243/ludlow-massacre Pictured: a striker's family in front of their tent https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=612124227627463&set=a.602588028581083&type=3
385 notes
·
View notes
Text
West Virginia miners, for various reasons, were slower to unionize than their counterparts in other states. This was true not only in comparison with northern Appalachian miners in the states of Pennsylvania, Illinois, Ohio, and Indiana (labeled the Central Competitive Field), but also in comparison with those in Alabama and other parts of southern Appalachia. They gave only partial support at best to national strikes in 1894, 1897, and 1902–1903. However, as many analysts have noted, they were eventually to become the most fervent of union supporters. There were several interrelated reasons for these two characteristics. First, a larger percentage of West Virginia miners in the early 1930s lived in small, isolated towns (93% in towns with fewer than twenty-five hundred residents) and in company housing (75%) than in other coal mining states. Second, fear of the union led coal miner associations to hire hundreds of Baldwin-Felts guards and "detectives," so that by 1910, there was not a coal town in West Virginia in which they were not stationed. Whereas in earlier periods, union organizers moved around relatively freely in West Virginia, by this time not only union organizers but sympathetic miners were commonly harassed, brutalized, and murdered.
The growing militancy and solidarity of West Virginia miners was on full display when, in April 1912, Paint Creek and Cabin Creek miners struck. It was objective conditions (unsafe work, cheating on pay, company control, and sheer brutality), not southern or mountaineer culture, that led them to become a model of solidarity (a class solidarity so paradigmatic that it stimulated IWW (Industrial Workers of the World or Wobblies) songwriter Ralph Chapin to write the union anthem "Solidarity Forever". The mine owners were determined to crush the 1912 strike with force. Baldwin-Felts guards "built iron and concrete forts that they equipped with machine guns throughout the strike districts," evicting miners from company housing and destroying their furniture. They then began to murder striking miners singly and in groups. In the most celebrated instance, they drove an armored train, dubbed the "Bull Moose Special," through the mining districts, machine-gunning strikers and their families in tent colonies near the tracks. The miners, to be sure, fought back in kind, shooting mine guards and detectives with six machine guns and one thousand high-powered rifles supplied by the national union. Women in the company towns were equally combative, engaging in gun battles alongside the men. It was women who prevented the "Bull Moose Special" from returning by tearing up the railroad tracks and who often attacked strikebreakers, driving them away. According to Wobbly Ralph Chapin, this was the appeal of famed United Mine Workers of America (UMWA) organizer Mother Jones, "who might have been any coal miner’s wife ablaze with righteous fury". Mineworker families not only fought, but in the tent colonies sang and danced, creating a new union solidarity culture, making the union "an intense, emotional unity".
The Paint Creek/Cabin Creek strike lasted a year and was never broken, despite the declaration of martial law and the arrest and jailing, without trial, of hundreds of miners, while the mine operator and gunmen who drove the "Bull Moose Special" were never even questioned, much less indicted. Rank-and-file coal miners and their local leaders rejected a settlement brokered by district officials, UMWA national president John White, and Governor Henry Hatfield, continuing to strike until all their demands were met. They then demanded the replacement of all their district leaders, finally forcing the national union to call elections.
Michael Goldfield, The Southern Key: Class, Race, and Radicalism in the 1930s and 1940s
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
Alfred, what is your favorite thing each of your roommates has brought over to your country? And to Ireland, Romano, and Lithuania, what is your favorite thing about America? (the country not Alfred.)



As for the others...


Alfred can afford to be a little more idealistic, but that's just his way.
**Historical Note: Though immigrants from each of these groups contributed in a variety of ways, these are some of the ways in which they contributed most prominently.
Irish Americans were incredibly active in the entertainment industry, especially in music. Irish Americans were very prominent in vaudeville, and eventually Broadway. However, this was due to a pre-existing music tradition that stemmed from Irish immigrants bringing over their folk music. Many Irish airs became popular parlor songs in the UK, America, and Canada. The strong Irish presence in the Union Army during the Civil War also further popularized folk songs such as "McLeod's Reel." Though the Potato Famine caused the decline of traditional music in Ireland, many songs and playing styles were preserved by Irish Americans in the United States and later carried back to Ireland in the 1890s-1920s when recordings began to become accessible. These recordings were also among the first to be sold in the United States.
