20 | Bi | தமிழ் | Academia | I don't know what this blog is anymore ✌️🤧
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
A Post-colonial Analysis of Sinners: The Oppressed as the Oppressor, Hybridity and Appropriation
youtube
#sinners#smokestack twins#michael jordan#hailee steinfeld#postcolonial studies#postcolonial literature#analysis#race#Hybridity#homi k bhabha#assimilation#blues music#ryan coogler#remmick#african american spirituality#african american studies#Youtube#academia#cultural appropriation#culture#media studies#media#film studies
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
i'm always a bit unsettled by disdain for intellectual or creative labor in leftist spaces. there's this commonly held belief that academics are a bunch of rich old white men, rather than a wide variety of people who are barely getting by. most lecturers in universities are adjuncts living paycheck to paycheck. authors make very little money as a general rule. most researchers are overworked and underpaid. and yet there's still this idea that academics are overcompensated to sit around and smoke cigars together while making shit up
41K notes
·
View notes
Text

I just learned this fact and I can't help but share it with you!!!
In 13th-century European castles, separate fortresses were rarely built. Instead, one of the towers was significantly larger than the others and served as sleeping quarters for the lord or the king and his family.
Medieval life was full of changes and conflicts. Periods of peace were often interrupted by wars and sieges. To protect the ruler and his family, spiral staircases were built in the towers, winding clockwise. This design made it harder for attackers, as defenders could strike while using the wall as a shield, whereas attackers, especially right-handed ones, faced difficulties.

Additionally, the steps were uneven in height and length, making it easier for defenders, familiar with the layout, to move quickly. Attackers, in heavy armor and unfamiliar with the stairs, risked losing balance. This design significantly complicated sieges, particularly when climbing upward, giving defenders an advantage.
Thus, clockwise spiral staircases were not only convenient but also a crucial part of defensive strategy.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text

Dogs have had many jobs throughout history, in this case: Revenge.
136K notes
·
View notes
Text
Taking away the word “liminal” from nostalgia-bait accounts and so-called “aesthetic” webpages. Liminal is for rest stops. It’s for non-places, like parking garages or paths or BETWEEN PLACES. Your computer room in 2007 is NOT liminal, it’s an extremely specific place and time. The word you’re looking for is “nostalgia bait.”

You could also use the word “non-place” for some of these pictures- it is by definition subjective. But again, your family’s living room in 2002 is not it.
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dog keeps stealing my ball of yarn and all I can think of is this manuscript illustration 🥺

30K notes
·
View notes
Text

this Angela Carter quote is driving me wild
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
As someone who has actually studied the English language there's a common phrase about English that kinda annoys me because while it makes for a funny haha line it's such a gross oversimplification that it actually ceases to be funny. It's the one that goes "The English language is just three languages stacked on top of each other wearing a trenchcoat" or something to that effect.
I'm not going to go into detail as to why that sentence is inaccurate, just take my word for it as a person with a master's in English. I suggest we withdraw this expression from usage and replace it with the much more accurate "The English language is a dirty little slut that loves it when other languages cum big loads in it"
69K notes
·
View notes
Text
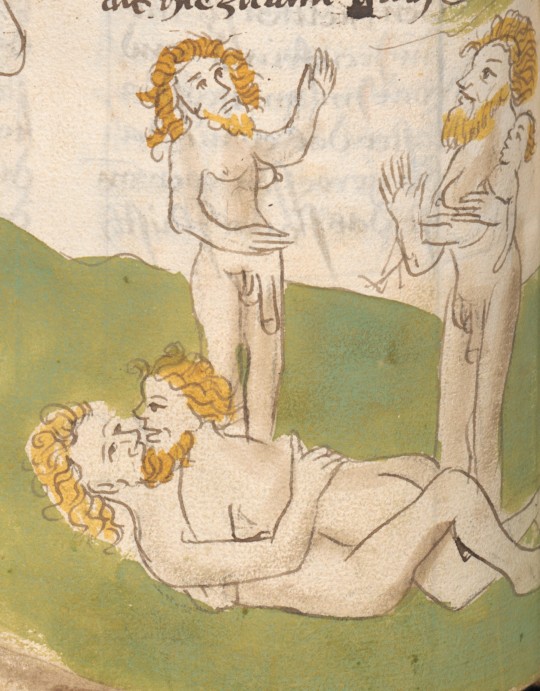


queer sex and more!
in an illustrated medieval travelogue (a german translation of "mandeville's travels"), bavaria/swabia, ca. 1476
source: Vienna, ÖNB, Cod. 2838, fol. 102v
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Imagine trying to explain online media piracy to a medieval peasant. If you managed to avoid getting stuck on trying to explain what the internet is or what a movie is, you'd get to the point where you're like "so the thing itself is a copy of a copy, infinite and immaterial, so obtaining it in these outlaw ways takes nothing out of someone else's hands. It used to be that people argued it was taking the bread from the table of the people who created the content, but it turns out that the official distributor isn't compensating them for their work anyhow."
And this guy just nods along like "ah, like the printing presses. I was taught to read and write you know, and once used the gift I was given to sin. I wrote out in grand detail of all the ways I would wish to fuck the miller's wife. Some typeblock-clacking print rat got his hands on it and is now printing copies of Confessions of Lewd Sinner Unnamed at great profit. I cannot take the matter to court because the miller is strong enough to pick up an ox and knows where I live."
805 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is possibly the dumbest way I've spent an evening recently, but nonetheless, here's a thing.

