Text
How to write charming characters
With both positive and negative aspects to their personalities, charming characters can be difficult to write convincingly.
Whether you're writing a romantic love interest or a compelling con man, here are some examples for giving your charming characters depth.
How do they behave?
Attentive listeners: they pay close attention to people around them
Take pride in their appearance
Are happy to share personal space
Speak with a strong voice and an energetic tone
Are often hospitable and give off an air of welcome
Always give the impression that they are happy to see you
Demonstrate empathy
How do they interact?
Have a firm handshake and make strong eye contact
Are often encouraging
Compliment freely
Use humour to create a fun atmosphere
Communicate physically (through touch and gesture)
Make a point of using a person's name
Initiate conversations
Describe their body language
Have a relaxed stance with a straight and confident posture
Inclusive and attentive
Mirroring: they will mirror the body language of the person they are interacting with
Will lean forward to show attention
Lightly touch to create connection
A slight head tilt to show interest
Rarely cross their arms or legs
Maintain eye contact
Describe their attitude
Carefree
Good sense of humour
Friendly and playful
Self-aware
Opinionated and confident
Exhude an impression of honesty
Good intuition
Highly social
Polite and respectful
Eager to please
Potentially manipulative
The positive aspects of charm
Charming characters put people at ease, praise them freely, and boost their confidence. They make friends easily, talk their way to favourable resolutions, and are often the centre of attention.
They have impeccable grooming, conveying trustworthiness and concern for others, leading to a sense that they have your best interests at heart.
The negative aspects of charm
A charming character can manipulate others for personal gain. They can be overbearing, exerting their will on less confident individuals.
Their charm often draws focus, making others feel inferior, making them perfect for a protagonist to exhibit personal growth, or for a villain that a reader will fall in love with.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to write the passage of time
Time is a crucial element in writing that shapes the narrative. From linear progression, to flashbacks and foreshadowing, it gives you complete control of how your story unfolds.
Here are some tips to describe the passage of time to make your narratives more compelling.
Use the natural world
Describe the changing seasons
Show plant growth and death
Visualise the ebb and flow of tides
Describe the decomposition of flora and fauna
Describe the ways that landscapes change on long journeys
Use the weather to illustrate time jumps
Illustrate the affect that shifting shadows have on a location
Use heavenly bodies like stars, the rise and set of the sun, and phases of the moon
Describe physical activities
Show family gatherings and how they change over the years
Describe the process of finishing a creative pursuit
Create repetitive activities and routines
Have a character engage in an activity, like gardening, that visually changes
Have your characters learn a new skill
Write a change in location that requires a journey to get from point A to point B
Use your setting's seasonal celebrations to illustrate a time shift for individual characters and their world
Use sound
Describe the ticking of clocks
Have your characters' voice change with their age
Illustrate changing musical styles
Have your characters improve an audible skill like singing, swordplay, or learning a musical instrument
Show a character's conversational style changing as they grow
Use the sounds of nature, like leaves becoming brittle as they crunch underfoot, or rain turning into storms
Use silence to illustrate it getting late
Describe objects
Have food left out go mouldy
Illustrate buildings and settings being overtaken by nature
Show the lifecycle of a family heirloom
Describe textiles fading and degrading over time
Describe the freshness of paint; is it wet and glistening, or cracked and dry?
Illustrate technological change and advancement
Describe the repairs in a beloved object
Show a common object like a pencil to describe how it changes with use
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
whats that defunct land quote again? every part of the film making process is awful, but not making film is even worse? idk something like that. anywah im being completely normal about art rn ::))
87K notes
·
View notes
Text
Stand out to literary agents by following these 6 rules
Here are six of my tips on what you should be looking out for when writing query letters in order to stand out to literary agents.
Personalise it
Amazing how many people don’t do this - Research your agents! Don’t query someone outside of your genre, and don’t address your query to a vague title. You should know exactly why you’re querying the specific agent, and let them know this.
