#vSphere Distributed Switch
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
vSphere Distributed Switch Configuration and Best Practices Guide
vSphere Distributed Switch Configuration and Best Practices Guide - Learn how to create and manage vsphere distributed switches and how they compare to vsphere standard switches #vmwarevsphere #vnetworkdistributedswitches #vmwarenetworking #vsphere
VMware vSphere has many advanced networking features as part of the solution. These allow VIadmins to configure just about any setting they need for their network. By default, the vSphere Standard Switch is the default network configuration that comes “out of the box” with a VMware ESXi host installation and virtual switches. However, there is another kind of switch that has many benefits to your…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Dell VxRail Deploy Exam (D-VXR-DY-01) Prep Guide & Practice Exam
The D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 exam is a qualifying exam for the Dell VxRail Deploy v2 Certification, designed to assess your knowledge of implementing and managing a VxRail cluster. This exam covers various topics, from solution planning to hardware and software installation, and troubleshooting, making it essential for IT professionals working with VxRail solutions.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the key aspects of the exam, explore its structure, and share the best tips for preparing, including how to make use of the D-VXR-DY-01 practice exam from Cert007 for optimal study results.
Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 Exam Overview
The Dell VxRail Deploy v2 Certification exam tests your ability to implement a basic VxRail cluster, including hardware installation, environment validation, software implementation, and post-deployment tasks. The exam is split into two parts:
Part 1: 90 minutes
Part 2: 30 minutes
To pass the exam, you need to meet the passing score requirements for both parts.
Understand Key Exam Topics
The following topics are essential for the D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 exam:
1. VxRail Physical Components (4%)
Understanding VxRail cluster architecture
Knowing rack requirements for VxRail clusters
2. VxRail Deployment Planning (12%)
vCenter server and its role in deployment
Networking components and vSphere Distributed Switches
DNS options, node discovery, and vSAN settings
3. Using VxRail Configuration Tools (4%)
Creating and reviewing VxRail projects and configurations
4. VxRail Hardware Installation and Initialization (8%)
Procedures for installing and cabling VxRail hardware
Configuring VxRail node iDRAC and system time settings
5. VxRail Network Environment Requirements and Initialization (8%)
Configuring and validating VxRail network settings manually
6. Deploying the VxRail Cluster (24%)
Initializing VxRail clusters with VxRail or customer-managed vCenter Server
vSAN ESA (vSAN Express Storage Architecture) setup
7. VxRail Post-Deployment Procedures (18%)
Performing post-installation validation
Configuring vSAN settings and native backups
8. VxRail Cluster Upgrade and Expansion (10%)
Understanding upgrade requirements and scale-out processes
9. VxRail Troubleshooting (6%)
Collecting logs and troubleshooting using VxRail and vSAN tools
10. VxRail REST API (6%)
Using VxRail REST APIs to automate tasks and troubleshoot issues
Study Tips for D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Exam
Preparing for the D-VXR-DY-01 exam requires a solid understanding of the VxRail system, hardware installation, networking, and troubleshooting. To maximize your chances of success, follow these steps:
Understand the Core Topics: Focus on the key areas of the exam, including deployment planning, hardware installation, and post-deployment procedures. Review Dell’s official documentation and guides related to VxRail clusters.
Hands-On Experience: Practical experience with VxRail components, vCenter Server, and networking setups is crucial. Try to work on a live or simulated VxRail environment to get familiar with the installation and configuration processes.
Use VxRail Tools: Gain proficiency with tools like the VxRail Configuration Portal and REST API. Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues using logs and vSAN tools will be particularly useful for the troubleshooting section.
Practice Exams: One of the best ways to prepare for the exam is by using D-VXR-DY-01 practice exams from Cert007. These practice exams closely simulate the real exam experience, helping you assess your readiness and pinpoint areas that need more study.
Review Study Materials: Cert007 offers comprehensive and up-to-date study materials specifically designed for the Dell VxRail Deploy v2 exam. These materials cover every exam topic in detail and provide insights into common issues and troubleshooting strategies.
Final Thoughts
The D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 Certification is an essential step for professionals looking to demonstrate their expertise in deploying and managing Dell VxRail clusters. By focusing on key exam topics, gaining hands-on experience, and leveraging practice exams from Cert007, you can confidently prepare for and pass the exam.
Invest in quality study materials and practice exams to ensure you're well-prepared for this important certification. Good luck on your journey to becoming Dell VxRail Deploy certified!
0 notes
Text


A distributed firewall (DFW) is s replicated among multiple hosts the way the vSphere distributed switch or logical router is replicated. With the DFW, it is possible to deploy any multitier application in the same Layer 2 broadcast domain for all tiers and have the same subnet and the same default gateway. https://www.dclessons.com/distributed-logical-firewall
#DistributedFirewall#NetworkSecurity#FirewallProtection#Cybersecurity#DCLessons#LogicalFirewall#FirewallManagement#DataCenterSecurity#NetworkProtection#SecurityBestPractices#FirewallTechnology#CyberDefense#InformationSecurity#FirewallSolutions#NetworkInfrastructure
0 notes
Text
Uncovering vSphere Virtual Networking Part-2: Switches
Uncovering vSphere Virtual Networking Part-2: Switches

As discussed in previous post Part-1: Basics, we have two types of switches that are available in vSphere i.e. Standard switch and Distributed switch. So in this post we will explore these switch types. But before we do that, let’s dive into basics of switches in virtual architecture first.
What is a virtual switch?
A virtual switch is a software program that emulates a switch as a layer-2…
View On WordPress
#distributed switch#dvs#esxi#ESXi 7#standard switch#vds#virtual switch#vSphere#vsphere 6.5#vsphere 6.7#vsphere 7
0 notes
Text
vSphere Distributed Switch
vSphere Distributed Switch
A vSphere Distributed Switch acts as a single virtual switch across all associated hosts. This allows virtual machines to maintain consistent network configuration as they migrate across hosts.
Like a virtual switch, a distributed virtual switch is a network hub for virtual machines. A vSphere Distributed Switch can route traffic internally between virtual machines or…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Cisco Nexus 1000 V Ova