Italian American cuisine is one of the most influential marks left by the community, especially from Southern Italians. Many innovations in Italian cuisine occurred in the United States, and many Italian immigrants became successful restauranteurs. This explosion occurred due to previously inaccessible foods suddenly being affordable in the United States, such as meat and imported cheese. Today, Italian American food is still one of the most popular cuisine choices in the United States.
Though all of the groups mentioned had involvement in labor union activity, Lithuanian Americans were particularly prominent activists. One of the most famous of these activists was Emma Goldman, but there were several others who formed the United Mine Workers and the Amalgated Clothing Workers Union. Sydney Hillman, a Lithuanian immigrant, was the head of the Amalgated Clothing Workers Union from the 1910s to the 1940s. Even in fiction, in Upton Sinclair's The Jungle, Lithuanian workers and their union activity are the central focus. Lithuanian Americans' strongest import really seemed to be their activism!
For all of these groups though, one big part of what made American so attractive was the comparative plenty to what they had in their countries of origin. Though many immigrants worked long, difficult manual labor jobs, they were able to afford new goods in the United States that had previously been unimaginable. This is mostly due to the United States' ability to produce goods en masse, which made them cheaper. Furthermore, in Ireland and Southern Italy, land ownership had become virtually impossible (through landlords hiking rent prices in Ireland or land distribution after the Risorgimento in Italy). Even if their positions were not enviable in the United States, from a financial standpoint, their salaries and the resources available put them in a slightly better position.
#hetalia#historical hetalia#hws america#hws romano#hws lithuania#hws ireland#nyo!ireland#immigrant trio#immigrant squad#hetalia ask blog#ask#last seminar my paper was on how the irish diaspora changed and preserved traditional music#so if i pop off a lot about that in the historical notes that is why (it is a roman empire in my brain of sorts)#this was a fun ask though! sorry for taking so long to answer!!
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Vice President Kamala Harris’s selection of Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz as her running mate was met with enthusiasm from Democrats across the party, including from the party’s left wing. A big part of this is Walz’s solidly pro-labor governing record and his appeal to working-class voters, which was on display on Wednesday when he spoke at the Democratic National Convention in Chicago.
Although his championing of working Americans’ jobs, pay, and rights has obvious and important domestic appeal, it also has a potentially significant implication for foreign policy under a Harris-Walz administration.
One of the Biden administration’s most important projects, sometimes summarized as “post-neoliberalism,” has been the move away from unfettered so-called free trade—the pro-corporate theology that dominated the past few decades of economic policymaking. The government is now fully back in the business of investing in U.S. workers and communities. (A 2023 report tracking this progress was published by the Roosevelt Institute, a think tank helping to drive this transformation.)
As vice president, Harris has played a key role in this pivotal project, and selecting one of the most pro-worker governors in the country as a running mate signals that she is all-in on this shift. This is great news, because not only is this post-neoliberal, pro-worker agenda likely where the election will be won, but it is also central to the larger goal of defending global democracy.
Conservatives have noticed. “By picking Tim Walz as her running mate, Harris has gone a long way toward bolstering her left-populist flank and neutralizing [Republican vice presidential candidate J.D.] Vance’s potential appeal,” wrote Sohrab Ahmari, the founder and editor of the conservative nationalist magazine Compact and a leading voice of the populist new right, when the pick was announced. “Walz can’t be framed as a neoliberal Democrat in the Clinton-Obama mold.”
Vance’s own speech at the Republican National Convention in July was billed as foreign policy-focused, but it was really all about how U.S. elites had failed the country’s struggling workers. Playing up his family roots in a small Ohio town—“a place that had been cast aside and forgotten by America’s ruling class in Washington”—Vance attacked U.S. President Joe Biden for his past support of the North American Free Trade Agreement, for China’s entry into the World Trade Organization, and for “the disastrous invasion of Iraq.”
“At each step of the way, in small towns like mine in Ohio, or next door in Pennsylvania or Michigan, in other states across our country, jobs were sent overseas, and our children were sent to war,” Vance said. While larded over with common right-wing tropes and xenophobic invective, the speech sounded like a road map for how the Republican Party intends to capture the working class.
In its own way, Vance’s speech was a darker, divisive version of a more affirmative and unifying address that U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan gave in April 2023, which laid out the Biden administration’s global economic agenda. Confronting the flawed assumptions that dominated U.S. statecraft in the past 40 years—“that markets always allocate capital productively and efficiently”—Sullivan rejected the philosophy that “championed tax cutting and deregulation, privatization over public action, and trade liberalization as an end in itself.”