Know your blurb
Your blurb should be a polished piece of work that shows your character, hints at the story question & themes, tells of the main story conflict, and most importantly — tells the agent that you know what your story is about and why it’s important.
Put some thought into synopsis prose
Most agents will ask for a synopsis with your submission, which should say exactly what happens in your novel from start to finish. But don’t write a cut and dry piece of information dump in this.
You should use this opportunity to build out the tone of your book and filter your narrator’s voices through it. Be very intentional with each word you put into it.
Know your comps
Don’t forget to include comparative titles of other books or pieces of media your project could be aligned with. This might become your target audience, and your agent needs to know this. But make sure whatever titles you throw out there — you’ve actually read them.
Respect the submission rules
This kind of goes hand-in-hand with knowing who you’re submitting to. But there’s nothing worse than not checking the rules and guidelines for each agent submission. They’re all going to be different, so don’t send a copy and pasted e-mail to each agent with all the same attachments.
Keep your bio short and sweet
The agent doesn’t need to know about your whole personality and aspirations as a writer. Mention the things that may matter, such as your education, awards, published pieces, experience in the industry, or social media following. This isn’t the key part of your submission, so if you don’t have much to mention, keep it simple.
Did you hear I’ve got my first book coming out this summer?

It will take you through the process of writing your first full draft!
It’s coming out August 15th but you can pre-order it now!
Grab it through the [link here] or below!
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
Body language cheat sheet: Jealousy
Here’s a quick cheat-sheet to behaviours you can use in showing jealousy in your characters. Remember, these depend largely on the context of the scene, but they’re good ideas to get you started on allowing your readers to interpret jealousy where you don’t want to outright tell them that’s what it is. It’s a good technique to use if you’re wanting to hide a romantic interest.
Clenched jaw or tightened facial muscles
Rapid blinking or increased eye contact
Tensing of the body, such as crossed arms or tightened fists
Increased fidgeting or restlessness
Reddening of the face or neck
Changes in breathing patterns
Increased heart rate or pulse
Breaking out into a cold sweat or feeling clammy
Darting eyes or side glances
Tightness or discomfort in the throat
Flaring of the nostrils
Clenching or grinding of the teeth
By the way...
💜 Do you need help getting your WIP organized?
Pick up my 3 extensive workbooks for writers, with dozens of fully-customisable templates. These are my first ever original E-books and templates available outside of my coaching programs!
💜 The Writer’s ToolBoox contains: The Character Bible, The Plotter’s Almanac, and The World-Builder’s Chronicle
Grab it through the [link here] or below!
321 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things that don't make you less of a writer:
-Writing dark topics/sad or tragic endings
-Writing fanfiction
-Writing a lot of projects at the same time or just focusing on a single one
-Having difficulty naming things
-Having difficulty writing dialogue or descriptions or action sequences
-Having areas in writing that you find difficult
-Only writing in a single genre
-Only really covering one topic in your writing
-Being scared to branch out of your comfort zone
-Never wanting to publish
-Being rejected by publishers
-Not using clever word play in your writing
-Having literal writing style
-Writing slower than those around you
-Being unable to finish any of your projects you start
-Having to take long breaks even though you didn't write a lot
-Getting exhausted by writing (it's not that you don't love it, it's just exhausting!)
There are so many more things I can add to this list. Literally every single habit of writers, I could add to this list. These are just some really big ones I've seen people get down on themselves about. So just remember: you are no less of a writer than those around you. Be proud, love your writing. You put the time and effort into it. No one has put the time you have into it, so you should love it more than anyone in the whole world.
Love your writing, no matter what kind of writing it is, no matter how diverse the subjects and genres are... it doesn't matter. YOU made it. You alone.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
this man killed half of salt lake city

35K notes
·
View notes
Text
Wishing all of you a very merry "I suddenly have the motivation and time to write a minimum 10k fic"... please
65K notes
·
View notes
Text
Are you frustrated you can't leave second kudos on AO3? or third kudos? or whatever-who's-counting kudos?
