#Azure data factory
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is a cloud-based data integration service provided by Microsoft Azure. It is designed to enable organizations to create, schedule, and manage data pipelines that can move data from various source systems to destination systems, transforming and processing it along the way.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
🌟 Master Azure Data Factory – Training in Hyderabad! 🌟
Ready to kickstart your career in Data Engineering? 🚀 Join the best Azure Data Factory training in Hyderabad and learn from the experts!
Here’s what you’ll get: ✅ 10+ Years Experienced Trainers ✅ Real-Time Mock Interviews ✅ Placement Assistance ✅ Certification Guidance
📍 Location: Hyderabad 📧 Email: [email protected] 📞 Call: +91 9882498844 🌐 Visit: www.azuretrainings.in
🎓 Don’t wait! Upskill today and take your career to the next level. 🔥 #AzureTraining #DataFactory #CareerGoals #CloudComputing #DataEngineering

#azurecertification#microsoft azure#azure data factory#azure training#azuredataengineer#certificationjourney
0 notes
Text
"In the world of data, Azure Data Factory transforms chaos into clarity, orchestrating workflows that drive insights."
0 notes
Text
Azure Data Factory ensures efficient data processing with parallel processing, data integration runtime, and built-in pipeline optimization.
0 notes
Text
Unraveling the Power of Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding Integration Runtime
Key Features and Benefits
Use Cases
Best Practices for Integration Runtime Implementation:
Conclusion
FAQS on Integration runtime In Azure Data Factory
Introduction
Within the time of data-driven decision-making, businesses depend on robust information integration arrangements to streamline their operations and gain important experiences. Azure Data Factory stands out as a chief choice for orchestrating and automating information workflows within the cloud. At the heart of Azure Data Factory lies Integration Runtime (IR), a flexible and effective engine that facilitates consistent data movement over diverse environments. Whether you are a seasoned data engineer or a newcomer to Azure Data Factory, this article aims to prepare you with the information to harness the total potential of Integration Runtime for your information integration needs. In this comprehensive guide, we dive profound into Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory, investigating its key features, benefits, use cases, and best practices.
Understanding Integration Runtime
Integration Runtime serves as the backbone of Azure Data Factory, enabling productive information development and change over different sources and goals. It functions as a compute framework inside Azure, encouraging a network between the data stores, compute services, and pipelines in Azure Data Factory.

There are three types of Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory
1. Azure Integration Runtime
This type of Integration Runtime is fully managed by Microsoft and is best suited for information movement within Azure administrations and between cloud environments.
2. Self-hosted Integration Runtime
Offering adaptability and control, self-hosted Integration Runtime allows data movement between on-premises data stores and cloud administrations without exposing your arrange to the web.
3. Azure-SSIS Integration Runtime
The platform-as-a-service (PaaS) environment offered by this runtime is tailored to run SQL Server Integration Administrations (SSIS) bundles in Azure Data Factory. This allows SSIS processes to be executed in the cloud.
Key Features and Benefits
Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory offers a plethora of features and benefits that enable organizations to proficiently manage their information integration workflows:
● Hybrid Connectivity
With self-hosted Integration Runtime, organizations can securely interface to on-premises data sources behind firewalls, ensuring seamless integration between cloud and on-premises situations.
● Scalability and Performance
Azure Integration Runtime scales dynamically to meet the demands of data-intensive workloads, giving high throughput and low latency information movement over Azure services.
● Fault Tolerance
Integration Runtime guarantees data integrity and reliability by naturally retrying failed information exchange operations and providing fault tolerance components for dealing with transitory errors.
● Data Encryption and Security
Integration Runtime employs industry-standard encryption protocols to secure information in transit and at rest, guaranteeing compliance with regulatory requirements and information administration policies.
● Extensibility
Integration Runtime seamlessly coordinating with other Azure services and third-party devices, allowing organizations to leverage a wealthy environment of data integration solutions.
Use Cases
Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory caters to a wide range of use cases over businesses:
● Real-time Analytics
Organizations can use Integration Runtime to ingest, change, and analyze streaming information in real-time, empowering timely decision-making and significant insights.