Like Vance a year later, Sullivan acknowledged that elites had failed working people in the United States. He said that not only had an economic integration approach failed as a geopolitical strategy—not stopping China from military expansion or deterring Russia from invading its neighbors—but it also radically increased economic and political inequality, both globally and domestically. The speech marked an important step forward in Washington’s thinking.
However, much less noticed was a speech that Sullivan gave a week later at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, which showed how the Biden administration still had one foot in the previous era. In that speech, Sullivan laid out the administration’s plan to maintain U.S. hegemony in the Middle East by buttressing relationships with various repressive, undemocratic regimes and stitching together an alliance intended both to contain Iran and box China out of the region.
I noted to administration colleagues at the time that the second speech was a formula for squandering the opportunities of the first. While the Biden administration had discarded some of the flawed foreign-policy assumptions of the past, it continued to hold fast to the idea that Washington can purchase security and prosperity for U.S. workers by exporting insecurity and repression to others, whether in the Middle East, China, or anywhere else. The past 10 months of catastrophic war in Gaza should have discredited that notion, if it wasn’t already.
The United States can build a more equitable global order, or it can frantically try to maintain global primacy, but it can’t do both. The Harris-Walz team has an important task and a big opportunity to diminish this contradiction and complete this transformation. Just as the neoliberal era proved that giving carte blanche to big corporations—whether they’re car companies or weapons manufacturers—is not a means for achieving broad economic progress or security, the past 20 years of the “war on terror” showed that a heavily militarized foreign policy feeds global insecurity and shreds the fabric of international norms.
As outlined by Trump and Vance, the Republican vision is essentially zero-sum: The United States and its workers only win by others losing, and vice versa. The Harris-Walz team can offer a vision of contrasting solidarity, which doesn’t seek to build political consensus by vilifying the foreign enemy of the moment but rather seeks ways to uplifts workers and their communities in every country.
The U.S. public needs to hear more about how diplomacy and cooperation—including with China, can provide other benefits for Americans, as evidenced recently when China imposed new controls on fentanyl precursor chemicals—and about how the issue of irregular migration, which has been a driving force in far-right populism, can only be addressed by improving conditions and reducing violence in the home countries of those migrants—a shared struggle that the labor movement understands and embraces.
A real pro-worker foreign policy doesn’t pit the security and prosperity of Americans against workers in other countries but recognizes that our security and prosperity are bound together. We saw the outlines of that in the speech from Walz, the good neighbor and the inspiring coach, on Wednesday. That is the winning global vision that he and Harris should embrace.
19 notes
·
View notes
Note
is lobbying just basically legalized bribing, or is there any other difference?
The difficulty is that lobbying is simultaneously "legalized bribery" and "influence peddling," and the core of the First Amendment's guarantee of "the right of the people...to petition the Government for a redress of grievances."
Whether it's done by an environmental group trying to preserve endangered species or a deeply corrupt corporation that wants to strip-mine public lands for pennies on the dollar while poisoning the planet, or by a civil rights group trying to achieve equal rights or a hate group trying to legalize oppression of minorities, it's all lobbying.
Now, professionalized lobbying is actually a fairly recent phenomenon. Back in the 19th century, wealthy elites simply just bought elected officials or entire branches of government outright, but during the Progressive Era this was uncovered by muck-raking journalists and led to a lot of people going to jail, so something had to take its place - and that was lobbying.

Even as late as 1945, there were barely 400 lobbying groups in the U.S compared to 17,000 today. The cause of the explosion of lobbying as an industry was a combination of the post-war expansion of the U.S government and changes to campaign finance law in the wake of Watergate. The Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) sought to regulate campaign spending and campaign finance in response to perceived corruption in Federal elections, and was further strengthened by major amendments in 1974 that set hard limits on contributions and spending and created the Federal Elections Commission to enforce FECA.
The Supreme Court, which had begun its slide to the right thanks to LBJ massively fumbling the ball with his Supreme Court nominations and letting Nixon get a bunch of Justices on the Court, struck down a lot of those limits in Buckley v. Valeo in 1976 - which started us down the road to Citizens United. Corporate lobbies very quickly realized that they could expand their influence enormously by acting as the middle-men between corporate cash and elected officials, which now meant that they could wield enormous carrots and sticks to get elected officials to comply with their wishes.