Cisco Nexus 1000 V Oval
Cisco Nexus 1000v Ova Download
Posted on 03 Apr 2012 by Ray Heffer
Installing the Cisco Nexus 1000V distributed virtual switch is not that difficult, once you have learned some new concepts. Before I jump straight into installing the Nexus 1000V, lets run through the vSphere networking options and some of the reasons you’d want to implement the Nexus 1000V.
vSS (vSphere Standard Switch)
Often referred to as vSwitch0, the standard vSwitch is the default virtual switch vSphere offers you, and provides essential networking features for the virtualisation of your environment. Some of these features include 802.1Q VLAN tagging, egress traffic shaping, basic security, and NIC teaming. However, the vSS or standard vSwitch, is an individual virtual switch for each ESX/ESXi host and needs to be configured as individual switches. Most large environments rule this out as they need to maintain a consistent configuration across all of their ESX/ESXi hosts. Of course, VMware Host Profiles go some way to achieving this but it’s still lacking in what features in distributed switches.
vDS (vSphere Distributed Switch)
So the vDS, also known as DVS (Distributed Virtual Switch) provides a single virtual switch that spans all of your hosts in the cluster, which makes configuration of multiple hosts in the virtual datacenter far easier to manage. Some of the features available with the vDS includes 802.1q VLAN tagging as before, but also ingress/egress traffic shaping, PVLANs (Private VLANs), and network vMotion. The key with using a distributed virtual switch is that you only have to manage a single switch.
Cisco Nexus 1000V Virtual Security Gateway Version 4.2(1)VSG2(1.1) for VMware vSphere 4.1 +. 1010 OVA - nexus-1000v.VSG2.1.1.1010.ova (md5.
Cisco Nexus 1000V cloud switch is a virtual appliance. It provides integration of physical and virtualized network infrastructure. Cisco Nexus 1000V switch is compatible with VMware ESX and vSphere (ESXi) hypervisors. There is a version for Microsoft Hyper-V and Open KVM as well for additional public cloud and platform support.
1 st – Create the VRF – here mgmt-vrf. 2 nd – Assign the interface to the VRF. As you can see, the interface is by default in shutdown. For my home lab setup I use the 192.168.0.9x range for labbing. I use the X to signify the router – to.91 will be CSR1000V-1,.92 will be CSR1000V-2, and.93 will be CSR1000V-3. Cisco Nexus 1000V Installation and Upgrade Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV1(5.2) Chapter Title. Installing the Cisco Nexus 1000V Software Using ISO or OVA Files. PDF - Complete Book (12.02 MB) PDF - This Chapter (2.79 MB) View with Adobe Reader on a variety of devices. EPub - Complete Book (4.38 MB). Cisco Nexus 1000v Secondary Switch Module Setup Cisco Nexus 1000v Secondary Switch. Open up your vCenter Management Console. Click on File and Deploy OVF Template. Select the same version OVA package that you used for your primary switch. A summary is shown of the Cisco Nexus 1000v virtual appliance.
Cisco Nexus 1000V
In terms of features and manageability, the Nexus 1000V is over and above the vDS as it’s going to be so familiar to those with existing Cisco skills, in addition to a heap of features that the vDS can’t offer. For example, QoS tagging, LACP, and ACLs (Access Control Lists). Recently I have come across two Cisco UCS implementations which require the Nexus 1000V to support PVLANs in their particular configuration (due to the Fabric Interconnects using End-Host Mode). There are many reasons one would choose to implement the Cisco Nexus 1000V, lets call it N1KV for short :)
Without further delay, grab a coffee and we’ll get the N1KV installed!
Components of the Cisco Nexus 1000V on VMware vSphere
There are two main components of the Cisco Nexus 1000V distributed virtual switch; the VSM (Virtual Supervisor Module) and the VEM (Virtual Ethernet Module). If you are familiar with Cisco products and have worked with physical Cisco switches, then you will already know what the supervisor module and ethernet modules are. In essence, a distributed virtual switch, whether we are talking about the vSphere (vDS) or N1KV have a common architecture. That is the control and data plane, which is what makes it ‘distributed’ in the first place. By separating the control plane (VSM), and the data plane (VEM), a distributed switch architecture is possible as illustrated in the diagram here (left).
Another similarity that is the use of port groups. You should be familiar with port groups as they are present on both the VMware vSS and vDS. In Cisco terms, we’re talking about ‘port profiles’, and they are configured with the relevant VLANs, QoS, ACLs, etc. Port profiles are presented to vSphere as a port group.
Installing the Cisco Nexus 1000V
What you need:
A licensed copy of the Cisco Nexus 1000V
vSphere environment with vCenter.
At least one ESX/ESXi host, preferably two or more! - If you are using a lab environment and don’t have the physical hardware available then create a virtual ESXi server (this post by VCritical details how to do this).
You’ll also need to create the following VLANs: Control, Management, and Packet
Note: If you are doing this in a lab environment then you can place all of the VLANs into a single VM network, but in production make sure you have separate VLANs for these.
In the latest release of the Nexus 1000V the Java based installer, which we will come on to in a moment, now deploys the VSM (or two VSMs in HA mode) to vCenter and a GUI install wizard guides you through the steps. This has made deployment of the N1KV even easier than before.
Once you have downloaded the Nexus 1000V from the Cisco website, continue on to the installation steps.
Installation Steps:
1) Extract the .zip file you downloaded from Cisco, and navigate to VSMInstaller_AppNexus1000V-install.jar. Open this (you need Java installed) and it will launch the installation wizard. Enter the vCenter IP address, along with a username and password.
2) Select the vSphere host where the VSM resides and click Next.

3) Select the OVA (in the VSMInstall directory), system redundancy option, virtual machine name and datastore, then click Next.
Note: This step is new, previously you had to deploy the OVA first, then run this wizard. If you choose HA as the redundancy option, it will append -1 or -2 to the virtual machine name.
4) Now configure the networking by selecting your Control, Management and Packet VLANs. Click Next.
Note: In my home lab, I just created three port groups to illustrate this. Obviously in production you would typically have these VLANs defined, otherwise you can create new ones here on the Nexus 1000V.
5) Configure the VSM by entering the switch name, admin password and IP address settings.
Note: The domain ID is common between the VSMs in HA mode, but you will need a unique domain ID if running multiple N1KV switches. For example, set the domain ID to 10. The native VLAN should be set to 1 unless otherwise specified by your network administrator.
6) You can now review your configuration. If it’s all correct, click Next. Alesis multimix 8 usb drivers.
7) The installer will now start deploying your VSM (or pair if using HA) with the configuration settings you entered during the wizard.
8) Once it has deployed you’ll get an option to migrate this host and networks to the N1KV. Choose No here as we’ll do this later.
Cisco Nexus 1000 V Oval
9) Finally you’ll get the installation summary, and you can close the wizard.
You’ll now see two Nexus 1000V VSM virtual machines in vCenter on your host. In a production environment you would typically have the VSMs on separate hosts for resilience. Within vCenter, if you navigate to Inventory > Networking you should now see the Nexus 1000V switch:
Installing the Cisco Nexus 1000V Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM) to ESXi 5
What we are actually doing here is installing the VEM on each of your ESX/ESXi hosts. In the real world I prefer to use VMware Update Manager (VUM) to do this, as it will automatically add the VEM to a host when it is added to the N1KV virtual switch. However, for this tutorial I will show you how to add the VEM using the command line with ESXi 5.
1) Open a web browser and open the Nexus 1000V web page, http://. You will then be presented with the Cisco Nexus 1000V extension (xml file) and the VEM software. It’s the VEM we are interested in here, so download the VIB that corresponds to your ESX/ESXi build.
2) Copy the VIB file on to your ESX/ESXi host. You must place this into /var/log/vmware as ESXi 5 expects the VIB to be present there.
Note: Use the datastore browser in vCenter to do this.
3) Log into the ESXi console either directly or using SSH (if it is enabled) and enter the following command:
# esxcli software vib install -v /var/log/vmware/cross_cisco-vem-v140-4.2.1.1.5.1.0-3.0.1.vib
You should then see the following result:
4) You can verify that the VEM is installed using the following commands:
Labtec driver keyboard. # esxcli software vib list | grep cisco
# vem status -v
Configuring the Nexus 1000V
Before we add our hosts to the Nexus 1000V we’ll need to create the port profiles, including the uplink port profile. The uplink port profile will be selected when we add our hosts to the switch, and this will typically be a trunk port containing all of the VLANs we wish to trunk to the hosts.
1) Log into the Nexus 1000V using SSH
2) Create a ethernet port profile as follows:
Adding ESX/ESXi Hosts to the Cisco Nexus 1000V
The final step is to add your host(s) to the Cisco Nexus 1000V.
1) Within vCenter, browse to Inventory > Networking and select the Cisco Nexus 1000V switch. Right click, and select ‘Add Host’.
2) Select the vmnic(s) of the host(s) you want to add and choose the VM_Uplink in the dropdown (we created this in the last step) and click Next.
Note: You’ll notice in the above screenshot that I’m adding a spare vmnic as I don’t want to lose connectivity with my standard vSwitch.
3) Migrate your port groups to the Nexus 1000V, such as the Management (vmk). Click Next.
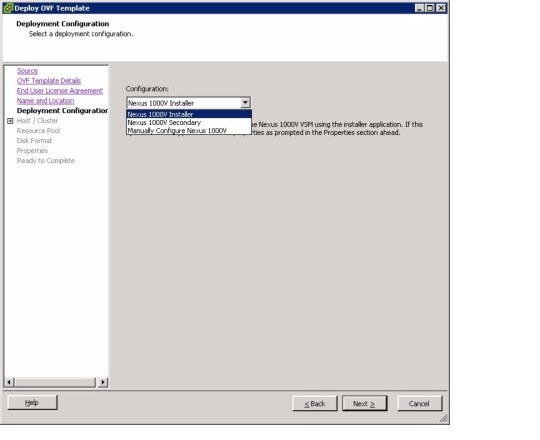
Note: I chose not to do this, this can be done later.
4) You will then have the opportunity to migrate your virtual machines to the N1KV. This is optional and can be done later. Click Next.
5) Review the summary and click Finish.

