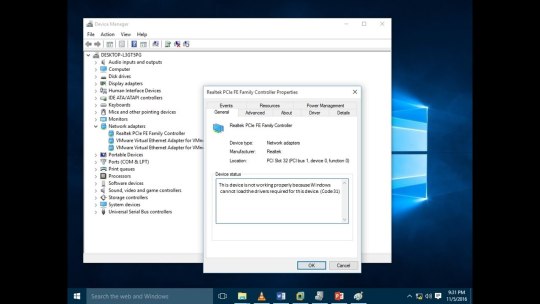
#vSAN Cluster Configuration
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top VMware Home Lab Configurations in 2023
Top VMware Home Lab Configurations in 2023 @vexpert #vmwarecommunities #100daysofhomelab #VMwareHomeLabSetup #VMwareWorkstationHomeLab #ESXiHostConfiguration #NestedVirtualizationVMware #vSANClusterConfiguration #BestVMwareHomeLabConfigurations2023
In 2023, many great options exist for delving into a home lab. Many get into running a home server to learn more skills for their day job, or they like to tinker and play around with technology as a hobby. For many, it is a mix of both. VMware vSphere is the market leader hypervisor in the enterprise. It arguably provides the most features and capabilities of any hypervisor on the market. This…

View On WordPress
#Best VMware Home Lab Configurations 2023.#ESXi Host Configuration#Nested Virtualization VMware#vCenter Server Deployment#VMUG Advantage for Home Labs#VMware Home Lab Setup#VMware vs Open Source Hypervisors#VMware vSAN Explanation#VMware Workstation Home Lab#vSAN Cluster Configuration
0 notes
Text
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator 2V0-11.25 Questions and Answers
In the rapidly changing IT landscape, staying ahead means embracing cloud technology—and VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 5.2 is leading that charge. The 2V0-11.25 VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator exam isn’t just another certification; it’s a proof point of your ability to manage cutting-edge hybrid cloud infrastructure. This professional-level credential shows employers you’re capable of handling complex deployments involving vSphere, vSAN, NSX, and the SDDC Manager, all integrated within VMware’s unified cloud platform. For IT professionals eyeing career growth in cloud, data center, or DevOps roles, this is one badge that carries serious weight.
What to Expect from the Exam: Format, Topics, and Objectives Uncovered
Before jumping in, you’ll want to understand what the exam entails. The 2V0-11.25 exam is comprised of 70 scenario-based multiple-choice questions, designed to test your real-world problem-solving skills across a variety of cloud management scenarios. You’ll have 130 minutes to complete it, and a scaled passing score of 300 out of 500. The exam objectives include everything from managing workload domains, troubleshooting infrastructure issues, and performing lifecycle management using SDDC Manager, to network and storage configurations. This isn’t a certification you can cram for in a weekend—it rewards hands-on experience and deep familiarity with VMware Cloud Foundation components.
Who Should Take This Exam? Exploring the Ideal Candidate Profile
Wondering if this certification is right for you? If you're a systems administrator, cloud engineer, network architect, or data center specialist working with VMware technologies, the answer is yes. It’s especially relevant for professionals managing private and hybrid cloud environments in medium to large enterprises. But even if you’re not yet in a senior role, this cert can help position you there. It’s also a great choice for consultants and freelancers looking to prove their expertise to clients. VMware certifications are recognized globally, so whether you're in the U.S., Europe, Asia, or beyond, this credential boosts your credibility across borders.
Real-World Skills Matter: Why Practical Experience Is Key
The 2V0-11.25 isn’t just about memorization—it’s about application. You'll need hands-on experience with deploying and managing VCF environments, including setting up NSX-T segments, configuring vSAN clusters, integrating vCenter, and updating components with SDDC Manager. This exam expects you to understand how these tools interact, not just as standalone platforms, but as a fully integrated ecosystem. Building your own lab environment using nested virtualization or VMware’s Hands-On Labs can help you bridge the gap between theory and real-world practice. The more you touch the tools, the more confident you'll feel come exam day.
Introducing Cert007: The Best Source for 2V0-11.25 Real Exam Questions
Need a shortcut to success? While nothing replaces hands-on experience, having access to realistic exam practice questions can be a game-changer—and that’s where Cert007 comes in. Known for their up-to-date and high-quality practice materials, Cert007 offers a specialized VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator 2V0-11.25 Questions and Answers that mirror the actual exam. These questions aren’t generic—they’re built to reflect VMware’s exam style and format, complete with scenario-based challenges and accurate answers. Whether you’re reviewing core concepts or simulating test-day conditions, Cert007 gives you the clarity and confidence to tackle every question head-on.
How to Use Cert007’s Practice Materials to Pass on Your First Try
Studying smarter is just as important as studying harder. With Cert007 VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator 2V0-11.25 Questions and Answers, you can structure your study sessions around actual exam objectives, practice in test mode, and get detailed explanations for each answer. This helps reinforce your understanding and spot knowledge gaps early. Their questions cover all the critical domains: infrastructure management, workload deployment, security, troubleshooting, and lifecycle operations. Many successful candidates have shared how Cert007 helped them pass the 2V0-11.25 on the first attempt. Combine these materials with hands-on labs, and you’ll walk into the exam room not just hopeful—but prepared.
Final Thoughts: Set Your Sights on Certification and Get Ready to Win
The VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator certification is more than just a line on your resume—it’s a strategic investment in your IT future. With the growing demand for professionals who can manage hybrid cloud environments, passing the 2V0-11.25 exam opens the door to exciting roles and career advancements. But don’t leave your preparation to chance. Pair your studies with Cert007’s premium Q&A packs to ensure you’re truly exam-ready. With the right tools, the right mindset, and a bit of hustle, you can conquer this certification and step confidently into your next career chapter.
0 notes
Text
VMware VMmark Wins, Powered By AMD EPYC Virtual Tasks

VMmark User Guide
After their introduction in 2017, AMD EPYC processors have become the preferred option for both public and private cloud deployments. High core counts, the fastest x86 memory bandwidth in the market, and cutting-edge security features make 4th generation AMD EPYC processors ideal for demanding private cloud workloads. AMD EPYC processors offer a strong platform for building private cloud infrastructures, as do VMware by Broadcom products including VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) and VMware vSphere Foundation (VVF), which comprise programmes like vSphere, vCenter, vSAN, and NSX. The strategic partnership between AMD and VMware By Broadcom helps organisations install and manage virtualized environments that meet their performance and scalability needs while optimising energy efficiency and TCO.
Two typical deployment scenarios for VCF/VVF exist:
Conventional VVF infrastructure typically comprises discrete networking, storage, and computation gear. Running this model requires managing each part independently, which frequently calls for specialised knowledge and equipment, but it produces the best results. The computational component is virtualized using software like VMware vSphere, which is controlled by a virtual infrastructure administrator. This configuration’s storage component depends on specialised Storage Area Network (SAN) or Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices under the control of a Storage Administrator. A contemporary method of managing data centres is called hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI), which integrates networking, storage, and processing into a single, cohesive system. Typically, HCI systems pool storage resources throughout the entire infrastructure for simple scaling and management by a Virtual Infrastructure Administrator. This is made possible by Software Defined Storage (SDS), which is made possible by products like vSAN. Compared to conventional VCF/VVF installations, this simplified method can maximise savings while enhancing agility and scalability. VMmark Benchmark
By offering thorough performance measurements that mimic real-world workloads to evaluate CPU, memory, storage, and networking performance, the VMmark benchmark helps enterprises to evaluate the effectiveness and scalability of their virtualized systems. Businesses may decide on hardware configurations, resource allocation, and workload management methods with knowledge thanks to this comprehensive picture of system capabilities under various workload scenarios.
By applying the smallest unit, or “tile,” of load, VMmark3 employs a weighted scoring system to assess a server’s performance. Nineteen virtual machines are included of each tile, which represents a typical enterprise virtualization scenario by executing a wide collection of tasks both concurrently and collaboratively. Each tile’s static nature allows for the size and scalability of the amount of work for every distinct VMmark3 cluster.
With a growth in hosts, sockets, and cores, there are usually more tiles. Each tile also serves as a representation of the maximum theoretical score and a Quality of Service (QoS) metric, which are used to appropriately scale each publication: an excessive number of tiles exceeds the benchmark latency requirements, while an insufficient number of tiles limits the maximum score.