I made all of the other guys Kens, but Chaucer gets to be an honorary Barbie. I don't know how he would feel about that.
To spare those of you who don't have long posts automatically trimmed, I'm putting the rest below a cut.





















82 notes
·
View notes
Text
A class on fairy tales (1)
As you might know (since I have been telling it for quite some times), I had a class at university which was about fairy tales, their history and evolution. But from a literary point of view - I am doing literary studies at university, it was a class of “Literature and Human sciences”, and this year’s topic was fairy tales, or rather “contes” as we call them in France. It was twelve seances, and I decided, why not share the things I learned and noted down here? (The titles of the different parts of this post are actually from me. The original notes are just a non-stop stream, so I broke them down for an easier read)
I) Book lists
The class relied on a main corpus which consisted of the various fairytales we studied - texts published up to the “first modernity” and through which the literary genre of the fairytale established itself. In chronological order they were: The Metamorphoses of Apuleius, Lo cunto de li cunti by Giambattista Basile, Le Piacevoli Notti by Giovan Francesco Straparola, the various fairytales of Charles Perrault, the fairytales of Marie-Catherine d’Aulnoy, and finally the Kinder-und Hausmärchen of Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm. There is also a minor mention for the fables of Faerno, not because they played an important historical role like the others, but due to them being used in comparison to Perrault’s fairytales ; there is also a mention of the fairytales of Leprince de Beaumont if I remember well.
After giving us this main corpus, we were given a second bibliography containing the most famous and the most noteworthy theorical tools when it came to fairytales - the key books that served to theorize the genre itself. The teacher who did this class deliberatly gave us a “mixed list”, with works that went in completely opposite directions when it came to fairytale, to better undersant the various differences among “fairytale critics” - said differences making all the vitality of the genre of the fairytale, and of the thoughts on fairytales. Fairytales are a very complex matter.
For example, to list the English-written works we were given, you find, in chronological order: Bruno Bettelheim’s The Uses of Enchantment ; Jack David Zipes’ Fairy Tales and the Art of Subversion ; Robert Bly’s Iron John: A Book about Men ; Marie-Louise von Franz, Interpretation of Fairy Tales ; Lewis C. Seifert, Fairy Tales, Sexuality and Gender in France (1670-1715) ; and Cristina Bacchilega’s Postmodern Fairy Tales: Gender and Narrative Strategies. If you know the French language, there are two books here: Jacques Barchilon’s Le conte merveilleux français de 1690 à 1790 ; and Jean-Michel Adam and Ute Heidmann’s Textualité et intertextualité des contes. We were also given quite a few German works, such as Märchenforschung und Tiefenpsychologie by Wilhelm Laiblin, Nachwort zu Deutsche Volksmärchen von arm und reich, by Waltraud Woeller ; or Märchen, Träume, Schicksale by Otto Graf Wittgenstein. And of course, the bibliography did not forget the most famous theory-tools for fairytales: Vladimir Propp’s Morfologija skazki + Poetika, Vremennik Otdela Slovesnykh Iskusstv ; as well as the famous Classification of Aarne Anti, Stith Thompson and Hans-Jörg Uther (the Aarne-Thompson-Uther Classification, aka the ATU).
By compiling these works together, one will be able to identify the two main “families” that are rivals, if not enemies, in the world of the fairytale criticism. Today it is considered that, roughly, if we simplify things, there are two families of scholars who work and study the fairy tales. One family take back the thesis and the theories of folklorists - they follow the path of those who, starting in the 19th century, put forward the hypothesis that a “folklore” existed, that is to say a “poetry of the people”, an oral and popular literature. On the other side, you have those that consider that fairytales are inscribed in the history of literature, and that like other objects of literature (be it oral or written), they have intertextual relationships with other texts and other forms of stories. So they hold that fairytales are not “pure, spontaneous emanations”. (And given this is a literary class, given by a literary teacher, to literary students, the teacher did admit their bias for the “literary family” and this was the main focus of the class).
Which notably led us to a third bibliography, this time collecting works that massively changed or influenced the fairytale critics - but this time books that exclusively focused on the works of Perrault and Grimm, and here again we find the same divide folklore VS textuality and intertextuality. It is Marc Soriano’s Les contes de Perrault: culture savante et traditions populaires, it is Ernest Tonnelat’s Les Contes des frères Grimm: étude sur la composition et le style du recueil des Kinder-und-Hausmärchen ; it is Jérémie Benoit’s Les Origines mythologiques des contes de Grimm ; it is Wilhelm Solms’ Die Moral von Grimms Märchen ; it is Dominqiue Leborgne-Peyrache’s Vies et métamorphoses des contes de Grimm ; it is Jens E. Sennewald’ Das Buch, das wir sind: zur Poetik der Kinder und-Hausmärchen ; it is Heinz Rölleke’s Die Märchen der Brüder Grimm: eine Einführung. No English book this time, sorry.
II) The Germans were French, and the French Italians
The actual main topic of this class was to consider the “fairytale” in relationship to the notions of “intertextuality” and “rewrites”. Most notably there was an opening at the very end towards modern rewrites of fairytales, such as Angela Carter’s The Bloody Chamber, “Le petit chaperon vert” (Little Green Riding Hood) or “La princesse qui n’aimait pas les princes” (The princess who didn’t like princes). But the main subject of the class was to see how the “main corpus” of classic fairytales, the Perrault, the Grimm, the Basile and Straparola fairytales, were actually entirely created out of rewrites. Each text was rewriting, or taking back, or answering previous texts - the history of fairytales is one of constant rewrite and intertextuality.
Keep reading
108 notes
·
View notes
Text