Well, have I got the html for you!
Plop any of these in a comment (by copy&pasting the code) to make an author's day and show your appreciation!
Second kudos:
<img src="https://i.ibb.co/tHMjbb6/second-kudos.png" alt="second kudos">
Third kudos:
<img src="https://i.ibb.co/52bggQH/third-kudos.png" alt="third kudos">
nth kudos:
<img src="https://i.ibb.co/6y7qGtC/nth-kudos.png" alt="nth kudos">
yet another kudos:
<img src="https://i.ibb.co/wKtcj0s/yet-another-kudos.png" alt="yet another kudos">

It will look something like this (and will be transparent with white outline on dark backgrounds):
Feel free to spread and use these as much as you like! (and if you have ideas for other variations, let me know ✌️)
90K notes
·
View notes
Text
Starting Strong Scenes in Your Writing
Scenes are the fundamental building blocks of novels and short stories, and each one should propel a story toward the climax.
Generally speaking, your scene structure should mirror the story structure. In other words, take a novel-writing approach to a scene, crafting a beginning, middle, and end. Like a story, the beginning of a scene should have a strong entry hook that pulls the reader in.
Start with the setting. Often a new scene signifies a change in time and location. Establishing the setting at the top of a scene helps your readers get oriented. It also sets the tone and mood of what will unfold in the coming pages. A setting can serve as much more than a backdrop in literature. Have your scene take place somewhere that builds tension and hinders your protagonist. If you’re writing a thriller, describe a dark and foreboding place where the worst might happen. Be descriptive and use sensory details to make your setting come alive before you jump into the action.
Use visual imagery. In screenwriting, writers have to think in pictures. What images will excite an audience at the top of a scene? Your approach should be the same when writing any kind of fiction. As you write the opening of a scene, use descriptive language to engage a reader through detailed imagery. Think like a screenwriter as you’re writing scenes.
Drop the reader into the middle of the action. Hit the ground running by starting a great scene in media res. It doesn’t have to be a fight scene or a car chase, but physical movement creates momentum and builds tension in a story. It’s also a way to instantly engage a reader. Be sure you begin the scene before the high points of the action so you build up to the scene’s climax.
Write a character-driven scene opener. A good scene starts by giving characters a goal. Start by putting your protagonist in a situation that creates an obstacle or opportunity for both the scene and the overarching storyline. Try starting with dialogue, like an intense conversation between your POV character and a mystery character whose identity is revealed later in the scene. If you’re writing from an omniscient third-person point of view, consider starting a scene with a secondary character, even the antagonist, and use it as a chance for deeper character development.
Summarize past events. You might choose to use the beginning of the scene to do a quick recap of what’s brought your main character to this place and moment in time. A summary is especially helpful if you’re writing in third-person and a new scene switches to a different character. Take the opportunity to remind the reader where we left off. Instead of a straight-forward update, get creative. Go into deep POV and let a character’s thoughts provide the summary instead of the narrator. Be sure to keep this summary brief—just a line or two—so you can get back into the action.
Introduce a plot twist. The start of a new scene is a chance to pivot and take your story in a new direction. Start a new scene at a turning point in your story. Dive into a flashback or character’s backstory, revealing critical information that changes the course of the story going forward.
Keep the purpose of the scene in mind. Effective scenes are clear about what they set out to accomplish and how they contribute to the overall plot. They might include plot points or reveal important information needed to move a story forward. Establish your scene’s intention from the very first word and keep the rest of the scene on point.
Rewrite until you’ve found the perfect scene opening. When you’ve finished the first draft of a scene, go back and read it through. If your scene needs something, but you can’t figure out what, it might be how the scene starts. The best way to know if your opening works is by reading how it plays with the rest of the scene. Review the last paragraph and see if it ties back to your beginning. If the intro feels weak, rewrite it. Maybe your real opener is hidden in plain sight somewhere else in the body of the scene.