While application performance accounts for a piece of the total score, the quantity of tiles is essential to comprehending the potential of a VCF deployment. Many of the capabilities that are exclusive to VCF, like XvMotion, Storage vMotion, vMotion, and the Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), are also utilised by standard virtualized deployments. By utilising these capabilities, VMmark workloads offer a more comprehensive view of what can be accomplished with the entire system as opposed to just one server. Depending on the underlying technology, these infrastructure processes can vary in scope and duration, accounting for 20% of the total score.
Benefits of Generational Performance AMD is committed to innovation and keeps delivering notable gains in efficiency and performance for important applications. As can be seen in Figure 1, AMD EPYC processors have significantly improved in performance with each iteration when used in VCF scenarios. These assessments include single- and dual-processor installations in both normal settings and vSAN configurations. The consistent dedication of AMD towards meeting the dynamic and ever-increasing demands of contemporary virtualized infrastructures is demonstrated by the notable performance improvements attained with every new generation of AMD EPYC CPUs.
Performance of Throughput
Thanks to continued AMD processor technology advances and collaborative VMware By Broadcom optimisations, the preceding section of this blog revealed constant performance increases across successive AMD EPYC processor generations. The performance domination of AMD EPYC processors over several processing generations is demonstrated in Figure 2, which highlights their unwavering commitment. In VMmark3 performance tests conducted on clusters comprising two dual-socket servers for a total of four processor sockets, the 4th generation AMD EPYC 9654 CPU outperforms even the most recent 5th generation Intel Xeon Platinum 8592+ processor.
Per-Core Efficiency
When it comes to power, space, and server count optimisation, per-server throughput is a crucial measure. Additionally, because per-core performance is frequently a major issue in software licencing models based on core count, it is especially important for workloads that are SLA-critical.
The performance improvements of 32-core AMD EPYC 9374F processors over 32-core Intel Xeon Gold 6548Y+ processors and 64-core AMD EPYC 9554 processors over 64-core 5th Gen Intel Xeon 8592+ processors are shown in Figure 3.
Power Effectiveness
In order to minimise cooling requirements, maximise utility costs, and support sustainability goals, modern data centres must have efficient power consumption. In comparison to both 4th and 5th Gen Intel Xeon processors, Figure 4 illustrates how 4th Gen AMD EPYC 9654 CPUs provide higher power efficiency.
Space for a Data Centre VMmark Scores Data centres have tremendous incentives to optimise space, electricity, and cooling for sustainability and TCO. Less servers that may offer more virtual machine consolidation without sacrificing the speed required for corporate operations can be used to achieve these goals. Suppose AMD workloads need to achieve business objectives with resources and quality of service equal to a total VMmark3 score of 500. This aggregate score can be attained with just 26 servers running 4th Gen AMD EPYC 9654 processors, as shown in Figure 5.
AMD will require 38 servers if they choose to employ servers with 5th generation Intel Xeon 8592+ processors. It may take up to 112 servers for customers with 2nd Gen Intel Xeon 8280 processor-based servers to get the same aggregate score! That’s more than 4 times the amount of AMD EPYC 9654 processor-based servers required to meet the same workload in business! This comparison emphasises the significance of not only power efficiency but also making the best use of server rack space in datacenters.
VMmark Benchmark Results This article demonstrated how VMmark victories and the next generation of AMD EPYC processors can drive consistent performance leadership, giving organisations optimal hardware consolidation and unparalleled x86 workload performance that may help reduce total cost of ownership. Businesses can safely depend on AMD EPYC processors to satisfy their changing virtualized infrastructure demands while maximising available power and capacity. Together, AMD and VMware by Broadcom are still dedicated to promoting innovation that continuously yields record-breaking virtualized environment performance and efficiency. Businesses can achieve new levels of agility, scalability, security, and reliability in their IT infrastructures by utilising Broadcom’s combination of experience in AMD and VMware.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
0 notes
Text
New Post has been published on VMware Virtualization Blog
New Post has been published on https://www.tayfundeger.com/vsan-capacity-reserve.html
vSAN Capacity Reserve
Merhaba,
vSAN Capacity Reserve isimli bu yazımda sizlere, vSAN’ın yeni özelliklerinden biri olan vSAN Capacity Reserve hakkında detaylı bilgi vereceğim. Daha önce yazmış olduğum vSAN makalelerine aşağıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
https://www.tayfundeger.com/kat/VSAN
Daha önceki makalelerimde sürekli belirtmiştimdir. vSAN kullanıyorsanız doluluk oranlarına dikkat etmeniz gerekiyor. Kapasitenin %25 veya %30 ‘unu boş bırakmanız gerekiyor. Bunun sebebi aslında hem rebuild işlemleri hemde policy üzerinde yapacağınız bir değişiklikte free alan’ın azalmasına sebep olmasından kaynaklanıyor. vSAN rebuild, repair gibi işlemlerde free alanı kullanır. Hatta bu konu ile ilgili yazmış olduğum yazılara aşağıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
VSAN – Resyncing Objects
SAN ve Arıza Senaryoları
VSAN – Advanced Options
vSAN Capacity Reserve
vSAN cluster’ında bir ESXi host’un down duruma gelmesi durumunda rebuild işlemi başlayacağı için bu free kapasite kullanılır. VSAN 7 U1’den önceki sürümlerde, önerilen free space’in takip edilmesi için vCenter Server alarm’larından veya vROPS gibi ürünlerden faydalanmak zorunda kalıyoruz. vSAN 7 U1 den itibaren artık bu free space’i özel olarak takip etmemize gerek bulunmuyor. vSAN ile birlikte gelen Reserved Capacity özelliği sayesinde, kapasitenin kritik değerleri aşmasını önlenmesine olanak sağlıyor.
Yukarıda da belirttiğim gibi rebuild ve repair işlemleri için free space kullanılırken, Storage Policy üzerinde değiştireceğiniz bir object konfigurasyonundan kaynaklı free space’i de kullanabilirsiniz. Örneğin disk kopyasını değiştirmeniz durumunda free space’de değişim olur. Çünkü var olan virtual machine’in disklerinin farklı bir diske senkronize olurken free space’in bir miktarını kullanır. Free space’i etkileyen bu şekilde etkenler bulunuyor iken, reserved capacity tam burada işimize yarıyor.
vSAN Capacity Reserve aktif etmenin 2 farklı yolu bulunuyor. İsterseniz vSAN cluster’ını seçip Configuration > vSAN Services Enable Capacity Reserve butonuna basabilirsiniz. İsterseniz de Monitor > Capacity bölümüne giriş yaptığınızda aşağıdaki bir ekran ile karşılaşırsınız.
vSAN Capacity Reserve
Burada, You can enable operations and host rebuild reserve yanında yer alan Configure butonuna basıyoruz.
Enable Capacity Reserve bölümüne giriş yaptığımızda karşımıza 2 adet seçenek çıkıyor.
Operations reserve: vSAN’ın cluster’daki internal işlemlerini yürütmek için ihtiyaç duyduğu alanı görüntüler . Kullanılan alan işlem eşiğini aşarsa, vSAN düzgün çalışmayabilir. Örneğin storage policy üzerinde bir ayar değiştirceksiniz ve bu değiştirdiğiniz ayar sonucunda vSAN cluster’ı içerisinde bulunan virtual machine dosyalarının senkronizasyon edilmesi gerekecek. Bu gibi durumlarda Operations reserve seçeneğini aktif durumda olur ise altyapımızı riske atmadan sorunsuz bir şekilde işlemlerimize devam edebiliriz.
Host rebuild reserve: Host rebuild reserve ise, bir ESXi host’un kapasitesine göre ayarlanmıştır. Bir vSAN Cluster’ında bir ESXi host arızalanırsa veya down olursa diyelim, böyle bir durumda üzerindeki diskleri kullanamaz ve bundan dolayı vSAN cluster’ındaki depolamaya katkıda bulunamaz. Bu gibi durumlar oluştuğunda cluster’da repair/rebuild işlemleri başlanır. Bu konu ile ilgili yazmış olduğum makalelere yukarıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz. Rebuild/Repair işlemlerinin yapılabilmesi için bir kapasiteye ihtiyaç bulunmaktadır. Eğer bu kapasite bulunmaz ise rebuild/repair işlemleri başarısız olablir. Host rebuild reserve sayesinde bu gibi kapasite ihtiyaçlarını kontrol etme imkanına artık sahibiz. Bu özellik default olarak devre dışıdır. Özelliği aktif edebilmek için Operations reserve’i ilk olarak aktif etmeniz gerekmektedir.