this slaps honestly
70K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cut the Old Queers Some Slack
This post brought to you by a review of Sandra Boehringer’s Female Homosexuality in Ancient Greece and Rome, which recent translation I posted about earlier with no little excitement. The BMCR review annoyed me for a couple reasons.
First was an assumption that when a book is translated, the author should retool it to modern terminology.* In the end, the reviewer said maybe just the forward from Boehringer should have addressed trans issues—which isn’t an invalid point—but other parts of the review seem to slam Boehringer for not doing more revisions for the new English translation (from a French original published in 2007). This leads me to….
Second issue: this assumes a uniquely Angliphone understanding, and even more, a British one (the reviewer teaches as Leeds), where the issue of TERFs is more pressing than in the US. Here, transphobia and transmisogyny is rooted more in religious objections than a subsect of radical feminists (who may not be religious at all). It’s not that the US has no TERFs, but it's not nearly the issue (ime) as in the UK.
Every country has its own quirks of bias. And the author is French. If I’ve learned anything about Queer culture in my almost 60 years on this planet, it’s that the pressing issues in one country are manifestly not the pressing issues in another—particularly across language lines. To assume they are (or should be) centers Angliphone culture in a way that annoys me.
OTOH, yes, especially US English-speakers have poor linguistic skills to read non-Anglophone scholarship as a result of bad public-school language education. But access to good language education is a matter of MONEY, which gets us into issues of social class, et al. That’s a different kettle of fish (which deserves its own post about wealth gate-keeping in academia).
But I do my best to remain cognizant that the ways we talk about queer culture and concerns differ even in Anglophone countries, never mind those of non-English speakers.
So that was my second big issue with this review.
The reviewer acknowledges that the original came out in 2007, and queer scholarship about the ancient world has moved on, particularly as regards recognition of non-binary ancient figures. But she can’t seem to keep from knocking Boehringer for not magically keeping up.
Folks, grant the Old Queers some slack here? When I was young, it was just LGB. Then LGBT. Now it’s an alphabet soup. I’m quite sure young queers who read “An Atypical Affair: Alexander the Great, Hephaistion Amyntoros, and the Nature of Their Relationship,” could take exception to my phrasing in places. Hell, I’ll revise portions of it for my bio on Hephaistion and Krateros.
But it was published in 1999! And I actually wrote the thing in 1996 as a class assignment, then revised it in 1998 for that 1999 publication date.
Remember, some of us have been in this fight a while. I do my best to keep up with current terminology—and do genuinely want to do so—but it’s kinda gauche to slam authors for material previously published, especially in such a rapidly changing field.
To expect an author to substantially retool a prior publication for a translation is uncool. Real revision takes a lot of time. Not something I think many people fully understand. It’s not a matter of a couple weeks’ tweaks. If she were to produce a revised/second edition, that might take years. I’d rather have the book translated than wait five years for Boehringer to revise it. I can take it in the spirit of its original publication date: 2007. Could she have been more straightforward in her new forward? Perhaps. But French concerns aren’t British ones.
——
*Let me also say—as someone whose work is currently being translated—we may not have as much control as readers assume. I sent a letter to the Italian publisher, all but begging them to PLEASE keep the Greek transliterations of names and Greek words with Dancing with the Lion. They said they would, but I can’t force them to do so. For all I know, the Italian translation could be a dumpster fire. I hope not, I trust not, but translations are dicey. And if academic translations are quite different from fiction, be aware of the limits original authors face with translations.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
the idea that men will in some psychic way be “better off” without patriarchy (able to foster more genuine interpersonal relationships, less obligated to constantly suppress their sympathy for the women they exploit in various ways, better able to express emotions without rerouting them into anger, less psychically fragmented) is in no way incompatible with the idea that material benefits (in money, prestige, and, vitally, time) accrue to men under patriarchy, and that this is the ‘point’ of patriarchy
2K notes
·
View notes