Summary
We have just downloaded and installed the Cisco Nexus 1000V, installed the VSMs to vCenter, installed the VEM to your host and added the host to the Cisco Nexus 1000V switch. The next steps are to configure the Nexus 1000V, port profiles, etc.Common Questions:
How many Cisco Nexus 1000V virtual switches can be added to vCenter?
vCenter can connect to up to 32 Distributed Virtual Switches, this includes the Nexus 1000V. You’ll need a VSM (or pair for redundancy) for each N1KV switch. A Nexus 1000V can only connect to a single vCenter.
Can the Nexus 1000V stretch across sites?
Since software release 4.2(1)SV1(4a), yes. Table 1 in the release notes contains the configuration limits.
Can the VSM reside on the same ESX/ESXi host as the VEM?
Cisco Nexus 1000v Ova Download
Yes (can also be on a separate host)
Tagged with: vmwarenetworking

0 notes
Text
Palo Alto Ova File

Palo Alto Ova For Vmware
Palo Alto Ova File

The VM-Series firewall is distributed using the Open Virtualization Alliance (OVA) format, which is a standard method of packaging and deploying virtual machines. You can install this solution on any x86 device that is capable of running VMware ESXi.
In order to deploy a VM-Series firewall, you must be familiar with VMware and vSphere including vSphere networking, ESXi host setup and configuration, and virtual machine guest deployment.
To get a Palo Alto virtual firewall working and see how to configure its basic security settings. Downloading the OVA File Go to the page linked below, and log in with the credentials given in class. Downloading the Virtual Machines. Find the 'CNIT 140' section and download the Palo Alto Firewall. Complete the following steps to prepare the heat templates, bootstrap files, and software images needed to deploy the VM-Series firewall. After preparing the files. The Palo Alto Networks Education department does not offer or provide free evaluations, trial licenses, OVA files, or VMs for lab practice. We recommend contacting a sales representative to see what other options are available to you. As an alternative, learners can pay a.
You can deploy one or more instances of the VM-Series firewall on the ESXi server. Where you place the VM-Series firewall on the network depends on your topology. Choose from the following options (for environments that are not using VMware NSX):
One VM-Series firewall per ESXi host—Every VM server on the ESXi host passes through the firewall before exiting the host for the physical network. VM servers attach to the firewall via virtual standard switches. The guest servers have no other network connectivity and therefore the firewall has visibility and control to all traffic leaving the ESXi host. One variation of this use case is to also require all traffic to flow through the firewall, including server to server (east-west traffic) on the same ESXi host.
One VM-Series firewall per virtual network—Deploy a VM-Series firewall for every virtual network. If you have designed your network such that one or more ESXi hosts has a group of virtual machines that belong to the internal network, a group that belongs to the external network, and some others to the DMZ, you can deploy a VM-Series firewall to safeguard the servers in each group. If a group or virtual network does not share a virtual switch or port group with any other virtual network, it is completely isolated from all other virtual networks within or across the host(s). Because there is no other physical or virtual path to any other network, the servers on each virtual network must use the firewall to talk to any other network. Therefore, it allows the firewall visibility and control to all traffic leaving the virtual (standard or distributed) switch attached to each virtual network.
Hybrid environment—Both physical and virtual hosts are used, the VM-Series firewall can be deployed in a traditional aggregation location in place of a physical firewall appliance to achieve the benefits of a common server platform for all devices and to unlink hardware and software upgrade dependencies.
System Requirements
You can create and deploy multiple instances of the VM-Series firewall on an ESXi server. Because each instance of the firewall requires a minimum resource allocation number of CPUs, memory and disk space—on the ESXi server, make sure to conform to the specifications below to ensure optimal performance.
The VM-Series firewall has the following requirements:
The host CPU must be a x86-based Intel or AMD CPU with virtualization extension.
VMware ESXi with vSphere 5.1, 5.5, 6.0, or 6.5 for VM-Series running PAN-OS 8.0. The VM-Series firewall on ESXi is deployed with VMware virtual machine hardware version 9 (vmx-09); no other VMware virtual machine hardware versions are supported.
See VM-Series System Requirements for the minimum hardware requirements for your VM-Series model.
Minimum of two network interfaces (vmNICs). One will be a dedicated vmNIC for the management interface and one for the data interface. You can then add up to eight more vmNICs for data traffic. For additional interfaces, use VLAN Guest Tagging (VGT) on the ESXi server or configure subinterfaces on the firewall.
The use of hypervisor assigned MAC address is enabled by default. vSphere assigns a unique vmNIC MAC address to each dataplane interface of the VM-Series firewall. If you disable the use hypervisor assigned MAC addresses, the VM-Series firewall assigns each interface of a MAC address from its own pool. Because this causes the MAC addresses on each interface to differ, you must enable promiscuous mode (see Before deploying the OVA file, set up virtual standard switch(es) and virtual distributed switch(es) that you will need for the VM-Series firewall.) on the port group of the virtual switch to which the dataplane interfaces of the firewall are attached to allow the firewall to receive frames. If neither promiscuous mode nor hypervisor assigned MAC address is enabled, the firewall will not receive any traffic. This is because vSphere will not forward frames to a virtual machine when the destination MAC address of the frame does not match the vmNIC MAC address.
Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) is enabled by default on VM-Series firewalls on ESXi. For more information about DPDK, see Enable DPDK on ESXi.
To achieve the best performance out of the VM-Series firewall, you can make the following adjustments to the host before deploying the VM-Series firewall. See Performance Tuning of the VM-Series for ESXi for more information.
Enable DPDK. DPDK allows the host to process packets faster by bypassing the Linux kernel. Instead, interactions with the NIC are performed using drivers and the DPDK libraries.
Enable SR-IOV. Single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) allows a single PCIe physical device under a single root port to appear to be multiple separate physical devices to the hypervisor or guest.
Do not configure a vSwitch on the physical port on which you enable SR-IOV. To communicate with the host or other virtual machines on the network, the VM-Series firewall must have exclusive access to the physical port and associated virtual functions (VFs) on that interface.
Enable multi-queue support for NICs. Multi-queue allows network performance to scale with the number of vCPUs and allows for parallel packet processing by creating multiple TX and RX queues.
Note:-
Do not use the VMware snapshots functionality on the VM-Series on ESXi. Snapshots can impact performance and result in intermittent and inconsistent packet loss.See VMWare’s best practice recommendation with using snapshots.