Capacity Reserve’i aktif etmezseniz, kapasitenin tükenmesi durumunda virtual machine’lerin oluşturulmasını veya virtual machine’lerin çalışması engellenir. Capacity Reserver’i aktif ederseniz, vSAN eşik sınırlarına ulaştıktan sonra bile virtual machine’den gelen IO talepleri karşılanmaya devam eder. Capacity Reserve etkinleştirdikten sonra, cluster’daki disk alanı, sağlık uyarılarını ve kapasite kullanımını izlemeli ve kapasite kullanımını eşik sınırlarının altında tutmak için uygun eylemleri gerçekleştirmelisiniz.
Bu özelliği kullanabilmeniz için bazı gereksinimleri karşılamanız gerekiyor. Capacity Reserve’i; Stretched Cluster, fault domain, ROBO Cluster ve vSAN Cluster’ı 4 node’dan az ise bu özelliği kullanamazsınız. Ayrıca vSAN Cluster’ında eşik değerinden yüksek bir kapasiteye sahipse zaten Capacity Reserve’i aktif edemezsiniz.
vSAN ‘ın yeni sürümleri ile birlikte sürekli yeni özellikler gelmeye devam ediyor. Capacity Reserve özelliğide vSAN ortamımı hem güvenli bir şekilde yönetmemize hemde operasyonel işlemler için gerekli tahmini boş kapasitenin dinamik olarak hesaplanmasını sağlıyor. Ayrıca cluster’ın kritik kapasite koşullarını aşmasını önlemeye yardımcı olduğu gibi güvenlik ve sağlık kontrollerinide kullanılmasına olanak tanıyor. vCenter Server üzerinden kritik kapasite koşullarını aşmasını önlemeye yardımcı olması oldukça güzel bir özellik. Çünkü yukarıda belirtmiş olduğum gibi ESXi host’un down olması durumunda gerekli olan rebuild işlemlerinde kullanılacak kapasiteyi hesaplaması önemli. Manuel olarak hesaplamak isteseniz farklı parametreleri toplamanız gerekir.
Bu özelliğin default olarak devre dışı geldiğini tekrar belirtmek isterim. Eğer free kapasitesiniz yeterli seviyede ise, yani %90 kullanım oranı bulunmuyor ise bu özellikleri aktif hale getirebilirsiniz.
Umarım faydalı olmuştur.
İyi çalışmalar.
1 note
·
View note
Text
In this article we will be looking at how you can enable file service in a vSAN Storage cluster configured in a VMware environment. The vSAN File Service allows a vSphere admin to provision a file share from their vSAN cluster. The file share created can be accessed using NFS protocol. Before you start the configuration you need few items already configured: Setup Pre-requisites A Working VMware vSphere implementation: Setup ESXi hosts and deploying vCenter Server Appliance. Configured and working DNS resolution for all ESXi hosts and vCenter Appliance Static IP address, subnet masks and gateway for file servers DNS name for each IP address or allow the system to do a reverse DNS lookup. The design implementation of the File Service is as captured in the diagram below. Enable NFS File Service in a VMware vSAN Storage Cluster The vSAN File services is supported on DVS version 6.6.0 or higher. You need to create a dedicated port group for vSAN File Service in the DVS. Click on the Cluster name you created in vCenter. The go to Configure > vSAN > Services. Click “ENABLE�� under the File Service section. Review requirements in the Introduction page and hit Next if the checklist is satisfied. In the File service agent page there are two options to choose from for downloading the OVF files. Automatic approach: This is the default option which lets the system search and download the OVF. Manual approach: This option allows you to browse and select an OVF that is already available on your local system. Using Manual approach If you don’t have internet connectivity from your VMware Infrastructure you’ll need to have the following files for deployment: VMware-vSAN-File-Services-Appliance-x.x.x.x-x_OVF10.mf VMware-vSAN-File-Services-Appliance-x.x.x.x-x-x_OVF10.cert VMware-vSAN-File-Services-Appliance-x.x.x.x-x-x-system.vmdk VMware-vSAN-File-Services-Appliance-x.x.x.x-x-cloud-components.vmdk VMware-vSAN-File-Services-Appliance-x.x.x.x-x-log.vmdk VMware-vSAN-File-Services-Appliance-x.x.x.x-x_OVF10.ovf Here is the list of the files I downloaded and I’ll be using Manual approach. For my installation I’ll choose Manual approach deployment method. Select all the files and hit Open. Confirm all the files were selected for use during deployment. Set File service domain name. DNS Servers and DNS suffixes. Select network to be used by file service, subnet mask and the network’s gateway. Provide IP addresses which should match the number of hosts in the cluster for best operation. Make sure the DNS names are configured in your DNS server. Confirm configuration details then click “Finish“. If the installation is successful the file service should show as enabled. In our next article we will look at how you can use vSAN NFS file service. Stay connected for updates.
0 notes
Text
Vmware quickboot flag metadata vib check

#Vmware quickboot flag metadata vib check drivers#
#Vmware quickboot flag metadata vib check update#
Then go to Admin view > Manage > Settings > Host/Cluster settings > Edit.
#Vmware quickboot flag metadata vib check update#
Launch the vSphere Web Client (Flash), select your vCenter, and go to Update Manager. It seems this is one last part of the UI that needs to transition to the modern HTML5 web-based interface. Where do you enable Quick Boot? ^įor now, the only way to enable Quick Boot is to use the Flash-based vSphere Web Client. Even if your hardware is compatible with Quick Boot, the server might "freeze" with the error message "LoadESX in progress" during the boot process. If you have an unsupported configuration, you might have problems. When using a VMware virtual storage area network (vSAN), it's imperative to follow the hardware compatibility list (HCL) to ensure you have a supported firmware/driver combination. esxupdate: imageprofile: INFO: Adding VIB virtuallyGhettobootbankghettoVCB1.0.0-0.0.0 to ImageProfile HP-ESXi-5.5.0-Update2-iso-5.77. The idea from VMware is great, and it can make you save a lot of time when patching VMware infrastructures because many servers can spend significant time during POST. Quick Boot is disabled in the Update Manager-you can easily check this in the UI (for now through the Flash-based web client only).
#Vmware quickboot flag metadata vib check drivers#
No other non-certified drivers loaded on your host.
No vmklinux drivers loaded on your host.
This cmdlet initializes a PowerShell runspace with a PowerCLI execution context retrieved from another PowerShell runspace. Using Quick Boot is supported with a limited set of hardware platforms, drivers, and is not supported on ESXi hosts that use TPM or passthru devices. This cmdlet retrieves the VMware PowerCLI execution context which you can use to simplify the use of PowerCLI in PowerShell runspaces. Passthrough devices: Another constraint is you can't use Quick Boot with any passthrough devices configured for VMs on your host. The Quick Boot of ESXi hosts is an option that allows Update Manager to reduce the time a host remediation takes by skipping the physical reboot of the host. The VMware vRealize Suite Lifecycle Manager automates the LCM of the vRealize Suite. Here is an example of using the remote vihostupdate utility for an ESXi host, you will need to specify the. The patch bundle needs to be uploaded to ESX host using scp or winSCP and then specifying the full path on the command-line: esxupdate bundleESX400-200907001.zip update. Update standalone ESXi hosts using images. Here is an example of using esxupdate on a classic ESX host. Run vCenter Server interoperability reports D. Host is not configured to use a Trusted Platform Module (TPM): You cannot have a TPM and Quick Boot active at the same time. Upgrade VMware Tools and virtual machine hardware C. Perhaps a future BIOS upgrade from your hardware manufacturer will allow Quick Boot, but nothing is certain. In such a case, there is nothing you can do about it. Host platform is unsupported: One of the first constraints is there's no support for a host platform. My hardware is not compatible with VMware Quick Boot What are the constraints and requirements for Quick Boot? ^

0 notes
Text
VMware vSAN Specialist 5V0-22.21 Practice Test Questions
If you are going to appear in 5V0-22.21 VMware vSAN Specialist exam,Make sure that you are going through PassQuestion VMware vSAN Specialist 5V0-22.21 Practice Test Questions that will help you prepare for the real exam.VMware vSAN Specialist 5V0-22.21 Practice Test Questions offer you real exam scenario which further helps you in familiarizing yourself with VMWare 5V0-22.21 exam. It will help you improve your preparation level so you can clear any 5V0-22.21 VMware vSAN Specialist exam on your first attempt. With the help of VMware vSAN Specialist 5V0-22.21 Practice Test Questions, you will surely pass your VMware 5V0-22.21 exam successfully.