● Data Warehousing
Integration Runtime encourages the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data into Azure Synapse Analytics and other data warehouse solutions, empowering comprehensive analytics and announcing.
● Data Migration
Whether moving from on-premises information centers to the cloud or between cloud environments, Integration Runtime simplifies the migration process by providing seamless data development and change capabilities.
● Batch Processing
Integration Runtime automates batch processing workflows, empowering organizations to effectively prepare expansive volumes of information at planned intervals for reporting, analytics, and archival purposes.
Best Practices for Integration Runtime Implementation
To maximize the viability of Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory, consider the following best practices:
1. Optimize Data Transfer: Utilize parallelism and dividing strategies to optimize data transfer performance and diminish latency.
2. Monitor and Troubleshoot: Regularly monitor Integration Runtime performance measurements and logs to recognize and troubleshoot issues proactively.
3. Secure Connectivity: Actualize network security best practices to safeguard data during travel between on-premises and cloud situations.
4. Adaptation Control: Keep up adaptation control for information integration pipelines and artifacts to ensure consistency and reproducibility over environments.
Conclusion
Integration Runtime in Azure Data Factory is a foundation of modern information integration design, enabling organizations to consistently interface, change, and analyze data over different situations. By understanding its key highlights, benefits, use cases, and best practices, businesses can open the total potential of Azure Data Factory to drive advancement, accelerate decision-making, and accomplish competitive advantage in today's data-driven world.
FAQS
Q1: How does Integration Runtime ensure data security during data movement?
Ans: Integration Runtime implements robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and compliance measures to secure data amid transit and at rest. It guarantees information integrity and privacy all through the information integration preparation.
Q2: What are the key highlights of Integration Runtime?
Ans: Integration Runtime offers features like network to diverse information sources, adaptability to handle changing workloads, fault tolerance mechanisms for reliability, effective information development, and adherence to stringent security guidelines.
Q3: Can Integration Runtime handle data movement between cloud and on-premises environments?
Ans: Yes, Self-hosted Integration Runtime enables information development between Azure cloud administrations and on-premises data sources safely. It acts as a bridge between cloud and on-premises situations, facilitating seamless data integration.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Explore the latest in data processing with our 2024 comparison of Azure Data Factory vs. Databricks. Uncover key differences and stay ahead in making informed decisions for your data integration journey.
0 notes
Text
#Azure Data Factory#azure data factory interview questions#adf interview question#azure data engineer interview question#pyspark#sql#sql interview questions#pyspark interview questions#Data Integration#Cloud Data Warehousing#ETL#ELT#Data Pipelines#Data Orchestration#Data Engineering#Microsoft Azure#Big Data Integration#Data Transformation#Data Migration#Data Lakes#Azure Synapse Analytics#Data Processing#Data Modeling#Batch Processing#Data Governance
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Build CI/CD Pipeline with the Azure DevOps

Building a Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline with Azure DevOps is essential for automating and streamlining the development, testing, and deployment of applications. With Azure DevOps, teams can enhance collaboration, automate processes, and efficiently manage code and releases. In this guide, we'll walk through the process of building a CI/CD pipeline, including key components, tools, and tips. Along the way, we'll integrate the keywords azure admin and Azure Data Factory to explore how these elements contribute to the overall process.
1. Understanding CI/CD and Azure DevOps
CI (Continuous Integration) is the process of automatically integrating code changes from multiple contributors into a shared repository, ensuring that code is tested and validated. CD (Continuous Deployment) takes this a step further by automatically deploying the tested code to a production environment. Together, CI/CD creates an efficient, automated pipeline that minimizes manual intervention and reduces the time it takes to get features from development to production.
Azure DevOps is a cloud-based set of tools that provides the infrastructure needed to build, test, and deploy applications efficiently. It includes various services such as:
Azure Pipelines for CI/CD
Azure Repos for version control
Azure Boards for work tracking
Azure Artifacts for package management
Azure Test Plans for testing
2. Prerequisites for Building a CI/CD Pipeline
Before setting up a CI/CD pipeline in Azure DevOps, you'll need the following:
Azure DevOps account: Create an account at dev.azure.com.