Make sure your opening scene is your strongest. While your entire book should be filled with compelling scenes that start strong, the very first scene of your book needs to lead the pack. This is the reader’s introduction to your story and where you’re revealing the characters, the setting, and kicking off the plotline with the inciting incident. This first scene has to hook the reader from the first line so they keep turning the pages.
Read a lot of books. If this is your first novel and you need some inspiration and ideas to help you start off your scenes, start by reading other books. Choose a book by a bestselling writer like Dan Brown or Margaret Atwood. Study the different ways they approach every scene. Reading other authors is a great way to hone your scene-writing skills.
Follow like and reblog if you find these helpful!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
all i do is rotate wips around in my head and not write anything down
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Things to say about your writing instead of “this is so bad”
My writing doesn’t have to be perfect all the time
The dialogue in this scene feels stale (or another adjective), but I can revise that later
The descriptions lack specificity (or another issue), but I can revise that later
The [another specific craft element] isn’t working the way I’d hoped, but I can revise that later
I don’t feel like I can objectively judge my work at this current moment
I’m not happy with my writing right now, but that doesn’t mean I’ll feel this way forever
I’ll reread this writing at a later time and move on for now
This scene isn’t turning out how I’d pictured in my head, but I can accept that for now and tweak it later
I trust myself to edit this in the future
I’m afraid people are going to judge my work, but I’ll accept that I can’t control the reactions of other people—my reaction matters most
This scene/subplot/character/etc is overwhelming me.
I’ll take my time through this scene/chapter/subplot as more time may allow me to immerse more in the draft.
I’ll write this scene/chapter/subplot as quickly as I can—I would like to get through this part ASAP.
It’s okay to make mistakes in my writing.
I’m not feeling very confident in my craft right now, but I know this will pass
This scene might be bad, and that’s okay. Sometimes I write gems, and sometimes my writing needs a bit more work (that’s normal)
This scene relies on [certain skill] that I’m still honing. I understand to get better at something, I have to practice and practicing requires mistakes.
I’m not excited about this scene right now
I had high expectations for this scene, and unfortunately, I don’t feel like I’m hitting them. However, it’s okay for expectations to change.
I’m disappointed with how my writing is turning out. That’s normal, even though it sucks.
I’m going to remind myself what I DO like about my writing because this feels bad, though I know this feeling won’t last forever.
Sometimes writers need to say “my writing is so bad,” and that’s fine too! Sometimes though, it’s good to note what is specifically wrong in case you need an extra boost forward! <3
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Survive the Editing Process
Writing a first draft takes so much of your time and energy. When you finish something, celebrate your accomplishment! It’s proof of your creativity and hard work.
If you want people to read your work, then it’s time to edit.
Editing can seem scary. Daunting. Confusing.
Use these tips to get started.
1. Take a Break from Your Work
It’s so important to let your brain reset after finishing any story. Close your draft and spend the next few days or weeks doing other hobbies. When you feel ready to return with a newly energized, distanced perspective, you’ll get your best editing work done.
2. Start With Developmental Editing
Writers often think that they have to start editing line by line, looking for grammar and spelling issues. While you’re free to do that, you’re likely going to add and remove plenty of content before your final draft is done.
Instead, start with developmental editing. Read through your work and take notes about how the larger plot points are working or not working. Does each chapter move your characters through each point on your plot outline or your visualized storyline?
This step may involve adding new scenes or removing others. It can also mean reworking old scenes so they’re less wordy, more descriptive, more actionable, or whatever you feel like is missing.
Take notes about plot holes too. You don’t have to fix them on your first read-through, but note where they’re happening and why they’re holes. You can return in your second read-through to address them.
You can also break your developmental editing into questions, like:
What is my story’s theme and does each chapter support that theme?
What does every character want and do they achieve that? Why or why not?
What motivates each character? Do they retain that motivation or develop a new one to better serve the plot? (Sometimes writers forget about initial character motivations while getting lost in the writing process. This is the time to revisit that!)