VMware vSAN Specialist 5V0-22.21 Exam
The VMware vSAN Specialist Exam (5V0-22.21) which leads to VMware Specialist – vSAN 2021 badge, is a 76-item exam, with a passing score of 300 using a scaled method. Exam time is 130 minutes. This exam tests candidate skills and abilities designing, implementing, and administering a VMware vSAN environment.
Exam Information
Exam Number: 1V0-31.21 Exam Language: English Associated Certification: VCTA-CMA Duration: 105 minutes Number of Questions: 58 Questions Passing Score: 300 Format: Single and Multiple Choice, Proctored
Exam Topics
Section 1 – Architecture and Technologies Section 2 – Products and Solutions Section 3 – Planning and Designing Section 4 – Installing, Configuring, and Setup Section 5 – Performance-tuning, Optimization, and Upgrades Section 6 – Troubleshooting and Repairing Section 7 – Administrative and Operational Task
View Online VMware vSAN Specialist 5V0-22.21 Free Questions
What is the purpose of host rebuild reserve in vSAN? A.Reserves space in case of single host failure B.Allocated capacity for vCLS C.Reconfigures data components D.Stores vSphere HA heartbeats Answer : A
Which solution can automate the deployment of a vSAN cluster as part of a full Software-Defined Datacenter? A.VMware Cloud Foundation B.vSphere Replication C.vRealize Suite Lifecycle Manager D.VMware Cloud Director Answer : A
A vSAN administrator of a network isolated vSAN environment wants to upgrade the environment from the vSAN 7.0 to the vSAN 7.0 U1 using vLCM. Which option, if any, should be used as a depot in this case? A.Configure the vSphere Lifecycle Manager to download the updates from an Online Depot. B.It is not possible to use the vSphere Lifecycle Manager on a network isolated environment. C.Configure the vSphere Lifecycle Manager to download updates from a local UMDS-shared repository. D.Configure the vSphere Lifecycle Manager to download the updates from the VMware Depot using HTTPS. Answer : D
After a server power failure, the administrator noticed the scheduled resyncing in the cluster monitor displays objects to be resynchronized under the pending category. What are these objects in this category? A.These objects belong to virtual machines, which are powered off. B.Object resynchronization must be started manually. C.There are too may objects to be synchronized. D.The delay timer has not expired. Answer : B
A remote location was configured with Cloud Native Storage. When the administrator put the host in maintenance mode to perform monthly patching, the File Server Health check was triggered. Which action, if any, should the administrator take to resolve the issue? A.Click the Repair Objects Immediately button in the VMware Skyline Health Checks. B.Remove the host from maintenance mode, and put it back with Full Data Migration. C.It will resolve after 60 seconds, so no action is necessary. D.Modify the repair delay timer to 75. Answer : A
A vSAN administrator is deploying multiple 2-node clusters to remote branch offices. The nodes already have an old vSphere 7.0 image, but the administrator would like to update the image and ensure consistency across all the nodes. The administrator configured vLCM on the first vSAN cluster and exported the image. Which format should the administrator choose? A.ISO Image B.TXT File C.ZIP File D.JSONFile Answer : A
0 notes
Text
Download Vmware Mobile Phones & Portable Devices Driver

Vmware Tools Device Drivers
Connect Usb Device Vmware
vSphere Mobile Client App
Mobile and other handheld devices are becoming a part of our life by helping us keep up with every possible thing, may it be our health, our social life, or our work. vSphere Client product team wanted to enable admins to keep an eye on their datacenters using these handheld devices.
We are happy to announce that vSphere Mobile Client fling is released to help you monitor your datacenters and take some quick actions to continue running your workloads without any disruption. This lightweight app is available for download for both Android and iOS devices. This app is built using the same vSphere Client (HTML5) APIs, and is compliant with Clarity theme, thus maintaining the consistent data and experience across different vSphere management platforms. Released as a fling since the start of 2019, this app has all the modern mobile app features like Bio-metric authentication, optimized for the touch interface, and offline notification capabilities (more about this later).
The complete list of VMware Mobile Apps This list is limited to the applications that have VMware (and AirWatch) as developer or company in its descriptions. I know there are much more applications that you can use to manage your VMware infrastructure. Krishnamurti said VMware hopes to have the first phones with the VMware Mobile Virtualization Platform appear by late 2009 or early 2010. Top Picks In Shopping Shopping 5 Peloton bike alternatives.
Vmware Tools Device Drivers
vSphere Mobile Client is built keeping monitoring in mind. You can monitor the resource utilization by VMs, Hosts, Clusters, etc., for the same granular metrics as that of vSphere Client (HTML5). You can also monitor the status of tasks, events, or alarms in your environment. There are only a limited set of operations supported in the app to allow you to mitigate any issues you would notice while you monitor. Ex: a host is running out of resources in a DRS enabled cluster and you want to put a host into maintenance mode so DRS can vMotion your application causing zero downtime or you want to take a snapshot of a VM or power reset a VM for a quick fix or have a quick peek at the VM’s remote console. You cannot perform any advanced operations like configuring a cluster or performing manual vMotions thus reducing the risk of “fat fingering” mistakes.
Another cool feature supported by vSphere Mobile Client is offline monitoring of long-running tasks. Let’s assume you are putting a host into maintenance mode which will trigger a bunch of vMotion operations that could take a lot of time to complete. Wouldn’t it be nice to send a notification to your phone when the task completes, so you can open your laptop only if there are any failures? You could achieve this by configuring a notification appliance that monitors these long-running tasks and sends push notifications to your phone app on task completion.
To use the vSphere Mobile Client app, all you need is a VPN connectivity from your phone app to a vCenter server in your datacenter. If your enterprise uses any form of Mobile Device Management (MDM) software, then you can connect using the built-in VPN in the MDM. Since it’s release in 2019 we have seen a significant increase in adoption and usage of the app across the geography. Some of the future capabilities we are considering bringing in the app are: the ability to manage multiple linked vCenter servers including VMware Cloud on AWS, integration between vSAN monitoring app, customizable notifications, vSphere Skyline health integrations, and browser to mobile handoff capabilities.
Before we want to make vSphere Mobile client app as an officially supported product, we want to get feedback from you. Could you use the app and share the feedback using the in-app feedback capability? Let us know what other features support would make you use this app to monitor your production environment. You can leave general feedback comments in the Fling’s comments section or in the device App stores.
Enjoy the app and let us know what you think about it!
Connect Usb Device Vmware
What happened to vSphere Mobile Watchlist?!
There used to be a mobile client to manage vSphere environment called vSphere Mobile Watchlist which was built a long time ago. Since this app was heavyweight, was not built to reuse the vSphere Client APIs, it was very expensive for us to enhance it to give a consistent experience. Rather we rebuilt the brand new lightweight vSphere Mobile client app. vSphere Watchlist is no longer supported/maintained.

0 notes
Text
Dell VxRail Deploy Exam (D-VXR-DY-01) Prep Guide & Practice Exam
The D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 exam is a qualifying exam for the Dell VxRail Deploy v2 Certification, designed to assess your knowledge of implementing and managing a VxRail cluster. This exam covers various topics, from solution planning to hardware and software installation, and troubleshooting, making it essential for IT professionals working with VxRail solutions.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the key aspects of the exam, explore its structure, and share the best tips for preparing, including how to make use of the D-VXR-DY-01 practice exam from Cert007 for optimal study results.
Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 Exam Overview
The Dell VxRail Deploy v2 Certification exam tests your ability to implement a basic VxRail cluster, including hardware installation, environment validation, software implementation, and post-deployment tasks. The exam is split into two parts:
Part 1: 90 minutes
Part 2: 30 minutes
To pass the exam, you need to meet the passing score requirements for both parts.