Azure subscription: To deploy the app, you'll need an Azure subscription (for services like Azure Data Factory).
Repository: Code repository (Azure Repos, GitHub, etc.).
Permissions: Access to configure Azure resources and manage pipeline configurations (relevant to azure admin roles).
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Building a CI/CD Pipeline
Step 1: Create a Project in Azure DevOps
The first step is to create a project in Azure DevOps. This project will house all your CI/CD components.
Navigate to Azure DevOps and sign in.
Click on “New Project.”
Name the project and choose visibility (public or private).
Select a repository type (Git is the most common).
Step 2: Set Up Your Code Repository
Once the project is created, you'll need a code repository. Azure DevOps supports Git repositories, which allow for version control and collaboration among developers.
Click on “Repos” in your project.
If you don’t already have a repo, create one by initializing a new repository or importing an existing Git repository.
Add your application’s source code to this repository.
Step 3: Configure the Build Pipeline (Continuous Integration)
The build pipeline is responsible for compiling code, running tests, and generating artifacts for deployment. The process starts with creating a pipeline in Azure Pipelines.
Go to Pipelines and click on "Create Pipeline."
Select your repository (either from Azure Repos, GitHub, etc.).
Choose a template for the build pipeline, such as .NET Core, Node.js, Python, etc.
Define the tasks in the YAML file or use the classic editor for a more visual experience.
Example YAML file for a .NET Core application:
yaml
Copy code
trigger: - master pool: vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest' steps: - task: UseDotNet@2 inputs: packageType: 'sdk' version: '3.x' - script: dotnet build --configuration Release displayName: 'Build solution' - script: dotnet test --configuration Release displayName: 'Run tests'
This pipeline will automatically trigger when changes are made to the master branch, build the project, and run unit tests.
Step 4: Define the Release Pipeline (Continuous Deployment)
The release pipeline automates the deployment of the application to various environments like development, staging, or production. This pipeline will be linked to the output of the build pipeline.
Navigate to Pipelines > Releases > New Release Pipeline.
Choose a template for your pipeline (Azure App Service Deployment, for example).
Link the build artifacts from the previous step to this release pipeline.
Add environments (e.g., Development, Staging, Production).
Define deployment steps, such as deploying to an Azure App Service or running custom deployment scripts.
Step 5: Integrating Azure Data Factory in CI/CD Pipeline
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is an essential service for automating data workflows and pipelines. If your CI/CD pipeline involves deploying or managing data workflows using ADF, Azure DevOps makes the integration seamless.
Export ADF Pipelines: First, export your ADF pipeline and configuration as ARM templates. This ensures that the pipeline definition is version-controlled and deployable across environments.
Deploy ADF Pipelines: Use Azure Pipelines to deploy the ADF pipeline as part of the CD process. This typically involves a task to deploy the ARM template using the az cli or Azure PowerShell commands.
Example of deploying an ADF ARM template:
yaml
Copy code
- task: AzureResourceManagerTemplateDeployment@3 inputs: deploymentScope: 'Resource Group' azureResourceManagerConnection: 'AzureServiceConnection' action: 'Create Or Update Resource Group' resourceGroupName: 'my-adf-resource-group' location: 'East US' templateLocation: 'Linked artifact' csmFile: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/drop/ARMTemplate.json' csmParametersFile: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/drop/ARMTemplateParameters.json'
This task ensures that the Azure Data Factory pipeline is automatically deployed during the release process, making it an integral part of the CI/CD pipeline.
Step 6: Set Up Testing
Testing is an essential part of any CI/CD pipeline, ensuring that your application is reliable and bug-free. You can use Azure Test Plans to manage test cases and run automated tests as part of the pipeline.
Unit Tests: These can be run during the build pipeline to test individual components.
Integration Tests: You can create separate stages in the pipeline to run integration tests after the application is deployed to an environment.
Manual Testing: Azure DevOps provides manual testing options where teams can create, manage, and execute manual test plans.