Do you have a beginning, an inciting incident, building through the middle, and payoff at the end? (You can have much more than these, but these are very basic plot mechanics to look for.)
3. Save and Start a Second Draft
After reading through your manuscript and noting the things above, create a copy for your second draft and start working on your notes. It’s good to have a separate second copy in case you want to include something from the original draft later on or just want to compare where you story started/how it ended up.
Again, you’re not supposed to worry about line work at this point. Focus on bigger-picture story issues like plot mechanics, how scenes work/don’t work, plot holes, and your theme(s).
Reminder: there’s no timeline for getting these steps done. Work when you have the energy and take breaks when you don’t. Your manuscript will stay right where you save it.
4. Reread Your Work
When you’ve worked through your list of notes, make a copy of your manuscript and start Round 3. Reread your story and start a new list of bigger-picture notes as needed. This time, the list should be shorter or include new notes that you didn’t catch before. They may also include notes for new scenes you just added.
The point of this reread is to make sure that your manuscript still works. Your plot shouldn’t have any holes, it should flow smoothly, and it should be engaging.
Here’s a key concern for many writers: how do you edit your story without getting away from your original intentions?
Keep your eyes locked on why you write your original draft. If you make edits/scene removals or additions with that purpose or theme in mind, your story will stay on track. It may eventually look completely different than what you originally wrote (if that’s your editing journey), but the heart of it will remain the same.
Try posting your story’s purpose or theme on a sticky note attached to your monitor.
You could also write the theme in your document’s header so it appears on every page.
5. Save and Start a Fourth Draft
Yes, it’s time for another new copy that’s your official fourth draft.
Remember—you can still walk away and return to your work later! Burnout won’t result in the story you’ve been working so hard to create. Get some sleep, see some friends, enjoy your other hobbies. You’ll come back ready to go.
The fourth draft is another chance to read through your work and ensure that everything works. Your chapters should get your characters closer to your theme/purpose with each page. The scenes should flow, not repeat information, and keep you engaged.
When you have a small list of edits or none at all, it’s time to start line work.
The spell check feature of any word processing software is a lifesaver, but it’s also not perfect. You’re going to have sentence structures that spell check deems incorrect when it actually works for your writing style or character. You’ll have fake names you made up that spell check wants to change.
If you use spell check, proceed slowly. Read every sentence with a flagged issue to make sure it’s a good or bad suggestion.
You can double your line work by combing through it by yourself. Print your story and grab a highlighter or use the highlight feature on your computer. Note linework issues that you can fix with a quick edit when you get a chance, like:
Misspellings
Missing punctuation
Wrong punctuation marks
Missing words
Inconsistent capitalization or spelling
Formatting issues (spelling out numbers vs using numerals, etc.)
Using the wrong tense in some paragraphs or chapters
Inserting indents as needed
Extra spaces between paragraphs
6. Send Your Work to Beta Readers
Repeat the saving, making a copy, and editing as many times as you want. When you feel like you’ve got your strongest draft yet, you can send it to beta readers.
How you define beta readers depends on your specific situation. You may have a few writing friends who know the craft well and will read your work with a professional eye. You might have a family member or best friend who doesn’t know about the craft of writing but always reads your work.
There are also places like Reddit threads and Facebook groups where people volunteer as beta readers.
The primary reason to get fresh eyes on your work is to get notes from someone who hasn’t been working on the content for months or years.
Their advice might not always be usable, but it’s still an important part of editing. Your beta reader might suggest points where they lost interest because your pacing slows down or point out places where you described your protagonist as having long hair when they have short hair during the rest of the story.
You’ll know which suggestions are actionable and which aren’t based on who’s speaking and how it resonates with your story’s purpose. You’ll probably get better advice from other writers who have been through editing before, but that doesn’t mean their advice will always be correct.
Check in with your story’s purpose or theme before taking action on a beta reader’s notes.
When Should You Stop Editing?