Understand Key Exam Topics
The following topics are essential for the D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 exam:
1. VxRail Physical Components (4%)
Understanding VxRail cluster architecture
Knowing rack requirements for VxRail clusters
2. VxRail Deployment Planning (12%)
vCenter server and its role in deployment
Networking components and vSphere Distributed Switches
DNS options, node discovery, and vSAN settings
3. Using VxRail Configuration Tools (4%)
Creating and reviewing VxRail projects and configurations
4. VxRail Hardware Installation and Initialization (8%)
Procedures for installing and cabling VxRail hardware
Configuring VxRail node iDRAC and system time settings
5. VxRail Network Environment Requirements and Initialization (8%)
Configuring and validating VxRail network settings manually
6. Deploying the VxRail Cluster (24%)
Initializing VxRail clusters with VxRail or customer-managed vCenter Server
vSAN ESA (vSAN Express Storage Architecture) setup
7. VxRail Post-Deployment Procedures (18%)
Performing post-installation validation
Configuring vSAN settings and native backups
8. VxRail Cluster Upgrade and Expansion (10%)
Understanding upgrade requirements and scale-out processes
9. VxRail Troubleshooting (6%)
Collecting logs and troubleshooting using VxRail and vSAN tools
10. VxRail REST API (6%)
Using VxRail REST APIs to automate tasks and troubleshoot issues
Study Tips for D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Exam
Preparing for the D-VXR-DY-01 exam requires a solid understanding of the VxRail system, hardware installation, networking, and troubleshooting. To maximize your chances of success, follow these steps:
Understand the Core Topics: Focus on the key areas of the exam, including deployment planning, hardware installation, and post-deployment procedures. Review Dell’s official documentation and guides related to VxRail clusters.
Hands-On Experience: Practical experience with VxRail components, vCenter Server, and networking setups is crucial. Try to work on a live or simulated VxRail environment to get familiar with the installation and configuration processes.
Use VxRail Tools: Gain proficiency with tools like the VxRail Configuration Portal and REST API. Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues using logs and vSAN tools will be particularly useful for the troubleshooting section.
Practice Exams: One of the best ways to prepare for the exam is by using D-VXR-DY-01 practice exams from Cert007. These practice exams closely simulate the real exam experience, helping you assess your readiness and pinpoint areas that need more study.
Review Study Materials: Cert007 offers comprehensive and up-to-date study materials specifically designed for the Dell VxRail Deploy v2 exam. These materials cover every exam topic in detail and provide insights into common issues and troubleshooting strategies.
Final Thoughts
The D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 Certification is an essential step for professionals looking to demonstrate their expertise in deploying and managing Dell VxRail clusters. By focusing on key exam topics, gaining hands-on experience, and leveraging practice exams from Cert007, you can confidently prepare for and pass the exam.
Invest in quality study materials and practice exams to ensure you're well-prepared for this important certification. Good luck on your journey to becoming Dell VxRail Deploy certified!
0 notes
Text
Next-gen Dell PowerEdge Servers Upgrade IT

Dell PowerEdge:
Organizations that switch to new server technology must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of investing in new infrastructure, including hardware, software, and the operating environment. Think about the performance improvements a data center would see with this new or updated gear and software. Organizations will benefit from the most recent security protection, system management tools, processing speed improvements, decreased downtime, and quicker results in addition to increased raw performance. A modernized infrastructure will also increase scalability to smoothly accommodate future growth and boost cluster performance per watt.
All of this suggests that modernizing your hardware, software, and operating system may enhance your data center’s overall performance. However, it can be difficult to align all three aspects at once because earlier choices might impede development.
Express Storage Architecture (ESA)-based vSAN 8.0 is an improved ReadyNode infrastructure offering from Dell, Intel, and VMware. Improved performance and efficiency are provided by this release to cater to the changing business needs of clients.
Customers who use Dell’s PowerEdge R760 server can take advantage of vSAN 8.0, but they must choose between upgrading to the new ESA ReadyNode architecture or staying with the current vSAN Original Storage Architecture (OSA) Ready Node. x86 servers that have been pre-configured, examined, and approved by Dell and VMware are known as vSAN ESA ReadyNodes. Every vSAN ESA ReadyNode is ideally configured with the necessary amount of CPU, memory, network IO, and storage NVMe devices for vSAN ESA or OSA. Dell has more than 250 configurations in total to meet all customer needs, raising the questions of which one to pick and how to migrate.
0 notes
Text
Step up Innovation with Dell EMC PowerEdge and VMware

Breaking new ground is one of the most difficult tasks an IT team can do. It requires knowledge, solid partnership, and trust into the new path forward. Organizations like yours might be looking at hybrid cloud as that next route ahead.
Your company’s IT landscape needs to provide efficiency, flexibility, and scalability along with ease of deployment and management so that you can avoid growing pains. At the same time, you need to help your team comply with key security features while managing the headcount in your organization. We’ve got your back! By using our solutions, customers like Trintech have increased operational efficiency, expanded globally, and achieved more IOPS without the need to expand their IT team.
With a solid partnership that extends over two decades, Dell Technologies and VMware consistently clear the path towards the new objectives your company needs to reach.
Solid partnership working for you
Dell EMC PowerEdge servers with VMware software combine industry leading x86 servers¹ with software in joint solutions that allow you to pick and choose optimal configurations that adapt to your needs. PowerEdge servers provide a secure infrastructure and foundation that’s flexible and scalable. Our partnership provides a unified solution that helps you flexibly architect and scale, automate and empower — regardless of workload. Learn more in our PowerEdge and VMware portfolio brochure.
Trust the Path Forward
Put your business on a solid path to success when you chose the optimal hardware and software partners in your integrated software stack. VMware brings virtualization with VMware vSphere®, and prepares your infrastructure for modern apps when you use vSphere with Tanzu on modern, agile Dell EMC PowerEdge servers. That’s why more businesses are choosing VMware vSphere with Tanzu™ and Dell EMC PowerEdge servers — to take business to the next level with greater ease, speed and confidence.
When it comes to modernizing and simplifying storage, you can boost efficiency with VMware vSAN™ 7 Update 2 on Dell EMC PowerEdge servers with improvements that supports several new vSAN use cases, whether you’re using them for core storage, stretched clusters, modern apps or remote/branch office (ROBO) deployments.
To complete your hybrid cloud, you can deploy VMware Cloud Foundation™ on premises as a private cloud, run it as a service within a public cloud, or take the hybrid cloud approach. At the end of the day improved performance + familiar deployment = a winning solution that makes everything more efficient and creates less headaches for your IT staff.
When it comes to workloads, we provide an easy path for your upgrades. PowerEdge and VMware can help organizations with a large SQL Server database upgrade to the latest SQL 2019 easily and achieve performance improvements of 53% on newer hardware and software. Take a look at the report here. Newer hardware and software solutions from Dell Technologies and VMware can help IT teams run more VMs in the same rack space and more easily manage large SQL Server deployments in a virtualized environment, all while providing a layered approach to high availability. With simplified OEM licensing and support options, PowerEdge and VMware together can help IT teams architect, validate, and build solutions that meet specific business needs.
Easier and faster lifecycle management
Managing your software and hardware lifecycle is something to important in your path; but don’t worry we got your back on this topic as well! Our sophisticated, unified lifecycle management solution across virtualized and non-virtualized environments between OpenManage Integration with VMware vCenter (OMIVV) and vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM) saves administrators valuable time. For example, you can check hardware compatibility on a single node with 87% less hands‑on time and 85% fewer steps.²
Certainly, Dell Technologies and VMware clients have a lot to celebrate – in addition to new solutions to discover during Dell Technologies World 2021. We invite you to join our session at Dell Technologies World: 4 Ways to Make Hybrid Clouds More Agile, Intelligent and Secure with PowerEdge and VMware. Let us guide you into your new path!
¹ IDC, WW Quarterly x86 Server Tracker, 4Q2020 Unit Shipments, March 11, 2021.
² Principled Technologies report commissioned by Dell Technologies, “New VMware vSphere 7.0 features reduced the time and complexity of routine update and hardware compliance tasks,” August 2020.