Now, I think there will always be problems with lobbying that come down to the issue of concentrated vs. diffuse interests. There are all kinds of political issues where the majority of the people are on one side of a debate, but where they aren't particularly aware of or engaged with that debate, and even though they have a stake in the outcome, it's rather vague and abstract not something they care about very much. But a lobbying group for a particular "special interest" that is on the other side of that debate and is very aware and engaged and cares about the outcome very much because they stand to gain or lose a lot of money from the outcome. So that lobbying group, which represents a minority position and should lose in the democratic process, will invest the necessary resources in order to win.
The only way to fight this, sadly, is for social movements to be just as organized as lobbyists. For the longest time, it was the labor movement that acted as the "countervailing power" in American politics, because they had the manpower and the money to effectively lobby the Federal government not just on behalf of unions but also on behalf of low-wage workers or racial minorities or consumers and so forth. The problem is that the labor movement doesn't really have that manpower and money any more, but nothing has really replaced it in American politics, in no small part because the left is not immune to America's instinctive hatred of politics and institutions.
And yes, the other major thing that we could do to fight "legalized bribery" is to break up the nexus between campaign finance and lobbying, but in order to do that, we'd have to overrule about fifty years of Supreme Court precedents, and that's not going to happen without the Democratic Party successfully taking back control of the Supreme Court.
#u.s politics#u.s history#political history#political science#lobbying#political economy#labor history#campaign finance
53 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! I had this thought the other day and I just wanted to share. I know you sometimes worry about making a character who is too Mary Sue but I just wanted to say that for an Indigenous woman in a male dominated field in 1940s America, that’s probably exactly what Lu would try to be. Like she wouldn’t have the luxury of getting to be brash or of getting to push buttons/be mildly irritating and still know that at the end of the day, she could do her job and be well liked and respected. The opposite actually, she’d probably have to try so so so hard to be perfect just to be on the same level as others. So I don’t feel that it’s at all unrealistic that she might seem “perfect” because she’s demeure and respectful of authority and a very hard worker, I think those are just things that she’d have to be. And of COURSE she’s extremely intelligent and competent, she would have to be!
Also, this is in no way a dig at any of the other OCs! Yes I did say some things that are specific to Maureen (not at all in a hateful way though I promise) and I’m not gonna lie and say that I didn’t, I just wanted to explain that I don’t think that behaviour would fly if it came from Lu, let alone allow her to receive promotions, and that’s why it makes sense that she’s NOT that person. I’m not saying that all the women didn’t have struggles because just as women, they obviously did, but the experience wouldn’t be identical for Lu. And I know you’ve acknowledged that several times, I more so just wanted to say this to try to articulate that I don’t think you should worry about her being too Mary Sue!
Starting off the day with this lovely encouragement and extremely hot take! Nonnie you’re on fire. 🔥
This was a debate I had with myself when crafting both Sanchez and Lu. And making them so very different on the surface. And why I chose to make Lu as she is beyond her original nature being sweet.
It’s a tiny pet peeve of mine in a period show or story when there is a constant and repeated effort to show a WOC being loud and brash and girl boss to the max and yet it has no ramifications in her male, white, no nonsense and very precarious field. Not that I don’t like or support of think there were WOC Girlbosses back then😂 but I do know they would unfairly be the first on the chopping block for demotion or washing out. Thats how it was. Unfair but real. So who ends up slipping through multiple gauntlets of discrimination? The ones like Lu, and that by the skin of her teeth and keeping a tight lid on a lot of injustice I’m sure she felt despite her mild outward manner. In other words -all the points you made above.
Sanchez on the other hand came from an entirely Mexican unit, she wasn’t an oddity alone, she was in good company with other Mexicans folded into the Air Force and kept apart (as the real Aztec Eagles were) and so she wasn’t been trying to integrate before. Her bearing is different. Since we’ve known her she’s lost and separated from that and her behavior as a result makes sense, I hope, as to why it’s not as meek as Smith’s.
Anyway, a ramble tacked onto you’re succinct and lovely take, don’t mine me
Xo
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Happy birthday, John L. Lewis! (February 12, 1880)
A founder of the Congress of Industrial Organizations and a longtime leader of the United Mine Workers of America, John L. Lewis looms large in the history of American organized labor. Lewis was born in a company town in Iowa built around a coal mine. He became a miner after high school and quickly became involved with the union. Lewis was a skilled organizer, working to build union power throughout the Midwest and Steel Belt. He became President of the UMWA in 1919, and ran a tight ship for decades thereafter. An industrial unionist, Lewis broke from the American Federation of Labor in 1938, with the CIO forming instead to organize America's industrial unions under one banner. Lewis' support helped usher Franklin Roosevelt into office, although Lewis' isolationism led him to sever ties with Roosevelt. During World War II, Lewis opposed the no-strike pledge of organized labor, leading a coal strike in 1943. After the war, he opposed the Taft-Hartley Act and its mandatory anti-communist pledges. He led the UMWA until 1960, leading many strikes and winning many concessions for mineworkers. He died in 1969.