Step 7: Configure Notifications and Approvals
Azure DevOps allows you to set up notifications and approvals in the pipeline. This is useful when manual intervention is required before promoting code to production.
Notifications: Set up email or Slack notifications for pipeline failures or successes.
Approvals: Configure manual approvals before releasing to critical environments such as production. This is particularly useful for azure admin roles responsible for overseeing deployments.
4. Best Practices for CI/CD in Azure DevOps
Here are a few best practices to consider when building CI/CD pipelines with Azure DevOps:
Automate Everything: The more you automate, the more efficient your pipeline will be. Automate builds, tests, deployments, and even infrastructure provisioning using Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
Use Branching Strategies: Implement a branching strategy like GitFlow to manage feature development, bug fixes, and releases in a structured way.
Leverage Azure Pipelines Templates: If you have multiple pipelines, use templates to avoid duplicating YAML code. This promotes reusability and consistency across pipelines.
Monitor Pipelines: Use Azure Monitor and Application Insights to keep track of pipeline performance, identify bottlenecks, and get real-time feedback on deployments.
Security First: Make security checks part of your pipeline by integrating tools like WhiteSource Bolt, SonarCloud, or Azure Security Center to scan for vulnerabilities in code and dependencies.
Rollbacks and Blue-Green Deployments: Implement rollback mechanisms to revert to the previous stable version in case of failures. Blue-Green deployments and canary releases are strategies that allow safer production deployments.
5. Roles of Azure Admin in CI/CD

An Azure admin plays a vital role in managing resources, security, and permissions within the Azure platform. In the context of CI/CD pipelines, the azure admin ensures that the necessary infrastructure is in place and manages permissions, such as creating service connections between Azure DevOps and Azure resources (e.g., Azure App Service, Azure Data Factory).
Key tasks include:
Resource Provisioning: Setting up Azure resources like VMs, databases, or storage that the application will use.
Security Management: Configuring identity and access management (IAM) to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive resources.
Cost Management: Monitoring resource usage to optimize costs during deployments.
6. Conclusion
Building a CI/CD pipeline with Azure DevOps streamlines software delivery by automating the integration, testing, and deployment of code. Integrating services like Azure Data Factory further enhances the ability to automate complex workflows, making the pipeline a central hub for both application and data automation.
The role of the azure admin is critical in ensuring that resources, permissions, and infrastructure are in place and securely managed, enabling development teams to focus on delivering quality code faster.
#azure devops#azurecertification#microsoft azure#azure data factory#azure training#azuredataengineer
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Microsoft Azure Data Factory course in Pune#Google Cloud course in Pune#Aws course in Pune#offline Data Science course in Pune#Power BI course in Pune#Iics Data Integration course in Pune#Devops classes in Pune#Snowflak course in Pune#Google Cloud course in pune#Devops Courses in Pune#cloud computing courses in pune#aws course in pune with placement#aws training in pune#data science courses in pune#data science course in pune offline#offline courses for data science#power bi courses in pune#power bi classes in pune with placement#power bi developer course in pune#iics data integration course in pune#iics data integration certification in Pune#software development classes in pune#snowflake course in pune#snowflake training in pune#snowflake training classes#selenium testing course in pune#software testing course pune#selenium testing course near me#power bi and power apps course in pune#IICS course in Pune
0 notes
Text
Misconfigured Kubernetes RBAC in Azure Airflow Could Expose Entire Cluster to Exploitation
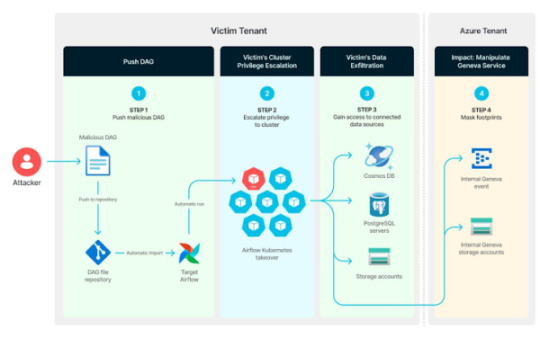
Source: https://thehackernews.com/2024/12/misconfigured-kubernetes-rbac-in-azure.html
More info: https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/azure-data-factory-apache-airflow-vulnerabilities/
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
What EDAV does:
Connects people with data faster. It does this in a few ways. EDAV:
Hosts tools that support the analytics work of over 3,500 people.