0 notes
Text
New Post has been published on VMware Virtualization Blog
New Post has been published on https://www.tayfundeger.com/vsan-disk-balance.html
vSAN Disk Balance
Merhaba,
vSAN Disk Balance isimli bu yazımda sizlere vSAN ortamında karşılaştığımız Disk Balance uyarısı hakkında detaylı bilgi vereceğim. Daha önce vSAN Automatic Rebalance ile ilgili bir yazı yazmıştım. Bu yazıma aşağıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
VSAN Automatic Rebalance
vSAN ortamı kullanıyorsanız, maintenance veya ESXi host’un down olması gibi durumlardan sonra, Cluster Summary’de aşağıdaki gibi bir uyarı ile karşılaşabilirsiniz.
Warning: Virtual SAN Disk Balance
vSAN ortamında bulunan bir ESXi host’u Evacuate all data seçeneği ile maintenance’a almanız durumunda vSAN node’u üzerindeki datalar farklı hostlara taşınacağı için node’lar üzerinde disklerde eşit yükler bulunmaz. Tabiki bu senaryoyu daha fazla genişletebilirsiniz. Zaten makalemin ilerleyen bölümlerinde buna yer vereceğim.
vSAN Cluster’ında herhangi bir ESXi host üzerindeki disk/disk grupları %80 dolabilir. Böyle bir durumda vSAN, doluluk yaşanan disk veya disk grubunda bu alanı %80’in altına düşene kadar cluster’i otomatik olarak dengeler. Burada %80 diye belirtiyorum ancak bu değer Rebalance işlemlerini manuel veya automatic yapmasanız bile %80 eşiğine geldiğinde otomatik olarak yapılır. Ayrıca isterseniz bu değeri değiştirebilirsiniz. Bu işlem yapılırken performans sorunları yaşayabilirsiniz. Performans sorunları derken, vSAN cluster’ınızda virtual machine çalışamayacak düzeyde bir performans sorunundan bahsetmiyorum 🙂 Disk rebalance işlemi, vSAN cluster’ınızın I/O performansını etkileyebilir. Bu performans etkisinden kaçınmak için automatic rebalance işlemini, altyapının yoğun olarak kullanılmadığı gün/saatlerde aktif edebilirsiniz.
vSAN Disk Balance
Daha önce yukarıda belirtmiş olduğum makale içerisinde de belirtmiştim ancak tekrar belirtmek istiyorum. Aşağıda belirteceğim işlemler disk kapasitelerinin %80 ‘e ulaşmasına ve rebalance işleminin başlamasına sebep olabilir.
Cluster’da donanım arızası olabilir.
vSAN ESXi host’ları Evacuate all data seçeneği seçilerek maintenance mode’a alınır.
FTT=0 olarak konfigure edilmiş bir vSAN cluster’ınız var ve Ensure data accessibility modu ile maintenance mode’a alınır.
Yukarıdaki durumların oluşması durumunda rebalance işlemi başlar.
Rebalance işlemini 2 farklı şekilde yapabilirsiniz. Ancak burada kullanmış olduğunuz versiyon önemli rol oynuyor.
Proactive Rebalance: vSAN 6.7 U2 ve daha eski bir sürüm kullanıyorsanız, Disk Balance uyarısını gördüğünüzde vSAN Health bölümüne giriş yapabilir ve buradan manuel olarak Proactive Rebalance işlemini gerçekleştirebilirsiniz.
Automatic Rebalance: vSAN 6.7 U3 veya daha yeni bir sürüm kullanıyorsanız, Disk balance uyarısını gördüğünüzde eğer Automatic Rebalance özelliği aktif durumda ise bu işlem otomatik olarak gerçekleştirilir.
vSAN Disk Balance
Öncelikle vSAN 6.7 U2 ve daha eski bir sürüm kullanıyorsanız Proactive Rebalance kullanmanız gerekiyor. Bunun için Monitor > vSAN > Health bölümüne giriş yapmanız gerekiyor. Bu bölüme giriş yaptığınızda karşınıza zaten vSAN Disk Balance warning’i ile karşılaşacaksınız. Bu bölümde Proactive Rebalance Disks butonuna bastığınızda işlem başlayacaktır.
ilk 30 dakika boyunca herhangi bir ilerleme göremeyebilirsiniz. Bunun nedeni, VSAN’ın herhangi bir nesneyi hareket ettirmeden önce dengesizliğin devam ettiğinden emin olmak için beklemek istemesidir. Sonuçta, yeniden dengeleme görevi nesneleri diskler/node’lar arasında taşımaktır. Bu işlem network üzerinden veri kopyalama işlemi yaptığı için, data’nın büyüklüğüne göre bant genişliği ve zaman gerektirir. Bu işlem 24 saat sürebilmektedir. 24 saat sonrasında otomatik durdurulacaktır. Ancak tekrar belirtmek istiyorum, bu işlemi minimum iş yükü olduğunda yapmanız tavsiye ediliyor.
vSAN 6.7 Update 3 ve sonraki versiyonları kullanıyorsanız artık Proactive Rebalance işlemini yapmanıza gerek bulunmuyor. Ancak Automatic Rebalance ‘i öncelikle aktif etmeniz gerekiyor. Bunun için isterseniz yukarıdaki ekrandaki gibi Configure Automatic Rebalance butonuna basabilirsiniz. İsterseniz de Cluster’ı seçtikten sonra Configure > vSAN > Services > Advanced options bölümüne girebilirsiniz.
Advanced Options bölümüne girdiğinizde Automatic Rebalance butonunu göreceksiniz. Default olarak bu seçenek disable durumda gelir. Automatic Rebalance ‘i aktif duruma getirdiğinizde hemen altında Rebalance Thereshold yüzdesi belirtebilirsiniz. Burada belirteceğiniz değerin üzerine disk üzerindeki veri miktarı çıktığında otomatik olarak rebalance işlemi başlar. Siz bu değeri istediğiniz gibi değiştirebilirsiniz.
Önemli: Rebalancing Thereshold değerini default olan %30 değerinde tutun. Bu değerin düşürülmesi, rebalance trafiğinin miktarını artırabilir ve hiçbir işlevsel fayda olmaksızın gereksiz yeniden rebalance’a neden olabilir.
Ancak şunu belirtmek istiyorum. Yukarıda da belirtmiştim aslında. Eğer diskler üzerindeki doluluk %80’e ulaştığında Automatic Rebalance aktif olmasa bile otomatik olarak rebalance işlemine başlanır. Yani %80 üzerine disk doluluğu çıktığında siz hiç bir işlem yapmasanızda, automatic rebalance aktif olmasada arka planda rebalance yapılır.
Rebalance işlemleri sadece disk grupları üzerinde yapılır. Yani, automatic rebalance’i cluster üzerinden aktif ediyorsunuz ancak sadece belirtilen eşik değerleri üzerinde bulunan ESXi hostlar üzerinde bu işlem gerçekleştirilir. Yani komple cluster üzerindeki tüm ESXi host’lar üzerinde bu işlem yapılmaz. Diskler veya disk grupları üzerindeki veriyi sadece ihtiyacı kadar hareket ettirecektir.
vSAN Cluster’ınızda automatic rebalance özelliğini etkinleştirmeniz önerilir. Özellik 6.7 U3’e eklendiğinde, VMware bu özelliği müşteri ortamlarına yavaş yavaş tanıtmak istedi ve vSAN 7’de bu şekilde kalmaya devam etti.
Daha öncede belirttiğim gibi, cluster üzerinde automatic rebalance’i geçici olarak devre dışı bırakmak isteyebileceğiniz birkaç nadir durum olabilir. Kısa bir süre içinde mevcut bir cluster’a çok sayıda ek ESXi host eklemek, bu olasılıklardan biri ve belki de testler için kullanılan nested vSAN ortamları olabilir. Ancak bunun dışında çoğu durumda, automatic rebalance etkinleştirilmelidir.
Umarım faydalı olmuştur.
İyi çalışmalar.
0 notes
Text
NetApp NS0-175 Practice Test Questions
Preparing for NS0-175 Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Design Specialist exam? PassQuestion has designed high quality NetApp NS0-175 Practice Test Questions that appear in the Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Design Specialist exam.We want to ensure your success in the Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Design Specialist exam so we worked hard to help you enhance your knowledge in the NetApp NS0-175 exam. You are required to use NS0-175 Practice Test Questions to help you pass the NetApp NS0-175 exam in the first attempt.Make sure you practice NS0-175 questions and answers multiple time to improve your confidence for your success.