If you need configuration backups, use Panorama or Export named configuration snapshot from the firewall (Device > Set up > Operations). Using the Export named configuration snapshot exports the active configuration (running-config.xml) on the firewall and allows you to save it to any network location.
Limitations
The VM-Series firewall functionality is very similar to the Palo Alto Networks hardware firewalls, but with the following limitations:
Dedicated CPU cores are recommended.
High Availability (HA) Link Monitoring is not supported on VM-Series firewalls on ESXi. Use Path Monitoring to verify connectivity to a target IP address or to the next hop IP address.
Up to 10 total ports can be configured; this is a VMware limitation. One port will be used for management traffic and up to 9 can be used for data traffic.
Only the vmxnet3 driver is supported.
Virtual systems are not supported.
vMotion of the VM-Series firewall is not supported. However, the VM-Series firewall can secure guest virtual machines that have migrated to a new destination host, if the source and destination hosts are members of all vSphere Distributed Switches that the guest virtual machine used for networking.
My videos 3d pro. MyVideos 3D+ Pro v3.0 Apk play your HD videos with real time 3D effects, 3D.
VLAN trunking must be enabled on the ESXi vSwitch port-groups that are connected to the interfaces (if configured in vwire mode) on the VM-Series firewall.
To use PCI devices with the VM-Series firewall on ESXi, memory mapped I/O (MMIO) must be below 4GB. You can disable MMIO above 4GB in your server’s BIOS. This is an ESXi limitation.
Deploy Paloalto VM-Series
Register your VM-Series firewall and obtain the OVA file from the Palo Alto Networks Customer Support web site.
Note:- The OVA is downloaded as a zip archive that is expanded into three files: the .ovf extension is for the OVF descriptor file that contains all metadata about the package and its contents; the .mf extension is for the OVF manifest file that contains the SHA-1 digests of individual files in the package; and the .vmdk extension is for the virtual disk image file that contains the virtualized version of the firewall.
Before deploying the OVA file, set up virtual standard switch(es) and virtual distributed switch(es) that you will need for the VM-Series firewall.
If you are deploying the VM-Series firewall with Layer 3 interfaces, your firewall will use Hypervisor Assigned MAC Addresses by default. If you choose to disable the use of hypervisor assigned MAC address, you must configure (set to Accept) any virtual switch attached to the VM-Series firewall to allow the following modes:
Promiscuous mode
MAC address changes
Forged transmits
Log in to vCenter from the vSphere Web Client. You can also go directly to the target ESXi host if needed.
From the vSphere client, select FileDeploy OVF Template.
Browse to the OVA file that you downloaded and select the file and then click Next. Review the templates details window and then click Next again.
Name the VM-Series firewall instance and in the Inventory Location window, select a Data Center and Folder and click Next
Select an ESXi host for the VM-Series firewall and click Next.
Select the datastore to use for the VM-Series firewall and click Next ( Default virtual disk format is thick and you may change to Thin )
Palo Alto Ova For Vmware
Select the networks to use
Review the details window, select the Power on after deployment check box and then click Next.

Initial Configuration
Access the console of the VM-Series firewall.
Enter the default username/password (admin/admin) to log in.

Enter configure to switch to configuration mode.
Configure the network access settings for the management interface. You should restrict access to the firewall and isolate the management network. Additionally, do not make the allowed network larger than necessary and never configure the allowed source as 0.0.0.0/0.
Now you have to exit from configuration mode by entering exit
Access the Firewall from a web browser
Open the Browse and type the IP you have assigned to the VM to access the console.
Enter the credentials
You are logged in to the PA firewall and you can start using it
Rascal flatts broken road mp3 download. Conclusion
Palo Alto Ova File
Here we shared detailed information about the deployment of paloalto VM-Series edition and steps to follow for a successful deployment. Also what is the limitation and system requirements for a virtual edition with reference links have been added to it, you have to refer them before starting the deployment

0 notes
Text
1V0-21.20 Real Questions To Pass Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization
1V0-21.20 Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization exam is one of the most popular VMware Certification exams. PassQuestion has the right solutions for you to pass your VMware 1V0-21.20 Exam with confidence. PassQuestion offers economic 1V0-21.20 Real Questions with best quality and dynamic updates. Use PassQuestion for accurate 1V0-21.20 Real Questions for a successful preparation of 1V0-21.20 Certification Exam. We guarantees that after using our 1V0-21.20 Real Questions, you will be prepared to take and pass your VCTA-DCV Certification 1V0-21.20 exam in a easy way.
1V0-21.20 Exam Information - Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization
The Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization Exam (1V0-21.20), which leads to VMware Certified Technical Associate –Data Center Virtualization 2020 is a 51-item exam, with a passing score of 300 using a scaled method. Exam time is 135 minutes.The Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization exam tests a candidate's basic understanding of virtualization and vSphere concepts, data center technology and basic troubleshooting concepts.
Exam Number: 1V0-21.20 Exam Language: English Associated Certification: VMware Certified Technical Associate – Data Center Virtualization 2020 Duration: 135 minutes Number of Questions: 51 Questions Passing Score: 300 Format: Single and Multiple Choice, Proctored
Sections Included in the ExamSection 1 -Architectureand Technologies
Objective1.1: Identify how physical resources are presented to multiple virtual machines. Objective 1.2: Identify how virtual resources can be shared across multiple virtual machines. Objective 1.3: Identify examples of type 1 and type 2hypervisors. Objective 1.4: Identify business challenges addressed by vSphere. Objective 1.5: Identify the components of a vSphere environment. Objective 1.6: Identify vSphere virtual networking components and types. Objective 1.7: Identify the characteristics of storage access protocols for vSphere. Objective 1.8: Identify the characteristics of vSphere storage technologies. Objective 1.9: Identify the purposes of different virtual machine files. Objective 1.10: Identify the types of OS that can run on virtual machines. Objective 1.11: Identifyuse cases for virtual machine snapshots, cloning and templates. Objective 1.12: Identify the functionality of the vSphere vMotion and Storage vMotion technology Objective 1.13: Identify the use cases of vSphere vMotion and Storage vMotion technology Objective 1.14: Identify the characteristics of vSphere High Availability and Fault Tolerance. Objective 1.15: Identify use cases of High Availability and Disaster Recovery. Objective 1.16: Identify the functionality of VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS). Objective 1.17: Given a DRS score, identify the meaning. Objective 1.18: Identify the use cases for Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC).
Section 2 -VMware Products and Solutions–There are no testable objectives for this sectionSection 3 -Planning and Designing–There are no testable objectives for this sectionSection 4 -Installing, Configuring, and Setup
Objective 4.1: Identify Virtual Switch configuration options. Objective 4.2: Identify how to configure different types of datastores. Objective 4.3: Identify how to configure vSphere HA. Objective 4.4: Identify how to configure vSphere DRS. Objective 4.5: Identify how to configure EVC.
Section 5 -Performance-tuning, Optimization, Upgrades–There are no testable objectives for this sectionSection 6 -Troubleshooting and Repairing–There are no testable objectives for this sectionSection 7 -Administrative and Operational Tasks
Objective 7.1: Identify how to create and manage VM snapshots. Objective 7.2: Identify how to manage VM templates and clones. Objective 7.3: Identify the considerations when provisioning a VM. Objective 7.4: Identify the options that can be performed on different inventory objects. Objective 7.5: Identify the concepts of role-based user management Objective 7.6: Identify virtual networking issues that impact vSphere. Objective 7.7: Identify virtual storage issues that impact vSphere. Objective 7.8: Identifythe purpose of monitoring alarms, tasks and events. Objective 7.9: Identify how to monitor vSphere Cluster and SDRS Cluster. Objective 7.10: Identify how to perform and monitor vMotion, Storage vMotion, and Cold migrations. Objective 7.11: Given a vSphere environment, identify how to use performance charts to monitor the environment. Objective 7.12: Identify the purpose for VMware Tools.
View Online Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization 1V0-21.20 Free Questions
What is the default encrypted vSphere vMotion state for virtual machines that are not encrypted? A. Enabled B. Disabled C. Opportunistic D. Required Answer: C
Which feature must be enabled to use vSphere Fault Tolerance? A. vSphere HA B. vSphere DRS C. vSphere Replication D. vSAN Answer: A
Which hypetvisor is a type-1 hypervisor? A.Oracle VM VirtualBox B.VMware ESXi C.VMware Fusion D.VMware Workstation Answer : B
A system administrator is preparing a host In a vSphere DRS cluster in partially automated mode for firmware patching and puts a host into maintenance mode. After several minutes, the host still has not entered maintenance mode. How should the system administrator resolve this problem? A.The system administrator needs to schedule DRS to run again. B.vSphere Lifecycle Manager and DRS integration need to be configured. C.vSphere HA admission control needs to be enabled on the cluster. D.The system administrator needs to migrate virtual machines using vSphere vMotion. Answer : D
Which IP storage is supported on vSphere? A.SCSI B.vSAN C.SAN D.ISCSI Answer : D
Which vSphere feature protects against host hardware failures by restarting virtual machines (VMs) on hosts that are running in the cluster? A.vSphere HA B.vSphere vMotion C.vSphere Fault Tolerance D.vSphere DRS Answer : A
0 notes
Text
VMware Networking: 5 Concepts to Master
VMware Networking: 5 Concepts to Master #homelab #selfhosted #vmware #VMwareNetworkingEssentials #vSphereStandardVsDistributedSwitch #ManagingMultipleUplinks #UnderstandingVMwareFailovers #MasteringLoadBalancingInVirtualEnvironments #VLANTaggingInVMware
One of the challenges when getting into virtualization using VMware ESXi and vSphere with vCenter Server is understanding the many different networking concepts. There are a few foundational concepts in the VMware networking layer that you need to understand and master that will provide a basis for building your environment connected to the virtual network in your VMware environment. Table of…