Stores data on a common platform that is accessible to CDC's data scientists and partners.
Simplifies complex data analysis steps.
Automates repeatable tasks, such as dashboard updates, freeing up staff time and resources.
Keeps data secure. Data represent people, and the privacy of people's information is critically important to CDC. EDAV is hosted on CDC's Cloud to ensure data are shared securely and that privacy is protected.
Saves time and money. EDAV services can quickly and easily scale up to meet surges in demand for data science and engineering tools, such as during a disease outbreak. The services can also scale down quickly, saving funds when demand decreases or an outbreak ends.
Trains CDC's staff on new tools. EDAV hosts a Data Academy that offers training designed to help our workforce build their data science skills, including self-paced courses in Power BI, R, Socrata, Tableau, Databricks, Azure Data Factory, and more.
Changes how CDC works. For the first time, EDAV offers CDC's experts a common set of tools that can be used for any disease or condition. It's ready to handle "big data," can bring in entirely new sources of data like social media feeds, and enables CDC's scientists to create interactive dashboards and apply technologies like artificial intelligence for deeper analysis.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Azure Storage Plays The Same Role in Azure
Azure Storage is an essential service within the Microsoft Azure ecosystem, providing scalable, reliable, and secure storage solutions for a vast range of applications and data types. Whether it's storing massive amounts of unstructured data, enabling high-performance computing, or ensuring data durability, Azure Storage is the backbone that supports many critical functions in Azure.
Understanding Azure Storage is vital for anyone pursuing Azure training, Azure admin training, or Azure Data Factory training. This article explores how Azure Storage functions as the central hub of Azure services and why it is crucial for cloud professionals to master this service.

The Core Role of Azure Storage in Cloud Computing
Azure Storage plays a pivotal role in cloud computing, acting as the central hub where data is stored, managed, and accessed. Its flexibility and scalability make it an indispensable resource for businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises.
Data Storage and Accessibility: Azure Storage enables users to store vast amounts of data, including text, binary data, and large media files, in a highly accessible manner. Whether it's a mobile app storing user data or a global enterprise managing vast data lakes, Azure Storage is designed to handle it all.
High Availability and Durability: Data stored in Azure is replicated across multiple locations to ensure high availability and durability. Azure offers various redundancy options, such as Locally Redundant Storage (LRS), Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS), and Read-Access Geo-Redundant Storage (RA-GRS), ensuring data is protected against hardware failures, natural disasters, and other unforeseen events.
Security and Compliance: Azure Storage is built with security at its core, offering features like encryption at rest, encryption in transit, and role-based access control (RBAC). These features ensure that data is not only stored securely but also meets compliance requirements for industries such as healthcare, finance, and government.
Integration with Azure Services: Azure Storage is tightly integrated with other Azure services, making it a central hub for storing and processing data across various applications. Whether it's a virtual machine needing disk storage, a web app requiring file storage, or a data factory pipeline ingesting and transforming data, Azure Storage is the go-to solution.
Azure Storage Services Overview
Azure Storage is composed of several services, each designed to meet specific data storage needs. These services are integral to any Azure environment and are covered extensively in Azure training and Azure admin training.
Blob Storage: Azure Blob Storage is ideal for storing unstructured data such as documents, images, and video files. It supports various access tiers, including Hot, Cool, and Archive, allowing users to optimize costs based on their access needs.
File Storage: Azure File Storage provides fully managed file shares in the cloud, accessible via the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. It's particularly useful for lifting and shifting existing applications that rely on file shares.
Queue Storage: Azure Queue Storage is used for storing large volumes of messages that can be accessed from anywhere in the world. It’s commonly used for decoupling components in cloud applications, allowing them to communicate asynchronously.
Table Storage: Azure Table Storage offers a NoSQL key-value store for rapid development and high-performance queries on large datasets. It's a cost-effective solution for applications needing structured data storage without the overhead of a traditional database.