Cisco and NetApp FlexPod certification
You are proficient in designing and installing FlexPod solutions for a variety of business workloads. FlexPod solutions speed the deployment of infrastructure and business-critical applications while reducing cost, complexity, and risk.
NetApp offers two Cisco and NetApp FlexPod certifications: FlexPod Design Specialist and FlexPod Implementation and Administration Specialist.
FlexPod logos and certificates will be granted to those individuals who successfully pass either of the following: Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Design (NS0-175) certification exam. Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Implementation and Administration (NS0-176) certification exam.
Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Design Specialist
NS0-175 exam includes 60 test questions, with an allotted time of 90 minutes to complete. In countries where English is not the native language, candidates will be granted a 30-minute extension to the allotted examination completion time.
NS0-175 Exam Objectives
The NS0-175 exam covers the following topics:
Flexpod Design
Describe FlexPod components based upon customer workloads
Describe how to size a solution based on customer requirements in accordance with FlexPod best practices
Describe the support options for FlexPod
Networking
Describe Cisco networking components used within FlexPod designs
Demonstrate knowledge of FlexPod networking configurations
Security
Describe access control methods for FlexPod solutions
Describe the considerations in building a secure multitenancy design
Tools
Describe resources for determining supported FlexPod components
Demonstrate knowledge of using tools for managing FlexPod
Demonstrate knowledge of troubleshooting methodologies for FlexPod solutions
View Online Cisco and NetApp FlexPod Design Specialist NS0-175 Free Questions
A customer wants to monitor and analyze workloads for all of their NetApp ONTAP clusters including the storage system from their FlexPod environment. In this scenario, which two tools would satisfy this requirement? (Choose two.) A. Cisco Data Center Network Manager B. NetApp ONTAP System Manager C. NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager D. NetApp Active IQ Digital Advisor Answer: CD You have multiple clients that want to use FC. You want to ensure that data is kept separate across a FlexPod deployment. In this scenario, which two constructs would you use to accomplish this task? (Choose two.) A. VSANs B. FLOGI C. VLANs D. Storage VMs Answer: AD When configuring a volume to contain a LUN, which administrative tool automatically applies NetApp recommendations? A. Data ONTAP command-line interface B. Microsoft SystemCenter C. OnCommand System Manager D. VMware vSphere Answer: C
In a FlexPod design, when can NetApp storage be directly connected to a Cisco UCS server? A. Never B. Always C. Only in a FlexPod Select design D. Only in a FlexPod Express design E. Only in a FlexPod DataCenter design Answer: C An administrator is designing a FlexPod backup solution that includes replication to a remote site that includes the capability to restore to a prior point in time. In this scenario, which two technologies are required to accomplish this task? (Choose two.) A. NetApp SyncMirror B. NetApp SnapMirror C. NetApp SnapRestore D. NetApp FlexClone Answer: BC
How many cluster interconnect switch(es) are required for a 4-node NetApp cluster? A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 6 Answer: B
0 notes
Text
Essential Virtual SAN (VSAN) - Cormac Hogan & Duncan Epping
Essential Virtual SAN (VSAN) Administrator's Guide to VMware Virtual SAN Cormac Hogan & Duncan Epping Genre: Computers Price: $39.99 Publish Date: June 23, 2015 Publisher: Pearson Education Seller: Pearson Education Inc. Fully updated for the newest versions of VMware Virtual SAN, this guide show how to scale VMware's fully distributed storage architecture to meet any enterprise storage requirement. World-class Virtual SAN experts Cormac Hogan and Duncan Epping thoroughly explain how Virtual SAN integrates into vSphere 6.x and enables the Software Defined Data Center (SDDC). You'll learn how to take full advantage of Virtual SAN, and get up-to-the-minute insider guidance for architecture, implementation, and management. Writing for administrators, consultants, and architects, Hogan and Epping show how Virtual SAN implements both object-based storage and a policy platform that simplifies VM storage placement. You'll discover how the latest versions of Virtual SAN and vSphere combine to dramatically improve resiliency, scale-out storage functionality, and control over QoS. This edition's extensive new coverage includes: All new VMware Virtual SAN functionality and updates since the first edition An entirely new chapter on stretched clustering and ROBO configurations New discussions of the VM file format, de-deduplication, compression, checksums, encryption, and the Health UI Advanced techniques for delivering enterprise-grade storage capabilities with Virtual SAN Both an up-to-the-minute reference and hands-on tutorial, Essential Virtual SAN, Second Edition uses realistic examples to demonstrate Virtual SAN's most powerful capabilities. You'll learn how to plan, architect, and deploy Virtual SAN successfully, avoid gotchas, troubleshoot problems, and make the most of virtualized storage as you move towards the Software Defined Data Center. http://dlvr.it/R0ncBg
0 notes
Text
VMware vSAN Resilience
By Curtis Brown
VMware vSAN™ is VMware’s hyper-converged storage solution. It has quite a few different methods of providing resilience for the data hosted in it, but these all require some careful consideration when designing the cluster. In this blog I take a look at the configuration options and the design repercussions.
Storage Policy with respect to Resilience
All the approaches are ultimately defined by the VMware vSphere Storage Policy definitions. These policies are defined in VMware vCenter and are applied to objects (usually VMs, but can be individual disks, VM configuration files), subject to the compatibility with the underlying vSAN cluster. However, there are limitations.
The most basic, default policy is RAID-1 configured with a Failures to Tolerate (FTT) of 1 – classic mirroring. In vSAN, this means a complete mirror of the given object, creating two components. In addition, there’s a smaller Witness component. This means we must have a minimum of three nodes in a cluster (though four would be recommended for maintenance and failover). We can up the ante here by increasing FTT value, but while resilience improves there is an obvious impact on capacity.

We can also look at using Erasure Coding to give us RAID-5/6 protection. This takes our object and breaks it out into components, with the data striped across them for resilience. From a configuration perspective, all that separates them is that the FTT value of 1 means RAID-5, while FTT of 2 is RAID-6. However, this does impact the number of components created. In RAID-5, for any object, we have three components created with data striped with a parity bit across them. So rather than the 200% footprint as with RAID-1, we only need 133% instead and get the same resilience, though at a performance cost. RAID-6 requires a fourth object and an extra parity bit, so the footprint is in between at 150%. In either case, we still have a witness component too, so RAID-5 needs a minimum of 4 hosts (5 recommended) and RAID-6 needs 5 hosts (6 recommended).

Fault Domains
Of course, physically our clustered hosts are usually installed in one or more physical racks. Ideally, we’d spread the nodes across racks to mitigate the loss of a rack. vSAN provides Fault Domain functionality to provide an awareness of these physical boundaries.
Consider a Fault Domain as a grouping of hosts within the cluster to represent a boundary of resilience to ensure that vSAN objects subject to a Storage Policy are deployed across the domains, so providing resilience to a loss of a domain (i.e. the loss of a rack) outage.
However, it’s not quite as easy as slinging your hosts into a pair of racks and setting up two zones. As stated above, even RAID-1 requires three hosts due to three objects. This has a knock-on impact when defining Fault Domains too. For RAID-1 based policies, the number of Fault Domains can be represented by the formula (2 x FTT)+1, while RAID 5/6 is (2 x FTT)+2. Therefore, RAID-1 at a minimum requires three domains while RAID-6 would require at least six domains (6 = (2 x 2)+2).

This obviously has limitations as to how useful the feature is when mapped to physical racks – Are you going to spread a small 6-node cluster across six racks to achieve six domains? Or, perhaps across two racks and configure 6 zones, but you could lose three in the event of a rack failure so negating the effort of configuring Fault Domains in the first place.
We now see that the scale of the cluster and physical placement are important factors when deciding whether to use Fault Domains.
Stretch Clusters
This approach is designed to be used across different locations (latency permitting) and largely builds on the concept of Fault Domains. Here, we have two defined Fault Domains (a Preferred and Secondary). Alongside these, we also deploy a Witness appliance in a third location – this serves as a third Fault Domain. We also break out the Failures to Tolerate into two values.
Primary Failures to Tolerate – Refers to Site level failure and can be a value of zero (no resilience, all data resides on either the Preferred or Secondary site) or 1, where the data is replicated between the two domains in the manner of RAID-1.
Secondary Failures to Tolerate – Analogous to FTT in a single site, this is the resilient behaviour within the single site and so can be configured as RAID-1 or RAID-5/6 with various FTT values.