One of the final battles during your editing experience will be recognizing when you can stop working on your manuscript.
There will always be moments where you could think of a new scene or a new way to rewrite a scene. That doesn’t mean you have to!
Ask yourself these questions to finish your editing when your story is strongest:
Question 1: Have I Worked Through the Most Essential Plot Mechanics?
A finished manuscript doesn’t need more structural work. But structural, I mean that you’ll be at peace because your manuscript:
Doesn’t have any plot holes
Addresses your theme/message from beginning to end
Showcases each character’s growth through plot developments
Has natural dialogue
Has introduced and resolved conflicts (with the exception of conflicts that will continue in a sequel or series)
Has no known typos or grammar issues
Question 2: Are My Edits Improvements or Are They Inconsequential?
You could spend a lifetime swapping character names, adjusting your world map, or revising how you describe locations. You might like your edits better, but they aren’t vital to your story’s plot or character development. If there’s no substantial improvement with your edits, you’re likely done with your manuscript.
-----
Editing can be tricky at first, but using steps like these will help you whack through the densest parts of the work. Take your time, give yourself space to rest, and you’ll create the story you’ve been working so hard to finish!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Adding Complex Morality to Whumper/Villains
Complex morality can be really difficult to conjure, because as humans we can’t help but hold bias to morals. Some of us struggle more to make a heroic figure on truly good/lawful terms. Some of us struggle with the exact opposite like me. Here are some things that easily add complexity to moral situations for sadistic, evil, and/or villainous characters.
Character is a loving family member/parent figure for their double-sided life
Character’s actions are starting to wear morally on them, but their ego is still too high to do something to make change
Another character has forced the character into this path (remember this rarely ever reforms or excuses character’s actions)
Character’s actions are a retaliation of mistreatment or oppression in the past
Despite all of their actions, they are a loving compassionate kind partner to someone else
They genuinely believe their actions are for the greater good
People around character see them as an amazing figure
Character was raised to be the way they are
Character is actively working a strong overbearing force that they cannot easily get out of (governments, militaries, organizes, spyforce)
Insecurities pushed Character
Character is being mind controlled or possesses
Some of Character’s morals are on the greater spectrums (isn’t a bigot, won’t harm children, strong advocate for equal rights)
Character helps other characters previously or for temporary moments
Character is beginning to second guess their actions
Character is on the verge of realizing how horrible they are
Certain people are let go or spared by character for unknown reasons
Character has standards
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
List of fluff prompts
1. “I gave you one hundred and one reasons to walk away, yet you never did. Why?” “Because I love you. It’s really that simple.”
2. “Remember when we first met here?” “Yeah, of course. That was the day when you spilled coffee on me and apologised profusely but all I could think about was how gorgeous you are and how great it would have been to get your number.”
3. “It’s always been you, and it will always be you. Please never forget that.”
4. “You make me feel all soft and mushy inside.” “That is a good thing, right?” “Of course! You melt me, love.”
5. “You’re an idiot.” “Well, at least I’m your idiot, right?”
6. “You’re the reason why I believe in love, you know?”
7. “Stop back-hugging me while I’m trying to cook! You’re distracting me,” Character A whines, cheeks becoming a delicate shade of rosy pink as Character B nuzzles their neck and mumbles sleepily into their neck, arms only serving to tighten around their waist at their flustered protests.
8. “C’mere and rest next to me. You’ve worked hard enough today.”
9. “You feeling any better?” Character A asks, stroking their fingers through Character B’s hair. “So much better now that you’re here. I love you,” Character B mumbles, snuggling close to them.
10. “You always manage to make me feel like I’m worth it.” “That’s because you are worth it. You’ll always be worth it in my eyes.”