Disk Storage: Azure Disk Storage provides persistent, high-performance storage for Azure Virtual Machines. It supports both standard and premium SSDs, making it suitable for a wide range of workloads from general-purpose VMs to high-performance computing.
Azure Storage and Azure Admin Training
In Azure admin training, a deep understanding of Azure Storage is crucial for managing cloud infrastructure. Azure administrators are responsible for creating, configuring, monitoring, and securing storage accounts, ensuring that data is both accessible and protected.
Creating and Managing Storage Accounts: Azure admins must know how to create and manage storage accounts, selecting the appropriate performance and redundancy options. They also need to configure network settings, including virtual networks and firewalls, to control access to these accounts.
Monitoring and Optimizing Storage: Admins are responsible for monitoring storage metrics such as capacity, performance, and access patterns. Azure provides tools like Azure Monitor and Application Insights to help admins track these metrics and optimize storage usage.
Implementing Backup and Recovery: Admins must implement robust backup and recovery solutions to protect against data loss. Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery are tools that integrate with Azure Storage to provide comprehensive disaster recovery options.
Securing Storage: Security is a top priority for Azure admins. This includes managing encryption keys, setting up role-based access control (RBAC), and ensuring that all data is encrypted both at rest and in transit. Azure provides integrated security tools to help admins manage these tasks effectively.
Azure Storage and Azure Data Factory
Azure Storage plays a critical role in the data integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes managed by Azure Data Factory. Azure Data Factory training emphasizes the use of Azure Storage for data ingestion, transformation, and movement, making it a key component in data workflows.
Data Ingestion: Azure Data Factory often uses Azure Blob Storage as a staging area for data before processing. Data from various sources, such as on-premises databases or external data services, can be ingested into Blob Storage for further transformation.
Data Transformation: During the transformation phase, Azure Data Factory reads data from Azure Storage, applies various data transformations, and then writes the transformed data back to Azure Storage or other destinations.
Data Movement: Azure Data Factory facilitates the movement of data between different Azure Storage services or between Azure Storage and other Azure services. This capability is crucial for building data pipelines that connect various services within the Azure ecosystem.
Integration with Other Azure Services: Azure Data Factory integrates seamlessly with Azure Storage, allowing data engineers to build complex data workflows that leverage Azure Storage’s scalability and durability. This integration is a core part of Azure Data Factory training.
Why Azure Storage is Essential for Azure Training
Understanding Azure Storage is essential for anyone pursuing Azure training, Azure admin training, or Azure Data Factory training. Here's why:
Core Competency: Azure Storage is a foundational service that underpins many other Azure services. Mastery of Azure Storage is critical for building, managing, and optimizing cloud solutions.
Hands-On Experience: Azure training often includes hands-on labs that use Azure Storage in real-world scenarios, such as setting up storage accounts, configuring security settings, and building data pipelines. These labs provide valuable practical experience.
Certification Preparation: Many Azure certifications, such as the Azure Administrator Associate or Azure Data Engineer Associate, include Azure Storage in their exam objectives. Understanding Azure Storage is key to passing these certification exams.
Career Advancement: As cloud computing continues to grow, the demand for professionals with expertise in Azure Storage increases. Proficiency in Azure Storage is a valuable skill that can open doors to a wide range of career opportunities in the cloud industry.
Conclusion
Azure Storage is not just another service within the Azure ecosystem; it is the central hub that supports a wide array of applications and services. For anyone undergoing Azure training, Azure admin training, or Azure Data Factory training, mastering Azure Storage is a crucial step towards becoming proficient in Azure and advancing your career in cloud computing.
By understanding Azure Storage, you gain the ability to design, deploy, and manage robust cloud solutions that can handle the demands of modern businesses. Whether you are a cloud administrator, a data engineer, or an aspiring Azure professional, Azure Storage is a key area of expertise that will serve as a strong foundation for your work in the cloud.