The PFTT value effectively sits above the SFTT value, resulting in the following:

Logically speaking, for a given object, such as a VMDK, the Primary value essentially pushes a RAID-1 mirror across each site, with a Witness component in the appliance. The Secondary element in concert with the RAID setting defines the policy within a site, here a straightforward RAID-1 mirror.
For the numbers of hosts, we therefore need to adhere to the needs of the local policy (be that RAID-1, 5 or 6) and double-up for the second site.
As this resides in a stretch vSphere cluster, we also need to build in some stickiness with respect to compute – so designing DRS and HA accordingly to match the preferred sites.
Closing Thoughts…
When embarking on a vSphere with vSAN design, one should consider not just the compute factors when deciding the number of hosts, but what level of storage protection will be required for the VMs. In fact, by using the protection as a starting point (i.e. ‘We want RAID-6, so a minimum of five hosts is recommended’), the RAM and CPU can be defined above that – whether scaling upwards (five big hosts) or outwards (more, smaller hosts). Even the physical rack design might be a determining factor – whether you can spread across racks or not.
If you’re about to embark on a VMware vSphere based hyper-converged solution, then Xtravirt can help. We have considerable experience in this area and can help with advisory, design and implementation services to create the right solution for your organisation. Contact us and we’d be happy to use our wealth of knowledge and experience to assist you.
About the author
Curtis Brown is a Lead Consultant at Xtravirt. His specialist areas include End User Compute solutions and Virtual Infrastructure design and implementation with particular strength in VDI, storage integration, backup and Disaster Recovery design/implementation. He was awarded VMware vExpert 2018 and is a graduate of the VMware Advanced Architecture Course 2018.
About Xtravirt
Xtravirt is an independent cloud consulting business. We believe in empowering enterprises to innovate and thrive in an ever-changing digital world. We are experts in digital transformation and our portfolio of services cover digital infrastructure, digital workspace, automation, networking and security.
0 notes
Text
Windows amp Hypervisor Senior Analyst
Windows amp Hypervisor Senior Analyst
Windows amp Hypervisor Administrator Senior Analyst< p>
Location Riyadh Saudi Arabia< p>
About Accenture < p>
Accenture is a leading global professional services company providing a broad range of services in strategy and consulting interactive technology and operations with digital capabilities across all of these services. We combine unmatched experience and specialized capabilities across more than 40 industries – powered by the world’s largest network of Advanced Technology and Intelligent Operations centers. With 505 000 people serving clients in more than 120 countries Accenture brings continuous innovation to help clients improve their performance and create lasting value across their enterprises. Visit us at www.accenture.com.< p>
Join Accenture Technology and unleash your skills and transform the world around you. Shape the technology of tomorrow with the latest digital methodologies and design thinking like cloud AI intelligent automation DevOps and Agile. Implement innovative solutions to help clients drive disruption and stay ahead of the digital curve. Innovate with the newest technologies. Be part of the New now and change the world with New IT.< p>
Accenture Technology powers digital transformation through services designed to reinvent your application portfolio and a new style of IT. We combine business and industry insights with innovative technology to drive growth for your business. Accenture Technology delivers applications from design and development through testing and maintenance while helping clients shift to New IT with our leading edge capabilities in automation and connectivity. We provide comprehensive service and project delivery for clients around the world using the latest advances in robotics integrated analytics automation and artificial intelligence.< p>
Key Responsibilities < p>
· Managing VMWare virtualization UCS ESXi windows platforms< p>
· Virtualization VMWare vSphere Suite vCenter vSphere ESXi HA DR Configurations deployment and configurations vSAN vRealize< p>
· Operation Manager< p>
· Strong troubleshooting Knowledge and performance management for vSphere environment Strong knowledge of x86 server hardware platforms Knowledge of UCS Manager< p>
· Deployment and configuration Windows 2012 2019 Administration and Management Patching WSUS along with strong troubleshooting skills< p>
· Installing configuring managing operating and maintaining Windows server systems Windows Clusters e.g. Windows Server 2003 Windows Server 2008.< p>
· Server management including O.S Installing monitoring troubleshooting virus protection patch deployment resources observation and hardware software upgrade .< p>
· Creating maintaining User and group Accounts Deleting Unused Accounts and Implementing Group and user account policies.< p>
· Creating and managing system security policies and components.< p>
· Implementing and managing different disk configurations and formats e.g. NTFS and RAID. And providing connectivity to both local and network SAN storage.< p>
· Troubleshooting and resolving technical problems.< p>
· Providing technical support to users and addressing user issues related to the server system.< p>
· Installing and Configuring DNS FTP DHCP remote access and Terminal Server Services.< p>
· Installing and Configuring Internet Information Services IIS for Web hosting.< p>
· File and Print Server Administration including installation managing users' shares and permissions observing file growth and troubleshooting printing problems .< p>
· Creating implementing and managing backup restore plans and schedules both for tape and disk using either windows or third party software e.g.Netbackup.< p>
· Tuning systems cleanup and resource management.< p>
· Monitoring System status usage and performance.< p>
· Designing planning and executing migration plans and system upgrades.< p>
· Designing planning and executing disaster recovery plans.< p>
· Installing configuring and managing system related software packages and third party packages.< p>
· Generating daily and monthly reports on system status usage and performance.< p>
· General hardware troubleshooting.< p>
· Providing 24 7 on call support to avoid downtime and ensure fast resolution of problems.< p>
· Any other task not mentioned but is directly related to high standard system administration.< p>
Qualification < p>
Year of Experience < p>
· Minimum 3 years of the experience< p>
Technical Skills < p>
Working Knowledge amp experience is must< p>
· Hypervisors VMware ESXi 5.xx to 6.67 < p>
· MS Windows Windows Servers 2012 to 2019 < p>
Technical certifications < p>
· VCP Certified 6< p>
· MCSE MCITP Certified engineer< p>
Other Skills Process amp Soft Skills < p>
· ITIL V3 Awareness Foundation Certified< p>
· Fluent in spoken amp written English< p>
· Arabic Language spoken as “Nice to Have” skill < p>
· Ability to communicate thoroughly through verbal and written mediums.< p>
· Ability to observe ask questions listen actively and give and accept feedback effectively.< p>
· Organize and compile information from external and internal sources.< p>
· Communicate effectively with both external and internal customers.< p>
· Strong communications skills including the ability to communicate technical information in using non technical language< p>
Take part in 24x7 on call rotation< p>< li>
Saudi nationals are preferred in line with vision Saudi 2030.< p>< li> < ul>
· Work out of hours evenings nights weekends bank holidays at reasonable request to perform production changes< p>
Academic Degree < p>
· B. E. B.Tech. MCA MSc.< p>
· Other Graduates with Technical Certification is must < p>
Why join us?< p>
We offer a transparent fast paced approach career progression with a focus on your strengths and continuous coaching from senior colleagues< p>< li>
You will benefit from working alongside Accenture experts who are solving some of the biggest industry challenges with innovative thinking and pioneering tools< p>< li>
Flexible work arrangements and a range of benefits including competitive rewards< p>< li>
You will have access to state of the art technology that will give you the opportunity to deepen your existing skills even as you help create the latest business trends< p>< li>
You will also have opportunities to make a difference to the communities in which we work and live< p>
Next Steps< p>< li> < ul>
If this sounds like the ideal role career and company for you click below to apply.< p>
To learn more about life AccentureMiddleEast follow us on social media and keep up with our latest news.< p>
Accenture Middle East LinkedIn Instagram Facebook Twitter YouTube< p> * راتب مجزي جداً. * مكافأت و حوافز متنوعة. * توفير سكن مؤثث أو بدل سكن. * أنتقالات أو توفير بدل عنها. * توفير تذاكر السفر لمن يشغل الوظيفة و عائلته. * نسبة من الأرباح الربع سنوية. * أجازات سنوية مدفوعة الراتب بالكامل. * مسار وظيفي واضح للترقيات. * بيئة عمل محفزة و مناسبة لحالة الموظف. * تأمين طبي للموظيف و عائلته. * تأمينات أجتماعية. التقدم و التواصل مباشرة دون و سطاء عند توافر الألتزام و الجدية التامة و المؤهلات المطلوبة علي: [email protected]
0 notes