"The workers of the nation were tired of waiting for corporate industry to right their economic wrongs, to alleviate their social agony and to grant them their political rights. Despairing of fair treatment, they resolved to do something for themselves."
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

The dark-haired girl on the right with the impish smile, her name was Eddie Lou, she was about 8 years old when this photo was taken in 1909. The picture was taken at the Tifton Cotton Mill, Tifton, Georgia. The girls worked there.
The photograph was taken by Lewis Hine, who visited factories such as this mill and took photographs of the children who worked there as evidence for the National Child Labor Committee (NCLC).
In another part of the country, Mary Harris Jones, also known as "Mother Jones", led a march of children from Philadelphia to New York in what would be known as the March of the Mill Children, a three-week trek by striking child and adult textile workers on July 7, 1903.
Children had been forced to work in coal mines and mills, when their fathers were killed or injured, unable to support the families. As a result, many children suffered stunted growth and were injured, maimed. Mother Jones described the children, "some with their hands off, some with the thumb missing, some with their fingers off at the knuckle. They were stooped things, round shouldered and skinny. Many of them were not over ten years of age, the state law prohibited their working before they were twelve years of age."
“Since 2000, for nearly two decades, the world had been making steady progress in reducing child labour,” according to the United Nations. “But over the past few years, conflicts, crises and the COVID-19 pandemic, have plunged more families into poverty – and forced millions more children into child labour. Economic growth has not been sufficient, nor inclusive enough, to relieve the pressure that too many families and communities feel and that makes them resort to child labour. Today, 160 million children are still engaged in child labour. That is almost one in ten children worldwide.”
This is an update of a series of stories that have been posted for Labor Day. You can find those stories in the Peace Page archive or Google the information on your own to find out more.
~~~~~
“Over 100 years ago, the National Child Labor Committee used photos of children doing industrial work to demand change in America. Several states adopted child labor laws, and after much debate and several setbacks, the Fair Labor Standards Act became law in 1938. Its protections included the nation’s foundational child labor laws, including restrictions on the age of workers and hours they can toil,” wrote Michael Lazzeri, regional administrator of the U.S. Department of Labor’s Wage and Hour Division in Chicago
Max McCoy of the the Kansas Reflector wrote today on September 3, 2023:
“After more than a century of progress, you might think child labor is a thing of the past, something we condemn other countries for but that we don’t need to worry about here. Tragically, that shadow army of workers is still with us, and many of those workers are children. These underage exploited are often immigrants . . .”
“In February of this year, a cleaning company was fined $1.5 million for employing children ages 13 to 17 at meatpacking plants in eight states. The firm, Packers Sanitations Services Inc., was the target of a federal Department of Labor investigation that found 102 children working illegally, including 26 at the Cargill meatpacking plant at Dodge City.
“Appallingly, many states are now racing to loosen — not tighten — child labor laws.
“Arkansas, for example, in March did away with the requirement that the state’s Division of Labor had to give permission or verify the age of children under 16 to be employed. Although those under 14 still cannot be employed, the ending of age verification requirements is an invitation to child labor abuses.
“Other states are making similar moves.
“Iowa, for example, has made it legal for teenagers to work in meatpacking plants and children as young as 16 to bartend. New Jersey and New Hampshire have also lowered ages for some types of work. The argument goes that work builds character and that overly restrictive laws prevent young people from fully developing their capacity to earn a living.
“But such arguments stink like the stuff you find on a slaughterhouse floor.”
~~~~~
"In the early 1900s, Hine traveled across the United States to photograph preteen boys descending into dangerous mines, shoeless 7-year-olds selling newspapers on the street and 4-year-olds toiling on tobacco farms. Though the country had unions to protect laborers at that time — and Labor Day, a federal holiday to honor them — child labor was widespread and widely accepted. The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that around the turn of the century, at least 18 percent of children between the ages of 10 and 15 were employed," according to the Washington Post.