#azure devops#azurecertification#microsoft azure#azure data factory#azure training#azuredataengineer
0 notes
Text
Essential Guidelines for Building Optimized ETL Data Pipelines in the Cloud With Azure Data Factory
http://securitytc.com/TBwVgB
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

🚀 𝐉𝐨𝐢𝐧 𝐃𝐚𝐭𝐚𝐏𝐡𝐢'𝐬 𝐇𝐚𝐜𝐤-𝐈𝐓-𝐎𝐔𝐓 𝐇𝐢𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐇𝐚𝐜𝐤𝐚𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐧!🚀
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐩𝐚𝐭𝐞? 🌟 Showcase your skills in data engineering, data modeling, and advanced analytics. 💡 Innovate to transform retail services and enhance customer experiences.
📌𝐑𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐫 𝐍𝐨𝐰: https://whereuelevate.com/drills/dataphi-hack-it-out?w_ref=CWWXX9
🏆 𝐏𝐫𝐢𝐳𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐲: Winner 1: INR 50,000 (Joining Bonus) + Job at DataPhi Winners 2-5: Job at DataPhi
🔍 𝐒𝐤𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐬 𝐖𝐞'𝐫𝐞 𝐋𝐨𝐨𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐅𝐨𝐫: 🐍 Python,💾 MS Azure Data Factory / SSIS / AWS Glue,🔧 PySpark Coding,📊 SQL DB,☁️ Databricks Azure Functions,🖥️ MS Azure,🌐 AWS Engineering
👥 𝐏𝐨𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 𝐀𝐯𝐚𝐢𝐥𝐚𝐛𝐥𝐞: Senior Consultant (3-5 years) Principal Consultant (5-8 years) Lead Consultant (8+ years)
📍 𝐋𝐨𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧: 𝐏𝐮𝐧𝐞 💼 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞: 𝟑-𝟏𝟎 𝐘𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐬 💸 𝐁𝐮𝐝𝐠𝐞𝐭: ₹𝟏𝟒 𝐋𝐏𝐀 - ₹𝟑𝟐 𝐋𝐏𝐀
ℹ 𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐔𝐩𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐬: https://chat.whatsapp.com/Ga1Lc94BXFrD2WrJNWpqIa
Register now and be a part of the data revolution! For more details, visit DataPhi.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Azure Data Factory Training In Hyderabad
Key Features:
Hybrid Data Integration: Azure Data Factory supports hybrid data integration, allowing users to connect and integrate data from on-premises sources, cloud-based services, and various data stores. This flexibility is crucial for organizations with diverse data ecosystems.
Intuitive Visual Interface: The platform offers a user-friendly, visual interface for designing and managing data pipelines. Users can leverage a drag-and-drop interface to effortlessly create, monitor, and manage complex data workflows without the need for extensive coding expertise.

Data Movement and Transformation: Data movement is streamlined with Azure Data Factory, enabling the efficient transfer of data between various sources and destinations. Additionally, the platform provides a range of data transformation activities, such as cleansing, aggregation, and enrichment, ensuring that data is prepared and optimized for analysis.
Data Orchestration: Organizations can orchestrate complex workflows by chaining together multiple data pipelines, activities, and dependencies. This orchestration capability ensures that data processes are executed in a logical and efficient sequence, meeting business requirements and compliance standards.
Integration with Azure Services: Azure Data Factory seamlessly integrates with other Azure services, including Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Databricks, Azure Machine Learning, and more. This integration enhances the platform's capabilities, allowing users to leverage additional tools and services to derive deeper insights from their data.
Monitoring and Management: Robust monitoring and management capabilities provide real-time insights into the performance and health of data pipelines. Users can track execution details, diagnose issues, and optimize workflows to enhance overall efficiency.
Security and Compliance: Azure Data Factory prioritizes security and compliance, implementing features such as Azure Active Directory integration, encryption at rest and in transit, and role-based access control. This ensures that sensitive data is handled securely and in accordance with regulatory requirements.
Scalability and Reliability: The platform is designed to scale horizontally, accommodating the growing needs of organizations as their data volumes increase. With built-in reliability features, Azure Data Factory ensures that data processes are executed consistently and without disruptions.
2 notes
·
View notes