View On WordPress
#configuring VMkernel ports#ensuring security with virtual switches#managing multiple uplinks#mastering load balancing in virtual environments#optimizing virtual and physical network communication#understanding VMware failovers#VLAN tagging in VMware#VMware network traffic management#VMware networking essentials#vSphere Standard vs Distributed Switch
1 note
·
View note
Text
AWS Responds To Anthos And Azure Arc With Amazon EKS Anywhere
New Post has been published on https://perfectirishgifts.com/aws-responds-to-anthos-and-azure-arc-with-amazon-eks-anywhere/
AWS Responds To Anthos And Azure Arc With Amazon EKS Anywhere
Amazon made strategic announcements related to container services at the re:Invent 2020 virtual event. Here is an attempt to deconstruct the container strategy of AWS.
Containers
Amazon EKS Distribution – An Alternative to Commercial Kubernetes Distributions
The cloud native ecosystem is crowded and even fragmented with various distributions of Kubernetes. Customers can choose from upstream Kubernetes distribution available for free or choose a commercial offering such as Charmed Kubernetes from Canonical, Mirantis Container Cloud, Rancher Kubernetes Engine, Red Hat OpenShift and VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
Amazon has decided to jump the Kubernetes distribution bandwagon with Amazon EKS Distribution (EKS-D), which powers the managed EKS in the cloud. Customers can rely on the same versions of Kubernetes and its dependencies deployed by Amazon EKS, which includes the latest upstream updates and comprehensive security patching support.
Amazon EKS-D comes with source code, open source tooling, binaries and container images, and the required configuration via GitHub and S3 storage locations. With EKS- D, Amazon promises extended support for Kubernetes versions after community support expires, providing updated builds of previous versions, including the latest security patches.
Why Did Amazon Launch EKS-D?
Customers running OpenShift or VMware Tanzu are more likely to run the same flavor of Kubernetes in the cloud. Most of the commercial Kubernetes distributions come with services and support for managing hybrid clusters. In this case, ISVs like Red Hat and VMware will leverage Amazon EC2 to run their managed Kubernetes offering. They decouple the underlying infrastructure (AWS) from the workloads, making it possible to port applications to any cloud.
Amazon’s ultimate goal is to drive the adoption of its cloud platform. With EKS-D, AWS has built an open source bridge to its managed Kubernetes platform, EKS.
Backed by Amazon’s experience and the promise to maintain the distribution even after the community maintenance window expires, it’s a compelling option for customers. An enterprise running EKS-D will naturally use Amazon EKS for its hybrid workloads. This reduces the friction between using a different Kubernetes distribution for on-prem and cloud-based environments. Since it’s free, customers are more likely to evaluate it before considering OpenShift or Tanzu.
Additionally, Amazon can now claim that it made significant investments in open source by committing to maintain EKS-D.
The design of EKS-D, which is based on upstream Kubernetes, makes it easy to modify the components such as the storage, network, security, and observability. The cloud native ecosystem will eventually build reference architectures for using EKS-D with their tools and components. This makes EKS-D better than any other distribution available in the market.
In summary, EKS-D is an investment from Amazon to reduce the friction involved in adopting AWS when using a commercial Kubernetes distribution.
EKS Anywhere – Amazon’s Response to Anthos and Azure Arc
According to AWS, Amazon EKS Anywhere is a new deployment option for Amazon EKS that enables customers to easily create and operate Kubernetes clusters on-premises, including on their own virtual machines (VMs) and bare metal servers.
EKS Anywhere provides an installable software package for building and managing Kubernetes clusters on-premises and automation tooling for cluster lifecycle support.
EKS-A can be technically installed on any infrastructure with available compute, storage, and network resources. This includes on-premises and cloud IaaS such as Google Compute Engine and Azure VMs.
Simply put, Amazon EKS Anywhere is an installer for EKS-D with AWS specific parameters and options. The installer comes with the defaults that are optimized for AWS. It works best on Amazon Linux 2 OS and tightly integrated with App Mesh for service mesh, CloudWatch for observability and S3 for cluster backup. When installed in a VMware environment, it even provides infrastructure management through the integration with vSphere APIs and vCenter. EKS-A relies on GitOps to maintain the desired state of cluster and workloads. Customers can subscribe to an Amazon SNS channel to automatically get updates on patches and releases.
Amazon calls EKS-A an opinionated Kubernetes environment. The keyword here is opinionated, which translates to as proprietary as it can get. From container runtime to the CNI plug-in to cluster monitoring, it has a strong dependence on AWS building blocks.
There is nothing open source about EKS-A. It’s an opaque installer that rolls out an EKS-like cluster on a set of compute nodes. If you want to customize the cluster components, switch to EKS-D, and assemble your own stack.
EKS-A supports three profiles – fully connected, semi-connected and fully disconnected. Unlike ECS Anywhere, EKS-A clusters can be deployed in offline, air-gapped environments. Fully connected and semi-connected EKS-A clusters talk to AWS cloud but have no strict dependency on the cloud.
EKS-A is Amazon’s own version of Anthos. Just like Anthos, it’s tightly integrated with vSphere, can be installed on bare metal or any other cloud. But the key difference is that there is no meta control plane to manage all the EKS-A clusters from a single pane of glass. All other capabilities such as Anthos Service Mesh (ASM) and Anthos Config Management (ACM) will be extended to EKS-A through App Mesh and Flux.
Unlike Anthos, EKS-A doesn’t have the concept of admin clusters and user clusters. What it means is that customers cannot use EKS-A for the centralized lifecycle management of clusters. Every EKS-A cluster is independent of others with optional connectivity to the AWS cloud. This topology closely resembles the stand-alone mode of Anthos on bare metal.
EKS-A will eventually become the de facto compute environment for AWS Edge devices such as Snowball. Similar to K3s, Amazon may even plan to launch an EKS Anywhere Mini to target single node installations of Kubernetes for the edge. It may have tight integration with AWS Greengrass, the software for edge devices.
EKS-A is the first, real multi-cloud software coming from AWS. If you are not concerned about the lock-in it brings, EKS-A dramatically simplifies deploying and managing Kubernetes. It brings AWS a step closer to multi-cloud platforms such as Anthos, Azure Arc, Rancher, Tanzu Mission Control and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Manager for Kubernetes.
EKS Console – The Meta Control Plane for Kubernetes in the Making
Though EKS-A comes across as a proprietary installer for EKS, it goes beyond that. Combined with a new addition called EKS Console, multiple EKS-A clusters can be managed from the familiar AWS Console. Of course, the EKS Console will provide visibility into all the managed clusters running in AWS.
EKS-A clusters running in fully-connected and semi-connected modes can be centrally managed from the EKS Console. AWS may open up the ability to attach non-EKS clusters to the EKS console by running an agent in the target cluster. This brings the ability to apply policies and roll out deployments from a single window.
When Amazon connects the dots between the EKS Console and EKS-A, it will deliver what Azure Arc promises – a single pane of glass to manage registered Kubernetes clusters. Extending this, EKS Console may even spawn new clusters as long as it can talk to the remote infrastructure, which will resemble Anthos. You see the obvious direction in which Amazon is heading!
The investments in ECS Anywhere, EKS Distribution, EKS Anywhere and EKS Console play a significant role in Amazon’s container strategy. They lay a strong foundation for future hybrid cloud and multi-cloud services expected from AWS.
From Cloud in Perfectirishgifts
0 notes
Text
NSX-V vs NSX-T – Basic Comparison
NSX-V vs NSX-T – Basic Comparison
NSX-VNSX-TTight integration with vSphereYesNoWorks without vCenterNoYesSupport for multiple vCenter instances NoYesSupported virtualization platformsVMware vSphereVMware vSphere, KVM, Docker, Kubernetes, OpenStack, AWS native workloadsNSX Edge deploymentESXi VMVM or physical serverOverlay encapsulation protocolsVXLANGENEVEVirtual switches (N-VDS)vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS)Open vSwitch or…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP VMWARE Objective Questions and Answers
VMWARE Multiple Choice Questions :-
1.Which of the following dvPort binding types have been removed in vSphere 5? A. Dynamic Binding B. Ephemeral Binding C. Static Binding Ans: A 2.Your boss has asked you to setup 4 ESXi hosts to evaluate the new vSphere 5 release, which is the recommended install method to use in this situation? A. Interactive Installation B. Scripted Installation C. vSphere Auto Deploy Installation D. Upgrade via VMware Update Manager Ans: A 3.Your colleague has accidentally allocated more vRAM than your company are licensed for. What will happen to your virtual machines? A. All VM's will be Powered Off B. New VM's can not be Powered On C. VMware will be notified D. Nothing will happen Ans: B 4.In an HA cluster after an initial election process, host are either: A. Primary or Secondary B. Master or Slave C. King or Queen D. Live or Standby Ans: B 5.To get the maximum performance benefits of vNUMA it is recommended to: A. Make sure your clusters are composed entirely of hosts with matching NUMA architecture. B. Only use single vCPU virtual machines C. Enable EVC on your clusters D. Disable Hyper-Threading Ans: A 6.What is the name of the globally unique identifier assigned to each Fibre Channel Port? A. IP Address B. MAC Address (Mac) C. World Wide Name (WWN) D. Port_ID Ans: C 7.It is possible to Storage vMotion virtual machines that have snapshots? A. True B. False Ans: A 8.What are the 4 VM Restart Priority options available on an HA Cluster? A. Disabled, Low, Medium, High B. Enabled, Small, Medium, Large C. 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th D. Priority, 2nd Tier, 3rd Tier, Best Effort Ans: A 9.A memory reservation defines: A. the amount of virtual machine memory that can be paged to the VMkernel swapfile B. the amount of physical memory that is guaranteed to the VM C. the maximum amount of physical memory that will be used by a VM D. the amount of host memory reserved for the VMkernel Ans: D 10.Which of the following installation methods installs the ESXi image directly into the Host memory? A. Interactive ESXi Installation B. Scripted ESXi Installation C. vSphere Auto Deploy ESXi Installation Option D. Upgrade via VMware Update Manager Ans: D