Mother Jones would say after the march, "I held up their mutilated hands and showed them to the crowd and made the statement that Philadelphia's mansions were built on the broken bones, the quivering hearts and drooping heads of these children. That their little lives went out to make wealth for others. That neither state or city officials paid any attention to these wrongs. That they did not care that these children were to be the future citizens of the nation."
Many industries hid the fact that they employed children. They took advantage of poor families, such as Eddie Lou's family. Eddie Lou's father had died and left her mother with 11 children and no income. Her mother was forced to work at the cotton mill for $4.50 a week. Eddie Lou and four siblings also worked there and they were all together paid $4.50 as well. Eddie Lou and her youngest siblings would eventually be sent to an orphanage because her mother wasn't able to provide for them.
“If we don’t hold the line on child labor, we risk losing one of the things the has sets us apart as a nation founded not only on laws, but of morals,” wrote McCoy. “Of course children provide cheap labor, but business profits should not be the gauge of our society. In addition to the mental and physical tolls that children suffer in jobs that are inappropriate — and can you really imagine a 16-year-old wiping down the bar and asking what’s your poison? — there’s also a danger these children will become primary breadwinners for their families, with their educations coming a distant second.”
The children at the march carried banners that said, "We want more schools and less hospitals" and "We want time to play."
~ jsr
The Jon S. Randal Peace Page
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

On Both Sides of the Atlantic
In England the attacks on May Day were a necessary part of the wearisome, unending attempt to establish industrial work discipline. The attempt was led by the Puritans with their belief that toil was godly and less toil wicked. Absolute surplus value could be increased only by increasing the hours of labor and abolishing holydays. A parson wrote a piece of work propaganda called Funebria Florae, Or the Downfall of the May Games. He attacked, "ignorants, atheists, papists, drunkards, swearers, swashbucklers, maid-marians, morrice-dancers, maskers, mummers, Maypole stealers, health-drinkers, together with a rapscallion rout of fiddlers, fools fighters, gamesters, lewd-women, light-women, contemmers of magistracy, affronters of ministry, disobedients to parents, misspenders of time, and abusers of the creature, &c."
At about this time, Isaac Newton, the gravitationist and machinist of time, said work was a law of planets and apples alike. Thus work ceased to be merely the ideology of the Puritans, it became a law of the universe. In 1717 Newton purchased London's hundred foot Maypole and used it to prop up his telescope.
Chimney sweeps and dairy maids led the resistance. The sweeps dressed up as women on May Day, or put on aristocratic perriwigs. They sang songs and collected money. When the Earl of Bute in 1763 refused to pay, the opprobrium was so great that he was forced to resign. Milk maids used to go a-Maying by dressing in floral garlands, dancing and getting the dairymen to distribute their milk-yield freely. Soot and milk workers thus helped to retain the holyday right into the industrial revolution.
The ruling class used the day for its own purposes. Thus, when Parliament was forced to abolish slavery in the British dominions, it did so on May Day 1807. In 1820 the Cato Street conspirators plotted to destroy the British cabinet while it was having dinner. Irish, Jamaican, and Cockney were hanged for the attempt on May Day 1820. A conspirator wrote his wife saying "justice and liberty have taken their flight... to other distant shores." He meant America, where Boston Brahmin, Robber Baron, and Southern Plantocrat divided and ruled an arching rainbow of people.
Two bands of that rainbow came from English and Irish islands. One was Green. Robert Owen, union leader, socialist, and founder of utopian communities in America, announced the beginning of the millennium after May Day 1833. The other was Red. On May Day 1830, a founder of the Knights of Labor, the United Mine Workers of America, and the Wobblies was born in Ireland, Mary Harris Jones, a.k.a., "Mother Jones." She was a Maia of the American working class.
May Day continued to be commemorated in America, one way or another, despite the victory of the Puritans at Merry Mount. On May Day 1779 the revolutionaries of Boston confiscated the estates of "enemies of Liberty." On May Day 1808 "twenty different dancing groups of the wretched Africans" in New Orleans danced to the tunes of their own drums until sunset when the slave patrols showed themselves with their cutlasses. "The principal dancers or leaders are dressed in a variety of wild and savage fashions, always ornamented with a number of tails of the small wild beasts," observed a strolling white man.
#may day#may 1st#anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#community building#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#anarchy#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economics#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#anti colonialism#mutual aid#survival
6 notes
·
View notes