4K notes
·
View notes
Photo

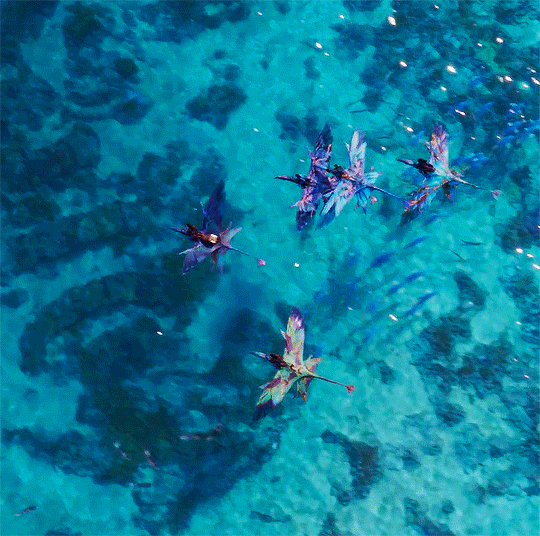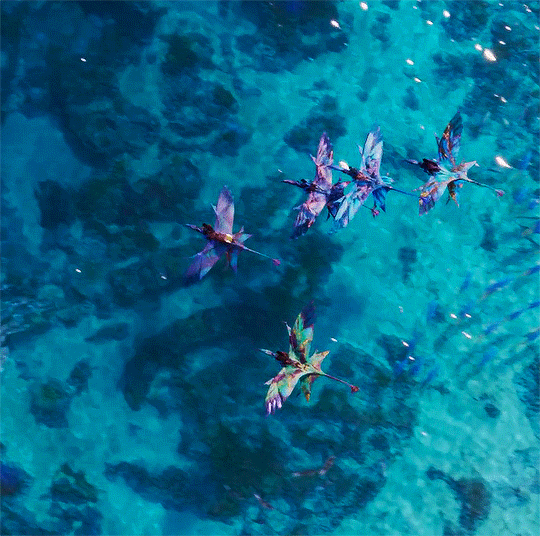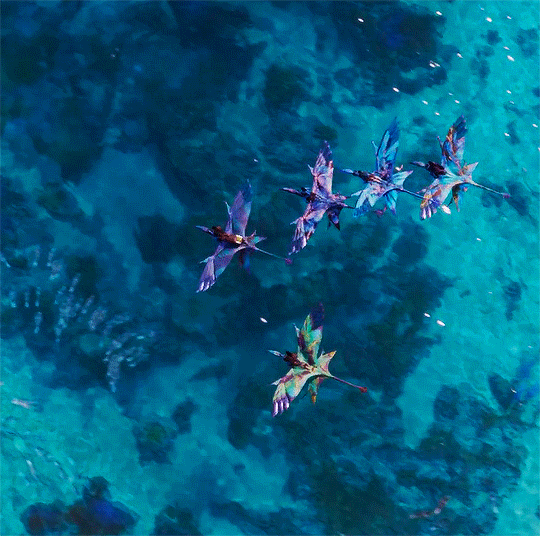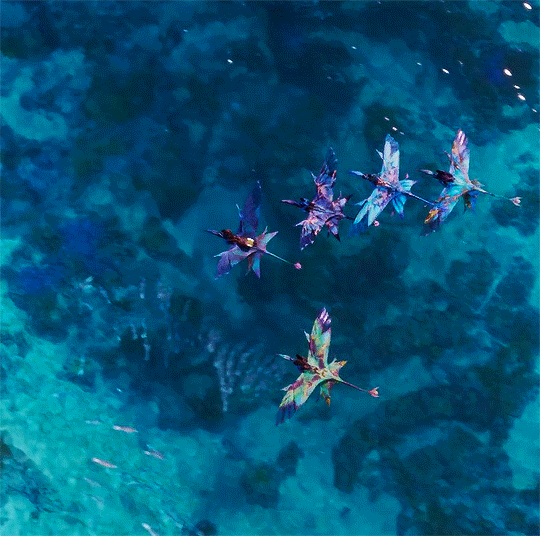


I know one thing, wherever we go, this family is our fortress.
Avatar: The Way of Water (2022) dir. James Cameron
14K notes
·
View notes