VMWARE MCQs 11.VMFS-5 upgraded from VMFS-3 continues to use the previous file block size which may be larger than the unified 1MB file block size. A. True B. False Ans: A 12.Which of the following formulas defines the amount of virtual machine memory that will always be composed of disk pages? A. Memory allocated -(minus) memory limit B. Memory limit -(minus) memory reservation C. Memory limit -(minus) memory available D. Memory allocated -(minus) memory available Ans: D 13.The upgrade procedure from VMFS-3 to VMFS-5 will require downtime of that datastore? A. False B. True Ans: A 14.Which of the following actions would be LEAST likely to reduce resource contention? A. Powering off a VM B. Enabling Swap-To-Cache C. Disable transparent memory page sharing D. Enabling vNUMA Ans: C 15.When is vNUMA enable by default on a virtual machines? A. When a virtual machine has more than 8 vCPU's B. When the guestOS is configured using an SMP HAL C. All the time D. vNUMA is never enabled by default Ans: A 16.Which new feature of vSphere 5 is used to collect host core dumps? A. vMA 5.0 B. ESXi Dump Collector C. ESXi Syslog Collector D. VMware vDR 2.0 Ans: B 17.After an upgrade from ESX4.X to ESXi5.0 you notice that when you run the following command via the vMA: "esxcfg-vswif -l" you notice that their are no configure vswif interfaces listed. Why would this be? A. The Service Console is no longer available with vSphere 5. All vswif interfaces are removed during the upgrade. B. During the upgrade process all vswif interfaces are migrated to vmk interfaces. C. During the upgrade process, vswif interfaces are disable by default, they'll need to be enable before they will be listed. D. The wrong command is being used. "vicfg-vswif -l" is the correct command to display all vswif interfaces. Ans: B 18.How has vMotion been improved in vSphere 5? A. Multiple vMotion vmknics, allowing for more and faster vMotion operations B. Long distance vMotion, allowing for vMotions over a large geographical area C. Multi-platform vMotion, allowing for vMotions between vSphere and Hyper-V platforms D. Storage vMotion, allowing for virtual machines storage to be moved between datastores Ans: D 19.What are the Automation Levels on a DRS Cluster? A. Manual, Partially Automatic, Fully Automatic B. Manual, Partially Automated, Fully Automated C. Manual, Semi Automated, Fully Automatic D. Manual, Semi Automatic, Automatic Ans: D 20.What are the two iSCSI discovery methods that are supported by an ESXi host? A. Static Targets, Dynamic Targets B. Static Discovery, SendTargets C. Static Discovery, FindTargets D. Dynamic Discovery, FindTargets Ans: A 21.After an upgrade from ESX4.X to ESXi5.0 you notice that your Port Group named "Service Console" is missing. Where has it gone? A. Because ESXi 5.0 has no Service Console, upgrading from ESX 4.x to ESXi 5.0 removes the Service Console port group. B. During the upgrade all Port Groups are removed. The Service Console Port Group will need to be recreated. C. During the upgrade all Port Groups are moved to Distributed Switches. D. During the upgrade all Port Groups are moved to Standard Switches. Ans: A 22.You have been asked to provide high availability for your vCenter server. Which product would you use to help achieve this? A. Fault-Tolerance B. vCenter Linked-Mode C. vCenter Heartbeat D. Microsoft Clustering Services Ans: C 23.VMware vSphere can be evaluated prior to purchase. What is the maximum number of days the evaluation can be used before a license must be purchased? A. 30 Days B. 60 Days C. 90 Days D. 120 Days Ans: B 24.Which feature of vSphere 5 can be used to increase network throughput to virtual machines? A. SplitRX B. NPIV C. VMDirectpath I/O D. RDM Ans: A 25.Which feature of vSphere 5 can be used to reduce virtual machine memory overhead? A. VMX Swap B. SplitRX C. Swap to Host D. Memory Reservations Ans: A VMWARE Objective type Questions with Answers 26.By default, where do hosts deployed with VMware Auto Deploy store logs? A. In Memory B. First mounted LUN C. Local disk D. vMA Ans: A 27.Which new feature of vSphere 5 is used to create ESXi installation images with a customized set of updates, patches, and drivers? A. Image Builder B. Host Profiles C. Auto Deploy D. Esxcli Ans: D 28.Which of the following is not a new feature made available with vSphere 5? A. sDRS B. vDR C. VSA D. vSphere Web Client Ans: B 29.What protocol is used by an ESXi host to communicate with NAS devices? A. NFS B. iSCSI C. CIFS D. SMB Ans: B 30.After an upgrade from ESX/ESXi 4.1 to ESXi 5.0, your monitoring department are reporting that they have stopped receiving Syslog data from all of the ESXi hosts. What could be the problem? A. Custom ports that were opened by using the ESX/ESXi 4.1 esxcfg-firewall command do not remain open after the upgrade to ESXi 5.0. B. Custom ports that were opened by using the ESX/ESXi 4.1 esxcfg-firewall command do not do not get copied during the upgrade to ESXi 5.0. C. Tech Support Mode is disable by default after an upgrade to ESXi 5.0 stopping all traffic on all ports D. ESXi 5.0 cannot send logs to Syslog servers. Ans: D 31.The default security policy on a Port Group is: A. Reject, Accept, Accept B. Reject, Reject, Reject C. Accept, Accept, Accept D. Reject, Reject, Accept Ans: A 32.When deploying hosts with VMware Auto Deploy, which is the recommended method to configure ESXi once it has been installed? A. Host Profiles B. PowerCLI C. Manually D. via Direct Console Ans: A 33.What is an HA Slot? A. A slot is a logical representation of the memory and CPU resources that satisfy the requirements for any powered-on virtual machine in the cluster. B. A slot is a given to each Host in an HA Cluster, there is a maximum of 32 in an HA Cluster C. A slot is given to each Virtual Machine, this determines the restart priority. D. A slot has nothing to do with HA, it's how DRS calculates which Virtual Machine should be placed where. Ans: A 34.Which new version of VMFS is introduced by vSphere 5? A. VMFS-2 B. VMFS-3 C. VMFS-5 D. VMFS-4 Ans: C 35.ESXi 5.0 supports only LAHF and SAHF CPU instructions? A. True B. False Ans: A 36.Which of the following is no longer available with vSphere 5? A. ESX B. vCenter C. vSphere Client D. PowerCLI Ans: D 37.Which if the following is not a supported location for a host diagnostic partition? A. Shared local storage B. Private local storage C. Private SAN storage D. Shared SAN storage Ans: A 38.Which of the following actions is not available via the Direct Console? A. Shutdown host B. Enter host into Maintenance Mode C. View host logs D. Configure host DNS Ans: B 39.Which vSphere feature provides dynamic allocation of storage capacity? A. vStorage APIs / VCB B. Thinapp C. sDRS D. vStorage Thin Provisioning Ans: C 40.To improve security which new feature has been added to ESXi? A. Firewall B. Local Mode C. Anti-Virus D. vShield Ans: A 41.What the packaging format used by the VMware ESXi Image Builder? A. .rar B. .zip C. .iso D. VIB Ans: C 42.What are the three default roles provided on an ESXi host? A. No Access, Read Only and Administrator B. Read only, Operator Access and Administrator C. Virtual Machine User, Virtual Machine Power User and Administrator D. Network Consumer, Datastore Consumer and Resource Pool Administrator Ans: A 43.Which of the following is a requirement for vCenter? A. A Static IP address B. A DHCP IP address C. A valid (internal) domain name system (DNS) registration. Ans: C 44.Which two users are assigned the Administrator role at the ESX Server level by default? A. root, administrator B. root, vpxuser C. root, vpxa D. root, hostd Ans: B 45.After an upgrade from ESXi4.0 to ESXi5.0 you are unable to putty to your hosts. What could have caused this? A. SSH configuration is not migrated for ESX 4.x hosts or ESXi 4.0 hosts. For these hosts, SSH access is disabled during the upgrade or migration process B. SSH is not available with ESXi 5.0, it is only available with ESX 5.0. C. SSH is always disabled after an upgrade or clean installation. D. The SSH port in ESXi 5.0 has changed to 443 for added security. Ans: A 46.What are the three Host Isolation Response options available on an HA Cluster? A. Shut down, Power off, Leave powered on B. Shut down, Power off, Leave powered off C. Shut down, Restart, Leave powered on D. Shut down, Restart, power on Ans: B 47.You boss has asked you deploy 40 ESXi hosts as quickly as possible, which is the recommended install method to use in this situation? A. Interactive Installation B. Scripted Installation C. VMware Auto Deploy Installation D. Upgrade via VMware Update Manager Ans: D 48.Distributed Power Management (DPM) requires which technology to be available on the NIC? A. Wake On LAN (WOL) B. DNS C. BMC D. NetBIOS Ans: A 49.The organisation you work for is currently running vSphere 4.1 U1. Your team have just created a new Test/Dev environment based on vSphere 5. The VM management team have asked if you could combine the current 4.1 U1 environment and 5.0 vCenters with Linked-Mode. What is the correct response to the VM management team? A. vCenter 4.1 and vCenter cannot be joined with Linked-Mode B. Additional licensing is required to use Linked-Mode C. Only vCenter Administrators can use Linked-Mode D. No problem Ans: D 50.Which of the following is not a benefit of VMware Auto Deploy? A. Decouples the VMware ESXi host from the physical server and eliminates the boot disk B. Eliminates configuration drift C. Simplifies patching and updating D. Accelerates deployment of virtual machi VMWARE Questions and Answers pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
L2 bridging with VMware NSX-T
by Michal Grzeszczak
My name is Michal Grzeszczak and I am a senior consultant at Xtravirt (www.xtravirt.com), an independent cloud consulting business and VMware Master Services Competent Partner. In this blog, I’d like to share with you my experience of L2 bridging with VMware® NSX-T Data Center and help you to understand some of the differences between NSX-T and NSX-V, as well as cover some NSX use cases.
Customer background:
The customer is one of the leading organisations in the betting and gambling industry and have been using NSX-V for some time now. When it came to their new greenfield environment, they decided to deploy NSX-T 2.4 Data Center. This decision was largely based on the fact that NSX-T Data Center provides bridging firewalls natively for L2 software bridging, which was their main requirement. Also, given that NSX-T will be the de facto network and security virtualisation platform offered by VMware going forward, by specifying it for this environment the customer is able to future proof the deployment.
Future upgrades are also accounted for as upgrading from NSX-T 2.4 to future NSX-T releases is simpler than performing upgrades from a previous version of V or T.
NSX-T 2.4 was a major update and brought many changes to the architecture of the product, the main ones being:
The NSX Manager and NSX Controllers were merged into one appliance deployed in a Cluster of 3 Nodes therefore minimising the footprint of the solution and operational complexity.
The other major change was the introduction of the new Simplified UI which “requires just the bare minimum of user input, offering strong default values with prescriptive guidance for ease of use. This means fewer clicks and page hops are required to complete configuration tasks.”
NOTE: In NSX 2.4 two UIs are presented - one is the new Simplified UI, the other one is Advanced. The latter is taken from NSX-T 2.3. The future plan is to remove the Advanced UI and provide all of the functionality via the Simplified UI.
What are the key benefits of choosing NSX-T over NSX-V?
There are many benefits of NSX-T over NSX-V, to name a few:
NSX-T doesn’t require vCenter, however it can be added to NSX-T as a Compute Manager and allows for up to 16 Compute Managers per NSX 2.4 solution . There is no longer a 1:1 requirement like there was with NSX-V.
KVM Hypervisor support
Bare Metal Edges provide sub-second failover
Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) Optimising Forwarding - DPDK is a set of data plane libraries and network interface controller drivers for fast packet processing
New, more flexible Overlay technology - Geneve replaces VXLAN https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Validated-Design/4.3/com.vmware.vvd.sddc-nsxt-design.doc/GUID-CF3C47CA-9BEB-4213-8F08-1494261BF3EC.html
Bi-directional Forwarding Detection support
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) expanded functionality with features like Route Maps
Much clearer User Interface (UI)
What were the specific use cases for this case customer and the design considerations?
USE CASE 1 - NSX-T Edge L2 Bridging - Integration of physical, non-virtualised database servers that require L2 connectivity to the virtualised environment.
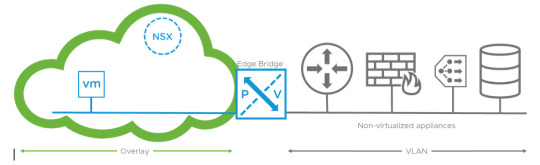
Design considerations:
In NSX-T 2.4 two options are possible to bridge L2 workloads - using ESXi Bridge Clusters or Edge Bridge Profiles. The latter is recommended to use as the former will be deprecated in future.
Ideally the use of dedicated Bare Metal Edges, however this is not a requirement.
The possibility to deploy Edge Bridges in collapsed vSphere Clusters > Management + Edge or Compute + Edge
Consider having active and standby Edge Nodes on different hosts to avoid throughput drop, because VLAN traffic needs to be forwarded to both Edge Nodes in promiscuous mode.
Overlay traffic can be tagged on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Profile, but please avoid double tagging.
VLAN traffic should not be tagged on the Uplink Profile.
Distributed Port Group for VLAN traffic connecting to the Edge Node should be in a Trunk Mode. The reason for this is due to the fact that Edge doing Bridging adds 802.1Q tag when transposing Overlay traffic to VLAN.
Consider having the same MTU value across your environment - if you can, choose MTU of 9000 for better performance.
Several Bridge Profiles can be configured, and a given Edge can belong to several Bridge Profiles. By creating two separate Bridge Profiles, alternating active and backup Edge in the configuration, the user can easily make sure that two Edge nodes simultaneously bridge traffic between Overlay and VLAN

Constraints:
Edge Cluster with minimum 2 Edge Nodes in Active/Standby mode is needed.
Standby uplinks are not supported on the Edge Node.
Source Based Load Based Teaming is not supported on the Edge Node.
The port group on the VSS/VDS sending and receiving traffic on the VLAN side should be in promiscuous mode, allowing MAC Address changes and Forge Transmits.
Deployment:
Follow the deployment guide here - https://youtu.be/IwpujflzJhY
Or here https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/2.3/com.vmware.nsxt.admin.doc/GUID-7B21DF3D-C9DB-4C10-A32F-B16642266538.html
Validation:
Log in to the Edge Node with your credentials.
Type “nsxcli”.
“Get l2bridge-ports-config” will show the Bridge Port State (Active Edge will have Forwarding, Standby will have Stopped), VLAN ID configured and Bridge UUID which can be copied and used to do a packet capture on the Edge Node.
To do the packet capture type “start capture interface “copied Bridge UUID” and hit enter, ping from VM to Physical Server to see the flows.
USE CASE 2 - NSX bridging firewall - Secure communication between physical database servers and Overlay workloads.
The configuration of the bridging firewall can be done currently only on the Advanced UI.
Security rules are configured per Logical Switch aka Segment in Simplified UI.
NSX-T grouping objects like NSGroups can be used to provide abstraction from the IP based approach.
USE CASE 3 - vRealize Network Insight - Monitoring tool that can provide visibility into both Physical and Virtual environments.
NSX-T 2.4 is fully supported with the latest vRealize Network Insight version 4.1.
Make sure you are allowing ports for communication between vRNI and other devices after the deployment. For example, ESXi Hosts to vRNI Collector on UDP 2055. The full list of ports needed can be found here - https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vRealize-Network-Insight/3.9/com.vmware.vrni.install.doc/GUID-FDDA5F2F-7C3B-472A-A17D-39582FBD5996.html
There is a new website that provides in-depth information about new features in vRNI, definitely worth visiting - https://vrealize.vmware.com/t/vmware-network-management/
What were the outcomes?
Overall, this deployment was a complete success as we were able to satisfy all of the requirements that the customer had. All the production physical databases were able to communicate on the same L2 segments, virtualised and connected to NSX-T segments workloads. On top of that, communication between those workloads was secured by NSX-T Bridging Firewall. vRealize Network Insight was used to provide visibility into the environment. Its ability to quickly troubleshoot network and firewall related issues in both virtual and physical realms allows admins to take a breath in the never-ending battle of making the networks stable.
I hope you enjoyed my blog, if you’d like to talk to Xtravirt about your business’s networking and security requirements, then please send an email to [email protected]
Some Useful links:
You can read more about the NSX-T 2.4 release here: https://blogs.vmware.com/networkvirtualization/2019/02/introducing-nsx-t-2-4-a-landmark-release-in-the-history-of-nsx.html/
0 notes
Link
#vmware#esxi#vsphere#vcenter#virtual networking#distributed switch#standard switch#json#migration#powercli
0 notes
Photo

VMWare Training – Online Certification training
MindMajix is the globally professional in IT courses training which emphasize on hands-on experience with examples from real-time scenarios by experts. It is the largest provider of high quality online training courses.
It is conceptualized and initiated by several multidisciplinary and ingenious software technocrats having a combined experience of more than 10 yrs in the industry.
About NetSuite Training: Mindmajix VMware Training makes you an expert in concepts like Vmware Fault Tolerance (FT), Vmware VSphere CLI, Network IO Control, VSphere Storage Appliance (VSA), VSphere Web Client, and VSphere Distributed Virtual Switch (Dvswitch)….etc.
Key Features:
-Flexible Timings
-Certified & Industry Experts Trainers
-Multiple Training Delivery Models
-Customize Course
-24/7 Support
-Hands On Experience
-Real Time Use Cases
-Q&A with Trainers
-Small Batches (1to5)
-Flexible Payments
-Job Support
-Placement Assistance
For Free Demo Please Contact:
USA: +1- 201 378 0518,
INDIA: +91 9246333245
Email: [email protected]
https://mindmajix.com/vmware-training
Website: https://mindmajix.com
0 notes
Text
0 notes